a31120bc102d217aa7b6897237bd7023.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 81
 Marketing in the “New” Economy CRM Service Marketing Internet Marketing Int’l Marketing
Marketing in the “New” Economy CRM Service Marketing Internet Marketing Int’l Marketing
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 Service Perspectives: Not a “Product” Intangible human act- that is produced at the time of consumption & can’t be standardized or inventoried… No Difference. Products are just appliances that provide services- Shift perspective from Mfgr to consumer… and focus on benefits No One. Automatio n, Virtualizati on & Outsourci ng
Service Perspectives: Not a “Product” Intangible human act- that is produced at the time of consumption & can’t be standardized or inventoried… No Difference. Products are just appliances that provide services- Shift perspective from Mfgr to consumer… and focus on benefits No One. Automatio n, Virtualizati on & Outsourci ng
 Defining -a Service • An act or performance offered by one party for another • An economic activity that does not result in ownership • A process that creates benefits by facilitating a desired change in: – customers themselves –get a haircut – physical possessions- get a wig – intangible assets- get therapy
Defining -a Service • An act or performance offered by one party for another • An economic activity that does not result in ownership • A process that creates benefits by facilitating a desired change in: – customers themselves –get a haircut – physical possessions- get a wig – intangible assets- get therapy
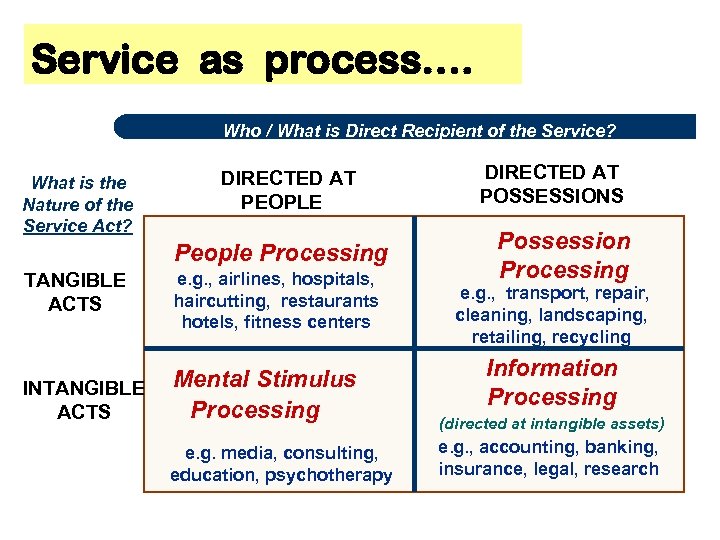 Service as process…. Who / What is Direct Recipient of the Service? What is the Nature of the Service Act? DIRECTED AT PEOPLE People Processing TANGIBLE ACTS e. g. , airlines, hospitals, haircutting, restaurants hotels, fitness centers INTANGIBLE ACTS Mental Stimulus Processing e. g. media, consulting, education, psychotherapy DIRECTED AT POSSESSIONS Possession Processing e. g. , transport, repair, cleaning, landscaping, retailing, recycling Information Processing (directed at intangible assets) e. g. , accounting, banking, insurance, legal, research
Service as process…. Who / What is Direct Recipient of the Service? What is the Nature of the Service Act? DIRECTED AT PEOPLE People Processing TANGIBLE ACTS e. g. , airlines, hospitals, haircutting, restaurants hotels, fitness centers INTANGIBLE ACTS Mental Stimulus Processing e. g. media, consulting, education, psychotherapy DIRECTED AT POSSESSIONS Possession Processing e. g. , transport, repair, cleaning, landscaping, retailing, recycling Information Processing (directed at intangible assets) e. g. , accounting, banking, insurance, legal, research
 Importance of Service Sector In most countries, services add more economic value than agriculture, raw materials and manufacturing combined In developed economies, employment is dominated by http: //earthtrends. wri. org/searchable_db/index. php? action=se service jobs and lect_countries&theme=5&variable_ID=216 most new job growth
Importance of Service Sector In most countries, services add more economic value than agriculture, raw materials and manufacturing combined In developed economies, employment is dominated by http: //earthtrends. wri. org/searchable_db/index. php? action=se service jobs and lect_countries&theme=5&variable_ID=216 most new job growth
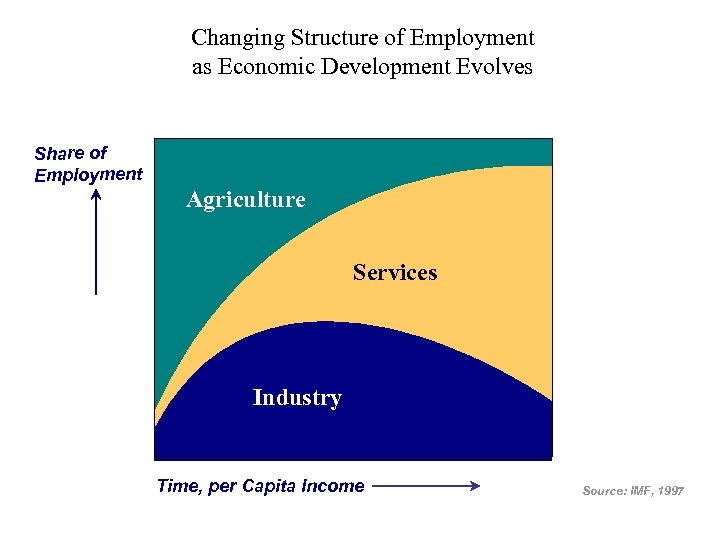 Changing Structure of Employment as Economic Development Evolves Share of Employment Agriculture Services Industry Time, per Capita Income Source: IMF, 1997
Changing Structure of Employment as Economic Development Evolves Share of Employment Agriculture Services Industry Time, per Capita Income Source: IMF, 1997
