Kotler06_media.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 6 Analyzing Consumer Markets Kotler Keller
MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 6 Analyzing Consumer Markets Kotler Keller
 Chapter Questions • How do consumer characteristics influence buying behavior? • What major psychological processes influence consumer responses to the marketing program? • How do consumers make purchasing decisions? • How do marketers analyze consumer decision making? 2
Chapter Questions • How do consumer characteristics influence buying behavior? • What major psychological processes influence consumer responses to the marketing program? • How do consumers make purchasing decisions? • How do marketers analyze consumer decision making? 2
 Emerging Trends in Consumer Behavior Metrosexual – Straight urban man who enjoys shopping and using grooming products 3
Emerging Trends in Consumer Behavior Metrosexual – Straight urban man who enjoys shopping and using grooming products 3
 What Influences Consumer Behavior? Cultural Factors Social Factors Personal Factors 4
What Influences Consumer Behavior? Cultural Factors Social Factors Personal Factors 4
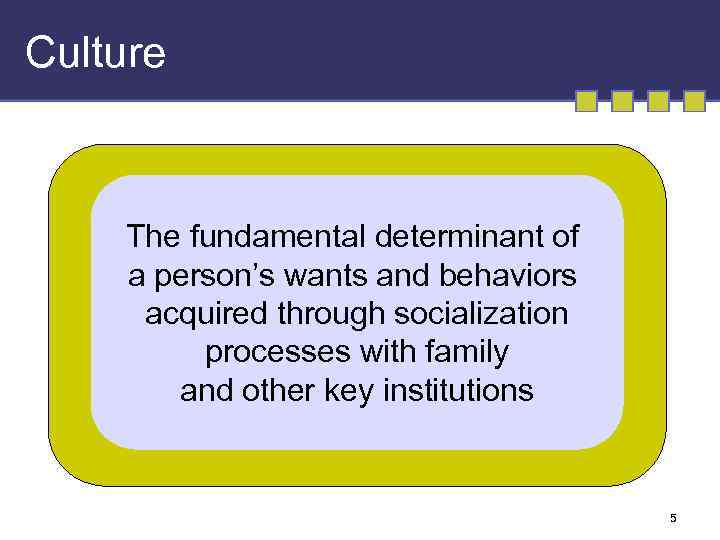 Culture The fundamental determinant of a person’s wants and behaviors acquired through socialization processes with family and other key institutions 5
Culture The fundamental determinant of a person’s wants and behaviors acquired through socialization processes with family and other key institutions 5
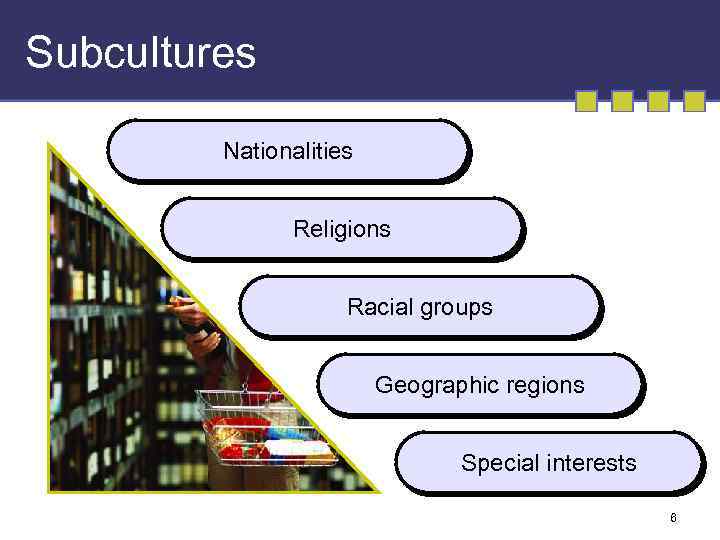 Subcultures Nationalities Religions Racial groups Geographic regions Special interests 6
Subcultures Nationalities Religions Racial groups Geographic regions Special interests 6
 Insight into the subculture of wine enthusiasts 7
Insight into the subculture of wine enthusiasts 7
 Fast Facts About American Culture • The average American: – chews 300 sticks of gum a year – goes to the movies 9 times a year – takes 4 trips per year – attends a sporting event 7 times each year 8
Fast Facts About American Culture • The average American: – chews 300 sticks of gum a year – goes to the movies 9 times a year – takes 4 trips per year – attends a sporting event 7 times each year 8
