Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh





































question_5_39_-_lecture12.ppt
- Размер: 3.7 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 43
Описание презентации Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh по слайдам
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 1 Slide 17 -2 PERSONAL SELLING AND SALES MANAGEMENTC HAPTER Lecture 12_Personal selling Associate professor of Plekhanov REA marketing department Irina I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D)
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 1 Slide 17 -2 PERSONAL SELLING AND SALES MANAGEMENTC HAPTER Lecture 12_Personal selling Associate professor of Plekhanov REA marketing department Irina I. Skorobogatykh (Ph. D)
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 2 Slide 17 -5 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: • Recognize different types of personal selling. • Describe the stages in the personal selling process. • Specify the functions and tasks in the sales management process.
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 2 Slide 17 -5 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: • Recognize different types of personal selling. • Describe the stages in the personal selling process. • Specify the functions and tasks in the sales management process.
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 3 Slide 17 -6 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: • Understand how firms recruit, select, train, motivate, compensate, and evaluate salespeople. • Describe recent applications of sales force automation and customer relationship management.
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 3 Slide 17 -6 AFTER READING THIS CHAPTER YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO: • Understand how firms recruit, select, train, motivate, compensate, and evaluate salespeople. • Describe recent applications of sales force automation and customer relationship management.
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 4 SCOPE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF PERSONAL SELLING AND SALES MANAGEMENT Slide 17 -8 • Nature of Personal Selling and Sales Management Personal Selling Sales Management • Selling Happens Almost Everywhere
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 4 SCOPE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF PERSONAL SELLING AND SALES MANAGEMENT Slide 17 -8 • Nature of Personal Selling and Sales Management Personal Selling Sales Management • Selling Happens Almost Everywhere
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 5 Slide 17 -61 Personal selling involves the two-way flow of communication between a buyer and seller, often in a face-to-face encounter, designed to influence a person’s or group’s purchase decision. Personal Selling
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 5 Slide 17 -61 Personal selling involves the two-way flow of communication between a buyer and seller, often in a face-to-face encounter, designed to influence a person’s or group’s purchase decision. Personal Selling
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 6 Slide 17 -62 Sales management involves planning the selling program and implementing and controlling the personal selling effort of the firm. Sales Management
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 6 Slide 17 -62 Sales management involves planning the selling program and implementing and controlling the personal selling effort of the firm. Sales Management