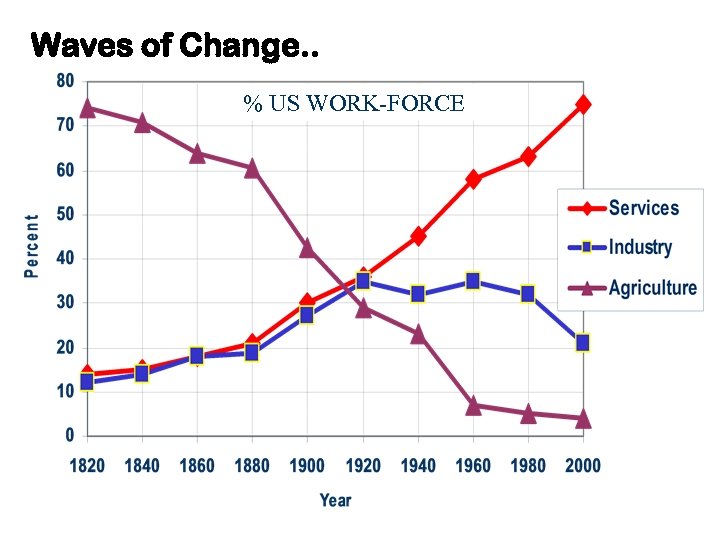 Waves of Change. . % US WORK-FORCE The Economist, 1996
Waves of Change. . % US WORK-FORCE The Economist, 1996
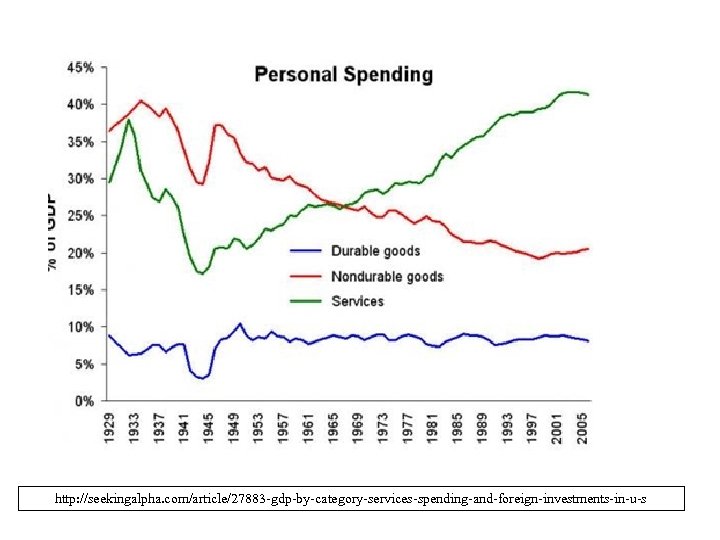 http: //seekingalpha. com/article/27883 -gdp-by-category-services-spending-and-foreign-investments-in-u-s
http: //seekingalpha. com/article/27883 -gdp-by-category-services-spending-and-foreign-investments-in-u-s
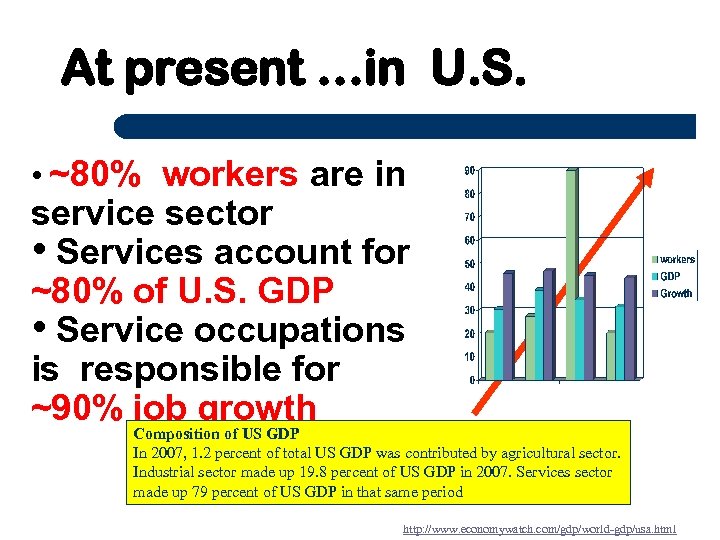 At present …in U. S. • ~80% workers are in service sector • Services account for ~80% of U. S. GDP • Service occupations is responsible for ~90% job growth Composition of US GDP In 2007, 1. 2 percent of total US GDP was contributed by agricultural sector. Industrial sector made up 19. 8 percent of US GDP in 2007. Services sector made up 79 percent of US GDP in that same period http: //www. economywatch. com/gdp/world-gdp/usa. html
At present …in U. S. • ~80% workers are in service sector • Services account for ~80% of U. S. GDP • Service occupations is responsible for ~90% job growth Composition of US GDP In 2007, 1. 2 percent of total US GDP was contributed by agricultural sector. Industrial sector made up 19. 8 percent of US GDP in 2007. Services sector made up 79 percent of US GDP in that same period http: //www. economywatch. com/gdp/world-gdp/usa. html
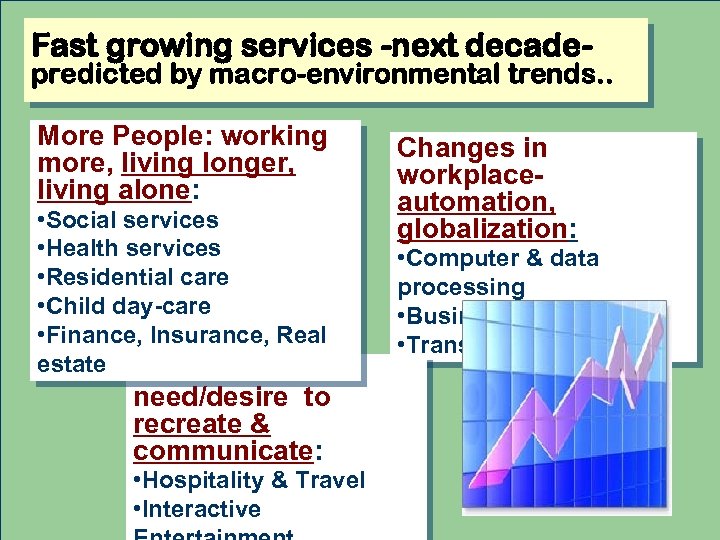 Fast growing services -next decade- predicted by macro-environmental trends. . More People: working more, living longer, living alone: • Social services • Health services • Residential care • Child day-care • Finance, Insurance, Real estate Increased need/desire to recreate & communicate: • Hospitality & Travel • Interactive Changes in workplaceautomation, globalization: • Computer & data processing • Business services • Transportation
Fast growing services -next decade- predicted by macro-environmental trends. . More People: working more, living longer, living alone: • Social services • Health services • Residential care • Child day-care • Finance, Insurance, Real estate Increased need/desire to recreate & communicate: • Hospitality & Travel • Interactive Changes in workplaceautomation, globalization: • Computer & data processing • Business services • Transportation
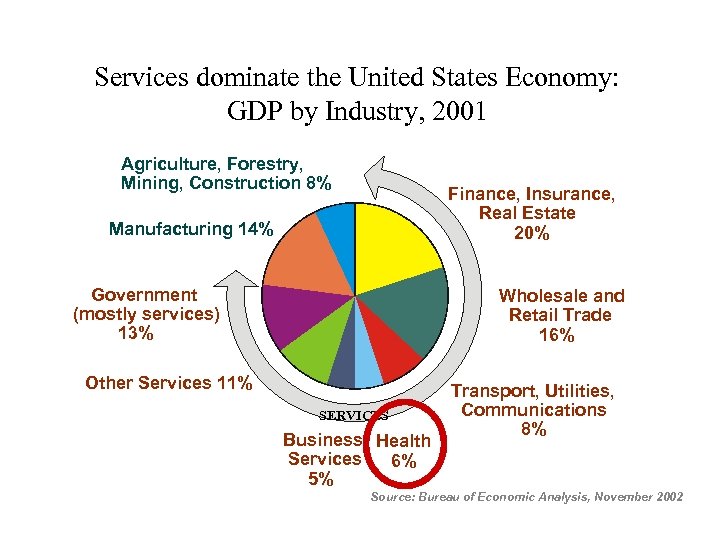 Services dominate the United States Economy: GDP by Industry, 2001 Agriculture, Forestry, Mining, Construction 8% Finance, Insurance, Real Estate 20% Manufacturing 14% Government (mostly services) 13% Wholesale and Retail Trade 16% Other Services 11% SERVICES Business Health Services 6% 5% Transport, Utilities, Communications 8% Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, November 2002
Services dominate the United States Economy: GDP by Industry, 2001 Agriculture, Forestry, Mining, Construction 8% Finance, Insurance, Real Estate 20% Manufacturing 14% Government (mostly services) 13% Wholesale and Retail Trade 16% Other Services 11% SERVICES Business Health Services 6% 5% Transport, Utilities, Communications 8% Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis, November 2002
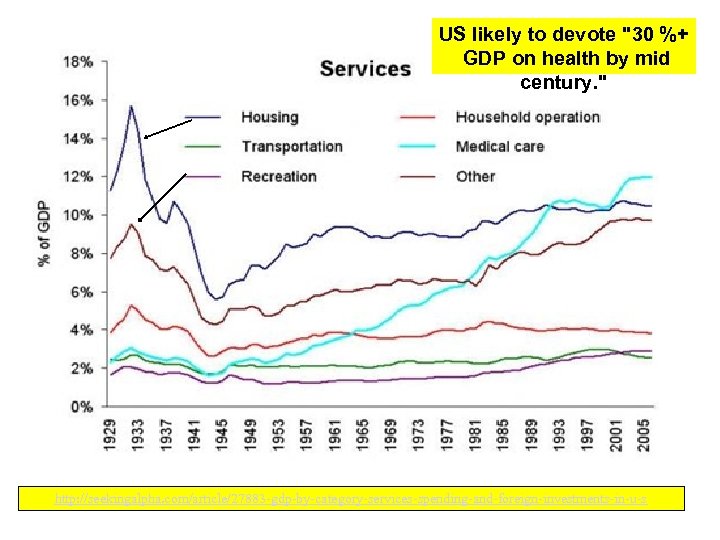 US likely to devote "30 %+ GDP on health by mid century. " http: //seekingalpha. com/article/27883 -gdp-by-category-services-spending-and-foreign-investments-in-u-s
US likely to devote "30 %+ GDP on health by mid century. " http: //seekingalpha. com/article/27883 -gdp-by-category-services-spending-and-foreign-investments-in-u-s
 Critical Questions 1. What is the “debate” all about regarding how services should be defined / envisioned? o How does the definition of a service affect your marketing strategy? 2. What are the key P’s to meeting service management challenges? 3. What are some of the factors & considerations affecting the near future of “services” marketing?
