ea8af9b70d60d19a3cd60cc8c9b4739b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Marketing Essentials n Chapter 25 Price Planning Section 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Chapter 25 n Price Planning 1
Marketing Essentials n Chapter 25 Price Planning Section 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Chapter 25 n Price Planning 1
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning What You'll Learn = The four market factors that affect price planning = What demand elasticity is in relation to supply and demand theory = The government regulations that affect price planning Chapter 25 n Price Planning 2
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning What You'll Learn = The four market factors that affect price planning = What demand elasticity is in relation to supply and demand theory = The government regulations that affect price planning Chapter 25 n Price Planning 2
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Why It's Important Pricing a product may seem like an easy task, but there are many factors affecting that decision that must be taken into consideration. Skipping even one aspect of this process could cost a business millions of dollars in lost sales, or even in fines or lawsuits if the laws governing pricing are not followed. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 3
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Why It's Important Pricing a product may seem like an easy task, but there are many factors affecting that decision that must be taken into consideration. Skipping even one aspect of this process could cost a business millions of dollars in lost sales, or even in fines or lawsuits if the laws governing pricing are not followed. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 3
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Key Terms = = = = break-even point elastic demand law of diminishing marginal utility inelastic demand price fixing price discrimination loss leader unit pricing Chapter 25 n Price Planning 4
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Key Terms = = = = break-even point elastic demand law of diminishing marginal utility inelastic demand price fixing price discrimination loss leader unit pricing Chapter 25 n Price Planning 4
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Market Factors Affecting Prices Pricing decisions are not necessarily easy. Most price planning begins with an analysis of costs and expenses, many of which are related to current market conditions. An organization's goals also must be considered. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 5
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Market Factors Affecting Prices Pricing decisions are not necessarily easy. Most price planning begins with an analysis of costs and expenses, many of which are related to current market conditions. An organization's goals also must be considered. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 5
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Costs and Expenses Businesses constantly monitor, analyze, and project prices and sales in the light of costs and expenses because sales, costs, and expenses together determine a firm's profit. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 6
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Costs and Expenses Businesses constantly monitor, analyze, and project prices and sales in the light of costs and expenses because sales, costs, and expenses together determine a firm's profit. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 6
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Responses to Declining Profit Margins When profits decline, some businesses increase price. Others feel that price is so important in the marketing strategy of a product that instead of making price changes, they will change the product to maintain profit margin. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 7
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Responses to Declining Profit Margins When profits decline, some businesses increase price. Others feel that price is so important in the marketing strategy of a product that instead of making price changes, they will change the product to maintain profit margin. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 7
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Responses to Lower Costs/Expenses Prices may occasionally be lowered because of decreased costs and expenses. Improved technology and less expensive materials may help create better-quality products at lower costs. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 8
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Responses to Lower Costs/Expenses Prices may occasionally be lowered because of decreased costs and expenses. Improved technology and less expensive materials may help create better-quality products at lower costs. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 8
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Break-Even Point The break-even point is the point at which sales revenue equals the costs and expenses of making and distributing a product. This is especially important to consider when marketing a new product or establishing a new price. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 9
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Break-Even Point The break-even point is the point at which sales revenue equals the costs and expenses of making and distributing a product. This is especially important to consider when marketing a new product or establishing a new price. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 9
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Supply and Demand The degree to which demand for a product is affected by its price is called demand elasticity. Demand elasticity is affected by: = brand loyalty = price relative to income = availability of substitutes = luxury vs. necessity = urgency of purchase Slide 1 of 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 10
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Supply and Demand The degree to which demand for a product is affected by its price is called demand elasticity. Demand elasticity is affected by: = brand loyalty = price relative to income = availability of substitutes = luxury vs. necessity = urgency of purchase Slide 1 of 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 10
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Supply and Demand The law of diminishing marginal utility states that consumers will buy only so much of a given product, even though the price is low. Elastic Demand A change in price creates a change in demand. Inelastic Demand A change in price has very little effect on demand for a product. Slide 2 of 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 11
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Supply and Demand The law of diminishing marginal utility states that consumers will buy only so much of a given product, even though the price is low. Elastic Demand A change in price creates a change in demand. Inelastic Demand A change in price has very little effect on demand for a product. Slide 2 of 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 11
