MARKETING course Instructor Didar Ilyassov Topic 1 Introduction





























14194-topic_1_marketing_.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 MARKETING course Instructor Didar Ilyassov Topic 1 Introduction to Marketing 1-1
MARKETING course Instructor Didar Ilyassov Topic 1 Introduction to Marketing 1-1
 Content The scope of marketing Marketing concepts and tools Marketing mix How marketing and business are changing 1-2
Content The scope of marketing Marketing concepts and tools Marketing mix How marketing and business are changing 1-2
 Say hello to Marketing! Marketing and Management Historical background of Marketing in US 1.Production concept (1900-1930) 2. Product concept (1930-1950) 3. Selling Concept (1950-1970) 4. Marketing Concept (1970-1990) 5. Societal Marketing Concept (from 1990) 1-3
Say hello to Marketing! Marketing and Management Historical background of Marketing in US 1.Production concept (1900-1930) 2. Product concept (1930-1950) 3. Selling Concept (1950-1970) 4. Marketing Concept (1970-1990) 5. Societal Marketing Concept (from 1990) 1-3
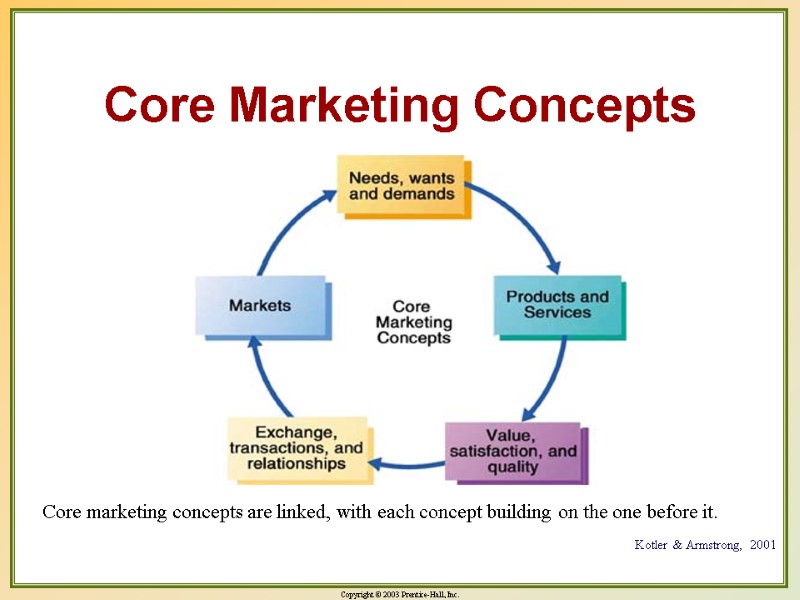
 Core Marketing Concepts Core marketing concepts are linked, with each concept building on the one before it. Kotler & Armstrong, 2001
Core Marketing Concepts Core marketing concepts are linked, with each concept building on the one before it. Kotler & Armstrong, 2001
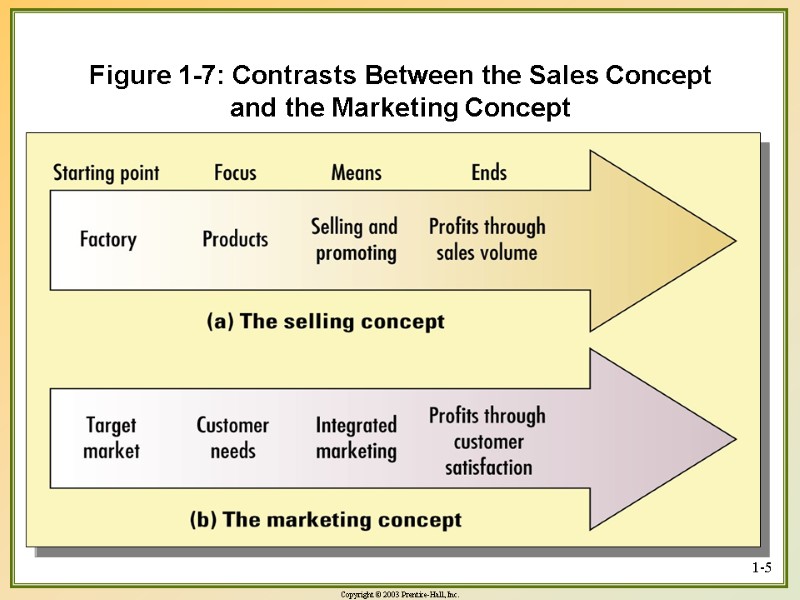
 1-5 Figure 1-7: Contrasts Between the Sales Concept and the Marketing Concept
1-5 Figure 1-7: Contrasts Between the Sales Concept and the Marketing Concept
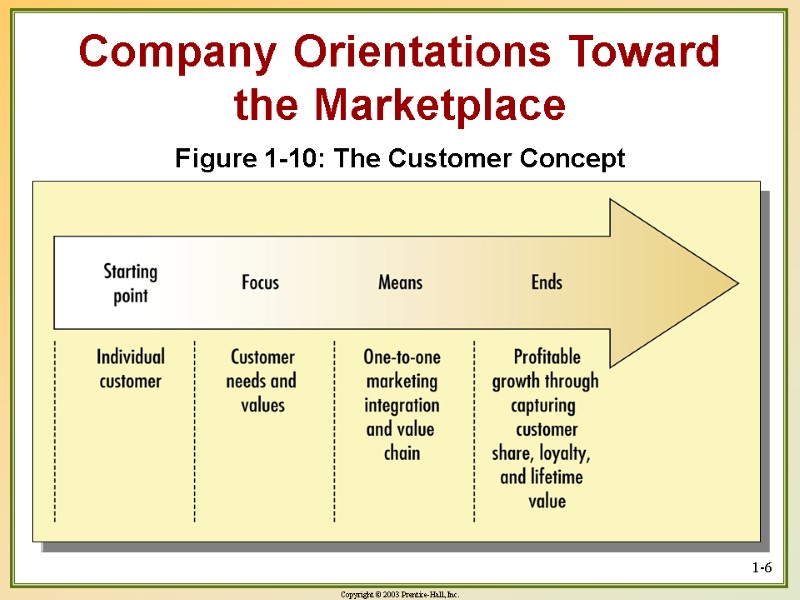
 1-6 Figure 1-10: The Customer Concept Company Orientations Toward the Marketplace
1-6 Figure 1-10: The Customer Concept Company Orientations Toward the Marketplace
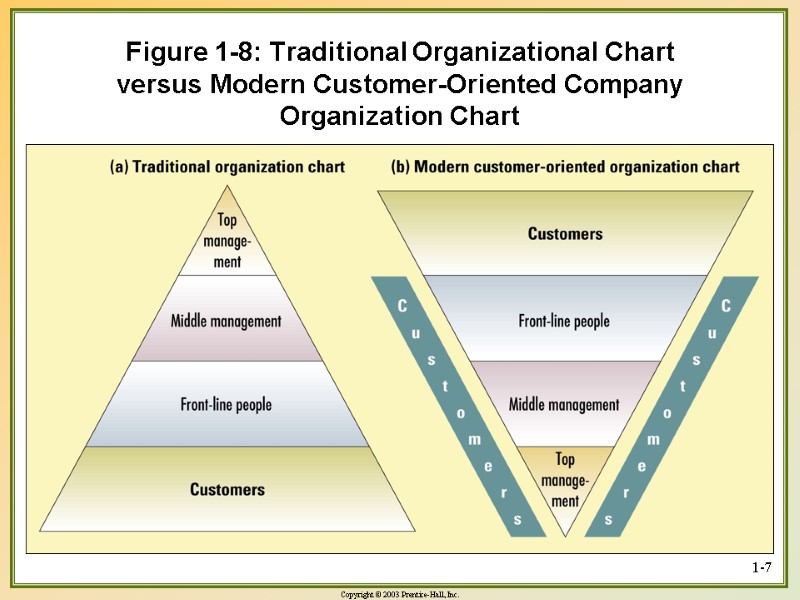
 1-7 Figure 1-8: Traditional Organizational Chart versus Modern Customer-Oriented Company Organization Chart
