3c7fb4f48a45be664997b0ca751ef1f9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 86
 MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 1 Defining Marketing for the 21 st Century Kotler Keller 1 -
MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 1 Defining Marketing for the 21 st Century Kotler Keller 1 -
 Chapter Questions n Why is marketing important? n What is the scope of marketing? n What are some of the fundamental marketing concepts? n How has marketing management changed? n What are the tasks necessary for successful marketing management? 2
Chapter Questions n Why is marketing important? n What is the scope of marketing? n What are some of the fundamental marketing concepts? n How has marketing management changed? n What are the tasks necessary for successful marketing management? 2
 What is Marketing? Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders. 3
What is Marketing? Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders. 3
 What is Marketing Management? Marketing management is the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers through creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value. 4
What is Marketing Management? Marketing management is the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers through creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value. 4
 For an exchange to occur…. . There at least two parties. n Each party has something that might be of value to the other party. n Each party is capable of communication and delivery. n Each party is free to reject the exchange offer. n Each party believes it is appropriate or desirable to deal with the other party. n 5
For an exchange to occur…. . There at least two parties. n Each party has something that might be of value to the other party. n Each party is capable of communication and delivery. n Each party is free to reject the exchange offer. n Each party believes it is appropriate or desirable to deal with the other party. n 5
 What is Marketed? n n n Goods Services Events Experiences Persons n n n Places Properties Organizations Information Ideas 6
What is Marketed? n n n Goods Services Events Experiences Persons n n n Places Properties Organizations Information Ideas 6
 Demand States n n Negative Nonexistent Latent Declining n n Irregular Unwholesome Full Overfull 7
Demand States n n Negative Nonexistent Latent Declining n n Irregular Unwholesome Full Overfull 7
 Key Customer Markets Consumer markets n Business markets n Global markets n Nonprofit/Government markets n 8
Key Customer Markets Consumer markets n Business markets n Global markets n Nonprofit/Government markets n 8
 The marketplace isn’t what it used to be…. n n Changing technology Globalization Deregulation Privatization n n Empowerment Customization Convergence Disintermediation 9
The marketplace isn’t what it used to be…. n n Changing technology Globalization Deregulation Privatization n n Empowerment Customization Convergence Disintermediation 9
 Company Orientations Production n Product n Selling n Marketing n 10
Company Orientations Production n Product n Selling n Marketing n 10
 Marketing Mix and the Customer Four Ps n Product n Price n Place n Promotion Four Cs n Customer solution n Customer cost n Convenience n Communication 11
Marketing Mix and the Customer Four Ps n Product n Price n Place n Promotion Four Cs n Customer solution n Customer cost n Convenience n Communication 11
 Core Concepts n n Needs, wants, and demands Target markets, positioning, segmentation Offerings and brands Value and satisfaction n n Marketing channels Supply chain Competition Marketing environment Marketing planning 12
Core Concepts n n Needs, wants, and demands Target markets, positioning, segmentation Offerings and brands Value and satisfaction n n Marketing channels Supply chain Competition Marketing environment Marketing planning 12
