c35b86796e5ed028b9a40d3252e9c935.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 MARKETING RESEARCH DR. D. ISRAEL
MARKETING RESEARCH DR. D. ISRAEL
 DEFINITION A systematic and objective gathering, recording and analyzing of data about problems relating to marketing of goods and services
DEFINITION A systematic and objective gathering, recording and analyzing of data about problems relating to marketing of goods and services
 l MR is a function that links the consumer, customer and public to the marketer through information used to - generate, refine and evaluate marketing actions; - monitor marketing performance; and - improve understanding of marketing as a process.
l MR is a function that links the consumer, customer and public to the marketer through information used to - generate, refine and evaluate marketing actions; - monitor marketing performance; and - improve understanding of marketing as a process.
 WHAT MARKETING RESEARCH CAN DO? l l l Enhances the effectiveness of decisions made Analyzes customer preferences Identifies new users and new uses of the product Identifies the core-customers Differentiates customers from others on values, perception, life-style etc.
WHAT MARKETING RESEARCH CAN DO? l l l Enhances the effectiveness of decisions made Analyzes customer preferences Identifies new users and new uses of the product Identifies the core-customers Differentiates customers from others on values, perception, life-style etc.
 l l l l Analyzing the customer purchase patterns Continual monitoring of customers Forecasting Measures the characteristics of the market Market tracking Market segmentation Market performance
l l l l Analyzing the customer purchase patterns Continual monitoring of customers Forecasting Measures the characteristics of the market Market tracking Market segmentation Market performance
 l Making Decisions on Marketing-Mix variables: - Product - Price - Place - Promotion
l Making Decisions on Marketing-Mix variables: - Product - Price - Place - Promotion
 MARKETING RESEARCH LIMITATIONS l l l MR does not guarantee success MR is quite expensive MR is time consuming MR is susceptible to extraneous factors MR yields misleading results owing to the improper use of analytical techniques
MARKETING RESEARCH LIMITATIONS l l l MR does not guarantee success MR is quite expensive MR is time consuming MR is susceptible to extraneous factors MR yields misleading results owing to the improper use of analytical techniques
 MARKET RESEARCH Vs. MARKETING RESEARCH l l Market Research limits interest to the information relating to market and customers only. Marketing Research covers issues pertaining to everything: market, customers, distribution strategies, impact studies, experimentation etc.
MARKET RESEARCH Vs. MARKETING RESEARCH l l Market Research limits interest to the information relating to market and customers only. Marketing Research covers issues pertaining to everything: market, customers, distribution strategies, impact studies, experimentation etc.
 ROOTS OF MARKETING RESEARCH l l l Statistics Economics Psychology Sociology Anthropology
ROOTS OF MARKETING RESEARCH l l l Statistics Economics Psychology Sociology Anthropology
 SCIENTIFIC METHOD IN THE PHYSICAL SCIENCE AND MARKETING SCIENCE Similarities Body of knowledge Systematic inquiry Welfare of humanity
SCIENTIFIC METHOD IN THE PHYSICAL SCIENCE AND MARKETING SCIENCE Similarities Body of knowledge Systematic inquiry Welfare of humanity
 Dissimilarities Verification Method of research Prediction Precision Objectivity of investigation Influence of measurement process
Dissimilarities Verification Method of research Prediction Precision Objectivity of investigation Influence of measurement process
 MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS STEP 1: Problem Formulation: This involves identifying the management problem and translating the management problem into a research problem.
MARKETING RESEARCH PROCESS STEP 1: Problem Formulation: This involves identifying the management problem and translating the management problem into a research problem.
 Management Problem Should a new product be introduced in the market?
Management Problem Should a new product be introduced in the market?
 Marketing Research Problem l l l Profile of consumers likely to buy the product; Consumers’ attitude toward the company and features of the product; Extent of consumer brand loyalty for the existing products; Demand pattern for the product in the longrun; Technical, financial and managerial resources to achieve the objective;
Marketing Research Problem l l l Profile of consumers likely to buy the product; Consumers’ attitude toward the company and features of the product; Extent of consumer brand loyalty for the existing products; Demand pattern for the product in the longrun; Technical, financial and managerial resources to achieve the objective;
 DISCUSSION QUESTIONS Management Problem a) Should the advertisement be changed? b) Should the price be changed? Question: Identify the marketing research problems for each of the above cases.