1-7 Figure 1-8: Traditional Organizational Chart versus Modern Customer-Oriented Company Organization Chart
 1-8 Marketing Concepts and Tools Marketers and Prospects Needs, Wants, and Demands Product, Offering, and Brand Value and Satisfaction Customer value triad Value Value = Benefits / Costs = (Functional benefits + Emotional benefits) / (Monetary costs + Time costs + Energy costs + Psychic costs)
1-8 Marketing Concepts and Tools Marketers and Prospects Needs, Wants, and Demands Product, Offering, and Brand Value and Satisfaction Customer value triad Value Value = Benefits / Costs = (Functional benefits + Emotional benefits) / (Monetary costs + Time costs + Energy costs + Psychic costs)
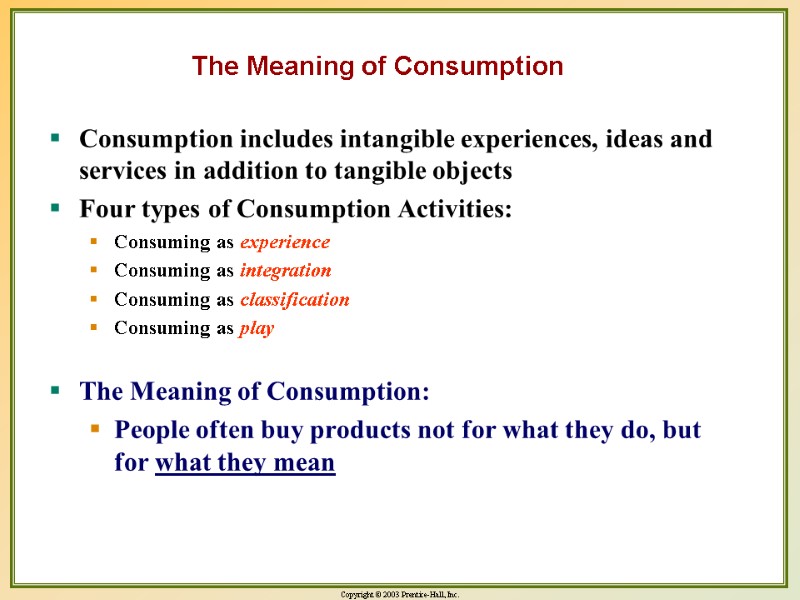
 The Meaning of Consumption Consumption includes intangible experiences, ideas and services in addition to tangible objects Four types of Consumption Activities: Consuming as experience Consuming as integration Consuming as classification Consuming as play The Meaning of Consumption: People often buy products not for what they do, but for what they mean
The Meaning of Consumption Consumption includes intangible experiences, ideas and services in addition to tangible objects Four types of Consumption Activities: Consuming as experience Consuming as integration Consuming as classification Consuming as play The Meaning of Consumption: People often buy products not for what they do, but for what they mean
 Choice Criteria: Value & Satisfaction Customer-Driven Quality
Choice Criteria: Value & Satisfaction Customer-Driven Quality
 1-11 The future is not ahead of us. It has already happened. Unfortunately, it is unequally distributed among companies, industries and nations. Kotler on Marketing
1-11 The future is not ahead of us. It has already happened. Unfortunately, it is unequally distributed among companies, industries and nations. Kotler on Marketing
