ccd14c144415e4126e8d9fd257a10e9b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 114
 Marke. Trak VI: Hearing Aid Industry Market Tracking Survey 1984 -2000 Sergei Kochkin, Ph. D. Knowles Electronics, Inc. February 27, 2002
Marke. Trak VI: Hearing Aid Industry Market Tracking Survey 1984 -2000 Sergei Kochkin, Ph. D. Knowles Electronics, Inc. February 27, 2002
 Method • National family opinion panel – 80, 000 households • Balanced to key census variables – HIA survey in 1984 used NFO – All Marke. Trak surveys • Screening Question – Phase I (November 2000) – “Does anyone in your household have a hearing difficulty in one or both ears without the use of a hearing aid? ” – Physician screening for hearing loss during last physical within last six months. – Self, Spouse, Other, Child (Under age 18) – 15, 800 hearing-impaired individuals – 72% response rate
Method • National family opinion panel – 80, 000 households • Balanced to key census variables – HIA survey in 1984 used NFO – All Marke. Trak surveys • Screening Question – Phase I (November 2000) – “Does anyone in your household have a hearing difficulty in one or both ears without the use of a hearing aid? ” – Physician screening for hearing loss during last physical within last six months. – Self, Spouse, Other, Child (Under age 18) – 15, 800 hearing-impaired individuals – 72% response rate
 Method • Hearing Aid Owner Survey - Phase II – Detailed questionnaire 3, 000 hearing aid owners based on Phase I response. – Response rate 87% • Topics: – – – – – Customer satisfaction (more than 50 areas) Hearing aid usage (e. g. hours worn) Use of ALDs First time user influences Brand selection Factors impacting choice of audiologist/dispenser Suggestions for improving hearing aids Perceived quality of life changes Use of computers in hearing healthcare
Method • Hearing Aid Owner Survey - Phase II – Detailed questionnaire 3, 000 hearing aid owners based on Phase I response. – Response rate 87% • Topics: – – – – – Customer satisfaction (more than 50 areas) Hearing aid usage (e. g. hours worn) Use of ALDs First time user influences Brand selection Factors impacting choice of audiologist/dispenser Suggestions for improving hearing aids Perceived quality of life changes Use of computers in hearing healthcare
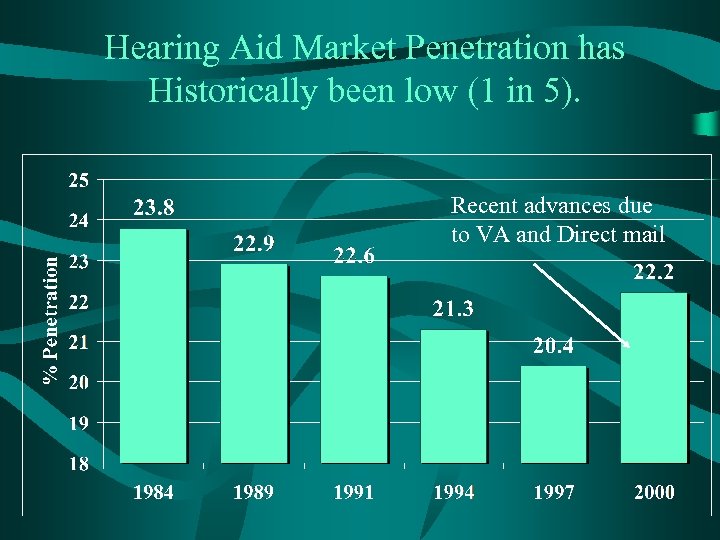 Hearing Aid Market Penetration has Historically been low (1 in 5). Recent advances due to VA and Direct mail
Hearing Aid Market Penetration has Historically been low (1 in 5). Recent advances due to VA and Direct mail
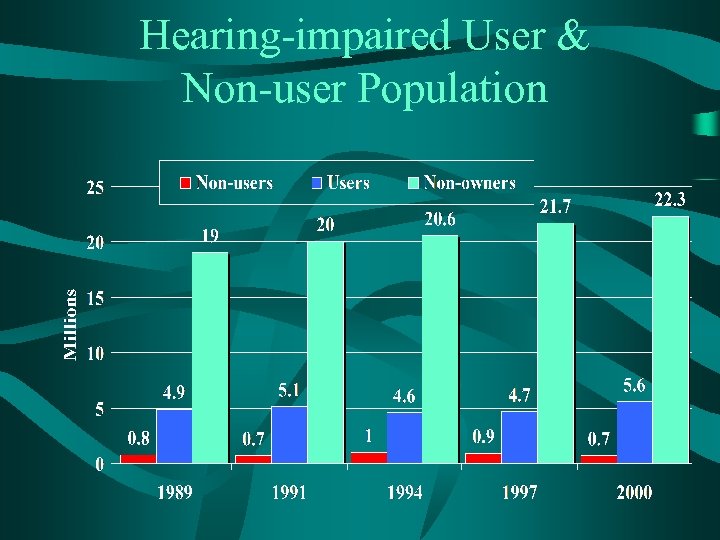 Hearing-impaired User & Non-user Population
Hearing-impaired User & Non-user Population
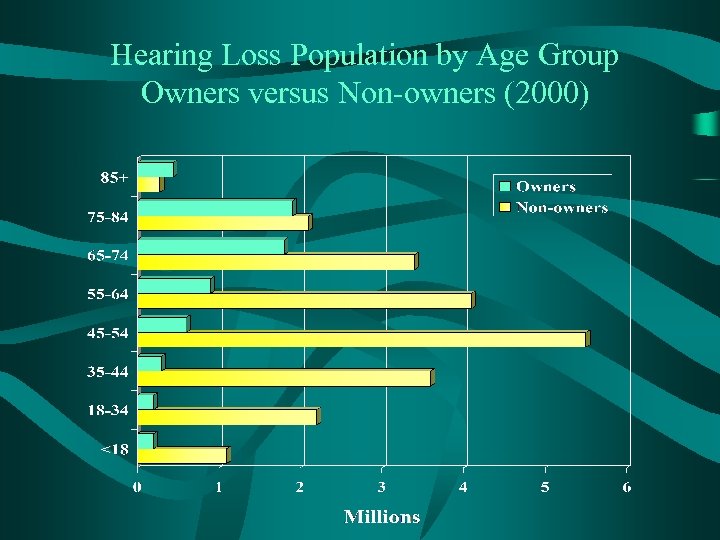 Hearing Loss Population by Age Group Owners versus Non-owners (2000)
Hearing Loss Population by Age Group Owners versus Non-owners (2000)
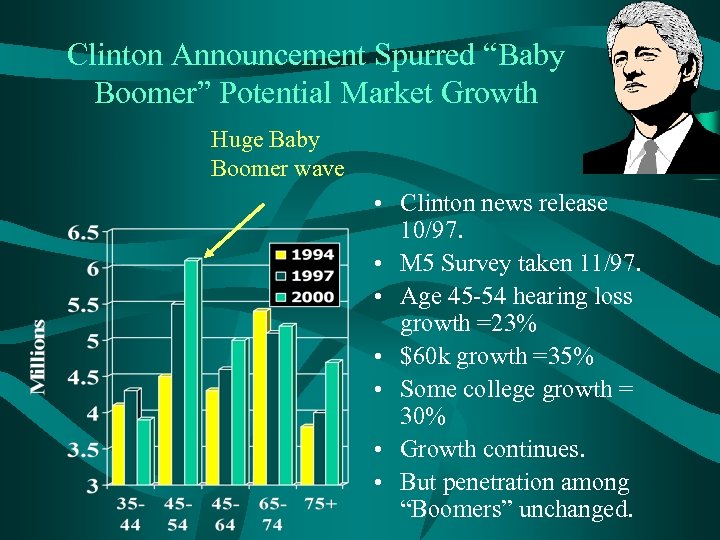 Clinton Announcement Spurred “Baby Boomer” Potential Market Growth Huge Baby Boomer wave • Clinton news release 10/97. • M 5 Survey taken 11/97. • Age 45 -54 hearing loss growth =23% • $60 k growth =35% • Some college growth = 30% • Growth continues. • But penetration among “Boomers” unchanged.
Clinton Announcement Spurred “Baby Boomer” Potential Market Growth Huge Baby Boomer wave • Clinton news release 10/97. • M 5 Survey taken 11/97. • Age 45 -54 hearing loss growth =23% • $60 k growth =35% • Some college growth = 30% • Growth continues. • But penetration among “Boomers” unchanged.
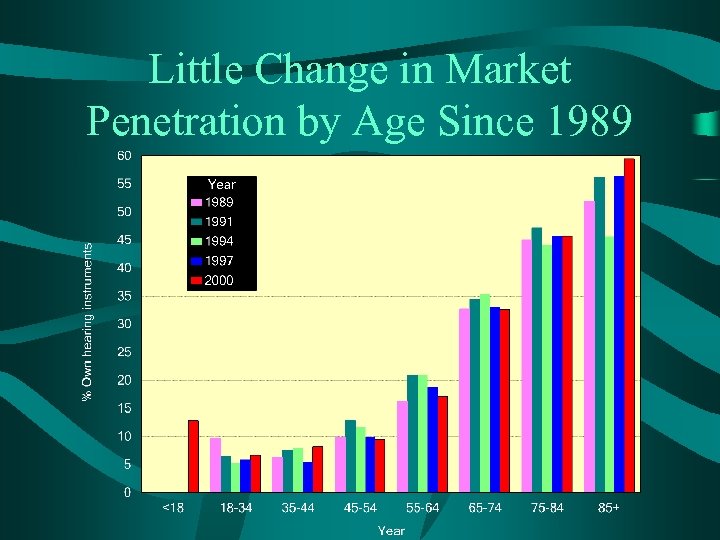 Little Change in Market Penetration by Age Since 1989
Little Change in Market Penetration by Age Since 1989
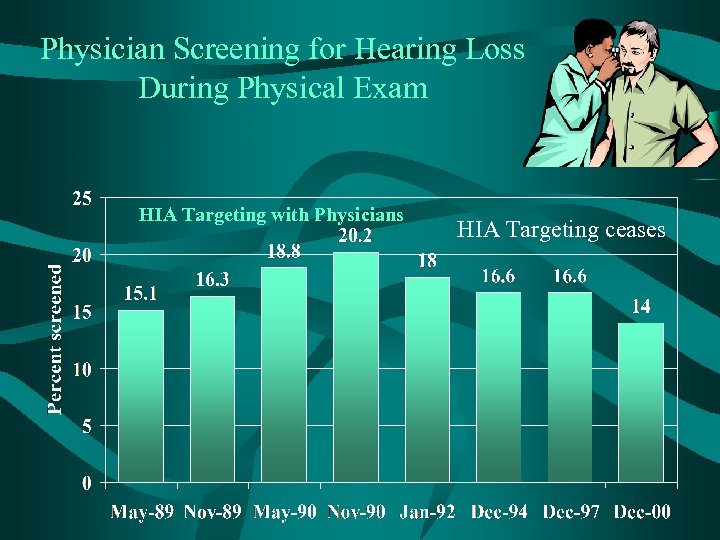 Physician Screening for Hearing Loss During Physical Exam HIA Targeting with Physicians HIA Targeting ceases
Physician Screening for Hearing Loss During Physical Exam HIA Targeting with Physicians HIA Targeting ceases
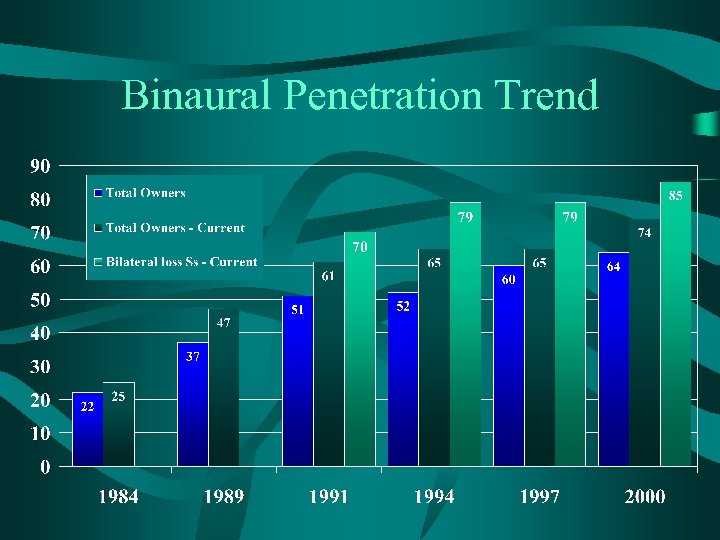 Binaural Penetration Trend
Binaural Penetration Trend
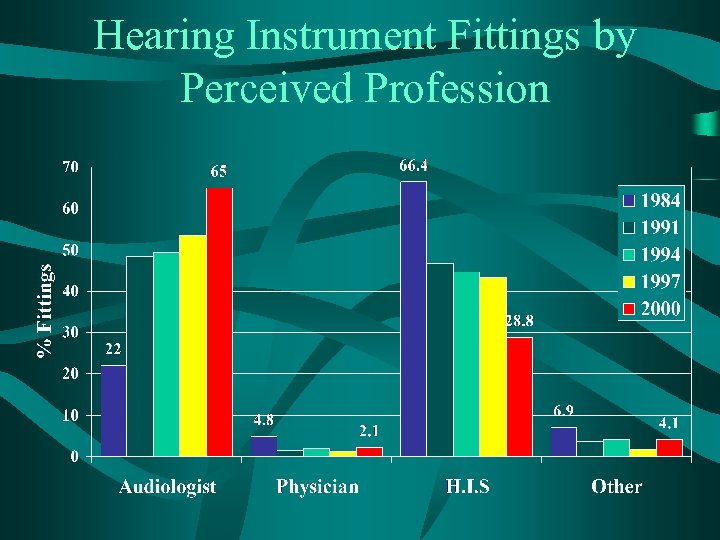 Hearing Instrument Fittings by Perceived Profession
Hearing Instrument Fittings by Perceived Profession
 Hearing Instrument Fittings by Source of Distribution ØMail Order has grown 91% since 1997; 124, 000 hearing aid users. ØVA has grown 83% since 1997; 411, 000 hearing aid users.
Hearing Instrument Fittings by Source of Distribution ØMail Order has grown 91% since 1997; 124, 000 hearing aid users. ØVA has grown 83% since 1997; 411, 000 hearing aid users.
