655c8904afe89ebb3a8f2549191871b6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Manugistics Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 1
Manugistics Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 1
 Introduction A strategic decision support tool l Permits benchmarking and “optimization” of existing and prospective supply chains l Support for network design, network utilization, and resource utilization analyses l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 2
Introduction A strategic decision support tool l Permits benchmarking and “optimization” of existing and prospective supply chains l Support for network design, network utilization, and resource utilization analyses l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 2
 Introduction (continued) Net WORKS Strategy is a module in a suite of enterprise profit optimization products from Manugistics. l The software employs proprietary database structures and tools to interact with the databases. l Other Manugistics modules are l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 3
Introduction (continued) Net WORKS Strategy is a module in a suite of enterprise profit optimization products from Manugistics. l The software employs proprietary database structures and tools to interact with the databases. l Other Manugistics modules are l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 3
 Other Manugistics Products Net. WORKS Demand l Net. WORKS Fulfillment l Net. WORKS Procurement l Net. WORKS Transport l Net. WORKS Collaborate l Net. WORKS Sequencing l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 4
Other Manugistics Products Net. WORKS Demand l Net. WORKS Fulfillment l Net. WORKS Procurement l Net. WORKS Transport l Net. WORKS Collaborate l Net. WORKS Sequencing l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 4
 Software Architecture and Structure l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 uses a Server – Client Networked Architecture – Fat Server l l l Stores object oriented databases Runs the model processes Manages the Manugistics domains – Thin clients l l l Interacts with data objects Initiates model processes Displays outputs of Optimizer output Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 5
Software Architecture and Structure l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 uses a Server – Client Networked Architecture – Fat Server l l l Stores object oriented databases Runs the model processes Manages the Manugistics domains – Thin clients l l l Interacts with data objects Initiates model processes Displays outputs of Optimizer output Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 5
 Net. WORKS Strategy 7. 0 Scheduled for release fall ’ 02. l Transitioning to a Fat Client – Thin Server Web Enabled Architecture in Version 7. 0 scheduled for release later this year. l The new version will use relational databases rather than proprietary object oriented databases. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 6
Net. WORKS Strategy 7. 0 Scheduled for release fall ’ 02. l Transitioning to a Fat Client – Thin Server Web Enabled Architecture in Version 7. 0 scheduled for release later this year. l The new version will use relational databases rather than proprietary object oriented databases. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 6
 Currently Supported Operating Systems and Platforms l Server – Unix – Windows NT, Windows 2000 Professional l Clients – Unix based – Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000 Professional, Windows XP(? ) Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 7
Currently Supported Operating Systems and Platforms l Server – Unix – Windows NT, Windows 2000 Professional l Clients – Unix based – Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000 Professional, Windows XP(? ) Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 7