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS Management Problem a) Should the advertisement be changed? b) Should the price be changed? Question: Identify the marketing research problems for each of the above cases.
 Step 2: Developing an Approach to the Problem: This involves framing research questions, models and hypotheses in order to obtain information.
Step 2: Developing an Approach to the Problem: This involves framing research questions, models and hypotheses in order to obtain information.
 l l l Research questions help the researcher in determining the specific information that are needed to be collected toward solving the research problem. Each subcomponent of research problem is broken into an interrogative form. Enables the researcher in formulating the research hypotheses.
l l l Research questions help the researcher in determining the specific information that are needed to be collected toward solving the research problem. Each subcomponent of research problem is broken into an interrogative form. Enables the researcher in formulating the research hypotheses.
 l Hypotheses: l Off-shoots of Research questions Tentative statement that requires scientific testing for acceptance or rejection Connects two or more variables Declarative forms Enables to decide what variables are to be measured and how they need to be measured Helps deciding on the type of analytical tools Stated in two major forms: Null and Alternate l l l
l Hypotheses: l Off-shoots of Research questions Tentative statement that requires scientific testing for acceptance or rejection Connects two or more variables Declarative forms Enables to decide what variables are to be measured and how they need to be measured Helps deciding on the type of analytical tools Stated in two major forms: Null and Alternate l l l
 l Model A frame that specifies a set of variables and their interrelationships. It is of three types: Verbal Model is a written representation of relationships among variables; Graphical Model is a visual representation of relationships among variables; and Mathematical Model is a equation-representation of relationships among variables.
l Model A frame that specifies a set of variables and their interrelationships. It is of three types: Verbal Model is a written representation of relationships among variables; Graphical Model is a visual representation of relationships among variables; and Mathematical Model is a equation-representation of relationships among variables.
 Management Problem What should be done to improve the store patronage?
Management Problem What should be done to improve the store patronage?
 Marketing Research Problem l l l Measure customers’ perception of quality of services and goods provided by the store; Measure customers’ perception of level of service satisfaction; Comparing the store with other similar stores in respect of major attributes such as convenient location, parking facilities, assortment of goods available, friendliness of sales personnel etc. Measure whether the customers are intending to buy from the store in future; Determine whether customer perception of service quality and service satisfaction lead to increased customer patronage (loyalty).
Marketing Research Problem l l l Measure customers’ perception of quality of services and goods provided by the store; Measure customers’ perception of level of service satisfaction; Comparing the store with other similar stores in respect of major attributes such as convenient location, parking facilities, assortment of goods available, friendliness of sales personnel etc. Measure whether the customers are intending to buy from the store in future; Determine whether customer perception of service quality and service satisfaction lead to increased customer patronage (loyalty).
 l Research Questions and Hypotheses: RQ 1: Do the customers perceive favorably the quality of services provided in the store? HYPO 1: Customers have favorable perception toward the quality of services provided by the store. RQ 2: Are customers satisfied with the quality of services extended by the store? HYPO 2: Customers are highly satisfied with the quality of services provided by the store. RQ 3: Do customers have an intention to buy from the same store in future? HYPO 3: Customers exhibit a strong willingness to make their future purchase from the store.
l Research Questions and Hypotheses: RQ 1: Do the customers perceive favorably the quality of services provided in the store? HYPO 1: Customers have favorable perception toward the quality of services provided by the store. RQ 2: Are customers satisfied with the quality of services extended by the store? HYPO 2: Customers are highly satisfied with the quality of services provided by the store. RQ 3: Do customers have an intention to buy from the same store in future? HYPO 3: Customers exhibit a strong willingness to make their future purchase from the store.
 RQ 4: Is there any significant difference between the loyalists and defectors? HYPO 4: ? ? RQ 5: Are service quality and service satisfaction important parameters in explaining store loyalty? HYPO 5: ? ?
RQ 4: Is there any significant difference between the loyalists and defectors? HYPO 4: ? ? RQ 5: Are service quality and service satisfaction important parameters in explaining store loyalty? HYPO 5: ? ?
 l Verbal Model: Customers who perceive the store quality favorably will tend to have store satisfaction. Both store quality and store satisfaction influence customers' intended store patronage (loyalty) behavior.
l Verbal Model: Customers who perceive the store quality favorably will tend to have store satisfaction. Both store quality and store satisfaction influence customers' intended store patronage (loyalty) behavior.
