5bbead7fd832b0ce54311b96d041f13f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty OVERVIEW 1
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty OVERVIEW 1
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Content Page n Introduction to Loyalty Programmes 3 n Change Drivers for Loyalty Programmes 6 n Loyalty and Relationship Marketing 8 n Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme 9 n Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes 16 n Loyalty and Industry Specific Situations 24 n Pros and Cons of Loyalty Programmes 26 n Customer Perception of Loyalty Programmes - The Loyalty Paradox n Benchmarks 31 n Citations 34 © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 28 2 2
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Content Page n Introduction to Loyalty Programmes 3 n Change Drivers for Loyalty Programmes 6 n Loyalty and Relationship Marketing 8 n Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme 9 n Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes 16 n Loyalty and Industry Specific Situations 24 n Pros and Cons of Loyalty Programmes 26 n Customer Perception of Loyalty Programmes - The Loyalty Paradox n Benchmarks 31 n Citations 34 © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 28 2 2
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Introduction to Customer Loyalty Programmes (1/3) Customer loyalty is a key success driver for G-500 companies n Several G-500 companies face the challenge, that they have to retain their customer base, when going global and standing in front of competition. Empirical studies show, that an ongoing customer relationship does not only cost less, but also secures a higher revenue stream. n Retaining customer means building up a long-term customer relationship based on the clients whishes, needs and requirements. The customer loyalty programme helps installing a dialogue between the customer and the company; enabling the last to target its offers and to customize its marketing and sales activities. The Pw. C Guide to Customer Loyalty gives an insight how to handle customer retention and delivers instruments to make it come true n With this Guide, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers provides not only the best in class examples of loyalty programmes, but also shows the complex interactions, which determine the success of these kind of programmes. n In addition, the Guide gives a structured approach of the handling of customer loyalty projects. Specific instruments help recognize the most important issues and support the consultant in the client specific situation. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 3 3
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Introduction to Customer Loyalty Programmes (1/3) Customer loyalty is a key success driver for G-500 companies n Several G-500 companies face the challenge, that they have to retain their customer base, when going global and standing in front of competition. Empirical studies show, that an ongoing customer relationship does not only cost less, but also secures a higher revenue stream. n Retaining customer means building up a long-term customer relationship based on the clients whishes, needs and requirements. The customer loyalty programme helps installing a dialogue between the customer and the company; enabling the last to target its offers and to customize its marketing and sales activities. The Pw. C Guide to Customer Loyalty gives an insight how to handle customer retention and delivers instruments to make it come true n With this Guide, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers provides not only the best in class examples of loyalty programmes, but also shows the complex interactions, which determine the success of these kind of programmes. n In addition, the Guide gives a structured approach of the handling of customer loyalty projects. Specific instruments help recognize the most important issues and support the consultant in the client specific situation. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 3 3
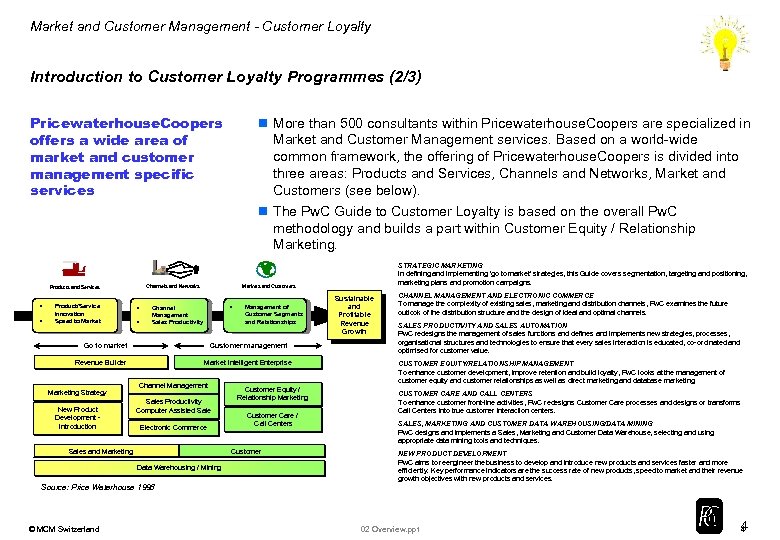 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Introduction to Customer Loyalty Programmes (2/3) Pricewaterhouse. Coopers offers a wide area of market and customer management specific services • Product/Service Innovation Speed to Market • • • Channel Management Sales Productivity Go to market Marketing Strategy New Product Development Introduction Market Intelligent Enterprise Channel Management Sales Productivity Computer Assisted Sale Electronic Commerce Sales and Marketing Customer Equity / Relationship Marketing Customer Care / Call Centers Customer Data Warehousing / Mining Source: Price Waterhouse 1998 © MCM Switzerland Management of Customer Segments and Relationships Customer management Revenue Builder STRATEGIC MARKETING In defining and implementing 'go to market' strategies, this Guide covers segmentation, targeting and positioning, marketing plans and promotion campaigns. Markets and Customers Channels and Networks Products and Services • n More than 500 consultants within Pricewaterhouse. Coopers are specialized in Market and Customer Management services. Based on a world-wide common framework, the offering of Pricewaterhouse. Coopers is divided into three areas: Products and Services, Channels and Networks, Market and Customers (see below). n The Pw. C Guide to Customer Loyalty is based on the overall Pw. C methodology and builds a part within Customer Equity / Relationship Marketing. Sustainable and Profitable Revenue Growth CHANNEL MANAGEMENT AND ELECTRONIC COMMERCE To manage the complexity of existing sales, marketing and distribution channels, Pw. C examines the future outlook of the distribution structure and the design of ideal and optimal channels. SALES PRODUCTIVITY AND SALES AUTOMATION Pw. C redesigns the management of sales functions and defines and implements new strategies, processes, organisational structures and technologies to ensure that every sales interaction is educated, co-ordinated and optimised for customer value. CUSTOMER EQUITY/RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT To enhance customer development, improve retention and build loyalty, Pw. C looks at the management of customer equity and customer relationships as well as direct marketing and database marketing. CUSTOMER CARE AND CALL CENTERS To enhance customer front-line activities, Pw. C redesigns Customer Care processes and designs or transforms Call Centers into true customer interaction centers. SALES, MARKETING AND CUSTOMER DATA WAREHOUSING/DATA MINING Pw. C designs and implements a Sales, Marketing and Customer Data Warehouse, selecting and using appropriate data mining tools and techniques. NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT Pw. C aims to reengineer the business to develop and introduce new products and services faster and more efficiently. Key performance indicators are the success rate of new products, speed to market and their revenue growth objectives with new products and services. 02 Overview. ppt 4 4
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Introduction to Customer Loyalty Programmes (2/3) Pricewaterhouse. Coopers offers a wide area of market and customer management specific services • Product/Service Innovation Speed to Market • • • Channel Management Sales Productivity Go to market Marketing Strategy New Product Development Introduction Market Intelligent Enterprise Channel Management Sales Productivity Computer Assisted Sale Electronic Commerce Sales and Marketing Customer Equity / Relationship Marketing Customer Care / Call Centers Customer Data Warehousing / Mining Source: Price Waterhouse 1998 © MCM Switzerland Management of Customer Segments and Relationships Customer management Revenue Builder STRATEGIC MARKETING In defining and implementing 'go to market' strategies, this Guide covers segmentation, targeting and positioning, marketing plans and promotion campaigns. Markets and Customers Channels and Networks Products and Services • n More than 500 consultants within Pricewaterhouse. Coopers are specialized in Market and Customer Management services. Based on a world-wide common framework, the offering of Pricewaterhouse. Coopers is divided into three areas: Products and Services, Channels and Networks, Market and Customers (see below). n The Pw. C Guide to Customer Loyalty is based on the overall Pw. C methodology and builds a part within Customer Equity / Relationship Marketing. Sustainable and Profitable Revenue Growth CHANNEL MANAGEMENT AND ELECTRONIC COMMERCE To manage the complexity of existing sales, marketing and distribution channels, Pw. C examines the future outlook of the distribution structure and the design of ideal and optimal channels. SALES PRODUCTIVITY AND SALES AUTOMATION Pw. C redesigns the management of sales functions and defines and implements new strategies, processes, organisational structures and technologies to ensure that every sales interaction is educated, co-ordinated and optimised for customer value. CUSTOMER EQUITY/RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT To enhance customer development, improve retention and build loyalty, Pw. C looks at the management of customer equity and customer relationships as well as direct marketing and database marketing. CUSTOMER CARE AND CALL CENTERS To enhance customer front-line activities, Pw. C redesigns Customer Care processes and designs or transforms Call Centers into true customer interaction centers. SALES, MARKETING AND CUSTOMER DATA WAREHOUSING/DATA MINING Pw. C designs and implements a Sales, Marketing and Customer Data Warehouse, selecting and using appropriate data mining tools and techniques. NEW PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT Pw. C aims to reengineer the business to develop and introduce new products and services faster and more efficiently. Key performance indicators are the success rate of new products, speed to market and their revenue growth objectives with new products and services. 02 Overview. ppt 4 4
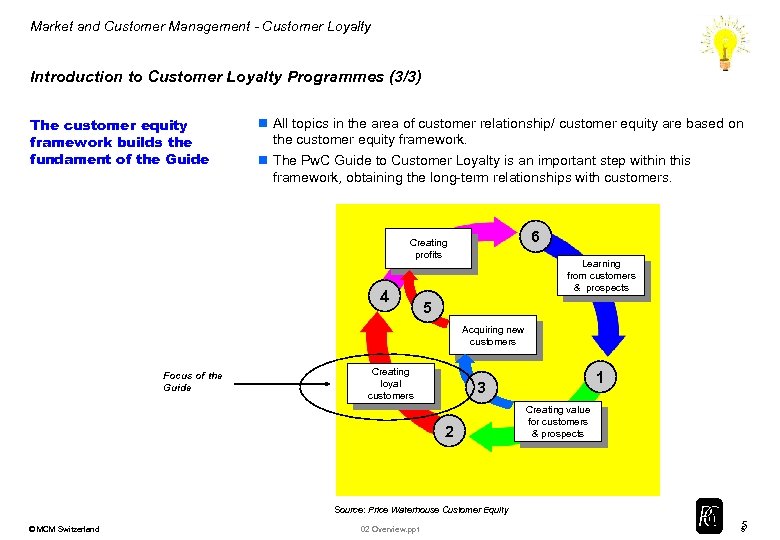 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Introduction to Customer Loyalty Programmes (3/3) The customer equity framework builds the fundament of the Guide n All topics in the area of customer relationship/ customer equity are based on the customer equity framework. n The Pw. C Guide to Customer Loyalty is an important step within this framework, obtaining the long-term relationships with customers. 6 Creating profits 4 Learning from customers & prospects 5 Acquiring new customers Focus of the Guide Creating loyal customers 1 3 2 Creating value for customers & prospects Source: Price Waterhouse Customer Equity © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 5 5
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Introduction to Customer Loyalty Programmes (3/3) The customer equity framework builds the fundament of the Guide n All topics in the area of customer relationship/ customer equity are based on the customer equity framework. n The Pw. C Guide to Customer Loyalty is an important step within this framework, obtaining the long-term relationships with customers. 6 Creating profits 4 Learning from customers & prospects 5 Acquiring new customers Focus of the Guide Creating loyal customers 1 3 2 Creating value for customers & prospects Source: Price Waterhouse Customer Equity © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 5 5