 I want it, I need it…. . 5 Types of Needs Stated needs n Real needs n Unstated needs n Delight needs n Secret needs n 13
I want it, I need it…. . 5 Types of Needs Stated needs n Real needs n Unstated needs n Delight needs n Secret needs n 13
 Marketing Management Tasks n n Developing marketing strategies Capturing marketing insights Connecting with customers Building strong brands n n Shaping market offerings Delivering value Communicating value Creating long-term growth 14
Marketing Management Tasks n n Developing marketing strategies Capturing marketing insights Connecting with customers Building strong brands n n Shaping market offerings Delivering value Communicating value Creating long-term growth 14
 MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 3 Gathering Information and Scanning the Environment Kotler Keller 1 -
MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 3 Gathering Information and Scanning the Environment Kotler Keller 1 -
 Chapter Questions_1 n What are the components of a modern marketing information system? n What are useful internal records? n What is involved in a marketing intelligence system? 16
Chapter Questions_1 n What are the components of a modern marketing information system? n What are useful internal records? n What is involved in a marketing intelligence system? 16
 Chapter Questions_2 n What are the key methods for tracking and identifying opportunities in the macroenvironment? n What are some important macroenvironment developments? 17
Chapter Questions_2 n What are the key methods for tracking and identifying opportunities in the macroenvironment? n What are some important macroenvironment developments? 17
 MIS Probes for Information n n n What decisions do you regularly make? What information do you need to make these decisions? What information do you regularly get? What special studies do you periodically request? What information would you want that you are not getting now? What are the four most helpful improvements that could be made in the present marketing information system? 18
MIS Probes for Information n n n What decisions do you regularly make? What information do you need to make these decisions? What information do you regularly get? What special studies do you periodically request? What information would you want that you are not getting now? What are the four most helpful improvements that could be made in the present marketing information system? 18
 Internal Records Order-to-Payment Cycle n Sales Information System n Databases, Warehousing, Data mining n Marketing Intelligence System n 19
Internal Records Order-to-Payment Cycle n Sales Information System n Databases, Warehousing, Data mining n Marketing Intelligence System n 19
 Steps to Improve Marketing Intelligence n n n n Train and motivate sales force Motivate channel members to share intelligence Network externally Utilize customer advisory panel Utilize government data resources Purchase information Collect customer feedback online 20
Steps to Improve Marketing Intelligence n n n n Train and motivate sales force Motivate channel members to share intelligence Network externally Utilize customer advisory panel Utilize government data resources Purchase information Collect customer feedback online 20
 Needs and Trends Fad Trend Megatrend 21
Needs and Trends Fad Trend Megatrend 21
 10 Megatrends Shaping the Consumer Landscape n n n Aging boomers Delayed retirement Changing nature of work Greater educational attainment Labor shortages n n n Increased immigration Rising Hispanic influence Shifting birth trends Widening geographic differences Changing age structure 22
10 Megatrends Shaping the Consumer Landscape n n n Aging boomers Delayed retirement Changing nature of work Greater educational attainment Labor shortages n n n Increased immigration Rising Hispanic influence Shifting birth trends Widening geographic differences Changing age structure 22