Critical Questions 1. What is the “debate” all about regarding how services should be defined / envisioned? o How does the definition of a service affect your marketing strategy? 2. What are the key P’s to meeting service management challenges? 3. What are some of the factors & considerations affecting the near future of “services” marketing?
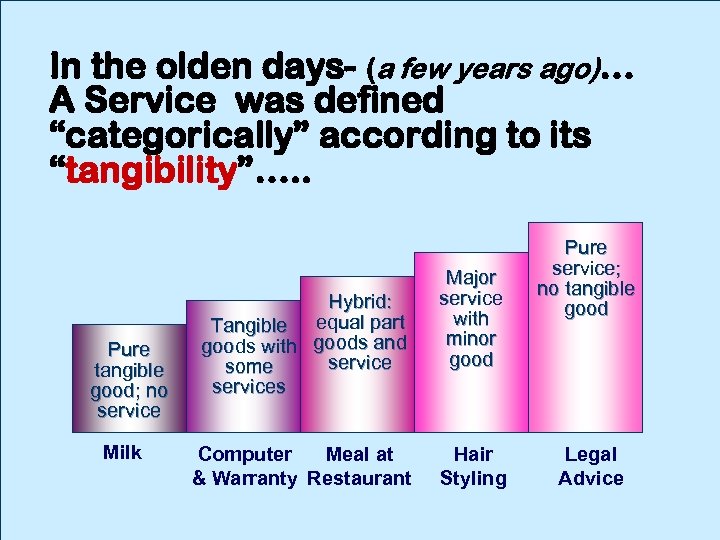 In the olden days- (a few years ago)… A Service was defined “categorically” according to its “tangibility”…. . Pure tangible good; no service Milk Hybrid: Tangible equal part goods with goods and service some services Computer Meal at & Warranty Restaurant Major service with minor good Hair Styling Pure service; no tangible good Legal Advice
In the olden days- (a few years ago)… A Service was defined “categorically” according to its “tangibility”…. . Pure tangible good; no service Milk Hybrid: Tangible equal part goods with goods and service some services Computer Meal at & Warranty Restaurant Major service with minor good Hair Styling Pure service; no tangible good Legal Advice
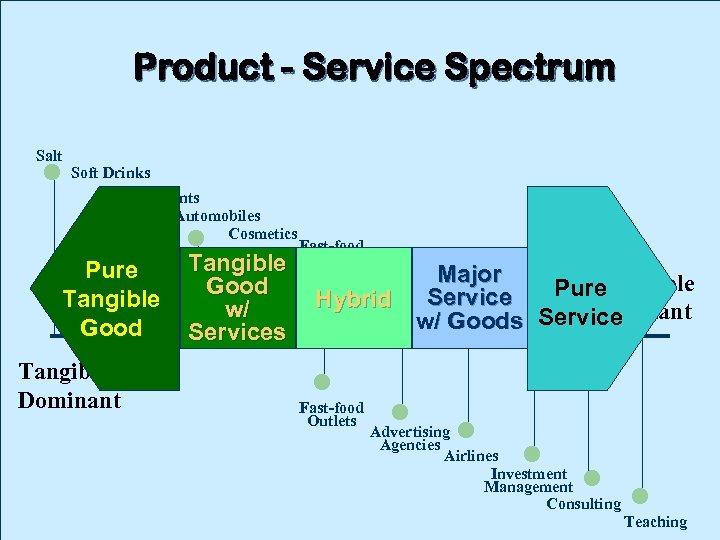 Product - Service Spectrum Salt Soft Drinks Detergents Automobiles Cosmetics Fast-food Tangible Outlets Pure Good Tangible Hybrid Good Tangible Dominant w/ Services Fast-food Outlets Major Intangible Pure Service Dominant w/ Goods Service Advertising Agencies Airlines Investment Management Consulting Teaching
Product - Service Spectrum Salt Soft Drinks Detergents Automobiles Cosmetics Fast-food Tangible Outlets Pure Good Tangible Hybrid Good Tangible Dominant w/ Services Fast-food Outlets Major Intangible Pure Service Dominant w/ Goods Service Advertising Agencies Airlines Investment Management Consulting Teaching
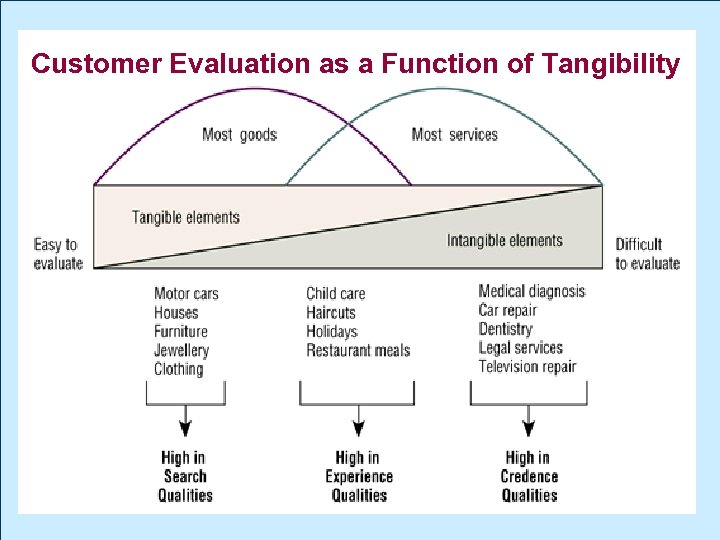 Customer Evaluation as a Function of Tangibility
Customer Evaluation as a Function of Tangibility
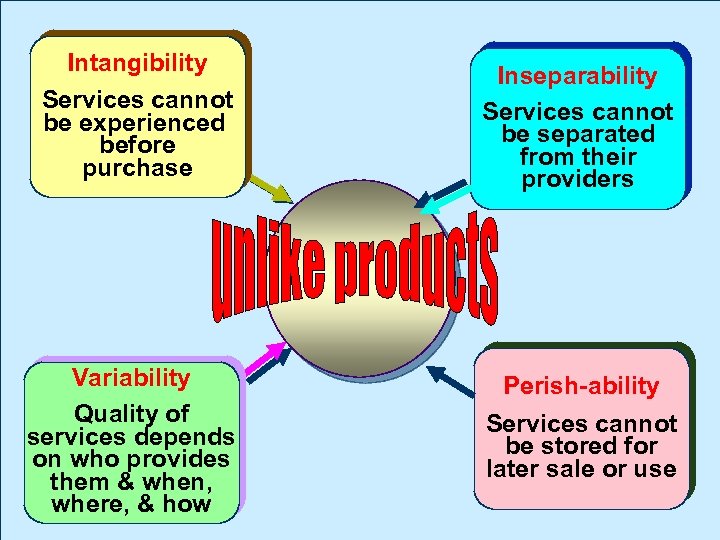 Intangibility Services cannot be experienced before purchase Variability Quality of services depends on who provides them & when, where, & how Inseparability Services cannot be separated from their providers Perish-ability Services cannot be stored for later sale or use
Intangibility Services cannot be experienced before purchase Variability Quality of services depends on who provides them & when, where, & how Inseparability Services cannot be separated from their providers Perish-ability Services cannot be stored for later sale or use
 Intangibility Services mrktg: • Describe the invisible • Articulate the imaginary • & Define the indistinct
Intangibility Services mrktg: • Describe the invisible • Articulate the imaginary • & Define the indistinct
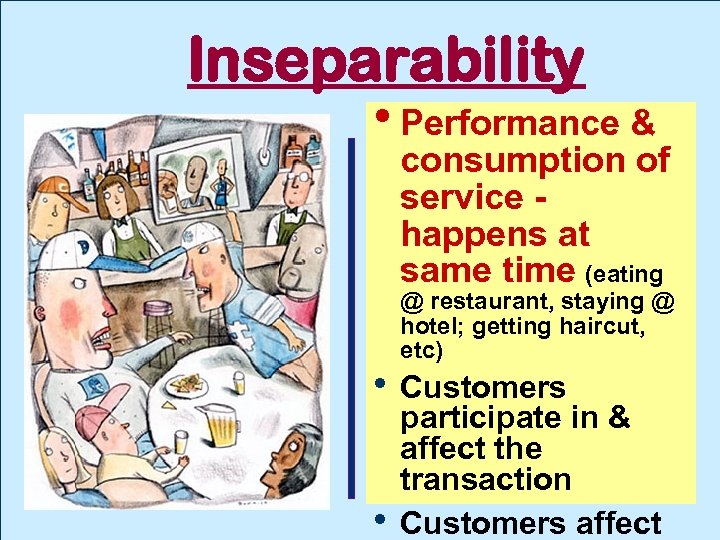 Inseparability • Performance & consumption of service happens at same time (eating @ restaurant, staying @ hotel; getting haircut, etc) • Customers • participate in & affect the transaction Customers affect
Inseparability • Performance & consumption of service happens at same time (eating @ restaurant, staying @ hotel; getting haircut, etc) • Customers • participate in & affect the transaction Customers affect
 Variability-Heterogeneity • Difficult to standardize Delivery, Quality & Customer Satisfaction depend on employee actions • Employees vary - attitudes, skills, mood, etc. • No assurance service delivered
Variability-Heterogeneity • Difficult to standardize Delivery, Quality & Customer Satisfaction depend on employee actions • Employees vary - attitudes, skills, mood, etc. • No assurance service delivered
 Perishability Can not be inventoried • Difficult to synchronize supply & demand with services • Services cannot be returned or resold
Perishability Can not be inventoried • Difficult to synchronize supply & demand with services • Services cannot be returned or resold