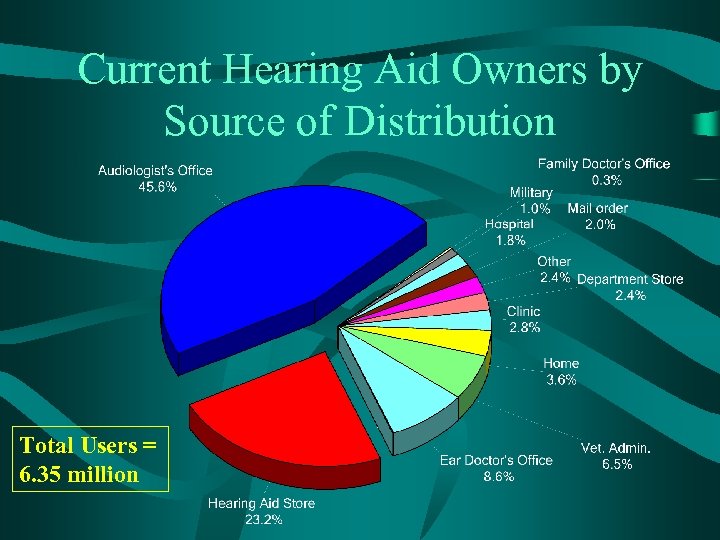 Current Hearing Aid Owners by Source of Distribution Total Users = 6. 35 million
Current Hearing Aid Owners by Source of Distribution Total Users = 6. 35 million
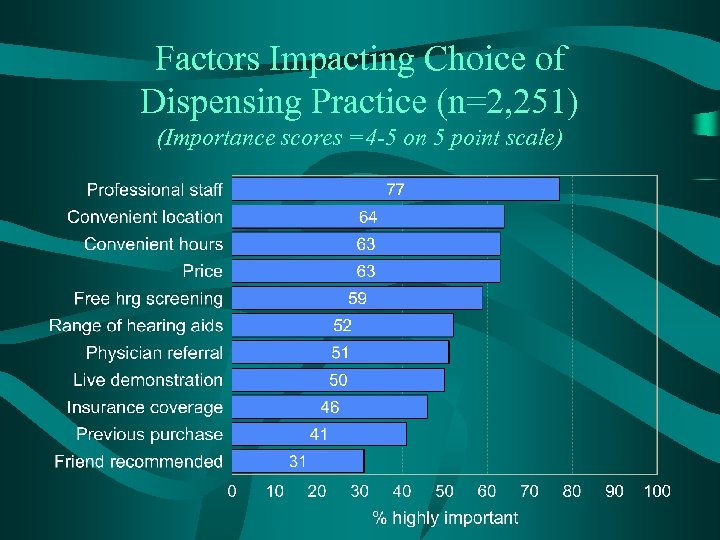 Factors Impacting Choice of Dispensing Practice (n=2, 251) (Importance scores =4 -5 on 5 point scale)
Factors Impacting Choice of Dispensing Practice (n=2, 251) (Importance scores =4 -5 on 5 point scale)
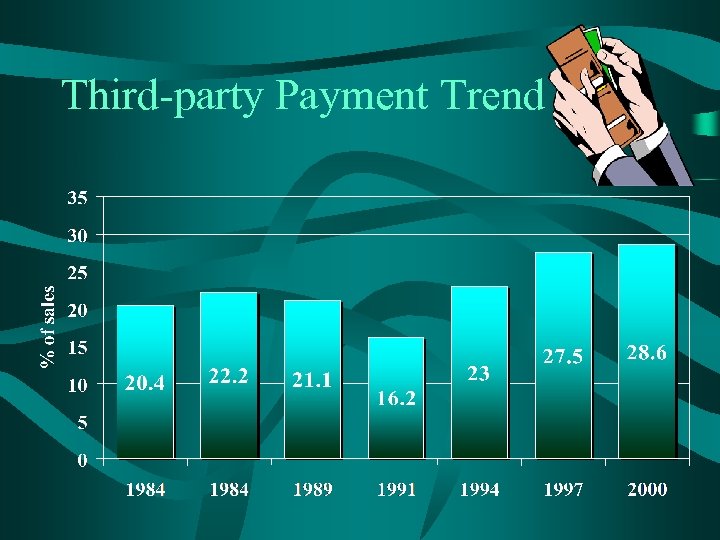 Third-party Payment Trend
Third-party Payment Trend
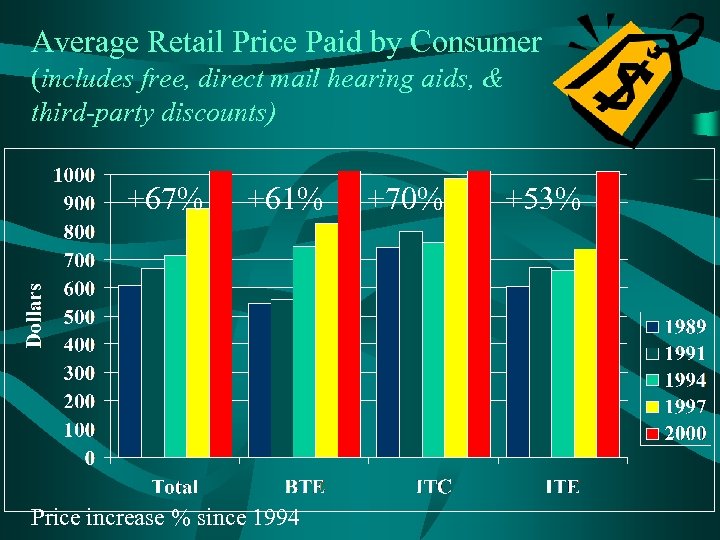 Average Retail Price Paid by Consumer (includes free, direct mail hearing aids, & third-party discounts) +67% +61% Price increase % since 1994 +70% +53%
Average Retail Price Paid by Consumer (includes free, direct mail hearing aids, & third-party discounts) +67% +61% Price increase % since 1994 +70% +53%
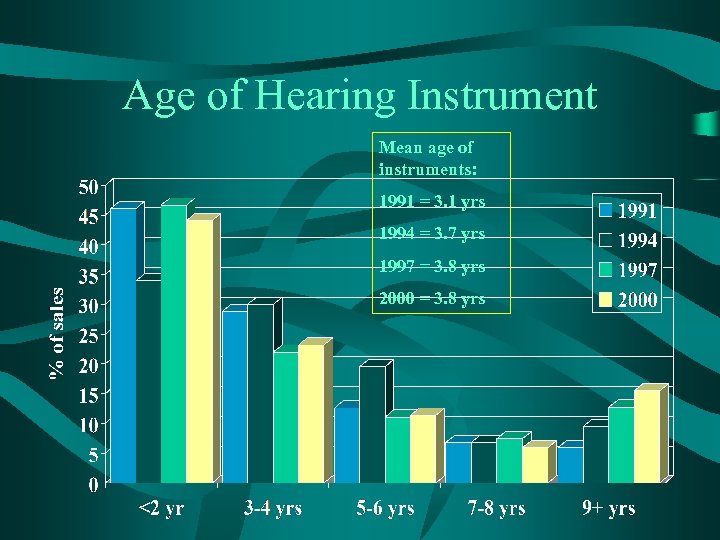 Age of Hearing Instrument Mean age of instruments: 1991 = 3. 1 yrs 1994 = 3. 7 yrs 1997 = 3. 8 yrs 2000 = 3. 8 yrs
Age of Hearing Instrument Mean age of instruments: 1991 = 3. 1 yrs 1994 = 3. 7 yrs 1997 = 3. 8 yrs 2000 = 3. 8 yrs
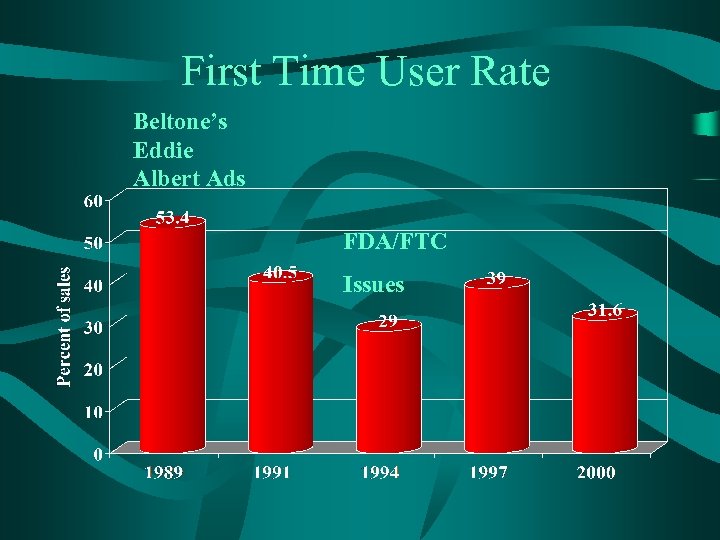 First Time User Rate Beltone’s Eddie Albert Ads FDA/FTC Issues
First Time User Rate Beltone’s Eddie Albert Ads FDA/FTC Issues
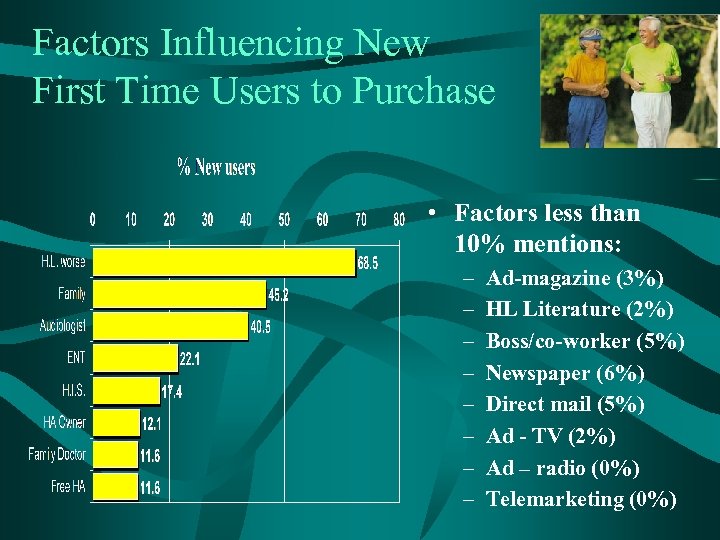 Factors Influencing New First Time Users to Purchase • Factors less than 10% mentions: – – – – Ad-magazine (3%) HL Literature (2%) Boss/co-worker (5%) Newspaper (6%) Direct mail (5%) Ad - TV (2%) Ad – radio (0%) Telemarketing (0%)
Factors Influencing New First Time Users to Purchase • Factors less than 10% mentions: – – – – Ad-magazine (3%) HL Literature (2%) Boss/co-worker (5%) Newspaper (6%) Direct mail (5%) Ad - TV (2%) Ad – radio (0%) Telemarketing (0%)
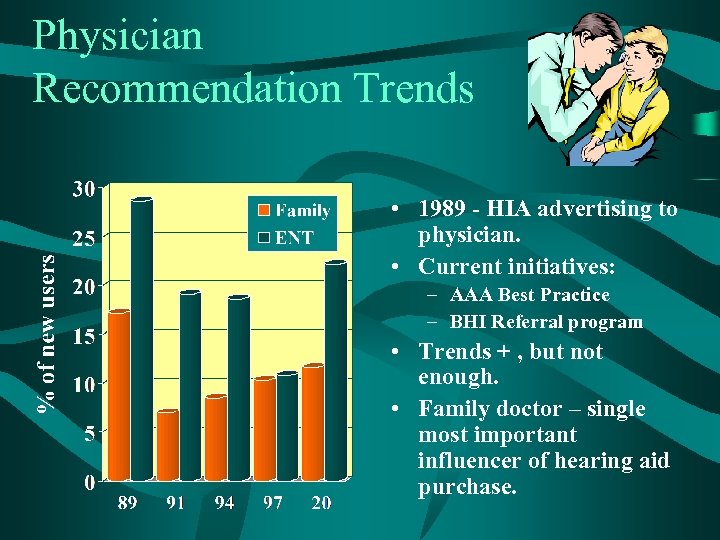 Physician Recommendation Trends • 1989 - HIA advertising to physician. • Current initiatives: – AAA Best Practice – BHI Referral program • Trends + , but not enough. • Family doctor – single most important influencer of hearing aid purchase.
Physician Recommendation Trends • 1989 - HIA advertising to physician. • Current initiatives: – AAA Best Practice – BHI Referral program • Trends + , but not enough. • Family doctor – single most important influencer of hearing aid purchase.
 Factors Influencing New First Time Users to Purchase • Notable changes since last Marke. Trak: – Audiologist influence increased to 40. 5% - up from 26% in 1997. – ENT influence increased to 22. 1% - up from 10. 8% in 1997. – “Free” hearing aid influence nearly doubled.
Factors Influencing New First Time Users to Purchase • Notable changes since last Marke. Trak: – Audiologist influence increased to 40. 5% - up from 26% in 1997. – ENT influence increased to 22. 1% - up from 10. 8% in 1997. – “Free” hearing aid influence nearly doubled.