 Environmental Forces Demographic n Economic n Socio-Cultural n Natural n Technological n Political-Legal n 23
Environmental Forces Demographic n Economic n Socio-Cultural n Natural n Technological n Political-Legal n 23
 Population and Demographics Size n Growth rate n Age distribution n Ethnic mix n Educational levels n Household patterns n Regional characteristics n Movement n 24
Population and Demographics Size n Growth rate n Age distribution n Ethnic mix n Educational levels n Household patterns n Regional characteristics n Movement n 24
 Economic Environment $ Purchasing Power $ Income Distribution $ Savings Rate $ Debt $ Credit Availability 25
Economic Environment $ Purchasing Power $ Income Distribution $ Savings Rate $ Debt $ Credit Availability 25
 Types of Industrial Structures Industrial economies n Industrializing economies n Raw-material exporting economies n Subsistence economies n 26
Types of Industrial Structures Industrial economies n Industrializing economies n Raw-material exporting economies n Subsistence economies n 26
 Social-Cultural Environment Views of themselves n Views of others n Views of organizations n Views of society n Views of nature n Views of the universe n 27
Social-Cultural Environment Views of themselves n Views of others n Views of organizations n Views of society n Views of nature n Views of the universe n 27
 Natural Environment Shortage of raw materials n Increased energy costs n Anti-pollution pressures n Governmental protections n 28
Natural Environment Shortage of raw materials n Increased energy costs n Anti-pollution pressures n Governmental protections n 28
 Technological Environment Pace of change n Opportunities for innovation n Varying R&D budgets n Increased regulation of change n 29
Technological Environment Pace of change n Opportunities for innovation n Varying R&D budgets n Increased regulation of change n 29
 MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 21 Tapping Into Global Markets Kotler Keller 1 -
MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 21 Tapping Into Global Markets Kotler Keller 1 -
 Chapter Questions n n n What factors should a company review before deciding to go abroad? How can companies evaluate and select specific foreign markets to enter? What are the major ways of entering a foreign market? To what extent must the company adapt its products and marketing program to each foreign country? How should the company manage and organize its international activities? 31
Chapter Questions n n n What factors should a company review before deciding to go abroad? How can companies evaluate and select specific foreign markets to enter? What are the major ways of entering a foreign market? To what extent must the company adapt its products and marketing program to each foreign country? How should the company manage and organize its international activities? 31
 Global Firm A firm that operates in more than one country and captures R&D, production, logistical, marketing, and financial advantages in its costs and reputation that are not available to purely domestic competitors. 32
Global Firm A firm that operates in more than one country and captures R&D, production, logistical, marketing, and financial advantages in its costs and reputation that are not available to purely domestic competitors. 32
 Major Decisions in International Marketing Deciding whether to go Deciding which markets to enter Deciding how to enter Deciding on the marketing program Deciding on the marketing organization 33
Major Decisions in International Marketing Deciding whether to go Deciding which markets to enter Deciding how to enter Deciding on the marketing program Deciding on the marketing organization 33
