0322de155131ed8ab79520eecd11086c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 MARKETING MANAGEMENT Adapting marketing for the new economy and Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty Kotler Keller
MARKETING MANAGEMENT Adapting marketing for the new economy and Creating Customer Value, Satisfaction, and Loyalty Kotler Keller
 Major drivers of the new economy • Digitization and connectivity • Disintermediation and re-intermediation • Online middlemen • Customization and customerization • Individually differentiated products vs. personalized products and channels • Industry convergence • Blurring of boundaries • Disney, Kodak etc
Major drivers of the new economy • Digitization and connectivity • Disintermediation and re-intermediation • Online middlemen • Customization and customerization • Individually differentiated products vs. personalized products and channels • Industry convergence • Blurring of boundaries • Disney, Kodak etc
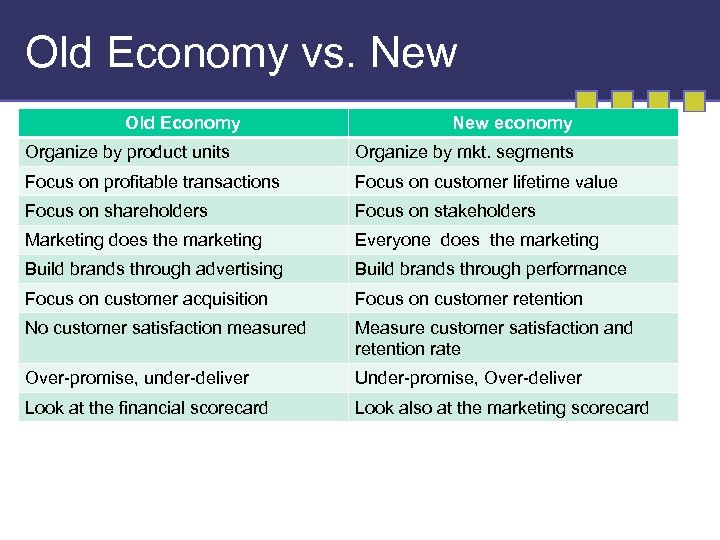 Old Economy vs. New Old Economy New economy Organize by product units Organize by mkt. segments Focus on profitable transactions Focus on customer lifetime value Focus on shareholders Focus on stakeholders Marketing does the marketing Everyone does the marketing Build brands through advertising Build brands through performance Focus on customer acquisition Focus on customer retention No customer satisfaction measured Measure customer satisfaction and retention rate Over-promise, under-deliver Under-promise, Over-deliver Look at the financial scorecard Look also at the marketing scorecard
Old Economy vs. New Old Economy New economy Organize by product units Organize by mkt. segments Focus on profitable transactions Focus on customer lifetime value Focus on shareholders Focus on stakeholders Marketing does the marketing Everyone does the marketing Build brands through advertising Build brands through performance Focus on customer acquisition Focus on customer retention No customer satisfaction measured Measure customer satisfaction and retention rate Over-promise, under-deliver Under-promise, Over-deliver Look at the financial scorecard Look also at the marketing scorecard
 E-commerce • E-commerce vs. e-business • Online transactions • Four major internet domains – B 2 C: – B 2 B: web procurement • Which is greater? Forrester and Gartner – C 2 C: information creation • Chat-rooms, blogs, IM, WOM vs. WOW – C 2 B: • Email suggestions and complaints
