a686bce66f5ec4315e6c3d55098c4f59.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Marketing Chapter 4 Marketing Planning and Organization Strategy Gilbert A. Churchill, Jr. J. Paul Peter
Marketing Chapter 4 Marketing Planning and Organization Strategy Gilbert A. Churchill, Jr. J. Paul Peter
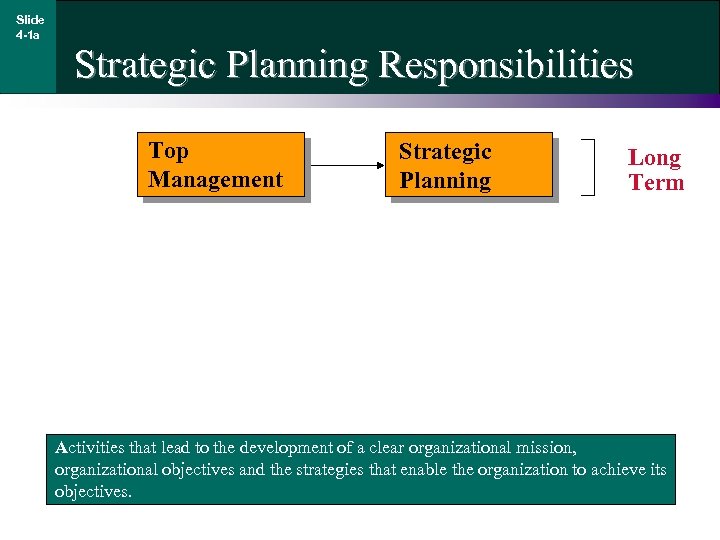 Slide 4 -1 a Strategic Planning Responsibilities Top Management Strategic Planning Long Term Activities that lead to the development of a clear organizational mission, organizational objectives and the strategies that enable the organization to achieve its objectives.
Slide 4 -1 a Strategic Planning Responsibilities Top Management Strategic Planning Long Term Activities that lead to the development of a clear organizational mission, organizational objectives and the strategies that enable the organization to achieve its objectives.
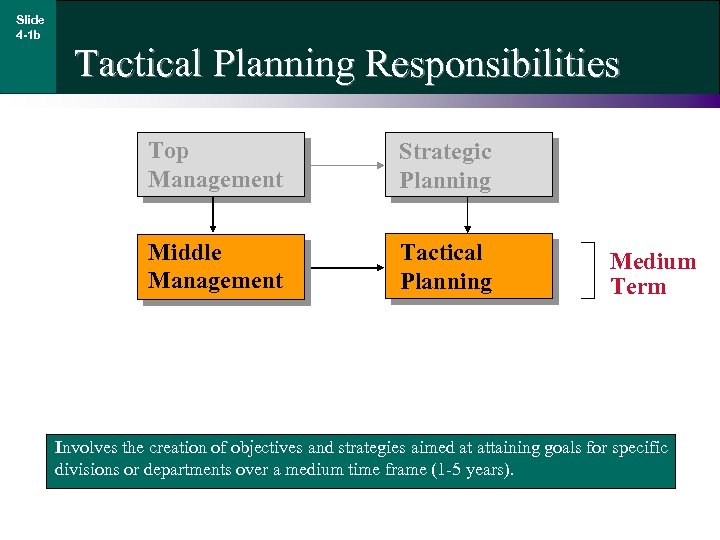 Slide 4 -1 b Tactical Planning Responsibilities Top Management Strategic Planning Middle Management Tactical Planning Medium Term Involves the creation of objectives and strategies aimed at attaining goals for specific divisions or departments over a medium time frame (1 -5 years).
Slide 4 -1 b Tactical Planning Responsibilities Top Management Strategic Planning Middle Management Tactical Planning Medium Term Involves the creation of objectives and strategies aimed at attaining goals for specific divisions or departments over a medium time frame (1 -5 years).
