606917e5fc867c49434af004a52b5a32.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

MAR 4721 Professor Charles Hofacker Module 4 Consumer-Business Relationships Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 0

Lecture Overview q q q Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing All About Relationships Harrah Entertainment CRM Digital Data Evaluating Customers Loyalty 1

Relationships vs. Transactions q Long lasting mutually beneficial win-win relationships between supplier and buyer q Integration of all marketing activities toward establishing, developing and maintaining successful relational exchanges loyalty retention profitability Retention Is Cheaper than Acquisition Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 2

Relationship Life Cycle q q Attract – identify and invest, create joint goals Retain – deepen loyalty, educate, encourage relationship specific investments q Extend – broaden the relationship, new or complementary products and channels q Leverage - referrals, resell third-party offerings, increase prices Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing Sawhney, Mohanbir and Jeff Zabin (2002), "Managing and Measuring Relational Equity in the Network Economy, " Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 30 (4), 313 -332. 3

Harrah Entertainment, Inc. 1. Each player is offered tailored hotel and recreation deals – Describe how Harrah Entertainment might choose the hotel price 2. If you were to sort all Harrah customers with the “top” or “best” customer first, and the “bottom” or “worst” customer last, how would you do that? Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing from Business Week, October 29, 2001 4

Customer Relationship Management “CRM is a strategic posture calling for iterative processes designed to turn customer data into customer relationships through active use of, and learning from, the information collected. ” Swift, Ronald S. (2001) Accelerating Customer Relationships Using CRM and Relationship Technologies, Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ. “CRM is information-enabled relationship marketing” Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing Ryals, Lynette and Adrian F. T. Payne (2001), “Customer Relatoinship Management in Financial Services: Towards Information-Enabled Relationship Marketing, ” Journal of Strategic Marketing, 9 (March), 1 -25. 5

CRM Overview q Historic shift in marketing from managing products to managing customer relationships q Emphasis on marketing via customer information databases (“Database Marketing”) q Emphasis on measuring the value of and for each customer (“Dual Value Process”) Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 6
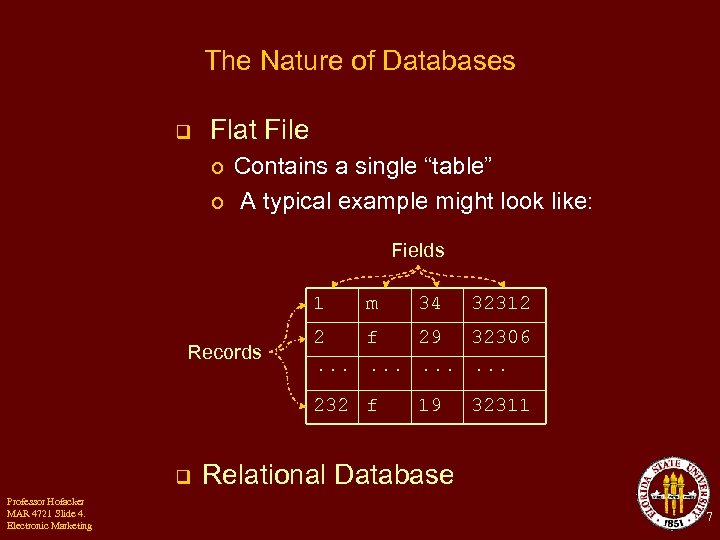
The Nature of Databases q Flat File o Contains a single “table” o A typical example might look like: Fields 1 Records m 34 32312 2 f 29 32306 ··· ··· 232 f q Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 19 32311 Relational Database 7

