dc87ff6f17f7ebedae93ec76aba16ac4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 MARC-HI Everest Framework HL 7 v 3 RMIM API Overview Jan 2010
MARC-HI Everest Framework HL 7 v 3 RMIM API Overview Jan 2010
 Agenda • Introduction • Overview – – What is the Everest Framework? Components From MIF to XML Instance Roadmap • Developer Experience
Agenda • Introduction • Overview – – What is the Everest Framework? Components From MIF to XML Instance Roadmap • Developer Experience
 What is MARC-HI? • Mohawk Applied Research Centre in Health Informatics – 3 Faculty Members – 3 Full Time Developers – 6 Course release and co-op students • Began work with HL 7 v 3 in summer 2007 • NSERC operational funding for 2009 -2014 • Focused on building reference implementation of the CHI EHR Infostructure (HL 7 v 3 using p. CS)
What is MARC-HI? • Mohawk Applied Research Centre in Health Informatics – 3 Faculty Members – 3 Full Time Developers – 6 Course release and co-op students • Began work with HL 7 v 3 in summer 2007 • NSERC operational funding for 2009 -2014 • Focused on building reference implementation of the CHI EHR Infostructure (HL 7 v 3 using p. CS)
 Accomplishments to date • Operational (online sandbox) HIAL supporting approximately 20% of the p. CS interactions • Acted as HIAL infrastructure for e. Health 2008 and 2009 • Have built reference implementations of TLI, Referral, i. EHR domain, etc. • Have completed contract based investigation work for CIHI, CHI, 3 M, etc.
Accomplishments to date • Operational (online sandbox) HIAL supporting approximately 20% of the p. CS interactions • Acted as HIAL infrastructure for e. Health 2008 and 2009 • Have built reference implementations of TLI, Referral, i. EHR domain, etc. • Have completed contract based investigation work for CIHI, CHI, 3 M, etc.
 MARC-HI EVEREST FRAMEWORK
MARC-HI EVEREST FRAMEWORK
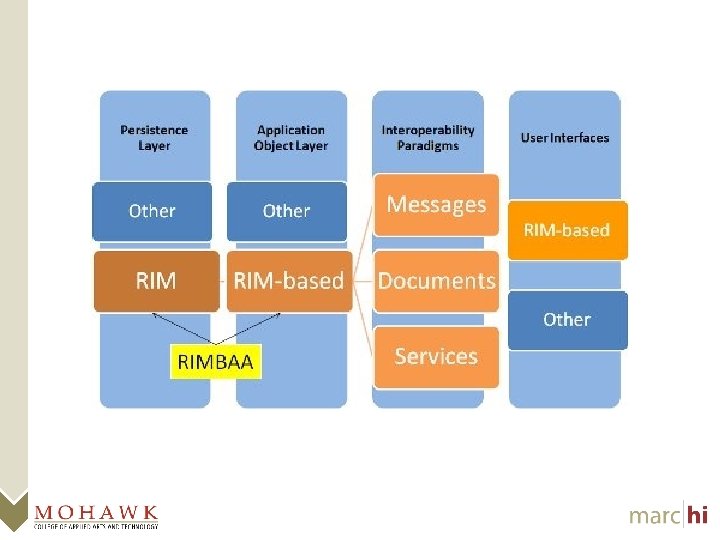
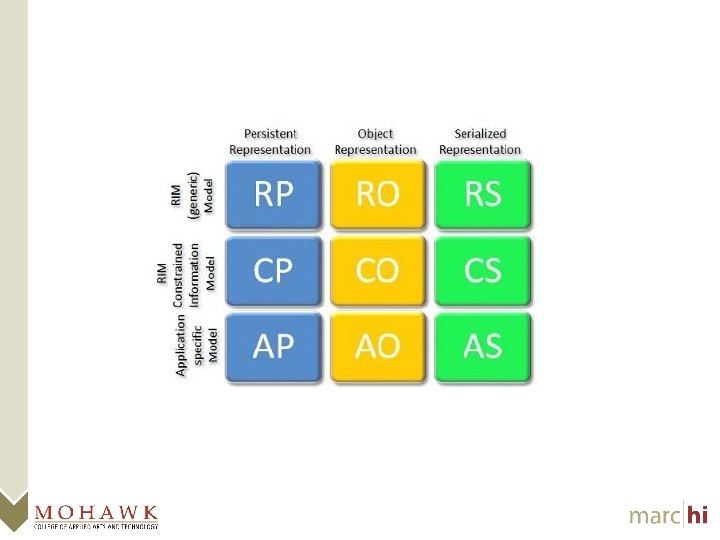
