f24a7040a10108ff78fa4487742006d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Manufacturing Systems Manufacturing System Design & Control
Manufacturing Systems Manufacturing System Design & Control
 Manufacturing System Design & Control Facility Layout and Work Flow Arrangement within a factory of: • Machines • Departments • Workstations • Storage areas • Aisles and common areas Ensures a smooth flow of work, material, people and information through the system
Manufacturing System Design & Control Facility Layout and Work Flow Arrangement within a factory of: • Machines • Departments • Workstations • Storage areas • Aisles and common areas Ensures a smooth flow of work, material, people and information through the system
 Manufacturing System Design & Control 3 three basic types of layout: • Process • Product • Fixed-Position 3 hybrid layouts: • Cellular • Flexible Manufacturing Systems • Mixed-model Assembly Lines
Manufacturing System Design & Control 3 three basic types of layout: • Process • Product • Fixed-Position 3 hybrid layouts: • Cellular • Flexible Manufacturing Systems • Mixed-model Assembly Lines
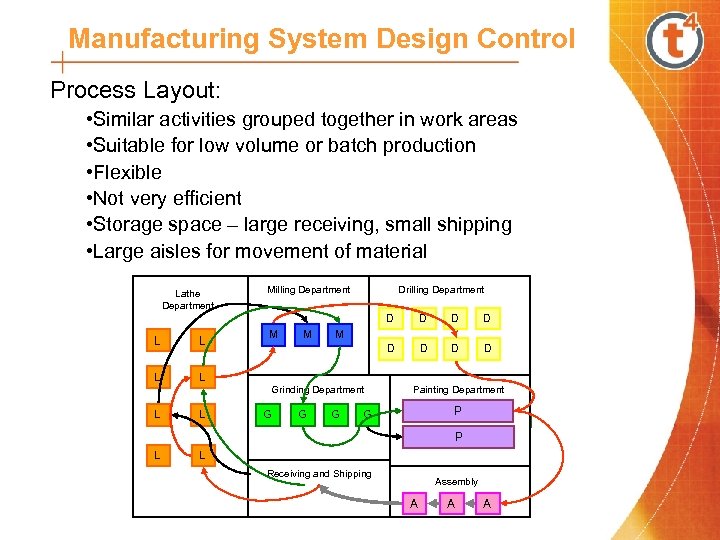 Manufacturing System Design Control Process Layout: • Similar activities grouped together in work areas • Suitable for low volume or batch production • Flexible • Not very efficient • Storage space – large receiving, small shipping • Large aisles for movement of material Lathe Department Drilling Department Milling Department D L L L M D D D D M L Grinding Department L L G G G Painting Department P G P L L Receiving and Shipping Assembly A A A
