5cc9ea909546b84ebaa1c821c5adf9b1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Mapping the Israeli high tech industry Project: IFISE Work package 7 Arie Sadovski
Mapping the Israeli high tech industry Project: IFISE Work package 7 Arie Sadovski
 Methodology • Database from a commercially available source • Eight hundreds companies were contacted in two cycles • Companies: estb. 1993 or later and hdqtrs in Israel • Received 143 qualified, filled-in questionnaires • Each company was contacted at least two times; in most cases three times: 1 st call to identify the founders, then interview via fax/email and followup
Methodology • Database from a commercially available source • Eight hundreds companies were contacted in two cycles • Companies: estb. 1993 or later and hdqtrs in Israel • Received 143 qualified, filled-in questionnaires • Each company was contacted at least two times; in most cases three times: 1 st call to identify the founders, then interview via fax/email and followup
 The companies
The companies
 Major industrial sectors • Communication (hardware) and electronic components • Software for internet • Software for other applications • Electronic medical instruments and devices • Software for telecommunication (ex internet) • Biotechnology (excluding pharmaceuticals) • Computer (hardware) semiconductor devices and electronic components • Optical instruments and materials (including optical communication items)
Major industrial sectors • Communication (hardware) and electronic components • Software for internet • Software for other applications • Electronic medical instruments and devices • Software for telecommunication (ex internet) • Biotechnology (excluding pharmaceuticals) • Computer (hardware) semiconductor devices and electronic components • Optical instruments and materials (including optical communication items)
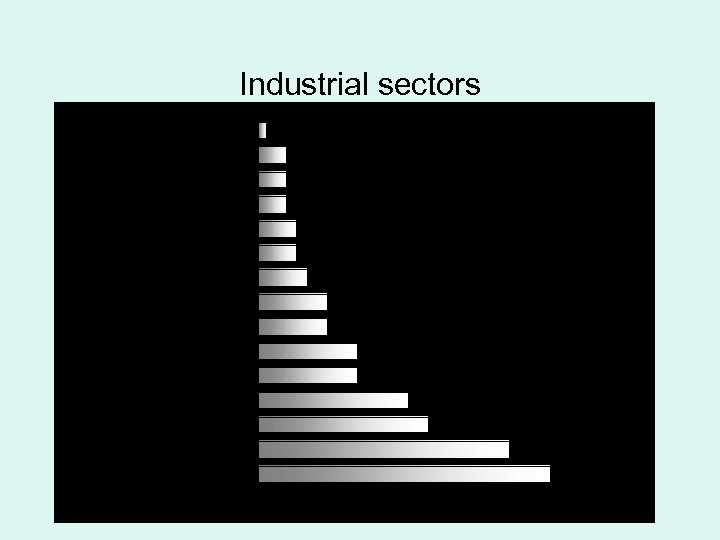 Industrial sectors
Industrial sectors
