0cb7ba7b70dc6138376c56472c2dc541.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 107
 Marketing Management Summer 2012 Jihye Lee Framework for Marketing Management BUS 463
Marketing Management Summer 2012 Jihye Lee Framework for Marketing Management BUS 463
 Last Class Review • Need, wants and demands. • Type of needs. - 5 types Stated, Real, Unstated, Delight, Secret • Value and Satisfaction - Value: the sum of tangible and intangible benefits costs and to customers - Value perceptions increase with quality service and but decrease with price To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -1
Last Class Review • Need, wants and demands. • Type of needs. - 5 types Stated, Real, Unstated, Delight, Secret • Value and Satisfaction - Value: the sum of tangible and intangible benefits costs and to customers - Value perceptions increase with quality service and but decrease with price To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -1
 Last Class Review • Satisfaction - reflects a person’s judgment of a product’s performance perceived in relationship to expectations - If the performance falls short of he customer , the customer is disappointed. If it matches expectations, the customer is satisfied. If it exceeds them, the customer is delighted To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -2
Last Class Review • Satisfaction - reflects a person’s judgment of a product’s performance perceived in relationship to expectations - If the performance falls short of he customer , the customer is disappointed. If it matches expectations, the customer is satisfied. If it exceeds them, the customer is delighted To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -2
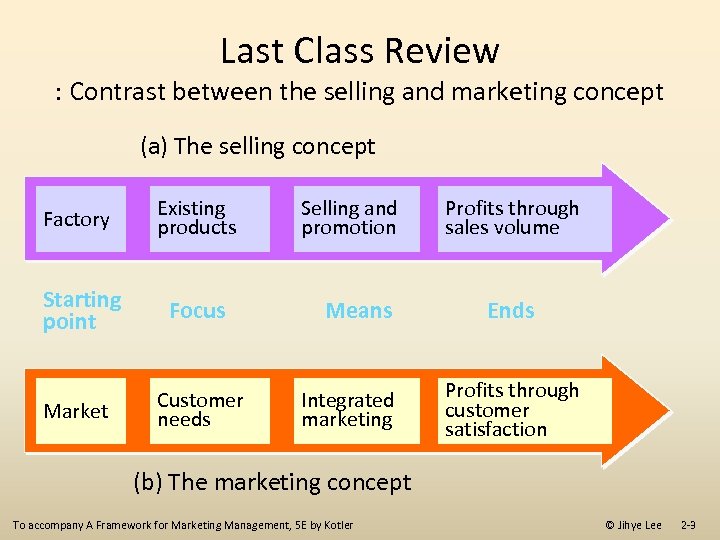 Last Class Review : Contrast between the selling and marketing concept (a) The selling concept Factory Existing products Starting point Focus Market Customer needs Selling and promotion Means Integrated marketing Profits through sales volume Ends Profits through customer satisfaction (b) The marketing concept To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -3
Last Class Review : Contrast between the selling and marketing concept (a) The selling concept Factory Existing products Starting point Focus Market Customer needs Selling and promotion Means Integrated marketing Profits through sales volume Ends Profits through customer satisfaction (b) The marketing concept To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -3
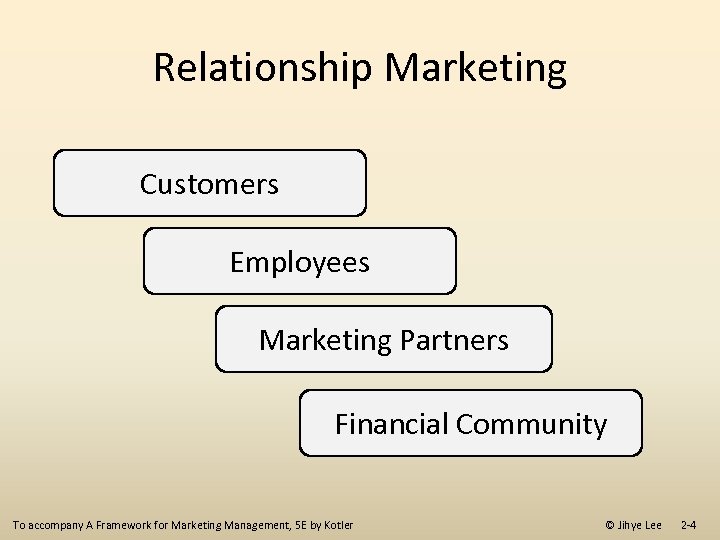 Relationship Marketing Customers Employees Marketing Partners Financial Community To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -4
Relationship Marketing Customers Employees Marketing Partners Financial Community To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -4
 The New Four Ps People Processes Programs Performance To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -5
The New Four Ps People Processes Programs Performance To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -5
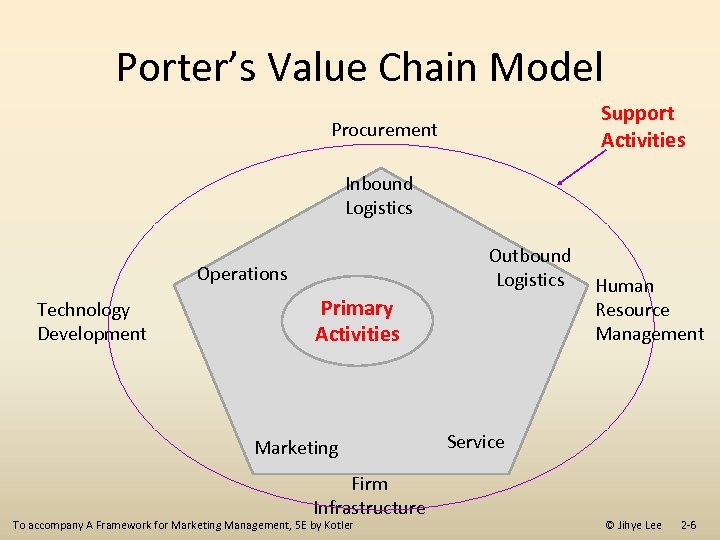 Porter’s Value Chain Model Support Activities Procurement Inbound Logistics Operations Technology Development Primary Activities Marketing Firm Infrastructure Outbound Logistics Human Resource Management Service To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -6
Porter’s Value Chain Model Support Activities Procurement Inbound Logistics Operations Technology Development Primary Activities Marketing Firm Infrastructure Outbound Logistics Human Resource Management Service To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -6
 Characteristics of Core Competencies • A source of competitive advantage • Applications in a wide variety of markets • Difficult to imitate To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -7
Characteristics of Core Competencies • A source of competitive advantage • Applications in a wide variety of markets • Difficult to imitate To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -7
 Holistic Marketing • It sees itself as integrating the value exploration, value creation, and value delivery activities with the purpose of building longterm, mutually satisfying relationships and coprosperity among key stakeholders. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -8
Holistic Marketing • It sees itself as integrating the value exploration, value creation, and value delivery activities with the purpose of building longterm, mutually satisfying relationships and coprosperity among key stakeholders. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -8
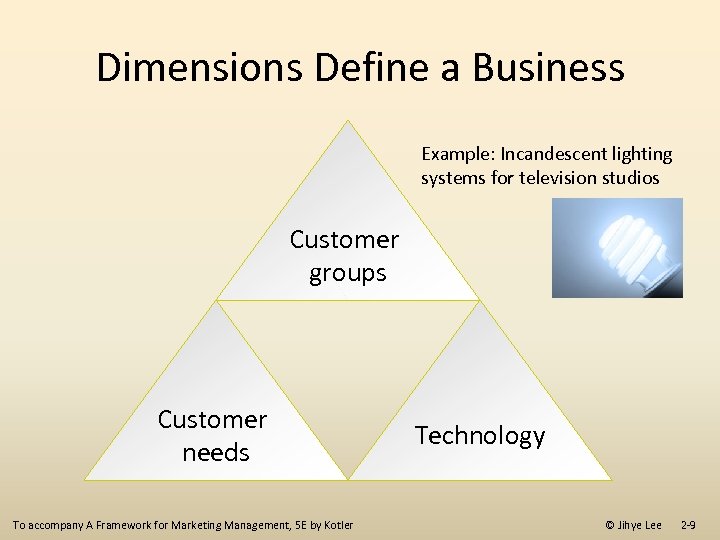 Dimensions Define a Business Example: Incandescent lighting systems for television studios Customer groups Customer needs Technology To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -9
Dimensions Define a Business Example: Incandescent lighting systems for television studios Customer groups Customer needs Technology To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -9
 Porter’s Generic Strategies Overall cost leadership Differentiation Focus To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -10
Porter’s Generic Strategies Overall cost leadership Differentiation Focus To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -10
 Categories of Marketing Alliances • • Product or service alliance Promotional alliance Logistics alliances Pricing collaborations To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -11
Categories of Marketing Alliances • • Product or service alliance Promotional alliance Logistics alliances Pricing collaborations To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -11