 Social Classes Upper uppers Lower uppers Upper middles Middle class Working class Upper lowers Lower lowers 9
Social Classes Upper uppers Lower uppers Upper middles Middle class Working class Upper lowers Lower lowers 9
 Characteristics of Social Classes • Within a class, people tend to behave alike • Social class conveys perceptions of inferior or superior position • Class may be indicated by a cluster of variables (occupation, income, wealth) • Class designation is mobile over time 10
Characteristics of Social Classes • Within a class, people tend to behave alike • Social class conveys perceptions of inferior or superior position • Class may be indicated by a cluster of variables (occupation, income, wealth) • Class designation is mobile over time 10
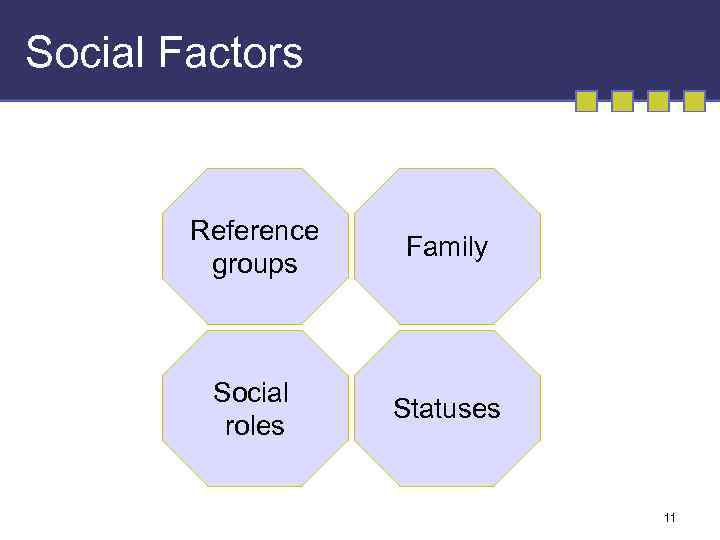 Social Factors Reference groups Family Social roles Statuses 11
Social Factors Reference groups Family Social roles Statuses 11
 Reference Groups Membership groups Primary groups Secondary groups Aspirational groups Dissociative groups 12
Reference Groups Membership groups Primary groups Secondary groups Aspirational groups Dissociative groups 12