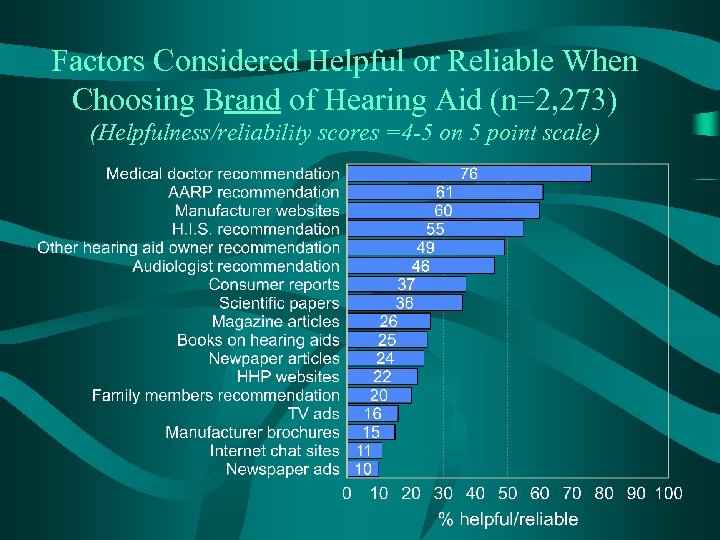 Factors Considered Helpful or Reliable When Choosing Brand of Hearing Aid (n=2, 273) (Helpfulness/reliability scores =4 -5 on 5 point scale)
Factors Considered Helpful or Reliable When Choosing Brand of Hearing Aid (n=2, 273) (Helpfulness/reliability scores =4 -5 on 5 point scale)
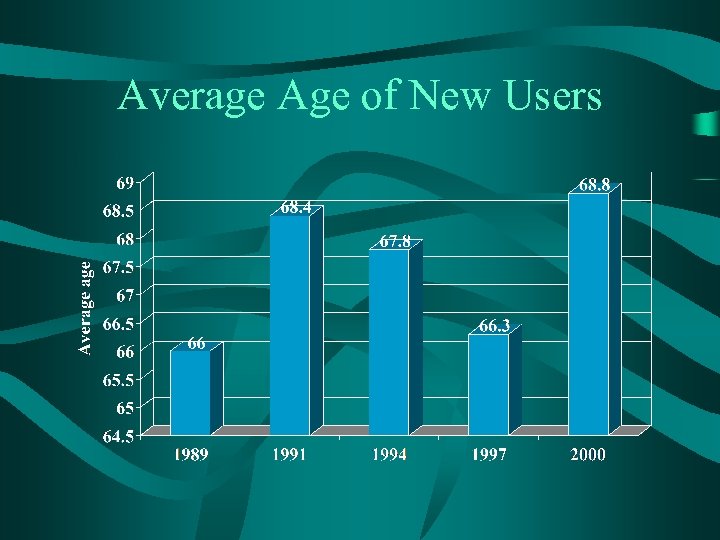 Average Age of New Users
Average Age of New Users
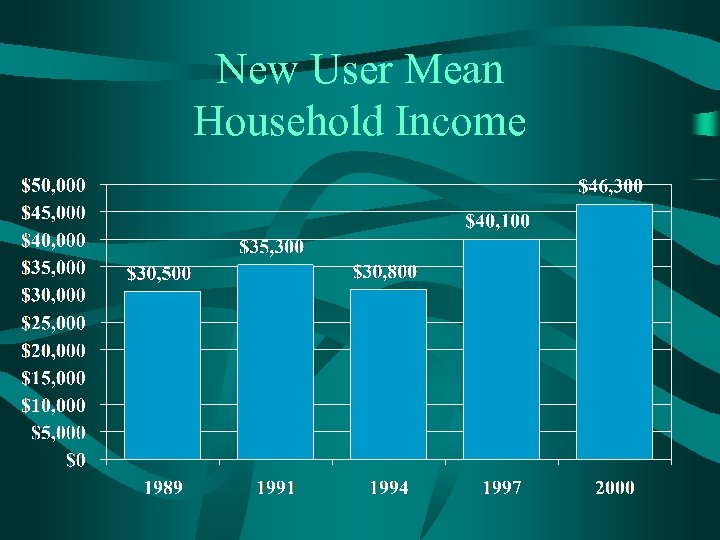 New User Mean Household Income
New User Mean Household Income
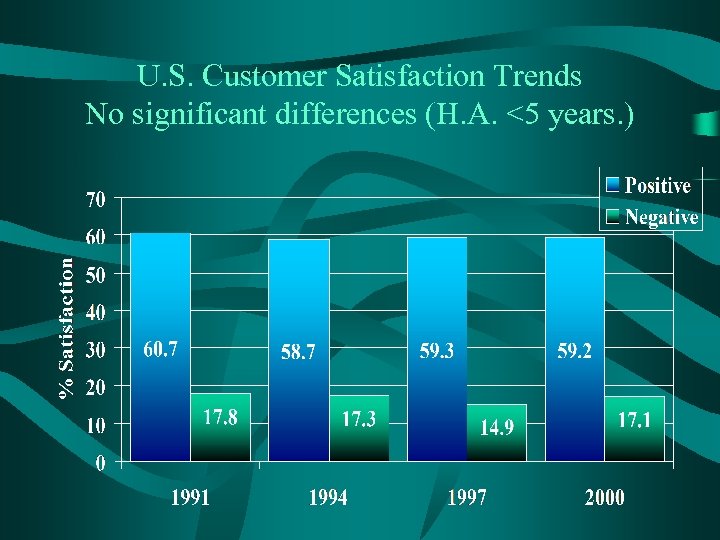 U. S. Customer Satisfaction Trends No significant differences (H. A. <5 years. )
U. S. Customer Satisfaction Trends No significant differences (H. A. <5 years. )
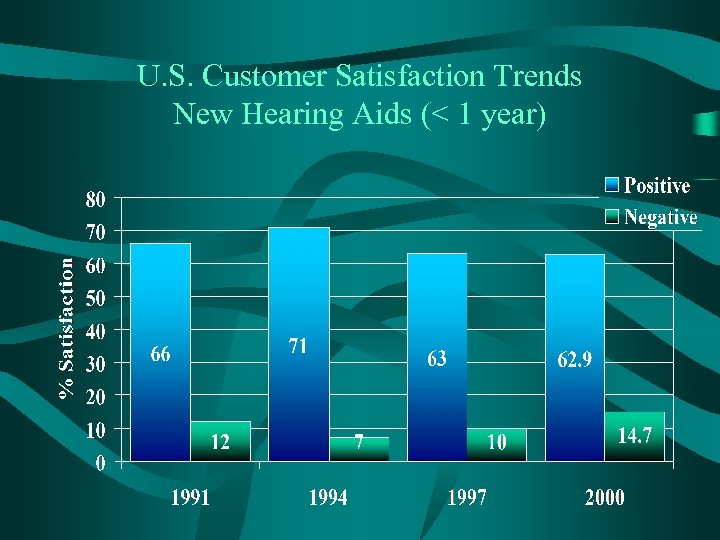 U. S. Customer Satisfaction Trends New Hearing Aids (< 1 year)
U. S. Customer Satisfaction Trends New Hearing Aids (< 1 year)
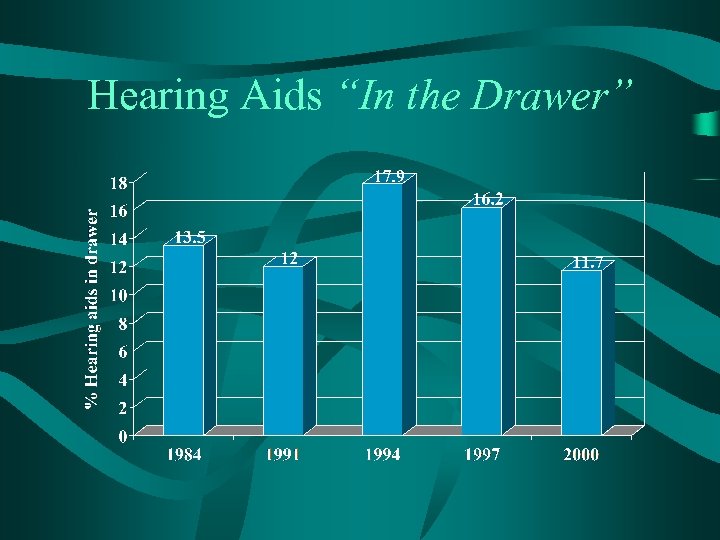 Hearing Aids “In the Drawer”
Hearing Aids “In the Drawer”
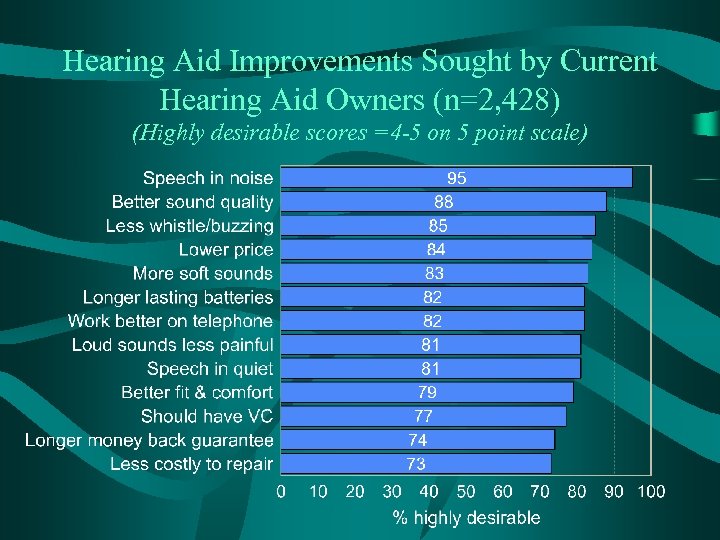 Hearing Aid Improvements Sought by Current Hearing Aid Owners (n=2, 428) (Highly desirable scores =4 -5 on 5 point scale)
Hearing Aid Improvements Sought by Current Hearing Aid Owners (n=2, 428) (Highly desirable scores =4 -5 on 5 point scale)
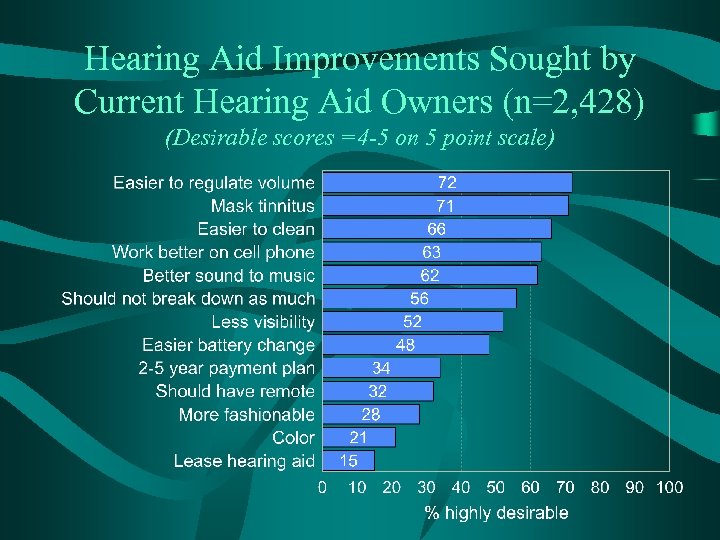 Hearing Aid Improvements Sought by Current Hearing Aid Owners (n=2, 428) (Desirable scores =4 -5 on 5 point scale)
Hearing Aid Improvements Sought by Current Hearing Aid Owners (n=2, 428) (Desirable scores =4 -5 on 5 point scale)
 Non-owner Demography “The Opportunity”
Non-owner Demography “The Opportunity”
 The Non-Owner Opportunities Self-admitted Hearing Loss Gender (Millions)
The Non-Owner Opportunities Self-admitted Hearing Loss Gender (Millions)
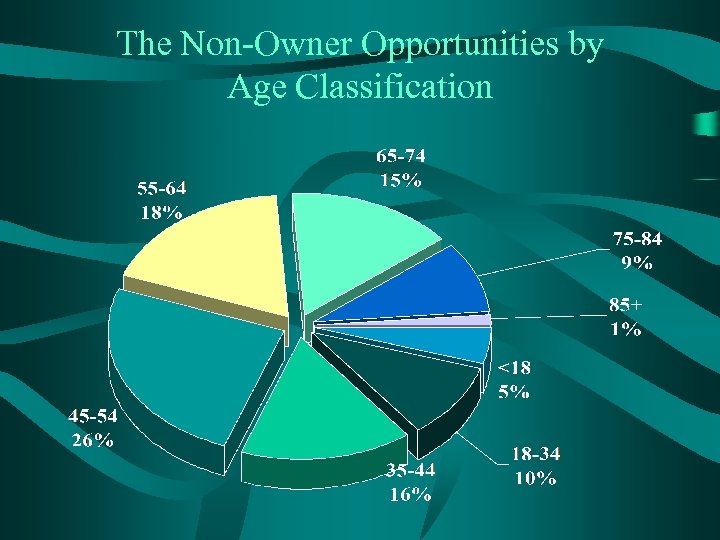 The Non-Owner Opportunities by Age Classification
The Non-Owner Opportunities by Age Classification
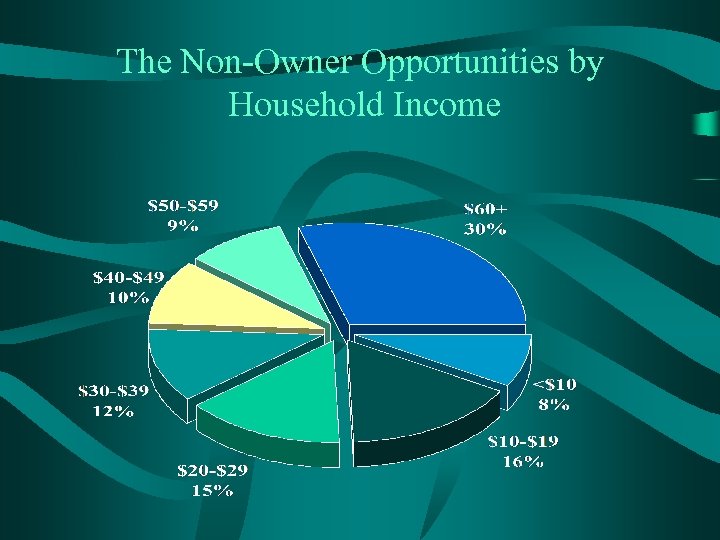 The Non-Owner Opportunities by Household Income
The Non-Owner Opportunities by Household Income
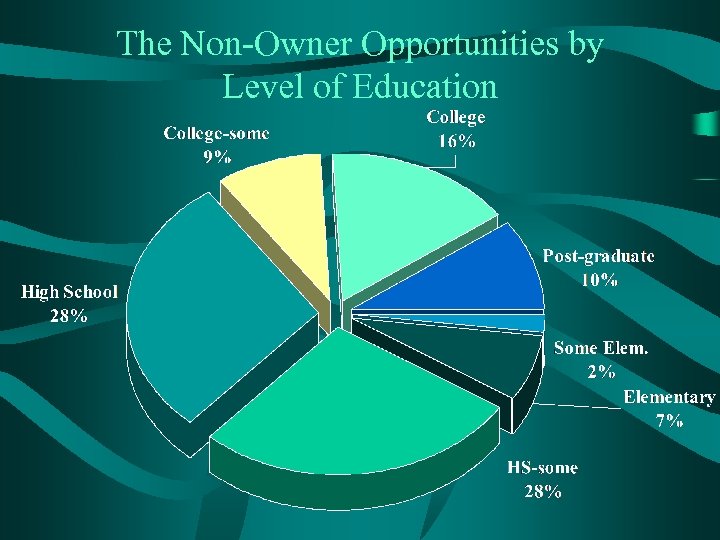 The Non-Owner Opportunities by Level of Education
The Non-Owner Opportunities by Level of Education
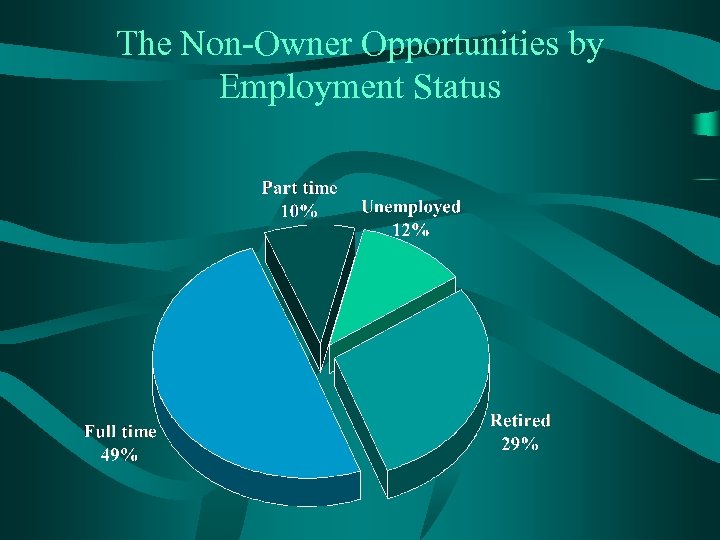 The Non-Owner Opportunities by Employment Status
The Non-Owner Opportunities by Employment Status
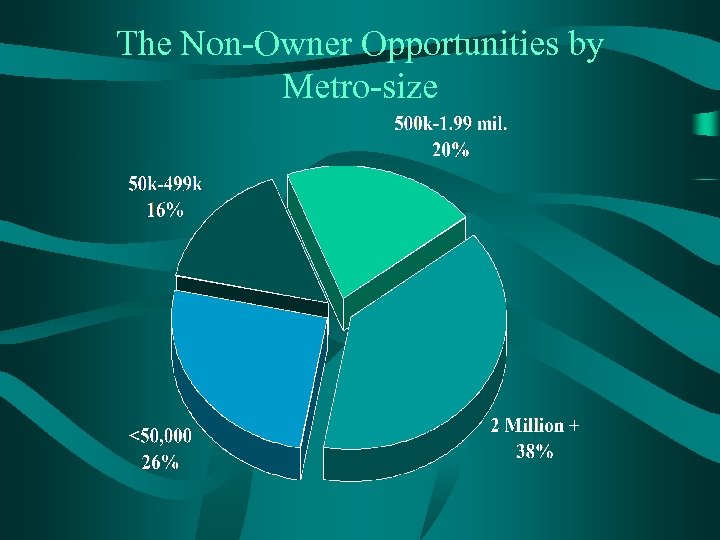 The Non-Owner Opportunities by Metro-size
The Non-Owner Opportunities by Metro-size
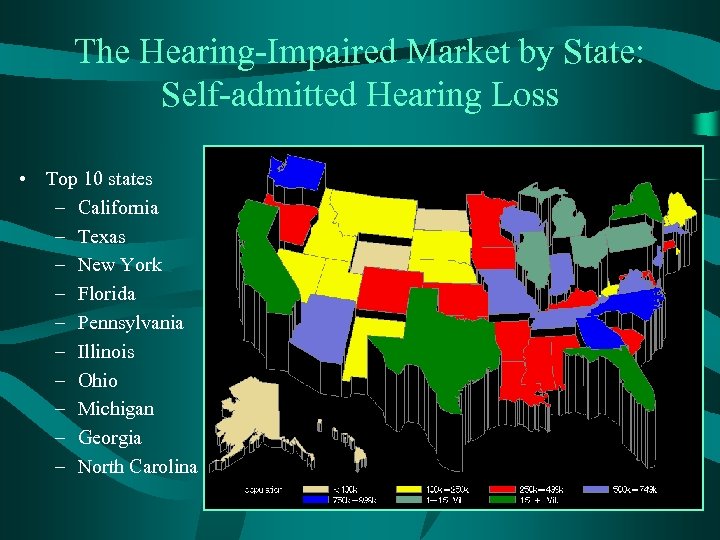 The Hearing-Impaired Market by State: Self-admitted Hearing Loss • Top 10 states – California – Texas – New York – Florida – Pennsylvania – Illinois – Ohio – Michigan – Georgia – North Carolina
The Hearing-Impaired Market by State: Self-admitted Hearing Loss • Top 10 states – California – Texas – New York – Florida – Pennsylvania – Illinois – Ohio – Michigan – Georgia – North Carolina
 Conclusions • Hearing-impaired population > to 28. 6 million. • Major increases in “Baby Boomer” and 75+ age brackets. • Penetration increased to 22. 2%: – Free and direct mail impact • Physician screenings declined to 14%. • Overall customer satisfaction unchanged. – New hearing aid satisfaction on decline • Hearing aids in the drawer improved to 11. 7%. • Audiologist influence in dispensing continues to grow.