E-commerce • E-commerce vs. e-business • Online transactions • Four major internet domains – B 2 C: – B 2 B: web procurement • Which is greater? Forrester and Gartner – C 2 C: information creation • Chat-rooms, blogs, IM, WOM vs. WOW – C 2 B: • Email suggestions and complaints
 E-commerce • • • business-to-employee (B 2 E) business-to-government (B 2 G) government-to-business (G 2 B) government-to-government (G 2 G) government-to-citizen (G 2 C)
E-commerce • • • business-to-employee (B 2 E) business-to-government (B 2 G) government-to-business (G 2 B) government-to-government (G 2 G) government-to-citizen (G 2 C)
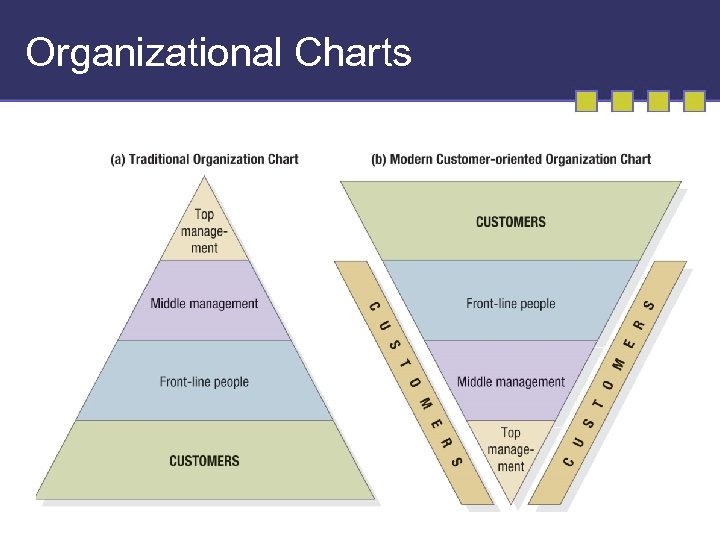 Organizational Charts
Organizational Charts
 Customer value and satisfaction • Customer perceived value • Difference between the prospective customer’s evaluation of all benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceived alternatives. • Total customer value • Perceived monetary value of the bundles of economic, functional and psychological benefits customers expect from a given market offering.
Customer value and satisfaction • Customer perceived value • Difference between the prospective customer’s evaluation of all benefits and all the costs of an offering and the perceived alternatives. • Total customer value • Perceived monetary value of the bundles of economic, functional and psychological benefits customers expect from a given market offering.
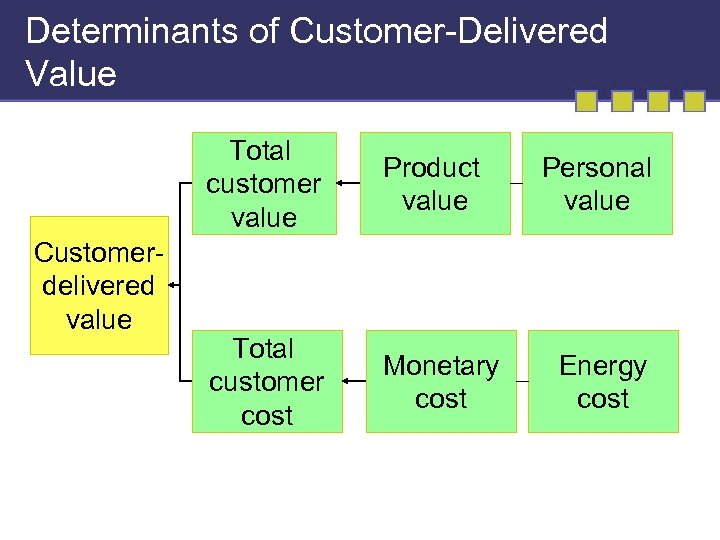 Determinants of Customer-Delivered Value Total customer value Customerdelivered value Product value Total customer cost Monetary cost Personal value Energy cost
Determinants of Customer-Delivered Value Total customer value Customerdelivered value Product value Total customer cost Monetary cost Personal value Energy cost
 Customer value and satisfaction • The real price of anything is the toil and trouble of acquiring it • Satisfaction: • Feeling of pleasure or displeasure resulting from comparing a product’s performance with the expectations.
Customer value and satisfaction • The real price of anything is the toil and trouble of acquiring it • Satisfaction: • Feeling of pleasure or displeasure resulting from comparing a product’s performance with the expectations.
 Loyalty A deeply held commitment to re-buy or re-patronize a preferred product or service in the future despite situational influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching behavior.