 Family • Family of Orientation – Religion – Politics – Economics • Family of Procreation – Everyday buying behavior 13
Family • Family of Orientation – Religion – Politics – Economics • Family of Procreation – Everyday buying behavior 13
 Targeting Women and Their Families 14
Targeting Women and Their Families 14
 Roles and Statuses What degree of status is associated with various occupational roles? 15
Roles and Statuses What degree of status is associated with various occupational roles? 15
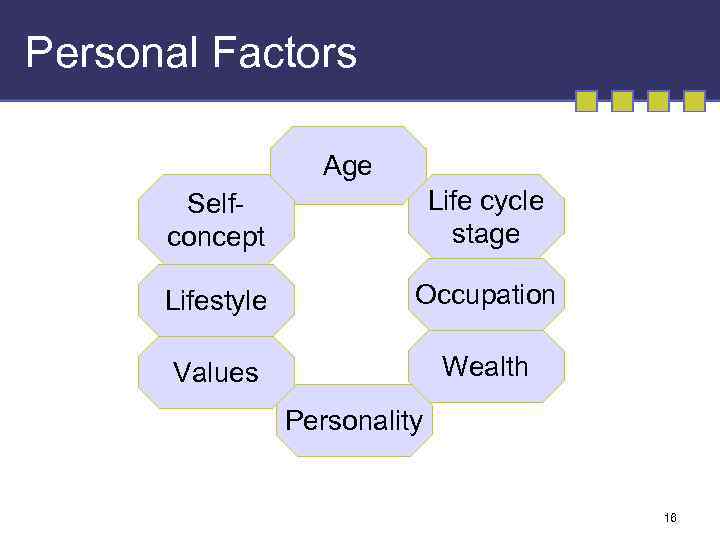 Personal Factors Age Selfconcept Life cycle stage Lifestyle Occupation Values Wealth Personality 16
Personal Factors Age Selfconcept Life cycle stage Lifestyle Occupation Values Wealth Personality 16
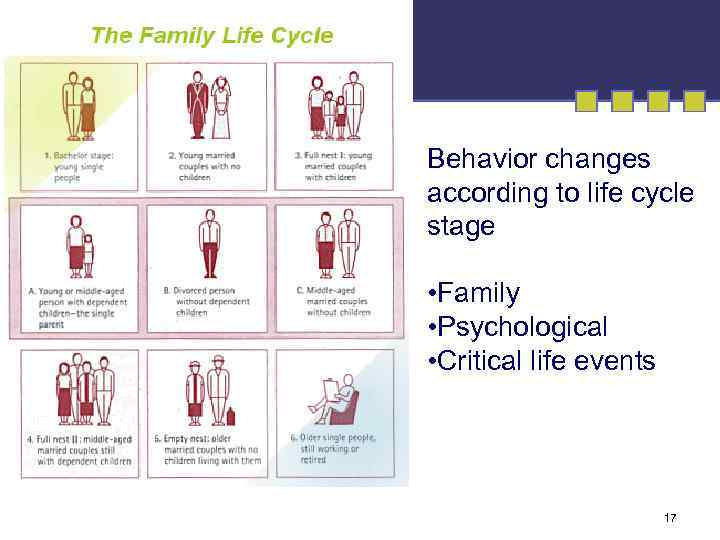 Behavior changes according to life cycle stage • Family • Psychological • Critical life events 17
Behavior changes according to life cycle stage • Family • Psychological • Critical life events 17
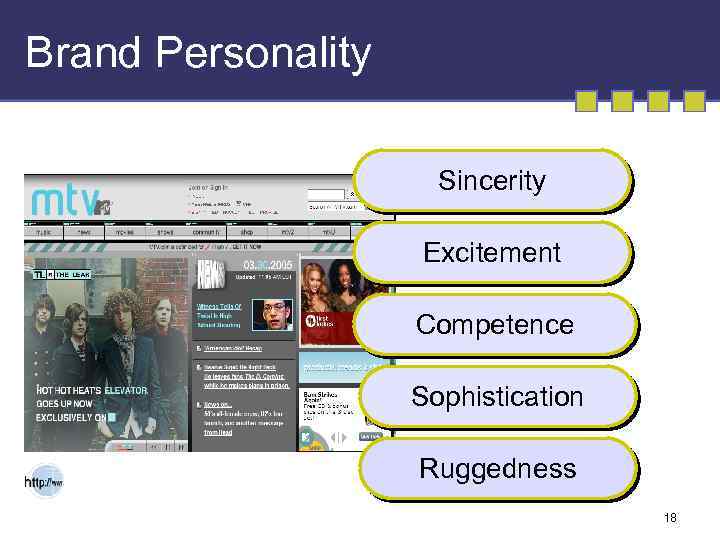 Brand Personality Sincerity Excitement Competence Sophistication Ruggedness 18
Brand Personality Sincerity Excitement Competence Sophistication Ruggedness 18
