Kotler02_media.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans Kotler Keller
MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans Kotler Keller
 Chapter Questions • How does marketing affect customer value? • How is strategic planning carried out at different levels of the organization? • What does a marketing plan include? 2
Chapter Questions • How does marketing affect customer value? • How is strategic planning carried out at different levels of the organization? • What does a marketing plan include? 2
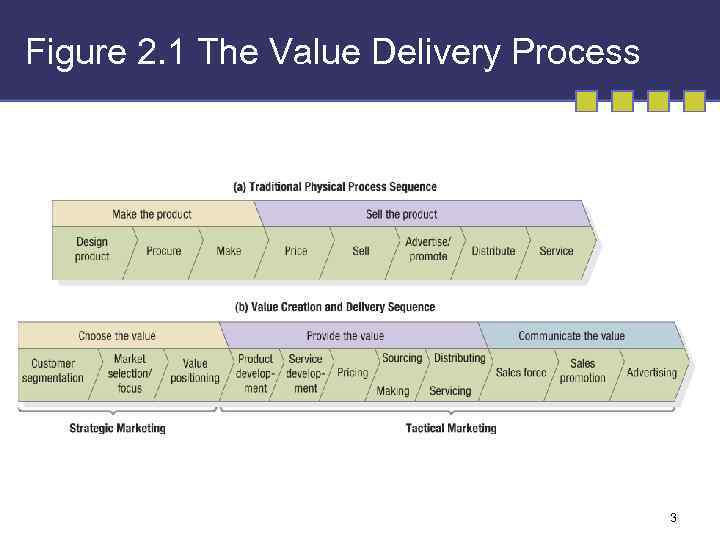 Figure 2. 1 The Value Delivery Process 3
Figure 2. 1 The Value Delivery Process 3
 Nike Creates Value 4
Nike Creates Value 4
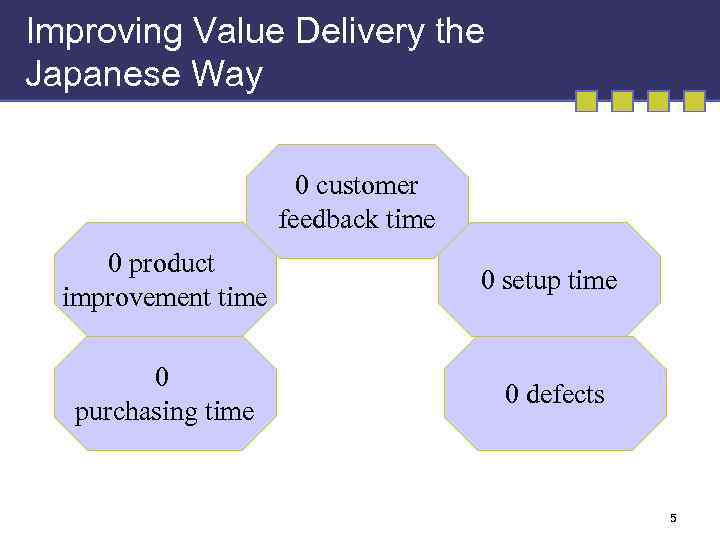 Improving Value Delivery the Japanese Way 0 customer feedback time 0 product improvement time 0 setup time 0 purchasing time 0 defects 5
Improving Value Delivery the Japanese Way 0 customer feedback time 0 product improvement time 0 setup time 0 purchasing time 0 defects 5
 3 V’s Approach to Marketing Define the value segment Define the value proposition Define the value network 6
3 V’s Approach to Marketing Define the value segment Define the value proposition Define the value network 6
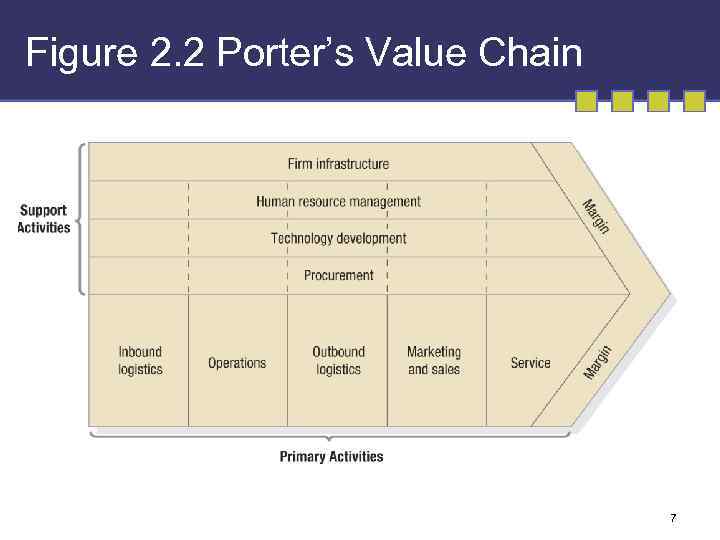 Figure 2. 2 Porter’s Value Chain 7
Figure 2. 2 Porter’s Value Chain 7
 Benchmarks Organizational costs and performance measures Competitor costs and performance measures 8
Benchmarks Organizational costs and performance measures Competitor costs and performance measures 8
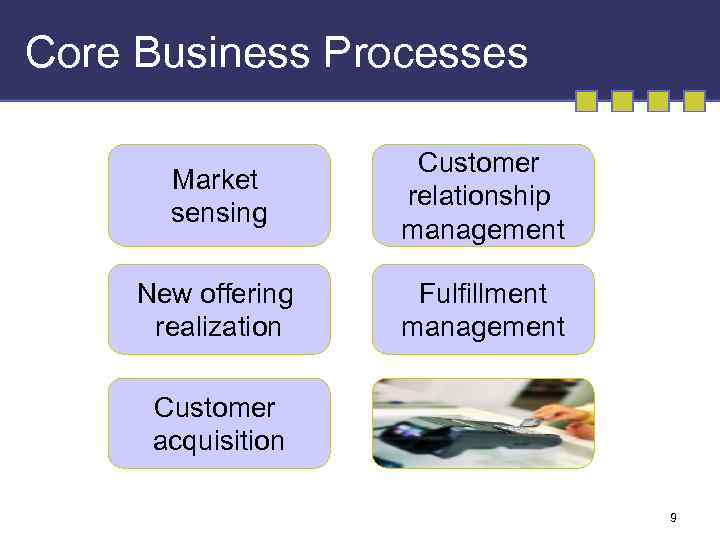 Core Business Processes Market sensing Customer relationship management New offering realization Fulfillment management Customer acquisition 9
Core Business Processes Market sensing Customer relationship management New offering realization Fulfillment management Customer acquisition 9