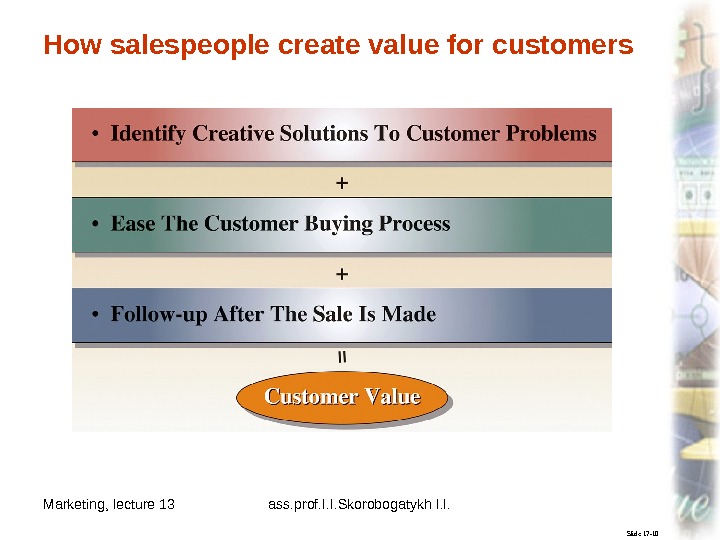
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 7 SCOPE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF PERSONAL SELLING AND SALES MANAGEMENT Slide 17 -9 Relationship Selling • Personal Selling in Marketing • Creating Customer Value Through Salespeople: Relationship Selling
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 7 SCOPE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF PERSONAL SELLING AND SALES MANAGEMENT Slide 17 -9 Relationship Selling • Personal Selling in Marketing • Creating Customer Value Through Salespeople: Relationship Selling
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 8 Slide 17 -63 Relationship selling is the practice of building ties to customers based on a salesperson’s attention and commitment to customer needs over time. Relationship Selling
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 8 Slide 17 -63 Relationship selling is the practice of building ties to customers based on a salesperson’s attention and commitment to customer needs over time. Relationship Selling
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 9 Slide 17 -10 How salespeople create value for customers
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 9 Slide 17 -10 How salespeople create value for customers
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 10 Slide 17 -12 1. What is personal selling? A: Personal selling involves the two-way flow of communication between a buyer and seller, often in a face-to-face encounter, designed to influence a person’s or group’s purchase decision. Concept Check
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 10 Slide 17 -12 1. What is personal selling? A: Personal selling involves the two-way flow of communication between a buyer and seller, often in a face-to-face encounter, designed to influence a person’s or group’s purchase decision. Concept Check
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 11 Slide 17 -13 2. What is involved in sales management? A: Sales management involves planning the selling program and implementing and controlling the personal selling effort of the firm. Concept Check
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 11 Slide 17 -13 2. What is involved in sales management? A: Sales management involves planning the selling program and implementing and controlling the personal selling effort of the firm. Concept Check
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 12 THE MANY FORMS OF PERSONAL SELLING Slide 17 -14 • Order Taker Outside Order Takers Inside Order Takers, Order Clerks, or Salesclerks Inbound Telemarketing Outbound Telemarketing • Order Getter
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 12 THE MANY FORMS OF PERSONAL SELLING Slide 17 -14 • Order Taker Outside Order Takers Inside Order Takers, Order Clerks, or Salesclerks Inbound Telemarketing Outbound Telemarketing • Order Getter
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 13 Slide 17 -64 An order taker processes routine orders or reorders for products that were already sold by the company. Order Taker
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 13 Slide 17 -64 An order taker processes routine orders or reorders for products that were already sold by the company. Order Taker
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 14 Slide 17 -65 An order getter sells in a conventional sense and identifies prospective customers, provides customers with information, persuades customers to buy, closes sales, and follows up on customers’ use of a product or service. Order Getter