 Class Activity 1 • Work with a group • Please write down answers to the questions • Please submit piece of paper (with group – 1 answer sheet per a group) before you leave To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -12
Class Activity 1 • Work with a group • Please write down answers to the questions • Please submit piece of paper (with group – 1 answer sheet per a group) before you leave To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -12
 Gathering Information for Marketing Research To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -13
Gathering Information for Marketing Research To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -13
 Marketing is becoming a battle based more on information than sales power (by Kotler) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -14
Marketing is becoming a battle based more on information than sales power (by Kotler) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -14
 This chapter covers. . • • Components of Marketing Information System Marketing Research Develop Marketing Research Plan Marketing Decision Support System To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -15
This chapter covers. . • • Components of Marketing Information System Marketing Research Develop Marketing Research Plan Marketing Decision Support System To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -15
 Marketing Information System • A marketing information system consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -16
Marketing Information System • A marketing information system consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute needed, timely, and accurate information to marketing decision makers. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -16
 Internal Records • Order-to-Payment Cycle - The heart of the internal records system • Sales information System - Technology has allowed sales reps to have immediate access to information about their prospects and customers. (e. g. Salesforce. com) • Database, Data Warehousing, and Data Mining - Marketing databases facilitate data mining efforts which provide customer and prospect insights To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -17
Internal Records • Order-to-Payment Cycle - The heart of the internal records system • Sales information System - Technology has allowed sales reps to have immediate access to information about their prospects and customers. (e. g. Salesforce. com) • Database, Data Warehousing, and Data Mining - Marketing databases facilitate data mining efforts which provide customer and prospect insights To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -17
 Marketing Intelligence • A set of procedures and sources that managers use to obtain everyday information about developments in the marketing environments. • Internal records systems supplies “results” data, and the marketing intelligence system supplies “happening” data. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -18
Marketing Intelligence • A set of procedures and sources that managers use to obtain everyday information about developments in the marketing environments. • Internal records systems supplies “results” data, and the marketing intelligence system supplies “happening” data. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -18
 Marketing Intelligence (cont. , ) • Steps for improving marketing intelligence (refer to table 3. 1) a) Train sales force to observe and report new developments b) Motivate channel members and others to share intelligence c) Network externally to collect intelligence on competitors d) Develop customer advisory panels e) Purchase information from outside suppliers f) Gather customer feedback on competition To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -19
Marketing Intelligence (cont. , ) • Steps for improving marketing intelligence (refer to table 3. 1) a) Train sales force to observe and report new developments b) Motivate channel members and others to share intelligence c) Network externally to collect intelligence on competitors d) Develop customer advisory panels e) Purchase information from outside suppliers f) Gather customer feedback on competition To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -19
 Marketing Research • Defining a marketing problem and opportunity • Systematically collecting and analyzing information • Recommending actions to improve an organization’s marketing activities. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -20
Marketing Research • Defining a marketing problem and opportunity • Systematically collecting and analyzing information • Recommending actions to improve an organization’s marketing activities. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -20
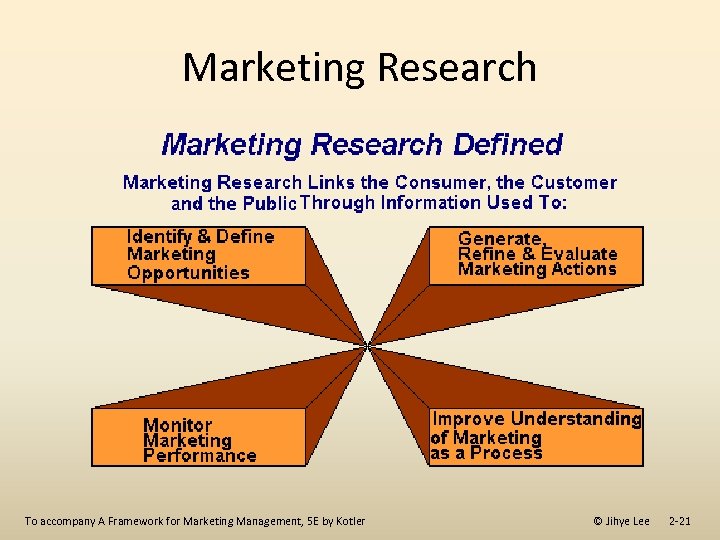 Marketing Research To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -21
Marketing Research To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -21
 Good Marketing Research. . • Is difficult • Why? ØDo consumers really know whether they are likely to buy new product? ØIf they know the answer, will they tell? ØWill they buy it if they say that they will To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -22
Good Marketing Research. . • Is difficult • Why? ØDo consumers really know whether they are likely to buy new product? ØIf they know the answer, will they tell? ØWill they buy it if they say that they will To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -22
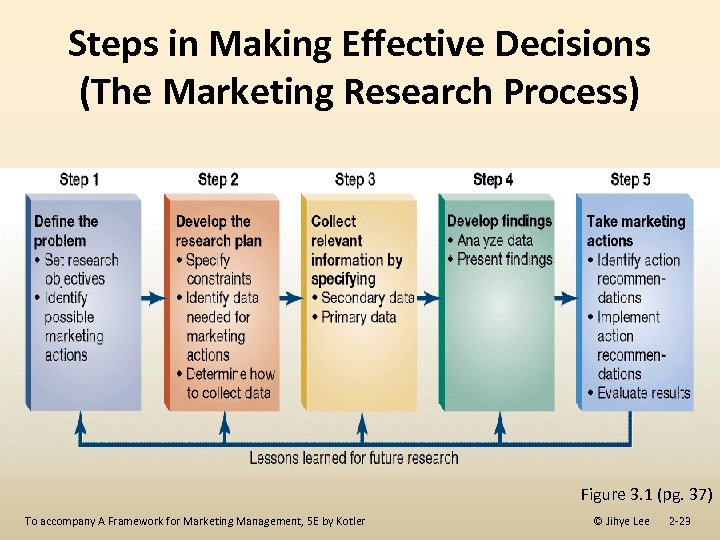 Steps in Making Effective Decisions (The Marketing Research Process) Figure 3. 1 (pg. 37) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -23
