217356482ef9aca73dae820b249805d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Mars Environmental Observer A Scout Mission Concept Final report 25 February 2002 M. Janssen M. Allen
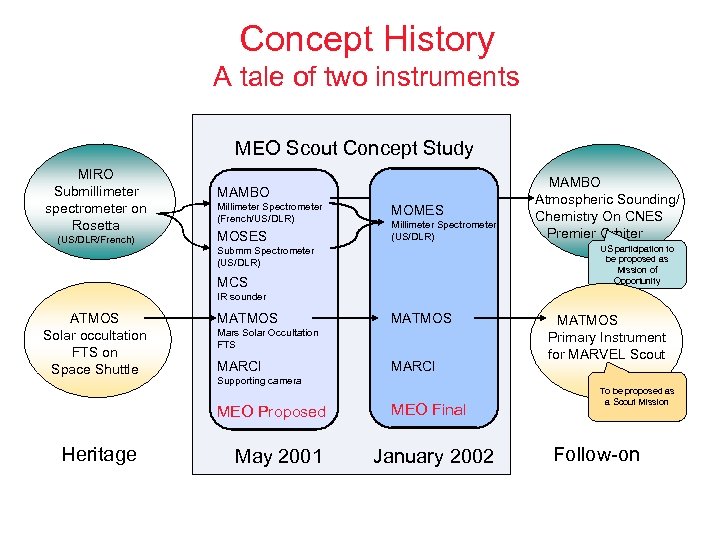
Concept History A tale of two instruments MEO Scout Concept Study MIRO Submillimeter spectrometer on Rosetta (US/DLR/French) MAMBO Millimeter Spectrometer (French/US/DLR) MOSES MOMES Millimeter Spectrometer (US/DLR) MAMBO Atmospheric Sounding/ Chemistry On CNES Premier Orbiter US participation to be proposed as Mission of Opportunity Submm Spectrometer (US/DLR) MCS IR sounder ATMOS Solar occultation FTS on Space Shuttle MATMOS Mars Solar Occultation FTS MARCI MATMOS Primary Instrument for MARVEL Scout Supporting camera MEO Proposed Heritage MATMOS May 2001 MEO Final January 2002 To be proposed as a Scout Mission Follow-on

Agenda MEO Janssen 15 min MAMBO Janssen 15 min MARVEL Allen 15 min

MEO Science Goals and Objectives The Mars Environmental Observer (MEO) concept addresses the key Mars Exploration Program Goals of Life, Climate, Geology, and Human Exploration (MEPAG goals I-IV). MEO Objectives are: LIFE CLIMATE GEOLOGY HUMAN EXPLORATION 1. Seek evidence of extant life by a uniquely broad and sensitive mapping of the global distribution of atmospheric water (I. A. 1). 2. Seek evidence of extant life by an ultra-high sensitivity search for trace atmospheric disequilibrium biosignatures (addresses objectives in I. A. 2 by remote means). 3. Determine the oxidation state of the lower atmosphere and surface through highly sensitive global measurements of key trace photochemical oxidized species (II. A. 6). 4. Characterize the present Mars climate by acquiring a complete global measurement of the physical state of the atmosphere— temperature and winds—over a wide altitude range and under all atmospheric conditions (II. A. 1, IV. A. 4). 5. Characterize present Mars climate processes through simultaneous measurements of temperature and water (II. A. 1, II. A. 3, II. A. 4, II. A. 5). 6. Determine the composition of surface dust by characterizing the mineralogy of atmospheric dust (addresses aspects of I. A. 4, I. C. 3, II. B. 1, III. A. 2, III. A. 5). 7. Infer the presence of active volcanism through the detection of trace tectonic-formed gas emissions. (III. A. 4) 8. Support the preparation for human exploration through a better understanding of upper atmospheric phenomena relevant to aerobraking and aerocapture (IV. A. 4).

Mission and Flight System Architecture • • • Payload mass, power, and viewing requirements are accommodated by Lockheed-Martin Odyssey spacecraft. Launched by the Delta 2925 for the 2007 opportunity. The limb-sounding and solar occultation observing requirements are satisfied by the sun-synchronous polar orbit.