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 14 Slide 17 -65 An order getter sells in a conventional sense and identifies prospective customers, provides customers with information, persuades customers to buy, closes sales, and follows up on customers’ use of a product or service. Order Getter
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 15 Slide 17 -15 Comparing order takers and order getters
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 15 Slide 17 -15 Comparing order takers and order getters
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 16 Slide 17 -18 1. What is the main difference between an order taker and an order getter? A: An order taker processes routine orders or reorders for products that were already sold by the company. An order getter sells in a conventional sense and identifies prospective customers, provides customers with information, persuades customers to buy, closes sales, and follows up on their use of a product or service. Concept Check
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 16 Slide 17 -18 1. What is the main difference between an order taker and an order getter? A: An order taker processes routine orders or reorders for products that were already sold by the company. An order getter sells in a conventional sense and identifies prospective customers, provides customers with information, persuades customers to buy, closes sales, and follows up on their use of a product or service. Concept Check
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 17 Slide 17 -19 2. What percentage of an order-getting salesperson’s time is spent selling? A: About 54% (25% selling over the phone and 29% selling face-to-face). Concept Check
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 17 Slide 17 -19 2. What percentage of an order-getting salesperson’s time is spent selling? A: About 54% (25% selling over the phone and 29% selling face-to-face). Concept Check
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 18 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -25 Stimulus-Response Format • Presentation • Stimulus-Response Presentation • Suggestive Selling Formula Selling Format • Formula Selling Presentation • Canned Selling Presentation
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 18 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -25 Stimulus-Response Format • Presentation • Stimulus-Response Presentation • Suggestive Selling Formula Selling Format • Formula Selling Presentation • Canned Selling Presentation
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 19 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -26 Need-Satisfaction Format • Presentation • Need-Satisfaction Presentation • Adaptive Selling • Consultative Selling
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 19 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -26 Need-Satisfaction Format • Presentation • Need-Satisfaction Presentation • Adaptive Selling • Consultative Selling
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 20 Slide 17 -67 Adaptive selling involves adjusting the presentation to fit the selling situation, such as knowing when to offer solutions and when to ask for more information. Adaptive Selling
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 20 Slide 17 -67 Adaptive selling involves adjusting the presentation to fit the selling situation, such as knowing when to offer solutions and when to ask for more information. Adaptive Selling