Steps in Making Effective Decisions (The Marketing Research Process) Figure 3. 1 (pg. 37) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -23
 Step 1: Define the Problem A. Define the Problem B. State Research Objectives C. Identify Possible Marketing Actions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -24
Step 1: Define the Problem A. Define the Problem B. State Research Objectives C. Identify Possible Marketing Actions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -24
 Step 1: Define the Problem A. Define the problem: “Will offering an in-flight Internet service create enough preference and profit for American Airlines to justify its cost against other possible investments in service enhancements American might make? ” To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -25
Step 1: Define the Problem A. Define the problem: “Will offering an in-flight Internet service create enough preference and profit for American Airlines to justify its cost against other possible investments in service enhancements American might make? ” To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -25
 Step 1: Define the Problem B. Set the research objectives: Ø Objectives are specific measurable goals the decision maker seeks to achieve in solving a problem Ø Typical marketing objectives • Increasing revenues and profits • Discovering what consumers are aware of and want • Finding out why a product isn’t selling well. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -26
Step 1: Define the Problem B. Set the research objectives: Ø Objectives are specific measurable goals the decision maker seeks to achieve in solving a problem Ø Typical marketing objectives • Increasing revenues and profits • Discovering what consumers are aware of and want • Finding out why a product isn’t selling well. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -26
 Step 1: Define the Problem B. Set the research objectives(Example: AA) Ø What types of first-class passengers would respond to an inflight internet services? Ø How many first-class passengers might choose AA because of this service? Ø How much long-term goodwill this service add to the AA’s image? Ø Relative to other services, how important is Internet service to the first-class passengers? To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -27
Step 1: Define the Problem B. Set the research objectives(Example: AA) Ø What types of first-class passengers would respond to an inflight internet services? Ø How many first-class passengers might choose AA because of this service? Ø How much long-term goodwill this service add to the AA’s image? Ø Relative to other services, how important is Internet service to the first-class passengers? To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -27
 Step 1: Define the Problem C. Identify Possible Marketing Actions
Step 1: Define the Problem C. Identify Possible Marketing Actions
 Types of Research Exploratory Descriptive Causal To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -29
Types of Research Exploratory Descriptive Causal To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -29
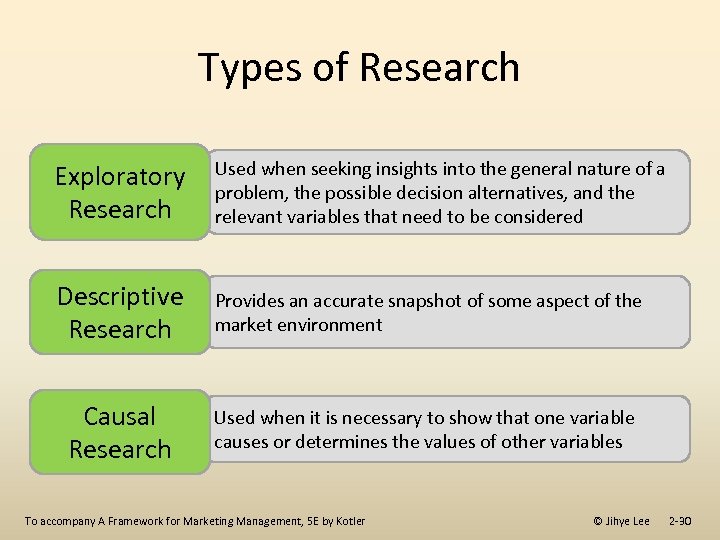 Types of Research Exploratory Research Used when seeking insights into the general nature of a problem, the possible decision alternatives, and the relevant variables that need to be considered Descriptive Research Provides an accurate snapshot of some aspect of the market environment Causal Research Used when it is necessary to show that one variable causes or determines the values of other variables To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -30
Types of Research Exploratory Research Used when seeking insights into the general nature of a problem, the possible decision alternatives, and the relevant variables that need to be considered Descriptive Research Provides an accurate snapshot of some aspect of the market environment Causal Research Used when it is necessary to show that one variable causes or determines the values of other variables To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -30
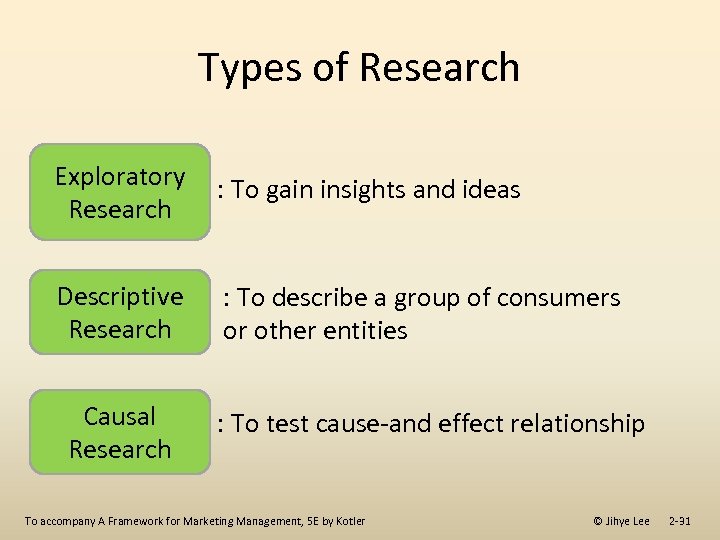 Types of Research Exploratory : To gain insights and ideas Research Descriptive Research : To describe a group of consumers or other entities Causal Research : To test cause-and effect relationship To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -31
Types of Research Exploratory : To gain insights and ideas Research Descriptive Research : To describe a group of consumers or other entities Causal Research : To test cause-and effect relationship To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -31
 Type of Research A. Exploratory • Why do people buy chocolates? -As gifts -For lovers -Tradition • What kind of questions can exploratory answer?
Type of Research A. Exploratory • Why do people buy chocolates? -As gifts -For lovers -Tradition • What kind of questions can exploratory answer?
 Type of Research A. Descriptive Research • What percentage of consumers buy chocolates for gifts, and what percentage for selfconsumption? • What kind of questions can descriptive answer? ?
Type of Research A. Descriptive Research • What percentage of consumers buy chocolates for gifts, and what percentage for selfconsumption? • What kind of questions can descriptive answer? ?
 Type of Research A. Causal Research • If you make the package red instead of green, will they buy more? • What kind of questions can causal answer?
Type of Research A. Causal Research • If you make the package red instead of green, will they buy more? • What kind of questions can causal answer?
