95b3389588f953480169a69fd84a5463.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Manipulating files in UNIX
Manipulating files in UNIX
 Common operations of files • Common operations: • Create a file • Print a file • Delete a file • Rename a file • Move a file from one directory into another directory We will learn to do these operations and more. .
Common operations of files • Common operations: • Create a file • Print a file • Delete a file • Rename a file • Move a file from one directory into another directory We will learn to do these operations and more. .
 Identifying a file • We need to identify a file before we can perform an operation (like delete) on the file. • A file can be identified using: • An absolute (file) path, or • An relative (file) path
Identifying a file • We need to identify a file before we can perform an operation (like delete) on the file. • A file can be identified using: • An absolute (file) path, or • An relative (file) path
 Absolute file path • Absolute file path: • An absolute file path tells the computer how to find a file starting from the root directory • An absolute file path of a particular file x consists of a list of directory names starting from the root directory "/" to the directory containing the file x and then followed by the name of the file (x) • The list of names is separated by the "/" symbol
Absolute file path • Absolute file path: • An absolute file path tells the computer how to find a file starting from the root directory • An absolute file path of a particular file x consists of a list of directory names starting from the root directory "/" to the directory containing the file x and then followed by the name of the file (x) • The list of names is separated by the "/" symbol
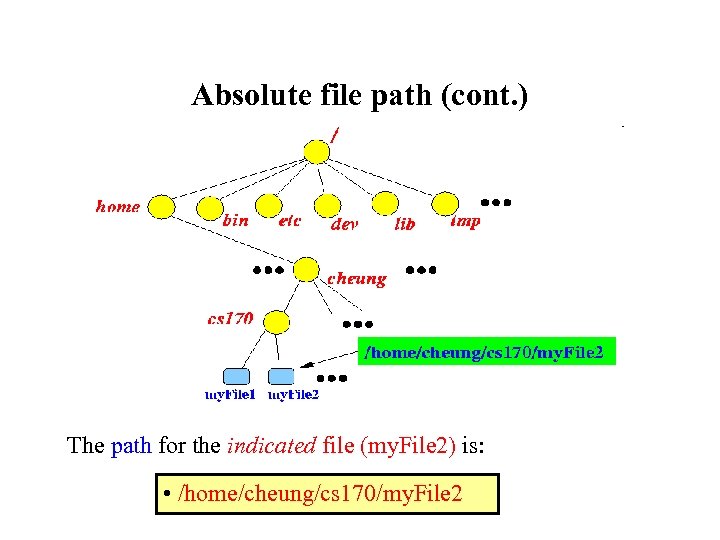 Absolute file path (cont. ) The path for the indicated file (my. File 2) is: • /home/cheung/cs 170/my. File 2
Absolute file path (cont. ) The path for the indicated file (my. File 2) is: • /home/cheung/cs 170/my. File 2
 Relative file path • Relative file path: • An relative file path tells the computer how to find a file starting from the current directory • An relative file path of a particular file x consists of a list of directory names starting from the current directory to the directory containing the file x and then followed by the name of the file (x) • The list of names is separated by the "/" symbol