 Wal-Mart’s stock replenishment process is legendary 10
Wal-Mart’s stock replenishment process is legendary 10
 Characteristics of Core Competencies • A source of competitive advantage • Applications in a wide variety of markets • Difficult to imitate 11
Characteristics of Core Competencies • A source of competitive advantage • Applications in a wide variety of markets • Difficult to imitate 11
 Netflix’s Distinctive Capabilities 12
Netflix’s Distinctive Capabilities 12
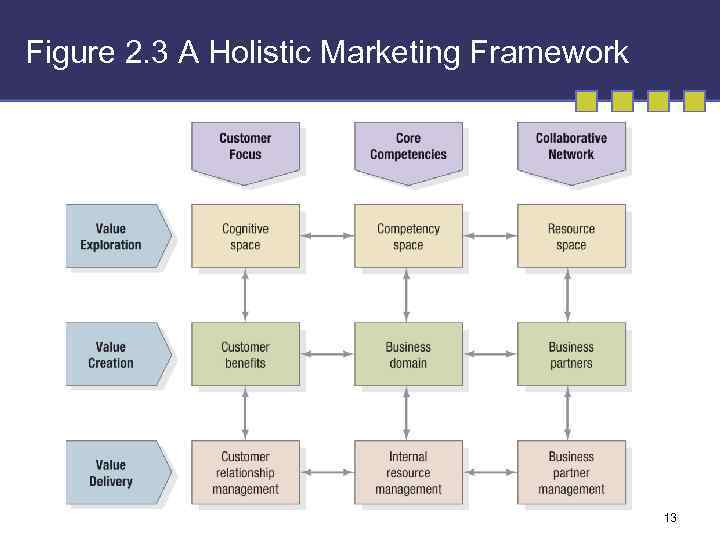 Figure 2. 3 A Holistic Marketing Framework 13
Figure 2. 3 A Holistic Marketing Framework 13
 Challenges Facing CMO’s Doing more with less Driving new business development Becoming a full business partner 14
Challenges Facing CMO’s Doing more with less Driving new business development Becoming a full business partner 14
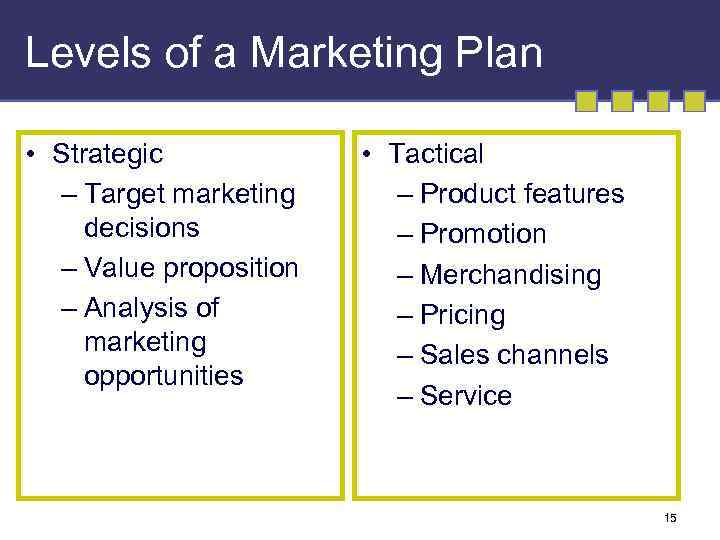 Levels of a Marketing Plan • Strategic – Target marketing decisions – Value proposition – Analysis of marketing opportunities • Tactical – Product features – Promotion – Merchandising – Pricing – Sales channels – Service 15
Levels of a Marketing Plan • Strategic – Target marketing decisions – Value proposition – Analysis of marketing opportunities • Tactical – Product features – Promotion – Merchandising – Pricing – Sales channels – Service 15
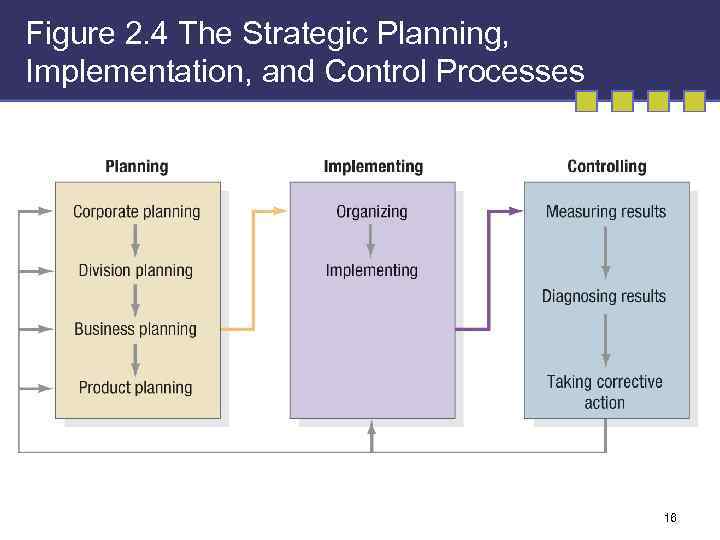 Figure 2. 4 The Strategic Planning, Implementation, and Control Processes 16
Figure 2. 4 The Strategic Planning, Implementation, and Control Processes 16
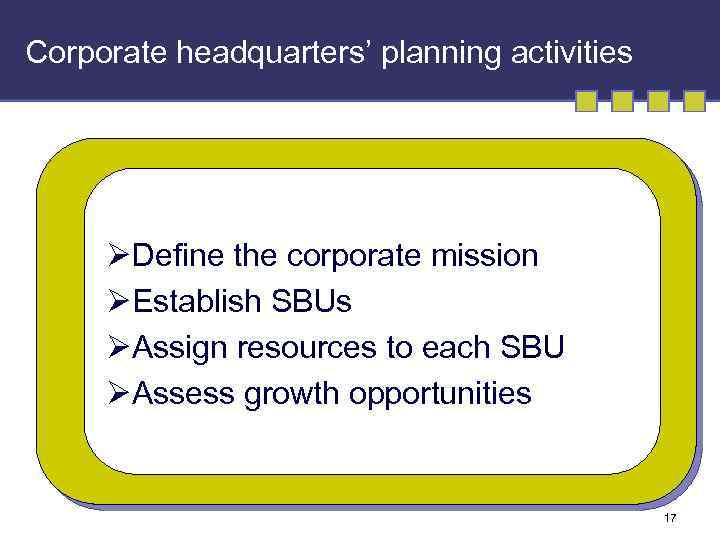 Corporate headquarters’ planning activities ØDefine the corporate mission ØEstablish SBUs ØAssign resources to each SBU ØAssess growth opportunities 17