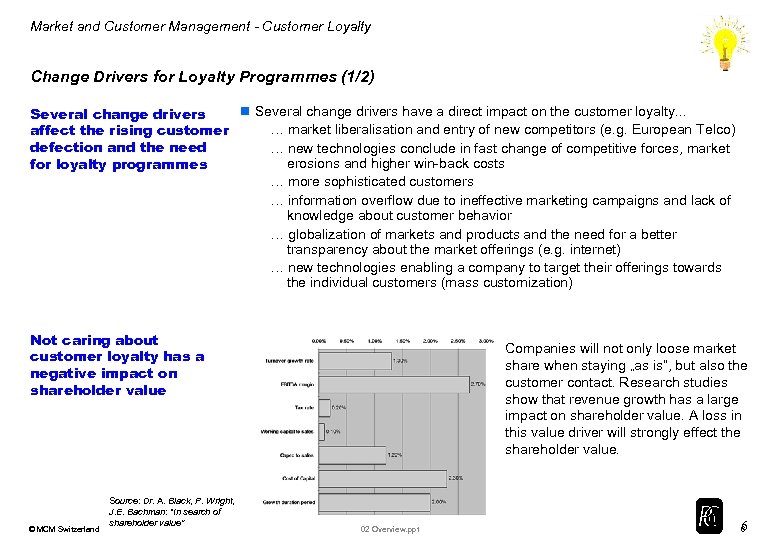 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Change Drivers for Loyalty Programmes (1/2) n Several change drivers have a direct impact on the customer loyalty. . . Several change drivers … market liberalisation and entry of new competitors (e. g. European Telco) affect the rising customer defection and the need … new technologies conclude in fast change of competitive forces, market erosions and higher win-back costs for loyalty programmes … more sophisticated customers … information overflow due to ineffective marketing campaigns and lack of knowledge about customer behavior … globalization of markets and products and the need for a better transparency about the market offerings (e. g. internet) … new technologies enabling a company to target their offerings towards the individual customers (mass customization) Not caring about customer loyalty has a negative impact on shareholder value © MCM Switzerland Source: Dr. A. Black, P. Wright, J. E. Bachman: “In search of shareholder value” Companies will not only loose market share when staying „as is“, but also the customer contact. Research studies show that revenue growth has a large impact on shareholder value. A loss in this value driver will strongly effect the shareholder value. 02 Overview. ppt 6 6
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Change Drivers for Loyalty Programmes (1/2) n Several change drivers have a direct impact on the customer loyalty. . . Several change drivers … market liberalisation and entry of new competitors (e. g. European Telco) affect the rising customer defection and the need … new technologies conclude in fast change of competitive forces, market erosions and higher win-back costs for loyalty programmes … more sophisticated customers … information overflow due to ineffective marketing campaigns and lack of knowledge about customer behavior … globalization of markets and products and the need for a better transparency about the market offerings (e. g. internet) … new technologies enabling a company to target their offerings towards the individual customers (mass customization) Not caring about customer loyalty has a negative impact on shareholder value © MCM Switzerland Source: Dr. A. Black, P. Wright, J. E. Bachman: “In search of shareholder value” Companies will not only loose market share when staying „as is“, but also the customer contact. Research studies show that revenue growth has a large impact on shareholder value. A loss in this value driver will strongly effect the shareholder value. 02 Overview. ppt 6 6
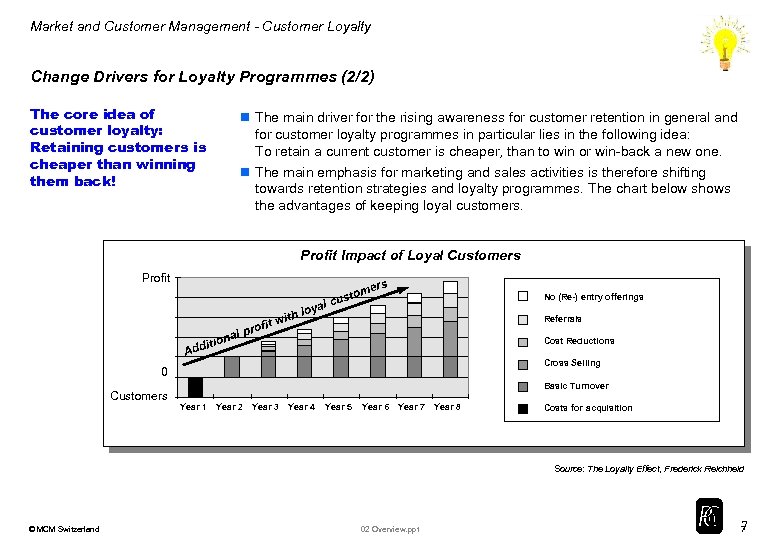 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Change Drivers for Loyalty Programmes (2/2) The core idea of customer loyalty: Retaining customers is cheaper than winning them back! n The main driver for the rising awareness for customer retention in general and for customer loyalty programmes in particular lies in the following idea: To retain a current customer is cheaper, than to win or win-back a new one. n The main emphasis for marketing and sales activities is therefore shifting towards retention strategies and loyalty programmes. The chart below shows the advantages of keeping loyal customers. Profit Impact of Loyal Customers Profit ers l pr iona it Add No (Re-) entry offerings y th lo wi ofit tom cus al Referrals Cost Reductions Cross Selling 0 Basic Turnover Customers Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Year 8 Costs for acquisition Source: The Loyalty Effect, Frederick Reichheld © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 7 7
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Change Drivers for Loyalty Programmes (2/2) The core idea of customer loyalty: Retaining customers is cheaper than winning them back! n The main driver for the rising awareness for customer retention in general and for customer loyalty programmes in particular lies in the following idea: To retain a current customer is cheaper, than to win or win-back a new one. n The main emphasis for marketing and sales activities is therefore shifting towards retention strategies and loyalty programmes. The chart below shows the advantages of keeping loyal customers. Profit Impact of Loyal Customers Profit ers l pr iona it Add No (Re-) entry offerings y th lo wi ofit tom cus al Referrals Cost Reductions Cross Selling 0 Basic Turnover Customers Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Year 7 Year 8 Costs for acquisition Source: The Loyalty Effect, Frederick Reichheld © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 7 7
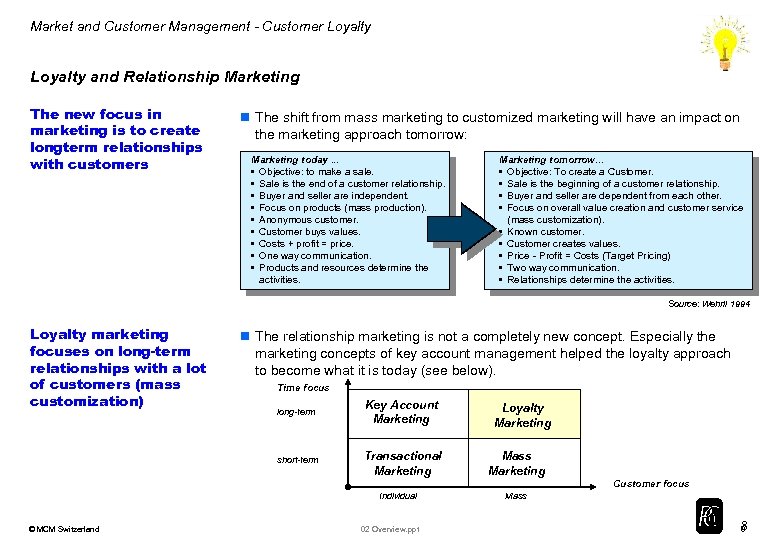 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty and Relationship Marketing The new focus in marketing is to create longterm relationships with customers n The shift from mass marketing to customized marketing will have an impact on the marketing approach tomorrow: Marketing today. . . • Objective: to make a sale. • Sale is the end of a customer relationship. • Buyer and seller are independent. • Focus on products (mass production). • Anonymous customer. • Customer buys values. • Costs + profit = price. • One way communication. • Products and resources determine the activities. Marketing tomorrow. . . • Objective: To create a Customer. • Sale is the beginning of a customer relationship. • Buyer and seller are dependent from each other. • Focus on overall value creation and customer service (mass customization). • Known customer. • Customer creates values. • Price - Profit = Costs (Target Pricing) • Two way communication. • Relationships determine the activities. Source: Wehrli 1994 Loyalty marketing focuses on long-term relationships with a lot of customers (mass customization) n The relationship marketing is not a completely new concept. Especially the marketing concepts of key account management helped the loyalty approach to become what it is today (see below). Time focus long-term Key Account Marketing short-term Transactional Marketing Loyalty Marketing Mass Marketing Customer focus Individual © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt Mass 8 8
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty and Relationship Marketing The new focus in marketing is to create longterm relationships with customers n The shift from mass marketing to customized marketing will have an impact on the marketing approach tomorrow: Marketing today. . . • Objective: to make a sale. • Sale is the end of a customer relationship. • Buyer and seller are independent. • Focus on products (mass production). • Anonymous customer. • Customer buys values. • Costs + profit = price. • One way communication. • Products and resources determine the activities. Marketing tomorrow. . . • Objective: To create a Customer. • Sale is the beginning of a customer relationship. • Buyer and seller are dependent from each other. • Focus on overall value creation and customer service (mass customization). • Known customer. • Customer creates values. • Price - Profit = Costs (Target Pricing) • Two way communication. • Relationships determine the activities. Source: Wehrli 1994 Loyalty marketing focuses on long-term relationships with a lot of customers (mass customization) n The relationship marketing is not a completely new concept. Especially the marketing concepts of key account management helped the loyalty approach to become what it is today (see below). Time focus long-term Key Account Marketing short-term Transactional Marketing Loyalty Marketing Mass Marketing Customer focus Individual © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt Mass 8 8
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (1/7) What is loyalty … ? n Loyalty is the perception of trust and commitment to an institution or a person. The loyalty term comes historically from the relationship to its government and nationality. Loyalty is a feeling of being indepted something to somebody. n Loyalty doesn’t start with a first impression, but needs a long time to be built up. A company gets loyal customers, when these customers get more for their money, than they could expect before buying something. n Loyalty is not a short term oriented feeling, which a customers gets when giving him just a present. Loyalty means for a company “having trust be honest to its customers”. n Excellent products, services and a good quality builds up the ground for loyal customer but is not enough. The customer must believe to the brand must become an active player for the company and its products and services (word of mouth). Loyalty also means very intensive communication n Excellent products and services are not enough to “create” loyal customer. In addition, a company has to build up a two way communication with its customer. The communication flow can be the following: n Company asks - customer answers n Company says thank you - customer enjoys n Company improves - customers perceives n Company asks again - customer gets more and more loyal © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 9
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (1/7) What is loyalty … ? n Loyalty is the perception of trust and commitment to an institution or a person. The loyalty term comes historically from the relationship to its government and nationality. Loyalty is a feeling of being indepted something to somebody. n Loyalty doesn’t start with a first impression, but needs a long time to be built up. A company gets loyal customers, when these customers get more for their money, than they could expect before buying something. n Loyalty is not a short term oriented feeling, which a customers gets when giving him just a present. Loyalty means for a company “having trust be honest to its customers”. n Excellent products, services and a good quality builds up the ground for loyal customer but is not enough. The customer must believe to the brand must become an active player for the company and its products and services (word of mouth). Loyalty also means very intensive communication n Excellent products and services are not enough to “create” loyal customer. In addition, a company has to build up a two way communication with its customer. The communication flow can be the following: n Company asks - customer answers n Company says thank you - customer enjoys n Company improves - customers perceives n Company asks again - customer gets more and more loyal © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 9
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (2/7) Basic principles of a good loyalty programme A good customer loyalty programme works by improving the long-term relationship between the company and its target customers. A good loyalty programme is interesting for the target customer To be interesting to the target customer, the loyalty programme must. . . offer interesting rewards (a mixture of discounts, rewards and recognition) … that are achievable by the customer within their normal buying behaviour … offer good two-way channels of communication A good loyalty programme is hard to copy A loyalty programme is a powerful marketing instrument and should be hard to copy for competitors. The programme should therefore allow the company to leverage an inherent advantage that cannot easily be copied or improved upon by its competitors. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 10
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (2/7) Basic principles of a good loyalty programme A good customer loyalty programme works by improving the long-term relationship between the company and its target customers. A good loyalty programme is interesting for the target customer To be interesting to the target customer, the loyalty programme must. . . offer interesting rewards (a mixture of discounts, rewards and recognition) … that are achievable by the customer within their normal buying behaviour … offer good two-way channels of communication A good loyalty programme is hard to copy A loyalty programme is a powerful marketing instrument and should be hard to copy for competitors. The programme should therefore allow the company to leverage an inherent advantage that cannot easily be copied or improved upon by its competitors. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 10