Conclusions • Hearing-impaired population > to 28. 6 million. • Major increases in “Baby Boomer” and 75+ age brackets. • Penetration increased to 22. 2%: – Free and direct mail impact • Physician screenings declined to 14%. • Overall customer satisfaction unchanged. – New hearing aid satisfaction on decline • Hearing aids in the drawer improved to 11. 7%. • Audiologist influence in dispensing continues to grow.
 Conclusions • New user rate has dropped to 31. 6%. – Average increase to 69 – Household income increase to $46. 3 k • Binaural rate is at an all time high of 84. 5% for bilateral loss consumers. • Third-party payments continue to increase. • “Out-of-pocket” retail price to consumer increased 67% since 1994. • “Baby-boomer” age wave continues to grow with no indication that industry has tapped this segment.
Conclusions • New user rate has dropped to 31. 6%. – Average increase to 69 – Household income increase to $46. 3 k • Binaural rate is at an all time high of 84. 5% for bilateral loss consumers. • Third-party payments continue to increase. • “Out-of-pocket” retail price to consumer increased 67% since 1994. • “Baby-boomer” age wave continues to grow with no indication that industry has tapped this segment.
 Conclusions • The top hearing aid improvements sought by current hearing aid owners: – – – Hearing in noise Better sound quality Less whistling & feedback Lower price More soft sounds • Least important improvements: – Leasing a hearing aid – Color of hearing aid – More fashionable hearing aids
Conclusions • The top hearing aid improvements sought by current hearing aid owners: – – – Hearing in noise Better sound quality Less whistling & feedback Lower price More soft sounds • Least important improvements: – Leasing a hearing aid – Color of hearing aid – More fashionable hearing aids
 Conclusions • Top factors in choosing dispenser: – – Professionalism Convenient location Convenient hours Price • Top factors considered to be helpful and reliable when choosing a hearing aid brand: – – Medical doctor recommendation AARP recommendation Manufacturer website Hearing instrument specialist recommendation
Conclusions • Top factors in choosing dispenser: – – Professionalism Convenient location Convenient hours Price • Top factors considered to be helpful and reliable when choosing a hearing aid brand: – – Medical doctor recommendation AARP recommendation Manufacturer website Hearing instrument specialist recommendation
 Key Findings from Knowles Market Development Studies
Key Findings from Knowles Market Development Studies
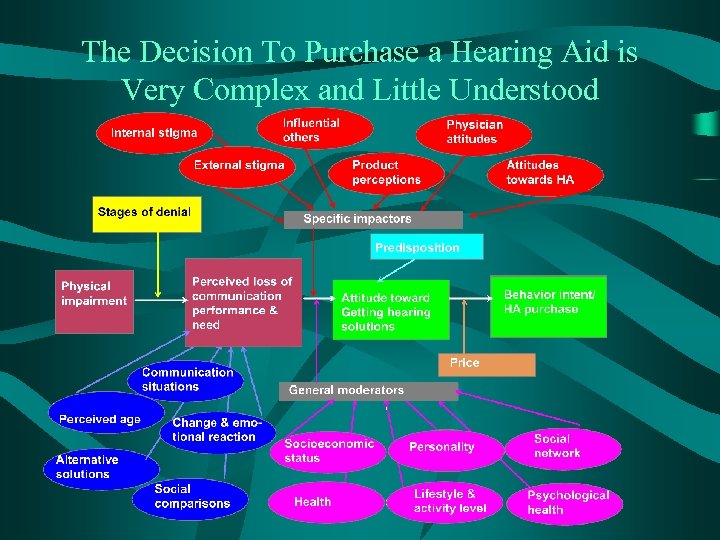 The Decision To Purchase a Hearing Aid is Very Complex and Little Understood
The Decision To Purchase a Hearing Aid is Very Complex and Little Understood
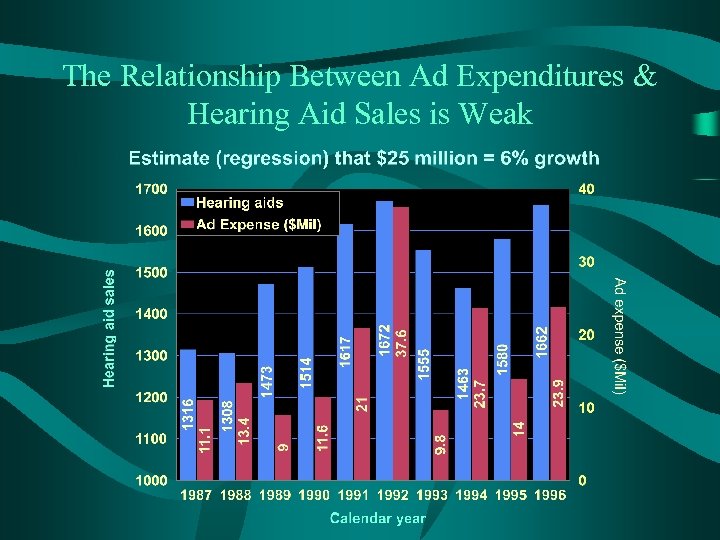 The Relationship Between Ad Expenditures & Hearing Aid Sales is Weak
The Relationship Between Ad Expenditures & Hearing Aid Sales is Weak
 The Issue of Price & Value
The Issue of Price & Value
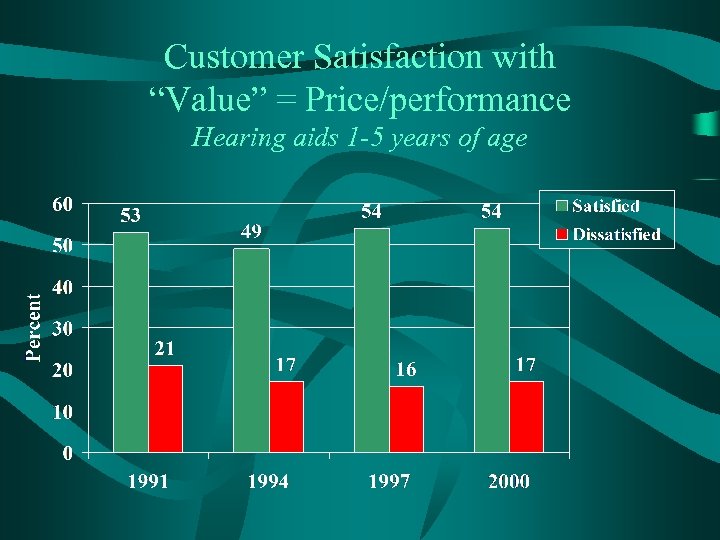 Customer Satisfaction with “Value” = Price/performance Hearing aids 1 -5 years of age
Customer Satisfaction with “Value” = Price/performance Hearing aids 1 -5 years of age
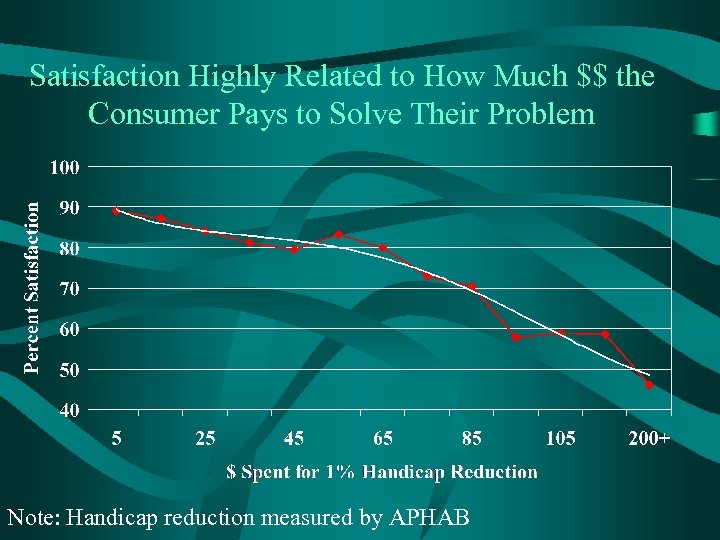 Satisfaction Highly Related to How Much $$ the Consumer Pays to Solve Their Problem Note: Handicap reduction measured by APHAB
Satisfaction Highly Related to How Much $$ the Consumer Pays to Solve Their Problem Note: Handicap reduction measured by APHAB
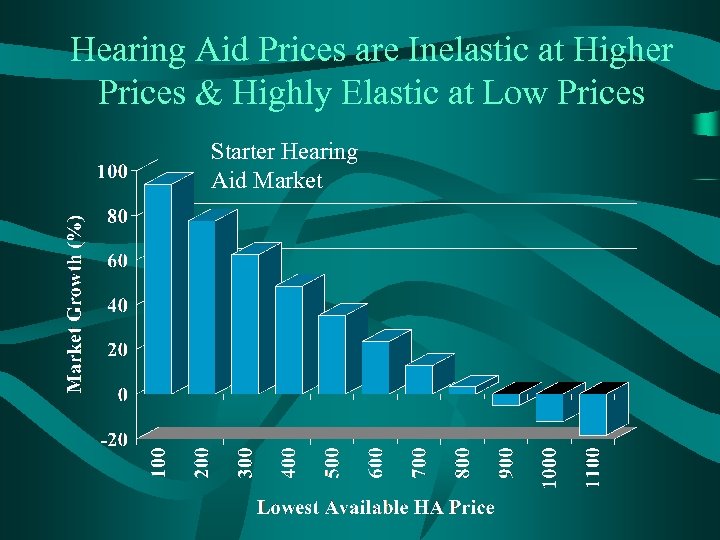 Hearing Aid Prices are Inelastic at Higher Prices & Highly Elastic at Low Prices Starter Hearing Aid Market
Hearing Aid Prices are Inelastic at Higher Prices & Highly Elastic at Low Prices Starter Hearing Aid Market
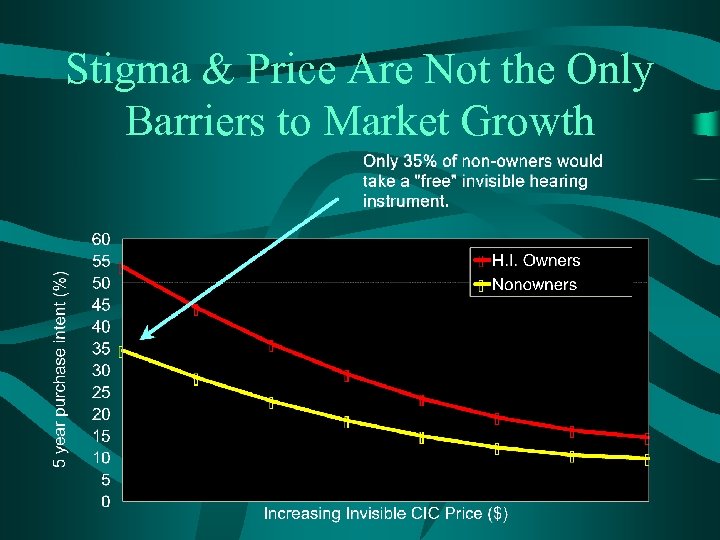 Stigma & Price Are Not the Only Barriers to Market Growth
Stigma & Price Are Not the Only Barriers to Market Growth
 The Issue of Stigma
The Issue of Stigma
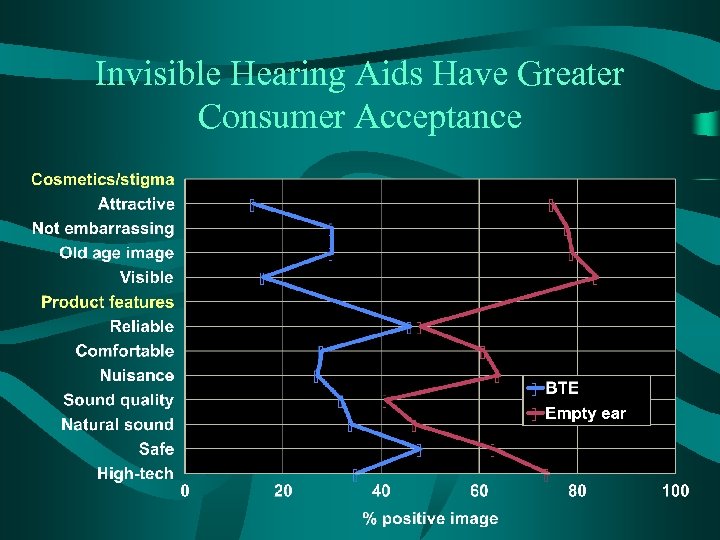 Invisible Hearing Aids Have Greater Consumer Acceptance
Invisible Hearing Aids Have Greater Consumer Acceptance
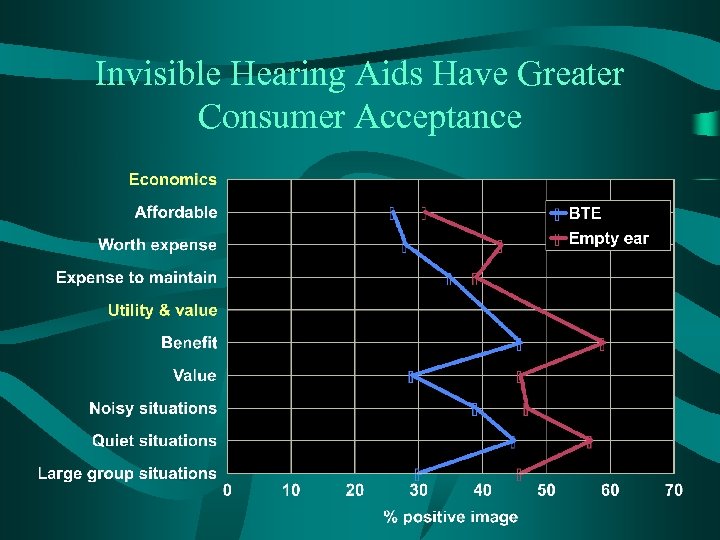 Invisible Hearing Aids Have Greater Consumer Acceptance
Invisible Hearing Aids Have Greater Consumer Acceptance
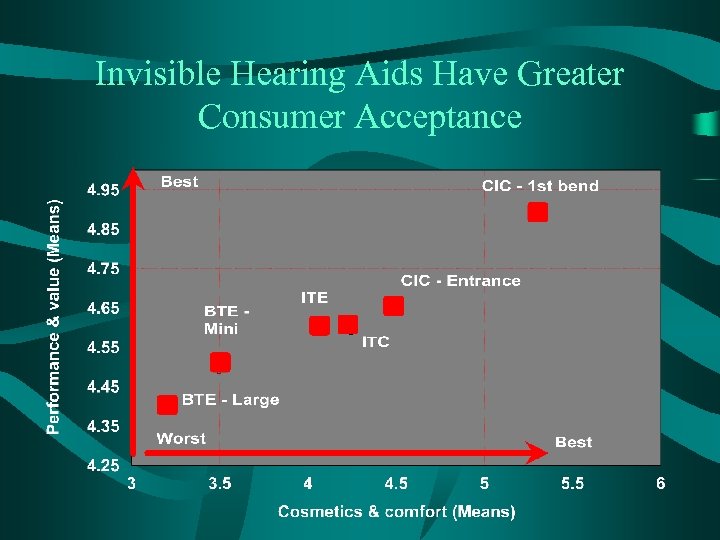 Invisible Hearing Aids Have Greater Consumer Acceptance
Invisible Hearing Aids Have Greater Consumer Acceptance
 Can Positive Role Models Help Consumers Overcome Stigma? • Only Two examples I am aware of in our industry: – President Reagan – 1983 (associated with 20% growth) – Eddie Albert in Beltone commercials – 1989 • Apparent Clinton effect in Fall of 1997 – Probable impact on admission of hearing loss by male “baby -boomers” – No impact on sales to date
Can Positive Role Models Help Consumers Overcome Stigma? • Only Two examples I am aware of in our industry: – President Reagan – 1983 (associated with 20% growth) – Eddie Albert in Beltone commercials – 1989 • Apparent Clinton effect in Fall of 1997 – Probable impact on admission of hearing loss by male “baby -boomers” – No impact on sales to date
 What is The Viable Market for Hearing Aids?