 Fundamental Tasks We Will Cover Installing the server l Installing the client l Administering the system l Scoping an analysis l Inputting data and relationships l Troubleshooting l Analyzing and generating reports l Interpreting reports l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 8
Fundamental Tasks We Will Cover Installing the server l Installing the client l Administering the system l Scoping an analysis l Inputting data and relationships l Troubleshooting l Analyzing and generating reports l Interpreting reports l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 8
 “Optimizing” the Supply Chain l l Optimizing - Achieving the best possible solution to a problem in terms of a specified objective function subject to model inputs. The objective function can either be profit maximization or cost minimization. Optimum is defined subject to a set of constraints and the input data. LP or MIP solutions to the Optimization problem. Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 9
“Optimizing” the Supply Chain l l Optimizing - Achieving the best possible solution to a problem in terms of a specified objective function subject to model inputs. The objective function can either be profit maximization or cost minimization. Optimum is defined subject to a set of constraints and the input data. LP or MIP solutions to the Optimization problem. Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 9
 Revenues and Costs Data Selling prices l Purchase costs of raw materials l Transportation Costs l Manufacturing Costs l Storage Costs l Resource Costs l Taxes/ Tariffs l Stock out Costs l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 10
Revenues and Costs Data Selling prices l Purchase costs of raw materials l Transportation Costs l Manufacturing Costs l Storage Costs l Resource Costs l Taxes/ Tariffs l Stock out Costs l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 10
 Constraints Manufacturing capacity l Storage Space l Transportation and handling capacity l Throughput capacity l Inventory levels l Sourcing restrictions l Pre-build limitations l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 11
Constraints Manufacturing capacity l Storage Space l Transportation and handling capacity l Throughput capacity l Inventory levels l Sourcing restrictions l Pre-build limitations l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 11
 Why a Model? Across an enterprise the number of possible solutions is extremely large. l An automated, systematic tool that seeks the best solution is valuable in supporting the decision making process. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 12
Why a Model? Across an enterprise the number of possible solutions is extremely large. l An automated, systematic tool that seeks the best solution is valuable in supporting the decision making process. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 12
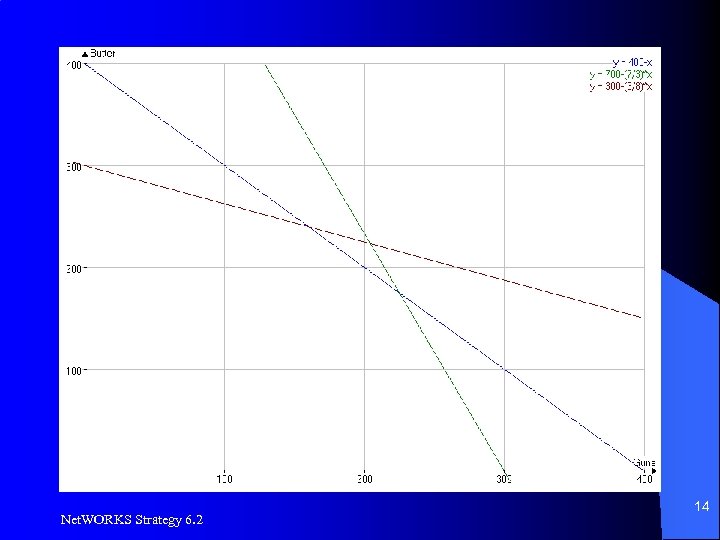
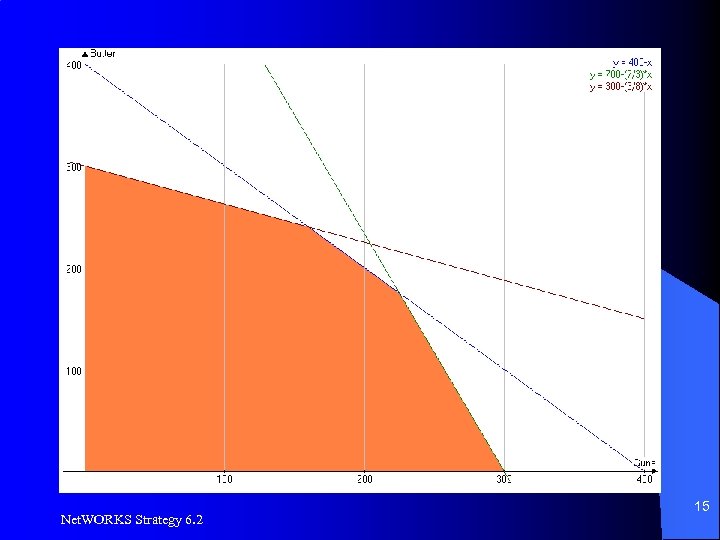
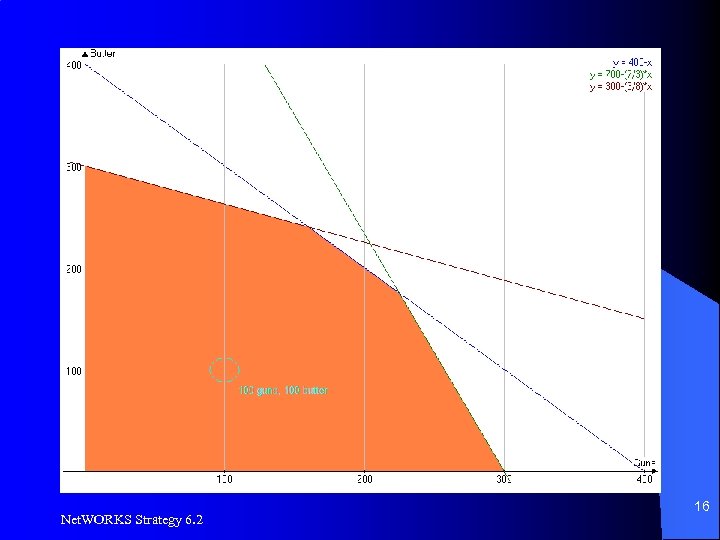
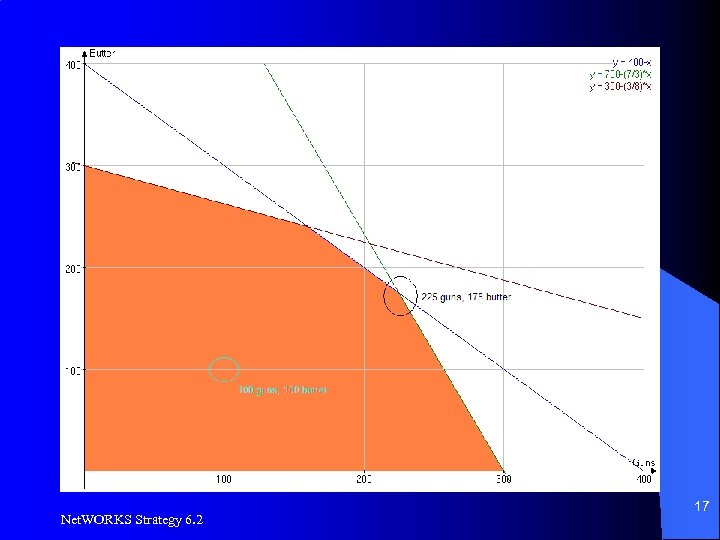
 Optimization Example, LP l l Profit: Guns = $2 per unit, Butter = $1 per unit 2100 units of raw material available – Butter requires 3 units, guns require 7 units per unit produced l 2400 units of machine time available – Butter requires 8 units, guns require 3 units per unit produced l 400 units of labor available – Guns and butter require 1 unit each to produce Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 13
Optimization Example, LP l l Profit: Guns = $2 per unit, Butter = $1 per unit 2100 units of raw material available – Butter requires 3 units, guns require 7 units per unit produced l 2400 units of machine time available – Butter requires 8 units, guns require 3 units per unit produced l 400 units of labor available – Guns and butter require 1 unit each to produce Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 13
 Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 14
Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 14
 Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 15
Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 15
 Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 16
Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 16
 Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 17
Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 17
 Optimization Example, MIP Suppose that we can construct one or two plants to make guns and or butter and that each plant has a unique set of labor, machinery, and raw materials constraints. l Further suppose that each plant sells their output into markets with different output prices and service requirements. l Requires MIP as some decision variables are discreet. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 18
Optimization Example, MIP Suppose that we can construct one or two plants to make guns and or butter and that each plant has a unique set of labor, machinery, and raw materials constraints. l Further suppose that each plant sells their output into markets with different output prices and service requirements. l Requires MIP as some decision variables are discreet. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 18
 Real World Example Monsanto Corporation l 1000’s of products, 1000’s of resources, hundreds of suppliers, thousands of customers, world-wide distribution. l Millions of constraints. l Need a model. Need a reliable, automated technique to solve the model. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 19
Real World Example Monsanto Corporation l 1000’s of products, 1000’s of resources, hundreds of suppliers, thousands of customers, world-wide distribution. l Millions of constraints. l Need a model. Need a reliable, automated technique to solve the model. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 19
 Class Resources Installation/Administration Manual l Reference Manual l Classroom Guide l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 20
Class Resources Installation/Administration Manual l Reference Manual l Classroom Guide l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 20
 Using Net. WORKS 6. 2 Invest some time in scoping out your analysis. l Include just enough detail necessary to answer the questions being asked of you. l Do not let the scope of your analysis expand. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 21
Using Net. WORKS 6. 2 Invest some time in scoping out your analysis. l Include just enough detail necessary to answer the questions being asked of you. l Do not let the scope of your analysis expand. l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 21
 Supply Chain Model Flow Chart l l l l l Define Problem, Objective, and Scope Create Calendars Create Items Create Locations Create Lanes Create Resources Create SKUs Create and Edit Processes Enter Costs, Prices, and Constraints Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 22
Supply Chain Model Flow Chart l l l l l Define Problem, Objective, and Scope Create Calendars Create Items Create Locations Create Lanes Create Resources Create SKUs Create and Edit Processes Enter Costs, Prices, and Constraints Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 22
 Supply Chain Model Flow Chart Create a Scenario for Analysis l Run the Optimizer l Review the Exceptions l Review the Solution l Create a new analytical scenario l Run the Optimizer l Review the Exceptions and Solution l Compare the Scenario Solutions l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 23
Supply Chain Model Flow Chart Create a Scenario for Analysis l Run the Optimizer l Review the Exceptions l Review the Solution l Create a new analytical scenario l Run the Optimizer l Review the Exceptions and Solution l Compare the Scenario Solutions l Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 23
 Manugistics Explorer Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 24
Manugistics Explorer Net. WORKS Strategy 6. 2 24