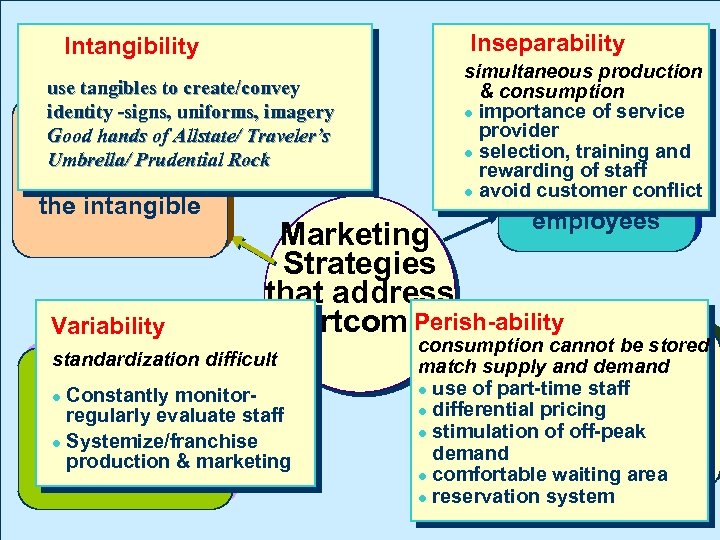 Inseparability Intangibility use tangibles to create/convey identity -signs, uniforms, imagery Good hands of Allstate/ Traveler’s Intangibility Umbrella/ Prudential Rock “Tangibilize” the intangible Variability simultaneous production & consumption importance of service Inseparability provider selection, training and Increase rewarding of staff professionalism avoid customer conflict of employees Marketing Strategies that address Perish-ability “shortcoming” standardization difficult Variability Constantly monitor. Systematize regularly evaluate staff service Systemize/franchise production marketing production & & delivery consumption cannot be stored match supply and demand Perish-ability use of part-time staff differential pricing Match supply stimulation of off-peak & demand comfortable waiting area reservation system
Inseparability Intangibility use tangibles to create/convey identity -signs, uniforms, imagery Good hands of Allstate/ Traveler’s Intangibility Umbrella/ Prudential Rock “Tangibilize” the intangible Variability simultaneous production & consumption importance of service Inseparability provider selection, training and Increase rewarding of staff professionalism avoid customer conflict of employees Marketing Strategies that address Perish-ability “shortcoming” standardization difficult Variability Constantly monitor. Systematize regularly evaluate staff service Systemize/franchise production marketing production & & delivery consumption cannot be stored match supply and demand Perish-ability use of part-time staff differential pricing Match supply stimulation of off-peak & demand comfortable waiting area reservation system
 Re: service marketing – for decades this has been the thinking- But is it the
Re: service marketing – for decades this has been the thinking- But is it the
 The Four Service Marketing Myths: Remnants of a Goods-Based, Manufacturing Model The 4 characteristics: 1. Do not distinguish services from goods 2. Only have meaning from a manufacturing perspective, and 3. Suggest inappropriate marketing strategies
The Four Service Marketing Myths: Remnants of a Goods-Based, Manufacturing Model The 4 characteristics: 1. Do not distinguish services from goods 2. Only have meaning from a manufacturing perspective, and 3. Suggest inappropriate marketing strategies
 Key Point- Product-service differentiation is result of industrial age-2 nd wave thinking Ø Ø Re- Variabilty: Customizaton not standardization is the goal Re-Inseparability: “Customer-ization” not isolation = goal Re-Perishability: Services can be/are inventoried (ie-knowledge in databases & experts head) AND Inventory management not maximization is the objective; Everything is perishable—if not in substance certainly in style… Re: Intangibility: its not the product that people are buying. It’s the functions served & benefits rendered- as it is
Key Point- Product-service differentiation is result of industrial age-2 nd wave thinking Ø Ø Re- Variabilty: Customizaton not standardization is the goal Re-Inseparability: “Customer-ization” not isolation = goal Re-Perishability: Services can be/are inventoried (ie-knowledge in databases & experts head) AND Inventory management not maximization is the objective; Everything is perishable—if not in substance certainly in style… Re: Intangibility: its not the product that people are buying. It’s the functions served & benefits rendered- as it is
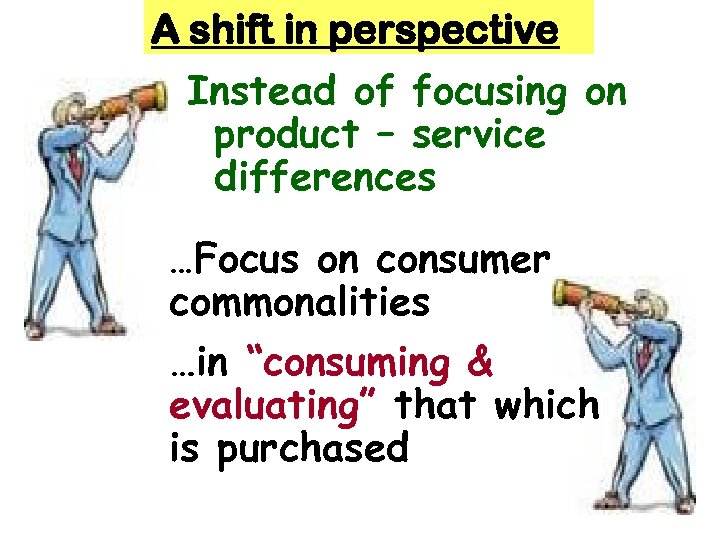 A shift in perspective Instead of focusing on product – service differences …Focus on consumer commonalities …in “consuming & evaluating” that which is purchased
A shift in perspective Instead of focusing on product – service differences …Focus on consumer commonalities …in “consuming & evaluating” that which is purchased
 Critical Questions 1. What is the “debate” all about regarding how services should be defined / envisioned? o How does the definition of a service affect your marketing strategy? 2. What are the key P’s to meeting service management challenges? 3. What are some of the factors & considerations affecting the near future of “services” marketing?
Critical Questions 1. What is the “debate” all about regarding how services should be defined / envisioned? o How does the definition of a service affect your marketing strategy? 2. What are the key P’s to meeting service management challenges? 3. What are some of the factors & considerations affecting the near future of “services” marketing?