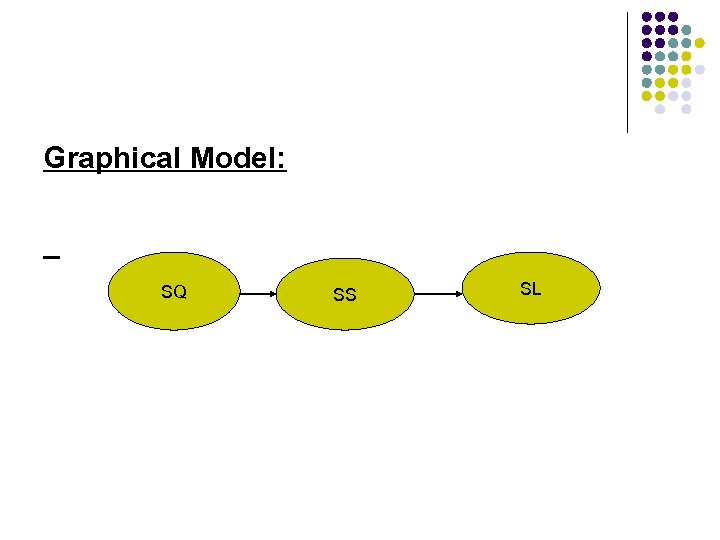 Graphical Model: SQ SS SL
Graphical Model: SQ SS SL
 Mathematical Model Y = a + b 1 x 1 +b 2 x 2 Where Y= willingness to repurchase a= constant b 1, b 2 = model parameters or coefficients x 1, x 2 = store quality and store satisfaction
Mathematical Model Y = a + b 1 x 1 +b 2 x 2 Where Y= willingness to repurchase a= constant b 1, b 2 = model parameters or coefficients x 1, x 2 = store quality and store satisfaction
 Step 3: Research Design Formulation This involves preparing a framework on how to execute the marketing research project for obtaining information for solving the research problem.
Step 3: Research Design Formulation This involves preparing a framework on how to execute the marketing research project for obtaining information for solving the research problem.
 Research Design involves detailed description on l l l Type of research Data collection methods Data collection instruments Units to be interviewed/observed Sampling design Plan of analysis
Research Design involves detailed description on l l l Type of research Data collection methods Data collection instruments Units to be interviewed/observed Sampling design Plan of analysis
 Step 4: Organizing Fieldwork and Data Collection This involves considerations on selection, training, supervision and evaluation of the field-force in minimizing data collection errors.
Step 4: Organizing Fieldwork and Data Collection This involves considerations on selection, training, supervision and evaluation of the field-force in minimizing data collection errors.
 Step 5: Data preparation and Analysis This involves editing, coding, transforming, tabulating and Analyzing the data collected
Step 5: Data preparation and Analysis This involves editing, coding, transforming, tabulating and Analyzing the data collected
 Step 6: Report Preparation This involves the procedure involved in documenting the entire research process involved. Should contain all relevant information Should be comprehendible and easy to use
Step 6: Report Preparation This involves the procedure involved in documenting the entire research process involved. Should contain all relevant information Should be comprehendible and easy to use
 MARKETING RESEARCH SUPPLIERS Two sources: Internal and External l Internal Supplier Nothing but the MR department within the firm. l External Suppliers The outside firms hired by organization for supply of information. l
MARKETING RESEARCH SUPPLIERS Two sources: Internal and External l Internal Supplier Nothing but the MR department within the firm. l External Suppliers The outside firms hired by organization for supply of information. l
 Types of External Suppliers a) Full service suppliers which provide the full range of marketing research services from the beginning to the end
Types of External Suppliers a) Full service suppliers which provide the full range of marketing research services from the beginning to the end
 b) Syndicated services: - Involves collection and tabulation of marketing information from a large sample base, with large number of questions on a continuing basis for sale to a large number of clients; - Provides wealth of information, involves low cost, and no proprietorship; - Example: collection of information on TV viewer ship, newspaper and magazine readership etc. - Research is done voluntarily by the research organization; - Research is conducted on a particular theme or product; - Everything is decided by the research firm;
b) Syndicated services: - Involves collection and tabulation of marketing information from a large sample base, with large number of questions on a continuing basis for sale to a large number of clients; - Provides wealth of information, involves low cost, and no proprietorship; - Example: collection of information on TV viewer ship, newspaper and magazine readership etc. - Research is done voluntarily by the research organization; - Research is conducted on a particular theme or product; - Everything is decided by the research firm;
 Some more examples for Syndicated services: l Continuous analysis of brand positioning for all brands of a specific product; l Continuous analysis of brand-switching and brand-loyalty for a specific product; l Life-style profiles of users of different brands; l Trends & shifts in competitors’ pricing, their promotion effort and their impact.