Corporate headquarters’ planning activities ØDefine the corporate mission ØEstablish SBUs ØAssign resources to each SBU ØAssess growth opportunities 17
 Good Mission Statements Focus on limited number of goals Stress major policies and values Define major competitive spheres 18
Good Mission Statements Focus on limited number of goals Stress major policies and values Define major competitive spheres 18
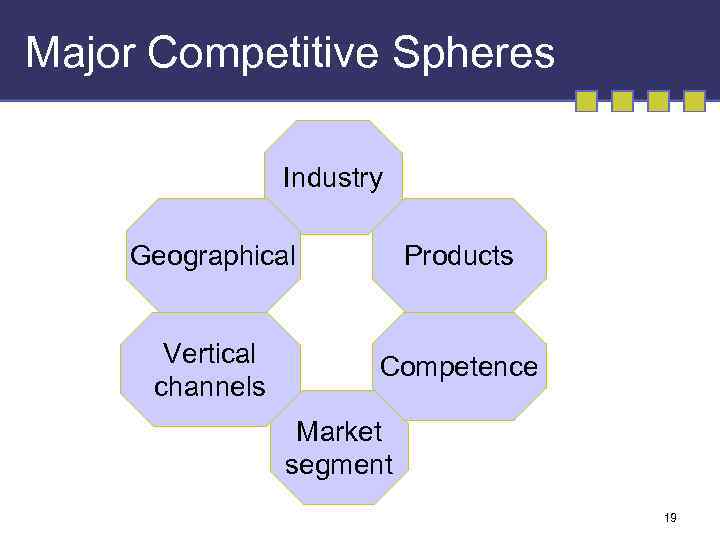 Major Competitive Spheres Industry Geographical Products Vertical channels Competence Market segment 19
Major Competitive Spheres Industry Geographical Products Vertical channels Competence Market segment 19
 GE’s breakthroughs in the process of desalination crosses multiple competitive spheres By 2015, twothirds of the world will be waterstressed. Desalination plants like this one help to relieve water shortages. 20
GE’s breakthroughs in the process of desalination crosses multiple competitive spheres By 2015, twothirds of the world will be waterstressed. Desalination plants like this one help to relieve water shortages. 20
 Rubbermaid Commercial Products, Inc. “Our vision is to be the Global Market Share Leader in each of the markets we serve. We will earn this leadership position by providing to our distributor and end-user customers innovative, high-quality, costeffective and environmentally responsible products. We will add value to these products by providing legendary customer service through our uncompromising Commitment to Customer Satisfaction. ” 21
Rubbermaid Commercial Products, Inc. “Our vision is to be the Global Market Share Leader in each of the markets we serve. We will earn this leadership position by providing to our distributor and end-user customers innovative, high-quality, costeffective and environmentally responsible products. We will add value to these products by providing legendary customer service through our uncompromising Commitment to Customer Satisfaction. ” 21