 Challenges for Service Mgt Same as Product Mgt 1. Creating & offering the consumer value 2. Communicating a desired & distinct image 3. Create, sustain & enhance customer relationships 4. Defining- maintainingimproving quality
Challenges for Service Mgt Same as Product Mgt 1. Creating & offering the consumer value 2. Communicating a desired & distinct image 3. Create, sustain & enhance customer relationships 4. Defining- maintainingimproving quality
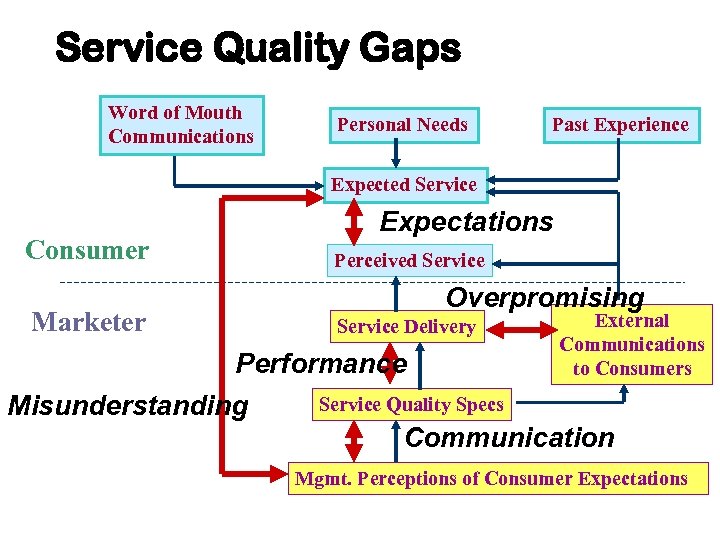 Service Quality Gaps Word of Mouth Communications Personal Needs Past Experience Expected Service Consumer Marketer Expectations Perceived Service Overpromising Service Delivery External Communications to Consumers Performance Service Quality Specs Misunderstanding Communication Mgmt. Perceptions of Consumer Expectations
Service Quality Gaps Word of Mouth Communications Personal Needs Past Experience Expected Service Consumer Marketer Expectations Perceived Service Overpromising Service Delivery External Communications to Consumers Performance Service Quality Specs Misunderstanding Communication Mgmt. Perceptions of Consumer Expectations
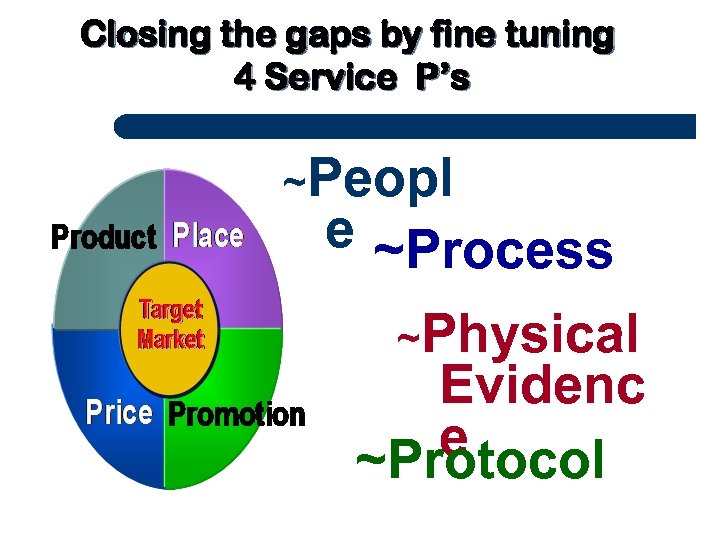 Closing the gaps by fine tuning 4 Service P’s ~Peopl e ~Process ~Physical Evidenc e ~Protocol
Closing the gaps by fine tuning 4 Service P’s ~Peopl e ~Process ~Physical Evidenc e ~Protocol
 People are your Product In many instancespeople performing the service are the product They are the service and/or organization in customer’s eyes. They are the brand.
People are your Product In many instancespeople performing the service are the product They are the service and/or organization in customer’s eyes. They are the brand.
 Recruit, Hire, Train, Monitor, Motivate, Reward Why customer satisfaction starts with HR Delivering excellent service: Lessons from the best firms
Recruit, Hire, Train, Monitor, Motivate, Reward Why customer satisfaction starts with HR Delivering excellent service: Lessons from the best firms
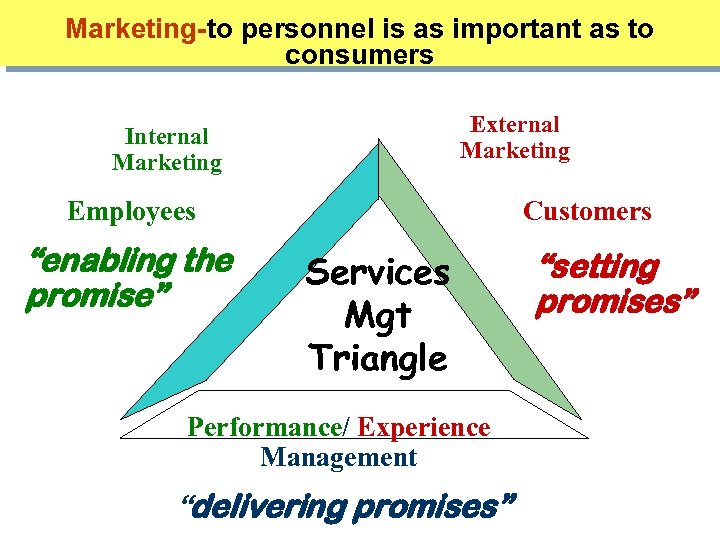 Marketing-to personnel is as important as to consumers External Marketing Internal Marketing Employees “enabling the promise” Customers Services Mgt Triangle Performance/ Experience Management “delivering promises” “setting promises”
Marketing-to personnel is as important as to consumers External Marketing Internal Marketing Employees “enabling the promise” Customers Services Mgt Triangle Performance/ Experience Management “delivering promises” “setting promises”
 Process Trade-off between Standardization & Personalization Same as w/ Products Limiting the variability in your service by standardizing the process of delivery & level of consumer involvement will lower expenses but comes w/ a cost: “Although standardization may provide for manufacturing efficiency, this efficiency comes at expense of marketing effectiveness. . . the consumer orientation screams heterogeneity” Vargo & Lusch: The Four Service
Process Trade-off between Standardization & Personalization Same as w/ Products Limiting the variability in your service by standardizing the process of delivery & level of consumer involvement will lower expenses but comes w/ a cost: “Although standardization may provide for manufacturing efficiency, this efficiency comes at expense of marketing effectiveness. . . the consumer orientation screams heterogeneity” Vargo & Lusch: The Four Service
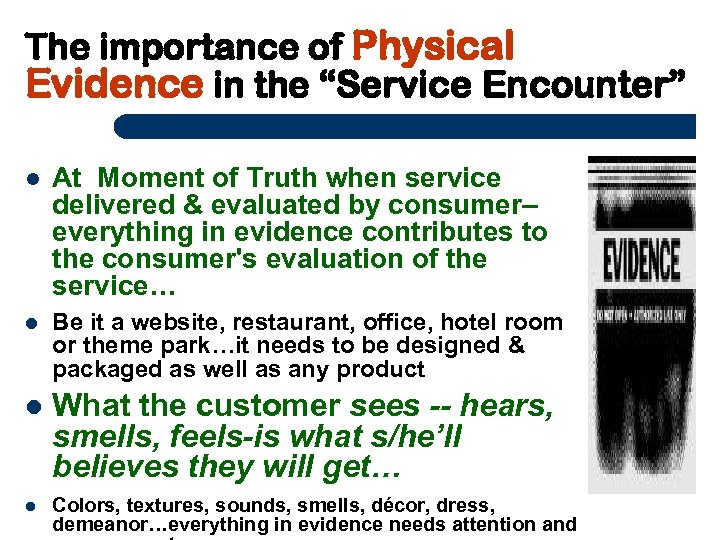 The importance of Physical Evidence in the “Service Encounter” At Moment of Truth when service delivered & evaluated by consumer– everything in evidence contributes to the consumer's evaluation of the service… Be it a website, restaurant, office, hotel room or theme park…it needs to be designed & packaged as well as any product What the customer sees -- hears, smells, feels-is what s/he’ll believes they will get… Colors, textures, sounds, smells, décor, dress, demeanor…everything in evidence needs attention and
The importance of Physical Evidence in the “Service Encounter” At Moment of Truth when service delivered & evaluated by consumer– everything in evidence contributes to the consumer's evaluation of the service… Be it a website, restaurant, office, hotel room or theme park…it needs to be designed & packaged as well as any product What the customer sees -- hears, smells, feels-is what s/he’ll believes they will get… Colors, textures, sounds, smells, décor, dress, demeanor…everything in evidence needs attention and
 It’s the little things that count How you design your service encounter is critical in a highly competitive market where consumers hard pressed to discern a significant difference in service performance … Ø Herein the design of your service encounter will prove the most critical variable in your marketing mix Ø Again – a lesson proven equally
It’s the little things that count How you design your service encounter is critical in a highly competitive market where consumers hard pressed to discern a significant difference in service performance … Ø Herein the design of your service encounter will prove the most critical variable in your marketing mix Ø Again – a lesson proven equally
 Identifiable apparel: An image-making marketing tool By ~ 8 -to-1 ratio, US consumers prefer employees wear identifiable apparel
Identifiable apparel: An image-making marketing tool By ~ 8 -to-1 ratio, US consumers prefer employees wear identifiable apparel
 A good uniform makes all the difference
A good uniform makes all the difference
 Identifiable apparel: An image-making marketing tool 1. Improves your image: Customers equate a professional-looking worker w/ a well-run company 2. Increases employee commitment: Adding employee's name can boost morale & loyalty 3. Provides a popular employment "perk": . 4. Shows off your firm's experience and expertise: "certification" -job titles, slogans & performance emblems on shirts/ sleeves…
Identifiable apparel: An image-making marketing tool 1. Improves your image: Customers equate a professional-looking worker w/ a well-run company 2. Increases employee commitment: Adding employee's name can boost morale & loyalty 3. Provides a popular employment "perk": . 4. Shows off your firm's experience and expertise: "certification" -job titles, slogans & performance emblems on shirts/ sleeves…
 Instill Proper Protocol so as to avoid the air of indifference Most common aspect of service complaints is lack of respect for the customer.
