e3ec676465565c39604069a3d7e96985.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

MARKETING Pricing Strategies Prof. Bauer-Ramazani

Overview Definition of price Factors that influence the pricing decision Pricing objectives Pricing strategies over the product life cycle Three major pricing strategies and their advantages and disadvantages + Exercises applying different pricing strategies + Pricing tactics + + +

Price -- Definition • the amount of money charged for a product or service • the sum of all the values that consumers exchange for the benefits of having or using the product or service • Examples of “price? ” – Tuition, rent, fare, retainer, toll, salary, dues
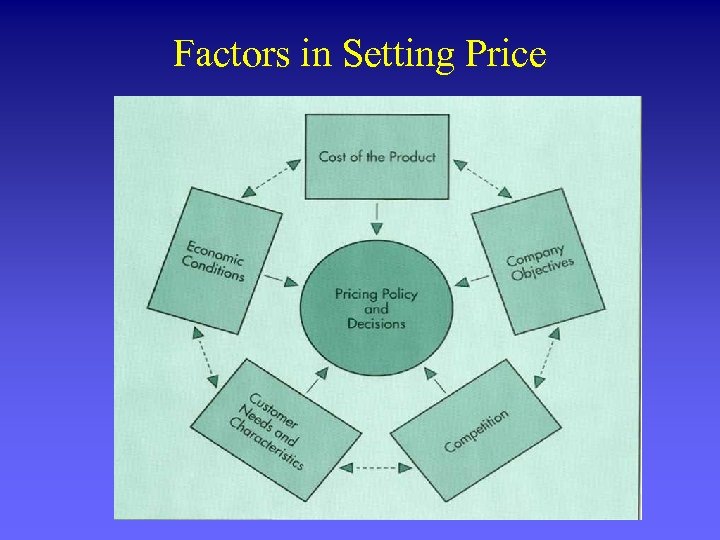
Factors in Setting Price

Pricing Objectives
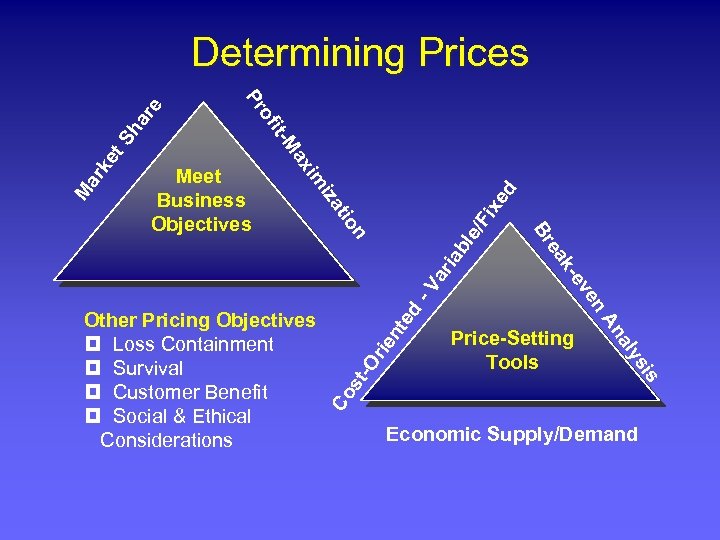
ha Fi xe d e/ t. S ke ar -V ar nt -O rie Co is ys st al Price-Setting Tools An ed n ve -e ak ia bl n Other Pricing Objectives ¥ Loss Containment ¥ Survival ¥ Customer Benefit ¥ Social & Ethical Considerations e Br tio iza M im Meet Business Objectives ax M it- of Pr re Determining Prices Economic Supply/Demand
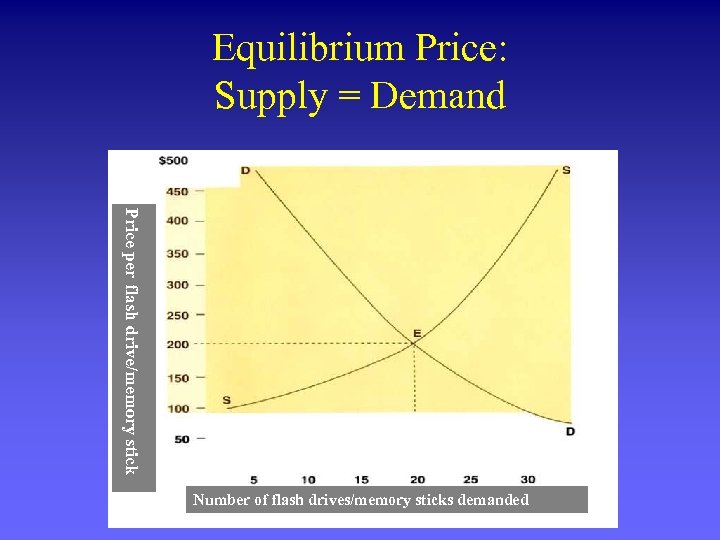
Equilibrium Price: Supply = Demand Price per flash drive/memory stick Number of flash drives/memory sticks demanded
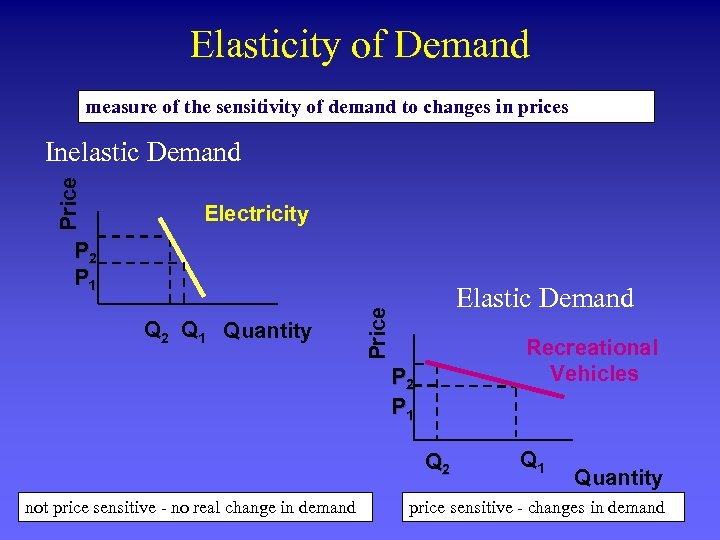
Elasticity of Demand measure of the sensitivity of demand to changes in prices Price Inelastic Demand Electricity P 2 P 1 Price Q 2 Q 1 Quantity Elastic Demand Recreational Vehicles P 2 P 1 Q 2 not price sensitive - no real change in demand Q 1 Quantity price sensitive - changes in demand