 Number of employees • • The average number is 36 80% of the firms have < 50 15% of the companies have < 10 Mean employees' number having formal academic degrees is 23. 4 • on the average at least 65% of the employees have academic degrees
Number of employees • • The average number is 36 80% of the firms have < 50 15% of the companies have < 10 Mean employees' number having formal academic degrees is 23. 4 • on the average at least 65% of the employees have academic degrees
 Companies’ age Age 1 year 2 -3 years 4 -5 years 6+ years Total resp Mean 3. 5 Companies # % 29 20 54 38 31 22 29 20 143 100
Companies’ age Age 1 year 2 -3 years 4 -5 years 6+ years Total resp Mean 3. 5 Companies # % 29 20 54 38 31 22 29 20 143 100
 *Number of employees Employees 1 -5 6 -9 10 -19 20 -49 50 -99 100 -249 250+ Total * From data base companies % 9 20 46 33 18 7 3 136 7 15 34 25 13 5 2 100 Mean 35. 6
*Number of employees Employees 1 -5 6 -9 10 -19 20 -49 50 -99 100 -249 250+ Total * From data base companies % 9 20 46 33 18 7 3 136 7 15 34 25 13 5 2 100 Mean 35. 6
 Product development phases # Research and development 21 Technological demonstration 6 Prototype 12 ß site 17 Initial sales 43 Sales 41 Total respondents % 15 4 9 12 31 29 140 100
Product development phases # Research and development 21 Technological demonstration 6 Prototype 12 ß site 17 Initial sales 43 Sales 41 Total respondents % 15 4 9 12 31 29 140 100
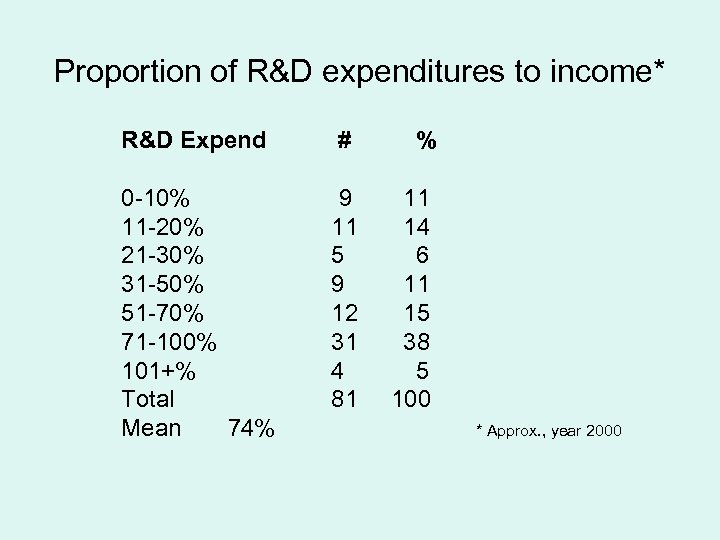 Proportion of R&D expenditures to income* R&D Expend # % 0 -10% 11 -20% 21 -30% 31 -50% 51 -70% 71 -100% 101+% Total Mean 74% 9 11 5 9 12 31 4 81 11 14 6 11 15 38 5 100 * Approx. , year 2000
Proportion of R&D expenditures to income* R&D Expend # % 0 -10% 11 -20% 21 -30% 31 -50% 51 -70% 71 -100% 101+% Total Mean 74% 9 11 5 9 12 31 4 81 11 14 6 11 15 38 5 100 * Approx. , year 2000
 The founders
The founders
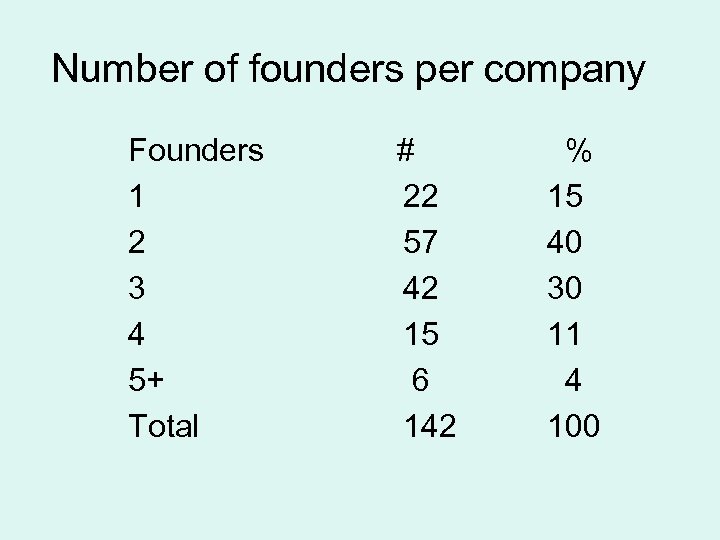 Number of founders per company Founders 1 2 3 4 5+ Total # 22 57 42 15 6 142 % 15 40 30 11 4 100
Number of founders per company Founders 1 2 3 4 5+ Total # 22 57 42 15 6 142 % 15 40 30 11 4 100