Instill Proper Protocol so as to avoid the air of indifference Most common aspect of service complaints is lack of respect for the customer.
 Why services lose customers ~3 ______% move away ~30 _______% lost due to competitive reasons and/or unhappy w/ the service ~67 ______% suspend patronage because of an attitude of indifference from owner, manager or an employee
Why services lose customers ~3 ______% move away ~30 _______% lost due to competitive reasons and/or unhappy w/ the service ~67 ______% suspend patronage because of an attitude of indifference from owner, manager or an employee
 What Customers Desire: 2500 shoppers said courtesy, knowledge & friendliness are most important components of customer service.
What Customers Desire: 2500 shoppers said courtesy, knowledge & friendliness are most important components of customer service.
 The Multiplier Effect When a customer has a minor service problem: • In transactions >$100 - s/he will tell 9 to 10 people. • In transactions over $100, s/he will tell 16 people. TARP statistics.
The Multiplier Effect When a customer has a minor service problem: • In transactions >$100 - s/he will tell 9 to 10 people. • In transactions over $100, s/he will tell 16 people. TARP statistics.
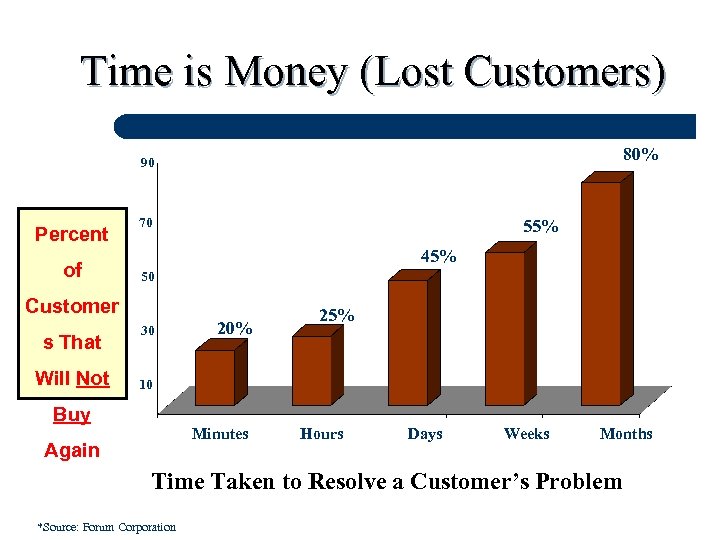 Time is Money (Lost Customers) 80% 90 Percent of 70 55% 45% 50 Customer s That Will Not 30 20% 25% 10 Buy Minutes Again Hours Days Weeks Months Time Taken to Resolve a Customer’s Problem *Source: Forum Corporation
Time is Money (Lost Customers) 80% 90 Percent of 70 55% 45% 50 Customer s That Will Not 30 20% 25% 10 Buy Minutes Again Hours Days Weeks Months Time Taken to Resolve a Customer’s Problem *Source: Forum Corporation
 Where and Who Complains Most complaints made to service provider (employee) at time & place of service Less than 5% of complaints about services ever reach corporate headquarters. High-income households, younger people, and service-knowledgeable customers are more likely to complain.
Where and Who Complains Most complaints made to service provider (employee) at time & place of service Less than 5% of complaints about services ever reach corporate headquarters. High-income households, younger people, and service-knowledgeable customers are more likely to complain.

 Actively Encourage Complaints Average company does not hear from 95% of its unhappy customers. Many complaints go unregistered because customers do not think it will help and/or do not know best way to register complaint Encouraging complaints is a good way to “break the
Actively Encourage Complaints Average company does not hear from 95% of its unhappy customers. Many complaints go unregistered because customers do not think it will help and/or do not know best way to register complaint Encouraging complaints is a good way to “break the
 Attitude is Crucial Customers value acknowledged w/ every transaction… Customers lose confidence when: – Complaints not readily or personally addressed
Attitude is Crucial Customers value acknowledged w/ every transaction… Customers lose confidence when: – Complaints not readily or personally addressed
 E-pologies? Email response should include options/names & telephone numbers for further assistance. . Tarp Research -
E-pologies? Email response should include options/names & telephone numbers for further assistance. . Tarp Research -
 Service Guarantees Relatively new w/ respect to services. Service guarantees provide both consumer & business benefits:
Service Guarantees Relatively new w/ respect to services. Service guarantees provide both consumer & business benefits:
 Service Guarantee: Customer Benefits – Customers perceive better value. – Lower perceived risk. – Higher perceived reliability – Reinforces customer loyalty
Service Guarantee: Customer Benefits – Customers perceive better value. – Lower perceived risk. – Higher perceived reliability – Reinforces customer loyalty
 Service Guarantee: Organizational Benefits é Forces firm to focus on customer. States a clear performance goal. é Provides measures for tracking poor service. é Forces examination of service delivery system. é Source of pride. é
Service Guarantee: Organizational Benefits é Forces firm to focus on customer. States a clear performance goal. é Provides measures for tracking poor service. é Forces examination of service delivery system. é Source of pride. é
 Critical Questions 1. What is the “debate” all about regarding how services should be defined / envisioned? o How does the definition of a service affect your marketing strategy? 2. What are the key P’s to meeting service management challenges? 3. What are some of the factors & considerations affecting the near future of “services” marketing?
Critical Questions 1. What is the “debate” all about regarding how services should be defined / envisioned? o How does the definition of a service affect your marketing strategy? 2. What are the key P’s to meeting service management challenges? 3. What are some of the factors & considerations affecting the near future of “services” marketing?