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Consumer Perceptions Price planning is affected by the following consumer perceptions about price: = Some consumers equate quality with price. = Some consumers are willing to pay more for status, prestige, and exclusiveness, as well as extra services. Subjective price is the price consumers see as the value they are getting for the price. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 12
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Consumer Perceptions Price planning is affected by the following consumer perceptions about price: = Some consumers equate quality with price. = Some consumers are willing to pay more for status, prestige, and exclusiveness, as well as extra services. Subjective price is the price consumers see as the value they are getting for the price. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 12
 SECTION 25. 2 Competition Factors Involved in Price Planning Price must be evaluated in relation to the target market and is one of the four Ps of the marketing mix. Companies can compete with: = price competition—offering lower prices = nonprice competition—attracting customers with prestige, service, or quality Slide 1 of 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 13
SECTION 25. 2 Competition Factors Involved in Price Planning Price must be evaluated in relation to the target market and is one of the four Ps of the marketing mix. Companies can compete with: = price competition—offering lower prices = nonprice competition—attracting customers with prestige, service, or quality Slide 1 of 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 13
 SECTION 25. 2 Competition Factors Involved in Price Planning Marketers change prices to reflect: = consumer demand = cost = competition Similar products sometimes differ only in price, so when one company changes its prices, others usually react. Sometimes price wars produce financial losses that can ruin businesses. Slide 2 of 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 14
SECTION 25. 2 Competition Factors Involved in Price Planning Marketers change prices to reflect: = consumer demand = cost = competition Similar products sometimes differ only in price, so when one company changes its prices, others usually react. Sometimes price wars produce financial losses that can ruin businesses. Slide 2 of 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 14
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Government Regulations Affecting Price Federal and state governments have enacted laws regarding: = price fixing = price discrimination = resale price maintenance = minimum pricing = unit pricing = price advertising Slide 1 of 4 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 15
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Government Regulations Affecting Price Federal and state governments have enacted laws regarding: = price fixing = price discrimination = resale price maintenance = minimum pricing = unit pricing = price advertising Slide 1 of 4 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 15
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Government Regulations Affecting Price fixing occurs when competitors agree on certain price ranges within which they set their own prices. Price discrimination occurs when a firm charges different prices to similar customers in similar situations. Slide 2 of 4 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 16
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Government Regulations Affecting Price fixing occurs when competitors agree on certain price ranges within which they set their own prices. Price discrimination occurs when a firm charges different prices to similar customers in similar situations. Slide 2 of 4 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 16
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Government Regulations Affecting Price Resale price maintenance occurs when a manufacturer forces retailers to sell an item at a minimum price. Minimum price laws prevent retailers from selling goods below cost plus a percentage for expenses and profit. Some states do not have minimum price laws and allow loss leaders, items sold at cost to attract customers. Slide 3 of 4 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 17
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Government Regulations Affecting Price Resale price maintenance occurs when a manufacturer forces retailers to sell an item at a minimum price. Minimum price laws prevent retailers from selling goods below cost plus a percentage for expenses and profit. Some states do not have minimum price laws and allow loss leaders, items sold at cost to attract customers. Slide 3 of 4 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 17
 SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Government Regulations Affecting Price Unit pricing allows consumers to compare prices in relation to a standard unit or measure, such as an ounce or a pound. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) price advertising guidelines forbid fraudulent and misleading pricing advertisements. Slide 4 of 4 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 18
SECTION 25. 2 Factors Involved in Price Planning Government Regulations Affecting Price Unit pricing allows consumers to compare prices in relation to a standard unit or measure, such as an ounce or a pound. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) price advertising guidelines forbid fraudulent and misleading pricing advertisements. Slide 4 of 4 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 18
 25. 2 ASSESSMENT Reviewing Key Terms and Concepts 1. Name four market factors that affect price planning. 2. In response to increased costs and expenses, what three pricing options might a business consider to maintain their profit margins? 3. What is demand elasticity, and how does it apply to theories of supply and demand? 4. What is the difference between price fixing and price discrimination? What laws govern each? Chapter 25 n Price Planning 19
25. 2 ASSESSMENT Reviewing Key Terms and Concepts 1. Name four market factors that affect price planning. 2. In response to increased costs and expenses, what three pricing options might a business consider to maintain their profit margins? 3. What is demand elasticity, and how does it apply to theories of supply and demand? 4. What is the difference between price fixing and price discrimination? What laws govern each? Chapter 25 n Price Planning 19
 25. 2 ASSESSMENT Thinking Critically Many people with diabetes depend on insulin to stay alive. If the price of insulin went up $10, would the demand for insulin go down as is suggested by theory of supply and demand? Explain your answer in terms of demand elasticity. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 20
25. 2 ASSESSMENT Thinking Critically Many people with diabetes depend on insulin to stay alive. If the price of insulin went up $10, would the demand for insulin go down as is suggested by theory of supply and demand? Explain your answer in terms of demand elasticity. Chapter 25 n Price Planning 20
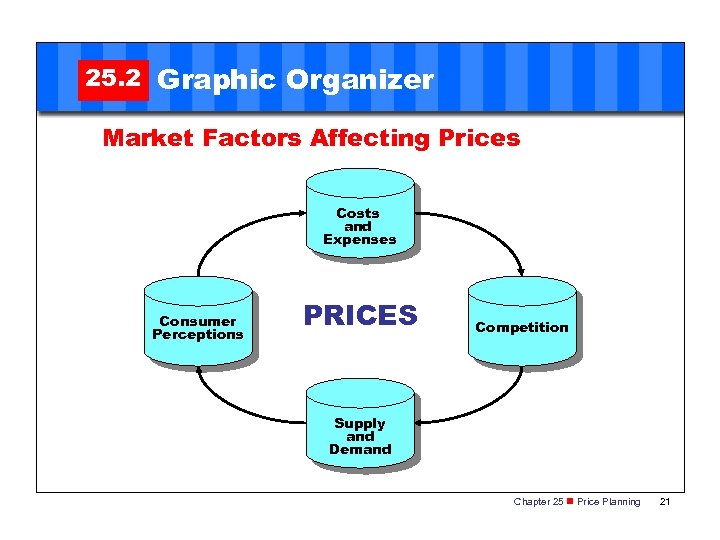 25. 2 Graphic Organizer Market Factors Affecting Prices Costs and Expenses Consumer Perceptions PRICES Competition Supply and Demand Chapter 25 n Price Planning 21
25. 2 Graphic Organizer Market Factors Affecting Prices Costs and Expenses Consumer Perceptions PRICES Competition Supply and Demand Chapter 25 n Price Planning 21
 Marketing Essentials End of Section 25. 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 22
Marketing Essentials End of Section 25. 2 Chapter 25 n Price Planning 22