 Founders’ formal schooling Non academic Vocational Engineers B. Sc. /B. A M. Sc. /M. A Ph. D. Military courses # 11 8 73 63 67 15 % 8 6 51 44 47 10
Founders’ formal schooling Non academic Vocational Engineers B. Sc. /B. A M. Sc. /M. A Ph. D. Military courses # 11 8 73 63 67 15 % 8 6 51 44 47 10
 Founders’ professional training disciplines Engineering MBA Exact / Computer Science Management/Economic Life Science # 64 24 77 21 26 % 45 17 54 15 18
Founders’ professional training disciplines Engineering MBA Exact / Computer Science Management/Economic Life Science # 64 24 77 21 26 % 45 17 54 15 18
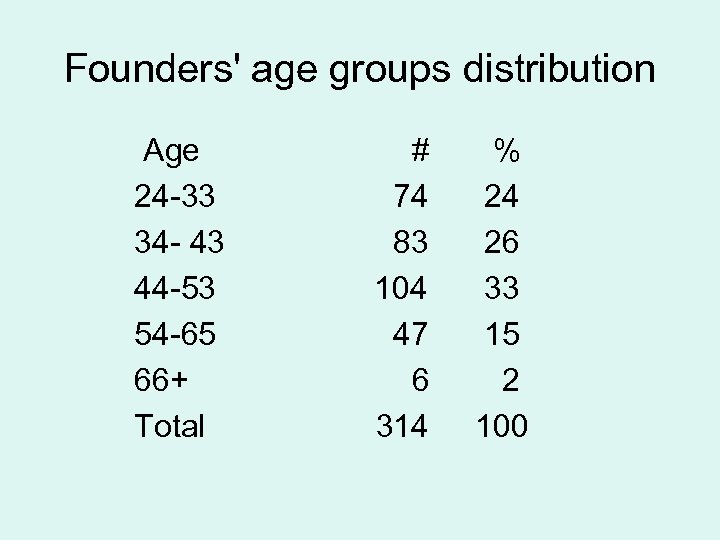 Founders' age groups distribution Age 24 -33 34 - 43 44 -53 54 -65 66+ Total # 74 83 104 47 6 314 % 24 26 33 15 2 100
Founders' age groups distribution Age 24 -33 34 - 43 44 -53 54 -65 66+ Total # 74 83 104 47 6 314 % 24 26 33 15 2 100
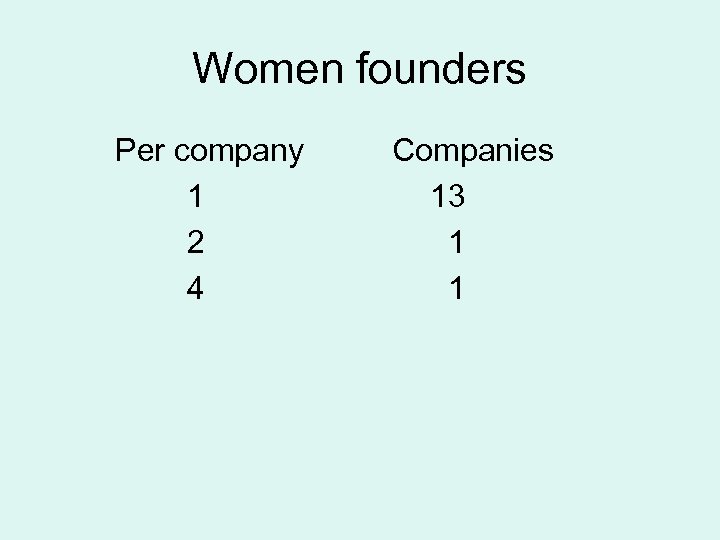 Women founders Per company 1 2 4 Companies 13 1 1
Women founders Per company 1 2 4 Companies 13 1 1
 Changes in the founders' position Yes, all of them are still in the lead No, part of them are in the lead No, none of them are in the lead Total respondents # % 94 67 30 21 16 11 140 100
Changes in the founders' position Yes, all of them are still in the lead No, part of them are in the lead No, none of them are in the lead Total respondents # % 94 67 30 21 16 11 140 100
 The entrepreneurial environment and background
The entrepreneurial environment and background
 The geographical birth place of the new technology # Israel 128 Abroad 12 Both 2 Total respondents 142 % 90 8. 5 1. 4 100
The geographical birth place of the new technology # Israel 128 Abroad 12 Both 2 Total respondents 142 % 90 8. 5 1. 4 100
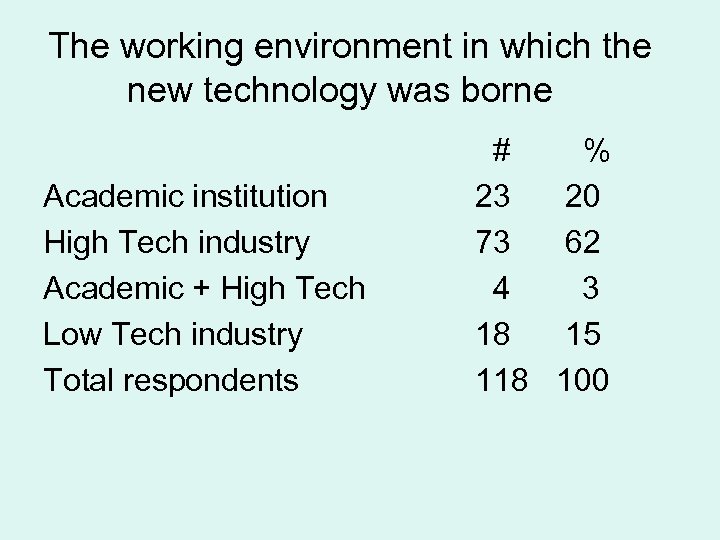 The working environment in which the new technology was borne Academic institution High Tech industry Academic + High Tech Low Tech industry Total respondents # % 23 20 73 62 4 3 18 15 118 100