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (3/7) It is attractive for the company n To be interesting for the company, the loyalty programme must be … affordable with limited long-term liability … flexible enough to cope with changes in the customer’s behaviour or in the competitive market, and … able to terminate the programme without incurring heavy closure costs or alienating the customer. Customer information is the key enabler n Although the best loyalty programmes are based on delivering superior value to the customer through the products offered, customer service and value-adding marketing communications are often forgotten. Most programmes start out by offering points for purchases which can be exchanged for rewards, to build an interactive relationship with the target customer. This facilitates the collection of customer information which can be leveraged to improve the company’s basic value proposition - better products, better customer service and more value-adding marketing communications at lower prices. Loyalty is not just customer satisfaction n Loyalty cannot be set equal with customer satisfaction. A satisfied customer doesn’t have to be loyal to a company. A loyal customer is one, who has the feeling of getting more from a company, than he/ she could expect. Satisfaction is therefore not enough to keep a customer loyal. AT&T had 95% satisfied customers, but lost 6% market share. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 11
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (3/7) It is attractive for the company n To be interesting for the company, the loyalty programme must be … affordable with limited long-term liability … flexible enough to cope with changes in the customer’s behaviour or in the competitive market, and … able to terminate the programme without incurring heavy closure costs or alienating the customer. Customer information is the key enabler n Although the best loyalty programmes are based on delivering superior value to the customer through the products offered, customer service and value-adding marketing communications are often forgotten. Most programmes start out by offering points for purchases which can be exchanged for rewards, to build an interactive relationship with the target customer. This facilitates the collection of customer information which can be leveraged to improve the company’s basic value proposition - better products, better customer service and more value-adding marketing communications at lower prices. Loyalty is not just customer satisfaction n Loyalty cannot be set equal with customer satisfaction. A satisfied customer doesn’t have to be loyal to a company. A loyal customer is one, who has the feeling of getting more from a company, than he/ she could expect. Satisfaction is therefore not enough to keep a customer loyal. AT&T had 95% satisfied customers, but lost 6% market share. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 11
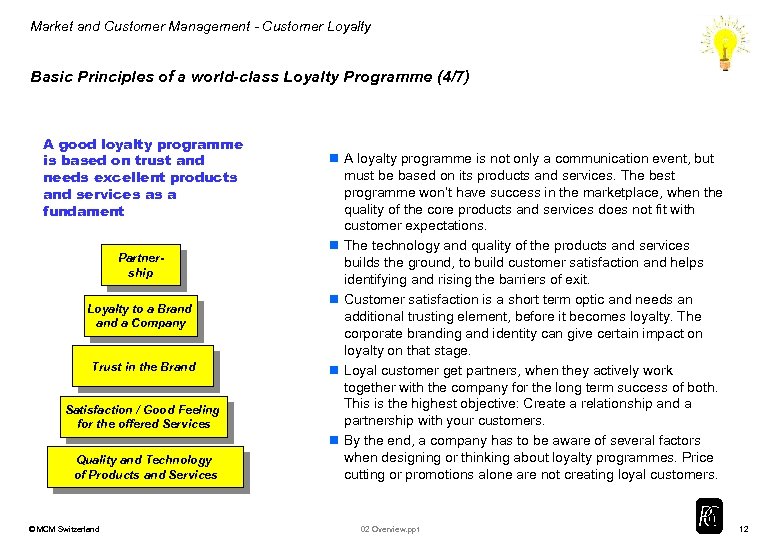 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (4/7) A good loyalty programme is based on trust and needs excellent products and services as a fundament Partnership Loyalty to a Brand a Company Trust in the Brand Satisfaction / Good Feeling for the offered Services Quality and Technology of Products and Services © MCM Switzerland n A loyalty programme is not only a communication event, but must be based on its products and services. The best programme won’t have success in the marketplace, when the quality of the core products and services does not fit with customer expectations. n The technology and quality of the products and services builds the ground, to build customer satisfaction and helps identifying and rising the barriers of exit. n Customer satisfaction is a short term optic and needs an additional trusting element, before it becomes loyalty. The corporate branding and identity can give certain impact on loyalty on that stage. n Loyal customer get partners, when they actively work together with the company for the long term success of both. This is the highest objective: Create a relationship and a partnership with your customers. n By the end, a company has to be aware of several factors when designing or thinking about loyalty programmes. Price cutting or promotions alone are not creating loyal customers. 02 Overview. ppt 12
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (4/7) A good loyalty programme is based on trust and needs excellent products and services as a fundament Partnership Loyalty to a Brand a Company Trust in the Brand Satisfaction / Good Feeling for the offered Services Quality and Technology of Products and Services © MCM Switzerland n A loyalty programme is not only a communication event, but must be based on its products and services. The best programme won’t have success in the marketplace, when the quality of the core products and services does not fit with customer expectations. n The technology and quality of the products and services builds the ground, to build customer satisfaction and helps identifying and rising the barriers of exit. n Customer satisfaction is a short term optic and needs an additional trusting element, before it becomes loyalty. The corporate branding and identity can give certain impact on loyalty on that stage. n Loyal customer get partners, when they actively work together with the company for the long term success of both. This is the highest objective: Create a relationship and a partnership with your customers. n By the end, a company has to be aware of several factors when designing or thinking about loyalty programmes. Price cutting or promotions alone are not creating loyal customers. 02 Overview. ppt 12
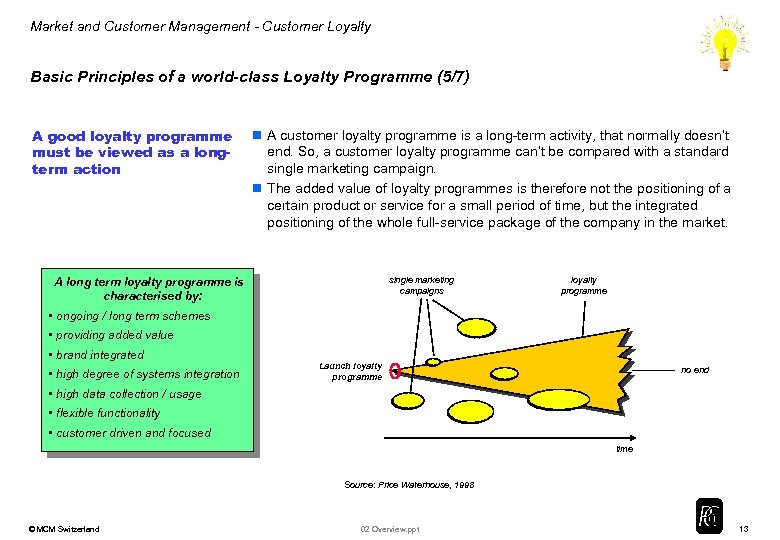 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (5/7) A good loyalty programme must be viewed as a longterm action n A customer loyalty programme is a long-term activity, that normally doesn’t end. So, a customer loyalty programme can’t be compared with a standard single marketing campaign. n The added value of loyalty programmes is therefore not the positioning of a certain product or service for a small period of time, but the integrated positioning of the whole full-service package of the company in the market. single marketing campaigns A long term loyalty programme is characterised by: loyalty programme • ongoing / long term schemes • providing added value • brand integrated • high degree of systems integration Launch loyalty programme no end • high data collection / usage • flexible functionality • customer driven and focused time Source: Price Waterhouse, 1998 © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 13
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (5/7) A good loyalty programme must be viewed as a longterm action n A customer loyalty programme is a long-term activity, that normally doesn’t end. So, a customer loyalty programme can’t be compared with a standard single marketing campaign. n The added value of loyalty programmes is therefore not the positioning of a certain product or service for a small period of time, but the integrated positioning of the whole full-service package of the company in the market. single marketing campaigns A long term loyalty programme is characterised by: loyalty programme • ongoing / long term schemes • providing added value • brand integrated • high degree of systems integration Launch loyalty programme no end • high data collection / usage • flexible functionality • customer driven and focused time Source: Price Waterhouse, 1998 © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 13
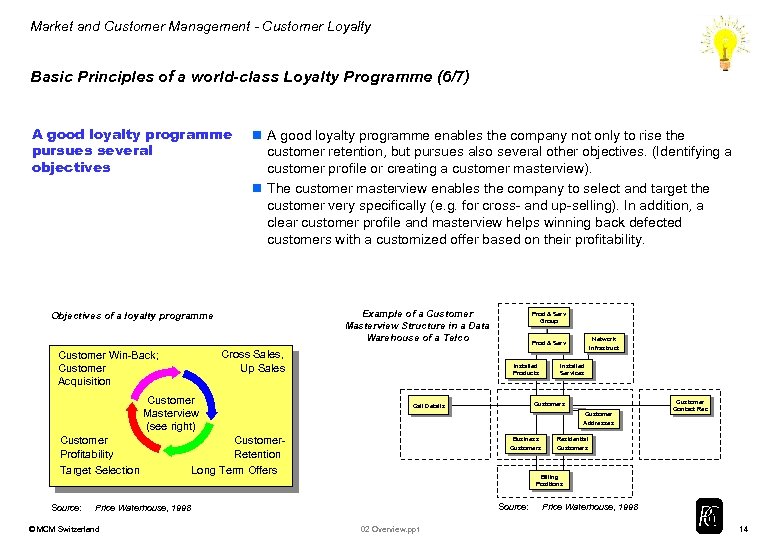 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (6/7) A good loyalty programme pursues several objectives n A good loyalty programme enables the company not only to rise the customer retention, but pursues also several other objectives. (Identifying a customer profile or creating a customer masterview). n The customer masterview enables the company to select and target the customer very specifically (e. g. for cross- and up-selling). In addition, a clear customer profile and masterview helps winning back defected customers with a customized offer based on their profitability. Example of a Customer Masterview Structure in a Data Warehouse of a Telco Objectives of a loyalty programme Cross Sales, Up Sales Customer Win-Back; Customer Acquisition Customer Masterview (see right) Customer Profitability Target Selection Source: Network Prod & Serv Installed Products Infrastruct Installed Services Customers Call Details Customer Contact Rec Addresses Customer. Retention Business Residential Customers Long Term Offers Billing Positions Source: Price Waterhouse, 1998 © MCM Switzerland Prod & Serv Group 02 Overview. ppt Price Waterhouse, 1998 14
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (6/7) A good loyalty programme pursues several objectives n A good loyalty programme enables the company not only to rise the customer retention, but pursues also several other objectives. (Identifying a customer profile or creating a customer masterview). n The customer masterview enables the company to select and target the customer very specifically (e. g. for cross- and up-selling). In addition, a clear customer profile and masterview helps winning back defected customers with a customized offer based on their profitability. Example of a Customer Masterview Structure in a Data Warehouse of a Telco Objectives of a loyalty programme Cross Sales, Up Sales Customer Win-Back; Customer Acquisition Customer Masterview (see right) Customer Profitability Target Selection Source: Network Prod & Serv Installed Products Infrastruct Installed Services Customers Call Details Customer Contact Rec Addresses Customer. Retention Business Residential Customers Long Term Offers Billing Positions Source: Price Waterhouse, 1998 © MCM Switzerland Prod & Serv Group 02 Overview. ppt Price Waterhouse, 1998 14
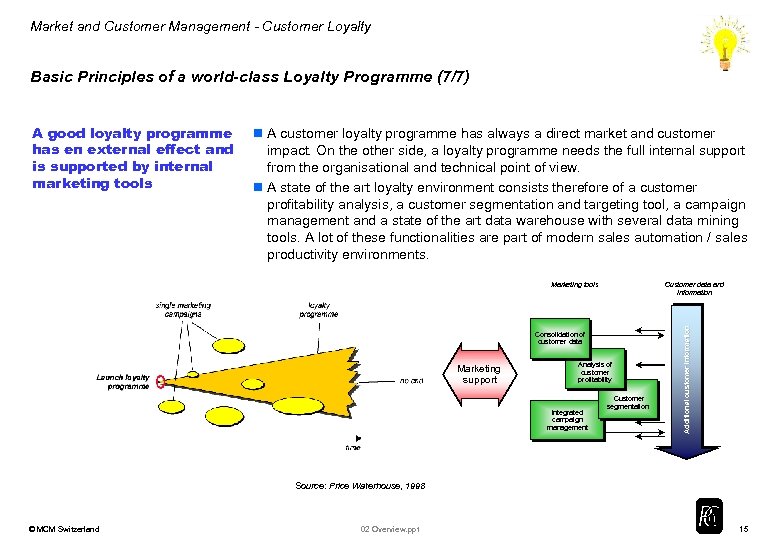 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (7/7) n A customer loyalty programme has always a direct market and customer impact. On the other side, a loyalty programme needs the full internal support from the organisational and technical point of view. n A state of the art loyalty environment consists therefore of a customer profitability analysis, a customer segmentation and targeting tool, a campaign management and a state of the art data warehouse with several data mining tools. A lot of these functionalities are part of modern sales automation / sales productivity environments. Marketing tools Customer data and information Consolidation of customer data Marketing support Analysis of customer profitability Integrated campaign management Customer segmentation Additional customer information A good loyalty programme has en external effect and is supported by internal marketing tools Source: Price Waterhouse, 1998 © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 15
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Basic Principles of a world-class Loyalty Programme (7/7) n A customer loyalty programme has always a direct market and customer impact. On the other side, a loyalty programme needs the full internal support from the organisational and technical point of view. n A state of the art loyalty environment consists therefore of a customer profitability analysis, a customer segmentation and targeting tool, a campaign management and a state of the art data warehouse with several data mining tools. A lot of these functionalities are part of modern sales automation / sales productivity environments. Marketing tools Customer data and information Consolidation of customer data Marketing support Analysis of customer profitability Integrated campaign management Customer segmentation Additional customer information A good loyalty programme has en external effect and is supported by internal marketing tools Source: Price Waterhouse, 1998 © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 15