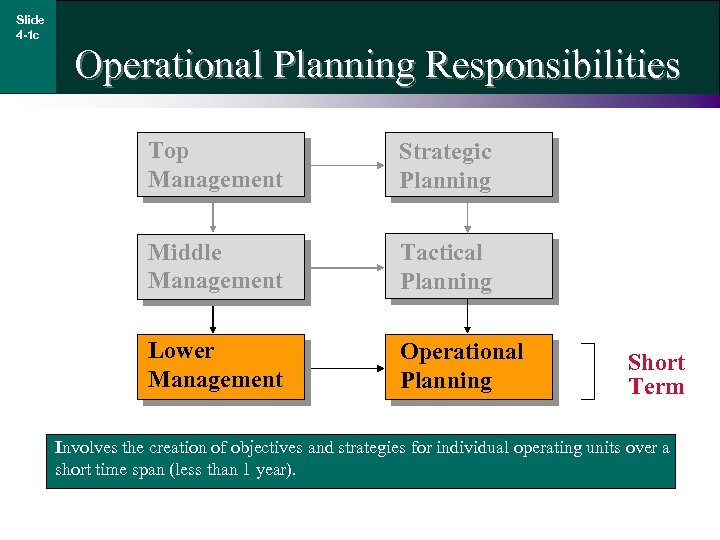 Slide 4 -1 c Operational Planning Responsibilities Top Management Strategic Planning Middle Management Tactical Planning Lower Management Operational Planning Short Term Involves the creation of objectives and strategies for individual operating units over a short time span (less than 1 year).
Slide 4 -1 c Operational Planning Responsibilities Top Management Strategic Planning Middle Management Tactical Planning Lower Management Operational Planning Short Term Involves the creation of objectives and strategies for individual operating units over a short time span (less than 1 year).
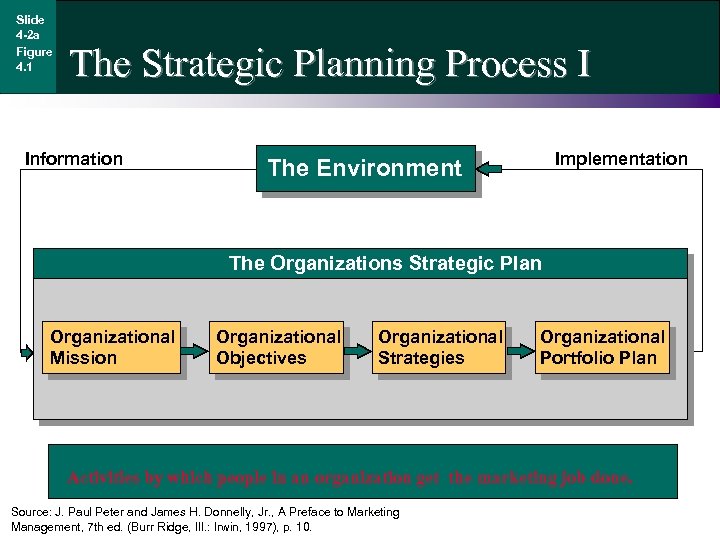 Slide 4 -2 a Figure 4. 1 The Strategic Planning Process I Information Implementation The Environment The Organizations Strategic Plan Organizational Mission Organizational Objectives Organizational Strategies Organizational Portfolio Plan Activities by which people in an organization get the marketing job done. Source: J. Paul Peter and James H. Donnelly, Jr. , A Preface to Marketing Management, 7 th ed. (Burr Ridge, Ill. : Irwin, 1997), p. 10.
Slide 4 -2 a Figure 4. 1 The Strategic Planning Process I Information Implementation The Environment The Organizations Strategic Plan Organizational Mission Organizational Objectives Organizational Strategies Organizational Portfolio Plan Activities by which people in an organization get the marketing job done. Source: J. Paul Peter and James H. Donnelly, Jr. , A Preface to Marketing Management, 7 th ed. (Burr Ridge, Ill. : Irwin, 1997), p. 10.