Relational Database q Consists of a set of tables q Accompanying software can be used to access data in more than one table, and to relate data elements from those tables q Each table will generally have a key field Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 8
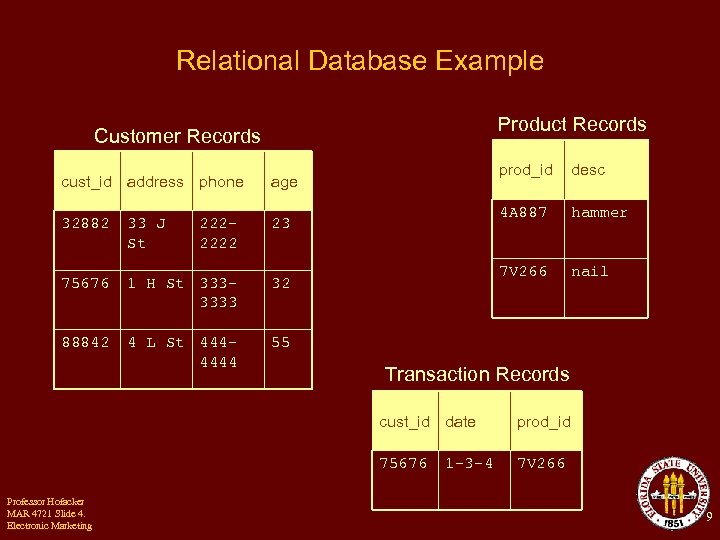
Relational Database Example Product Records Customer Records cust_id address phone 32882 33 J St 2222222 1 H St 3333333 88842 4 L St 4444444 hammer 7 V 266 32 desc 4 A 887 23 75676 prod_id age nail 55 Transaction Records cust_id date 75676 Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing prod_id 7 V 266 1 -3 -4 9

Useful Customer Information q q q Customer preferences Customer importance weights Consideration sets Cognitive style Customer characteristics q q q Transaction information Contact history Marketing exposure history Product usage Profitability o Demographic o Psychographic Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 10

Database Marketing Leverages All Customer Touch Points A financial services company might have many channels Call center q Web site q ATM q Automated voice response system q Cashiers and customer service reps q Mobile devices q POS card swipe q Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 11

Discussion Question 1. What is the difference between the economic concept of elasticity and marketing concept of customer lifetime value? Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 12
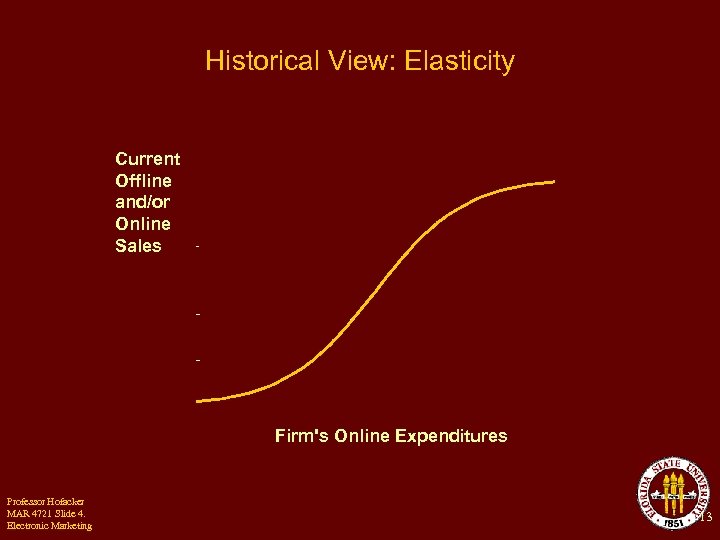
Historical View: Elasticity Current Offline and/or Online Sales Firm's Online Expenditures Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 13