 What is the Everest Framework? • Everest is the foundation for an HL 7 v 3 Messaging API – Class/Object representation of structures from p. CS HL 7 v 3 MIFs – Improved v 3 experience • Extensive documentation in developer’s IDE brought forward from MIFs • Parameterized constructors, operators, and helper functions
What is the Everest Framework? • Everest is the foundation for an HL 7 v 3 Messaging API – Class/Object representation of structures from p. CS HL 7 v 3 MIFs – Improved v 3 experience • Extensive documentation in developer’s IDE brought forward from MIFs • Parameterized constructors, operators, and helper functions
 What is the Everest Framework? – Flexible ITS and Transport layers – Current version. NET based, ports to Java underway – Primarily used by higher level APIs, but also used directly by application programmers
What is the Everest Framework? – Flexible ITS and Transport layers – Current version. NET based, ports to Java underway – Primarily used by higher level APIs, but also used directly by application programmers
 Why bother? • Productivity raised 10 -100 x by simplifying application developer environment (no requirement to learn XML for example) • Built-in message conformance testing • Enables higher-level business APIs, advanced tooling (interaction wizards, canonical data mapping, automated message creation, automated testing tools, etc. )
Why bother? • Productivity raised 10 -100 x by simplifying application developer environment (no requirement to learn XML for example) • Built-in message conformance testing • Enables higher-level business APIs, advanced tooling (interaction wizards, canonical data mapping, automated message creation, automated testing tools, etc. )
 Components • Data-Types – Hand written (not possible to auto-generate) – Combination of R 1 and R 2 data type structures – Provide validation, operator overloading and other valuable functionality (compression, formatting data, etc. . ) • RMIM Classes – Automatically generated from MIF v 2