 Motorola “ The purpose of Motorola is to honorably serve the needs of the community by providing products and services of superior quality at a fair price to our customers; to do this so as to earn an adequate profit which is required for the total enterprise to grow; and by doing so, provide the opportunity for our employees and shareholders to achieve their personal o b j e c t i v e s. ” 22
Motorola “ The purpose of Motorola is to honorably serve the needs of the community by providing products and services of superior quality at a fair price to our customers; to do this so as to earn an adequate profit which is required for the total enterprise to grow; and by doing so, provide the opportunity for our employees and shareholders to achieve their personal o b j e c t i v e s. ” 22
 e. Bay “We help people trade anything on earth. We will continue to enhance the online trading experiences of all – collectors, dealers, small businesses, unique item seekers, bargain hunters, opportunity s e l l e r s , a n d b r o w s e r s. ” 23
e. Bay “We help people trade anything on earth. We will continue to enhance the online trading experiences of all – collectors, dealers, small businesses, unique item seekers, bargain hunters, opportunity s e l l e r s , a n d b r o w s e r s. ” 23
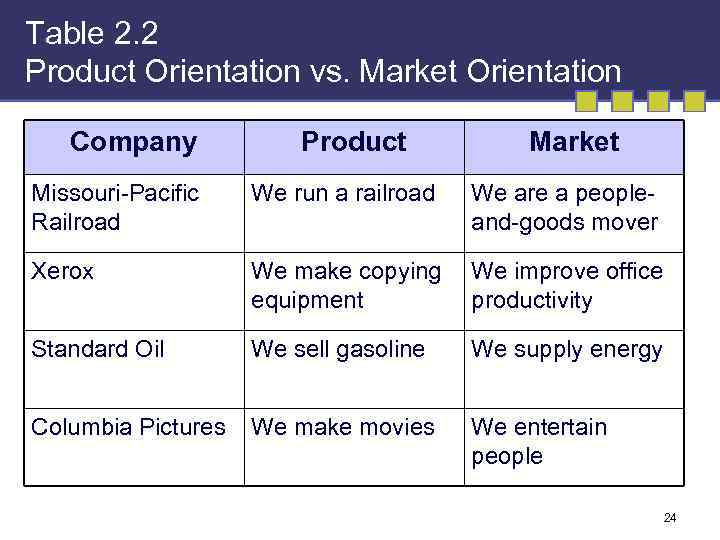 Table 2. 2 Product Orientation vs. Market Orientation Company Product Market Missouri-Pacific Railroad We run a railroad We are a peopleand-goods mover Xerox We make copying equipment We improve office productivity Standard Oil We sell gasoline We supply energy Columbia Pictures We make movies We entertain people 24