 Four Stages of Internationalization No regular export activities Export via independent agents Establish sales subsidiaries Establish production facilities abroad 34
Four Stages of Internationalization No regular export activities Export via independent agents Establish sales subsidiaries Establish production facilities abroad 34
 Regional Free Trade Zones European Union n NAFTA n MERCOSUL n APEC n 35
Regional Free Trade Zones European Union n NAFTA n MERCOSUL n APEC n 35
 Five Modes of Entry into Foreign Markets Indirect exporting n Direct exporting n Licensing n Joint venture n Direct investment n 36
Five Modes of Entry into Foreign Markets Indirect exporting n Direct exporting n Licensing n Joint venture n Direct investment n 36
 Direct Exporting Methods n Domestic-based export department n Overseas sales branch or subsidiary n Traveling export sales representatives n Foreign-based distributors or agents 37
Direct Exporting Methods n Domestic-based export department n Overseas sales branch or subsidiary n Traveling export sales representatives n Foreign-based distributors or agents 37
 Table 21. 1 Global Marketing Advantages n Economies of scale n Lower marketing costs n Power and scope n Consistency in brand image n Ability to leverage n Uniformity of marketing practices Disadvantages n Differences in consumer needs, wants, usage patterns n Differences in consumer response to marketing mix n Differences in brand development process n Differences in environment 38
Table 21. 1 Global Marketing Advantages n Economies of scale n Lower marketing costs n Power and scope n Consistency in brand image n Ability to leverage n Uniformity of marketing practices Disadvantages n Differences in consumer needs, wants, usage patterns n Differences in consumer response to marketing mix n Differences in brand development process n Differences in environment 38
 Cultural Dimensions Individualism vs. collectivism n High vs. lower power distance n Masculine vs. feminine n Weak vs. strong uncertainty avoidance n 39
Cultural Dimensions Individualism vs. collectivism n High vs. lower power distance n Masculine vs. feminine n Weak vs. strong uncertainty avoidance n 39
 International Product and Communication Strategies Straight extension n Communication adaptation n Product adaptation n Dual adaptation n Product invention n 40
International Product and Communication Strategies Straight extension n Communication adaptation n Product adaptation n Dual adaptation n Product invention n 40
 Price Choices • Set a uniform price everywhere • Set a market-based price in each country • Set a cost-based price in each country 41
Price Choices • Set a uniform price everywhere • Set a market-based price in each country • Set a cost-based price in each country 41
 Whole-Channel Concept for International Marketing Seller International headquarters Channels between nations Channels within nations Final buyers 42
Whole-Channel Concept for International Marketing Seller International headquarters Channels between nations Channels within nations Final buyers 42
 Global Organization Strategies World as single market n Multinational n Glocal n 43
Global Organization Strategies World as single market n Multinational n Glocal n 43
 MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 6 Analyzing Consumer Markets Kotler Keller 1 -
MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 6 Analyzing Consumer Markets Kotler Keller 1 -
 Chapter Questions How do consumer characteristics influence buying behavior? n What major psychological processes influence consumer responses to the marketing program? n How do consumers make purchasing decisions? n How do marketers analyze consumer decision making? n 45