Discussion Question 2. What might it mean to analyze the “net present value” of a customer? What pieces might go into an equation for this? Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 14
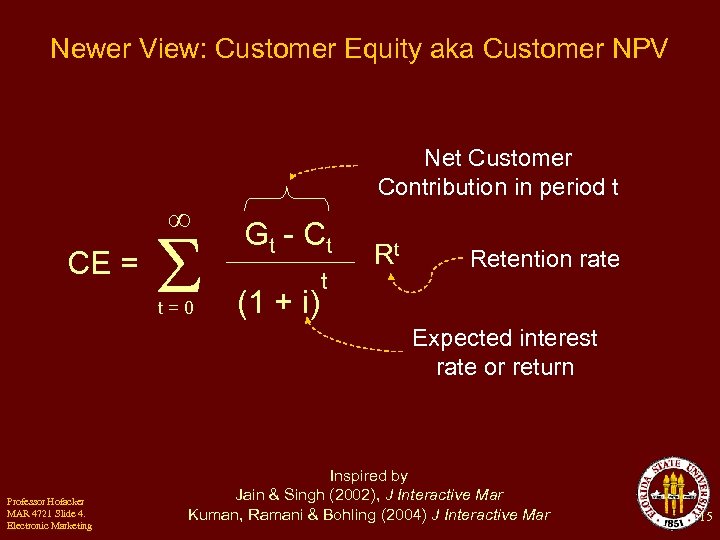
Newer View: Customer Equity aka Customer NPV CE = t=0 Net Customer Contribution in period t Gt - C t (1 + i) t Rt Retention rate Expected interest rate or return Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing Inspired by Jain & Singh (2002), J Interactive Mar Kuman, Ramani & Bohling (2004) J Interactive Mar 15
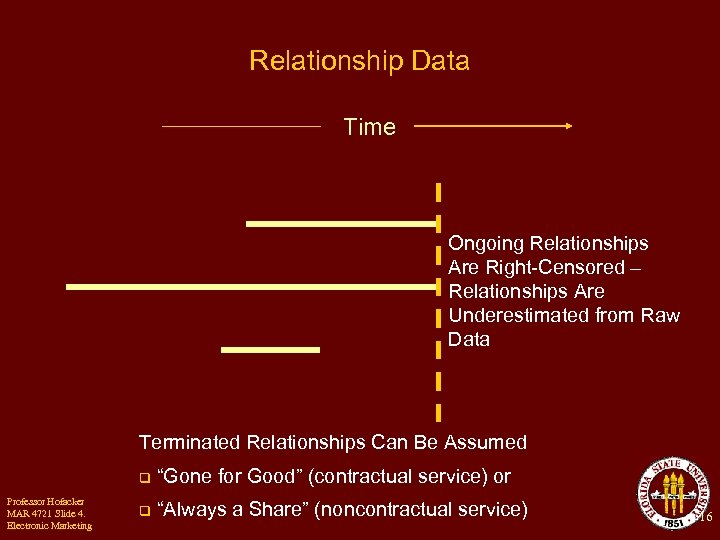
Relationship Data Time Ongoing Relationships Are Right-Censored – Relationships Are Underestimated from Raw Data Terminated Relationships Can Be Assumed q Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing “Gone for Good” (contractual service) or q “Always a Share” (noncontractual service) 16

Switching Costs q Procedural switching costs economic risk, evaluation, learning, setup q Financial switching costs benefit, monetary loss q Relational switching costs personal, brand Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing 17
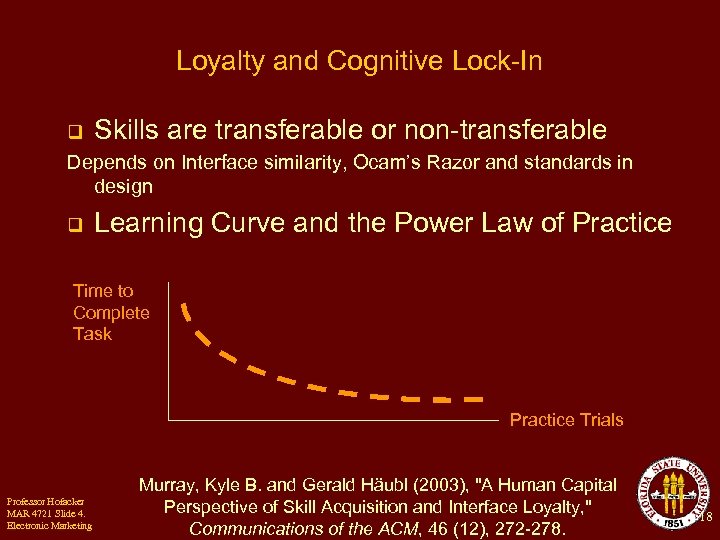
Loyalty and Cognitive Lock-In q Skills are transferable or non-transferable Depends on Interface similarity, Ocam’s Razor and standards in design q Learning Curve and the Power Law of Practice Time to Complete Task Practice Trials Professor Hofacker MAR 4721 Slide 4. Electronic Marketing Murray, Kyle B. and Gerald Häubl (2003), "A Human Capital Perspective of Skill Acquisition and Interface Loyalty, " Communications of the ACM, 46 (12), 272 -278. 18
606917e5fc867c49434af004a52b5a32.ppt