Relative file path • Relative file path: • An relative file path tells the computer how to find a file starting from the current directory • An relative file path of a particular file x consists of a list of directory names starting from the current directory to the directory containing the file x and then followed by the name of the file (x) • The list of names is separated by the "/" symbol
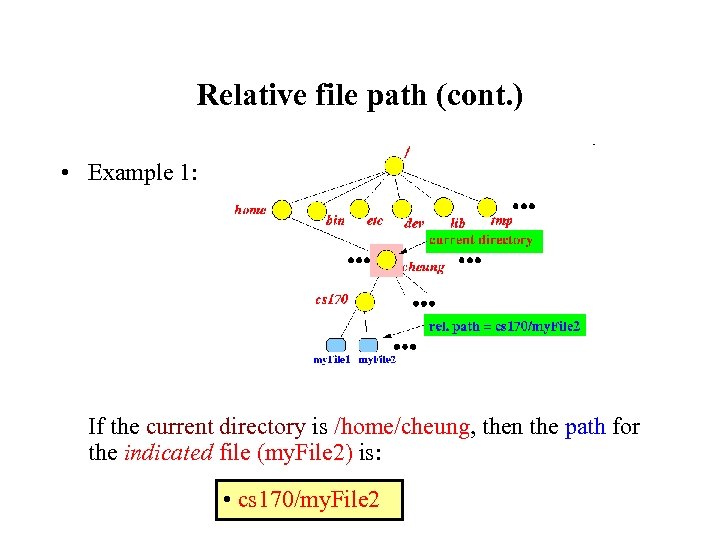 Relative file path (cont. ) • Example 1: If the current directory is /home/cheung, then the path for the indicated file (my. File 2) is: • cs 170/my. File 2
Relative file path (cont. ) • Example 1: If the current directory is /home/cheung, then the path for the indicated file (my. File 2) is: • cs 170/my. File 2
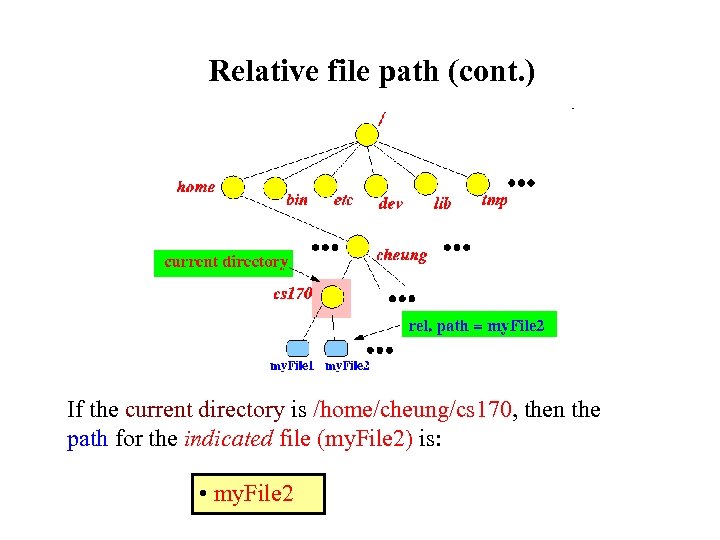 Relative file path (cont. ) If the current directory is /home/cheung/cs 170, then the path for the indicated file (my. File 2) is: • my. File 2
Relative file path (cont. ) If the current directory is /home/cheung/cs 170, then the path for the indicated file (my. File 2) is: • my. File 2
 Relative file path (cont. ) • Advice: • When working on files, always change the working directory to the one that contains the files. • It will save you a lot of key strokes (typing)
Relative file path (cont. ) • Advice: • When working on files, always change the working directory to the one that contains the files. • It will save you a lot of key strokes (typing)
 Common operations on files • Common operations on files: • Create a file • Print a file to the terminal • Print a file to the printer • Delete a file • Rename a file • Move a file from one directory (folder) to another directory (folder)
Common operations on files • Common operations on files: • Create a file • Print a file to the terminal • Print a file to the printer • Delete a file • Rename a file • Move a file from one directory (folder) to another directory (folder)
 Create a file • An electronic file is created using a computer application (program) called an editor (An editor in computer lingo is a program !!!) • Some commonly used editors that you have used on a PC: • Microsoft Word • Notepad • We will learn to use gedit (GNU editor) in another webnote.
Create a file • An electronic file is created using a computer application (program) called an editor (An editor in computer lingo is a program !!!) • Some commonly used editors that you have used on a PC: • Microsoft Word • Notepad • We will learn to use gedit (GNU editor) in another webnote.