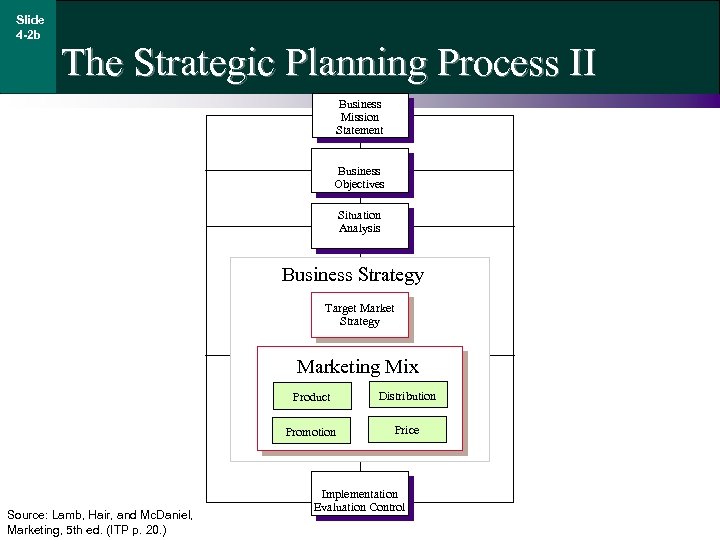 Slide 4 -2 b The Strategic Planning Process II Business Mission Statement Business Objectives Situation Analysis Business Strategy Target Market Strategy Marketing Mix Product Promotion Source: Lamb, Hair, and Mc. Daniel, Marketing, 5 th ed. (ITP p. 20. ) Distribution Price Implementation Evaluation Control
Slide 4 -2 b The Strategic Planning Process II Business Mission Statement Business Objectives Situation Analysis Business Strategy Target Market Strategy Marketing Mix Product Promotion Source: Lamb, Hair, and Mc. Daniel, Marketing, 5 th ed. (ITP p. 20. ) Distribution Price Implementation Evaluation Control
 Slide 4 -3 Mission Statement A statement of the organization’s distinct purpose (i. e. , what business are we in). A good mission statement must: Define and satisfy the key stakeholders (i. e. , customers, shareholders, employees) Not suffer from marketing myopia (i. e. , defining it in terms of the offering rather than benefits; e. g. , “railway business”, “slide-rule business”) Not depart too radically from history Fit the market environment (e. g. , GSA - “To prepare young girls for motherhood and wifely duties”) Specific and Realistic (e. g. , SIA - “to become the worlds largest airline”)
Slide 4 -3 Mission Statement A statement of the organization’s distinct purpose (i. e. , what business are we in). A good mission statement must: Define and satisfy the key stakeholders (i. e. , customers, shareholders, employees) Not suffer from marketing myopia (i. e. , defining it in terms of the offering rather than benefits; e. g. , “railway business”, “slide-rule business”) Not depart too radically from history Fit the market environment (e. g. , GSA - “To prepare young girls for motherhood and wifely duties”) Specific and Realistic (e. g. , SIA - “to become the worlds largest airline”)
 Slide 4 -4 Criteria for Organizational Objectives Realistic Measurable - 15% ROI, Increase sales by 10% Clear - for a Defined Period of Time Consistent with Organizational Objectives A statement of what is to be accomplished through marketing activities.
Slide 4 -4 Criteria for Organizational Objectives Realistic Measurable - 15% ROI, Increase sales by 10% Clear - for a Defined Period of Time Consistent with Organizational Objectives A statement of what is to be accomplished through marketing activities.
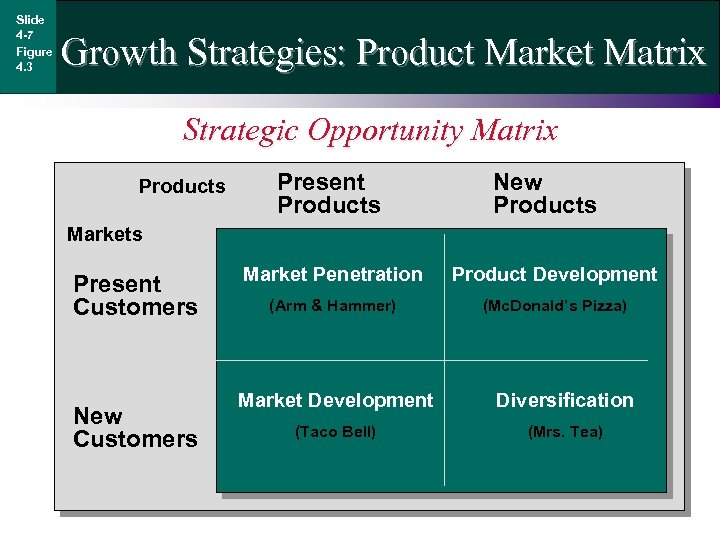 Slide 4 -7 Figure 4. 3 Growth Strategies: Product Market Matrix Strategic Opportunity Matrix Products Present Products New Products Markets Present Customers New Customers Market Penetration Product Development (Arm & Hammer) (Mc. Donald’s Pizza) Market Development Diversification (Taco Bell) (Mrs. Tea)