What is The Viable Market for Hearing Aids?
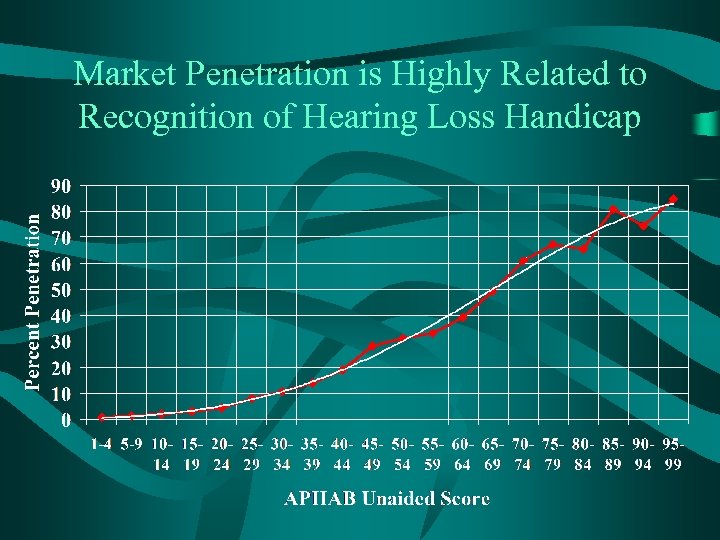 Market Penetration is Highly Related to Recognition of Hearing Loss Handicap
Market Penetration is Highly Related to Recognition of Hearing Loss Handicap
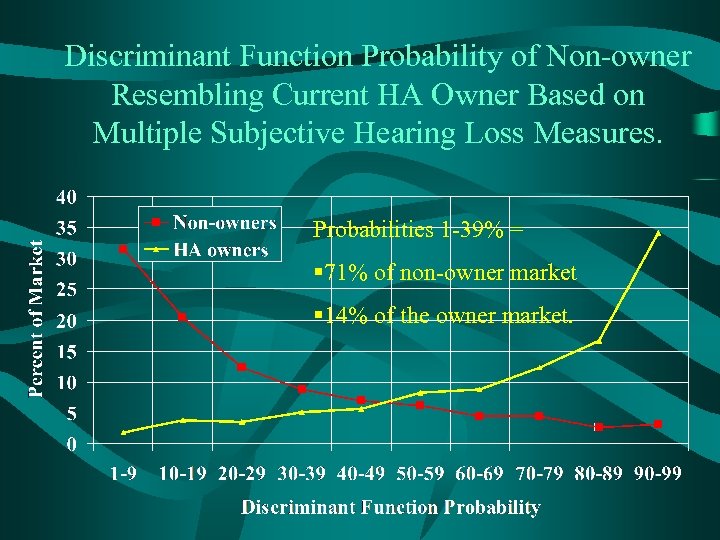 Discriminant Function Probability of Non-owner Resembling Current HA Owner Based on Multiple Subjective Hearing Loss Measures. Probabilities 1 -39% = § 71% of non-owner market § 14% of the owner market.
Discriminant Function Probability of Non-owner Resembling Current HA Owner Based on Multiple Subjective Hearing Loss Measures. Probabilities 1 -39% = § 71% of non-owner market § 14% of the owner market.
 Four Methods of Measuring Viable US Hearing Aid Market • Based totally on hearing loss measures the additional possible market growth is: § § Gallaudet Scores (est. d. B Loss Better ear) = 125% Hearing Handicap Inventory (HHIE) = 154% APHAB = 127% Discriminant Function Modeling = 102% • Clear that the current market could easily double based totally on hearing handicap. • And, even more based on situational need.
Four Methods of Measuring Viable US Hearing Aid Market • Based totally on hearing loss measures the additional possible market growth is: § § Gallaudet Scores (est. d. B Loss Better ear) = 125% Hearing Handicap Inventory (HHIE) = 154% APHAB = 127% Discriminant Function Modeling = 102% • Clear that the current market could easily double based totally on hearing handicap. • And, even more based on situational need.
 Why Buy Hearing Aids?
Why Buy Hearing Aids?
 Attitudes Per Se are Important, But Relationship to Hearing Aid Purchase Intent is Perhaps More Important • Sample of 2, 753 non-owners • Measured their attitudes on 76 issues. • Measured their hearing aid purchase intent in the next five years. • Categorized them as a high or low purchase intenders. • Took ratio of high/low purchase intenders for each attitude item. • Ranked ratios • First – present their attitudes in key categories. – On following charts – view red (negative) as “barrier” to growth.
Attitudes Per Se are Important, But Relationship to Hearing Aid Purchase Intent is Perhaps More Important • Sample of 2, 753 non-owners • Measured their attitudes on 76 issues. • Measured their hearing aid purchase intent in the next five years. • Categorized them as a high or low purchase intenders. • Took ratio of high/low purchase intenders for each attitude item. • Ranked ratios • First – present their attitudes in key categories. – On following charts – view red (negative) as “barrier” to growth.
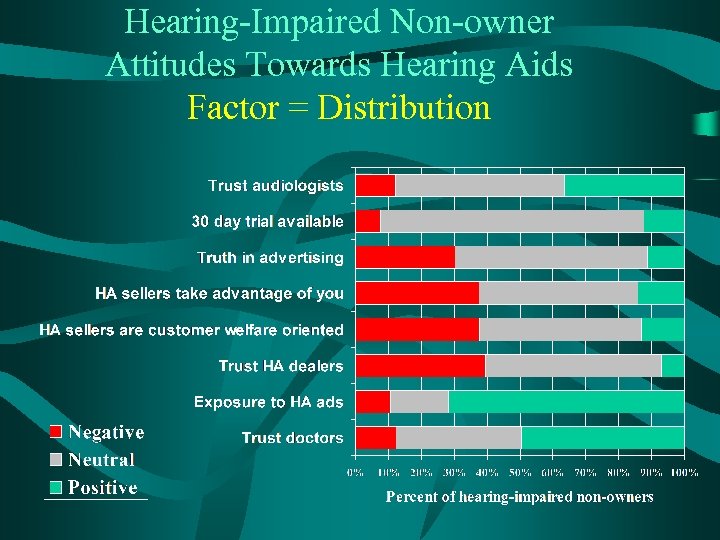 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor = Distribution
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor = Distribution
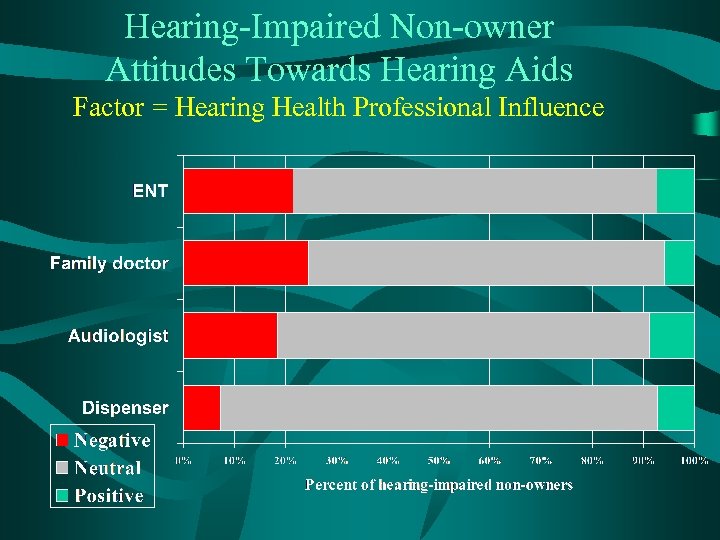 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor = Hearing Health Professional Influence
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor = Hearing Health Professional Influence
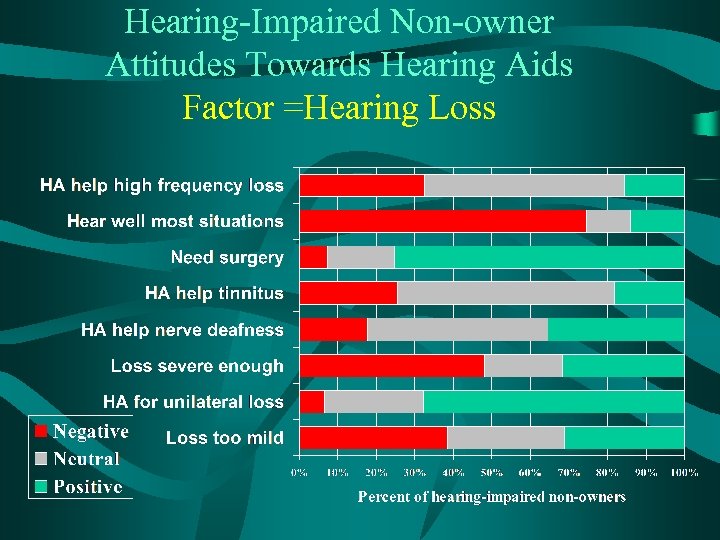 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Hearing Loss
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Hearing Loss
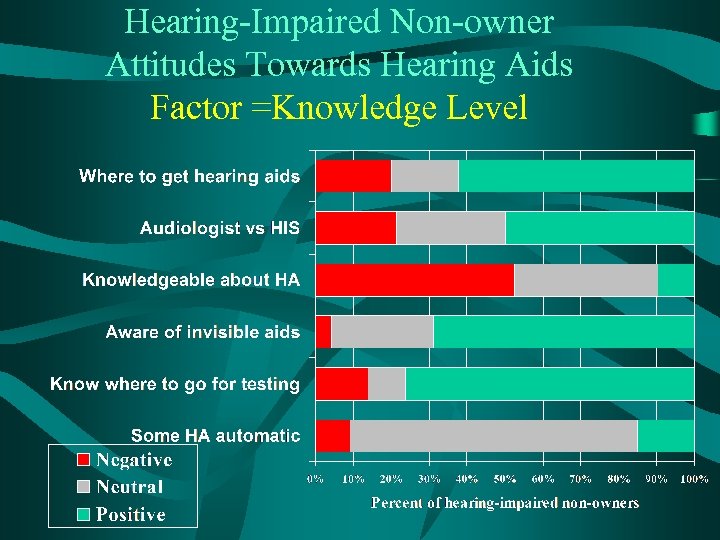 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Knowledge Level
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Knowledge Level
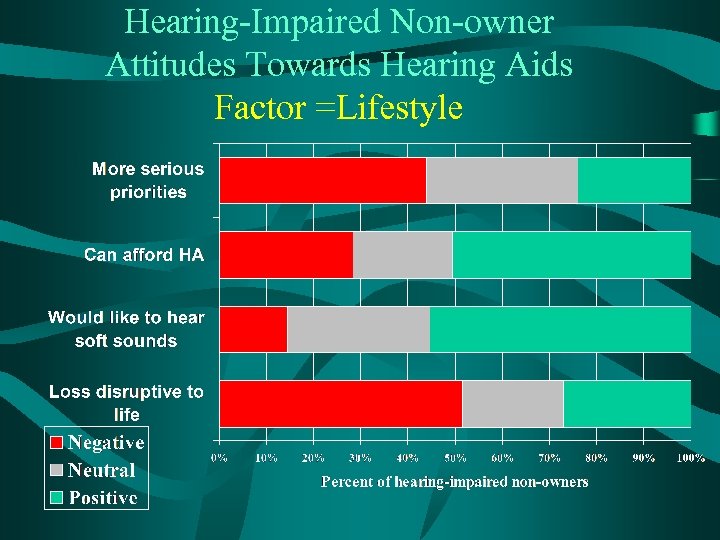 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Lifestyle
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Lifestyle
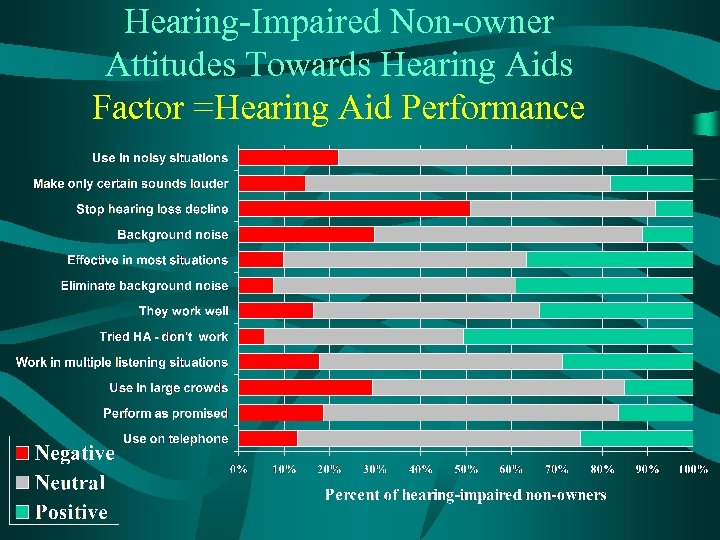 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Hearing Aid Performance
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Hearing Aid Performance
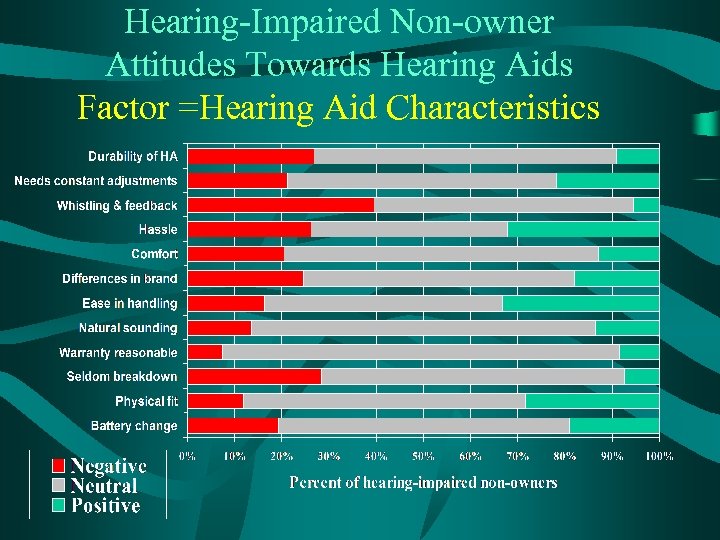 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Hearing Aid Characteristics
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Hearing Aid Characteristics
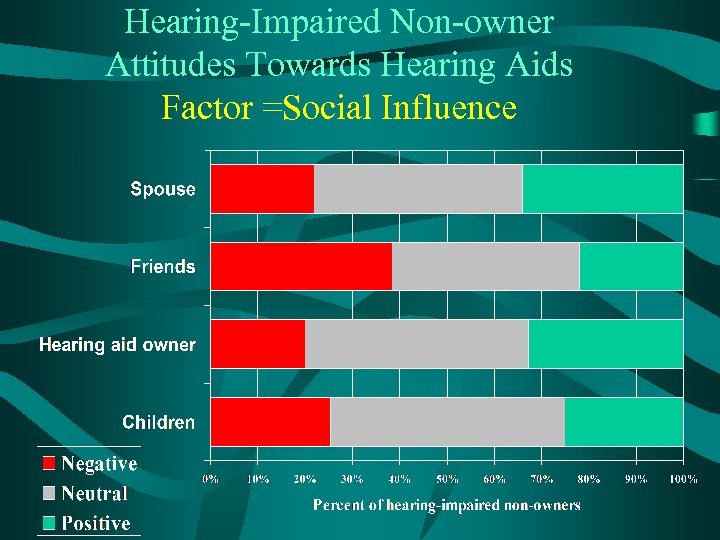 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Social Influence
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Social Influence
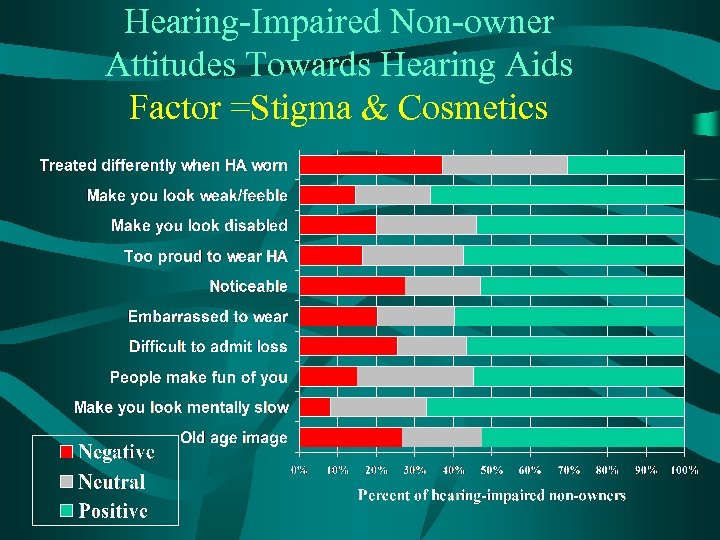 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Stigma & Cosmetics
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Stigma & Cosmetics
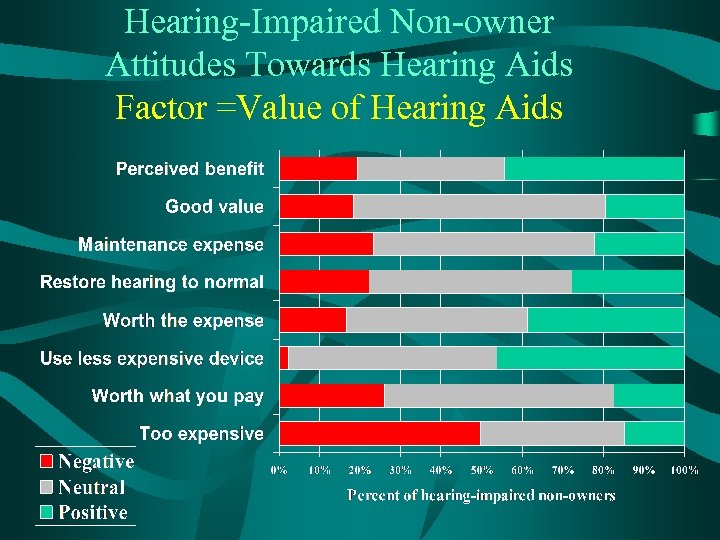 Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Value of Hearing Aids
Hearing-Impaired Non-owner Attitudes Towards Hearing Aids Factor =Value of Hearing Aids
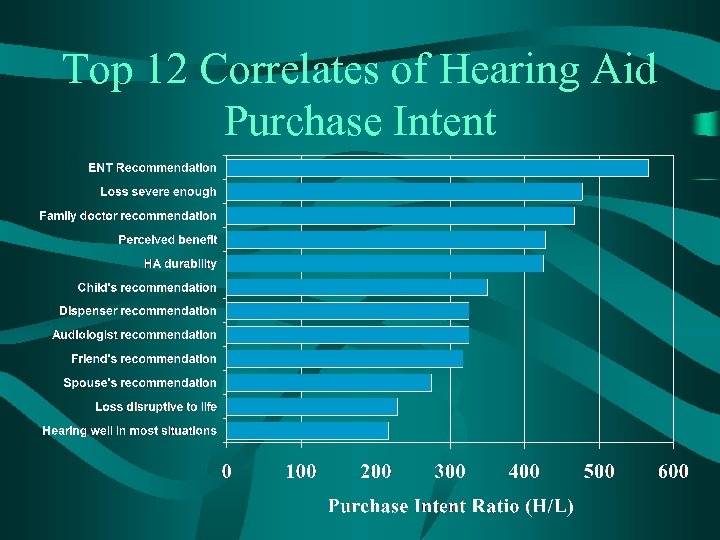 Top 12 Correlates of Hearing Aid Purchase Intent
Top 12 Correlates of Hearing Aid Purchase Intent
 Lowest Correlates of Hearing Aid Purchase Intent • Brand • HA make only certain sounds louder • Too expensive • HA sellers take advantage of you • Can afford hearing aids • Need surgery • Know where to go for hearing tests • Know where to buy hearing aids • Old image of hearing aids • Use lower expense product • Customer orientation of dispensers • HA warranty • Knowledge of hearing aids
Lowest Correlates of Hearing Aid Purchase Intent • Brand • HA make only certain sounds louder • Too expensive • HA sellers take advantage of you • Can afford hearing aids • Need surgery • Know where to go for hearing tests • Know where to buy hearing aids • Old image of hearing aids • Use lower expense product • Customer orientation of dispensers • HA warranty • Knowledge of hearing aids
 Optimizing Quality of Life Benefits for the Consumer of Hearing Aids
Optimizing Quality of Life Benefits for the Consumer of Hearing Aids
 Summary of Quality of Life Benefits Associated with Hearing Aids (NCOA Study – January 2000 Hearing Review) • >Interpersonal relationships •
Summary of Quality of Life Benefits Associated with Hearing Aids (NCOA Study – January 2000 Hearing Review) • >Interpersonal relationships •
 Leveraging the Quality of Life Findings • Best way to leverage is to assure that your clients have achieved significant benefit with their hearing aids. • Post-fitting benefit measurement and customer opinion surveys critical. • Minimize hearing aids in the drawer. • Use technology and processes which enhance customer satisfaction.
Leveraging the Quality of Life Findings • Best way to leverage is to assure that your clients have achieved significant benefit with their hearing aids. • Post-fitting benefit measurement and customer opinion surveys critical. • Minimize hearing aids in the drawer. • Use technology and processes which enhance customer satisfaction.
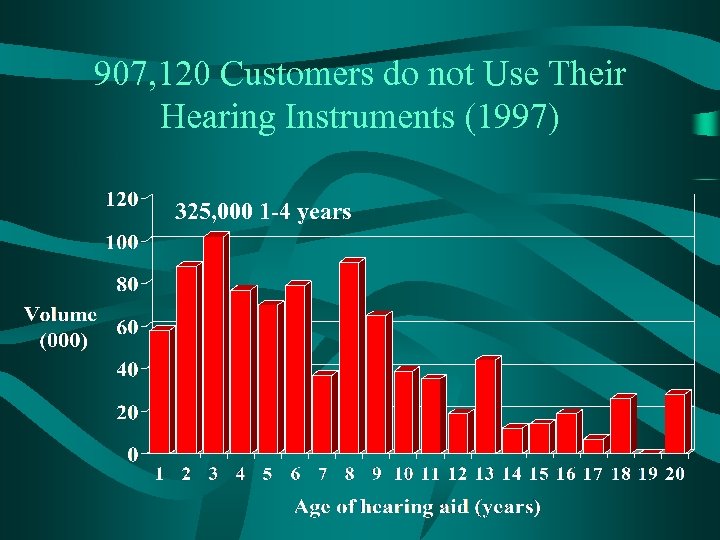 907, 120 Customers do not Use Their Hearing Instruments (1997) 325, 000 1 -4 years
907, 120 Customers do not Use Their Hearing Instruments (1997) 325, 000 1 -4 years