Chapter Questions How do consumer characteristics influence buying behavior? n What major psychological processes influence consumer responses to the marketing program? n How do consumers make purchasing decisions? n How do marketers analyze consumer decision making? n 45
 What Influences Consumer Behavior? Cultural factors n Social factors n Personal factors n 46
What Influences Consumer Behavior? Cultural factors n Social factors n Personal factors n 46
 Culture The fundamental determinant of a person’s wants and behaviors acquired through socialization processes with family and other key institutions. 47
Culture The fundamental determinant of a person’s wants and behaviors acquired through socialization processes with family and other key institutions. 47
 Subcultures Nationalities n Religions n Racial groups n Geographic regions n Special interests n 48
Subcultures Nationalities n Religions n Racial groups n Geographic regions n Special interests n 48
 Fast Facts About American Culture n The average American ¨ chews 300 sticks of gum a year ¨ goes to the movies 9 times a year ¨ takes 4 trips per year ¨ attends a sporting event 7 times each year 49
Fast Facts About American Culture n The average American ¨ chews 300 sticks of gum a year ¨ goes to the movies 9 times a year ¨ takes 4 trips per year ¨ attends a sporting event 7 times each year 49
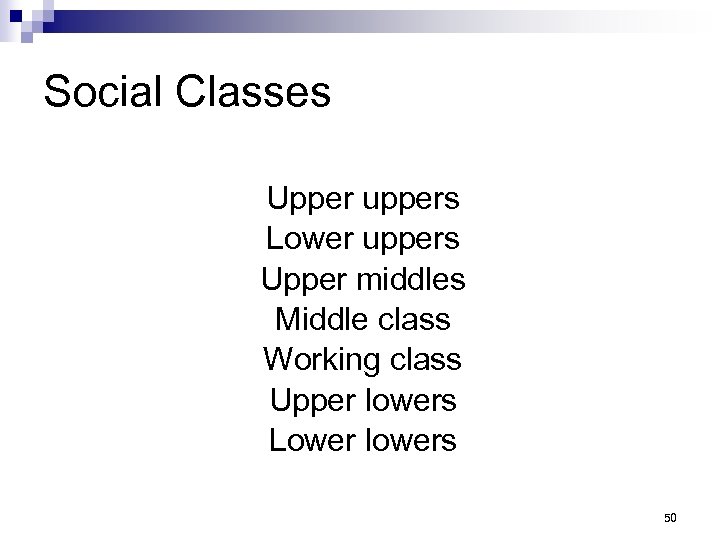 Social Classes Upper uppers Lower uppers Upper middles Middle class Working class Upper lowers Lower lowers 50
Social Classes Upper uppers Lower uppers Upper middles Middle class Working class Upper lowers Lower lowers 50
 Characteristics of Social Classes Within a class, people tend to behave alike. n Social class conveys perceptions of inferior or superior position. n Class may be indicated by a cluster of variables (occupation, income, wealth). n Class designation is mobile over time. n 51
Characteristics of Social Classes Within a class, people tend to behave alike. n Social class conveys perceptions of inferior or superior position. n Class may be indicated by a cluster of variables (occupation, income, wealth). n Class designation is mobile over time. n 51
 Social Factors Reference groups Family Social roles Statuses 52
Social Factors Reference groups Family Social roles Statuses 52
 Reference Groups Membership n Primary n Secondary n Aspirational n Dissociative n 53
Reference Groups Membership n Primary n Secondary n Aspirational n Dissociative n 53
 Family n n Family of Orientation ¨ Religion ¨ Politics ¨ Economics Family of Procreation ¨ Everyday buying behavior 54
Family n n Family of Orientation ¨ Religion ¨ Politics ¨ Economics Family of Procreation ¨ Everyday buying behavior 54
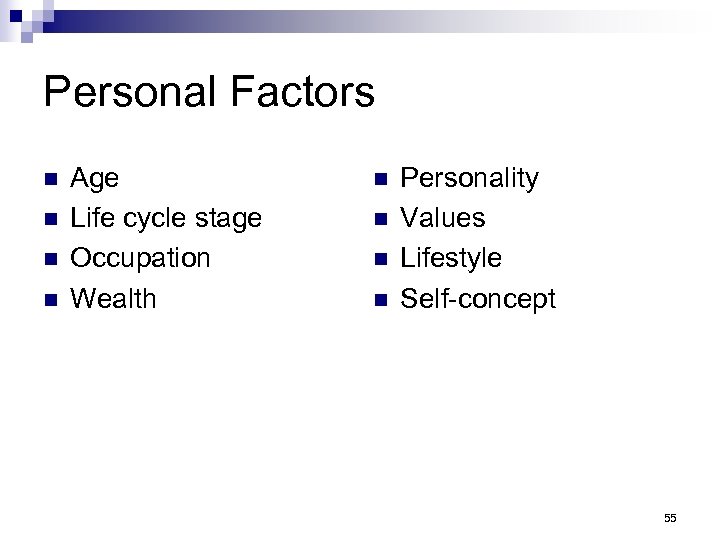 Personal Factors n n Age Life cycle stage Occupation Wealth n n Personality Values Lifestyle Self-concept 55
Personal Factors n n Age Life cycle stage Occupation Wealth n n Personality Values Lifestyle Self-concept 55
 Brand Personality Sincerity n Excitement n Competence n Sophistication n Ruggedness n 56
Brand Personality Sincerity n Excitement n Competence n Sophistication n Ruggedness n 56
 Key Psychological Processes Motivation n Perception n Learning n Memory n 57
Key Psychological Processes Motivation n Perception n Learning n Memory n 57
 Motivation Freud’s theory n Maslow’s hierarchy of needs n Herzberg’s two-factor theory n 58
Motivation Freud’s theory n Maslow’s hierarchy of needs n Herzberg’s two-factor theory n 58
 Perception Selective attention n Selective retention n Selective distortion n Subliminal perception n 59
Perception Selective attention n Selective retention n Selective distortion n Subliminal perception n 59
 Figure 6. 4 Consumer Buying Process Problem recognition n Information search n Evaluation n Purchase decision n Postpurchase behavior n 60
Figure 6. 4 Consumer Buying Process Problem recognition n Information search n Evaluation n Purchase decision n Postpurchase behavior n 60