 Step 2: Develop the Research Plan A. Specify the constraints on the research activity B. Identifying the data needed for marketing actions C. Determine how to collect the data To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -35
Step 2: Develop the Research Plan A. Specify the constraints on the research activity B. Identifying the data needed for marketing actions C. Determine how to collect the data To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -35
 Step 2: Develop the Research Plan A. Specify the constraints on the research activity ØRestrictions placed on potential solutions by the nature and importance of the problem. ØCommon constraints are limitations on time and money available to solve problems. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -36
Step 2: Develop the Research Plan A. Specify the constraints on the research activity ØRestrictions placed on potential solutions by the nature and importance of the problem. ØCommon constraints are limitations on time and money available to solve problems. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -36
 Step 2: Develop the Research Plan B. Identifying the data needed for marketing actions Ø Often research studies collect data that are interesting but irrelevant for marketing decisions that result in marketing actions. Ø Focus on collecting data that help managers make clear decisions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -37
Step 2: Develop the Research Plan B. Identifying the data needed for marketing actions Ø Often research studies collect data that are interesting but irrelevant for marketing decisions that result in marketing actions. Ø Focus on collecting data that help managers make clear decisions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -37
 Step 2: Develop the Research Plan C. Determine how to collect the data. 1) Concepts ü Hypothesis: Idea about the relationship of two or more factors or what might happen in the future e. g. "Red meat consumption increases as real disposable incomes increase. “ ü Hypothesis can come from many sources; • Theoretical reasoning • Marketing studies • Technical breakthroughs • Informal conversations • Educated guesses • Customer suggestions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -38
Step 2: Develop the Research Plan C. Determine how to collect the data. 1) Concepts ü Hypothesis: Idea about the relationship of two or more factors or what might happen in the future e. g. "Red meat consumption increases as real disposable incomes increase. “ ü Hypothesis can come from many sources; • Theoretical reasoning • Marketing studies • Technical breakthroughs • Informal conversations • Educated guesses • Customer suggestions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -38
 Step 2: Develop the Research Plan C. Determine how to collect the data. 2) Methods ü The approaches that can be used to collect data to solve all or part of a problem. ü Sampling Plan -Sampling unit: who is to be surveyed? -Sample size: How many people should be surveyed? -Sampling procedure: How should the respondents be chosen? To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -39
Step 2: Develop the Research Plan C. Determine how to collect the data. 2) Methods ü The approaches that can be used to collect data to solve all or part of a problem. ü Sampling Plan -Sampling unit: who is to be surveyed? -Sample size: How many people should be surveyed? -Sampling procedure: How should the respondents be chosen? To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -39
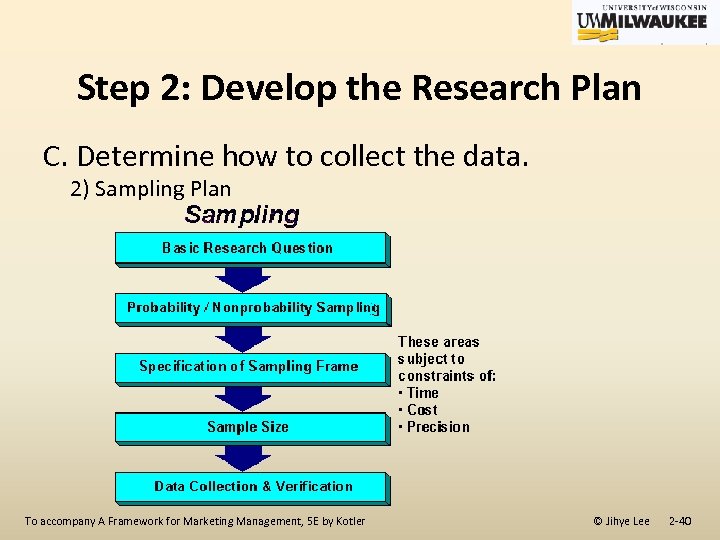 Step 2: Develop the Research Plan C. Determine how to collect the data. 2) Sampling Plan To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -40
Step 2: Develop the Research Plan C. Determine how to collect the data. 2) Sampling Plan To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -40
 Step 3: Collect Relevant Information Gathering Information • Why do we need to gather information? • What do we gather information for? To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -41
Step 3: Collect Relevant Information Gathering Information • Why do we need to gather information? • What do we gather information for? To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -41
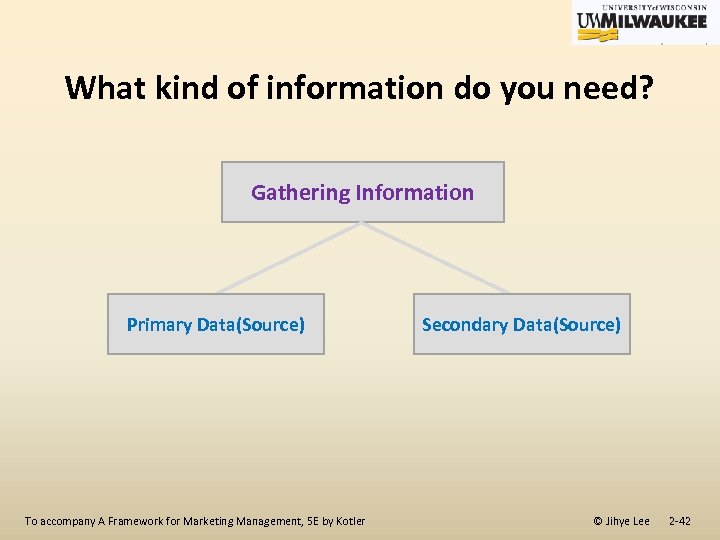 What kind of information do you need? Gathering Information Primary Data(Source) Secondary Data(Source) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -42
What kind of information do you need? Gathering Information Primary Data(Source) Secondary Data(Source) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -42
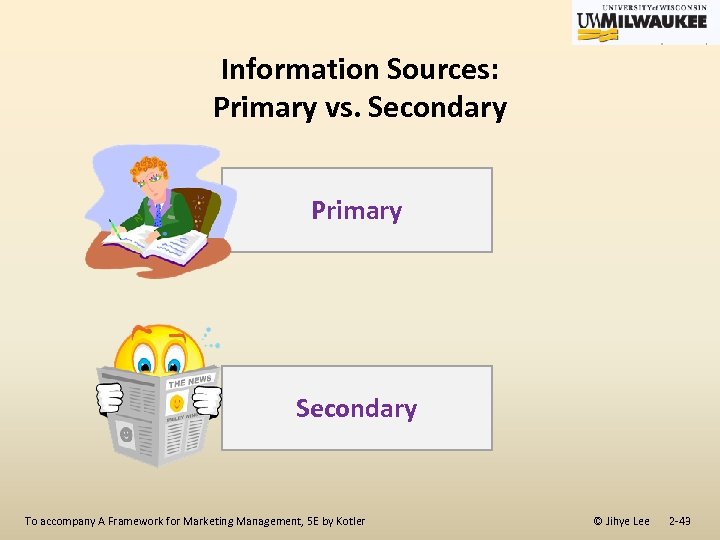 Information Sources: Primary vs. Secondary Primary Secondary To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -43
Information Sources: Primary vs. Secondary Primary Secondary To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -43
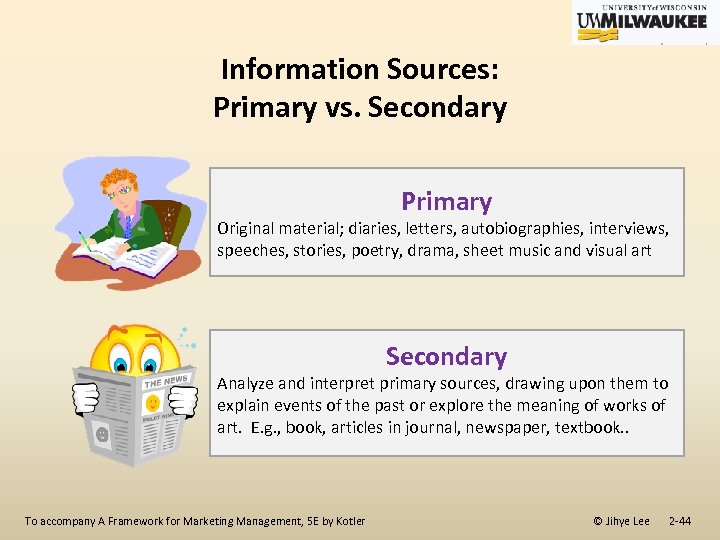 Information Sources: Primary vs. Secondary Primary Original material; diaries, letters, autobiographies, interviews, speeches, stories, poetry, drama, sheet music and visual art Secondary Analyze and interpret primary sources, drawing upon them to explain events of the past or explore the meaning of works of art. E. g. , book, articles in journal, newspaper, textbook. . To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -44
Information Sources: Primary vs. Secondary Primary Original material; diaries, letters, autobiographies, interviews, speeches, stories, poetry, drama, sheet music and visual art Secondary Analyze and interpret primary sources, drawing upon them to explain events of the past or explore the meaning of works of art. E. g. , book, articles in journal, newspaper, textbook. . To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -44
 The Rice Analogy: Primary vs. Secondary?
The Rice Analogy: Primary vs. Secondary?