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (1/8) A variety of loyalty schemes have been proofed in marketplace n The structure of loyalty programmes depend on several factors like … industry … customer behaviour and customer segments … market structure … company‘s strategy … timing n Loyalty programmes based on a point collection/ point redemption scheme are the most known ones. Nevertheless, several other loyalty programmes are possible and can be turned into market success. Examples for these programmes are shown below. ABB creates loyal customer with its “lead customer approach” © MCM Switzerland n The European industry giant Asea Brown Bovery (ABB) involves its most important customers in the construction of their latest products and services. E. g. the Swiss Railway Company was involved in the construction of the new electric railway during the whole construction and design process. The advantage for the customer was that they could give their inputs and needs directly and in an early production stage. n The advantage for ABB were that the Swiss Railway Corporation brought their extensive railway know-how into the construction and that they became a loyal customer. This example is typical for a cost intensive industry with only a limited amount of customers. 02 Overview. ppt 16 16
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (1/8) A variety of loyalty schemes have been proofed in marketplace n The structure of loyalty programmes depend on several factors like … industry … customer behaviour and customer segments … market structure … company‘s strategy … timing n Loyalty programmes based on a point collection/ point redemption scheme are the most known ones. Nevertheless, several other loyalty programmes are possible and can be turned into market success. Examples for these programmes are shown below. ABB creates loyal customer with its “lead customer approach” © MCM Switzerland n The European industry giant Asea Brown Bovery (ABB) involves its most important customers in the construction of their latest products and services. E. g. the Swiss Railway Company was involved in the construction of the new electric railway during the whole construction and design process. The advantage for the customer was that they could give their inputs and needs directly and in an early production stage. n The advantage for ABB were that the Swiss Railway Corporation brought their extensive railway know-how into the construction and that they became a loyal customer. This example is typical for a cost intensive industry with only a limited amount of customers. 02 Overview. ppt 16 16
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (2/8) Sabre and Fed. Ex create loyal customers by involving them in their value creating service process n Federal Express has with its world famous tracking system a powerful loyalty programme. The customer can track his letters and packages and check where they currently are. n The advantage of this programme is, that the customer remains loyal to Fed. Ex. On the other hand, Fed. Ex gets less request from customers and can concentrate on controlling the delivery process better and less cost intensively. n A similar loyalty strategy has Sabre with its flight booking system. The travel agency remain loyal to the company because of the handy online information about the available flights and seats. Microsoft creates “loyal” customer by setting industry wide standards n Microsoft has rigorous approach of loyalty creation. The company sets industry standards with its Microsoft Office. The customers are not yet able to switch to other operating systems because of this standard. n The advantage for the customer is a cheap operating system that offers a wide range of software on this platform. Microsoft's advantage is the high revenue stream created by the standard. Swatch built up a “cult” with its watches n Swatch has a more informal approach for customer loyalty. With their fast changing sets of trendy watches the company built up a „watch cult“ and attracted a lot of loyal collectors all over the world. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 17 17
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (2/8) Sabre and Fed. Ex create loyal customers by involving them in their value creating service process n Federal Express has with its world famous tracking system a powerful loyalty programme. The customer can track his letters and packages and check where they currently are. n The advantage of this programme is, that the customer remains loyal to Fed. Ex. On the other hand, Fed. Ex gets less request from customers and can concentrate on controlling the delivery process better and less cost intensively. n A similar loyalty strategy has Sabre with its flight booking system. The travel agency remain loyal to the company because of the handy online information about the available flights and seats. Microsoft creates “loyal” customer by setting industry wide standards n Microsoft has rigorous approach of loyalty creation. The company sets industry standards with its Microsoft Office. The customers are not yet able to switch to other operating systems because of this standard. n The advantage for the customer is a cheap operating system that offers a wide range of software on this platform. Microsoft's advantage is the high revenue stream created by the standard. Swatch built up a “cult” with its watches n Swatch has a more informal approach for customer loyalty. With their fast changing sets of trendy watches the company built up a „watch cult“ and attracted a lot of loyal collectors all over the world. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 17 17
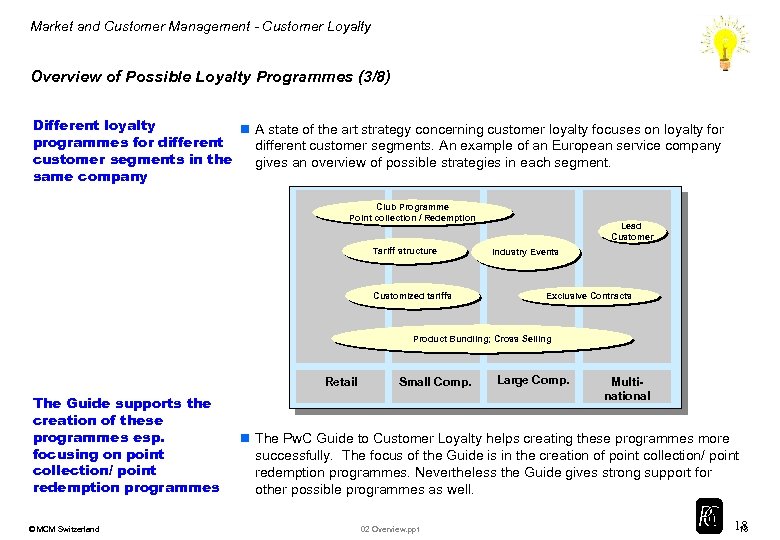 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (3/8) Different loyalty n A state of the art strategy concerning customer loyalty focuses on loyalty for programmes for different customer segments. An example of an European service company customer segments in the gives an overview of possible strategies in each segment. same company Club Programme Point collection / Redemption Tariff structure Customized tariffs Lead Customer Industry Events Exclusive Contracts Product Bundling; Cross Selling Retail The Guide supports the creation of these programmes esp. focusing on point collection/ point redemption programmes © MCM Switzerland Small Comp. Large Comp. Multinational n The Pw. C Guide to Customer Loyalty helps creating these programmes more successfully. The focus of the Guide is in the creation of point collection/ point redemption programmes. Nevertheless the Guide gives strong support for other possible programmes as well. 02 Overview. ppt 18 18
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (3/8) Different loyalty n A state of the art strategy concerning customer loyalty focuses on loyalty for programmes for different customer segments. An example of an European service company customer segments in the gives an overview of possible strategies in each segment. same company Club Programme Point collection / Redemption Tariff structure Customized tariffs Lead Customer Industry Events Exclusive Contracts Product Bundling; Cross Selling Retail The Guide supports the creation of these programmes esp. focusing on point collection/ point redemption programmes © MCM Switzerland Small Comp. Large Comp. Multinational n The Pw. C Guide to Customer Loyalty helps creating these programmes more successfully. The focus of the Guide is in the creation of point collection/ point redemption programmes. Nevertheless the Guide gives strong support for other possible programmes as well. 02 Overview. ppt 18 18
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (4/8) Tesco as a first mover in customer loyalty - an example Launch of Tesco Club n February 1995 Loyalty Scheme n 1 pound purchase = 1 point = worth of 1 penny n if 150 points and more per quarter, than the customer gets vouchers for use at the store together with money off product vouchers (money off vouchers are funded by manufacturers and suppliers) n Quarterly magazine n Special rules/schemes for students or pensioners n Associate cards for husband wife n Relationships with non-competing organisations such as B&G for home improvement goods and holidays Customer Reaction n February 1997: 9. 5 Mio. members although discount is just 1% (£ 3 - £ 4 savings as a quarterly average) Costs for Tesco n Earned vouchers 1996/7: £ 95 Mio. n Money of vouchers 1996/7: £ 162 Mio. (funded by manufacturers / suppliers) n August 1997 mailing distributed £ 75 Mio. vouchers n Important are also the cost at initial stages for computer developments needed to allow the cards to be recognised and processed at the POS © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 19 19
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (4/8) Tesco as a first mover in customer loyalty - an example Launch of Tesco Club n February 1995 Loyalty Scheme n 1 pound purchase = 1 point = worth of 1 penny n if 150 points and more per quarter, than the customer gets vouchers for use at the store together with money off product vouchers (money off vouchers are funded by manufacturers and suppliers) n Quarterly magazine n Special rules/schemes for students or pensioners n Associate cards for husband wife n Relationships with non-competing organisations such as B&G for home improvement goods and holidays Customer Reaction n February 1997: 9. 5 Mio. members although discount is just 1% (£ 3 - £ 4 savings as a quarterly average) Costs for Tesco n Earned vouchers 1996/7: £ 95 Mio. n Money of vouchers 1996/7: £ 162 Mio. (funded by manufacturers / suppliers) n August 1997 mailing distributed £ 75 Mio. vouchers n Important are also the cost at initial stages for computer developments needed to allow the cards to be recognised and processed at the POS © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 19 19
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (5/8) Tesco as a first mover in customer loyalty - an example Benefits for Tesco n Opportunity to know each of its customers spending habits perfectly. n The main benefit comes in the long term from: n the ability to communicate with customers on a one to one basis. n and to know the names and addresses of the most profitable customers in each store. n Payback from the positive reaction of customers when they feel their custom is appreciated and rewarded and the profits on incremental sales is not so important. This advantage is lost as soon as the first mover advantage disappear when the main rivals also offer similar rebate/discounts schemes. n Direction of the advertising budget can be aimed precisely. Tesco uses now far more cost effective advertising campaigns using direct contact methods such as direct mail and outward bound telemarketing. How Tesco uses the data n Analyse composition of a customer shopping basket n Identifying a “golden moment”, the point in time at which a customer is particularly susceptible to an offer for a particular product. (Tracking of a childless couple) n Organisation of club card customer evenings concentrating on topics such as hair styling or wine tasting, etc. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 20 20
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (5/8) Tesco as a first mover in customer loyalty - an example Benefits for Tesco n Opportunity to know each of its customers spending habits perfectly. n The main benefit comes in the long term from: n the ability to communicate with customers on a one to one basis. n and to know the names and addresses of the most profitable customers in each store. n Payback from the positive reaction of customers when they feel their custom is appreciated and rewarded and the profits on incremental sales is not so important. This advantage is lost as soon as the first mover advantage disappear when the main rivals also offer similar rebate/discounts schemes. n Direction of the advertising budget can be aimed precisely. Tesco uses now far more cost effective advertising campaigns using direct contact methods such as direct mail and outward bound telemarketing. How Tesco uses the data n Analyse composition of a customer shopping basket n Identifying a “golden moment”, the point in time at which a customer is particularly susceptible to an offer for a particular product. (Tracking of a childless couple) n Organisation of club card customer evenings concentrating on topics such as hair styling or wine tasting, etc. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 20 20