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 21 Slide 17 -68 Consultative selling focuses on problem identification, where the salesperson serves as an expert on problem recognition and resolution. Consultative Selling
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 21 Slide 17 -68 Consultative selling focuses on problem identification, where the salesperson serves as an expert on problem recognition and resolution. Consultative Selling
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 22 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -27 Handling Objections • Presentation • Acknowledge and Convert the Objection • Postpone • Agree and Neutralize • Accept the Objection • Denial • Ignore the Objection
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 22 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -27 Handling Objections • Presentation • Acknowledge and Convert the Objection • Postpone • Agree and Neutralize • Accept the Objection • Denial • Ignore the Objection
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 23 Slide 17 -28 Techniques for handling objections
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 23 Slide 17 -28 Techniques for handling objections
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 24 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -29 Close • Presentation • Trial Close • Assumptive Close • Urgency Close • Final Close Follow-up
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 24 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -29 Close • Presentation • Trial Close • Assumptive Close • Urgency Close • Final Close Follow-up
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 25 Slide 17 -30 1. What are the six stages in the personal selling process? A: They are: (1) prospecting, (2) preapproach, (3) approach, (4) presentation, (5) close, and (6) follow-up. Concept Check
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 25 Slide 17 -30 1. What are the six stages in the personal selling process? A: They are: (1) prospecting, (2) preapproach, (3) approach, (4) presentation, (5) close, and (6) follow-up. Concept Check
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 26 Slide 17 -31 2. Which presentation format is most consistent with the marketing concept? Why? A: The need-satisfaction format is most consistent with the marketing concept because it emphasizes problem solving. Concept Check
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 26 Slide 17 -31 2. Which presentation format is most consistent with the marketing concept? Why? A: The need-satisfaction format is most consistent with the marketing concept because it emphasizes problem solving. Concept Check
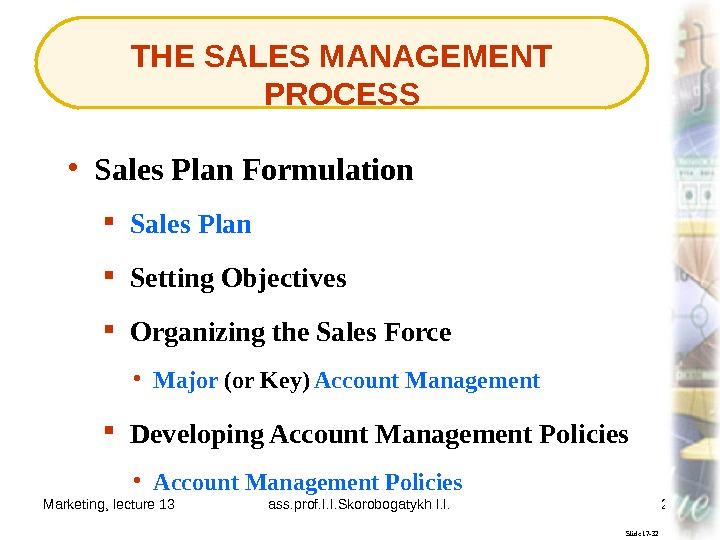
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 27 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -32 Sales Plan • Sales Plan Formulation Organizing the Sales Force • Major (or Key) Account Management Setting Objectives Developing Account Management Policies • Account Management Policies
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 27 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -32 Sales Plan • Sales Plan Formulation Organizing the Sales Force • Major (or Key) Account Management Setting Objectives Developing Account Management Policies • Account Management Policies
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 28 Slide 17 -69 The sales plan is a statement describing what is to be achieved and where and how the selling effort of salespeople is to be directed. Sales Plan