Manufacturing System Design Control Process Layout: • Similar activities grouped together in work areas • Suitable for low volume or batch production • Flexible • Not very efficient • Storage space – large receiving, small shipping • Large aisles for movement of material Lathe Department Drilling Department Milling Department D L L L M D D D D M L Grinding Department L L G G G Painting Department P G P L L Receiving and Shipping Assembly A A A
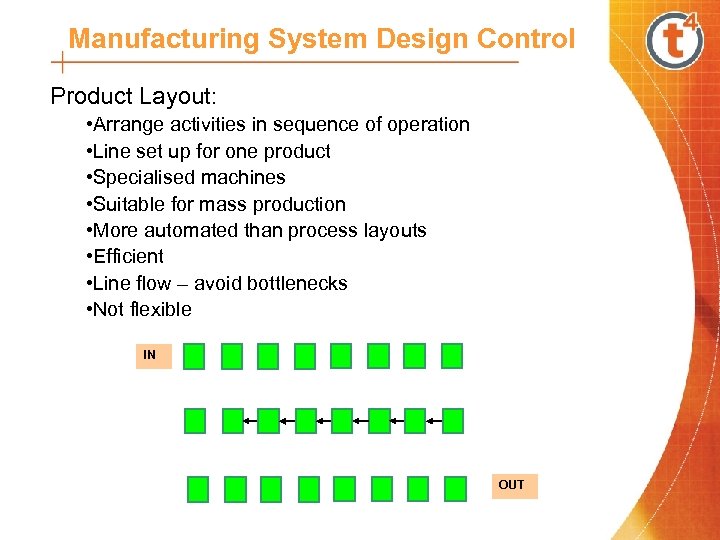 Manufacturing System Design Control Product Layout: • Arrange activities in sequence of operation • Line set up for one product • Specialised machines • Suitable for mass production • More automated than process layouts • Efficient • Line flow – avoid bottlenecks • Not flexible IN OUT
Manufacturing System Design Control Product Layout: • Arrange activities in sequence of operation • Line set up for one product • Specialised machines • Suitable for mass production • More automated than process layouts • Efficient • Line flow – avoid bottlenecks • Not flexible IN OUT
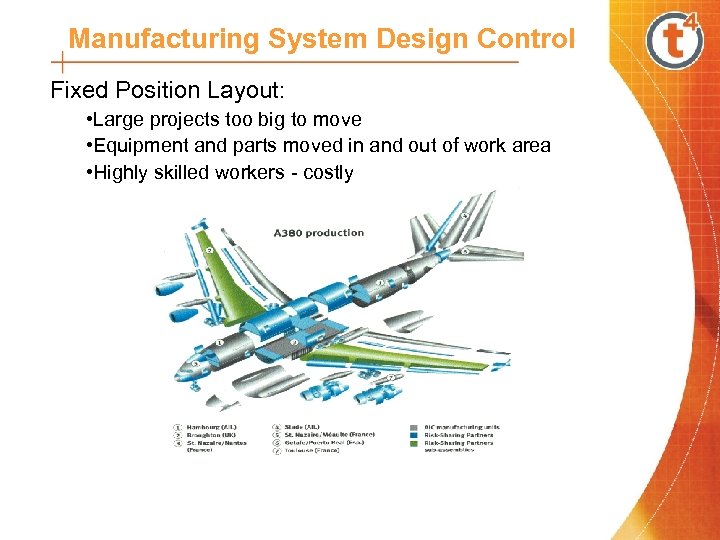 Manufacturing System Design Control Fixed Position Layout: • Large projects too big to move • Equipment and parts moved in and out of work area • Highly skilled workers - costly
Manufacturing System Design Control Fixed Position Layout: • Large projects too big to move • Equipment and parts moved in and out of work area • Highly skilled workers - costly
 Manufacturing System Design Control Hybrid Layouts: Try to mix flexibility of process layout with efficiency of product layout Cellular Layouts: • Machines grouped into cells • Cells process parts with similar features • Work cell resembles a small assembly line (product) • Layout between cells treated as process layout