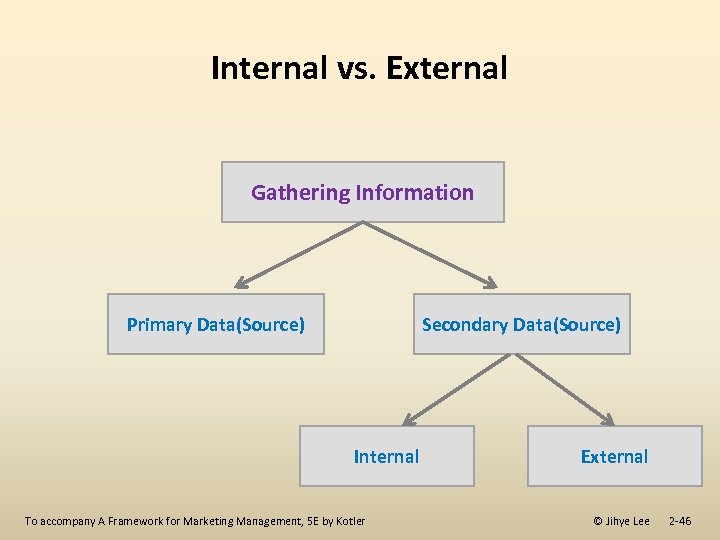 Internal vs. External Gathering Information Primary Data(Source) Secondary Data(Source) Internal External To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -46
Internal vs. External Gathering Information Primary Data(Source) Secondary Data(Source) Internal External To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -46
 Internal Source of Secondary Data • Financial statements • Sales reports • Research reports • Customer demographics • Customer database • Product purchase files • Inventory management
Internal Source of Secondary Data • Financial statements • Sales reports • Research reports • Customer demographics • Customer database • Product purchase files • Inventory management
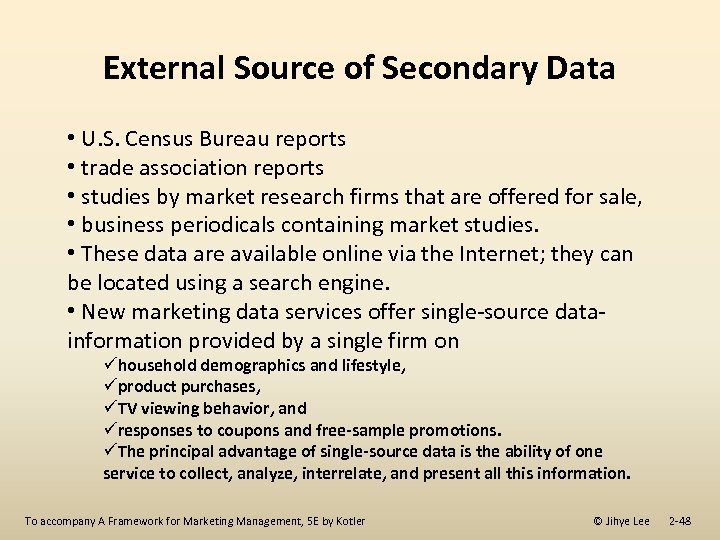 External Source of Secondary Data • U. S. Census Bureau reports • trade association reports • studies by market research firms that are offered for sale, • business periodicals containing market studies. • These data are available online via the Internet; they can be located using a search engine. • New marketing data services offer single-source datainformation provided by a single firm on ühousehold demographics and lifestyle, üproduct purchases, üTV viewing behavior, and üresponses to coupons and free-sample promotions. üThe principal advantage of single-source data is the ability of one service to collect, analyze, interrelate, and present all this information. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -48
External Source of Secondary Data • U. S. Census Bureau reports • trade association reports • studies by market research firms that are offered for sale, • business periodicals containing market studies. • These data are available online via the Internet; they can be located using a search engine. • New marketing data services offer single-source datainformation provided by a single firm on ühousehold demographics and lifestyle, üproduct purchases, üTV viewing behavior, and üresponses to coupons and free-sample promotions. üThe principal advantage of single-source data is the ability of one service to collect, analyze, interrelate, and present all this information. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -48
 External Source of Secondary Data (cont. , ) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -49
External Source of Secondary Data (cont. , ) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -49
 Secondary Data: Internal vs. External Source A. Internal • Records from the seller’s own company. • Orders, sales, inventory levels, costs, prices, etc. • Results data: What have happened. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -50
Secondary Data: Internal vs. External Source A. Internal • Records from the seller’s own company. • Orders, sales, inventory levels, costs, prices, etc. • Results data: What have happened. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -50
 Secondary Data: Internal vs. External Source B. External • Everyday information about developments in the marketing environment. • Books, newspapers, talking to customers, internet discussion groups, blogs, meetings with other company managers, etc. • Happenings-data: What are happening. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -51
Secondary Data: Internal vs. External Source B. External • Everyday information about developments in the marketing environment. • Books, newspapers, talking to customers, internet discussion groups, blogs, meetings with other company managers, etc. • Happenings-data: What are happening. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -51
 Discussion • Can you give us examples of gathering internal/external data by companies you work(ed) for? Or companies you know about? To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -52
Discussion • Can you give us examples of gathering internal/external data by companies you work(ed) for? Or companies you know about? To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -52
 Internal Data: Wal-Mart operates a sales and inventory data warehouse that captures data on every item, for every customer, for every store, every day and refreshes it every hour. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -53
Internal Data: Wal-Mart operates a sales and inventory data warehouse that captures data on every item, for every customer, for every store, every day and refreshes it every hour. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -53
 Internal Data: Trader Joe’s Trader Joe's stores offer an ever-changing inventory of about 2, 000 products. Many products are changed often due to popularity and prices. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -54
Internal Data: Trader Joe’s Trader Joe's stores offer an ever-changing inventory of about 2, 000 products. Many products are changed often due to popularity and prices. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -54
 Internal Data: Best Buy Like many other companies, Best Buy shows the availability of its products in every store. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -55
Internal Data: Best Buy Like many other companies, Best Buy shows the availability of its products in every store. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -55
 Internal Data • Q: Besides the research/analysis we can do with internal data, what else can we do with it? • We can better serve the customers with it. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -56
Internal Data • Q: Besides the research/analysis we can do with internal data, what else can we do with it? • We can better serve the customers with it. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -56
 Example: Amazon. com • Amazon tracked the purchases of its customers and told the customers what others bought. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -57
Example: Amazon. com • Amazon tracked the purchases of its customers and told the customers what others bought. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -57
 External Data • Independent customer goods and service review forums • Distributor or sales agent feedback sites • Combination sites offering customer reviews and expert opinions (Biz. Rate, Yelp. com, ZDNet…. ) • Customer complaint sites • Public blogs To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -58
External Data • Independent customer goods and service review forums • Distributor or sales agent feedback sites • Combination sites offering customer reviews and expert opinions (Biz. Rate, Yelp. com, ZDNet…. ) • Customer complaint sites • Public blogs To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -58
 External Data • Consumer report, trend of the market, TV viewership's, etc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -59
External Data • Consumer report, trend of the market, TV viewership's, etc. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -59
 External Data: Gizmodo offers reviews on all kinds of products, and companies can often find there information about their competitors and themselves. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -60
External Data: Gizmodo offers reviews on all kinds of products, and companies can often find there information about their competitors and themselves. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -60
 External Data: Websites • Facebook • Windows Live Space • Yahoo Groups To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -61
External Data: Websites • Facebook • Windows Live Space • Yahoo Groups To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -61
 Primary Data by Research Approach • Facts and figures that are newly collected for the project. • Two ways to collect new or primary data ü Observing people ü Asking them questions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -62
Primary Data by Research Approach • Facts and figures that are newly collected for the project. • Two ways to collect new or primary data ü Observing people ü Asking them questions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -62
 Dis/Advantage of Primary Data • Advantage Ø Answer specific questions Ø Current data Ø Known source Ø Secrecy can be maintained • Disadvantage Ø Time-consuming Ø Expensive
Dis/Advantage of Primary Data • Advantage Ø Answer specific questions Ø Current data Ø Known source Ø Secrecy can be maintained • Disadvantage Ø Time-consuming Ø Expensive
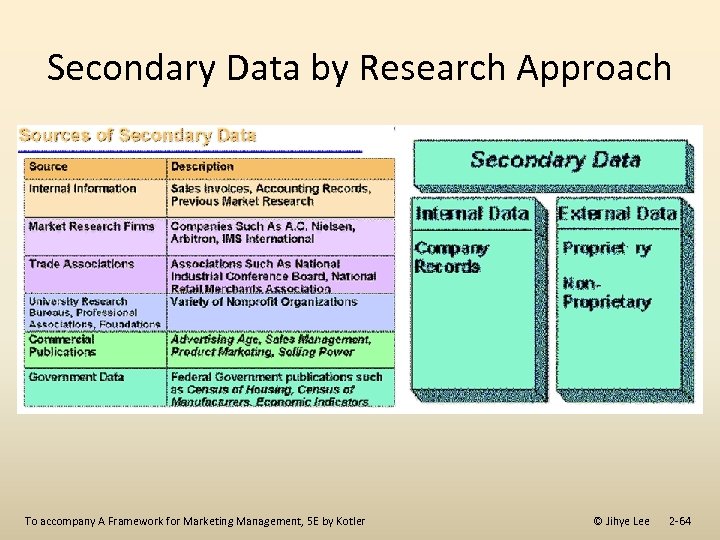 Secondary Data by Research Approach To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -64
Secondary Data by Research Approach To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -64
 Dis/Advantage of Secondary Data • Advantage Ø Time savings if data have already been collected(Rapid availability) ØLow cost, such as free or inexpensive census reports. ØGreater level of detail, especially in U. S. Census bureau data. • Disadvantage Ø May be obsolete or out of date. Ø Definitions or categories may not be quite right for your project. ØData collected for another purpose may not be specific enough for your project.