 Print the content of a file out to the terminal • The command (= application) that is used to print the content of a file is: cat FILE-PATH (cat is an abbreviation of the word catenate)
Print the content of a file out to the terminal • The command (= application) that is used to print the content of a file is: cat FILE-PATH (cat is an abbreviation of the word catenate)
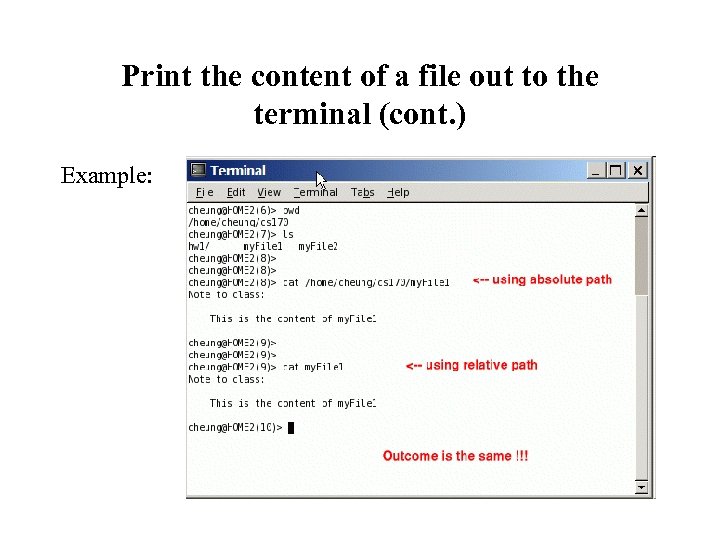 Print the content of a file out to the terminal (cont. ) Example:
Print the content of a file out to the terminal (cont. ) Example:
 Catenating multiple files • The cat command can catenate an arbitrary number of files to the terminal Example: catenate my. File 1 and my. File 2 to the terminal:
Catenating multiple files • The cat command can catenate an arbitrary number of files to the terminal Example: catenate my. File 1 and my. File 2 to the terminal:
 Redirecting the input and output to a file • In UNIX, the output that an application prints to the terminal, can be stored to a file Also, the input that an application reads from the keyboard, can be read from a file. This feature is called: • Input/Output redirection (or IO redirection for short)
Redirecting the input and output to a file • In UNIX, the output that an application prints to the terminal, can be stored to a file Also, the input that an application reads from the keyboard, can be read from a file. This feature is called: • Input/Output redirection (or IO redirection for short)
 Redirecting the input and output to a file (cont. ) • Redirecting the output to a file: • The output of any UNIX command can be sent to a file by adding " > File. Name" to the command • In other words: • any UNIX command > File. Name
Redirecting the input and output to a file (cont. ) • Redirecting the output to a file: • The output of any UNIX command can be sent to a file by adding " > File. Name" to the command • In other words: • any UNIX command > File. Name
 Redirecting the input and output to a file (cont. ) • Example: redirecting the output of "ls" into a file:
Redirecting the input and output to a file (cont. ) • Example: redirecting the output of "ls" into a file:
 Redirecting the input and output to a file (cont. ) • Example: redirecting the output of cat my. File 1 my. File 2 to a file (named my. File 3)
Redirecting the input and output to a file (cont. ) • Example: redirecting the output of cat my. File 1 my. File 2 to a file (named my. File 3)
 Redirecting the input and output to a file (cont. ) You can see that my. File 3 contains the catenation of the files my. File 1 and my. File 2 So the cat command can be used to catenate multiple files together !!! (Hence the name cat) • We will learn about input re-direction at a later lecture
Redirecting the input and output to a file (cont. ) You can see that my. File 3 contains the catenation of the files my. File 1 and my. File 2 So the cat command can be used to catenate multiple files together !!! (Hence the name cat) • We will learn about input re-direction at a later lecture
 Print a file to the printer • Use this command to print a file to the default printer: lpr File-Path • When you print a file from a computer in the Math. CS lab, the default printer is the printer located inside the area where the Lab assistant(s) sits
Print a file to the printer • Use this command to print a file to the default printer: lpr File-Path • When you print a file from a computer in the Math. CS lab, the default printer is the printer located inside the area where the Lab assistant(s) sits
 Print a file to the printer (cont. ) • Example: lpr my. File 1 will print the file named my. File 1 in the current directory to the printer
Print a file to the printer (cont. ) • Example: lpr my. File 1 will print the file named my. File 1 in the current directory to the printer