Components • Data-Types – Hand written (not possible to auto-generate) – Combination of R 1 and R 2 data type structures – Provide validation, operator overloading and other valuable functionality (compression, formatting data, etc. . ) • RMIM Classes – Automatically generated from MIF v 2
 Components (Cont’d) • Formatters – (De)Serializes class structures a variety of formats (XML, Binary, etc. . . ) – Can be combined – Provide built-in validation support – Optimizes mass processing of HL 7 v 3 structures • Connectors – Transports classes to/from remote endpoints using HL 7 v 3 (WS-*, File. Systems, Memory, etc. )
Components (Cont’d) • Formatters – (De)Serializes class structures a variety of formats (XML, Binary, etc. . . ) – Can be combined – Provide built-in validation support – Optimizes mass processing of HL 7 v 3 structures • Connectors – Transports classes to/from remote endpoints using HL 7 v 3 (WS-*, File. Systems, Memory, etc. )
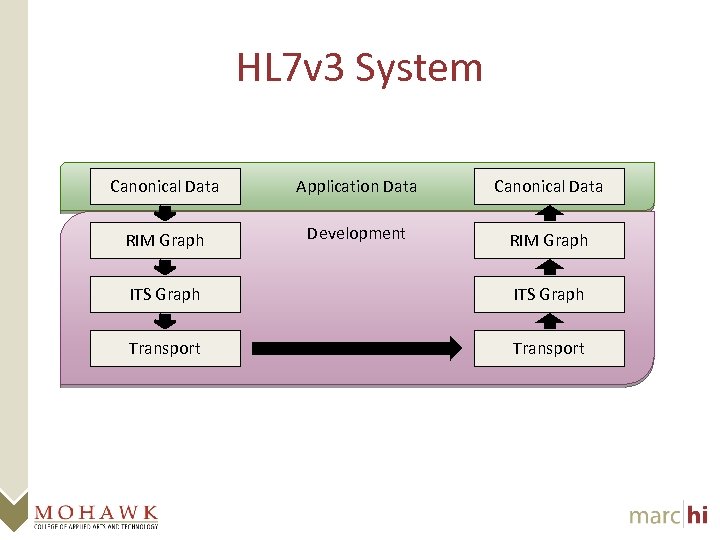 HL 7 v 3 System Canonical Data Application Data Canonical Data RIM Graph Development RIM Graph ITS Graph Transport
HL 7 v 3 System Canonical Data Application Data Canonical Data RIM Graph Development RIM Graph ITS Graph Transport
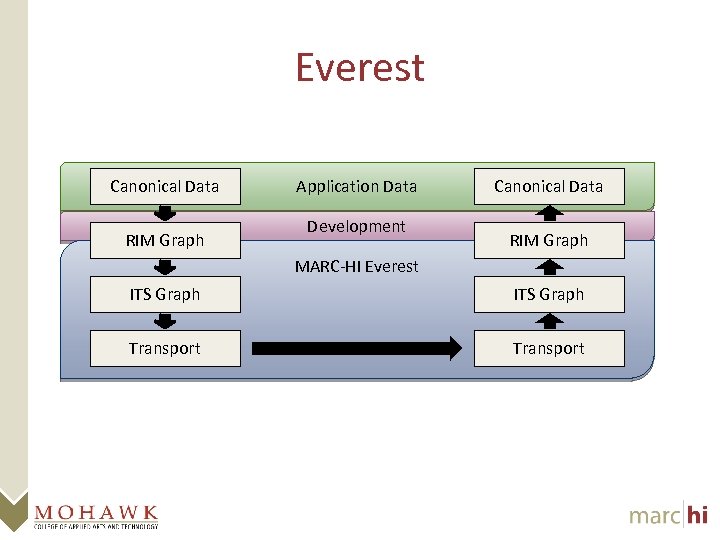 Everest Canonical Data RIM Graph Application Data Development Canonical Data RIM Graph MARC-HI Everest ITS Graph Transport
Everest Canonical Data RIM Graph Application Data Development Canonical Data RIM Graph MARC-HI Everest ITS Graph Transport
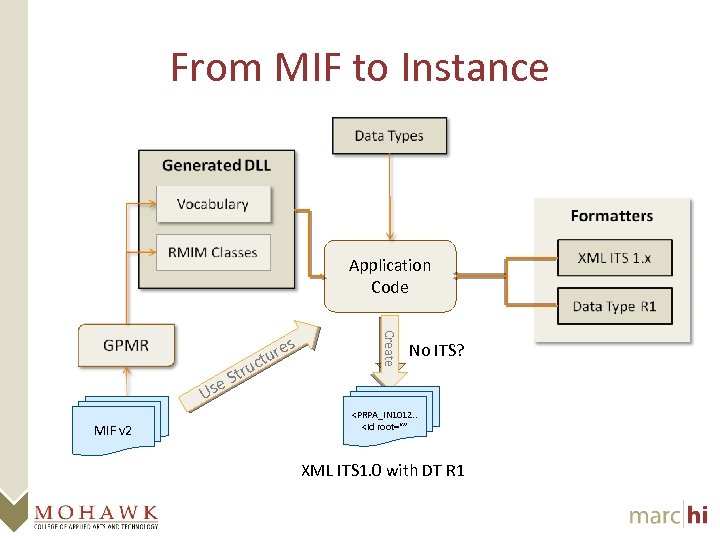 From MIF to Instance Application Code Us MIF v 2 Create tr e. S u s ure ct No ITS?
From MIF to Instance Application Code Us MIF v 2 Create tr e. S u s ure ct No ITS?
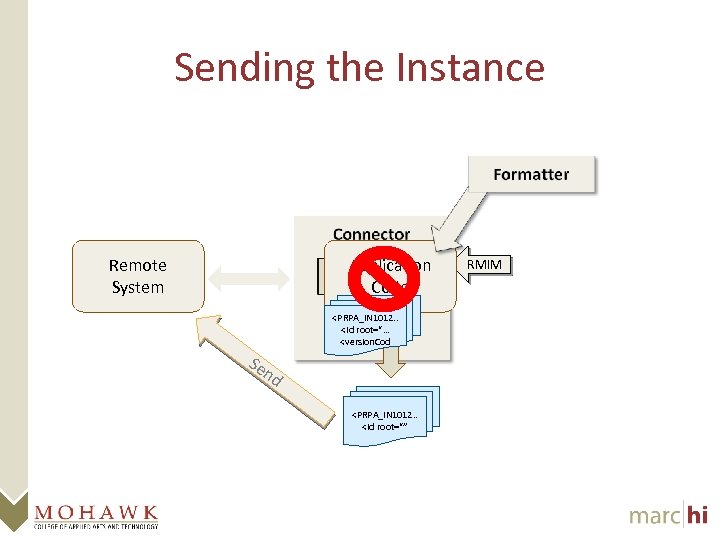 Sending the Instance Remote System Application Code RMIM
Sending the Instance Remote System Application Code RMIM