Table 2. 2 Product Orientation vs. Market Orientation Company Product Market Missouri-Pacific Railroad We run a railroad We are a peopleand-goods mover Xerox We make copying equipment We improve office productivity Standard Oil We sell gasoline We supply energy Columbia Pictures We make movies We entertain people 24
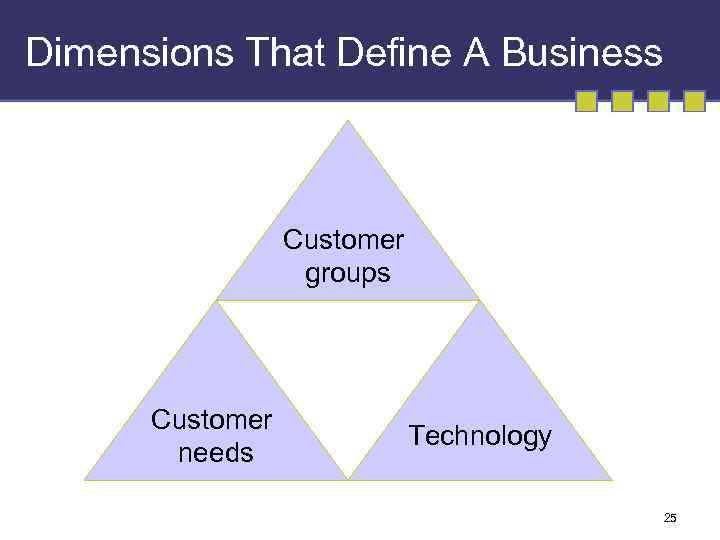 Dimensions That Define A Business Customer groups Customer needs Technology 25
Dimensions That Define A Business Customer groups Customer needs Technology 25
 Characteristics of SBUs • It is a single business or collection of related businesses • It has its own set of competitors • It has a leader responsible for – Strategic planning – Profitability – Efficiency 26
Characteristics of SBUs • It is a single business or collection of related businesses • It has its own set of competitors • It has a leader responsible for – Strategic planning – Profitability – Efficiency 26
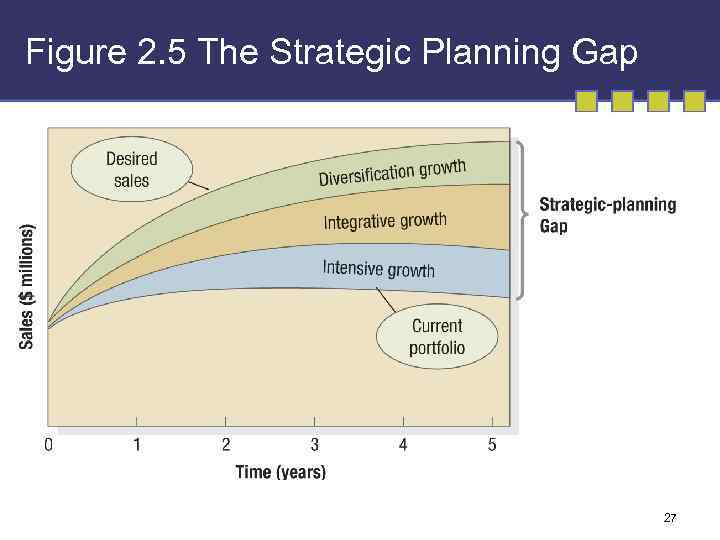 Figure 2. 5 The Strategic Planning Gap 27
Figure 2. 5 The Strategic Planning Gap 27
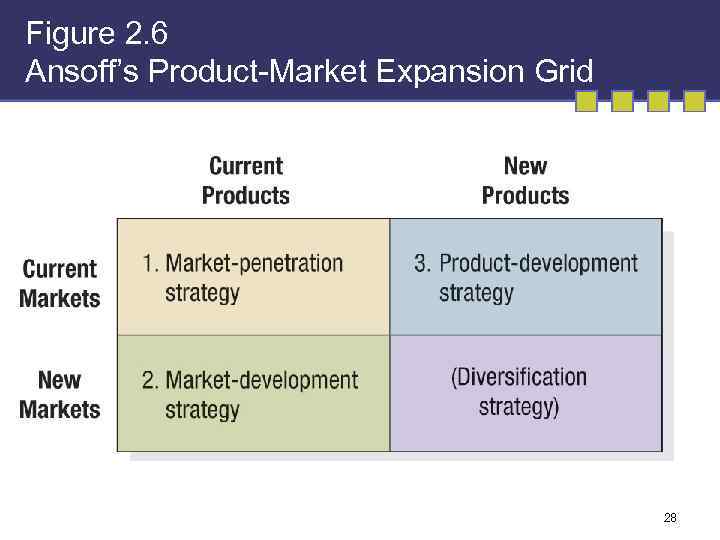 Figure 2. 6 Ansoff’s Product-Market Expansion Grid 28
Figure 2. 6 Ansoff’s Product-Market Expansion Grid 28
 The Growth of Starbucks 29
The Growth of Starbucks 29
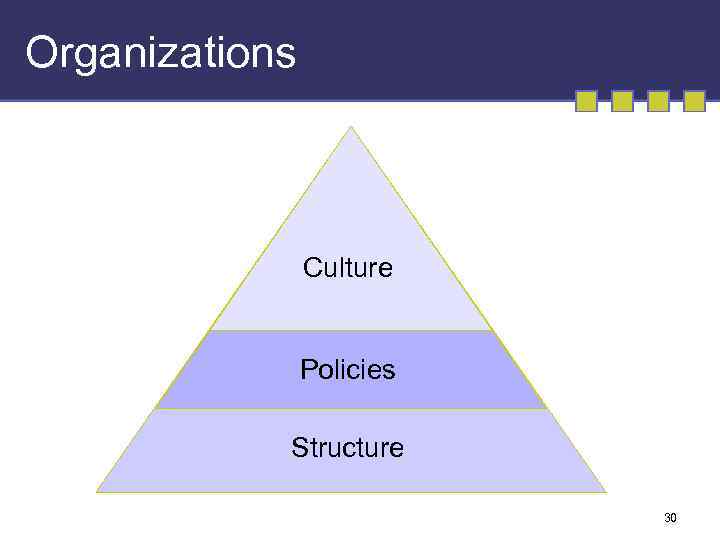 Organizations Culture Policies Structure 30
Organizations Culture Policies Structure 30
 Merging Corporate Culture? 31
Merging Corporate Culture? 31
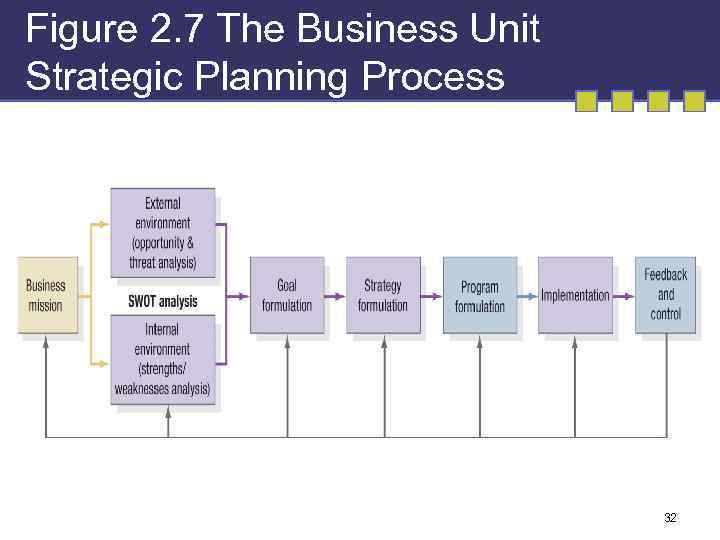 Figure 2. 7 The Business Unit Strategic Planning Process 32
Figure 2. 7 The Business Unit Strategic Planning Process 32
 SWOT Analysis Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats 33
SWOT Analysis Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats 33
 Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA) • Can the benefits involved in the opportunity be articulated convincingly to a defined target market? • Can the target market be located and reached with cost-effective media and trade channels? • Does the company possess or have access to the critical capabilities and resources needed to deliver the customer benefits? 34
Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA) • Can the benefits involved in the opportunity be articulated convincingly to a defined target market? • Can the target market be located and reached with cost-effective media and trade channels? • Does the company possess or have access to the critical capabilities and resources needed to deliver the customer benefits? 34
 Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA)_2 • Can the company deliver the benefits better than any actual or potential competitors? • Will the financial rate of return meet or exceed the company’s required threshold for investment? 35
Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA)_2 • Can the company deliver the benefits better than any actual or potential competitors? • Will the financial rate of return meet or exceed the company’s required threshold for investment? 35
 Fed. Ex added Sunday deliveries based on customer requests and market demand 36
Fed. Ex added Sunday deliveries based on customer requests and market demand 36
 Figure 2. 8 Opportunity Matrix 37
Figure 2. 8 Opportunity Matrix 37
 Figure 2. 8 Threat Matrix 38
Figure 2. 8 Threat Matrix 38
 Goal Formulation and MBO • Requirements for using MBO – Unit’s objectives must be hierarchical – Objectives should be quantitative – Goals should be realistic – Objectives must be consistent 39
Goal Formulation and MBO • Requirements for using MBO – Unit’s objectives must be hierarchical – Objectives should be quantitative – Goals should be realistic – Objectives must be consistent 39