 Value – Satisfaction – Profit So, Marketing is about creating customer value and satisfaction – leading to a profitable exchange Successful marketing is critical to the success of every organisation (Kotler, 2003) True in the not-for-profit sector? According to Kotler it is no longer enough to satisfy customers – they must be delighted (Kotler, 2003)
Value – Satisfaction – Profit So, Marketing is about creating customer value and satisfaction – leading to a profitable exchange Successful marketing is critical to the success of every organisation (Kotler, 2003) True in the not-for-profit sector? According to Kotler it is no longer enough to satisfy customers – they must be delighted (Kotler, 2003)
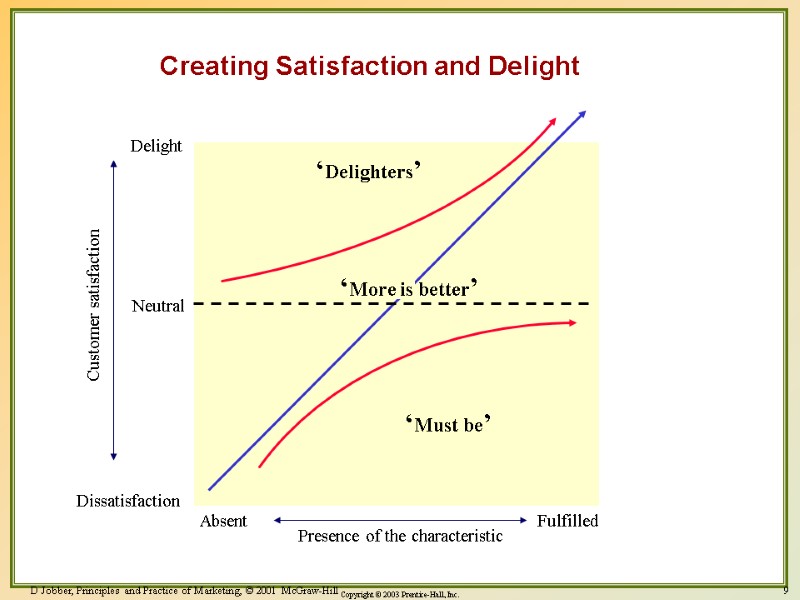
 9 D Jobber, Principles and Practice of Marketing, © 2001 McGraw-Hill Creating Satisfaction and Delight Delight Neutral Dissatisfaction Presence of the characteristic Customer satisfaction ‘Delighters’ ‘More is better’ ‘Must be’
9 D Jobber, Principles and Practice of Marketing, © 2001 McGraw-Hill Creating Satisfaction and Delight Delight Neutral Dissatisfaction Presence of the characteristic Customer satisfaction ‘Delighters’ ‘More is better’ ‘Must be’
 1-14 Marketing Task Ten rules of radical marketing The CEO must own the marketing function. Make sure the marketing department starts small and flat and stays small and flat. Get face to face with the people who matter most – the customers. Use market research cautiously. Hire only passionate missionaries.
1-14 Marketing Task Ten rules of radical marketing The CEO must own the marketing function. Make sure the marketing department starts small and flat and stays small and flat. Get face to face with the people who matter most – the customers. Use market research cautiously. Hire only passionate missionaries.
 1-15 Marketing Task Love and respect your customers. Create a community of consumers. Rethink the marketing mix. Celebrate common sense. Be true to the brand. Three stages of marketing practice Entrepreneurial Marketing Formulated Marketing Intrepreneurial Marketing