Loyalty A deeply held commitment to re-buy or re-patronize a preferred product or service in the future despite situational influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching behavior.
 Measuring Satisfaction Periodic Surveys Customer Loss Rate Mystery Shoppers Monitor competitive performance
Measuring Satisfaction Periodic Surveys Customer Loss Rate Mystery Shoppers Monitor competitive performance
 Countrywide received the #1 customer satisfaction rating from J. D. Power and Associates
Countrywide received the #1 customer satisfaction rating from J. D. Power and Associates
 Product and Service Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs.
Product and Service Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs.
 Customer Life Time Value • The present value of the stream of future profits expected over the customer’s lifetime purchases.
Customer Life Time Value • The present value of the stream of future profits expected over the customer’s lifetime purchases.
 Estimating Lifetime Value • • Annual customer revenue: $5, 000 Average number of loyal years: 2 Company profit margin: 10% Customer lifetime value: $1, 000
Estimating Lifetime Value • • Annual customer revenue: $5, 000 Average number of loyal years: 2 Company profit margin: 10% Customer lifetime value: $1, 000
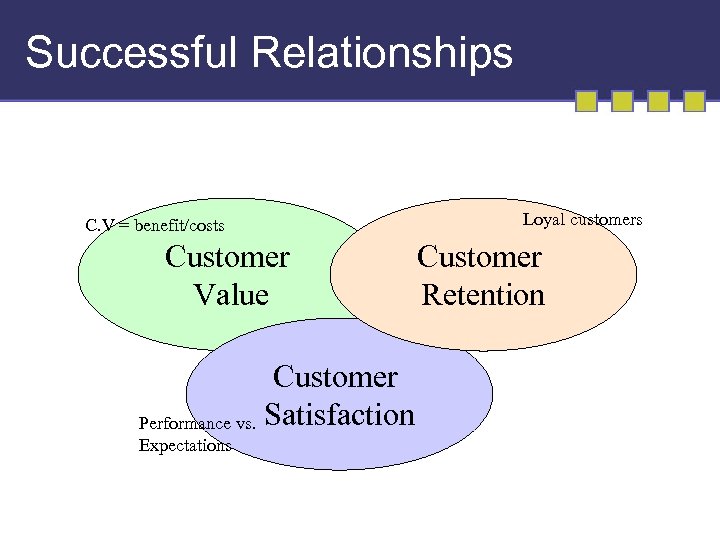 Successful Relationships C. V = benefit/costs Customer Value Customer Performance vs. Satisfaction Expectations Loyal customers Customer Retention
Successful Relationships C. V = benefit/costs Customer Value Customer Performance vs. Satisfaction Expectations Loyal customers Customer Retention
 Customer Profitability-Focused Marketing Tier 1: Platinum Tier 2: Gold Tier 3: Iron Tier 4: Lead Heavy users, not price sensitive, try new products Heavy users but price sensitive Spending volume implies no special treatment Cost the company and generate –ve WOM
Customer Profitability-Focused Marketing Tier 1: Platinum Tier 2: Gold Tier 3: Iron Tier 4: Lead Heavy users, not price sensitive, try new products Heavy users but price sensitive Spending volume implies no special treatment Cost the company and generate –ve WOM