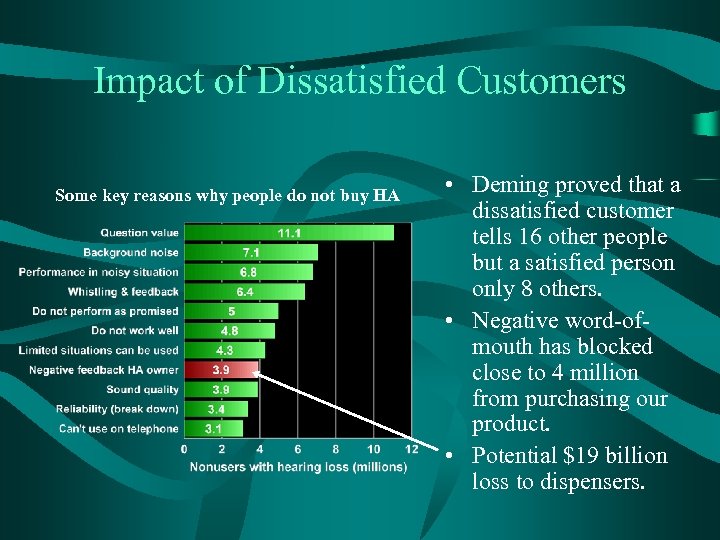 Impact of Dissatisfied Customers Some key reasons why people do not buy HA • Deming proved that a dissatisfied customer tells 16 other people but a satisfied person only 8 others. • Negative word-ofmouth has blocked close to 4 million from purchasing our product. • Potential $19 billion loss to dispensers.
Impact of Dissatisfied Customers Some key reasons why people do not buy HA • Deming proved that a dissatisfied customer tells 16 other people but a satisfied person only 8 others. • Negative word-ofmouth has blocked close to 4 million from purchasing our product. • Potential $19 billion loss to dispensers.
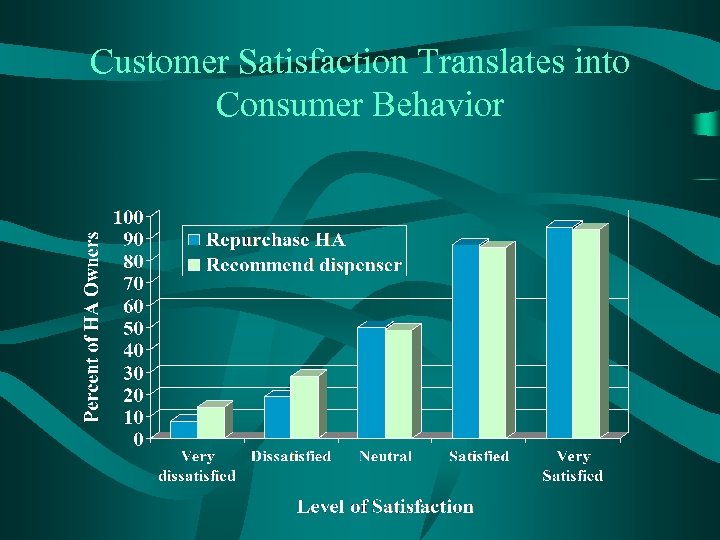 Customer Satisfaction Translates into Consumer Behavior
Customer Satisfaction Translates into Consumer Behavior
 Reasons for Non-Use • #1. Poor benefit (30%) - 268, 507 “When ______sold me the H. A. , I was confident it would help me hear better. When I received it and wore it every day, it did not make my hearing any better. So, I don’t wear the HA and feel like I wasted my money. I tried to return it and the person did not seem to want to help me. I am quite dissatisfied with the whole experience. ”
Reasons for Non-Use • #1. Poor benefit (30%) - 268, 507 “When ______sold me the H. A. , I was confident it would help me hear better. When I received it and wore it every day, it did not make my hearing any better. So, I don’t wear the HA and feel like I wasted my money. I tried to return it and the person did not seem to want to help me. I am quite dissatisfied with the whole experience. ”
 Reasons for Non-Use • #2. Background noise (25%) - 229, 383 I don’t wear my H. A. because I need it at a dance, restaurants, and large groups. All the H. A. does is increase all sound including background sounds. No help. ”
Reasons for Non-Use • #2. Background noise (25%) - 229, 383 I don’t wear my H. A. because I need it at a dance, restaurants, and large groups. All the H. A. does is increase all sound including background sounds. No help. ”
 Reasons for Non-Use • #3. Fit & Comfort (19%) - 169, 431 “It’s hard to keep it in my ear. I travel for business a lot and can’t risk it falling out of my ear. ”
Reasons for Non-Use • #3. Fit & Comfort (19%) - 169, 431 “It’s hard to keep it in my ear. I travel for business a lot and can’t risk it falling out of my ear. ”
 Reasons for Non-Use • #4. Negative side effects (11%) - 99, 048 “Ears that hurt, too much pressure in the ears, blisters in ears, rashes in ears, itching ears, dizzy, nervous, ears that sweat, builds up wax in inner ear, headache, hair gets caught in hearing aid, infections in ear, problems chewing or swallowing, plugs up ears”.
Reasons for Non-Use • #4. Negative side effects (11%) - 99, 048 “Ears that hurt, too much pressure in the ears, blisters in ears, rashes in ears, itching ears, dizzy, nervous, ears that sweat, builds up wax in inner ear, headache, hair gets caught in hearing aid, infections in ear, problems chewing or swallowing, plugs up ears”.
 Reasons for Non-Use • #5. Price & cost (10%) - 93, 839 “My H. A. was never dependable. Taking it in for an adjustment was only a headache as it never performed very long. Had to be looked at again. The last time I had trouble, the office wanted to send it to _____ at $200 & just to check it, plus another $200 to repair it. ”
Reasons for Non-Use • #5. Price & cost (10%) - 93, 839 “My H. A. was never dependable. Taking it in for an adjustment was only a headache as it never performed very long. Had to be looked at again. The last time I had trouble, the office wanted to send it to _____ at $200 & just to check it, plus another $200 to repair it. ”
 We must minimize hearing aids in the drawer • 907 k inactive hearing aid owners • Key reasons: – – – Poor benefit Background noise Fit and comfort Negative side effects Maintenance Cost/broken HA • Impossible for consumer to experience QOL changes if their hearing aid is in drawer. • Dispenser must find ways of optimizing the consumer’s experience
We must minimize hearing aids in the drawer • 907 k inactive hearing aid owners • Key reasons: – – – Poor benefit Background noise Fit and comfort Negative side effects Maintenance Cost/broken HA • Impossible for consumer to experience QOL changes if their hearing aid is in drawer. • Dispenser must find ways of optimizing the consumer’s experience
 Dispenser does have control over hearing aids in the drawer • # 1. Poor benefit: ü Use programmable technology (analog or DSP) ü Pre-post benefit measurement ü Real ear measurement ü 90 day post fitting customer satisfaction survey. ü 100% money back guarantee ü Aural rehabilitation • Significant impact on hearing aid satisfaction. • Return rates been shown to be cut in half.
Dispenser does have control over hearing aids in the drawer • # 1. Poor benefit: ü Use programmable technology (analog or DSP) ü Pre-post benefit measurement ü Real ear measurement ü 90 day post fitting customer satisfaction survey. ü 100% money back guarantee ü Aural rehabilitation • Significant impact on hearing aid satisfaction. • Return rates been shown to be cut in half.
 Dispenser does have control over hearing aids in the drawer • # 2. Hearing in noise ü 100% use of dual microphones – not just in high-end product ü DSP for comfort in noise ü Volume control necessary for some segments ü Manual omni/directional switch necessary for some consumers ü Binaural fitting for bilateral loss customers (85% rate in US- much lower in Europe) ü Deep-fitting CICs give some benefit. ü Aural rehabilitation
Dispenser does have control over hearing aids in the drawer • # 2. Hearing in noise ü 100% use of dual microphones – not just in high-end product ü DSP for comfort in noise ü Volume control necessary for some segments ü Manual omni/directional switch necessary for some consumers ü Binaural fitting for bilateral loss customers (85% rate in US- much lower in Europe) ü Deep-fitting CICs give some benefit. ü Aural rehabilitation
 Dispenser does have control over hearing aids in the drawer • #3. Fit and Comfort ü Extreme vigilance during impression taking. • Multiple shell impressions if necessary with “best” going to the manufacturer. • Silicon material considered superior. ü Explore emerging soft shell technology for difficult cases. ü Rework within office. ü Assess manual dexterity and visual acuity considerations relative to hearing aid style. ü 14 or 30 day trial post-fitting subjective measure of fit and comfort.
Dispenser does have control over hearing aids in the drawer • #3. Fit and Comfort ü Extreme vigilance during impression taking. • Multiple shell impressions if necessary with “best” going to the manufacturer. • Silicon material considered superior. ü Explore emerging soft shell technology for difficult cases. ü Rework within office. ü Assess manual dexterity and visual acuity considerations relative to hearing aid style. ü 14 or 30 day trial post-fitting subjective measure of fit and comfort.