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 28 Slide 17 -69 The sales plan is a statement describing what is to be achieved and where and how the selling effort of salespeople is to be directed. Sales Plan
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 29 Slide 17 -70 Major account management is the practice of using team selling to focus on important customers so as to build mutually beneficial, long-term, cooperative relationships. Major Account Management
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 29 Slide 17 -70 Major account management is the practice of using team selling to focus on important customers so as to build mutually beneficial, long-term, cooperative relationships. Major Account Management
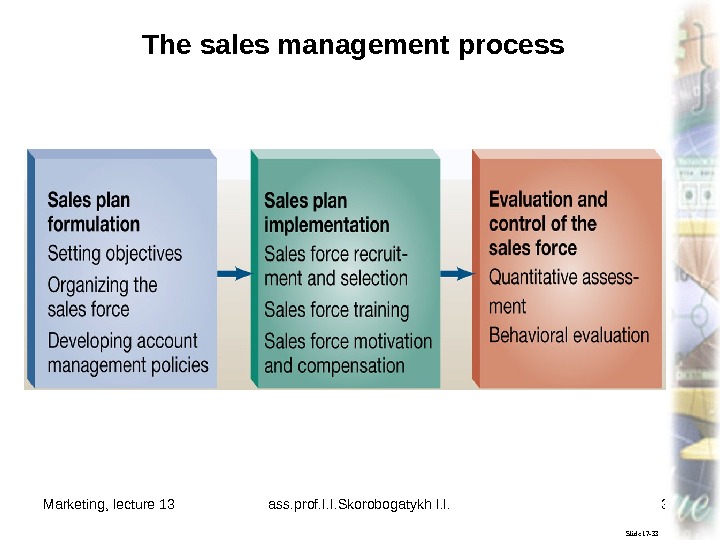
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 30 Slide 17 -33 The sales management process
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 30 Slide 17 -33 The sales management process
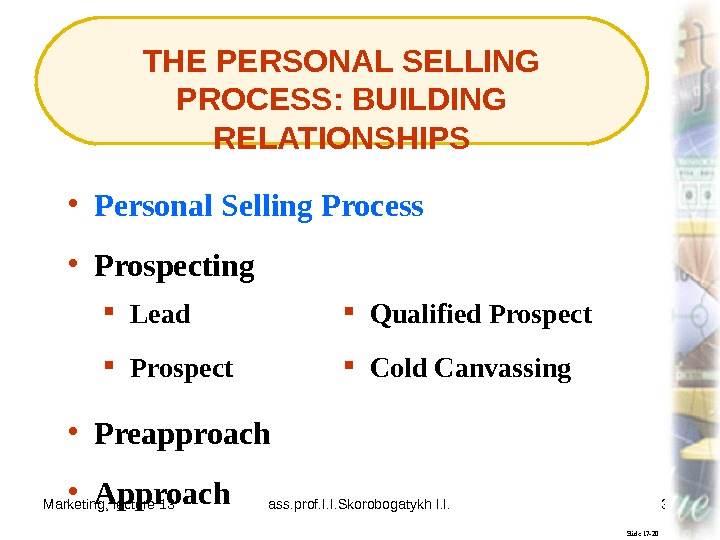
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 31 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -20 Lead • Personal Selling Process Prospect Qualified Prospect • Prospecting Cold Canvassing • Preapproach • Approach
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 31 THE PERSONAL SELLING PROCESS: BUILDING RELATIONSHIPS Slide 17 -20 Lead • Personal Selling Process Prospect Qualified Prospect • Prospecting Cold Canvassing • Preapproach • Approach
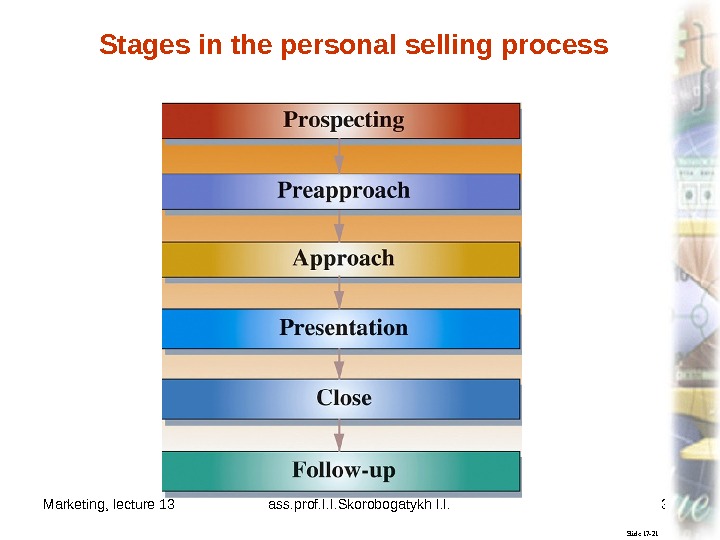
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 32 Slide 17 -66 The personal selling process consists of six stages: (1) prospecting, (2) preapproach, (3) approach, (4) presentation, (5) close, and (6) follow-up. Personal Selling Process
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 32 Slide 17 -66 The personal selling process consists of six stages: (1) prospecting, (2) preapproach, (3) approach, (4) presentation, (5) close, and (6) follow-up. Personal Selling Process
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 33 Slide 17 -21 Stages in the personal selling process
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 33 Slide 17 -21 Stages in the personal selling process
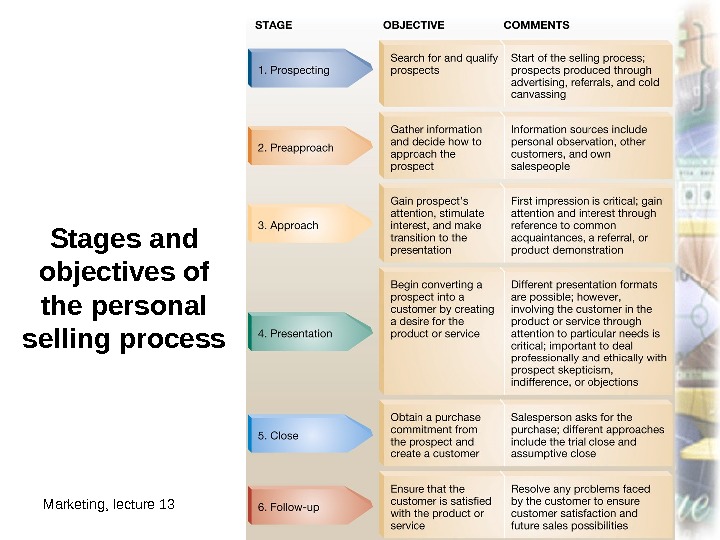
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 34 Slide 17 -22 Stages and objectives of the personal selling process
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 34 Slide 17 -22 Stages and objectives of the personal selling process
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 35 Slide 17 -35 Account management policy grid
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 35 Slide 17 -35 Account management policy grid
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 36 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -36 Sales Force Recruitment and Selection • Sales Plan Implementation • Job Analysis Sales Force Training • Job Description
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 36 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -36 Sales Force Recruitment and Selection • Sales Plan Implementation • Job Analysis Sales Force Training • Job Description
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 37 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -41 Sales Force Motivation and Compensation • Sales Plan Implementation • Straight Salary Compensation Plan • Straight Commission Compensation Plan • Combination Compensation Plan