Dis/Advantage of Secondary Data • Advantage Ø Time savings if data have already been collected(Rapid availability) ØLow cost, such as free or inexpensive census reports. ØGreater level of detail, especially in U. S. Census bureau data. • Disadvantage Ø May be obsolete or out of date. Ø Definitions or categories may not be quite right for your project. ØData collected for another purpose may not be specific enough for your project.
 Research Approach • • • Observational and ethnographic Focus group Survey Behavioral Experimental To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -66
Research Approach • • • Observational and ethnographic Focus group Survey Behavioral Experimental To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -66
 Ethnographic To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -67
Ethnographic To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -67
 Ethnographic (example) The goal was to discover how to get this consumer segment to open new checking and savings accounts. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -68
Ethnographic (example) The goal was to discover how to get this consumer segment to open new checking and savings accounts. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -68
 Focus Group To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -69
Focus Group To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -69
 Survey: Questionnaire Data • Facts and figures obtained by asking people about their attitudes, awareness, intentions, and behaviors. • Essential that the researcher concentrate on questions directly related to the marketing problem at hand. üMail, fax, and Internet or e-mail surveys üTelephone surveys
Survey: Questionnaire Data • Facts and figures obtained by asking people about their attitudes, awareness, intentions, and behaviors. • Essential that the researcher concentrate on questions directly related to the marketing problem at hand. üMail, fax, and Internet or e-mail surveys üTelephone surveys
 Questionnaire Do’s and Don’ts • Ensure questions are free of bias • Make questions simple • Make questions specific • • • Avoid jargon Avoid sophisticated words Avoid ambiguous words Avoid negatives Avoid hypotheticals Avoid words that could be misheard Use response bands Use mutually exclusive categories Allow for “other” in fixed response questions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -71
Questionnaire Do’s and Don’ts • Ensure questions are free of bias • Make questions simple • Make questions specific • • • Avoid jargon Avoid sophisticated words Avoid ambiguous words Avoid negatives Avoid hypotheticals Avoid words that could be misheard Use response bands Use mutually exclusive categories Allow for “other” in fixed response questions To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -71
 Research Instruments • Questionnaires • Qualitative Measures • Technological Devices To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -72
Research Instruments • Questionnaires • Qualitative Measures • Technological Devices To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -72
 Qualitative Techniques Word Associations Visualization Projective Techniques Laddering To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -73
Qualitative Techniques Word Associations Visualization Projective Techniques Laddering To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -73
 Projective Methods Word Associations Sentence Completion Storytelling Other Give people an incomplete stimulus and ask them to complete it, or give them an ambiguous stimulus and ask them to make sense of it. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -74
Projective Methods Word Associations Sentence Completion Storytelling Other Give people an incomplete stimulus and ask them to complete it, or give them an ambiguous stimulus and ask them to make sense of it. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -74
 Word Associations • Ask subjects what words come to mind when they hear the brand’s name. • “What does the Tiffany name mean to you? Tell me what comes to mind when you think of Tiffany jewelry. ” To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -75
Word Associations • Ask subjects what words come to mind when they hear the brand’s name. • “What does the Tiffany name mean to you? Tell me what comes to mind when you think of Tiffany jewelry. ” To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -75
 Sentence Completion To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -76
Sentence Completion To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -76
 Storytelling To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -77
Storytelling To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -77
 Visualization • Require people to create a collage from magazine photos or drawings to depict their perceptions. • Ex: ZMET technique asks participants to select a minimum of 12 images from their own sources to represent their thoughts and feelings about the brand; the in a one-on-one interview the study administrator explores the images with the participant and reveals hidden meanings; finally the participants use a computer program to create a collage with these images that communicates their subconscious thoughts and feelings about the brand To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -78
Visualization • Require people to create a collage from magazine photos or drawings to depict their perceptions. • Ex: ZMET technique asks participants to select a minimum of 12 images from their own sources to represent their thoughts and feelings about the brand; the in a one-on-one interview the study administrator explores the images with the participant and reveals hidden meanings; finally the participants use a computer program to create a collage with these images that communicates their subconscious thoughts and feelings about the brand To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -78