The working environment in which the new technology was borne Academic institution High Tech industry Academic + High Tech Low Tech industry Total respondents # % 23 20 73 62 4 3 18 15 118 100
 Previous occupation of the founders # % Unemployed 2 1 Students 9 6 Academia, Research Institute 24 17 Industry 108 76 Total respondents 143 100
Previous occupation of the founders # % Unemployed 2 1 Students 9 6 Academia, Research Institute 24 17 Industry 108 76 Total respondents 143 100
 Founders’ previous industrial positions # R&D % Manager 78 55 Staff 31 22 Production Manager Staff 10 1 7 1 Marketing /sales Manager Staff 33 6 23 4 Total responses 159
Founders’ previous industrial positions # R&D % Manager 78 55 Staff 31 22 Production Manager Staff 10 1 7 1 Marketing /sales Manager Staff 33 6 23 4 Total responses 159
 Fund raising patterns
Fund raising patterns
 Number of rounds used for fund raising Rounds 1 2 3 4 5 Respondents Companies 48 29 24 15 6 122 % 39 24 20 12 5 100
Number of rounds used for fund raising Rounds 1 2 3 4 5 Respondents Companies 48 29 24 15 6 122 % 39 24 20 12 5 100
 Sums raised in the different rounds Sums raised Seed <150 K 26 151 -600 K 37 2 -3 M 30 3+ 8 Total 100 1 st 8 14 48 29 100 2 nd 6 8 40 46 100
Sums raised in the different rounds Sums raised Seed <150 K 26 151 -600 K 37 2 -3 M 30 3+ 8 Total 100 1 st 8 14 48 29 100 2 nd 6 8 40 46 100
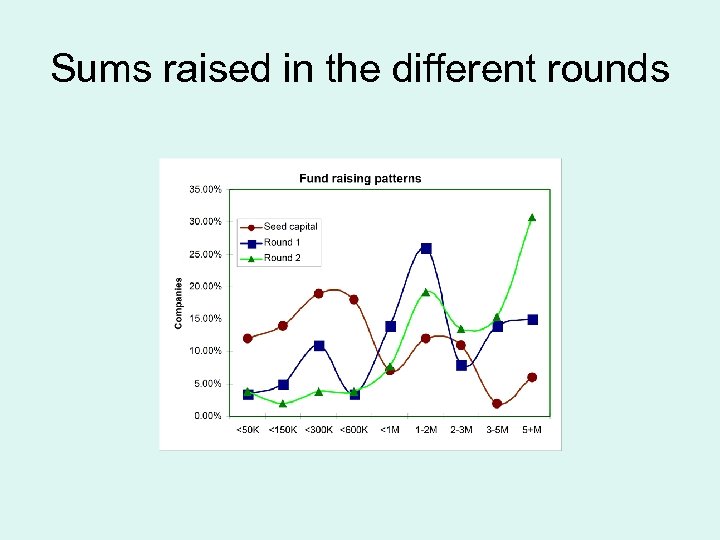 Sums raised in the different rounds
Sums raised in the different rounds
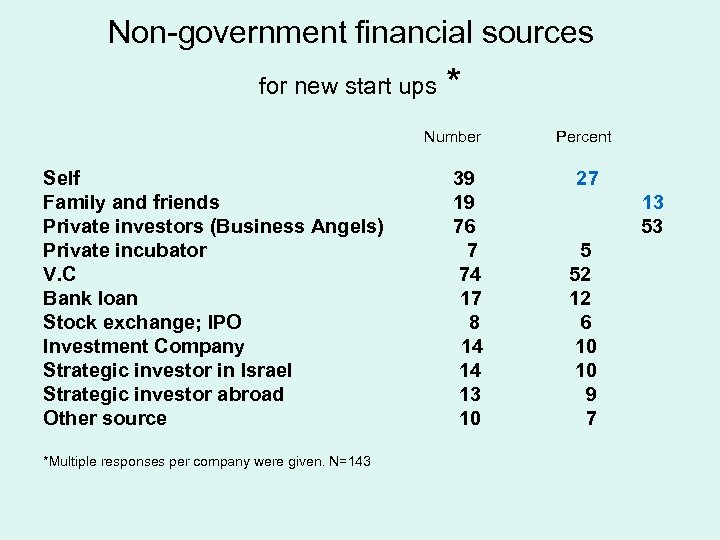 Non-government financial sources for new start ups * Number Self Family and friends Private investors (Business Angels) Private incubator V. C Bank loan Stock exchange; IPO Investment Company Strategic investor in Israel Strategic investor abroad Other source *Multiple responses per company were given. N=143 39 19 76 7 74 17 8 14 14 13 10 Percent 27 13 53 5 52 12 6 10 10 9 7