Market-based Pricing n Pricing Existing Products/Services - 3 options E Pricing below market prices price wars § EX: airlines, store brand vs. manufacturer’s brand § Dumping E Pricing above prevailing market prices for similar products § EX: Sony higher price = higher quality? E Pricing at or near market prices
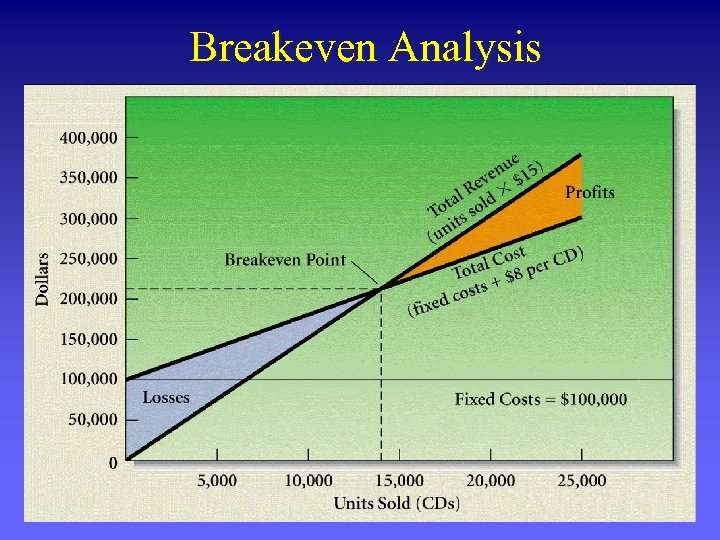
Breakeven Analysis

Breakeven Point Formula Breakeven Quantity = Fixed Costs Price/unit –Variable cost/unit (Contribution Margin)