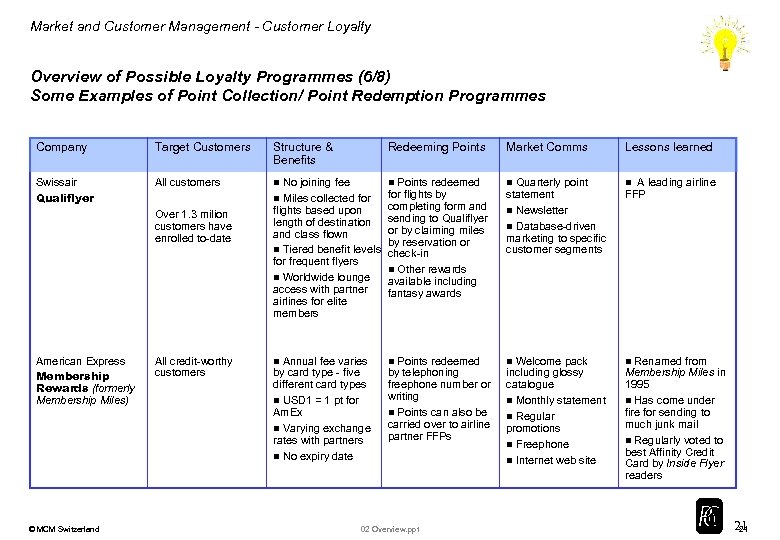 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (6/8) Some Examples of Point Collection/ Point Redemption Programmes Company Target Customers Structure & Benefits Redeeming Points Market Comms Lessons learned Swissair Qualiflyer All customers n No joining fee n Miles collected for flights based upon length of destination and class flown n Tiered benefit levels for frequent flyers n Worldwide lounge access with partner airlines for elite members n Points redeemed for flights by completing form and sending to Qualiflyer or by claiming miles by reservation or check-in n Other rewards available including fantasy awards n Quarterly point statement n Newsletter n Database-driven marketing to specific customer segments n Annual fee varies by card type - five different card types n USD 1 = 1 pt for Am. Ex n Varying exchange rates with partners n No expiry date n Points redeemed by telephoning freephone number or writing n Points can also be carried over to airline partner FFPs n Welcome pack including glossy catalogue n Monthly statement n Regular promotions n Freephone n Internet web site n Over 1. 3 milion customers have enrolled to-date American Express Membership Rewards (formerly Membership Miles) © MCM Switzerland All credit-worthy customers n 02 Overview. ppt A leading airline FFP Renamed from Membership Miles in 1995 n Has come under fire for sending to much junk mail n Regularly voted to best Affinity Credit Card by Inside Flyer readers 21 21
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (6/8) Some Examples of Point Collection/ Point Redemption Programmes Company Target Customers Structure & Benefits Redeeming Points Market Comms Lessons learned Swissair Qualiflyer All customers n No joining fee n Miles collected for flights based upon length of destination and class flown n Tiered benefit levels for frequent flyers n Worldwide lounge access with partner airlines for elite members n Points redeemed for flights by completing form and sending to Qualiflyer or by claiming miles by reservation or check-in n Other rewards available including fantasy awards n Quarterly point statement n Newsletter n Database-driven marketing to specific customer segments n Annual fee varies by card type - five different card types n USD 1 = 1 pt for Am. Ex n Varying exchange rates with partners n No expiry date n Points redeemed by telephoning freephone number or writing n Points can also be carried over to airline partner FFPs n Welcome pack including glossy catalogue n Monthly statement n Regular promotions n Freephone n Internet web site n Over 1. 3 milion customers have enrolled to-date American Express Membership Rewards (formerly Membership Miles) © MCM Switzerland All credit-worthy customers n 02 Overview. ppt A leading airline FFP Renamed from Membership Miles in 1995 n Has come under fire for sending to much junk mail n Regularly voted to best Affinity Credit Card by Inside Flyer readers 21 21
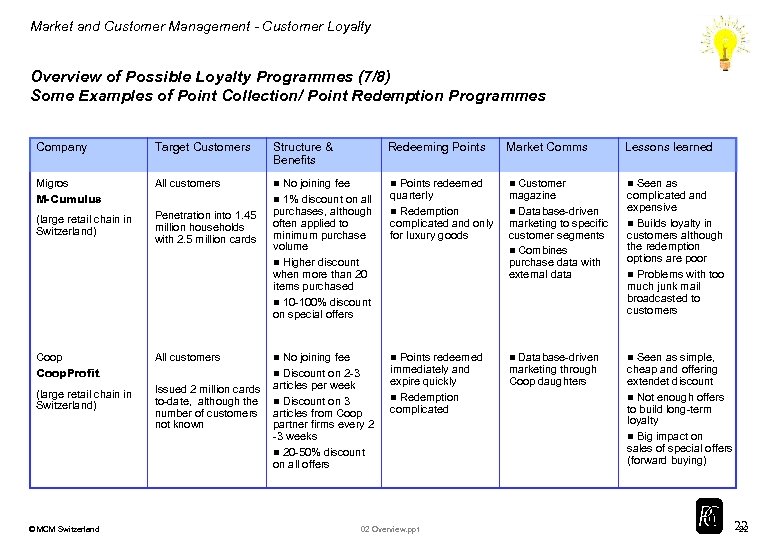 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (7/8) Some Examples of Point Collection/ Point Redemption Programmes Company Target Customers Structure & Benefits Redeeming Points Market Comms Lessons learned Migros M-Cumulus All customers n n Customer magazine n Database-driven marketing to specific customer segments n Combines purchase data with external data n Penetration into 1. 45 million households with 2. 5 million cards Points redeemed quarterly n Redemption complicated and only for luxury goods n (large retail chain in Switzerland) No joining fee n 1% discount on all purchases, although often applied to minimum purchase volume n Higher discount when more than 20 items purchased n 10 -100% discount on special offers Coop. Profit All customers n Database-driven marketing through Coop daughters n Issued 2 million cards to-date, although the number of customers not known Points redeemed immediately and expire quickly n Redemption complicated n (large retail chain in Switzerland) No joining fee n Discount on 2 -3 articles per week n Discount on 3 articles from Coop partner firms every 2 -3 weeks n 20 -50% discount on all offers © MCM Switzerland n 02 Overview. ppt Seen as complicated and expensive n Builds loyalty in customers although the redemption options are poor n Problems with too much junk mail broadcasted to customers Seen as simple, cheap and offering extendet discount n Not enough offers to build long-term loyalty n Big impact on sales of special offers (forward buying) 22 22
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (7/8) Some Examples of Point Collection/ Point Redemption Programmes Company Target Customers Structure & Benefits Redeeming Points Market Comms Lessons learned Migros M-Cumulus All customers n n Customer magazine n Database-driven marketing to specific customer segments n Combines purchase data with external data n Penetration into 1. 45 million households with 2. 5 million cards Points redeemed quarterly n Redemption complicated and only for luxury goods n (large retail chain in Switzerland) No joining fee n 1% discount on all purchases, although often applied to minimum purchase volume n Higher discount when more than 20 items purchased n 10 -100% discount on special offers Coop. Profit All customers n Database-driven marketing through Coop daughters n Issued 2 million cards to-date, although the number of customers not known Points redeemed immediately and expire quickly n Redemption complicated n (large retail chain in Switzerland) No joining fee n Discount on 2 -3 articles per week n Discount on 3 articles from Coop partner firms every 2 -3 weeks n 20 -50% discount on all offers © MCM Switzerland n 02 Overview. ppt Seen as complicated and expensive n Builds loyalty in customers although the redemption options are poor n Problems with too much junk mail broadcasted to customers Seen as simple, cheap and offering extendet discount n Not enough offers to build long-term loyalty n Big impact on sales of special offers (forward buying) 22 22
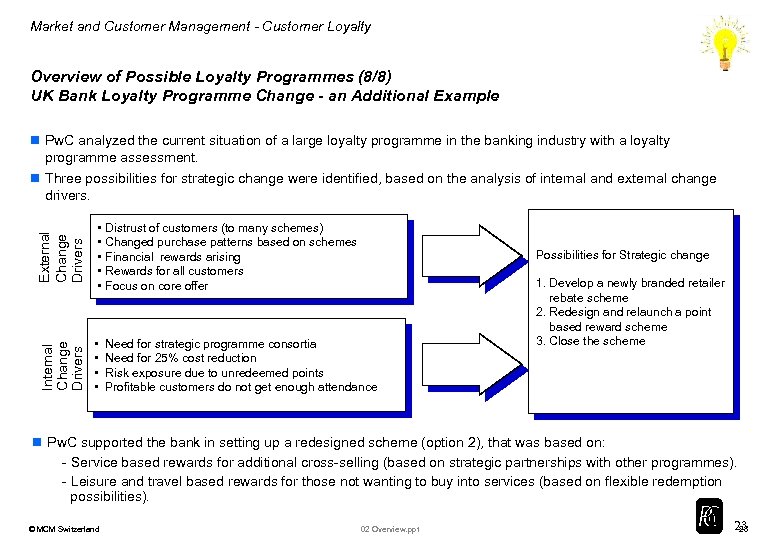 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (8/8) UK Bank Loyalty Programme Change - an Additional Example External Change Drivers • Distrust of customers (to many schemes) • Changed purchase patterns based on schemes • Financial rewards arising • Rewards for all customers • Focus on core offer Internal Change Drivers n Pw. C analyzed the current situation of a large loyalty programme in the banking industry with a loyalty programme assessment. n Three possibilities for strategic change were identified, based on the analysis of internal and external change drivers. • • Possibilities for Strategic change Need for strategic programme consortia Need for 25% cost reduction Risk exposure due to unredeemed points Profitable customers do not get enough attendance 1. Develop a newly branded retailer rebate scheme 2. Redesign and relaunch a point based reward scheme 3. Close the scheme n Pw. C supported the bank in setting up a redesigned scheme (option 2), that was based on: - Service based rewards for additional cross-selling (based on strategic partnerships with other programmes). - Leisure and travel based rewards for those not wanting to buy into services (based on flexible redemption possibilities). © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 23 23
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Overview of Possible Loyalty Programmes (8/8) UK Bank Loyalty Programme Change - an Additional Example External Change Drivers • Distrust of customers (to many schemes) • Changed purchase patterns based on schemes • Financial rewards arising • Rewards for all customers • Focus on core offer Internal Change Drivers n Pw. C analyzed the current situation of a large loyalty programme in the banking industry with a loyalty programme assessment. n Three possibilities for strategic change were identified, based on the analysis of internal and external change drivers. • • Possibilities for Strategic change Need for strategic programme consortia Need for 25% cost reduction Risk exposure due to unredeemed points Profitable customers do not get enough attendance 1. Develop a newly branded retailer rebate scheme 2. Redesign and relaunch a point based reward scheme 3. Close the scheme n Pw. C supported the bank in setting up a redesigned scheme (option 2), that was based on: - Service based rewards for additional cross-selling (based on strategic partnerships with other programmes). - Leisure and travel based rewards for those not wanting to buy into services (based on flexible redemption possibilities). © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 23 23
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty and Industry specific Situations (1/2) Each industry has its specific drivers which influence a loyalty strategy n In each industry a loyalty programme and strategy will look differently based on the specific forces of competition (e. g. competitors, barriers of entry, barriers of exit, substitutes, liberalisation and deregulation). Considering the industry and their competitive forces is therefore crucial when defining an effective loyalty programme. Banking - limited amount of services and high transparency n The Banking industry is confronting price aggressive new competitors (e. g. discount brokers, phone banking). They are using the transparency in the banking products and services as an advantage. Loyalty programmes will have cross industry character (e. g. in combination with hotels, airlines or others / and including attractive combinations, e. g. with credit card options). Insurance - long-term contracts and low involvement n The insurance industry is considered as a one time involvement business (that means involvement is high when defining a contract). Loyalty can therefore be created with long-term contracts and active cross selling of insurance services. Telecom - deregulation, cross selling potential and technology n In Telcos, the prices are coming down and defection of customers based on price hopping is very dangerous for the contribution margin. Loyalty programmes must have therefore a long-term benefit and enforce the economic advantages of having more than one service from the operator. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 24
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty and Industry specific Situations (1/2) Each industry has its specific drivers which influence a loyalty strategy n In each industry a loyalty programme and strategy will look differently based on the specific forces of competition (e. g. competitors, barriers of entry, barriers of exit, substitutes, liberalisation and deregulation). Considering the industry and their competitive forces is therefore crucial when defining an effective loyalty programme. Banking - limited amount of services and high transparency n The Banking industry is confronting price aggressive new competitors (e. g. discount brokers, phone banking). They are using the transparency in the banking products and services as an advantage. Loyalty programmes will have cross industry character (e. g. in combination with hotels, airlines or others / and including attractive combinations, e. g. with credit card options). Insurance - long-term contracts and low involvement n The insurance industry is considered as a one time involvement business (that means involvement is high when defining a contract). Loyalty can therefore be created with long-term contracts and active cross selling of insurance services. Telecom - deregulation, cross selling potential and technology n In Telcos, the prices are coming down and defection of customers based on price hopping is very dangerous for the contribution margin. Loyalty programmes must have therefore a long-term benefit and enforce the economic advantages of having more than one service from the operator. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 24