 Porter’s Generic Strategies Overall Cost Leadership Differentiation Focus 40
Porter’s Generic Strategies Overall Cost Leadership Differentiation Focus 40
 The Star Alliance 41
The Star Alliance 41
 Categories of Marketing Alliances Product or Service Alliances Promotional Alliances Logistics Alliances Pricing Collaborations 42
Categories of Marketing Alliances Product or Service Alliances Promotional Alliances Logistics Alliances Pricing Collaborations 42
 Feedback and Control 43
Feedback and Control 43
 Marketing Plan Contents ü Executive summary ü Table of contents ü Situation analysis ü Marketing strategy ü Financial projections ü Implementation controls 44
Marketing Plan Contents ü Executive summary ü Table of contents ü Situation analysis ü Marketing strategy ü Financial projections ü Implementation controls 44
 Evaluating a Marketing Plan ü Is the plan simple? ü Is the plan specific? ü Is the plan realistic? ü Is the plan complete? 45
Evaluating a Marketing Plan ü Is the plan simple? ü Is the plan specific? ü Is the plan realistic? ü Is the plan complete? 45
 Marketing Debate ü What good is a mission statement? Take a position: 1. Mission statements are critical to a 2. successful marketing organization. 3. 2. Mission statements rarely provide 4. useful marketing value. 46
Marketing Debate ü What good is a mission statement? Take a position: 1. Mission statements are critical to a 2. successful marketing organization. 3. 2. Mission statements rarely provide 4. useful marketing value. 46
 Marketing Debate ü What implications do Porter’s value chain and the holistic marketing orientation model have for marketing planning? 47
Marketing Debate ü What implications do Porter’s value chain and the holistic marketing orientation model have for marketing planning? 47