1-15 Marketing Task Love and respect your customers. Create a community of consumers. Rethink the marketing mix. Celebrate common sense. Be true to the brand. Three stages of marketing practice Entrepreneurial Marketing Formulated Marketing Intrepreneurial Marketing
 1-16 The Scope of Marketing Marketing: typically seen as the task of creating, promoting, and delivering goods and services to consumers and businesses. -as business philosophy is oriented on customer satisfaction
1-16 The Scope of Marketing Marketing: typically seen as the task of creating, promoting, and delivering goods and services to consumers and businesses. -as business philosophy is oriented on customer satisfaction
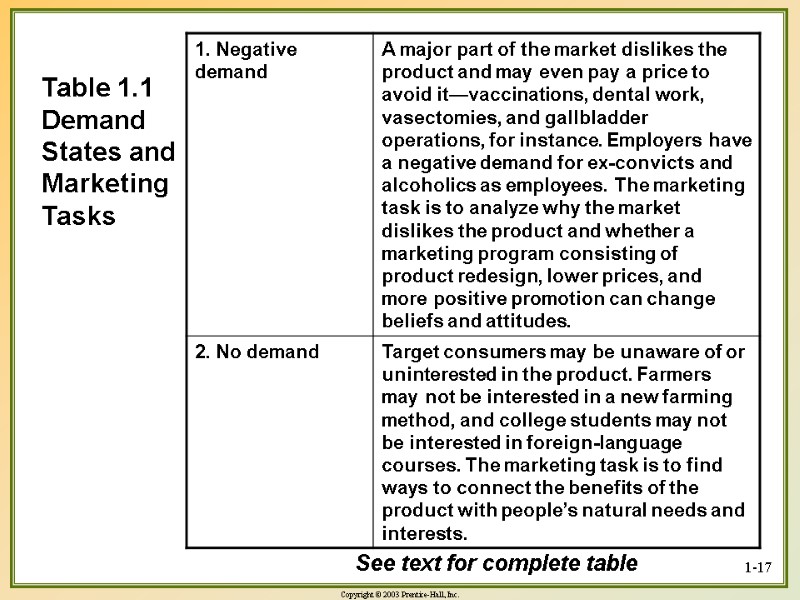
 1-17 Table 1.1 Demand States and Marketing Tasks See text for complete table
1-17 Table 1.1 Demand States and Marketing Tasks See text for complete table
 1-18 Can you name a category of products for which your negative feelings have softened? What precipitated this change? Discussion Question
1-18 Can you name a category of products for which your negative feelings have softened? What precipitated this change? Discussion Question
 1-19 The Scope of Marketing Places Properties Organizations Information Ideas Goods Services Experiences Events Persons
1-19 The Scope of Marketing Places Properties Organizations Information Ideas Goods Services Experiences Events Persons
 1-20 The Decisions Marketers Make Consumer Markets Business Markets Global Markets Nonprofit and Governmental Markets
1-20 The Decisions Marketers Make Consumer Markets Business Markets Global Markets Nonprofit and Governmental Markets
 1-21 Marketing Concepts and Tools Defining Marketing Marketing Marketing management Core Marketing Concepts Target Markets and Segmentation
1-21 Marketing Concepts and Tools Defining Marketing Marketing Marketing management Core Marketing Concepts Target Markets and Segmentation