MEO Budget Mission costs with full (MATMOS, MOMES, MARCI) instrument complement
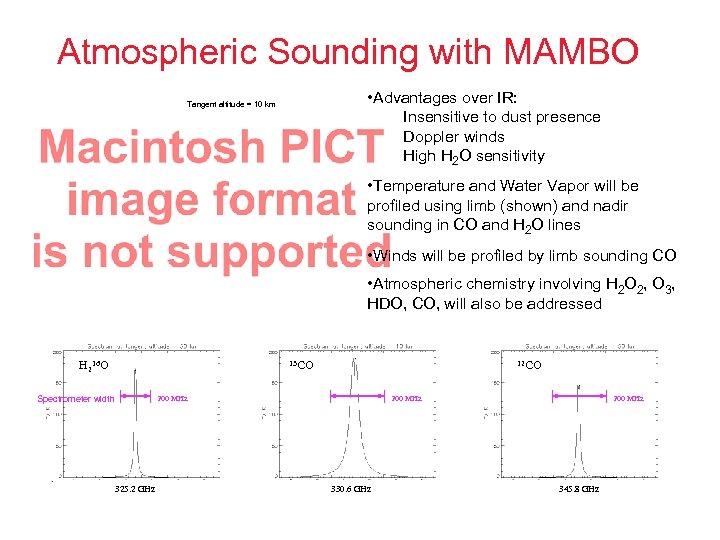
Atmospheric Sounding with MAMBO • Advantages over IR: Insensitive to dust presence Doppler winds High H 2 O sensitivity Tangent altitude = 10 km • Temperature and Water Vapor will be profiled using limb (shown) and nadir sounding in CO and H 2 O lines • Winds will be profiled by limb sounding CO • Atmospheric chemistry involving H 2 O 2, O 3, HDO, CO, will also be addressed H 216 O 13 CO 12 CO 200 MHz Spectrometer width 325. 2 GHz 200 MHz 330. 6 GHz 200 MHz 345. 8 GHz
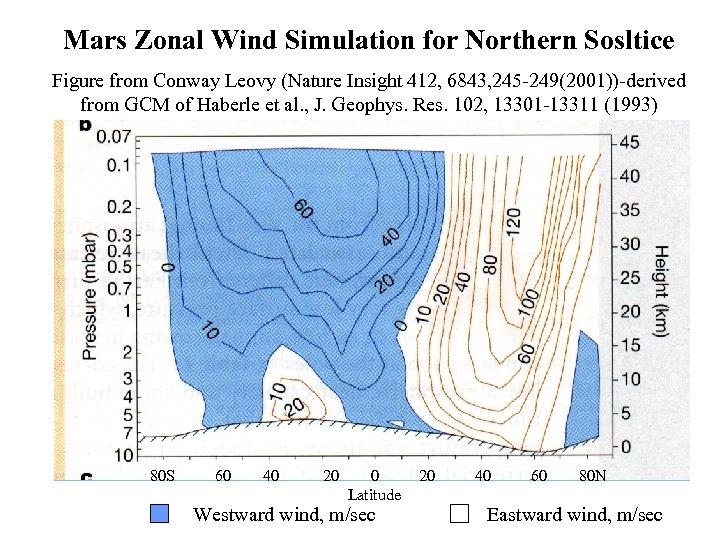
Mars Zonal Wind Simulation for Northern Sosltice Figure from Conway Leovy (Nature Insight 412, 6843, 245 -249(2001))-derived from GCM of Haberle et al. , J. Geophys. Res. 102, 13301 -13311 (1993) 80 S 60 40 20 0 Latitude Westward wind, m/sec 20 40 60 80 N Eastward wind, m/sec
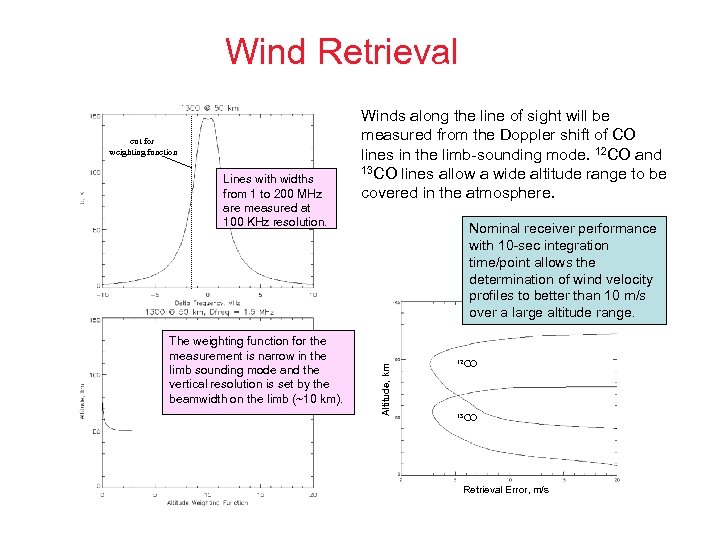
Wind Retrieval Lines with widths from 1 to 200 MHz are measured at 100 KHz resolution. The weighting function for the measurement is narrow in the limb sounding mode and the vertical resolution is set by the beamwidth on the limb (~10 km). Nominal receiver performance with 10 -sec integration time/point allows the determination of wind velocity profiles to better than 10 m/s over a large altitude range. Altitude, km cut for weighting function Winds along the line of sight will be measured from the Doppler shift of CO lines in the limb-sounding mode. 12 CO and 13 CO lines allow a wide altitude range to be covered in the atmosphere. 12 CO 13 CO Retrieval Error, m/s
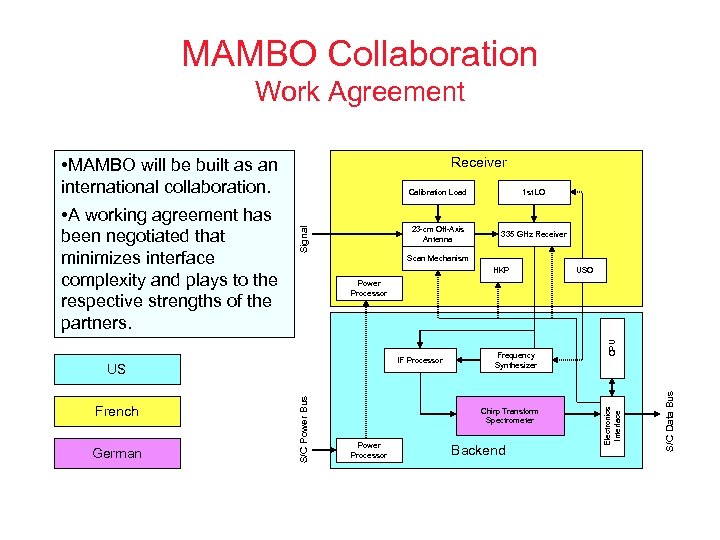
MAMBO Collaboration Work Agreement • MAMBO will be built as an international collaboration. Calibration Load HKP USO Chirp Transform Spectrometer Power Processor Backend S/C Data Bus Frequency Synthesizer Electronics Interface IF Processor CPU Power Processor S/C Power Bus German 335 GHz Receiver Scan Mechanism US French 1 st LO 23 -cm Off-Axis Antenna Signal • A working agreement has been negotiated that minimizes interface complexity and plays to the respective strengths of the partners. Receiver