 Visualization To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -79
Visualization To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -79
 Laddering • A series of increasingly more specific “why” questions can reveal consumer motivation and consumers’ deeper, more abstract goals. • “Why …” “Why…” To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -80
Laddering • A series of increasingly more specific “why” questions can reveal consumer motivation and consumers’ deeper, more abstract goals. • “Why …” “Why…” To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -80
 TAT: Thematic Apperception Test make up a story that reflects what you think is happening in this picture. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -81
TAT: Thematic Apperception Test make up a story that reflects what you think is happening in this picture. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -81
 Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
 Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research • Good for early stages of a study • the researcher freedom to let the study unfold more naturally • gains more detailed and rich data • the researcher a subjective view of the study • the researcher to measure and analyze data • measure data using statistics (IV &DV) • more objective about the findings of the research • does not study things in a natural setting • a large sample of the population must be studied To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -83
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research • Good for early stages of a study • the researcher freedom to let the study unfold more naturally • gains more detailed and rich data • the researcher a subjective view of the study • the researcher to measure and analyze data • measure data using statistics (IV &DV) • more objective about the findings of the research • does not study things in a natural setting • a large sample of the population must be studied To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -83
 Marketing Research: Qualitative vs. Quantitative To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -84
Marketing Research: Qualitative vs. Quantitative To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -84
 Qualitative VS Quantitative To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -85
Qualitative VS Quantitative To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -85
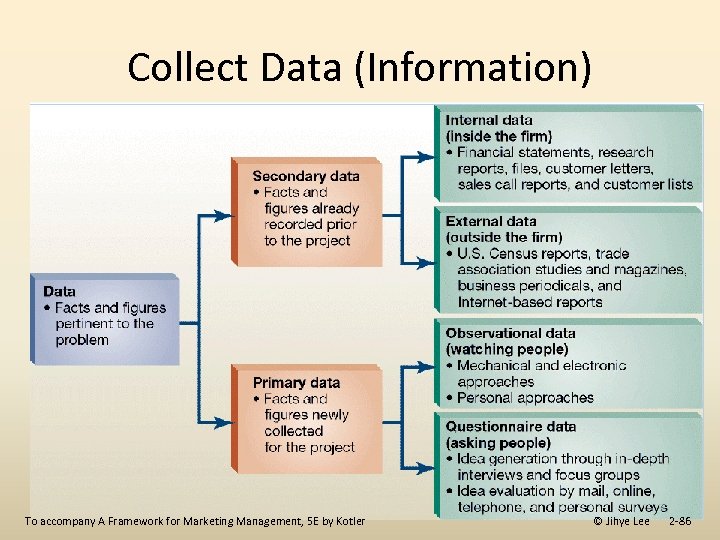 Collect Data (Information) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -86
Collect Data (Information) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -86
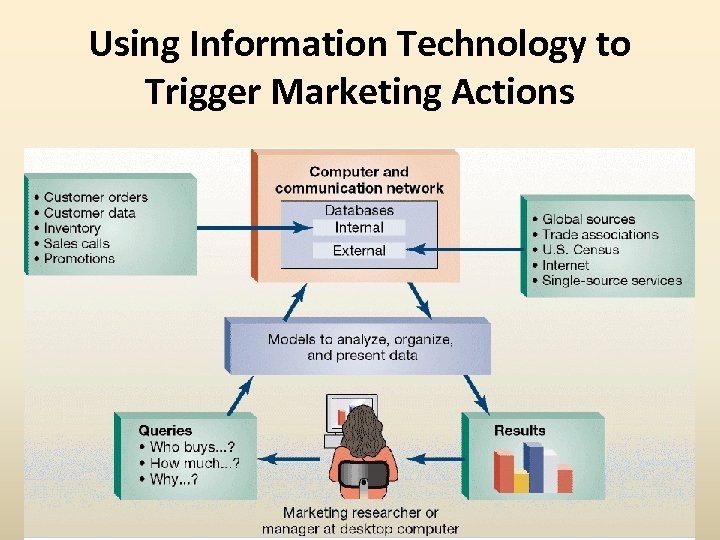 Using Information Technology to Trigger Marketing Actions
Using Information Technology to Trigger Marketing Actions
 Step 4. Analyze the information • The researchers may test different hypotheses and theories, applying sensitivity analysis to test assumptions and the strength of the conclusions • Clear, visual, and concise answers are a competitive advantage to decision makers. However, clear analysis takes time, expertise, and creativity. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -88
Step 4. Analyze the information • The researchers may test different hypotheses and theories, applying sensitivity analysis to test assumptions and the strength of the conclusions • Clear, visual, and concise answers are a competitive advantage to decision makers. However, clear analysis takes time, expertise, and creativity. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -88
 Step 5. Present the Findings • Findings must be clear. This means Øget to the heart of the matter Øavoiding distracting side issues Ødeliver results visually Øa single page if possible. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -89
Step 5. Present the Findings • Findings must be clear. This means Øget to the heart of the matter Øavoiding distracting side issues Ødeliver results visually Øa single page if possible. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -89
 Step 6. Make the decision • Identify the Action Recommendations • Implement the Action Recommendations Ø Actions are the whole point of the research: Ø You have to know what’s going on in the market Ø If you find that there is a problem, you have to take steps to fix it. • Evaluate the Results Ø Evaluate the decision itself Ø Evaluate the decision process used. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -90
Step 6. Make the decision • Identify the Action Recommendations • Implement the Action Recommendations Ø Actions are the whole point of the research: Ø You have to know what’s going on in the market Ø If you find that there is a problem, you have to take steps to fix it. • Evaluate the Results Ø Evaluate the decision itself Ø Evaluate the decision process used. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -90
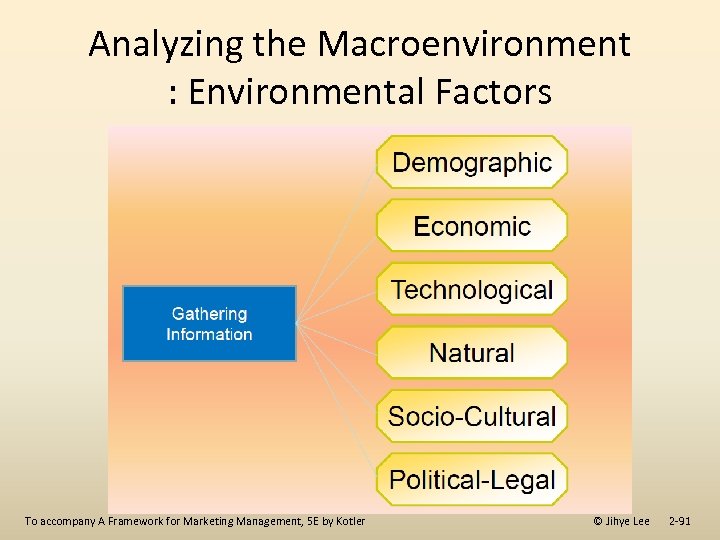 Analyzing the Macroenvironment : Environmental Factors To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -91
Analyzing the Macroenvironment : Environmental Factors To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -91
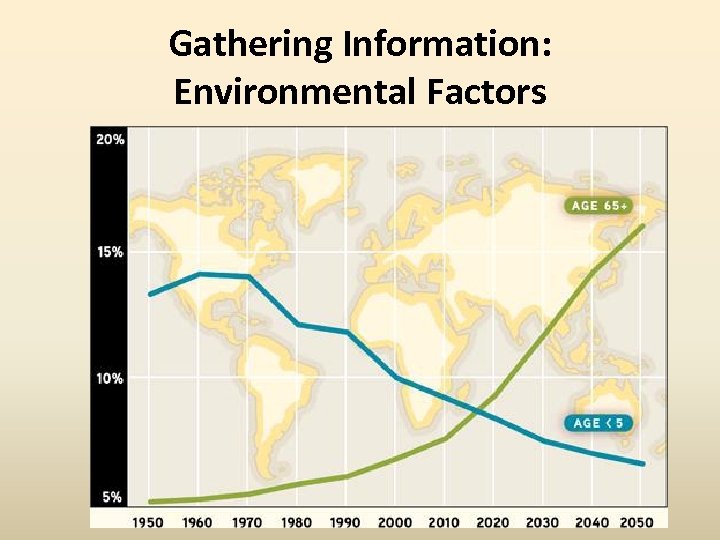 Gathering Information: Environmental Factors
Gathering Information: Environmental Factors
 Environmental Factors: Demographic Example: the Senior Market • Multivitamins • Food • Investment advice • Auto insurance
Environmental Factors: Demographic Example: the Senior Market • Multivitamins • Food • Investment advice • Auto insurance