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty and Industry specific Situations (2/2) Aircraft maintenance n The aircraft maintenance business because global and predictable. An transparency, globalization, established relationship with airline operators or even manufacturers is key account management crucial for success. Smaller airlines focus more on total care packages of and full service packages aircraft overhaul, engines and component maintenance. A key account management with personal professional services builds up loyalty and establishes the engineering capabilities in the operations mindset. Retail - different structure, forward integration and new channels © MCM Switzerland n The retail industry is structured differently in each nation. Manufacturers often try to integrate forward and getting in direct contact with customers (e. g. factory outlet). On the other side, customers will get direct access to globally offered services by new media (e. g. internet). Retail companies must therefore focus on getting customers into their stores by knowing their buying behaviour better than competitors. 02 Overview. ppt 25
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty and Industry specific Situations (2/2) Aircraft maintenance n The aircraft maintenance business because global and predictable. An transparency, globalization, established relationship with airline operators or even manufacturers is key account management crucial for success. Smaller airlines focus more on total care packages of and full service packages aircraft overhaul, engines and component maintenance. A key account management with personal professional services builds up loyalty and establishes the engineering capabilities in the operations mindset. Retail - different structure, forward integration and new channels © MCM Switzerland n The retail industry is structured differently in each nation. Manufacturers often try to integrate forward and getting in direct contact with customers (e. g. factory outlet). On the other side, customers will get direct access to globally offered services by new media (e. g. internet). Retail companies must therefore focus on getting customers into their stores by knowing their buying behaviour better than competitors. 02 Overview. ppt 25
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pros and Cons of Loyalty Programmes (1/2) Loyalty programmes might have a positive impact on profitability Pros of loyalty programmes: n Marketing and sales cost advantage: Retaining customers is cheaper than acquiring new ones. n Revenue and turnover advantage: Loyal customer buy more due to cross selling and up selling possibilities. In addition, not defecting customers will have their revenues for a longer period in the company. n Getting a better insight about customer behaviour and getting a better link between pre-sales, sales and after-sales. Gathering customer data as well as the risk of being copied by other competitors are the most important cons of loyalty programmes Cons of loyalty programmes: n Loyalty programmes are expensive and have a long-term perspective. It often takes its time, until these investments show additional profitability. n Loyalty programmes face the risk of being copied by other companies. The sustainability of the advantages are at risk. n The gathering of customer information in loyalty programmes can have legal impacts. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 26
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pros and Cons of Loyalty Programmes (1/2) Loyalty programmes might have a positive impact on profitability Pros of loyalty programmes: n Marketing and sales cost advantage: Retaining customers is cheaper than acquiring new ones. n Revenue and turnover advantage: Loyal customer buy more due to cross selling and up selling possibilities. In addition, not defecting customers will have their revenues for a longer period in the company. n Getting a better insight about customer behaviour and getting a better link between pre-sales, sales and after-sales. Gathering customer data as well as the risk of being copied by other competitors are the most important cons of loyalty programmes Cons of loyalty programmes: n Loyalty programmes are expensive and have a long-term perspective. It often takes its time, until these investments show additional profitability. n Loyalty programmes face the risk of being copied by other companies. The sustainability of the advantages are at risk. n The gathering of customer information in loyalty programmes can have legal impacts. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 26
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pros and Cons of Loyalty Programmes (2/2) Will a loyalty programme help? Situations when a loyalty programme will help n When loyalty programme directly supports the company’s value proposition for target customers n When the relationship increases the perceived value - in the mindset of the customers n When the target customer’s lifetime value is high n When customer retention costs are less than acquisition costs n When its possible rise barriers of exit for the customer Or just add to your costs? Situations when a loyalty programme will not help n When target customers buy many brands in the category (no brand loyalty) n When brands imitate each other’s strategies - any moves will be quickly neutralised by competitors n When technology changes lead to better price or performance - better value is the key Remark: Some additional points, when loyalty programmes will help or not, are listed in the evaluate stage. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 27
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pros and Cons of Loyalty Programmes (2/2) Will a loyalty programme help? Situations when a loyalty programme will help n When loyalty programme directly supports the company’s value proposition for target customers n When the relationship increases the perceived value - in the mindset of the customers n When the target customer’s lifetime value is high n When customer retention costs are less than acquisition costs n When its possible rise barriers of exit for the customer Or just add to your costs? Situations when a loyalty programme will not help n When target customers buy many brands in the category (no brand loyalty) n When brands imitate each other’s strategies - any moves will be quickly neutralised by competitors n When technology changes lead to better price or performance - better value is the key Remark: Some additional points, when loyalty programmes will help or not, are listed in the evaluate stage. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 27
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Customer Perception of Loyalty Programmes - The Loyalty Paradox (1/3) Are you making realistic assumptions about the programme, its members and your ability to influence them? © MCM Switzerland Most loyalty programmes are based upon a number of assumptions, which have very little documented proof for reality or relevance. Examples for assumptions which must be double checked when comparing pros and cons of possible loyalty programmes are listed below: n Many customers want a two-way, interactive relationship with the loyalty programme provider. n A high proportion of these customers are exclusively loyal to a single brand over extended periods of time. n The core group of loyal buyers are the most profitable group because Ø there are many of them Ø they are heavy and frequent buyers Ø marketing costs are lower Ø they are less price sensitive Ø they provide the company with new customers the through positive word of mouth n It is possible to influence their behaviour and to persuade them to buy more n Database marketing can be used to communicate directly with these core customers, to develop a dialogue and to influence their buying behaviour. 02 Overview. ppt 28
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Customer Perception of Loyalty Programmes - The Loyalty Paradox (1/3) Are you making realistic assumptions about the programme, its members and your ability to influence them? © MCM Switzerland Most loyalty programmes are based upon a number of assumptions, which have very little documented proof for reality or relevance. Examples for assumptions which must be double checked when comparing pros and cons of possible loyalty programmes are listed below: n Many customers want a two-way, interactive relationship with the loyalty programme provider. n A high proportion of these customers are exclusively loyal to a single brand over extended periods of time. n The core group of loyal buyers are the most profitable group because Ø there are many of them Ø they are heavy and frequent buyers Ø marketing costs are lower Ø they are less price sensitive Ø they provide the company with new customers the through positive word of mouth n It is possible to influence their behaviour and to persuade them to buy more n Database marketing can be used to communicate directly with these core customers, to develop a dialogue and to influence their buying behaviour. 02 Overview. ppt 28
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Customer Perception of Loyalty Programmes - The Loyalty Paradox (2/3) The Loyalty Paradox Companies and Customers have different understanding about Loyalty n Companies are attempting to engender loyalty, while consumers do not use the term ‘loyalty’ when describing their feelings for relationship with a company. n Current company practice concentrates on rewards eg. discounts, points, coupons, etc. but our research suggests the importance of core products and service benefits and the emotional components of trust and confidence to consumers n Communications with companies are welcomed by the majority yet customers do not perceive that they have a relationship with a company despite the fact that companies have been advocating relationship marketing and its benefits n Some information about the perception of customer loyalty is listed below (next page) © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 29
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Customer Perception of Loyalty Programmes - The Loyalty Paradox (2/3) The Loyalty Paradox Companies and Customers have different understanding about Loyalty n Companies are attempting to engender loyalty, while consumers do not use the term ‘loyalty’ when describing their feelings for relationship with a company. n Current company practice concentrates on rewards eg. discounts, points, coupons, etc. but our research suggests the importance of core products and service benefits and the emotional components of trust and confidence to consumers n Communications with companies are welcomed by the majority yet customers do not perceive that they have a relationship with a company despite the fact that companies have been advocating relationship marketing and its benefits n Some information about the perception of customer loyalty is listed below (next page) © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 29
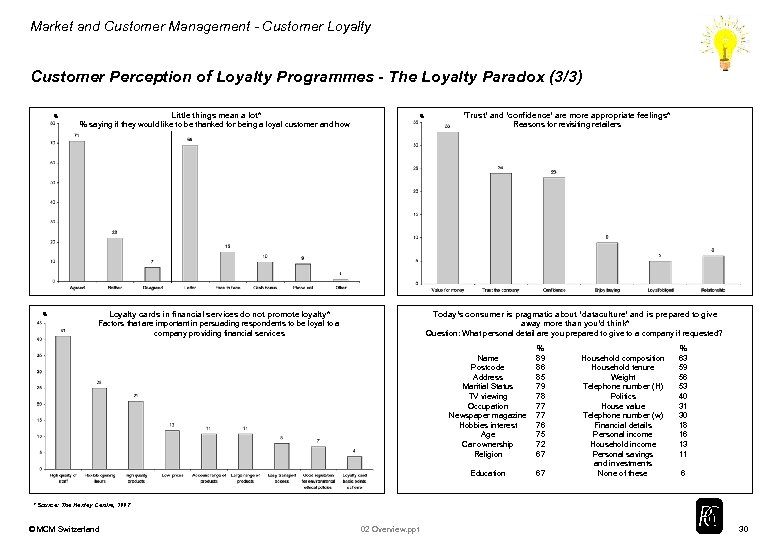 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Customer Perception of Loyalty Programmes - The Loyalty Paradox (3/3) % % Little things mean a lot* % saying if they would like to be thanked for being a loyal customer and how % Loyalty cards in financial services do not promote loyalty* Factors that are important in persuading respondents to be loyal to a company providing financial services ‘Trust’ and ‘confidence’ are more appropriate feelings* Reasons for revisiting retailers Today’s consumer is pragmatic about ‘dataculture’ and is prepared to give away more than you’d think* Question: What personal detail are you prepared to give to a company if requested? Name Postcode Address Maritial Status TV viewing Occupation Newspaper magazine Hobbies interest Age Car ownership Religion % 89 86 85 79 78 77 77 76 75 72 67 Education 67 Household composition Household tenure Weight Telephone number (H) Politics House value Telephone number (w) Financial details Personal income Household income Personal savings and investments None of these % 63 59 56 53 40 31 30 18 16 13 11 6 * Source: The Henley Centre, 1997 © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 30