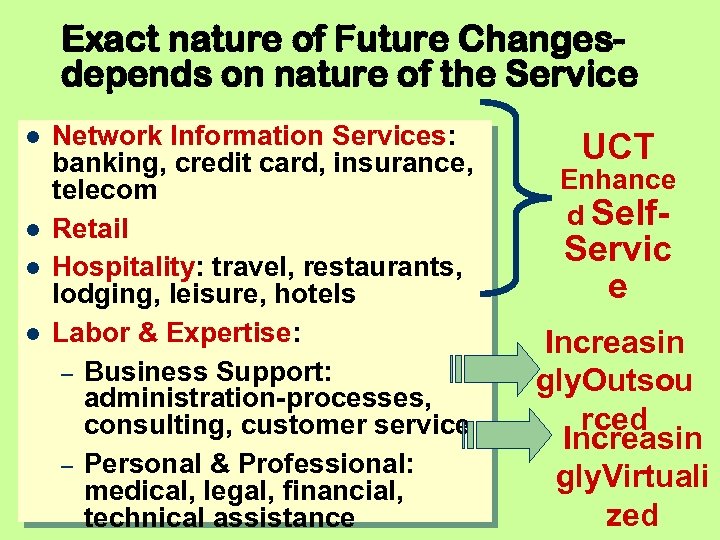 Exact nature of Future Changesdepends on nature of the Service Network Information Services: banking, credit card, insurance, telecom Retail Hospitality: travel, restaurants, lodging, leisure, hotels Labor & Expertise: – Business Support: administration-processes, consulting, customer service – Personal & Professional: medical, legal, financial, technical assistance UCT Enhance d Self- Servic e Increasin gly. Outsou rced Increasin gly. Virtuali zed
Exact nature of Future Changesdepends on nature of the Service Network Information Services: banking, credit card, insurance, telecom Retail Hospitality: travel, restaurants, lodging, leisure, hotels Labor & Expertise: – Business Support: administration-processes, consulting, customer service – Personal & Professional: medical, legal, financial, technical assistance UCT Enhance d Self- Servic e Increasin gly. Outsou rced Increasin gly. Virtuali zed
 Ubiquitious Com. Punication Technologies 3 G videophones w/ broadband – 2 meg per second – always online for self-service Mobile Kiosks AI Enhanced PDA devices w/ speech recognition & avatars RFID – everywhere & in everything
Ubiquitious Com. Punication Technologies 3 G videophones w/ broadband – 2 meg per second – always online for self-service Mobile Kiosks AI Enhanced PDA devices w/ speech recognition & avatars RFID – everywhere & in everything
 RFID- everywhere & in everything Smart. Code making 0. 25 mm chips target cost 5 -10 cents. . w/ 15 -20 feet range Manufacturing capacity
RFID- everywhere & in everything Smart. Code making 0. 25 mm chips target cost 5 -10 cents. . w/ 15 -20 feet range Manufacturing capacity
 UCT in Everything you wear washable garments w/ miniaturized in-ear speakers /solar cells to provide energy. technology woven into fabric, components allowing many functions to be almost `built in' to our bodies,
UCT in Everything you wear washable garments w/ miniaturized in-ear speakers /solar cells to provide energy. technology woven into fabric, components allowing many functions to be almost `built in' to our bodies,

 UCT Enhanced Jewelry embed functional technology into jewelry & body accessories -- rings, necklaces, earrings, glasses and watches. - for body adornment and for more intimate and discreet communication, information
UCT Enhanced Jewelry embed functional technology into jewelry & body accessories -- rings, necklaces, earrings, glasses and watches. - for body adornment and for more intimate and discreet communication, information
 Invisible, intelligent wireless tickets Can be read in your pocket at 25 metres Ultra-wide band frequency “One-ticket fits all”
Invisible, intelligent wireless tickets Can be read in your pocket at 25 metres Ultra-wide band frequency “One-ticket fits all”
 RFID Shopping App’s Future grocery shoppingintegrated – info system
RFID Shopping App’s Future grocery shoppingintegrated – info system
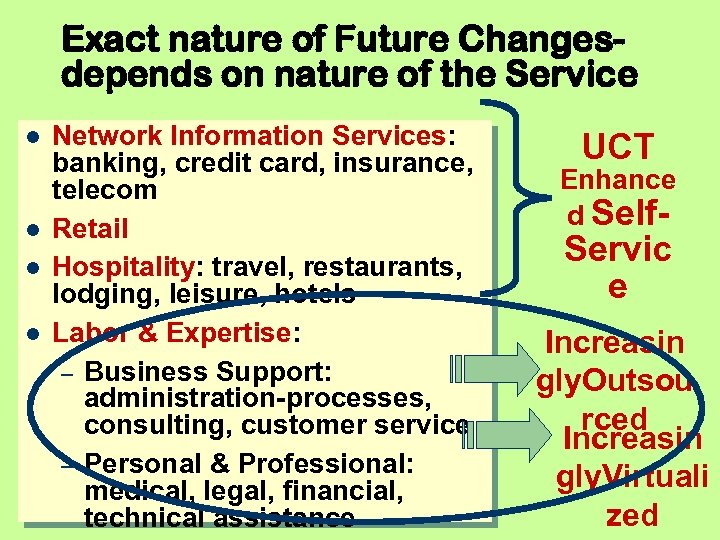 Exact nature of Future Changesdepends on nature of the Service Network Information Services: banking, credit card, insurance, telecom Retail Hospitality: travel, restaurants, lodging, leisure, hotels Labor & Expertise: – Business Support: administration-processes, consulting, customer service – Personal & Professional: medical, legal, financial, technical assistance UCT Enhance d Self- Servic e Increasin gly. Outsou rced Increasin gly. Virtuali zed
Exact nature of Future Changesdepends on nature of the Service Network Information Services: banking, credit card, insurance, telecom Retail Hospitality: travel, restaurants, lodging, leisure, hotels Labor & Expertise: – Business Support: administration-processes, consulting, customer service – Personal & Professional: medical, legal, financial, technical assistance UCT Enhance d Self- Servic e Increasin gly. Outsou rced Increasin gly. Virtuali zed
 Predicting a diverse future: Directions and issues in the marketing of services European Journal of Marketing ; Bradford; 2002; Angus Laing “Driven by technological developments, deregulation, and globalization - the service sector in post-industrial economies is facing unprecedented change”
Predicting a diverse future: Directions and issues in the marketing of services European Journal of Marketing ; Bradford; 2002; Angus Laing “Driven by technological developments, deregulation, and globalization - the service sector in post-industrial economies is facing unprecedented change”
 Increasing importance of technological mediation… Virtual Experiences Redefining concept of“Service Encounter” The Moment of Truth when a service is delivered & evaluated by consumer
Increasing importance of technological mediation… Virtual Experiences Redefining concept of“Service Encounter” The Moment of Truth when a service is delivered & evaluated by consumer
 Commodification… standardized "off-the-shelf" service packages Pre-Packaged, fill in the blank, instantservice forms & queries Some Computer generated…Expertsystem managed… Responses
Commodification… standardized "off-the-shelf" service packages Pre-Packaged, fill in the blank, instantservice forms & queries Some Computer generated…Expertsystem managed… Responses
 Professional Services To date-- characterized by high levels of limited/regulated interpersonal interaction NOW- 24/7 “access to specialist technical information, formerly the preserve of professionals, http: //www. psychadvisor. co m/counsel/index. cfm Free Advice on Any …fundamentally changed the Topic informational asymmetries Online From America's which have conventionally Elders characterized the delivery of Personal Reply to Each Request professional services” www. Elder. Wisdom. Circle. org