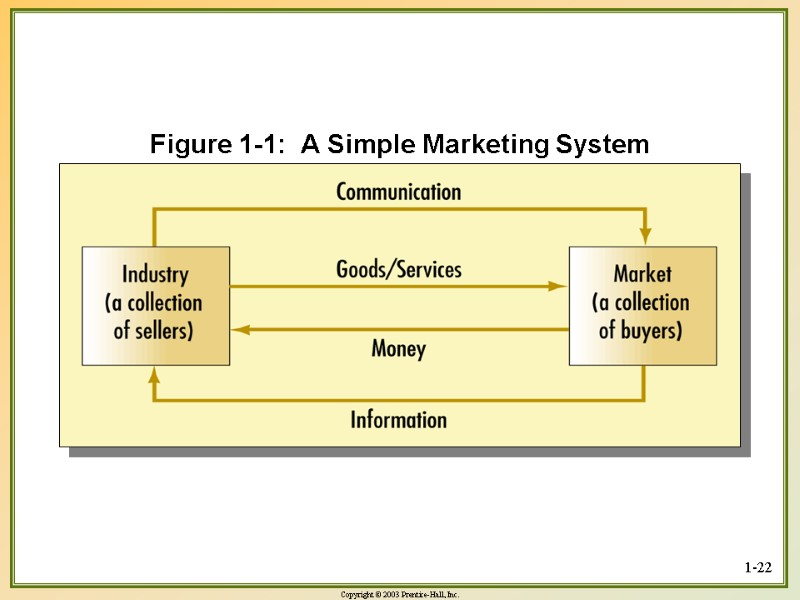
 1-22 Figure 1-1: A Simple Marketing System
1-22 Figure 1-1: A Simple Marketing System
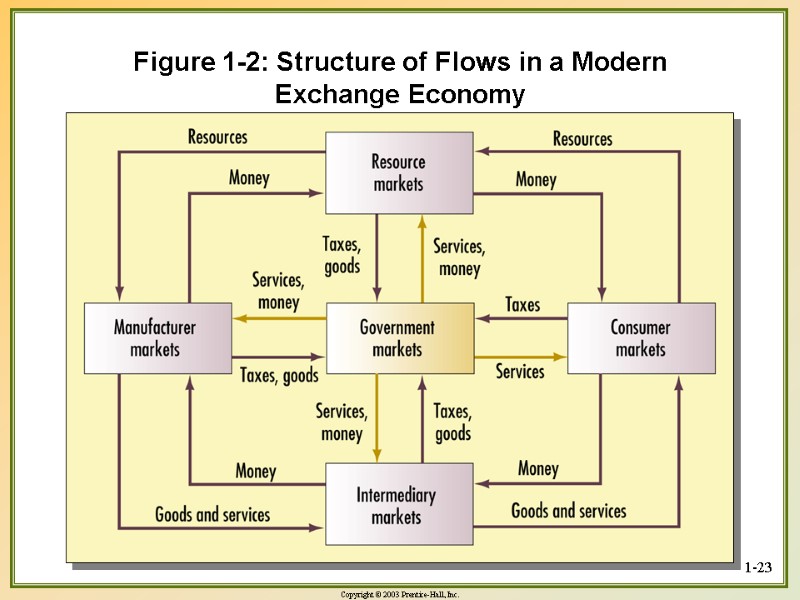
 1-23 Figure 1-2: Structure of Flows in a Modern Exchange Economy
1-23 Figure 1-2: Structure of Flows in a Modern Exchange Economy
 1-24 Marketing Concepts and Tools Relationships and Networks Relationship marketing Marketing network Marketing Channels Supply Chain Competition
1-24 Marketing Concepts and Tools Relationships and Networks Relationship marketing Marketing network Marketing Channels Supply Chain Competition
 1-25 Marketing Concepts and Tools Brand competition Industry competition Form competition Generic competition Marketing environment Task environment Broad environment Marketing Program Marketing program Marketing mix
1-25 Marketing Concepts and Tools Brand competition Industry competition Form competition Generic competition Marketing environment Task environment Broad environment Marketing Program Marketing program Marketing mix
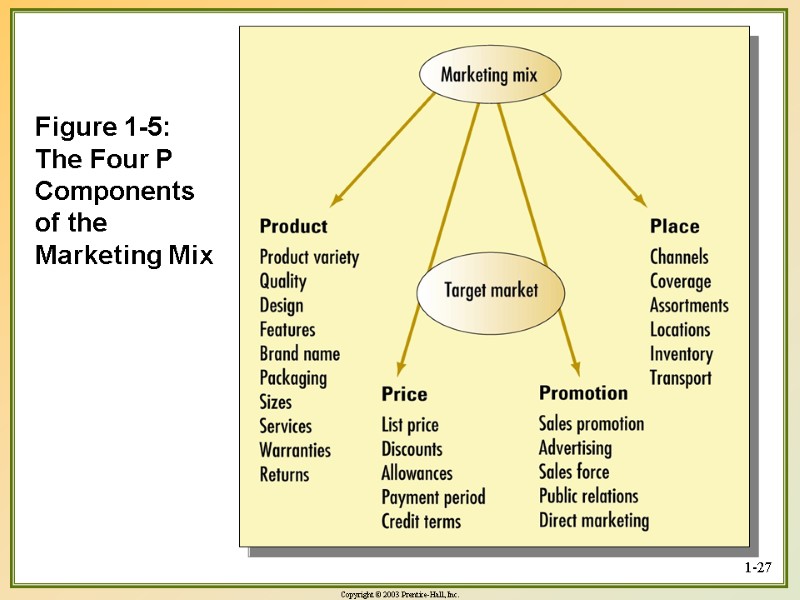
 Marketing Tools The ‘Marketing Mix’ consists of the key elements that need to be considered to bring products and services to the market that will offer value to consumers and satisfy their demands. The Marketing Mix is most commonly known as the 4Ps (concept first developed by Borden in 1950s whilst the ‘4Ps’ was first used by McCarthy in 1960)
Marketing Tools The ‘Marketing Mix’ consists of the key elements that need to be considered to bring products and services to the market that will offer value to consumers and satisfy their demands. The Marketing Mix is most commonly known as the 4Ps (concept first developed by Borden in 1950s whilst the ‘4Ps’ was first used by McCarthy in 1960)
 1-27 Figure 1-5: The Four P Components of the Marketing Mix
1-27 Figure 1-5: The Four P Components of the Marketing Mix
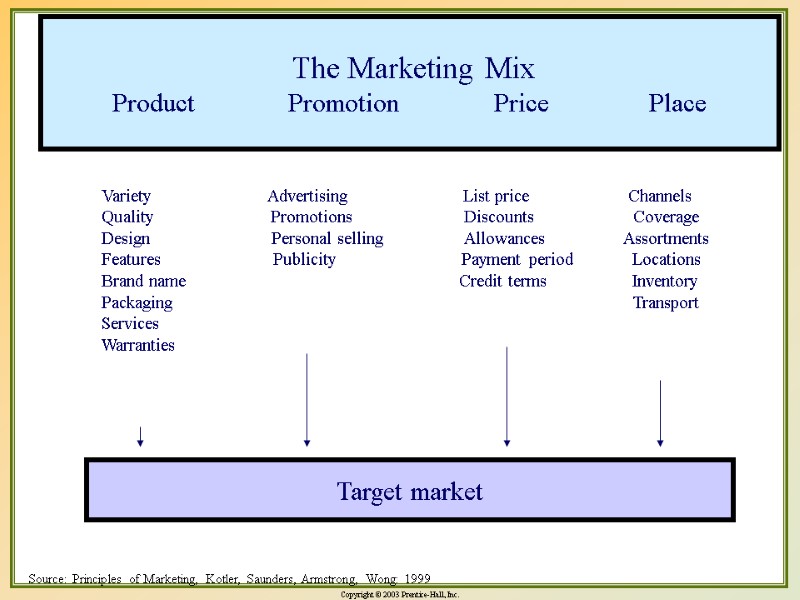