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Customer Perception of Loyalty Programmes - The Loyalty Paradox (3/3) % % Little things mean a lot* % saying if they would like to be thanked for being a loyal customer and how % Loyalty cards in financial services do not promote loyalty* Factors that are important in persuading respondents to be loyal to a company providing financial services ‘Trust’ and ‘confidence’ are more appropriate feelings* Reasons for revisiting retailers Today’s consumer is pragmatic about ‘dataculture’ and is prepared to give away more than you’d think* Question: What personal detail are you prepared to give to a company if requested? Name Postcode Address Maritial Status TV viewing Occupation Newspaper magazine Hobbies interest Age Car ownership Religion % 89 86 85 79 78 77 77 76 75 72 67 Education 67 Household composition Household tenure Weight Telephone number (H) Politics House value Telephone number (w) Financial details Personal income Household income Personal savings and investments None of these % 63 59 56 53 40 31 30 18 16 13 11 6 * Source: The Henley Centre, 1997 © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 30
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Some Benchmark Figures (1/3) Benchmarks for increased sales volume due to loyalty programmes © MCM Switzerland n British Airways - Executive Club provides £ 300 million revenue and supports a further £ 2 billion in revenue; costs £ 50 million per annum employing 100 people n Wells Fargo Bank - saved US$ 84 millions through offering online banking services to target customers; sales rate went up from 1. 8 to 2. 4 services per customer; aggregated customer information and personalised information has allowed to develop close customer relationships n NOP research - supermarket cards have failed to have a significant effect on shopping behaviour. n Boots Advantage - trials with 94, 000 customers produced an increase of 3% in sales; official target set to 4% for launch. n Safeway measures success not in response to promotions but in influence on buying behaviour of a wider circle of buyers (friends and family). n American Express Membership Rewards - introduction of programme increased card spend by 40%. n JD Power - loyal buyers of cars spend in average US$ 1, 200 more per vehicle than buyers who have switched from other brands. 02 Overview. ppt 31
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Some Benchmark Figures (1/3) Benchmarks for increased sales volume due to loyalty programmes © MCM Switzerland n British Airways - Executive Club provides £ 300 million revenue and supports a further £ 2 billion in revenue; costs £ 50 million per annum employing 100 people n Wells Fargo Bank - saved US$ 84 millions through offering online banking services to target customers; sales rate went up from 1. 8 to 2. 4 services per customer; aggregated customer information and personalised information has allowed to develop close customer relationships n NOP research - supermarket cards have failed to have a significant effect on shopping behaviour. n Boots Advantage - trials with 94, 000 customers produced an increase of 3% in sales; official target set to 4% for launch. n Safeway measures success not in response to promotions but in influence on buying behaviour of a wider circle of buyers (friends and family). n American Express Membership Rewards - introduction of programme increased card spend by 40%. n JD Power - loyal buyers of cars spend in average US$ 1, 200 more per vehicle than buyers who have switched from other brands. 02 Overview. ppt 31
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Some Benchmark Figures (2/3) Benchmarks for reduced customer defection rate due to loyalty programmes © MCM Switzerland n Jones Intercable, Fla, USA - offers seasonal rates and bulk billing for condo and homeowners associations; churn rates fallen from 4. 4% in April 96 to 2. 2% in April 97. n Tominaga M, ‘Die Kundenfeindliche Gesellschaft’ - customers defect because of failures in service (68%), failures in products (14%), wrong pricing (9%), changing buying requirements (5%), change of address (3%), death (1%). n Telecommunications, Nov 1996 - mobile customers defect because of price (40. 9%), geographic coverage and network problems (19. 3%), customer service problems (10. 2%), voice quality (5. 7%), incorrect billing (5. 7%) and other. 02 Overview. ppt 32
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Some Benchmark Figures (2/3) Benchmarks for reduced customer defection rate due to loyalty programmes © MCM Switzerland n Jones Intercable, Fla, USA - offers seasonal rates and bulk billing for condo and homeowners associations; churn rates fallen from 4. 4% in April 96 to 2. 2% in April 97. n Tominaga M, ‘Die Kundenfeindliche Gesellschaft’ - customers defect because of failures in service (68%), failures in products (14%), wrong pricing (9%), changing buying requirements (5%), change of address (3%), death (1%). n Telecommunications, Nov 1996 - mobile customers defect because of price (40. 9%), geographic coverage and network problems (19. 3%), customer service problems (10. 2%), voice quality (5. 7%), incorrect billing (5. 7%) and other. 02 Overview. ppt 32
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Some Benchmark Figures (3/3) Pricewaterhouse. Coopers has knowledge about several customer loyalty programmes. Out of these programmes, the following benchmarks are collected: Programme objectives: Benchmarks: © MCM Switzerland Higher average customer turnover due to cross-selling/ up-selling Airline in Europe: · 72% of the loyalty members spend club products and services instead of services of the competitors. The share of wallet is rising. Keebler (US; Food): · After launching a loyalty programme for a kids club, the turnover in this segment rose 100% and the market share rose from 21 to 29%. Burger Kids Club (US; Food): · The turnover tripled after launching a loyalty programme in the youth segment. Marks and Spencer (Retail Shops): · The turnover of loyalty club members is three times higher than for non-club members. Nieman Marcus direct: · After launching the In Circle Programme, the average turnover of a club member rose 25%. Amexco: · After launching a loyalty programme, the average turnover of a club member rose 55%. European Bank: · Loyalty programme members use the basic bank products and services between 100 -400% more than non-club members. European Telco: · The planned cross selling effect after launching a loyalty programme is between 5 -15% per year. Due to more loyal customers, win-back costs don’t arise Members in loyalty programmes defect less often than non- members Swiss Bank: · The set-up of a new bank account costs about 400 Swiss Francs. France Telecom (Source: Datamonitor): · The costs for customer win-back in mobile communications business is between 1’ 500 and 2’ 200 French Francs. US Telco (Quelle: Telecom Magazine): · The costs for customer win back in mobile communications business is between 300 and 600 US Dollars. The costs for customer retention is between 50 and 100 Dollar. · 60% of the customer defection is within the first three months. By focusing to the customers, the churn in the US mobile communications market could be reduced from 50 to 30%. Customer Retention Costs (Gartner): · To win back a new customer is 4 -10 times more expensive, than to hold an existing customer. MCI (US Telecommunication): · MCI gives 2‘ 000 points for new customers as a win back or acquisition present. · If a customer uses these points for miles in frequent flyer programmes, the value is about 400 US $. Swiss Bank: · The normal defection rate is 5% in the private market. The defection rate of members in the loyalty programme is 2%. The reduction therefore is 60%. European Telco: · The expected rate of not churning/ defecting due to a customer retention programme is 50% (mass market) Amexco: · The defection rate of non-members is 15%. The defection rate of Amexco Club members is 2%. The improvement due to the loyalty programme is 87%. MCI (US; Telco; Gannett News April 98): · MCI could rise its market share in international telephony with high spending customers from 19 to 40% by combining its loyalty programme with the ones of Airlines. 02 Overview. ppt 33 33
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Some Benchmark Figures (3/3) Pricewaterhouse. Coopers has knowledge about several customer loyalty programmes. Out of these programmes, the following benchmarks are collected: Programme objectives: Benchmarks: © MCM Switzerland Higher average customer turnover due to cross-selling/ up-selling Airline in Europe: · 72% of the loyalty members spend club products and services instead of services of the competitors. The share of wallet is rising. Keebler (US; Food): · After launching a loyalty programme for a kids club, the turnover in this segment rose 100% and the market share rose from 21 to 29%. Burger Kids Club (US; Food): · The turnover tripled after launching a loyalty programme in the youth segment. Marks and Spencer (Retail Shops): · The turnover of loyalty club members is three times higher than for non-club members. Nieman Marcus direct: · After launching the In Circle Programme, the average turnover of a club member rose 25%. Amexco: · After launching a loyalty programme, the average turnover of a club member rose 55%. European Bank: · Loyalty programme members use the basic bank products and services between 100 -400% more than non-club members. European Telco: · The planned cross selling effect after launching a loyalty programme is between 5 -15% per year. Due to more loyal customers, win-back costs don’t arise Members in loyalty programmes defect less often than non- members Swiss Bank: · The set-up of a new bank account costs about 400 Swiss Francs. France Telecom (Source: Datamonitor): · The costs for customer win-back in mobile communications business is between 1’ 500 and 2’ 200 French Francs. US Telco (Quelle: Telecom Magazine): · The costs for customer win back in mobile communications business is between 300 and 600 US Dollars. The costs for customer retention is between 50 and 100 Dollar. · 60% of the customer defection is within the first three months. By focusing to the customers, the churn in the US mobile communications market could be reduced from 50 to 30%. Customer Retention Costs (Gartner): · To win back a new customer is 4 -10 times more expensive, than to hold an existing customer. MCI (US Telecommunication): · MCI gives 2‘ 000 points for new customers as a win back or acquisition present. · If a customer uses these points for miles in frequent flyer programmes, the value is about 400 US $. Swiss Bank: · The normal defection rate is 5% in the private market. The defection rate of members in the loyalty programme is 2%. The reduction therefore is 60%. European Telco: · The expected rate of not churning/ defecting due to a customer retention programme is 50% (mass market) Amexco: · The defection rate of non-members is 15%. The defection rate of Amexco Club members is 2%. The improvement due to the loyalty programme is 87%. MCI (US; Telco; Gannett News April 98): · MCI could rise its market share in international telephony with high spending customers from 19 to 40% by combining its loyalty programme with the ones of Airlines. 02 Overview. ppt 33 33
