e95cd3efdaec4e3fcf1e0e8dc75f789d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Marketing 260 Buyer Behaviour ATTITUDES With Duane Weaver

OUTLINE • • • Attitude Defined Functional Theory ABC Model Forming Attitudes Attitude Models Predicting Behaviour

Attitude Defined ATTITUDE: …a lasting, general evaluation of people (including oneself), objects or issues. Attitude Object = anything toward which a person has an attitude, albeit tangible or intangible

Functional Theory • Attitudes exist because they serve some function for the person; determined by motives. – Utilitarian (reward & punishment) – Value-Expressive (enables outward expression of self) – Ego-Defensive (protects from internal or external feelings – to avoid facts or defend from low self-concept) – Knowledge (order, structure, and meaning) • Ads relevant to the prevalent function prompt favorable thoughts about product.

ABC Model Emphasizes interrelationships among knowing, feeling, and doing. • Affect – Feelings • Behaviour – Intention to do something with regard to an attitude object • Cognition – Beliefs about an attitude object
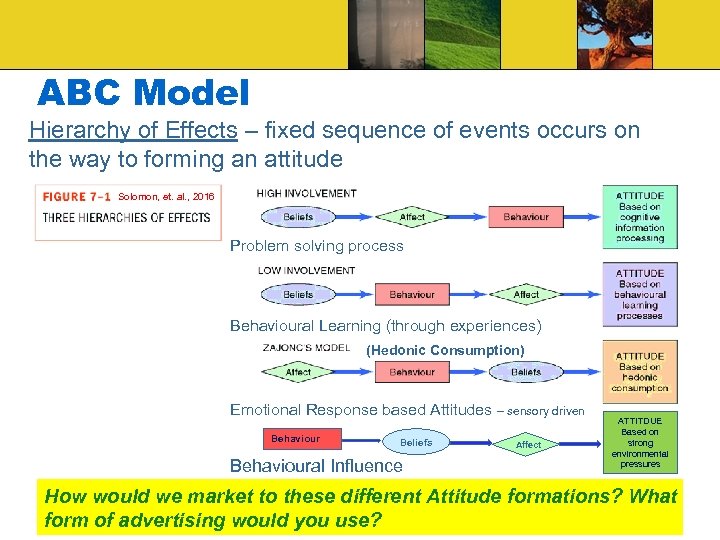
ABC Model Hierarchy of Effects – fixed sequence of events occurs on the way to forming an attitude Solomon, et. al. , 2016 Problem solving process Behavioural Learning (through experiences) (Hedonic Consumption) Emotional Response based Attitudes – sensory driven Behaviour Beliefs Behavioural Influence Affect ATTITDUE Based on strong environmental pressures How would we market to these different Attitude formations? What form of advertising would you use?

• • • Forming Attitudes Classical Conditioning (pairing product with repeated concepts) Instrumental Conditioning (reinforcing value of consumption) Complex Cognitive Process 1. Levels of Commitment – Compliance (low), Identification (medium), Internalization (high) 2. Consistency Principle (harmony) and Cognitive Dissonance Theory (congruence) 3. Self-Perception Theory (rationalization? ) 4. Social Judgment Theory (social accpetance? ) 5. Balance Theory (Triad of attitude structures: person’s perception, attitude object, & other person or object)
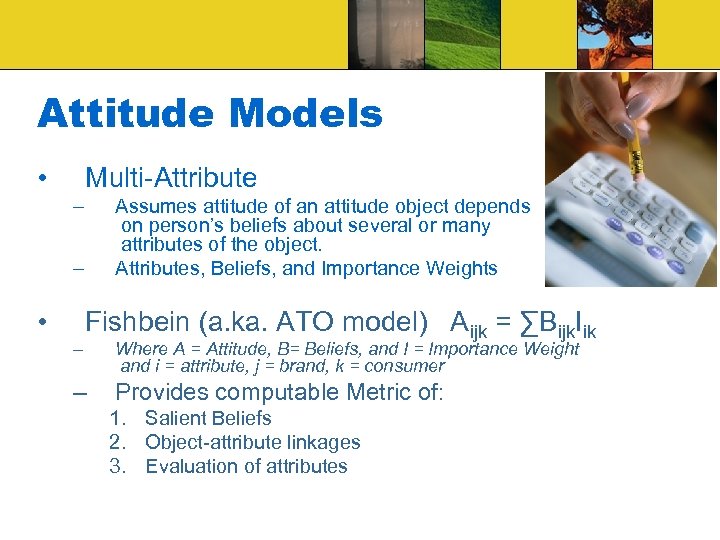
Attitude Models • Multi-Attribute – Assumes attitude of an attitude object depends on person’s beliefs about several or many attributes of the object. Attributes, Beliefs, and Importance Weights – • – Fishbein (a. ka. ATO model) Aijk = ∑Bijk. Iik – Where A = Attitude, B= Beliefs, and I = Importance Weight and i = attribute, j = brand, k = consumer Provides computable Metric of: 1. Salient Beliefs 2. Object-attribute linkages 3. Evaluation of attributes

Predicting Behaviour • Issues: – Low correlation between attitudes and behaviour – Inability to act due to unexpected circumstances (no banker available when want to get a mortgage) <<wasted marketing energy…get all the ducks in a row!! THIS IS MANAGEABLE! – Not all behaviour is intentional (impulse? !) – Timeframe – delay from time of attitude measurement to expected behaviour (attitudes do change over time) – Personal or environmental barriers between intent and goal • Extending Fishbein with Theory of Reasoned Action – Direction/degree or attitude (intensity) – Social Pressure (use of engineered theatres) – Attitude towards the actual “act of buying” • Past purchase behaviour is better predictor

Predicting Behaviour • Theory of Trying – Past frequency – Recency – Evaluations of consequences – The Process – Expectations of Success or Failure – Subjective norms towards trying

MESSAGE APPEALS • • Fear Humour Sex Slice-of-Life Rationality Music Emotions Scarcity

THANK YOU FOR YOUR TIME!
e95cd3efdaec4e3fcf1e0e8dc75f789d.ppt