 Marketing Mix Product Promotion Price Place Target market Variety Advertising List price Channels Quality Promotions Discounts Coverage Design Personal selling Allowances Assortments Features Publicity Payment period Locations Brand name Credit terms Inventory Packaging Transport Services Warranties The Marketing Mix Product Promotion Price Place Target market Source: Principles of Marketing, Kotler, Saunders, Armstrong, Wong: 1999
Marketing Mix Product Promotion Price Place Target market Variety Advertising List price Channels Quality Promotions Discounts Coverage Design Personal selling Allowances Assortments Features Publicity Payment period Locations Brand name Credit terms Inventory Packaging Transport Services Warranties The Marketing Mix Product Promotion Price Place Target market Source: Principles of Marketing, Kotler, Saunders, Armstrong, Wong: 1999
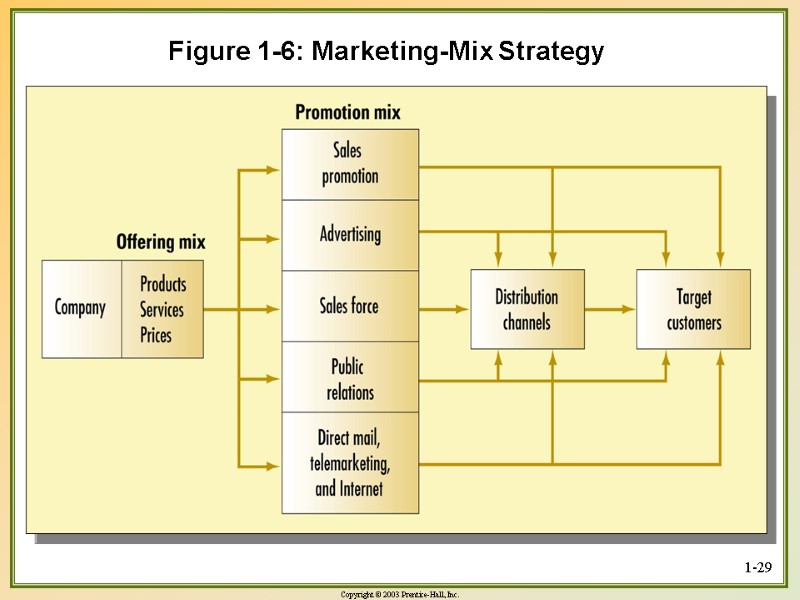
 1-29 Figure 1-6: Marketing-Mix Strategy
1-29 Figure 1-6: Marketing-Mix Strategy
 1-30 Company Orientations Toward the Marketplace Target Market Customer Needs Stated needs Real needs Unstated needs Delight needs Secret needs
1-30 Company Orientations Toward the Marketplace Target Market Customer Needs Stated needs Real needs Unstated needs Delight needs Secret needs
 Other functions of Marketing Except 4 “P”s the following functions are included Market segmentation Marketing research Strategic planning Global marketing 1-31
Other functions of Marketing Except 4 “P”s the following functions are included Market segmentation Marketing research Strategic planning Global marketing 1-31
 1-32 Company Orientations Toward the Marketplace Integrated Marketing External marketing Internal marketing
1-32 Company Orientations Toward the Marketplace Integrated Marketing External marketing Internal marketing
 1-33 Company Orientations Toward the Marketplace Profitability Sales decline Slow growth Changing buying patterns Increasing competition Increasing marketing expenditures