Manufacturing System Design Control Hybrid Layouts: Try to mix flexibility of process layout with efficiency of product layout Cellular Layouts: • Machines grouped into cells • Cells process parts with similar features • Work cell resembles a small assembly line (product) • Layout between cells treated as process layout
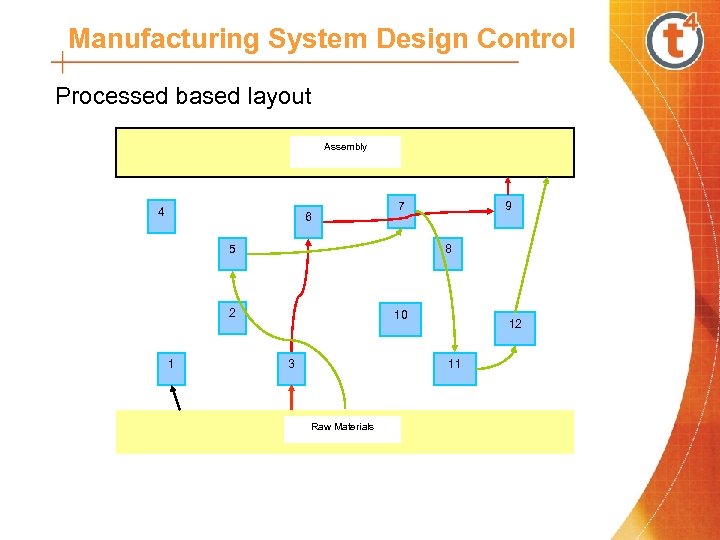 Manufacturing System Design Control Processed based layout Assembly 4 6 7 5 8 2 1 9 10 3 12 11 Raw Materials
Manufacturing System Design Control Processed based layout Assembly 4 6 7 5 8 2 1 9 10 3 12 11 Raw Materials
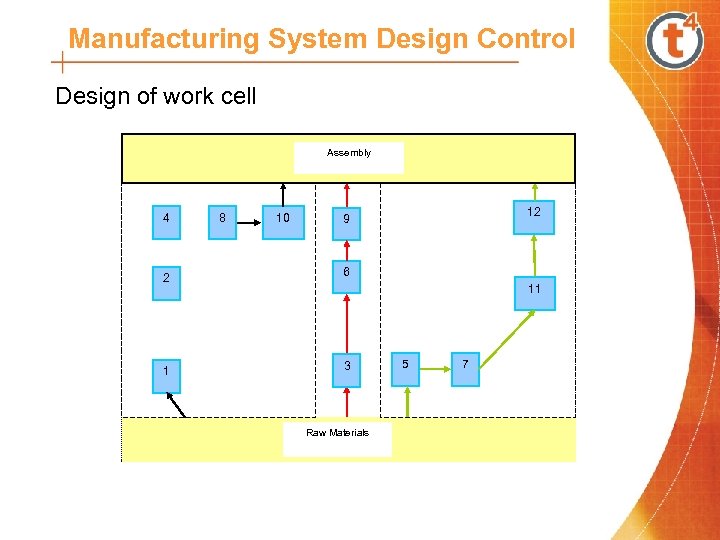 Manufacturing System Design Control Design of work cell Assembly 4 2 1 8 10 12 9 6 11 3 Raw Materials 5 7
Manufacturing System Design Control Design of work cell Assembly 4 2 1 8 10 12 9 6 11 3 Raw Materials 5 7
 Manufacturing System Design Control Flexible Manufacturing Systems: • Automates the entire manufacture of a product • Very costly • Complex software • Small number of FMS worldwide Flexible Manufacturing Cell: • Smaller version of FMS • One manufacturing process is automated
Manufacturing System Design Control Flexible Manufacturing Systems: • Automates the entire manufacture of a product • Very costly • Complex software • Small number of FMS worldwide Flexible Manufacturing Cell: • Smaller version of FMS • One manufacturing process is automated
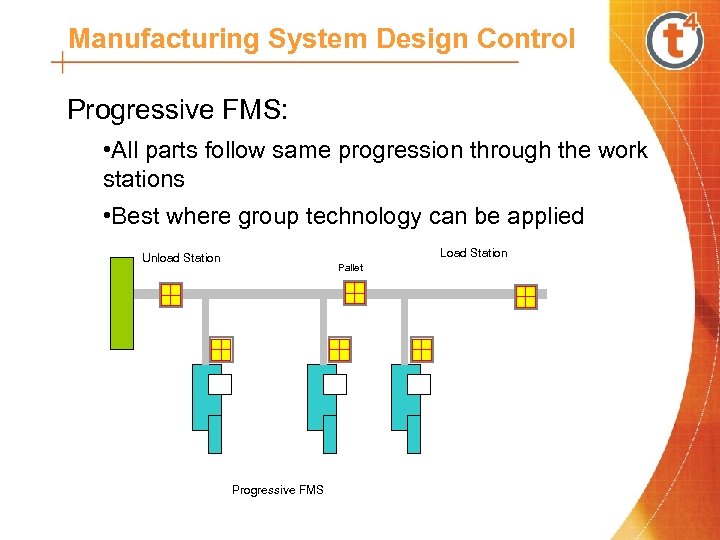 Manufacturing System Design Control Progressive FMS: • All parts follow same progression through the work stations • Best where group technology can be applied Load Station Unload Station Pallet Progressive FMS
Manufacturing System Design Control Progressive FMS: • All parts follow same progression through the work stations • Best where group technology can be applied Load Station Unload Station Pallet Progressive FMS