Some more examples for Syndicated services: l Continuous analysis of brand positioning for all brands of a specific product; l Continuous analysis of brand-switching and brand-loyalty for a specific product; l Life-style profiles of users of different brands; l Trends & shifts in competitors’ pricing, their promotion effort and their impact.
 c) Standardized services: - Make use of standardized procedure for providing research information to various clients. For example, the same questionnaire or even same or similar respondents may be used for obtaining information; - Help in comparing results across clients and across time;
c) Standardized services: - Make use of standardized procedure for providing research information to various clients. For example, the same questionnaire or even same or similar respondents may be used for obtaining information; - Help in comparing results across clients and across time;
 d) Customized services These are the research firms that fulfill the specific research requirements of the clients. Hence, each client is treated distinctly.
d) Customized services These are the research firms that fulfill the specific research requirements of the clients. Hence, each client is treated distinctly.
 e) Limited service suppliers: They are the specialists in any one or more of the marketing research process tasks. Some firms may offer only field services, other only coding and data entry and still others only data analysis services.
e) Limited service suppliers: They are the specialists in any one or more of the marketing research process tasks. Some firms may offer only field services, other only coding and data entry and still others only data analysis services.
 CRITERION IN SELECTING A RESEARCH SUPPLIER l l Economic feasibility Technical expertise Reputation Reliability
CRITERION IN SELECTING A RESEARCH SUPPLIER l l Economic feasibility Technical expertise Reputation Reliability
 ROLE OF MARKETING RESEARCHER & THE MANAGER Marketing Researcher: -Technical consultant - Performing data analysis & providing initial interpretation - Consultant in problem formulation & implementation stages
ROLE OF MARKETING RESEARCHER & THE MANAGER Marketing Researcher: -Technical consultant - Performing data analysis & providing initial interpretation - Consultant in problem formulation & implementation stages
 l Manager - providing adequate information formulating research problem; - responsible for implementing final recommendation; - needs to have at least non-technical understanding of basic design of the project; - reasonably realistic (e. g. , he should not ask for a single estimate for the sales forecast for next year, or set unrealistic time schedule); - accept research project as useful aid to decision making rather than a perfect panacea.
l Manager - providing adequate information formulating research problem; - responsible for implementing final recommendation; - needs to have at least non-technical understanding of basic design of the project; - reasonably realistic (e. g. , he should not ask for a single estimate for the sales forecast for next year, or set unrealistic time schedule); - accept research project as useful aid to decision making rather than a perfect panacea.
 MARKETING RESEARCH & MARKETING INFORMATION SYSTEMS MIS is a formalized set of procedures for generating, storing, analyzing and distribution information to marketing decision makers on an ongoing basis rather than adhoc. The information cannot be altered.
MARKETING RESEARCH & MARKETING INFORMATION SYSTEMS MIS is a formalized set of procedures for generating, storing, analyzing and distribution information to marketing decision makers on an ongoing basis rather than adhoc. The information cannot be altered.
