23ff7990e0181318ee05a1d8b1c5b714.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

MANUFACTURING AND PRODUCTION OF BIOLOGICAL PRODUCTS (ERT 455) GOOD MANUFACTURING PRACTICES (GMP) FOR BIOLOGICAL PRODUCTS Munira Mohamed Nazari School of Bioprocess Engineering Uni. MAP

COURSE OUTCOME (CO 3) Ability to FORMULATE and PROPOSE primary/secondary processing, and upscaling facilities for bio products manufacturing in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)

TOPIC OUTLINE Quality Management ◦ Quality assurance & Quality control Heating Ventilation and air-conditioning systems Validation – biological products Application of hazard analysis and critical control point (HACCP)

INTRODUCTION
QUALITY CONTROL GMP Goal & SAFETY
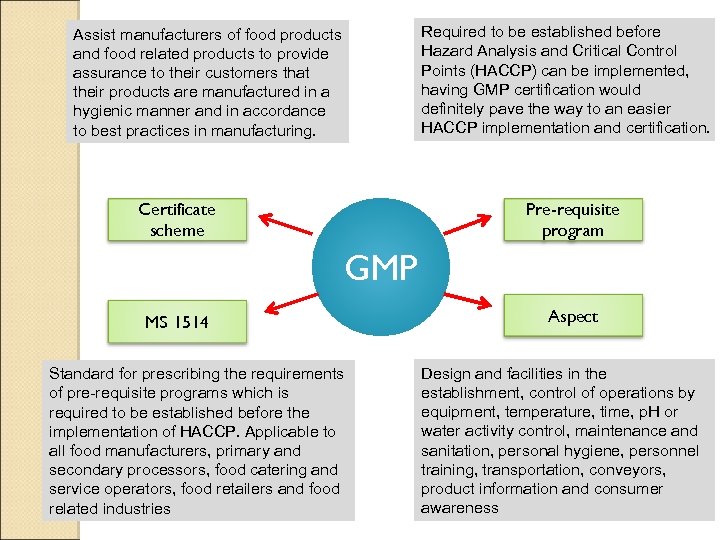
Required to be established before Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) can be implemented, having GMP certification would definitely pave the way to an easier HACCP implementation and certification. Assist manufacturers of food products and food related products to provide assurance to their customers that their products are manufactured in a hygienic manner and in accordance to best practices in manufacturing. Certificate scheme Pre-requisite program GMP MS 1514 Standard for prescribing the requirements of pre-requisite programs which is required to be established before the implementation of HACCP. Applicable to all food manufacturers, primary and secondary processors, food catering and service operators, food retailers and food related industries Aspect Design and facilities in the establishment, control of operations by equipment, temperature, time, p. H or water activity control, maintenance and sanitation, personal hygiene, personnel training, transportation, conveyors, product information and consumer awareness
GMP Certification Scheme For Food Processing GMP is a sanitary and processing requirement applicable to all food processing establishments. Many food industry companies have implemented the GMP certification scheme for food processing as the foundation upon which they have developed and implemented other food quality assurance systems and food safety management systems, such as HACCP, SQF 2000, ISO 9001 and ISO 22000. Certifying your food management system against the GMP standard will bring the following benefits: q. Enhancement of your food safety management system; q. Demonstration of your commitment to producing and trading safe food; q. Prepare you for HACCP certification; q. Increase in consumer confidence in your products; and q. Prepare you for inspection by regulatory authorities and other stakeholders (food processing regulation compliant)

GMP Basic Requirement What is GMP ? • Part of Quality Assurance (QA) which ensures that products are consistently produced and controlled to the quality standards appropriate to their intended use and as required by marketing authorization or product specification.

GMP Basic Requirement ◦ Engineering for c. GMP: those activities performed throughout the project lifecycle, which ensures that it will be easy and natural to operate the completed facility in accordance with current Good Manufacturing Practice. ◦ Project Life-Cycle means from project inception through feasibility studies/ conceptual design, engineering, construction, installation, start-up, operation, maintenance to final plant decommissioning or modification.

GMP Design requirements 1) Process issues - closed or open (piping and equipment, expose to environmentmeasure to prevent contamination) - level of batch to batch integrity required (simultaneous filling self-emptying vessels, or cleaning, or drying, sterilization between batches? ) 2) Layout issues - site location and layout – existing site, brown and green field, and overall site layout - facility layout – cored vs. linear layout, segregation of areas, environment, containment strategy, security etc.

GMP Design requirements 3) Automation Strategy issues - level of technology, use of design tools and models - availability / redundancy, modularization / expansion - instrumentation / cabling / field devices - paperless batch records, electronic signatures. 4) Flow issues - people (security, access, occupancy level) - equipment (mobile or fixed, use of hard piping, crosscontamination) - components / materials (materials handling systems, crosscontamination / mix-ups)

GMP Design requirements 5) Regulatory issues - stage of development and production, category of the product (sterile medical, biological medical, herbal medicinal, medical gases, liquid, creams, tablets etc) and production process employed, facility location etc. 6) Validation Strategy issues - validation required, validation team(s), validation plan(s).