 Lifestyle Influences Multi-tasking Time-starved Money-constrained 19
Lifestyle Influences Multi-tasking Time-starved Money-constrained 19
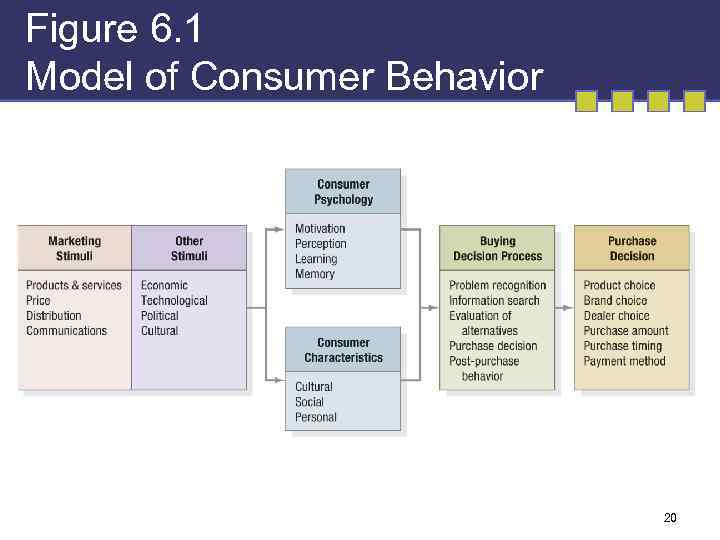 Figure 6. 1 Model of Consumer Behavior 20
Figure 6. 1 Model of Consumer Behavior 20
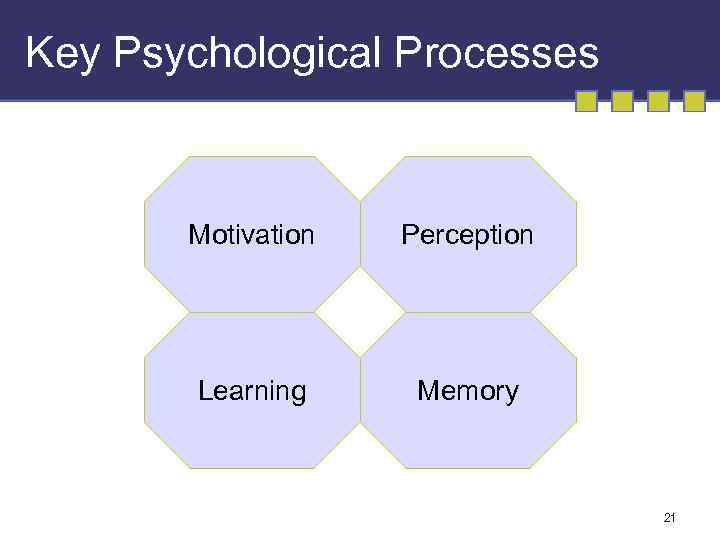 Key Psychological Processes Motivation Perception Learning Memory 21
Key Psychological Processes Motivation Perception Learning Memory 21
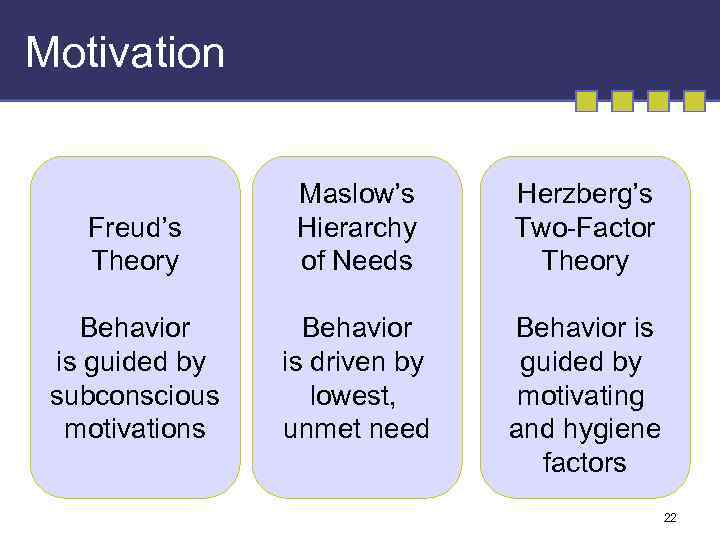 Motivation Freud’s Theory Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory Behavior is guided by subconscious motivations Behavior is driven by lowest, unmet need Behavior is guided by motivating and hygiene factors 22
Motivation Freud’s Theory Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory Behavior is guided by subconscious motivations Behavior is driven by lowest, unmet need Behavior is guided by motivating and hygiene factors 22
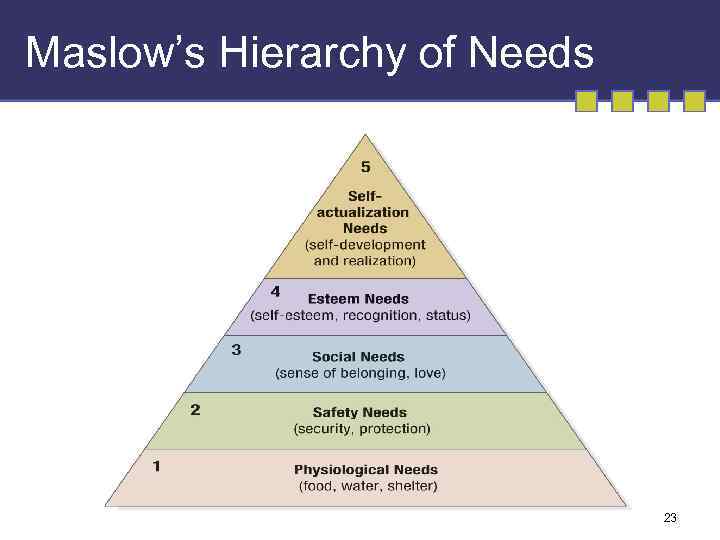 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 23
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 23