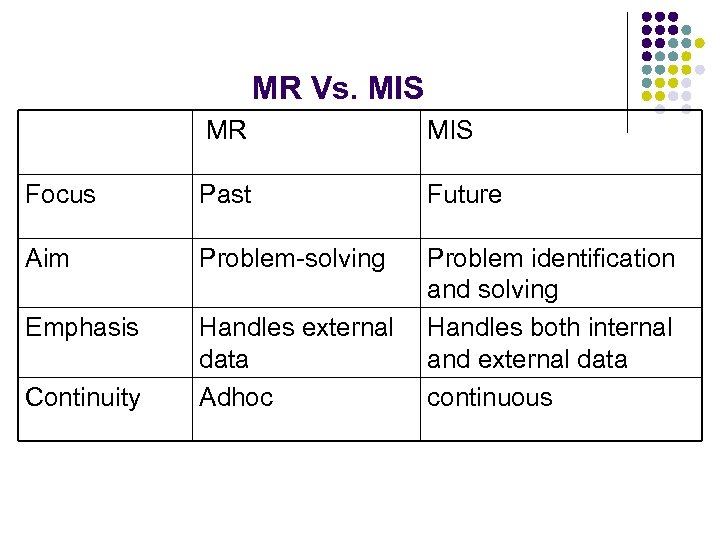 MR Vs. MIS MR MIS Focus Past Future Aim Problem-solving Emphasis Handles external data Adhoc Problem identification and solving Handles both internal and external data continuous Continuity
MR Vs. MIS MR MIS Focus Past Future Aim Problem-solving Emphasis Handles external data Adhoc Problem identification and solving Handles both internal and external data continuous Continuity
 MARKET RESEARCH AGENCIES IN INDIA – SOME HIGHLIGHTS l l l MR industry is estimated to be 500 crores with potential to grow 1000 crores MR is mainly used by MNCs Allocation to MR is between. 005 to. 01 of turnover (this includes HLL also) Presently it is only 4% the size of advertising industry Only 50 odd corporations make use of MR in India Stagnant growth rate in Indian MR industry(10%) while it is close to 50% in U. K. and U. S. A.
MARKET RESEARCH AGENCIES IN INDIA – SOME HIGHLIGHTS l l l MR industry is estimated to be 500 crores with potential to grow 1000 crores MR is mainly used by MNCs Allocation to MR is between. 005 to. 01 of turnover (this includes HLL also) Presently it is only 4% the size of advertising industry Only 50 odd corporations make use of MR in India Stagnant growth rate in Indian MR industry(10%) while it is close to 50% in U. K. and U. S. A.
 MAJOR MARKET RESEARCH AGENCIES IN INDIA A. C. Nielsen ORG-MARG IMRB International Pathfinders NCAER MRAS
MAJOR MARKET RESEARCH AGENCIES IN INDIA A. C. Nielsen ORG-MARG IMRB International Pathfinders NCAER MRAS
 l A. C. Nielsen - held by VNU, a Dutch company - Presently operates under dual brand - A. C. Nielsen ( for retail measurement) - A. C. Nielsen ORG-MARG ( for customized research services) - ORG-GKF (for retail audit for consumer durables) - Specialized in soft-drink audit, ice-cream audit, media audit, cigarette audit, & pharmaceutical audit
l A. C. Nielsen - held by VNU, a Dutch company - Presently operates under dual brand - A. C. Nielsen ( for retail measurement) - A. C. Nielsen ORG-MARG ( for customized research services) - ORG-GKF (for retail audit for consumer durables) - Specialized in soft-drink audit, ice-cream audit, media audit, cigarette audit, & pharmaceutical audit
 l IMRB International - 35 year old - operates as a division of HTA - major clients include Johnson &Johnson, Philips, Indian Oil, Indian Airlines, ITC. - enters in to consultancy service (The Henley Centre) for new product and development of product portfolios. - known for NRS, BRS, TRPS, Market Pulse, Rural Market Profile, CSMM, BIRD.
l IMRB International - 35 year old - operates as a division of HTA - major clients include Johnson &Johnson, Philips, Indian Oil, Indian Airlines, ITC. - enters in to consultancy service (The Henley Centre) for new product and development of product portfolios. - known for NRS, BRS, TRPS, Market Pulse, Rural Market Profile, CSMM, BIRD.
 CHALLENGES FOR MARKETING RESEARCH INDUSTRY IN INDIA l l Cost-consciousness (unwillingness on the part of the management to spend money on research); Lack of Professionalism (because MR draws on a variety of other disciplines); High turnover rate (resulting in dearth of skilled people) Absence of Databases
CHALLENGES FOR MARKETING RESEARCH INDUSTRY IN INDIA l l Cost-consciousness (unwillingness on the part of the management to spend money on research); Lack of Professionalism (because MR draws on a variety of other disciplines); High turnover rate (resulting in dearth of skilled people) Absence of Databases
 QUESTIONS?
QUESTIONS?