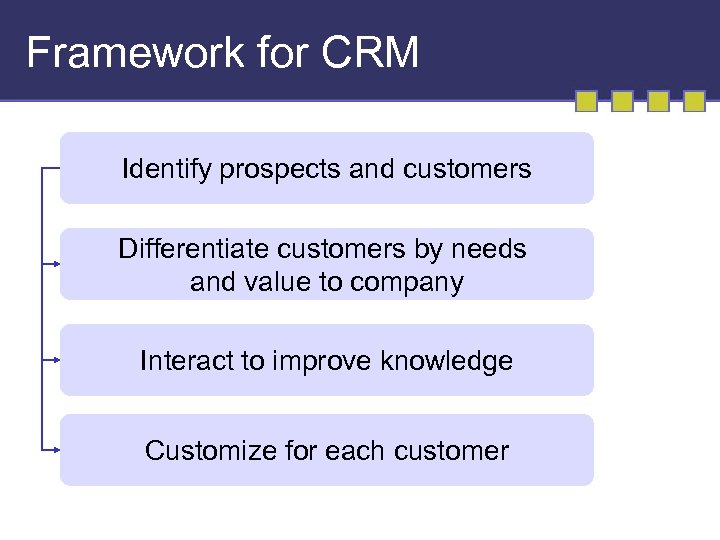 Framework for CRM Identify prospects and customers Differentiate customers by needs and value to company Interact to improve knowledge Customize for each customer
Framework for CRM Identify prospects and customers Differentiate customers by needs and value to company Interact to improve knowledge Customize for each customer
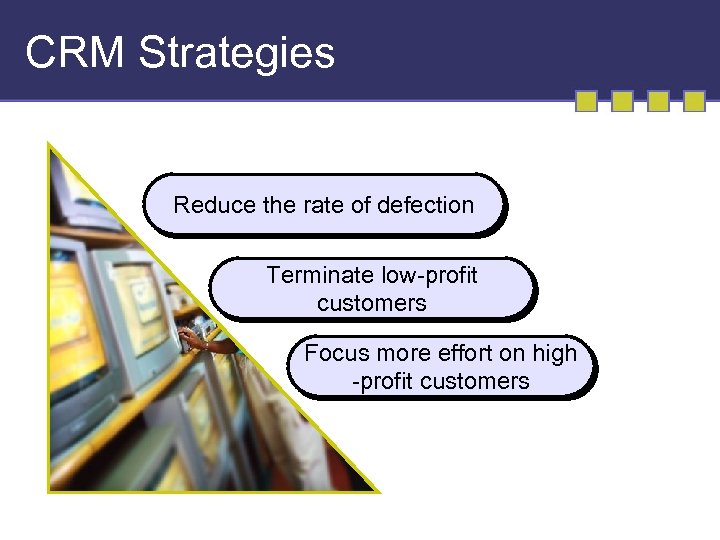 CRM Strategies Reduce the rate of defection Terminate low-profit customers Focus more effort on high -profit customers
CRM Strategies Reduce the rate of defection Terminate low-profit customers Focus more effort on high -profit customers
 Mass vs. One-to-One Marketing Mass • Average customer • Customer anonymity • Standard product • Mass production • Mass distribution • Mass advertising • One-way message • Economies of scale One-to-One • Individual customer • Customer profile • Customized market offering • Customized production • Economies of scope
Mass vs. One-to-One Marketing Mass • Average customer • Customer anonymity • Standard product • Mass production • Mass distribution • Mass advertising • One-way message • Economies of scale One-to-One • Individual customer • Customer profile • Customized market offering • Customized production • Economies of scope
 Customer Retention • Acquisition of customers can cost 5 times more than retaining current customers. • The average company loses 10% of its customers each year. • A 5% reduction to the customer defection rate can increase profits by 25% to 85%. • The customer profit rate increases over the life of a retained customer.
Customer Retention • Acquisition of customers can cost 5 times more than retaining current customers. • The average company loses 10% of its customers each year. • A 5% reduction to the customer defection rate can increase profits by 25% to 85%. • The customer profit rate increases over the life of a retained customer.