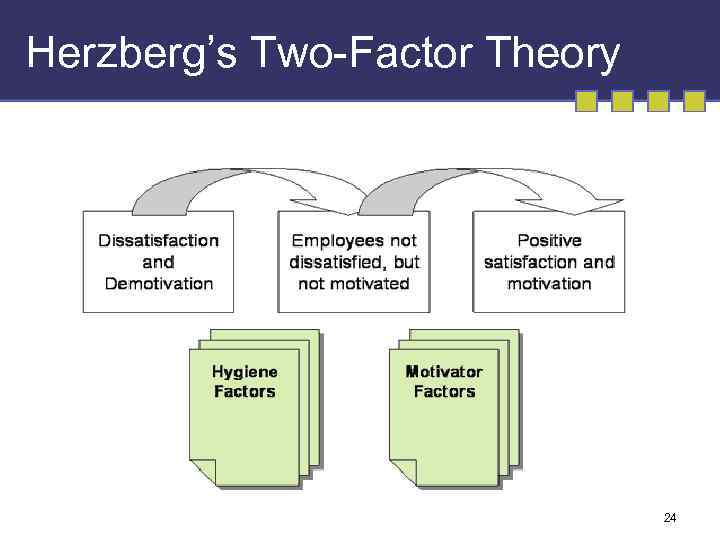 Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory 24
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory 24
 Perception Selective Attention Selective Retention Selective Distortion Subliminal Perception 25
Perception Selective Attention Selective Retention Selective Distortion Subliminal Perception 25
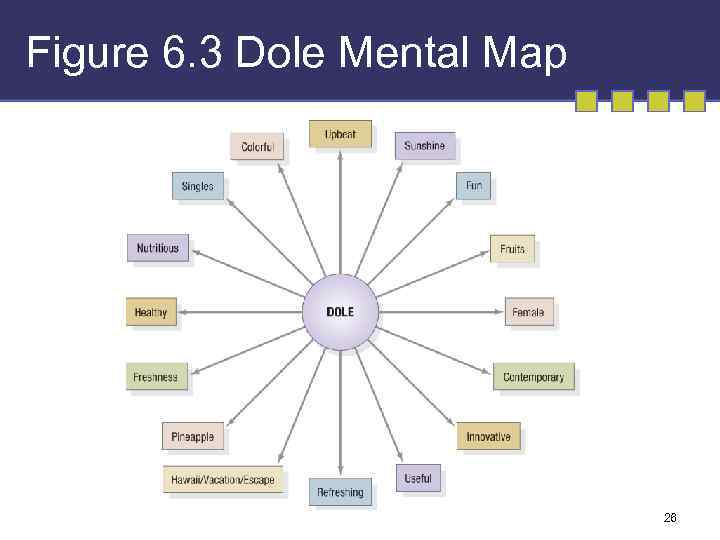 Figure 6. 3 Dole Mental Map 26
Figure 6. 3 Dole Mental Map 26
 Encoding Brand Associations 27
Encoding Brand Associations 27
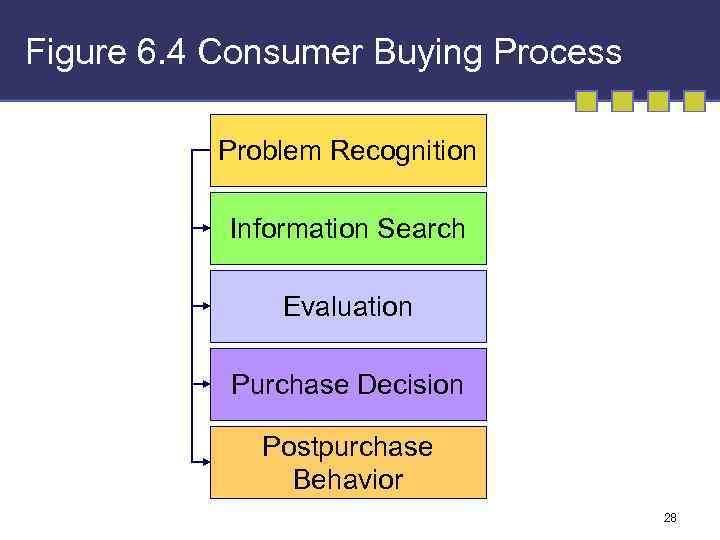 Figure 6. 4 Consumer Buying Process Problem Recognition Information Search Evaluation Purchase Decision Postpurchase Behavior 28
Figure 6. 4 Consumer Buying Process Problem Recognition Information Search Evaluation Purchase Decision Postpurchase Behavior 28
 Problem Recognition 29
Problem Recognition 29
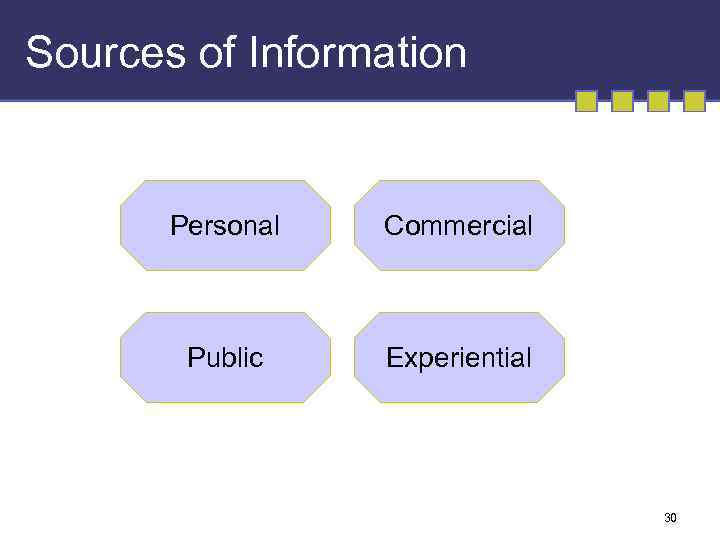 Sources of Information Personal Commercial Public Experiential 30
Sources of Information Personal Commercial Public Experiential 30
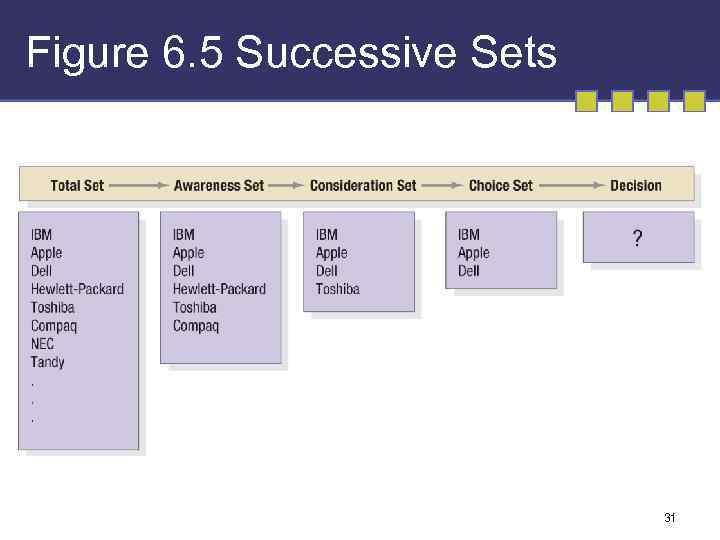 Figure 6. 5 Successive Sets 31
Figure 6. 5 Successive Sets 31