 Sources of Information Personal n Commercial n Public n Experiential n 61
Sources of Information Personal n Commercial n Public n Experiential n 61
 Non-compensatory Models of Choice Conjunctive n Lexicographic n Elimination-by-aspects n 62
Non-compensatory Models of Choice Conjunctive n Lexicographic n Elimination-by-aspects n 62
 Perceived Risk n n n Functional Physical Financial n n n Social Psychological Time 63
Perceived Risk n n n Functional Physical Financial n n n Social Psychological Time 63
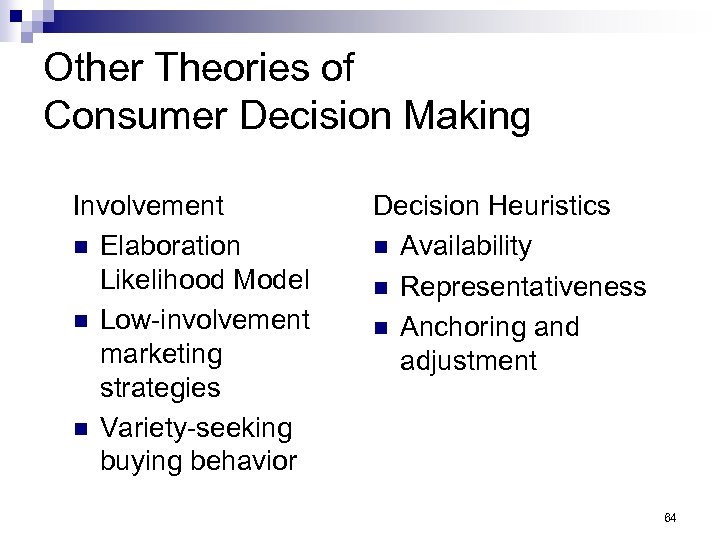 Other Theories of Consumer Decision Making Involvement n Elaboration Likelihood Model n Low-involvement marketing strategies n Variety-seeking buying behavior Decision Heuristics n Availability n Representativeness n Anchoring and adjustment 64
Other Theories of Consumer Decision Making Involvement n Elaboration Likelihood Model n Low-involvement marketing strategies n Variety-seeking buying behavior Decision Heuristics n Availability n Representativeness n Anchoring and adjustment 64
 Mental Accounting n Consumers tend to… ¨ Segregate gains ¨ Integrate losses ¨ Integrate smaller losses with larger gains ¨ Segregate small gains from large losses 65
Mental Accounting n Consumers tend to… ¨ Segregate gains ¨ Integrate losses ¨ Integrate smaller losses with larger gains ¨ Segregate small gains from large losses 65
 MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 7 Analyzing Business Markets Kotler Keller 1 -
MARKETING MANAGEMENT 12 th edition 7 Analyzing Business Markets Kotler Keller 1 -
 Chapter Questions What is the business market, and how does it differ from the consumer market? n What buying situations do organizational buyers face? n Who participates in the business-tobusiness buying process? n 67
Chapter Questions What is the business market, and how does it differ from the consumer market? n What buying situations do organizational buyers face? n Who participates in the business-tobusiness buying process? n 67
 Chapter Questions How do business buyers make their decisions? n How can companies build strong relationships with business customers? n How do institutional buyers and government agencies do their buying? n 68
Chapter Questions How do business buyers make their decisions? n How can companies build strong relationships with business customers? n How do institutional buyers and government agencies do their buying? n 68
 Organizational Buying Decision-making process by which formal organizations establish the need for purchased products and services, and identify evaluate, and choose among alternative brands and suppliers. 69
Organizational Buying Decision-making process by which formal organizations establish the need for purchased products and services, and identify evaluate, and choose among alternative brands and suppliers. 69
 Characteristics of Business Markets n n n Fewer, larger buyers Close suppliercustomer relationships Professional purchasing Many buying influences Multiple sales calls n n n Derived demand Inelastic demand Fluctuating demand Geographically concentrated buyers Direct purchasing 70
Characteristics of Business Markets n n n Fewer, larger buyers Close suppliercustomer relationships Professional purchasing Many buying influences Multiple sales calls n n n Derived demand Inelastic demand Fluctuating demand Geographically concentrated buyers Direct purchasing 70
 Buying Situation Straight rebuy n Modified rebuy n New task n 71
Buying Situation Straight rebuy n Modified rebuy n New task n 71
 The Buying Center Initiators n Users n Influencers n Deciders n Approvers n Buyers n Gatekeepers n 72
The Buying Center Initiators n Users n Influencers n Deciders n Approvers n Buyers n Gatekeepers n 72