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 37 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -41 Sales Force Motivation and Compensation • Sales Plan Implementation • Straight Salary Compensation Plan • Straight Commission Compensation Plan • Combination Compensation Plan
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 38 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -43 Quantitative Assessments • Sales Force Evaluation • Quotas Behavioral Evaluation
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 38 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -43 Quantitative Assessments • Sales Force Evaluation • Quotas Behavioral Evaluation
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 39 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -44 Sales Force Computerization • Sales Force Automation and Customer Relationship Management Sales Force Communication Sales Force Automation
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 39 THE SALES MANAGEMENT PROCESS Slide 17 -44 Sales Force Computerization • Sales Force Automation and Customer Relationship Management Sales Force Communication Sales Force Automation
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 40 Slide 17 -47 1. What are three types of selling objectives? A: They are: (1) output-related (dollars or unit sales, number of new customers, profit); (2) input-related (number of sales calls, selling expenses); and (3) behavioral-related (level of product knowledge, customer service, selling and communication skills). Concept Check
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 40 Slide 17 -47 1. What are three types of selling objectives? A: They are: (1) output-related (dollars or unit sales, number of new customers, profit); (2) input-related (number of sales calls, selling expenses); and (3) behavioral-related (level of product knowledge, customer service, selling and communication skills). Concept Check
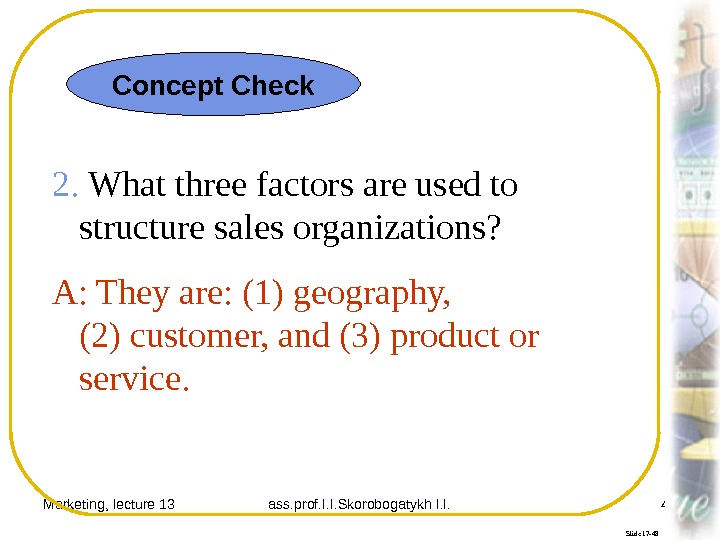
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 41 Slide 17 -48 2. What three factors are used to structure sales organizations? A: They are: (1) geography, (2) customer, and (3) product or service. Concept Check
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 41 Slide 17 -48 2. What three factors are used to structure sales organizations? A: They are: (1) geography, (2) customer, and (3) product or service. Concept Check
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 42 Slide 17 -71 Account management policies specify whom salespeople should contact, what kinds of selling and customer service activities should be engaged in, and how these activities should be carried out. Account Management Polices
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 42 Slide 17 -71 Account management policies specify whom salespeople should contact, what kinds of selling and customer service activities should be engaged in, and how these activities should be carried out. Account Management Polices
 Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 43 Slide 17 -72 Sales force automation (SFA) is the use of computer, information, communication, and Internet/Web technologies to make the sales function more effective and efficient. Sales Force Automation
Marketing, lecture 13 ass. prof. I. I. Skorobogatykh I. I. 43 Slide 17 -72 Sales force automation (SFA) is the use of computer, information, communication, and Internet/Web technologies to make the sales function more effective and efficient. Sales Force Automation