Non-government financial sources for new start ups * Number Self Family and friends Private investors (Business Angels) Private incubator V. C Bank loan Stock exchange; IPO Investment Company Strategic investor in Israel Strategic investor abroad Other source *Multiple responses per company were given. N=143 39 19 76 7 74 17 8 14 14 13 10 Percent 27 13 53 5 52 12 6 10 10 9 7
 Non government financial sources
Non government financial sources
 Yozma VC funds as a funding source Yozma VC funds Eurofund Medica Walden Gemini Nitzanim Apex Inventech Polaris Vertex Jerusalem Pacific Ventures Star *Multiple responses per company were given. N=27 Companies* Number Percent 4 1 4 3 1 3 4 9 2 0 4 15 11 4 11 15 33 7 0 15
Yozma VC funds as a funding source Yozma VC funds Eurofund Medica Walden Gemini Nitzanim Apex Inventech Polaris Vertex Jerusalem Pacific Ventures Star *Multiple responses per company were given. N=27 Companies* Number Percent 4 1 4 3 1 3 4 9 2 0 4 15 11 4 11 15 33 7 0 15
 Government financial sources Companies* Number Percent Government Incubators 21 15 R&D grant – Regular 49 34 R&D grant - For start-up 5 3 R&D grant - “Magnet” 7 5 Bi-National programme – BIRDF 11 8 Bi-National programme – Other 1 1 Investment Center – Grant/capital equipment 11 8 Investment Center – Income tax benefits 21 15 *Multiple responses per company were given. N=143
Government financial sources Companies* Number Percent Government Incubators 21 15 R&D grant – Regular 49 34 R&D grant - For start-up 5 3 R&D grant - “Magnet” 7 5 Bi-National programme – BIRDF 11 8 Bi-National programme – Other 1 1 Investment Center – Grant/capital equipment 11 8 Investment Center – Income tax benefits 21 15 *Multiple responses per company were given. N=143
 Incubators and Yozma programs affiliated companiescomparison of sales and growth - rates to the other respondents companies
Incubators and Yozma programs affiliated companiescomparison of sales and growth - rates to the other respondents companies



 Difficulties encountered
Difficulties encountered
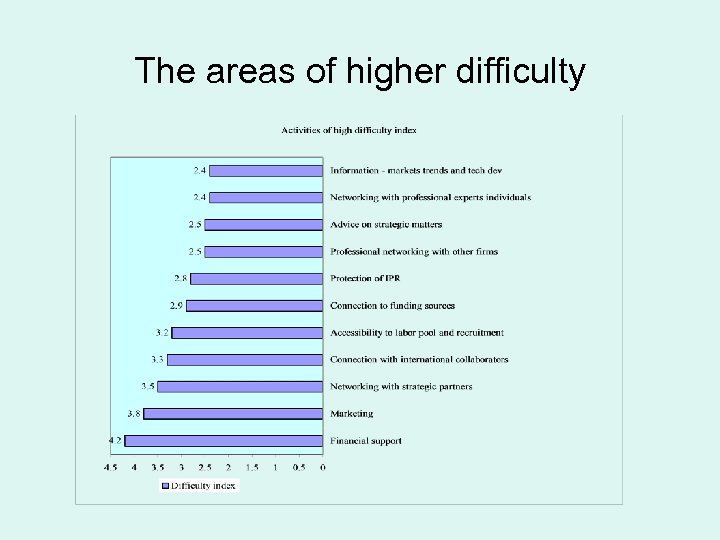