 Of Concern to Business Marketers Who are the major decision participants? n What decisions do they influence? n What is their level of influence? n What evaluation criteria do they use? n 73
Of Concern to Business Marketers Who are the major decision participants? n What decisions do they influence? n What is their level of influence? n What evaluation criteria do they use? n 73
 Types of Business Customers n n Price-oriented Solution-oriented n n Gold-standard Strategic-value 74
Types of Business Customers n n Price-oriented Solution-oriented n n Gold-standard Strategic-value 74
 Handling Price-Oriented Customers Limit quantity purchased n Allow no refunds n Make no adjustments n Provide no services n 75
Handling Price-Oriented Customers Limit quantity purchased n Allow no refunds n Make no adjustments n Provide no services n 75
 Purchasing Orientations Buying n Procurement n Supply chain management n 76
Purchasing Orientations Buying n Procurement n Supply chain management n 76
 Product-Related Purchasing Processes Routine products n Leverage products n Strategic products n Bottleneck products n 77
Product-Related Purchasing Processes Routine products n Leverage products n Strategic products n Bottleneck products n 77
 Methods of e-Procurement Websites organized using vertical hubs n Websites organized using functional hubs n Direct extranet links to major suppliers n Buying alliances n Company buying sites n 78
Methods of e-Procurement Websites organized using vertical hubs n Websites organized using functional hubs n Direct extranet links to major suppliers n Buying alliances n Company buying sites n 78
 Forms of Electronic Marketplaces Catalog sites n Vertical markets n Pure play auction sites n Spot markets n Private exchanges n Barter markets n Buying alliances n 79
Forms of Electronic Marketplaces Catalog sites n Vertical markets n Pure play auction sites n Spot markets n Private exchanges n Barter markets n Buying alliances n 79
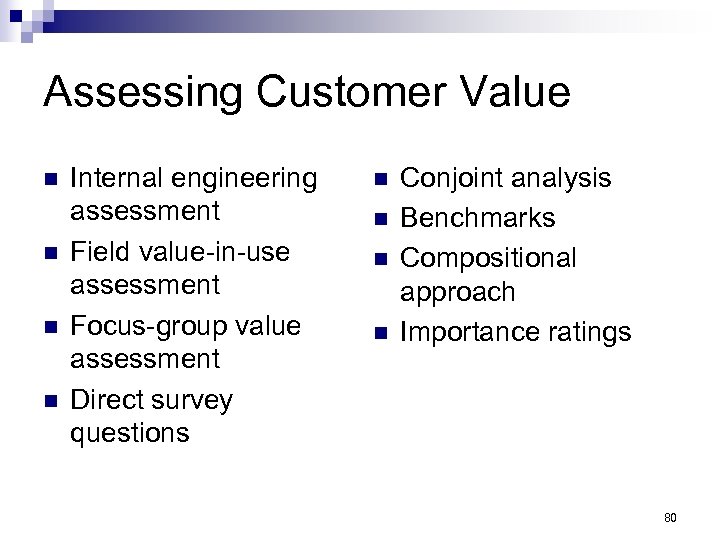 Assessing Customer Value n n Internal engineering assessment Field value-in-use assessment Focus-group value assessment Direct survey questions n n Conjoint analysis Benchmarks Compositional approach Importance ratings 80
Assessing Customer Value n n Internal engineering assessment Field value-in-use assessment Focus-group value assessment Direct survey questions n n Conjoint analysis Benchmarks Compositional approach Importance ratings 80
 Order Routine Specification and Inventory Stockless purchase plans n Vendor-managed inventory n Continuous replenishment n 81
Order Routine Specification and Inventory Stockless purchase plans n Vendor-managed inventory n Continuous replenishment n 81
 Desirable Outcomes of a B 2 B transaction: OTIFNE On time n In full n No error n 82
Desirable Outcomes of a B 2 B transaction: OTIFNE On time n In full n No error n 82
 Establishing Corporate Credibility Expertise n Trustworthiness n Likeability n 83
Establishing Corporate Credibility Expertise n Trustworthiness n Likeability n 83
 Factors Affecting Buyer-Supplier Relationships Availability of alternatives n Importance of supply n Complexity of supply n Supply market dynamism n 84
Factors Affecting Buyer-Supplier Relationships Availability of alternatives n Importance of supply n Complexity of supply n Supply market dynamism n 84
 Categories of Buyer-Seller Relationships n n Basic buying and selling Bare bones Contractual transaction Customer supply n n Cooperative systems Collaborative Mutually adaptive Customer is king 85
Categories of Buyer-Seller Relationships n n Basic buying and selling Bare bones Contractual transaction Customer supply n n Cooperative systems Collaborative Mutually adaptive Customer is king 85
 Opportunism Some form of cheating or undersupply relative to an implicit or explicit contract. 86
Opportunism Some form of cheating or undersupply relative to an implicit or explicit contract. 86