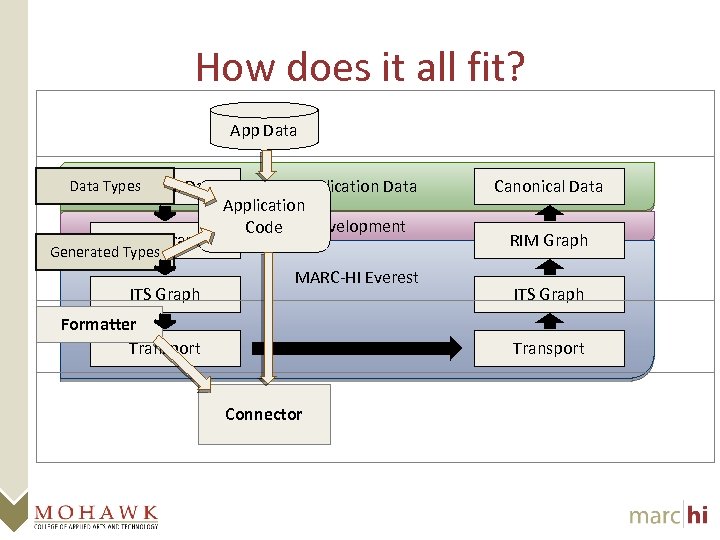 How does it all fit? App Data Types Canonical Data RIM Graph Application Data Application Code Development Generated Types ITS Graph MARC-HI Everest Formatter Transport Canonical Data RIM Graph ITS Graph Transport Connector
How does it all fit? App Data Types Canonical Data RIM Graph Application Data Application Code Development Generated Types ITS Graph MARC-HI Everest Formatter Transport Canonical Data RIM Graph ITS Graph Transport Connector
 Everest Roadmap • Everest November CTP (Infoway sponsored) – – Released October 30 2009 to OHT. NET edition Tutorials (online) Documentation (Reference Guide) • Business model API on top of Everest – Assists developers by abstracting messaging standard • Java Edition – Underway • Web Services (REST) Edition – Underway
Everest Roadmap • Everest November CTP (Infoway sponsored) – – Released October 30 2009 to OHT. NET edition Tutorials (online) Documentation (Reference Guide) • Business model API on top of Everest – Assists developers by abstracting messaging standard • Java Edition – Underway • Web Services (REST) Edition – Underway
 Demonstration at Tooling Demo • Everest support site – Downloads – Tutorials – Code documentation library • Using Everest in Visual Studio – Hello World example • From RMIM classes to instance • From instance to RMIM classes
Demonstration at Tooling Demo • Everest support site – Downloads – Tutorials – Code documentation library • Using Everest in Visual Studio – Hello World example • From RMIM classes to instance • From instance to RMIM classes
 Obtaining MARC-HI Everest • http: //everest. marc-hi. ca • Support available through: – Everest forums (website above) – Email (duane. bender@mohawkcollege. ca) – Telephone 905 -575 -1212 x 3653
Obtaining MARC-HI Everest • http: //everest. marc-hi. ca • Support available through: – Everest forums (website above) – Email (duane. bender@mohawkcollege. ca) – Telephone 905 -575 -1212 x 3653
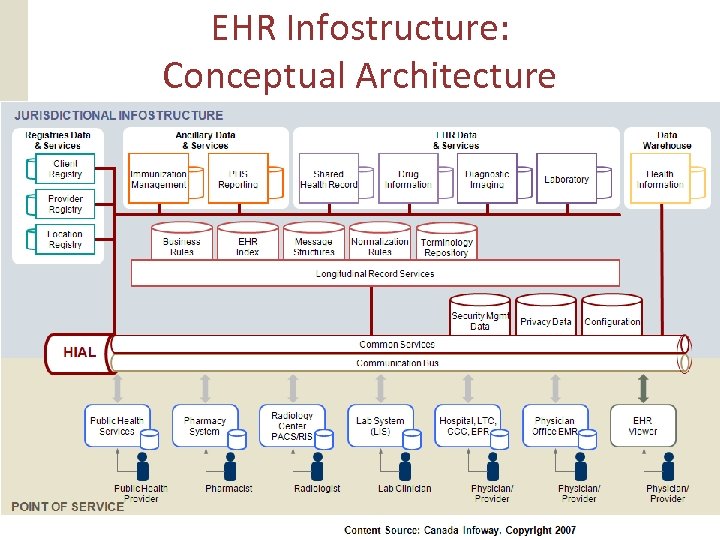 EHR Infostructure: Conceptual Architecture 19
EHR Infostructure: Conceptual Architecture 19