 Improving Customer Satisfaction with Hearing Aids Recent Research
Improving Customer Satisfaction with Hearing Aids Recent Research
 Strategic Objective of Knowles • Participate with the industry in a continued dialogue on factors impacting customer satisfaction. • Customer satisfaction improvement – critical to growth of the market – the only way to properly leverage QOL findings. • Knowles conducted research on 25, 000+ consumers. – Customer satisfaction – Subjective benefit • Publication of journal dedicated to customer satisfaction: High Performance Hearing Solutions.
Strategic Objective of Knowles • Participate with the industry in a continued dialogue on factors impacting customer satisfaction. • Customer satisfaction improvement – critical to growth of the market – the only way to properly leverage QOL findings. • Knowles conducted research on 25, 000+ consumers. – Customer satisfaction – Subjective benefit • Publication of journal dedicated to customer satisfaction: High Performance Hearing Solutions.
 Previous Marke. Trak Customer Satisfaction Research • Advanced technology enhances customer satisfaction: – Programmable (digital or manual) – Multiple memories – Multiple channels – Multiple microphones – directional hearing instruments (strongest factor) – Non-linear signal processing (e. g. WDRC)
Previous Marke. Trak Customer Satisfaction Research • Advanced technology enhances customer satisfaction: – Programmable (digital or manual) – Multiple memories – Multiple channels – Multiple microphones – directional hearing instruments (strongest factor) – Non-linear signal processing (e. g. WDRC)
 Previous Marke. Trak Customer Satisfaction Research • Other important factors – – Volume control (some segments) Telecoils Completely in the canal instruments (CIC) Binaural hearing aids • More recent research – Cerumen management systems (Sep. 2001 HR; Apr. 2002 HR) – Digital Hearing Aids (Nov. 2000 HR) 1. Now 40% of the market 2. Smaller clinical studies generally positive
Previous Marke. Trak Customer Satisfaction Research • Other important factors – – Volume control (some segments) Telecoils Completely in the canal instruments (CIC) Binaural hearing aids • More recent research – Cerumen management systems (Sep. 2001 HR; Apr. 2002 HR) – Digital Hearing Aids (Nov. 2000 HR) 1. Now 40% of the market 2. Smaller clinical studies generally positive
 Recent Research with Micro. Waxbuster Demonstrates it Will Dramatically Reduce Hearing Aid Service Rates Micro. Waxbuster Cutaway CIC with Micro. Waxbuster installed
Recent Research with Micro. Waxbuster Demonstrates it Will Dramatically Reduce Hearing Aid Service Rates Micro. Waxbuster Cutaway CIC with Micro. Waxbuster installed
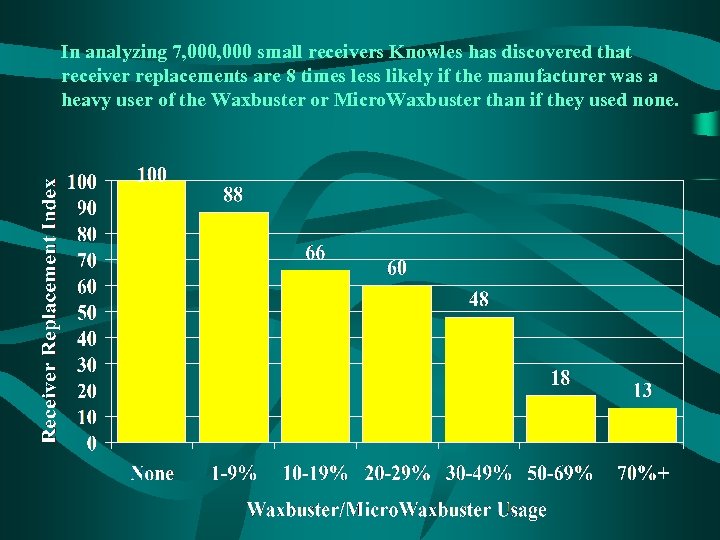 In analyzing 7, 000 small receivers Knowles has discovered that receiver replacements are 8 times less likely if the manufacturer was a heavy user of the Waxbuster or Micro. Waxbuster than if they used none.
In analyzing 7, 000 small receivers Knowles has discovered that receiver replacements are 8 times less likely if the manufacturer was a heavy user of the Waxbuster or Micro. Waxbuster than if they used none.
 Study # 2 – 90, 000+ Consumers • Database query of one US manufacturer. • 24 month study across three styles of hearing instruments: CIC, ITE. • Consumers segmented: – Age of instrument – 1 -24 months – Micro. Waxbuster usage or None. • Tracked receiver replacements in corporate service files.
Study # 2 – 90, 000+ Consumers • Database query of one US manufacturer. • 24 month study across three styles of hearing instruments: CIC, ITE. • Consumers segmented: – Age of instrument – 1 -24 months – Micro. Waxbuster usage or None. • Tracked receiver replacements in corporate service files.
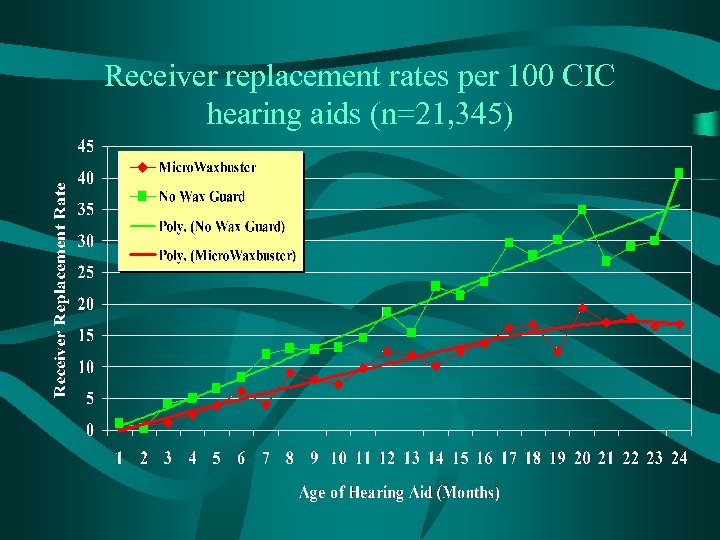 Receiver replacement rates per 100 CIC hearing aids (n=21, 345)
Receiver replacement rates per 100 CIC hearing aids (n=21, 345)
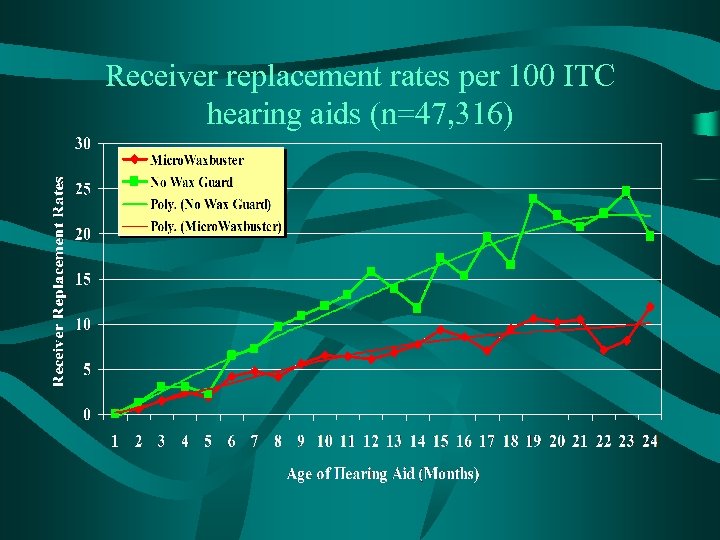 Receiver replacement rates per 100 ITC hearing aids (n=47, 316)
Receiver replacement rates per 100 ITC hearing aids (n=47, 316)
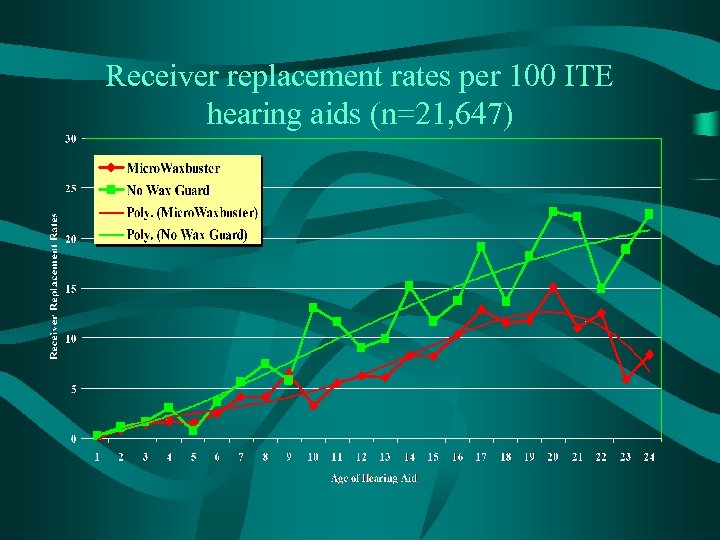 Receiver replacement rates per 100 ITE hearing aids (n=21, 647)
Receiver replacement rates per 100 ITE hearing aids (n=21, 647)
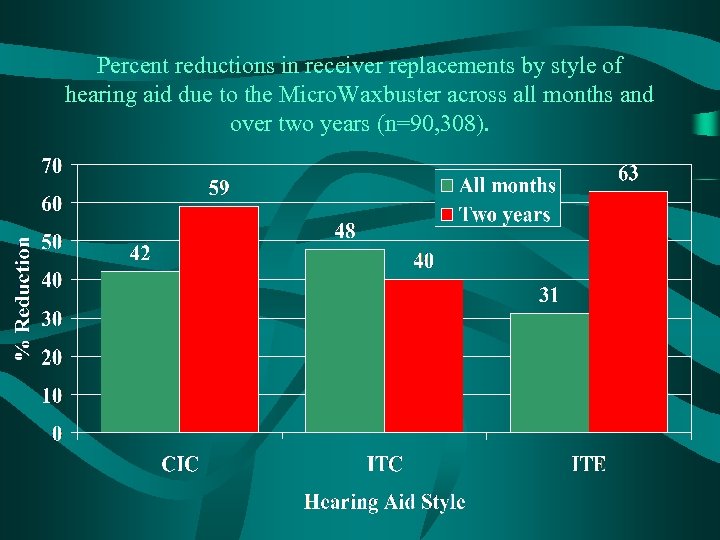 Percent reductions in receiver replacements by style of hearing aid due to the Micro. Waxbuster across all months and over two years (n=90, 308).
Percent reductions in receiver replacements by style of hearing aid due to the Micro. Waxbuster across all months and over two years (n=90, 308).
 Conclusions • Increased penetration of ITE, ITC, and CIC hearing instruments with the Micro. Waxbuster® product will have a positive impact on the market place. • Offer this as a strongly recommended option to your patients/customers. • Both manufacturers and dispensers should recognize increased profits by selling this optional component while reducing within-warranty repairs. • Consumers for a small additional fee, will experience: – Greater reliability in their product, – Resulting in fewer hearing instrument repairs, – Reduced frustration and therefore, – Increased consumer satisfaction.
Conclusions • Increased penetration of ITE, ITC, and CIC hearing instruments with the Micro. Waxbuster® product will have a positive impact on the market place. • Offer this as a strongly recommended option to your patients/customers. • Both manufacturers and dispensers should recognize increased profits by selling this optional component while reducing within-warranty repairs. • Consumers for a small additional fee, will experience: – Greater reliability in their product, – Resulting in fewer hearing instrument repairs, – Reduced frustration and therefore, – Increased consumer satisfaction.