Slide 4 -7 Figure 4. 3 Growth Strategies: Product Market Matrix Strategic Opportunity Matrix Products Present Products New Products Markets Present Customers New Customers Market Penetration Product Development (Arm & Hammer) (Mc. Donald’s Pizza) Market Development Diversification (Taco Bell) (Mrs. Tea)
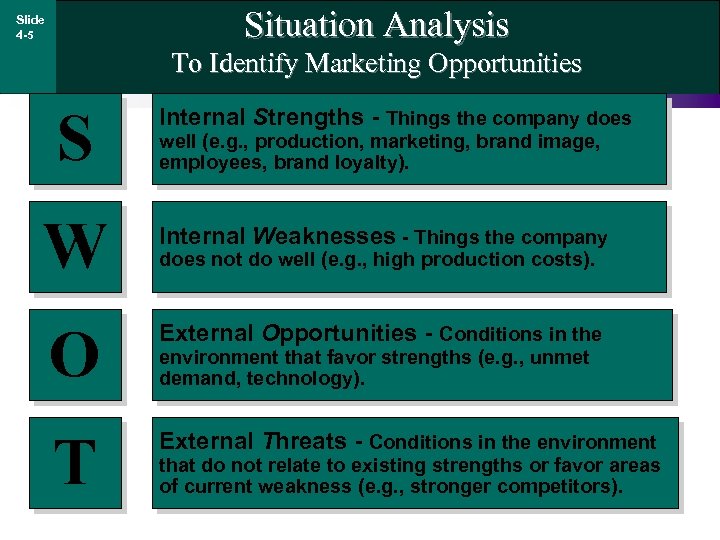 Situation Analysis Slide 4 -5 To Identify Marketing Opportunities S W Internal Strengths - Things the company does well (e. g. , production, marketing, brand image, employees, brand loyalty). Internal Weaknesses - Things the company does not do well (e. g. , high production costs). O External Opportunities - Conditions in the T External Threats - Conditions in the environment that favor strengths (e. g. , unmet demand, technology). that do not relate to existing strengths or favor areas of current weakness (e. g. , stronger competitors).
Situation Analysis Slide 4 -5 To Identify Marketing Opportunities S W Internal Strengths - Things the company does well (e. g. , production, marketing, brand image, employees, brand loyalty). Internal Weaknesses - Things the company does not do well (e. g. , high production costs). O External Opportunities - Conditions in the T External Threats - Conditions in the environment that favor strengths (e. g. , unmet demand, technology). that do not relate to existing strengths or favor areas of current weakness (e. g. , stronger competitors).
 Slide 4 -6 Table 4. 1 Examples of SWOT Issues Internal Environment Strengths Weaknesses Financial Resources Lack of Strategic Direction Well-known brands High Costs Technological Skills Obsolete Facilities External Environment Opportunities Threats Potential New Markets New Competition Potential New Products Slow Market Growth Falling International Trade Barriers New Regulations
Slide 4 -6 Table 4. 1 Examples of SWOT Issues Internal Environment Strengths Weaknesses Financial Resources Lack of Strategic Direction Well-known brands High Costs Technological Skills Obsolete Facilities External Environment Opportunities Threats Potential New Markets New Competition Potential New Products Slow Market Growth Falling International Trade Barriers New Regulations
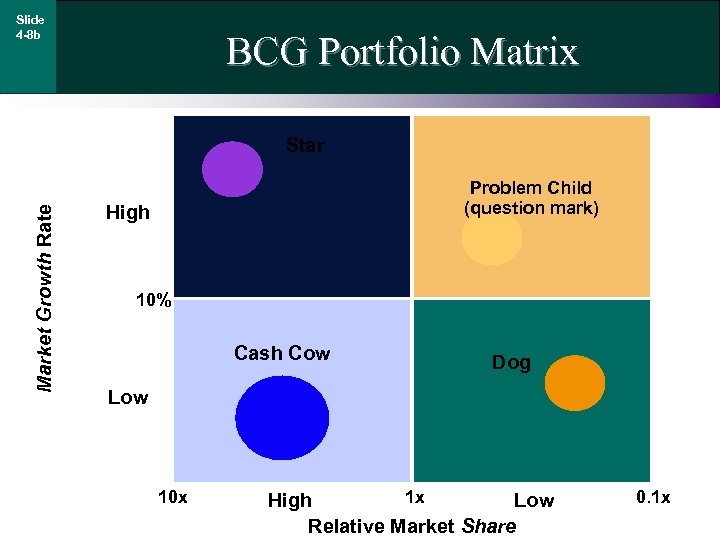 Slide 4 -8 b BCG Portfolio Matrix Market Growth Rate Star Problem Child (question mark) High 10% Cash Cow Dog Low 10 x 1 x High Low Relative Market Share 0. 1 x
Slide 4 -8 b BCG Portfolio Matrix Market Growth Rate Star Problem Child (question mark) High 10% Cash Cow Dog Low 10 x 1 x High Low Relative Market Share 0. 1 x
 Slide 4 -8 a The Boston Consulting Group Matrix High Industry Growth Rate Low High Market Share Low
Slide 4 -8 a The Boston Consulting Group Matrix High Industry Growth Rate Low High Market Share Low
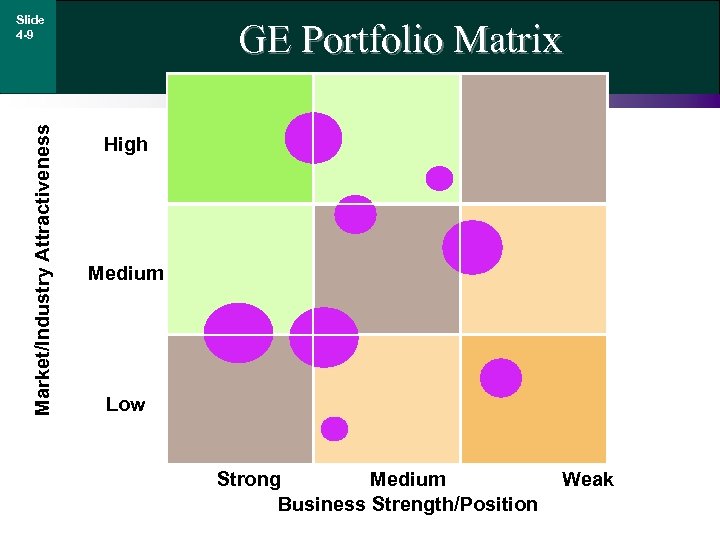 Market/Industry Attractiveness Slide 4 -9 GE Portfolio Matrix High Medium Low Strong Medium Business Strength/Position Weak