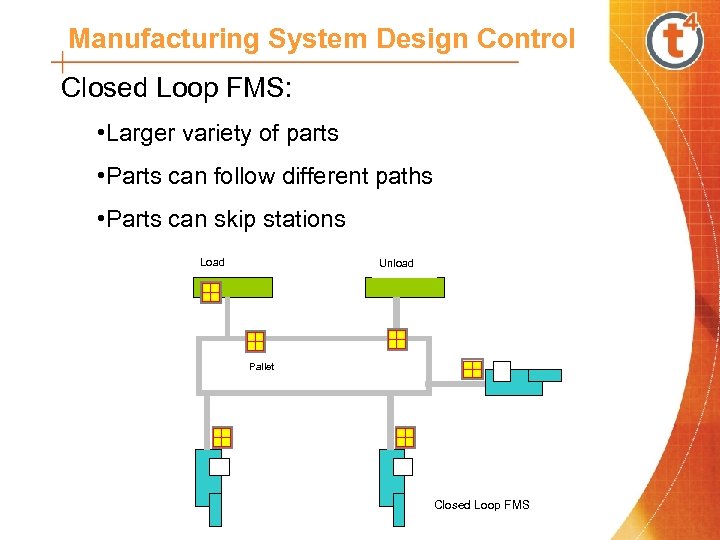 Manufacturing System Design Control Closed Loop FMS: • Larger variety of parts • Parts can follow different paths • Parts can skip stations Load Unload Pallet Closed Loop FMS
Manufacturing System Design Control Closed Loop FMS: • Larger variety of parts • Parts can follow different paths • Parts can skip stations Load Unload Pallet Closed Loop FMS
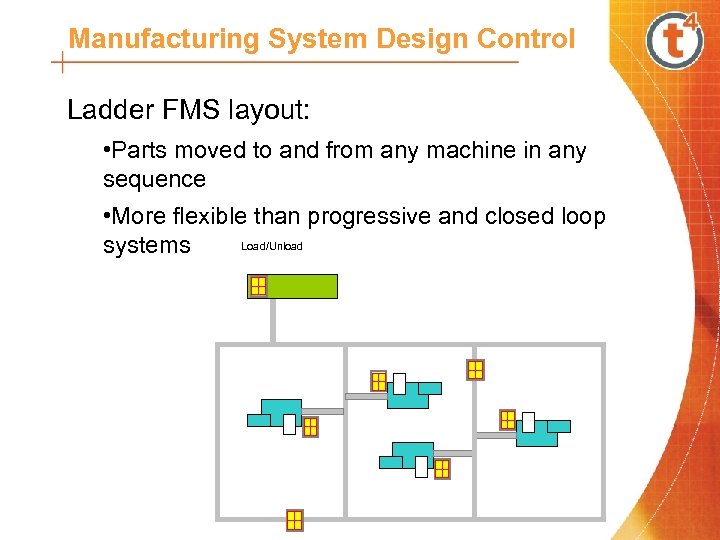 Manufacturing System Design Control Ladder FMS layout: • Parts moved to and from any machine in any sequence • More flexible than progressive and closed loop Load/Unload systems
Manufacturing System Design Control Ladder FMS layout: • Parts moved to and from any machine in any sequence • More flexible than progressive and closed loop Load/Unload systems
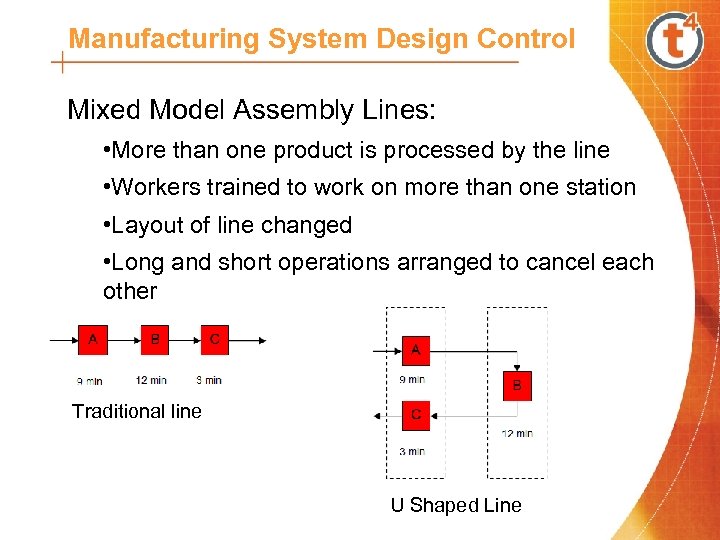 Manufacturing System Design Control Mixed Model Assembly Lines: • More than one product is processed by the line • Workers trained to work on more than one station • Layout of line changed • Long and short operations arranged to cancel each other Traditional line U Shaped Line
Manufacturing System Design Control Mixed Model Assembly Lines: • More than one product is processed by the line • Workers trained to work on more than one station • Layout of line changed • Long and short operations arranged to cancel each other Traditional line U Shaped Line
 Manufacturing System Design Control Capacity Management: • Demand for product can fluctuate over time • Capacity < demand - Lose business • Excess capacity: storage cost, labour cost etc. • Capacity planning: match capacity to present and anticipated demand Capacity Planning • Capacity Lead Strategy • Capacity Lag Strategy • Average Capacity Strategy