1-33 Company Orientations Toward the Marketplace Profitability Sales decline Slow growth Changing buying patterns Increasing competition Increasing marketing expenditures
 1-34 Can you identify the trends that have made the marketing concept, the customer concept, and the societal marketing concept more attractive models for contemporary marketing managers? Discussion Question
1-34 Can you identify the trends that have made the marketing concept, the customer concept, and the societal marketing concept more attractive models for contemporary marketing managers? Discussion Question
 1-35 How Business and Marketing are Changing Customers Brand manufacturers Store-based retailers
1-35 How Business and Marketing are Changing Customers Brand manufacturers Store-based retailers
 1-36 How Business and Marketing are Changing Company responses and adjustments Reengineering Outsourcing E-commerce Benchmarking Alliances Partner-suppliers Market-centered Global and local Decentralized
1-36 How Business and Marketing are Changing Company responses and adjustments Reengineering Outsourcing E-commerce Benchmarking Alliances Partner-suppliers Market-centered Global and local Decentralized
 1-37 How Business and Marketing are Changing Marketer Responses and Adjustments Customer relationship marketing Customer lifetime value Customer share Target marketing Customization Customer database Integrated marketing communications Channels as partners Every employee a marketer Model-based decision making
1-37 How Business and Marketing are Changing Marketer Responses and Adjustments Customer relationship marketing Customer lifetime value Customer share Target marketing Customization Customer database Integrated marketing communications Channels as partners Every employee a marketer Model-based decision making