 Digital Study November 2000 Hearing Review • Multiple manufacturer products were studied. • Results of first large-scale study on satisfaction with DSP hearing aids: – – – Single European based manufacturer 200 single mic (44% ITE / 56% ITC) 296 multiple mic (69% BTE / 31% ITE) Compared to 418 Marke. Trak (analog) norms Average of instruments 7 -8 months • Consumer completed Knowles Marke. Trak survey – 45 ratings of hearing aid and dispenser
Digital Study November 2000 Hearing Review • Multiple manufacturer products were studied. • Results of first large-scale study on satisfaction with DSP hearing aids: – – – Single European based manufacturer 200 single mic (44% ITE / 56% ITC) 296 multiple mic (69% BTE / 31% ITE) Compared to 418 Marke. Trak (analog) norms Average of instruments 7 -8 months • Consumer completed Knowles Marke. Trak survey – 45 ratings of hearing aid and dispenser
 Top ten correlates of overall satisfaction (in rank order) 1. Perceived benefit 2. Sound clarity 3. Value (price/performance) 4. Reliability 5. Use in leisure activities 6. Natural sounding 7. Use in noisy situations 8. Use in large groups 9. Use in restaurants 10. Use outdoors
Top ten correlates of overall satisfaction (in rank order) 1. Perceived benefit 2. Sound clarity 3. Value (price/performance) 4. Reliability 5. Use in leisure activities 6. Natural sounding 7. Use in noisy situations 8. Use in large groups 9. Use in restaurants 10. Use outdoors
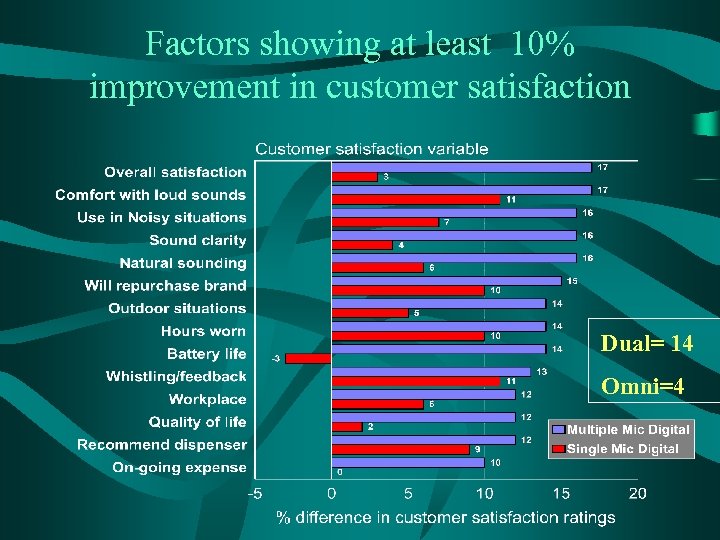 Factors showing at least 10% improvement in customer satisfaction Dual= 14 Omni=4
Factors showing at least 10% improvement in customer satisfaction Dual= 14 Omni=4
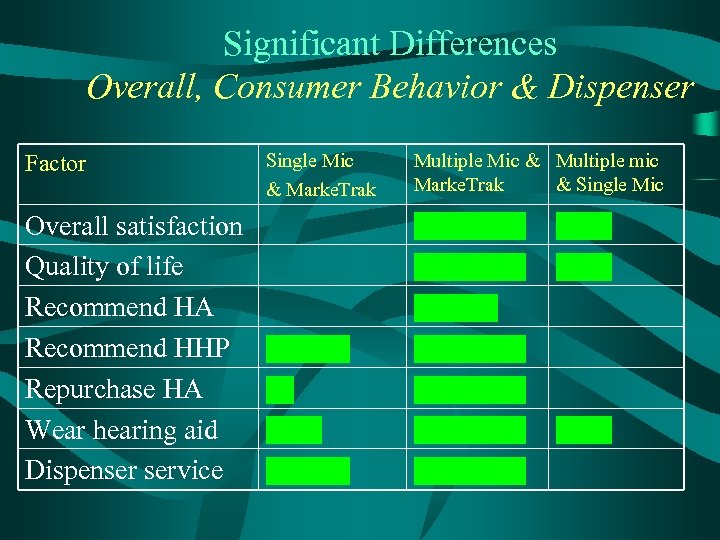 Significant Differences Overall, Consumer Behavior & Dispenser Factor Overall satisfaction Quality of life Recommend HA Recommend HHP Repurchase HA Wear hearing aid Dispenser service Single Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple Mic & Multiple mic Marke. Trak & Single Mic
Significant Differences Overall, Consumer Behavior & Dispenser Factor Overall satisfaction Quality of life Recommend HA Recommend HHP Repurchase HA Wear hearing aid Dispenser service Single Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple Mic & Multiple mic Marke. Trak & Single Mic
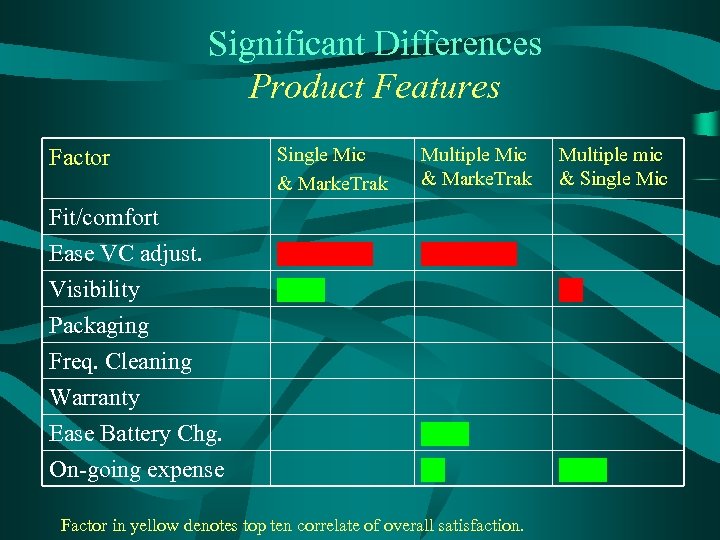 Significant Differences Product Features Factor Fit/comfort Ease VC adjust. Visibility Packaging Freq. Cleaning Warranty Ease Battery Chg. On-going expense Single Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple mic & Single Mic Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
Significant Differences Product Features Factor Fit/comfort Ease VC adjust. Visibility Packaging Freq. Cleaning Warranty Ease Battery Chg. On-going expense Single Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple mic & Single Mic Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
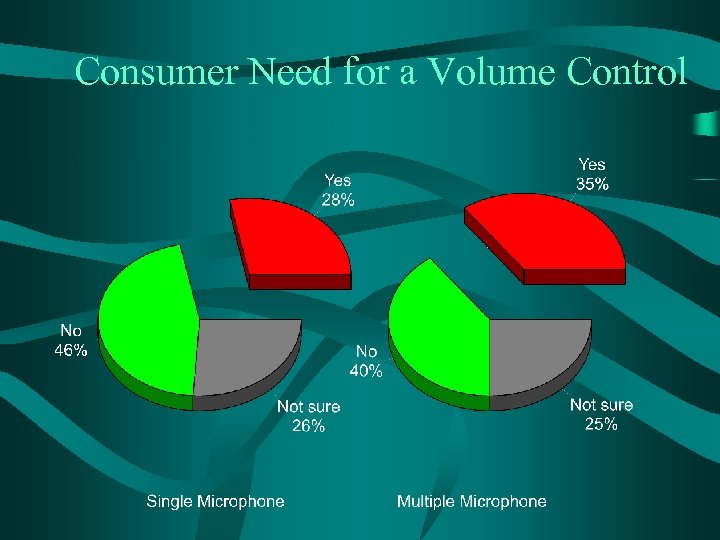 Consumer Need for a Volume Control
Consumer Need for a Volume Control
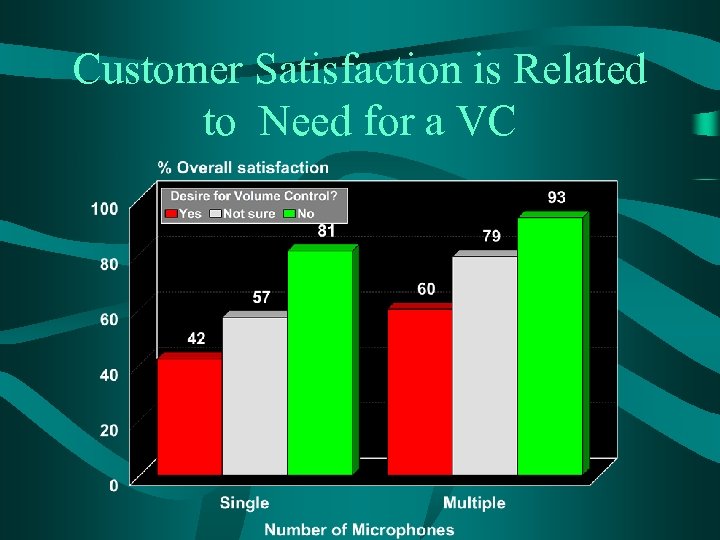 Customer Satisfaction is Related to Need for a VC
Customer Satisfaction is Related to Need for a VC
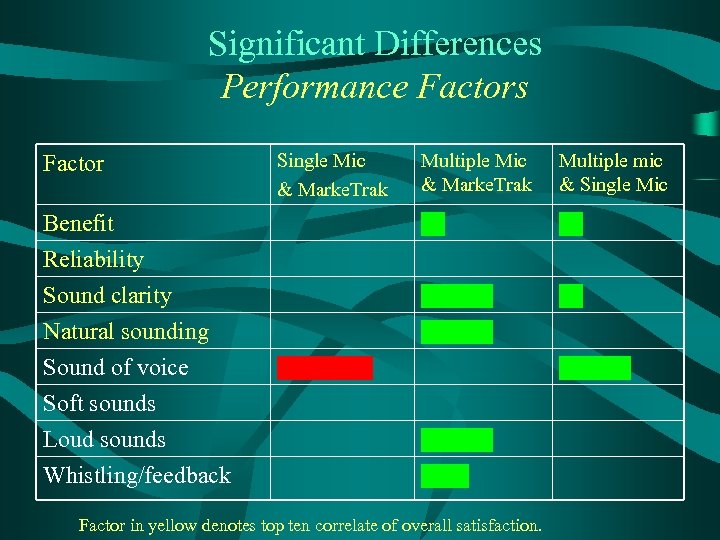 Significant Differences Performance Factors Multiple Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple mic & Single Mic Benefit Reliability Sound clarity Natural sounding Sound of voice Soft sounds Loud sounds Whistling/feedback Factor Single Mic & Marke. Trak Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
Significant Differences Performance Factors Multiple Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple mic & Single Mic Benefit Reliability Sound clarity Natural sounding Sound of voice Soft sounds Loud sounds Whistling/feedback Factor Single Mic & Marke. Trak Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
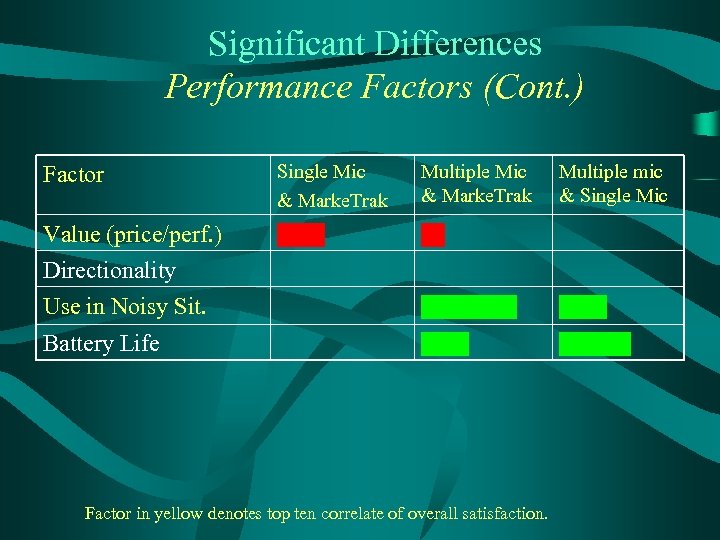 Significant Differences Performance Factors (Cont. ) Factor Single Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple Mic & Marke. Trak Value (price/perf. ) Directionality Multiple mic & Single Mic Use in Noisy Sit. Battery Life Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
Significant Differences Performance Factors (Cont. ) Factor Single Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple Mic & Marke. Trak Value (price/perf. ) Directionality Multiple mic & Single Mic Use in Noisy Sit. Battery Life Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
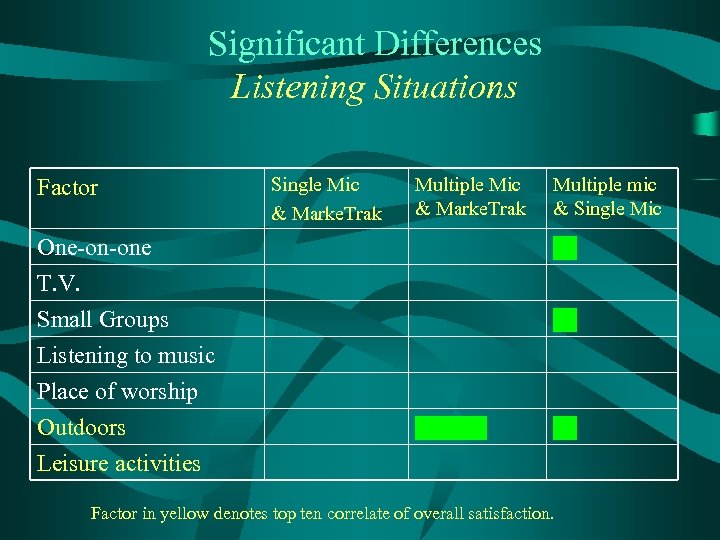 Significant Differences Listening Situations Factor Single Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple mic & Single Mic One-on-one T. V. Small Groups Listening to music Place of worship Outdoors Leisure activities Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
Significant Differences Listening Situations Factor Single Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple mic & Single Mic One-on-one T. V. Small Groups Listening to music Place of worship Outdoors Leisure activities Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
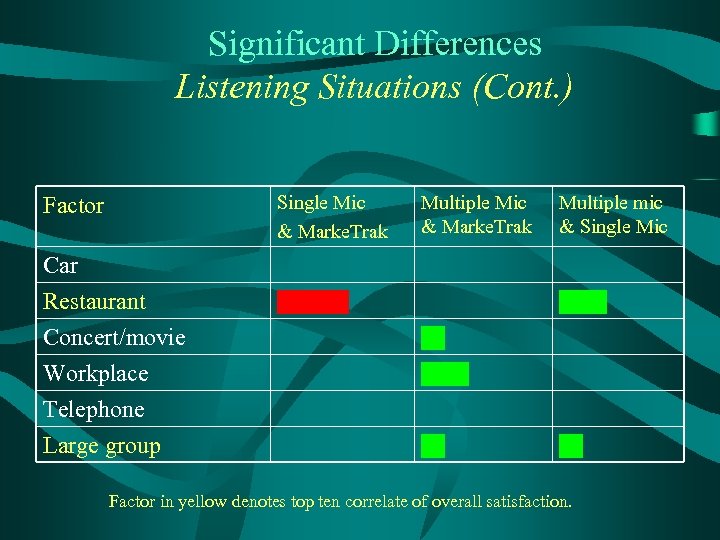 Significant Differences Listening Situations (Cont. ) Single Mic & Marke. Trak Factor Car Restaurant Concert/movie Workplace Telephone Large group Multiple Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple mic & Single Mic Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
Significant Differences Listening Situations (Cont. ) Single Mic & Marke. Trak Factor Car Restaurant Concert/movie Workplace Telephone Large group Multiple Mic & Marke. Trak Multiple mic & Single Mic Factor in yellow denotes top ten correlate of overall satisfaction.
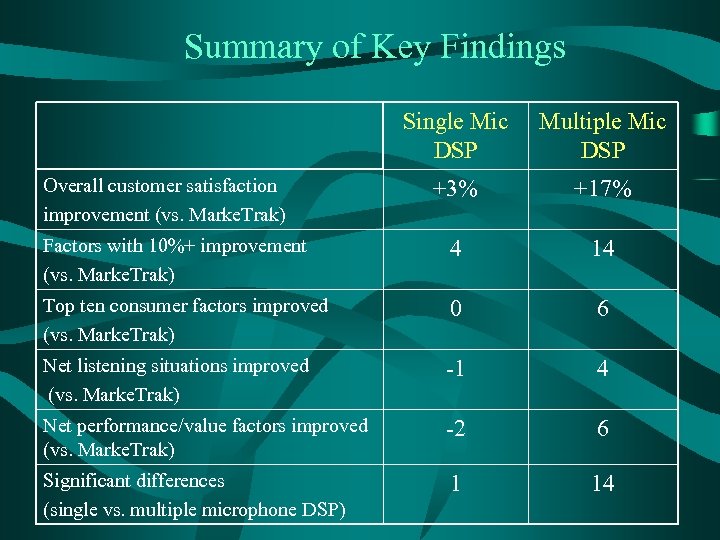 Summary of Key Findings Single Mic DSP Multiple Mic DSP +3% +17% Factors with 10%+ improvement (vs. Marke. Trak) 4 14 Top ten consumer factors improved (vs. Marke. Trak) 0 6 Net listening situations improved (vs. Marke. Trak) -1 4 Net performance/value factors improved (vs. Marke. Trak) -2 6 Significant differences (single vs. multiple microphone DSP) 1 14 Overall customer satisfaction improvement (vs. Marke. Trak)
Summary of Key Findings Single Mic DSP Multiple Mic DSP +3% +17% Factors with 10%+ improvement (vs. Marke. Trak) 4 14 Top ten consumer factors improved (vs. Marke. Trak) 0 6 Net listening situations improved (vs. Marke. Trak) -1 4 Net performance/value factors improved (vs. Marke. Trak) -2 6 Significant differences (single vs. multiple microphone DSP) 1 14 Overall customer satisfaction improvement (vs. Marke. Trak)
 Conclusions • Performance in noise: – Key reason why hearing-impaired do not buy hearing aids (Marke. Trak). – #1 hearing aid improvement sought by hearing aid users (United States Marke. Trak study - 2001). – #1 hearing aid improvement sought by hearing aid users (German study - 1995). – #2 reason why 907, 000 of our customers place their hearing aids in the drawer (Marke. Trak).
Conclusions • Performance in noise: – Key reason why hearing-impaired do not buy hearing aids (Marke. Trak). – #1 hearing aid improvement sought by hearing aid users (United States Marke. Trak study - 2001). – #1 hearing aid improvement sought by hearing aid users (German study - 1995). – #2 reason why 907, 000 of our customers place their hearing aids in the drawer (Marke. Trak).
 Conclusions • Consumer studies now demonstrate the superiority of multiple microphone hearing aids over omnidirectional only aids: – Kuk (Hearing Instruments, 1996) - analog – Kochkin (Hearing Review, 1996) - analog – Schuchman, Valente, Beck, Potts (HR, 1999) – analog (double blinded study) – Kochkin (Hearing Review, 2000)- digital • Consumer research supportive of dozens of small clinic/lab studies or theoretical papers.
Conclusions • Consumer studies now demonstrate the superiority of multiple microphone hearing aids over omnidirectional only aids: – Kuk (Hearing Instruments, 1996) - analog – Kochkin (Hearing Review, 1996) - analog – Schuchman, Valente, Beck, Potts (HR, 1999) – analog (double blinded study) – Kochkin (Hearing Review, 2000)- digital • Consumer research supportive of dozens of small clinic/lab studies or theoretical papers.
 Recommendations • Fit all qualified candidates with directional hearing aids (BTE, Full concha, half shell). • Ask manufacturers to extend directional feature to lower priced product (not just high end programmable. ) • Completely automatic aids are tremendous feature for some, but not all, consumers: – Make sure your patient can live without VC or directional/omni-directional switch. – Lack of control could dramatically impact satisfaction. • Consider active wax protection system as standard feature on all In-the-ear instruments.
Recommendations • Fit all qualified candidates with directional hearing aids (BTE, Full concha, half shell). • Ask manufacturers to extend directional feature to lower priced product (not just high end programmable. ) • Completely automatic aids are tremendous feature for some, but not all, consumers: – Make sure your patient can live without VC or directional/omni-directional switch. – Lack of control could dramatically impact satisfaction. • Consider active wax protection system as standard feature on all In-the-ear instruments.