Manufacturing System Design Control Capacity Management: • Demand for product can fluctuate over time • Capacity < demand - Lose business • Excess capacity: storage cost, labour cost etc. • Capacity planning: match capacity to present and anticipated demand Capacity Planning • Capacity Lead Strategy • Capacity Lag Strategy • Average Capacity Strategy
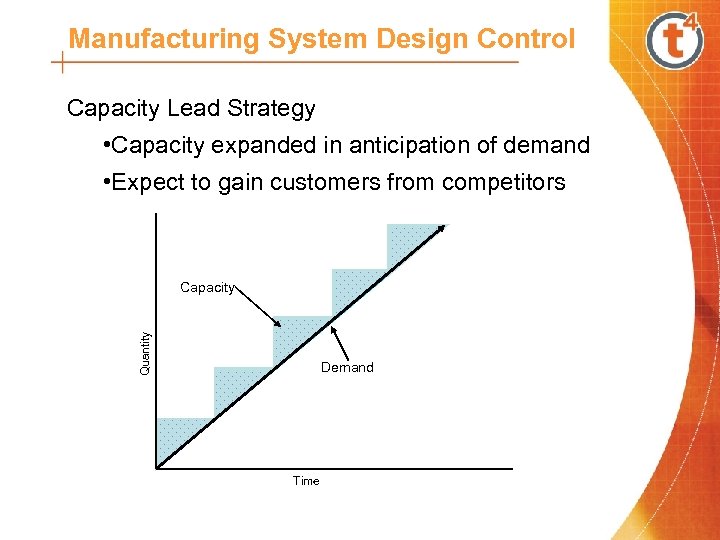 Manufacturing System Design Control Capacity Lead Strategy • Capacity expanded in anticipation of demand • Expect to gain customers from competitors Quantity Capacity Demand Time
Manufacturing System Design Control Capacity Lead Strategy • Capacity expanded in anticipation of demand • Expect to gain customers from competitors Quantity Capacity Demand Time
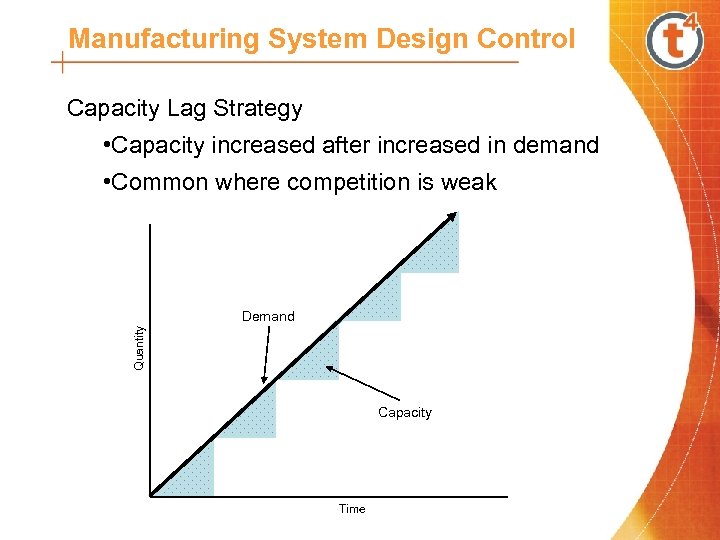 Manufacturing System Design Control Capacity Lag Strategy • Capacity increased after increased in demand • Common where competition is weak Quantity Demand Capacity Time
Manufacturing System Design Control Capacity Lag Strategy • Capacity increased after increased in demand • Common where competition is weak Quantity Demand Capacity Time
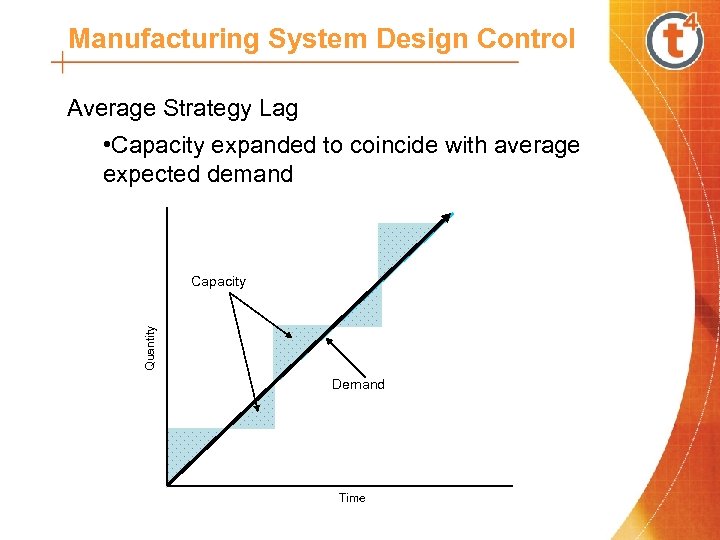 Manufacturing System Design Control Average Strategy Lag • Capacity expanded to coincide with average expected demand Quantity Capacity Demand Time
Manufacturing System Design Control Average Strategy Lag • Capacity expanded to coincide with average expected demand Quantity Capacity Demand Time
 Manufacturing System Design Control How much to increase capacity? • 100% capacity not efficient • 20% cushion is generally used • 20% capacity allows for unexpected demand • Negative capacity can be used - Airlines
Manufacturing System Design Control How much to increase capacity? • 100% capacity not efficient • 20% cushion is generally used • 20% capacity allows for unexpected demand • Negative capacity can be used - Airlines