Where to Apply Categories suggested for guidance Facilities and environment 2) Services and utilities 3) Personnel flows 4) Material flows 5) Equipment flows 6) Equipment design 7) Computerized systems 8) Maintenance and services 9) Waste management 10) Procedure and documentation 1)

QUALITY MANAGEMENT

QUALITY MANAGEMENT Objectives To understand key issues in quality assurance/ good manufacturing practices/quality control. To understand specific requirements on quality management and quality assurance including: äOrganization äProcedures, processes and resources.

Quality relationships QUALITY MANAGEMENT Quality Management Quality Assurance Defining the overall policy of the organization towards quality, is over everything else. Concept that ensures the policy is achieved. GMP Part of quality assurance. It deals with the risks that cannot be tested. It builds quality into the product. Production and Quality Control It is that part of GMP that is focused on testing of the environment and facilities, as well as the testing of the materials, components and product in accordance with the standard.

Philosophy and essential elements QUALITY MANAGEMENT What is Quality Management? ◦ Is defined as the aspect of management function that determines and implements the quality policy. ◦ The quality policy is a statement by the top management of the company of its overall intentions and direction relating to quality, formally expressed as a corporate policy. The top management of a company usually includes the board of directors or general manager of the company, the plant or factory managers together with the senior managers.

Philosophy and essential elements QUALITY MANAGEMENT The basic elements are: ◦ An appropriate infrastructure or “quality system” encompassing the organization structure, procedures, processes and resources. ◦ The systematic actions necessary to ensure adequate confidence that a product (or service) will satisfy given requirements for “Quality” The totality of these actions is termed “Quality Assurance”

Quality Management QUALITY MANAGEMENT Quality assurance is a management tool. In contractual situations, it also serves to generate confidence in a supplier. QA, GMP and Quality Control are interrelated aspects of Quality Management. ◦ They are described on the following slides in order to emphasize their relationship and their fundamental importance to the production and control of pharmaceutical products.

Principles of Quality Assurance (QA) QUALITY MANAGEMENT Wide-ranging concept ◦ covers all matters that individually or collectively influence the quality of a product. Totality of the arrangements ◦ to ensure that the drug is of the right quality for the intended use. Quality Assurance incorporates GMP ◦ and also product design and development which is outside the scope of this module

Quality Assurance (QA) QUALITY MANAGEMENT QA System should ensure: Products are designed and developed correctly. ä Complying with, e. g. GMP, GCP, GLP Production and control operations are defined. Managerial responsibilities are defined ä In job descriptions The manufacture, supply and use of correct starting and packaging materials. GMP – Good Manufacturing Practice GCP – Good Clinical Practice GLP – Good Laboratory Practice

Quality Assurance (QA) QUALITY MANAGEMENT QA System should ensure (cont. . . ): Controls are performed, including intermediates, bulk, calibration and validation Correct processing and checking of the finished product Products are sold/supplied only after review by the authorized person ä Complying with marketing authorization, production and QC requirements Proper storage, distribution and handling

Quality Assurance (QA) QUALITY MANAGEMENT QA System should ensure (cont. . . ): Procedures for self-inspection and/or quality audits Reporting, investigation and recording of deviations System for change control/approval Regular evaluation of product quality to verify consistency and continued improvement

Quality Assurance (QA) QUALITY MANAGEMENT Manufacturer is responsible for the quality of the product. äFit for intended use äComply with marketing authorization äSafety, efficacy and quality Senior management and commitment of all staff. Requires a comprehensively designed and well implemented QA system. Fully documented, and effectiveness monitored. Competent personnel, sufficient premises, equipment and facilities.

Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) QUALITY MANAGEMENT Is the part of QA that ensures that products are consistently produced and controlled. äQuality standards äMarketing authorization Aim: Diminishing risks that cannot be fully controlled by testing of the final product. äCross-contamination EXAMPLE This risk can best be controlled by having a properly managed system of working that takes them into account. This means that there must be good design, and planned maintenance of facilities. The quality checking system also must be designed with this risk in mind and set out to find whether any errors have occurred. If we do not know what sort of cross contamination we have, then the work of the analyst is very difficult. The analyst should ideally know what to test for before commencing testing. In other words, if we do not know what the likely cross-contaminant is, then we cannot analyse for it.

Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) QUALITY MANAGEMENT Basic Requirements for GMP. ◦ Clearly defined and systematically reviewed processes. ä Batch documentation ä Quality specification ä Standard of Procedures (SOP) ◦ Qualification and validation is performed. ◦ Appropriate resources are provided: ä Qualified and trained personnel ä Premises, space, equipment and services ä Materials, containers, labels ä Procedures, storage, transport ä Laboratories and in-process control

Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) QUALITY MANAGEMENT Basic Requirements for GMP. (cont. . ) Clear, written instructions and procedures Trained operators to carry out the procedures correctly. Records of actions, deviations and investigations Records for manufacture and distribution Proper storage and distribution of the products minimizes any risk to their quality. Systems for complaints and recalls from sale or supply.

Quality Control (QC) QUALITY MANAGEMENT Focused on testing of the environment and facilities, as well as the testing of the materials, components and product in accordance with the standard.

QUALITY MANAGEMENT

QUALITY MANAGEMENT References World Health Organization, Basic Principles of GMP, Module 2, January 2006 Quality Assurance of Pharmaceuticals, Volume 2, Good Manufacturing Practices and Inspection. World Health Organization. 2007


HEATING VENTILATION AND AIR-CONDITIONING SYSTEMS
23ff7990e0181318ee05a1d8b1c5b714.ppt