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pw. C Citations in the Area of Loyalty Programmes (1/3) n Large European Telecom Provider – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers delivered a customer retention strategy for the residential customer market. The introduction of a loyalty programme was the core for this retention strategy. – During the evaluation and envisioning of the loyalty programme, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers delivered the following: Loyalty programme structure, loyalty card evaluation and defining the card functionalities, processes and evaluation of a customer loyalty software, defining call center capacity and backoffice strategy, loyalty programme content including targeting, positioning, offering and third party cooperations, financial business plan for the loyalty programme and much more. – In addition to the loyalty programme, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers developed a to be data warehouse structure, that enables the company to structure and use the customer information effectively. n Leading European Airline – Based on an existing loyalty programme of this airline, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers supported the client with the clarification of the objectives and goal as well as with the more efficient use of the customer informations for target campaigns and programme edefinition. – The knowledge in topic as customer lifetimne value and customer profitability supported Pricewaterhouse. Coopers in defining current customer profiles and future customer potentials. – On the technical side, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers developed not only recommendations for database improvements, but implemented also the data warehouse itself. n Leading Financial Institute in Europe – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers conducted for a large UK Bank an assessment of their current loyalty card strategy. Based on some of the topics in the evaluation stage, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers could give detailled recommendations for future improvements. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 34 34
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pw. C Citations in the Area of Loyalty Programmes (1/3) n Large European Telecom Provider – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers delivered a customer retention strategy for the residential customer market. The introduction of a loyalty programme was the core for this retention strategy. – During the evaluation and envisioning of the loyalty programme, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers delivered the following: Loyalty programme structure, loyalty card evaluation and defining the card functionalities, processes and evaluation of a customer loyalty software, defining call center capacity and backoffice strategy, loyalty programme content including targeting, positioning, offering and third party cooperations, financial business plan for the loyalty programme and much more. – In addition to the loyalty programme, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers developed a to be data warehouse structure, that enables the company to structure and use the customer information effectively. n Leading European Airline – Based on an existing loyalty programme of this airline, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers supported the client with the clarification of the objectives and goal as well as with the more efficient use of the customer informations for target campaigns and programme edefinition. – The knowledge in topic as customer lifetimne value and customer profitability supported Pricewaterhouse. Coopers in defining current customer profiles and future customer potentials. – On the technical side, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers developed not only recommendations for database improvements, but implemented also the data warehouse itself. n Leading Financial Institute in Europe – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers conducted for a large UK Bank an assessment of their current loyalty card strategy. Based on some of the topics in the evaluation stage, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers could give detailled recommendations for future improvements. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 34 34
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pw. C Citations in the Area of Loyalty Programmes (2/3) n Large Credit Card Provider – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers has helped a large credit card company to target their customers in the retail segment more efficiently. The output of this assignment was the development of a transaction cost model which analysed the financial impact of accepting American Express on store profitability. – In another project for the same customer, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers implemented a program to support the corporate services reorganisation underway. This involves tracking and monitoring the progress of nine strategic initiatives and helping them to align their efforts with the reorganisation. Detailed activities involve tracking existing change initiatives, diagnosing areas needing most help and implementing plans for moving the change effort forward. n Credit Card Company World-wide – For this client, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers developed not only a data warehouse strategy, but conducted also their travel agency strategy for international travellers, who need more support in emergencies. The customer seeks to counter this perception by identifying travel related services partners to team with in providing a global travel support network that surpasses the level of service offered by competitors. n Credit Card Company World-wide – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers was engaged to evaluate the company‘s current co-branding strategy with retailers, provide an overview of retailers' current credit operations, suggest additional retail targets for co-branding. – After that, the customer was able to more effectively target the retail market with their co-branded card product, concentrating on retail lines of trade and specific retailers who could provide the biggest "bang for the buck. " In addition, they were able to focus their sales efforts on target retailers' "hot buttons, " notably an increase in information regarding customer purchases at their own and competitor stores. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 35 35
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pw. C Citations in the Area of Loyalty Programmes (2/3) n Large Credit Card Provider – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers has helped a large credit card company to target their customers in the retail segment more efficiently. The output of this assignment was the development of a transaction cost model which analysed the financial impact of accepting American Express on store profitability. – In another project for the same customer, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers implemented a program to support the corporate services reorganisation underway. This involves tracking and monitoring the progress of nine strategic initiatives and helping them to align their efforts with the reorganisation. Detailed activities involve tracking existing change initiatives, diagnosing areas needing most help and implementing plans for moving the change effort forward. n Credit Card Company World-wide – For this client, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers developed not only a data warehouse strategy, but conducted also their travel agency strategy for international travellers, who need more support in emergencies. The customer seeks to counter this perception by identifying travel related services partners to team with in providing a global travel support network that surpasses the level of service offered by competitors. n Credit Card Company World-wide – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers was engaged to evaluate the company‘s current co-branding strategy with retailers, provide an overview of retailers' current credit operations, suggest additional retail targets for co-branding. – After that, the customer was able to more effectively target the retail market with their co-branded card product, concentrating on retail lines of trade and specific retailers who could provide the biggest "bang for the buck. " In addition, they were able to focus their sales efforts on target retailers' "hot buttons, " notably an increase in information regarding customer purchases at their own and competitor stores. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 35 35
 Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pw. C Citations in the Area of Loyalty Programmes (3/3) n Japanese Credit Card Issuer – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers conducted an overview of the U. S. credit card industry for a large Japanese credit card issuer. The client was interested in expanding its presence in the United States as well as improving its back-office processes in Japan. Pw. C was contracted to provide best practices in cardholder and merchant servicing including transaction processing, sales and customer service and management. Also, Pw. C provided an overview of technology trends in the U. S. card industry as well as industry statistics and recent developments. – Research scope includes the largest firms in the U. S. card industry including bank card issuers, T&E card issuers, cardholder processors, merchant acquirers, merchant processors and independent sales organisations (ISOs). Sources of card industry information included internal sources such as work products produced by the FSIP Card Services group. n Additional Citations in the Loyalty Marketing Area – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers has a vast experience in benchmarking and best practice analysis. The experience, we also have in the loyalty card area. Developing a best practice study about Cardholder sales and marketing builds up a basic knowledge in this industry. – This study, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers developed with the support from 15 worlds known companies in the cardholder industry. The result was not only a detailed analysis of these programmes and strategies, but also a detailed understanding about scoring the clients behaviour and needs based on these schemes. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 36 36
Market and Customer Management - Customer Loyalty Pw. C Citations in the Area of Loyalty Programmes (3/3) n Japanese Credit Card Issuer – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers conducted an overview of the U. S. credit card industry for a large Japanese credit card issuer. The client was interested in expanding its presence in the United States as well as improving its back-office processes in Japan. Pw. C was contracted to provide best practices in cardholder and merchant servicing including transaction processing, sales and customer service and management. Also, Pw. C provided an overview of technology trends in the U. S. card industry as well as industry statistics and recent developments. – Research scope includes the largest firms in the U. S. card industry including bank card issuers, T&E card issuers, cardholder processors, merchant acquirers, merchant processors and independent sales organisations (ISOs). Sources of card industry information included internal sources such as work products produced by the FSIP Card Services group. n Additional Citations in the Loyalty Marketing Area – Pricewaterhouse. Coopers has a vast experience in benchmarking and best practice analysis. The experience, we also have in the loyalty card area. Developing a best practice study about Cardholder sales and marketing builds up a basic knowledge in this industry. – This study, Pricewaterhouse. Coopers developed with the support from 15 worlds known companies in the cardholder industry. The result was not only a detailed analysis of these programmes and strategies, but also a detailed understanding about scoring the clients behaviour and needs based on these schemes. © MCM Switzerland 02 Overview. ppt 36 36