Professional Services To date-- characterized by high levels of limited/regulated interpersonal interaction NOW- 24/7 “access to specialist technical information, formerly the preserve of professionals, http: //www. psychadvisor. co m/counsel/index. cfm Free Advice on Any …fundamentally changed the Topic informational asymmetries Online From America's which have conventionally Elders characterized the delivery of Personal Reply to Each Request professional services” www. Elder. Wisdom. Circle. org
 “Technologically driven productivity growth is-most important factor in shaping employment in U. S. & every country in the world. Productivity growth substitutes technology &/or more efficient techniques for physical & mental labor Inventors & investors always figure out ways to replace people with machines” Automation- 1 , 2 , 3
“Technologically driven productivity growth is-most important factor in shaping employment in U. S. & every country in the world. Productivity growth substitutes technology &/or more efficient techniques for physical & mental labor Inventors & investors always figure out ways to replace people with machines” Automation- 1 , 2 , 3
 Restaurants without waiters
Restaurants without waiters
 Ultimately most all your service needs will be handled by & thru your AI enhanced PDA…
Ultimately most all your service needs will be handled by & thru your AI enhanced PDA…
 “With the ruthlessness of Skynet in "The Terminator, " computerization in the tertiary sector is now committing mass Dilberticide, replacing receptionists with automated phone systems and travel agents with services like Priceline. Why Dilbert is doomed The jobs of tomorrow are not what you'd expect Recession creating a lost generation
“With the ruthlessness of Skynet in "The Terminator, " computerization in the tertiary sector is now committing mass Dilberticide, replacing receptionists with automated phone systems and travel agents with services like Priceline. Why Dilbert is doomed The jobs of tomorrow are not what you'd expect Recession creating a lost generation
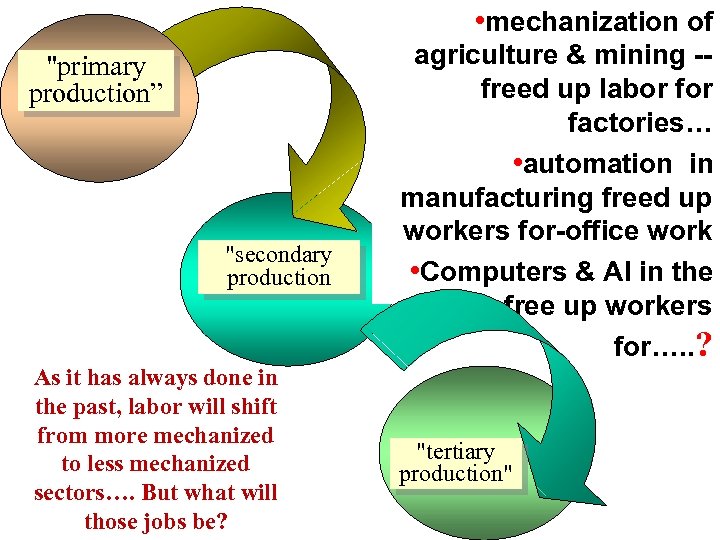 • mechanization of "primary production” "secondary production As it has always done in the past, labor will shift from more mechanized to less mechanized sectors…. But what will those jobs be? agriculture & mining -freed up labor factories… • automation in manufacturing freed up workers for-office work • Computers & AI in the office--free up workers for…. . ? "tertiary production"
• mechanization of "primary production” "secondary production As it has always done in the past, labor will shift from more mechanized to less mechanized sectors…. But what will those jobs be? agriculture & mining -freed up labor factories… • automation in manufacturing freed up workers for-office work • Computers & AI in the office--free up workers for…. . ? "tertiary production"
 The most numerous & stable jobs of tomorrow will be those that cannot be offshored • cannot be automated • require a high degree of creativity • & rely on the human touch in face-to-face interactions • these are called "proximity services" & include fastest-growing occupations, healthcare & education. Since the recession began, healthcare has added 559, 000 jobs. Even more remarkable, the average monthly gain of 22, 000 jobs during 2009 has been only slightly lower than the average increase of 30, 000 jobs a month in 2008. Why Dilbert is doomed The jobs of tomorrow are not what you'd expect
The most numerous & stable jobs of tomorrow will be those that cannot be offshored • cannot be automated • require a high degree of creativity • & rely on the human touch in face-to-face interactions • these are called "proximity services" & include fastest-growing occupations, healthcare & education. Since the recession began, healthcare has added 559, 000 jobs. Even more remarkable, the average monthly gain of 22, 000 jobs during 2009 has been only slightly lower than the average increase of 30, 000 jobs a month in 2008. Why Dilbert is doomed The jobs of tomorrow are not what you'd expect

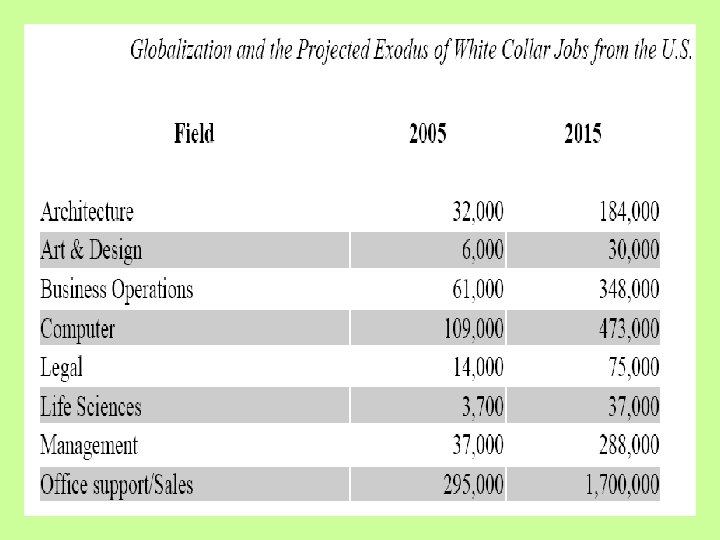
 Outsourcing of IT Services $10. 8 billion The value of IT outsourcing contracts signed in the first quarter of 2005. Source: TPI Index 3% Percentage of last year's total layoffs due to offshoring. Source: U. S. Department of Labor 400, 000 Number of service jobs sent overseas since 2000. Source: The Goldman Sachs Group Inc. 104, 000 Number of IT jobs lost due to offshore outsourcing between 2000 and 2003, equaling 2. 8% of U. S. IT jobs. Source: Information Technology Association of America 3. 5 million Number of U. S. white-collar jobs moving offshore by 2015, averaging 200, 000
Outsourcing of IT Services $10. 8 billion The value of IT outsourcing contracts signed in the first quarter of 2005. Source: TPI Index 3% Percentage of last year's total layoffs due to offshoring. Source: U. S. Department of Labor 400, 000 Number of service jobs sent overseas since 2000. Source: The Goldman Sachs Group Inc. 104, 000 Number of IT jobs lost due to offshore outsourcing between 2000 and 2003, equaling 2. 8% of U. S. IT jobs. Source: Information Technology Association of America 3. 5 million Number of U. S. white-collar jobs moving offshore by 2015, averaging 200, 000
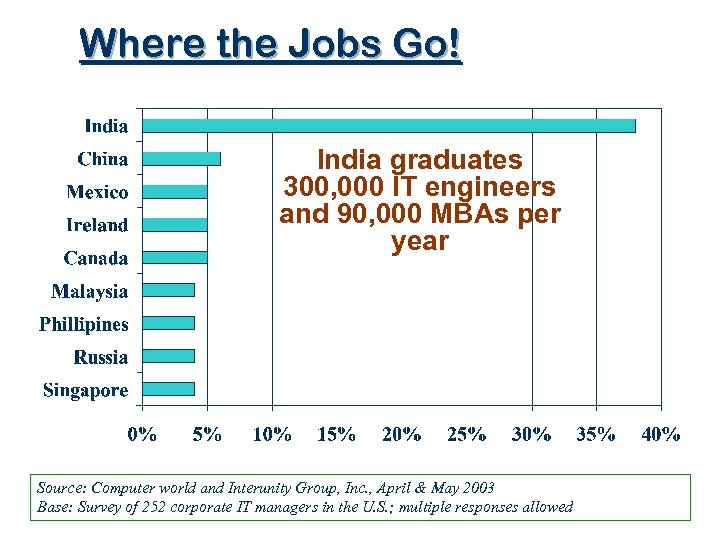 Where the Jobs Go! India graduates 300, 000 IT engineers and 90, 000 MBAs per year Source: Computer world and Interunity Group, Inc. , April & May 2003 Base: Survey of 252 corporate IT managers in the U. S. ; multiple responses allowed
Where the Jobs Go! India graduates 300, 000 IT engineers and 90, 000 MBAs per year Source: Computer world and Interunity Group, Inc. , April & May 2003 Base: Survey of 252 corporate IT managers in the U. S. ; multiple responses allowed
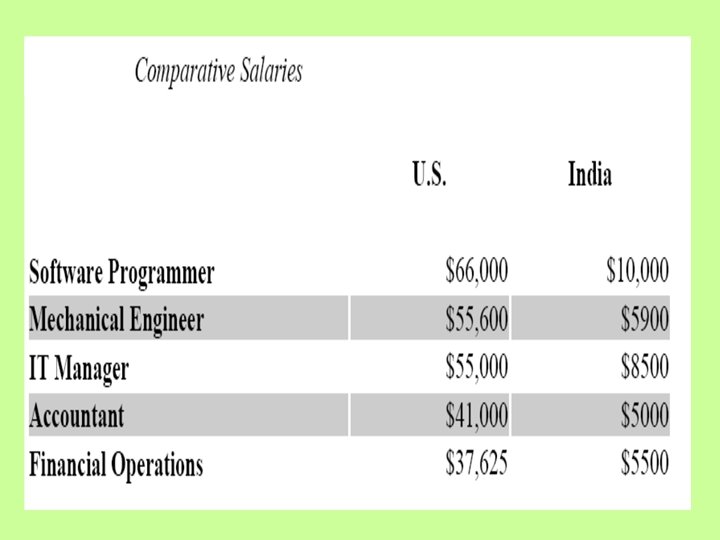
 The Other Side of Outsourcing
The Other Side of Outsourcing