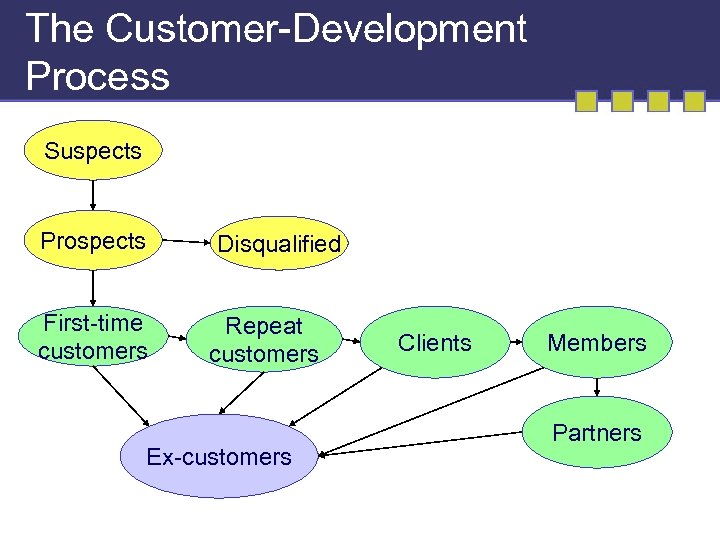 The Customer-Development Process Suspects Prospects First-time customers Disqualified Repeat customers Ex-customers Clients Members Partners
The Customer-Development Process Suspects Prospects First-time customers Disqualified Repeat customers Ex-customers Clients Members Partners
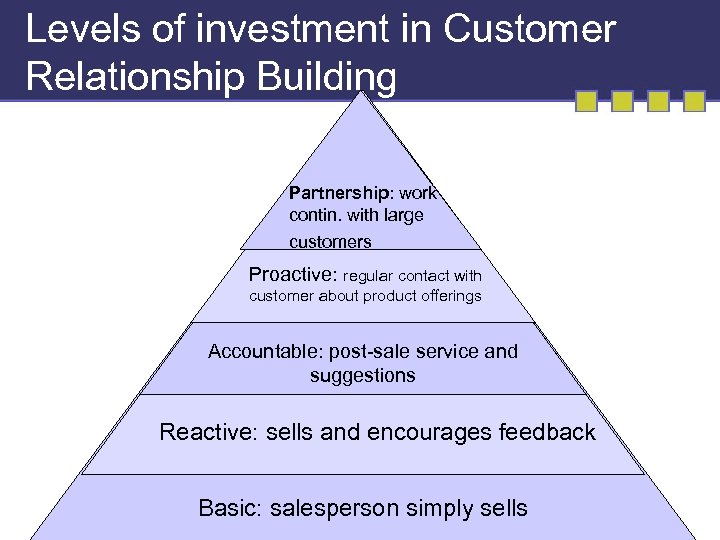 Levels of investment in Customer Relationship Building Partnership: work contin. with large customers Proactive: regular contact with customer about product offerings Accountable: post-sale service and suggestions Reactive: sells and encourages feedback Basic: salesperson simply sells
Levels of investment in Customer Relationship Building Partnership: work contin. with large customers Proactive: regular contact with customer about product offerings Accountable: post-sale service and suggestions Reactive: sells and encourages feedback Basic: salesperson simply sells
 Reducing Customer Defection • Define and measure retention rate. • Distinguish causes of customer attrition. • Estimate profit loss associated with loss of customers. • Assess cost to reduce defection rate. • Gather customer feedback.
Reducing Customer Defection • Define and measure retention rate. • Distinguish causes of customer attrition. • Estimate profit loss associated with loss of customers. • Assess cost to reduce defection rate. • Gather customer feedback.
 Cost of Lost Customer • A company has 64 k accounts • It lost 5% of its accounts this year due to poor service. Loss is 3, 200 accts (. 05* 64 k) • Avg. lost acct means a $40 k loss in revenue. Total loss in revenue is $128 million (3, 200*40 k) • If profit margin of company is 10% the total loss for 2009 is (. 10*$128 m)=$12. 8 million.
Cost of Lost Customer • A company has 64 k accounts • It lost 5% of its accounts this year due to poor service. Loss is 3, 200 accts (. 05* 64 k) • Avg. lost acct means a $40 k loss in revenue. Total loss in revenue is $128 million (3, 200*40 k) • If profit margin of company is 10% the total loss for 2009 is (. 10*$128 m)=$12. 8 million.
 Total Quality Management TQM is an organization-wide approach to continuously improving the quality of all the organization’s processes, products, and services.
Total Quality Management TQM is an organization-wide approach to continuously improving the quality of all the organization’s processes, products, and services.