Market/Industry Attractiveness Slide 4 -9 GE Portfolio Matrix High Medium Low Strong Medium Business Strength/Position Weak
 Slide 4 -10 Table 4. 2 Some Questions for Evaluating a Marketing Plan • Are the objectives clear? Specific? Measurable? Challenging, but achievable? Written? • Have the industries that are growing been identified? Those that are stagnant? Those that are declining? • Who are the principal competitors? • What are the organization’s strengths? Weaknesses? • Does the plan take advantage of the organization’s special competencies and vulnerabilities? • What are the target markets? • Do our products and services appeal to the needs and wants of the target markets? • What are the best ways to promote the products to customers? • Where do customers like to purchase? • How do our prices compare with the competition? • What are the costs and benefits of the plan?
Slide 4 -10 Table 4. 2 Some Questions for Evaluating a Marketing Plan • Are the objectives clear? Specific? Measurable? Challenging, but achievable? Written? • Have the industries that are growing been identified? Those that are stagnant? Those that are declining? • Who are the principal competitors? • What are the organization’s strengths? Weaknesses? • Does the plan take advantage of the organization’s special competencies and vulnerabilities? • What are the target markets? • Do our products and services appeal to the needs and wants of the target markets? • What are the best ways to promote the products to customers? • Where do customers like to purchase? • How do our prices compare with the competition? • What are the costs and benefits of the plan?
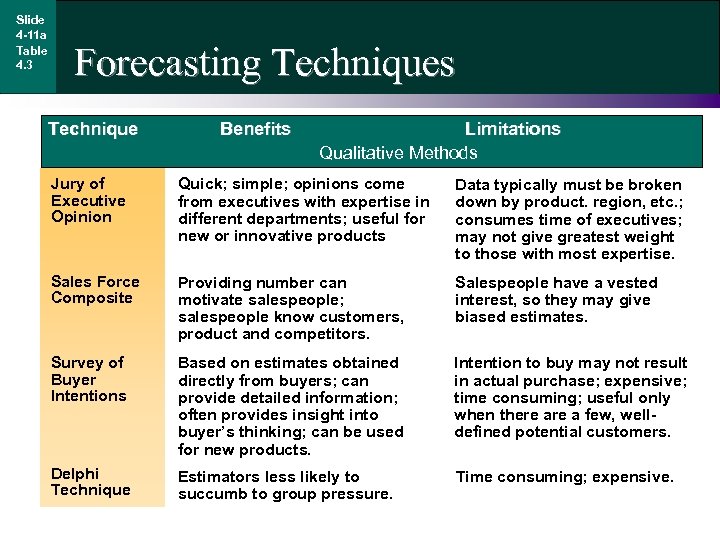 Slide 4 -11 a Table 4. 3 Forecasting Techniques Technique Benefits Limitations Qualitative Methods Jury of Executive Opinion Quick; simple; opinions come from executives with expertise in different departments; useful for new or innovative products Data typically must be broken down by product. region, etc. ; consumes time of executives; may not give greatest weight to those with most expertise. Sales Force Composite Providing number can motivate salespeople; salespeople know customers, product and competitors. Salespeople have a vested interest, so they may give biased estimates. Survey of Buyer Intentions Based on estimates obtained directly from buyers; can provide detailed information; often provides insight into buyer’s thinking; can be used for new products. Intention to buy may not result in actual purchase; expensive; time consuming; useful only when there a few, welldefined potential customers. Delphi Technique Estimators less likely to succumb to group pressure. Time consuming; expensive.