 Reading Read chapters in Kotler & Keller (1, 5 & 6) Marketing trends, Consumer behaviour Journal articles from EBSCO – look for recent articles – what are the current trends? How relevant is the 4Ps model? Look in newspapers (business sections) and think about your own experience – how customer-centric are businesses really?
Reading Read chapters in Kotler & Keller (1, 5 & 6) Marketing trends, Consumer behaviour Journal articles from EBSCO – look for recent articles – what are the current trends? How relevant is the 4Ps model? Look in newspapers (business sections) and think about your own experience – how customer-centric are businesses really?
 Homework, Part A, 50% Read Marketing Spotlight: Coca-Cola on p 31 – 32 of Kotler & Keller AND Marketing Insight: Disney on p 204 Discuss in a group: i) What value does Coca-Cola provide to the customer? ii) What value does Disney provide to the customer? Who is the customer? Is value provided to anyone other than the consumer of the product? Who? In what way? What are the implications of this for Disney’s marketing? iii) Give some examples of how Cola-Cola and Disney might use consumer decision-making models to increase their sales.
Homework, Part A, 50% Read Marketing Spotlight: Coca-Cola on p 31 – 32 of Kotler & Keller AND Marketing Insight: Disney on p 204 Discuss in a group: i) What value does Coca-Cola provide to the customer? ii) What value does Disney provide to the customer? Who is the customer? Is value provided to anyone other than the consumer of the product? Who? In what way? What are the implications of this for Disney’s marketing? iii) Give some examples of how Cola-Cola and Disney might use consumer decision-making models to increase their sales.
 Homework, Part B, 50% Prepare a group presentation devoted to marketing policy of any company in Kazakhstan. Briefly stay on key points of these presentation slides. 1-40
Homework, Part B, 50% Prepare a group presentation devoted to marketing policy of any company in Kazakhstan. Briefly stay on key points of these presentation slides. 1-40