MAMBO US Component Science Team The US MAMBO science team comes from a variety of universities and NASA centers, and brings world-class expertise in all aspects of the investigation: instrumentation, remote sensing, atmospheric dynamics and chemistry Mike Janssen (lead) Mark Allen Gordon Chin Todd Clancy Margaret Frerking Sam Gulkis Mark Gurwell Bob Haberle Mark Richardson Yuk Yung JPL GSFC U. Colo JPL Harvard ARC Caltech

MAMBO US Component Rationale • Continues international collaboration on heterodyne spectroscopy - this time with French lead • US responsibility for subsystem complements limited French workforce & experience • Choice of radiometer backend provides well-defined interface and minimizes risk, travel, ITAR issues, etc. • Backend experience will be valuable for future instruments • We have found no significant descope options that appear viable. Possibilities are being explored: – Swedish collaborators assume backend delivery responsibility, or – French contract to industry for this US role would be questionable in these cases
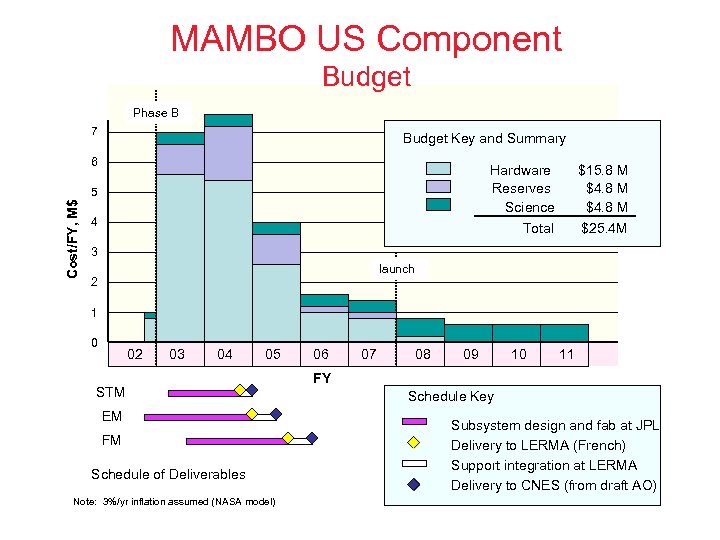
MAMBO US Component Budget Phase B 7 Budget Key and Summary 6 Hardware Reserves Science Total Cost/FY, M$ 5 $15. 8 M $4. 8 M $25. 4 M 4 3 launch 2 1 0 02 03 04 05 STM EM FM Schedule of Deliverables Note: 3%/yr inflation assumed (NASA model) 06 07 08 09 10 11 FY Schedule Key Subsystem design and fab at JPL Delivery to LERMA (French) Support integration at LERMA Delivery to CNES (from draft AO)
217356482ef9aca73dae820b249805d4.ppt