 Environmental Factors: Demographic • Population Growth: source of concern for two reasons ü Resources are required to support vast growth ü Growth is highest in areas that can lease afford it • Population age mix: strong determinant of needs • Ethnic markets • Educational groups: from illiterates to those with professional degrees • Household patterns: non-traditional households are growing quickly and have special needs (e. g. , live-alones, single parents, childless married couples… To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -94
Environmental Factors: Demographic • Population Growth: source of concern for two reasons ü Resources are required to support vast growth ü Growth is highest in areas that can lease afford it • Population age mix: strong determinant of needs • Ethnic markets • Educational groups: from illiterates to those with professional degrees • Household patterns: non-traditional households are growing quickly and have special needs (e. g. , live-alones, single parents, childless married couples… To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -94
 Environmental Factors: Economic • • Consumer Psychology Income Distribution Savings, Debt, and Credit Levi’s has responded to changes in income distribution by offering an upscale line and a mass market line To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -95
Environmental Factors: Economic • • Consumer Psychology Income Distribution Savings, Debt, and Credit Levi’s has responded to changes in income distribution by offering an upscale line and a mass market line To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -95
 Consumer Psychology To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -96
Consumer Psychology To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -96
 Income Distribution • Income distribution: four types of industrial structures Ø subsistence economies; few marketing opportunities Ø raw –material exporting economies Ø industrializing economies – new rich class and growing middle class Ø industrial economies – rich markets To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -97
Income Distribution • Income distribution: four types of industrial structures Ø subsistence economies; few marketing opportunities Ø raw –material exporting economies Ø industrializing economies – new rich class and growing middle class Ø industrial economies – rich markets To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -97
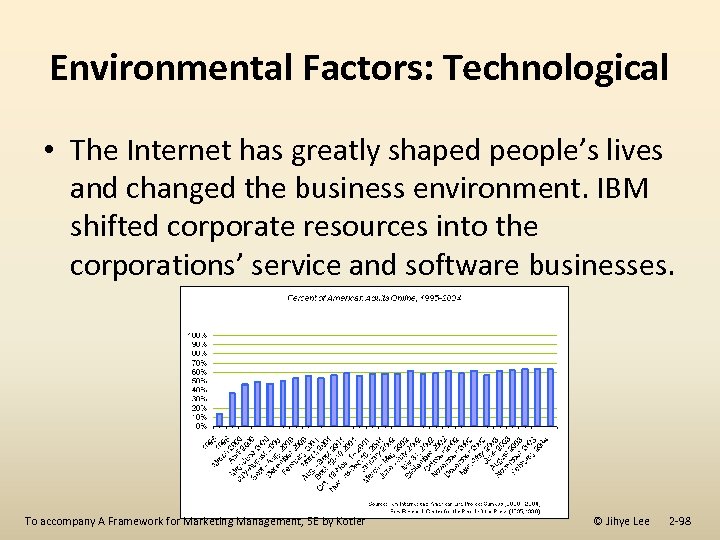 Environmental Factors: Technological • The Internet has greatly shaped people’s lives and changed the business environment. IBM shifted corporate resources into the corporations’ service and software businesses. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -98
Environmental Factors: Technological • The Internet has greatly shaped people’s lives and changed the business environment. IBM shifted corporate resources into the corporations’ service and software businesses. To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -98
 Environmental Factors: Natural • Example: “Green” cars Ø Shortage of raw materials Ø Increased energy costs Ø Anti-pollution pressures Ø Governmental protections To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -99
Environmental Factors: Natural • Example: “Green” cars Ø Shortage of raw materials Ø Increased energy costs Ø Anti-pollution pressures Ø Governmental protections To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -99
 Environmental Factors: Socio-Cultural Example: Whole Foods Market
Environmental Factors: Socio-Cultural Example: Whole Foods Market
 Environmental Factors: Socio-Cultural • Society shapes beliefs, values, and norms • People have views of themselves, others, organizations, society, nature, and the universe • High persistence of core values To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -101
Environmental Factors: Socio-Cultural • Society shapes beliefs, values, and norms • People have views of themselves, others, organizations, society, nature, and the universe • High persistence of core values To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -101
 Environmental Factors: Political-Legal • Increase in business legislation • Growth of special interest groups To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -102
Environmental Factors: Political-Legal • Increase in business legislation • Growth of special interest groups To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -102
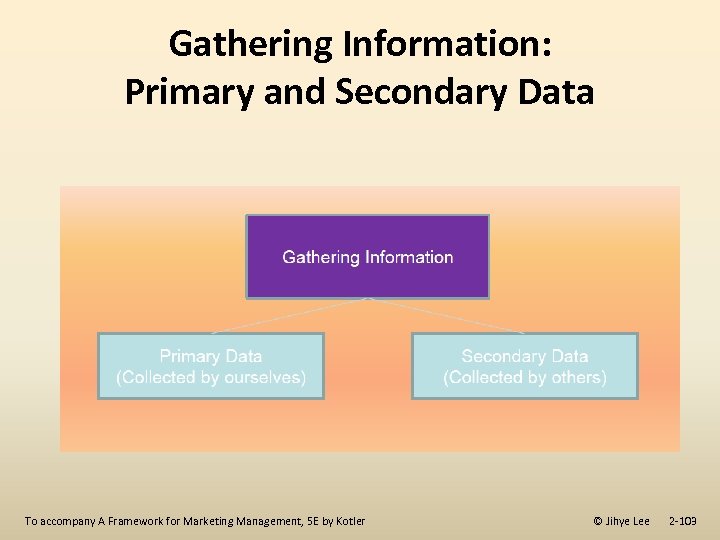 Gathering Information: Primary and Secondary Data To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -103
Gathering Information: Primary and Secondary Data To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -103
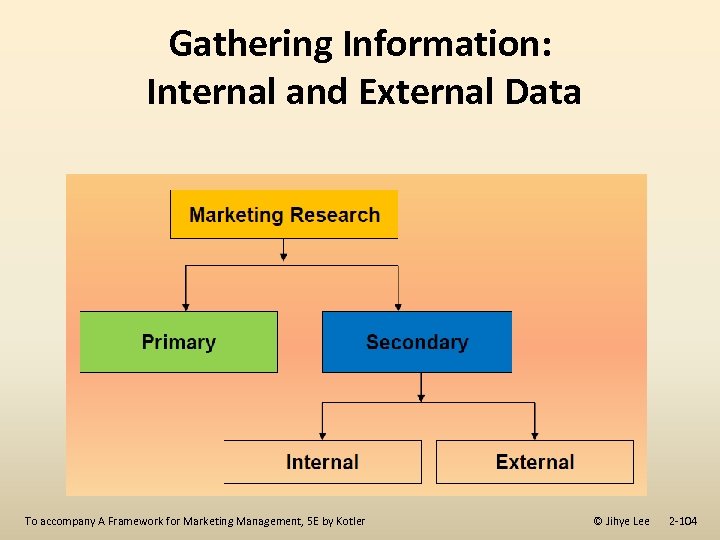 Gathering Information: Internal and External Data To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -104
Gathering Information: Internal and External Data To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -104
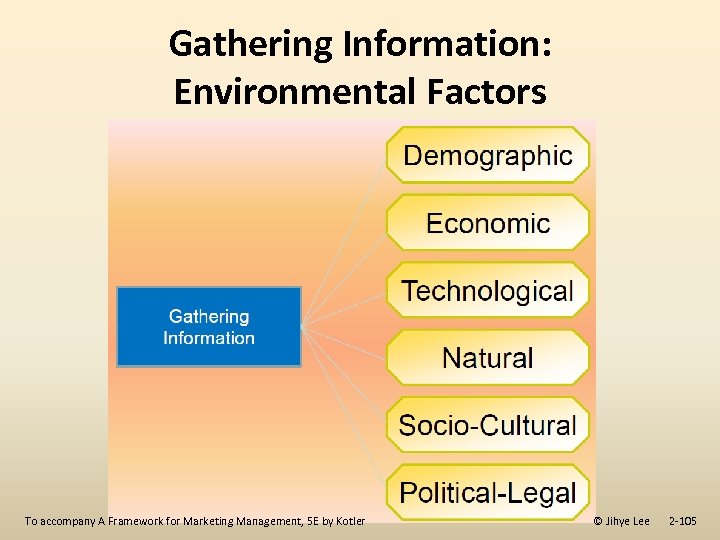 Gathering Information: Environmental Factors To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -105
Gathering Information: Environmental Factors To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -105
 Class Activity 2 • Work with a group • Please put down your choices, and explain why you made such choices • Present your choices to the class To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -106
Class Activity 2 • Work with a group • Please put down your choices, and explain why you made such choices • Present your choices to the class To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 5 E by Kotler © Jihye Lee 2 -106