Slide 4 -11 a Table 4. 3 Forecasting Techniques Technique Benefits Limitations Qualitative Methods Jury of Executive Opinion Quick; simple; opinions come from executives with expertise in different departments; useful for new or innovative products Data typically must be broken down by product. region, etc. ; consumes time of executives; may not give greatest weight to those with most expertise. Sales Force Composite Providing number can motivate salespeople; salespeople know customers, product and competitors. Salespeople have a vested interest, so they may give biased estimates. Survey of Buyer Intentions Based on estimates obtained directly from buyers; can provide detailed information; often provides insight into buyer’s thinking; can be used for new products. Intention to buy may not result in actual purchase; expensive; time consuming; useful only when there a few, welldefined potential customers. Delphi Technique Estimators less likely to succumb to group pressure. Time consuming; expensive.
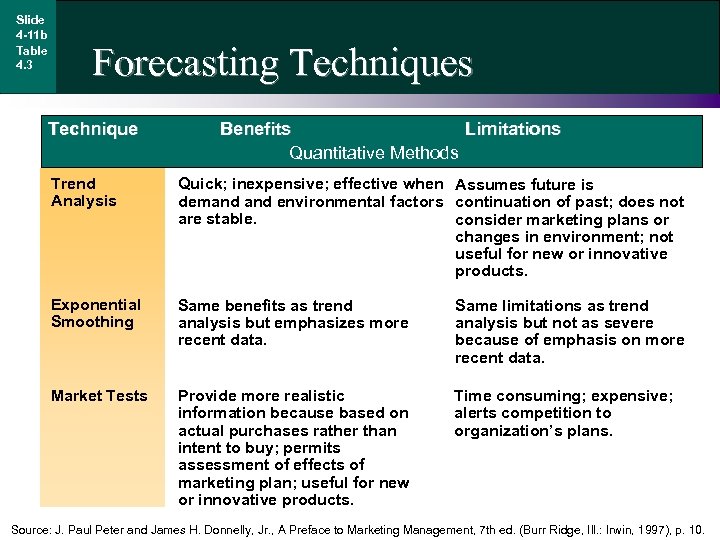 Slide 4 -11 b Table 4. 3 Forecasting Techniques Technique Benefits Limitations Quantitative Methods Trend Analysis Quick; inexpensive; effective when Assumes future is demand environmental factors continuation of past; does not are stable. consider marketing plans or changes in environment; not useful for new or innovative products. Exponential Smoothing Same benefits as trend analysis but emphasizes more recent data. Same limitations as trend analysis but not as severe because of emphasis on more recent data. Market Tests Provide more realistic information because based on actual purchases rather than intent to buy; permits assessment of effects of marketing plan; useful for new or innovative products. Time consuming; expensive; alerts competition to organization’s plans. Source: J. Paul Peter and James H. Donnelly, Jr. , A Preface to Marketing Management, 7 th ed. (Burr Ridge, Ill. : Irwin, 1997), p. 10.
Slide 4 -11 b Table 4. 3 Forecasting Techniques Technique Benefits Limitations Quantitative Methods Trend Analysis Quick; inexpensive; effective when Assumes future is demand environmental factors continuation of past; does not are stable. consider marketing plans or changes in environment; not useful for new or innovative products. Exponential Smoothing Same benefits as trend analysis but emphasizes more recent data. Same limitations as trend analysis but not as severe because of emphasis on more recent data. Market Tests Provide more realistic information because based on actual purchases rather than intent to buy; permits assessment of effects of marketing plan; useful for new or innovative products. Time consuming; expensive; alerts competition to organization’s plans. Source: J. Paul Peter and James H. Donnelly, Jr. , A Preface to Marketing Management, 7 th ed. (Burr Ridge, Ill. : Irwin, 1997), p. 10.