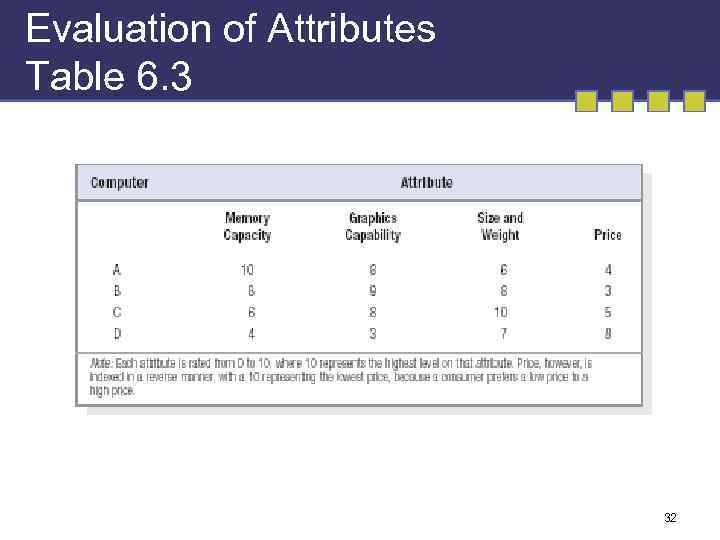 Evaluation of Attributes Table 6. 3 32
Evaluation of Attributes Table 6. 3 32
 Figure 6. 6 Stages between Evaluation of Alternatives and Purchase 33
Figure 6. 6 Stages between Evaluation of Alternatives and Purchase 33
 Non-compensatory Models of Choice • Conjunctive • Lexicographic • Elimination-by-aspects 34
Non-compensatory Models of Choice • Conjunctive • Lexicographic • Elimination-by-aspects 34
 Perceived Risk Functional Physical Financial Social Psychological Time 35
Perceived Risk Functional Physical Financial Social Psychological Time 35
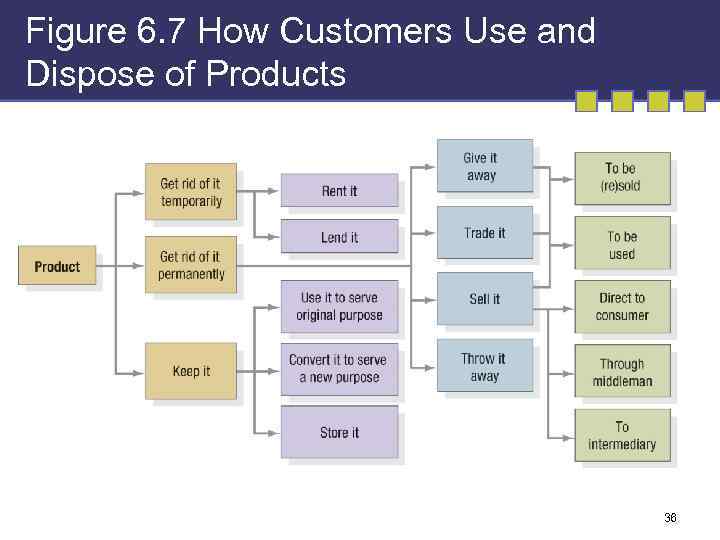 Figure 6. 7 How Customers Use and Dispose of Products 36
Figure 6. 7 How Customers Use and Dispose of Products 36
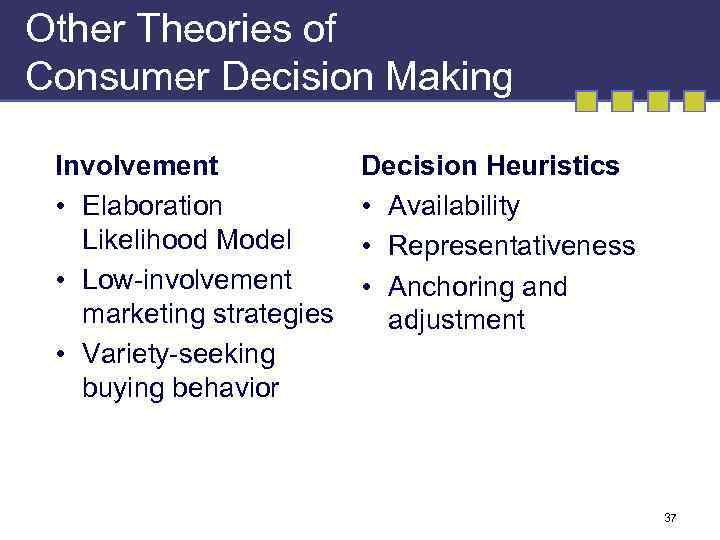 Other Theories of Consumer Decision Making Involvement • Elaboration Likelihood Model • Low-involvement marketing strategies • Variety-seeking buying behavior Decision Heuristics • Availability • Representativeness • Anchoring and adjustment 37
Other Theories of Consumer Decision Making Involvement • Elaboration Likelihood Model • Low-involvement marketing strategies • Variety-seeking buying behavior Decision Heuristics • Availability • Representativeness • Anchoring and adjustment 37
 Mental Accounting • Consumers tend to… – Segregate gains – Integrate losses – Integrate smaller losses with larger gains – Segregate small gains from large losses 38
Mental Accounting • Consumers tend to… – Segregate gains – Integrate losses – Integrate smaller losses with larger gains – Segregate small gains from large losses 38
 Marketing Debate ü Is Target Marketing Ever Bad? Take a position: 1. Targeting minorities is exploitative. 2. 2. Targeting minorities is a sound 3. business practice. 39
Marketing Debate ü Is Target Marketing Ever Bad? Take a position: 1. Targeting minorities is exploitative. 2. 2. Targeting minorities is a sound 3. business practice. 39
 Marketing Discussion ü What are your mental accounts? Do you have rules you employ in spending money? Do you follow Thaler’s four principles in reacting to gains and losses? 40
Marketing Discussion ü What are your mental accounts? Do you have rules you employ in spending money? Do you follow Thaler’s four principles in reacting to gains and losses? 40