Cost-based Pricing 1. Estimating the per-unit cost of production Ø Capital (K): land, building, equipment = fixed cost (FC) Ø Labor (L): workers’ wages = variable cost (VC) EX: $0. 50 + $0. 50 = $1. 00 (production cost) 2. Adding a mark-up Ø Desired profit per item: $0. 50 3. Sales price = cost of production + mark-up Ø $1. 00 + $0. 50 = $1. 50 Ø 50% markup
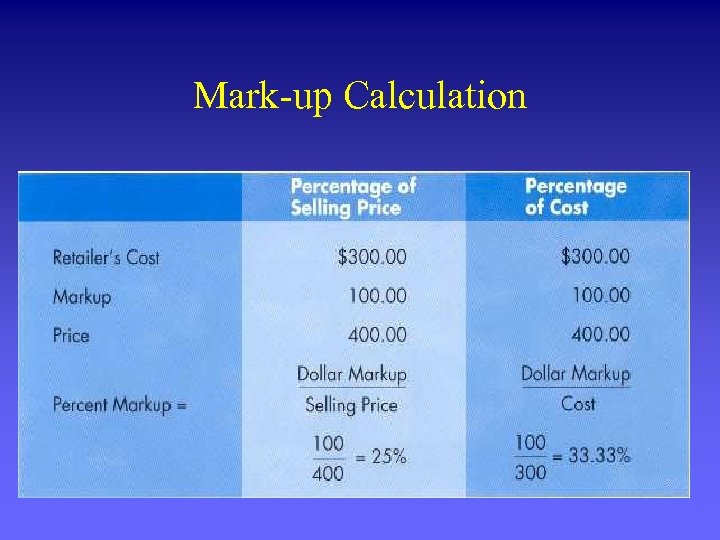
Mark-up Calculation
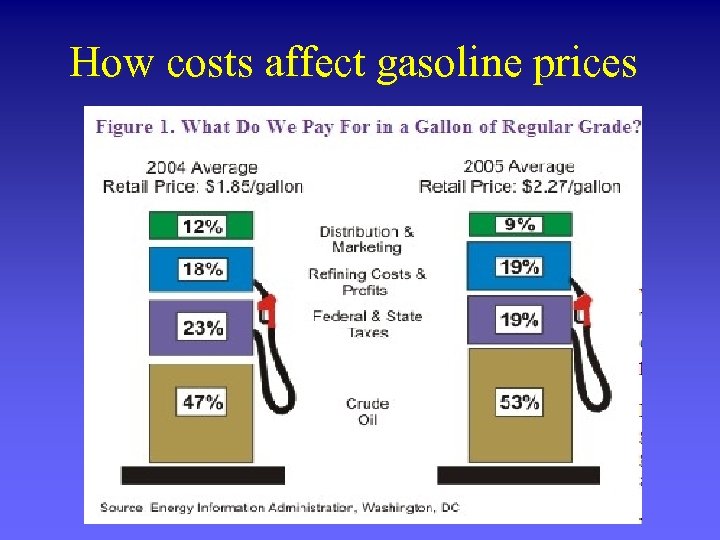
How costs affect gasoline prices
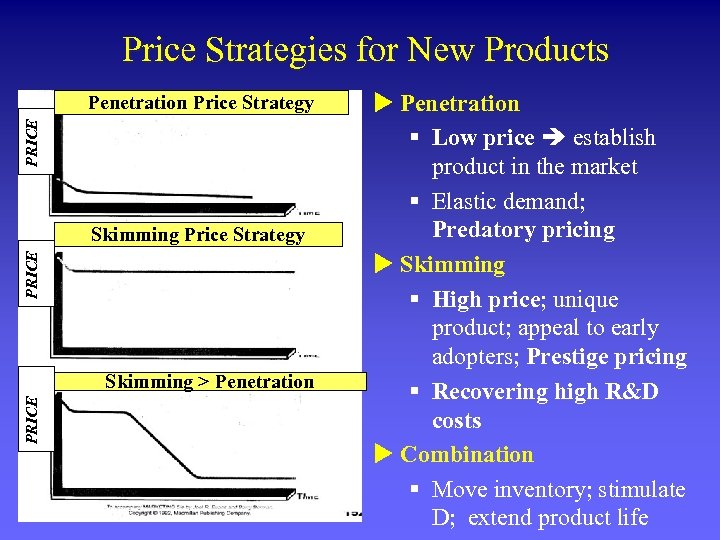
Price Strategies for New Products PRICE Penetration Price Strategy PRICE Skimming > Penetration u Penetration § Low price establish product in the market § Elastic demand; Predatory pricing u Skimming § High price; unique product; appeal to early adopters; Prestige pricing § Recovering high R&D costs u Combination § Move inventory; stimulate D; extend product life
Pricing of i. Phones
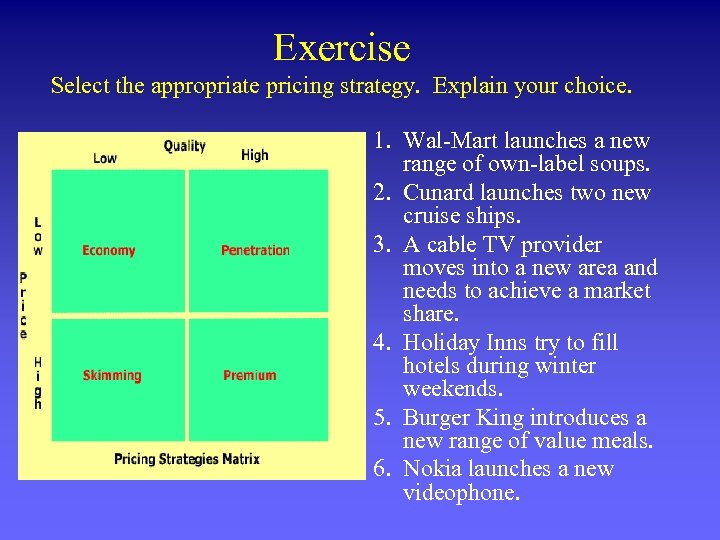
Exercise Select the appropriate pricing strategy. Explain your choice. 1. Wal-Mart launches a new range of own-label soups. 2. Cunard launches two new cruise ships. 3. A cable TV provider moves into a new area and needs to achieve a market share. 4. Holiday Inns try to fill hotels during winter weekends. 5. Burger King introduces a new range of value meals. 6. Nokia launches a new videophone.

Pricing Tactics n Price Lining • Setting a limited number of prices for certain categories of products n Psychological Pricing • Pricing to take advantage of the fact that consumers do not always respond rationally to stated prices n Discounting • Price reductions offered as an incentive to purchase ¢ High tech Pricing: giving it away!
e3ec676465565c39604069a3d7e96985.ppt