 The six most difficult areas and expectations for government assistance Areas of activity - Difficulty index (mean) * Gov. assistance Companies responding “YES” Fund raising - 4. 2 Marketing - 3. 8 Networking with strategic partners - 3. 5 Connection with international collaborators - 3. 3 Recruiting - 3. 2 Connection to funding sources - 2. 9 Protection of IPR – 2. 8 58% 45% 37% 49% 19% 44% 32% * The respondents were asked to rank each difficulty on a scale of 1 -5.
The six most difficult areas and expectations for government assistance Areas of activity - Difficulty index (mean) * Gov. assistance Companies responding “YES” Fund raising - 4. 2 Marketing - 3. 8 Networking with strategic partners - 3. 5 Connection with international collaborators - 3. 3 Recruiting - 3. 2 Connection to funding sources - 2. 9 Protection of IPR – 2. 8 58% 45% 37% 49% 19% 44% 32% * The respondents were asked to rank each difficulty on a scale of 1 -5.
 Other areas of activity Areas of activity - • • • Difficulty index (mean) * Locating the company in a building facility – 1. 8 Networking with suppliers – 1. 9 Sources for technical information - 2. 0 Training of personnel -1. 8 Advice on legal matters – 2. 1 Advice on management matters – 2. 2 Networking with experts – 2. 4 Information on trends in the market & tech-2. 4 Networking with other firms – 2. 5 Advice on strategic matters – 2. 5 Gov. assist. 19% 7% 22% 26% 17% 7% 24% 17% 16%
Other areas of activity Areas of activity - • • • Difficulty index (mean) * Locating the company in a building facility – 1. 8 Networking with suppliers – 1. 9 Sources for technical information - 2. 0 Training of personnel -1. 8 Advice on legal matters – 2. 1 Advice on management matters – 2. 2 Networking with experts – 2. 4 Information on trends in the market & tech-2. 4 Networking with other firms – 2. 5 Advice on strategic matters – 2. 5 Gov. assist. 19% 7% 22% 26% 17% 7% 24% 17% 16%
 The areas of higher difficulty
The areas of higher difficulty
 End
End