 Delete a file • The command (application) used to delete a file is: rm File-Path The word rm is an acronym for remove All files with names matching the File-Path will be removed
Delete a file • The command (application) used to delete a file is: rm File-Path The word rm is an acronym for remove All files with names matching the File-Path will be removed
 Delete a file (cont. ) • Example rm my. File 1 (will delete the file named "my. File 1" in the current directory) rm /home/cheung/cs 170/my. File 1 (will delete the file "my. File 1" in the directory/home/cheung/cs 170)
Delete a file (cont. ) • Example rm my. File 1 (will delete the file named "my. File 1" in the current directory) rm /home/cheung/cs 170/my. File 1 (will delete the file "my. File 1" in the directory/home/cheung/cs 170)
 Delete a file (cont. ) Important note: • Make sure that your current directory is the correct one when you use a relative path with all UNIX commands !!!
Delete a file (cont. ) Important note: • Make sure that your current directory is the correct one when you use a relative path with all UNIX commands !!!
 Recovering deleted files in UNIX • Very important: • When you delete a file (with rm, the file is really deleted in UNIX What I mean is: the file is not moved into a trash directory (That's what happens in Microsoft Windows) • In other words: your file is gone forever
Recovering deleted files in UNIX • Very important: • When you delete a file (with rm, the file is really deleted in UNIX What I mean is: the file is not moved into a trash directory (That's what happens in Microsoft Windows) • In other words: your file is gone forever
 Recovering deleted files in UNIX • Restoring a file with a backup version: • Every night, all files in a UNIX system is saved (backup) • If you deleted a file, you can recover an older version of the file as of yesterday • In other words: any work you do after the backup was made, will be lost. . • Send an email to: help@mathcs. emory. edu if you need to recover a file using a backup copy.
Recovering deleted files in UNIX • Restoring a file with a backup version: • Every night, all files in a UNIX system is saved (backup) • If you deleted a file, you can recover an older version of the file as of yesterday • In other words: any work you do after the backup was made, will be lost. . • Send an email to: help@mathcs. emory. edu if you need to recover a file using a backup copy.
 Rename a file • The command (application) used to rename a file with name old-File-Path to the name new-File-Path is: mv old-File-Path new-File-Path
Rename a file • The command (application) used to rename a file with name old-File-Path to the name new-File-Path is: mv old-File-Path new-File-Path
 Rename a file (cont. ) Important: • The new-File-Path file must not exist; otherwise, 2 things can happen: 1. If the new-File-Path exists and it is the name of a file, then the mv will report an error (and will not rename the file) 2. If the new-File-Path exists and it is the name of a directory, then the mv will move the file old-File. Path into the directory new-File-Path
Rename a file (cont. ) Important: • The new-File-Path file must not exist; otherwise, 2 things can happen: 1. If the new-File-Path exists and it is the name of a file, then the mv will report an error (and will not rename the file) 2. If the new-File-Path exists and it is the name of a directory, then the mv will move the file old-File. Path into the directory new-File-Path
 Rename a file (cont. ) • Example: mv my. File 2 decl-of-indep will rename the file named my. File 2 to the new name declof-indep
Rename a file (cont. ) • Example: mv my. File 2 decl-of-indep will rename the file named my. File 2 to the new name declof-indep
 Rename a file (cont. ) • Illustrated: Notice that after the file is renamed, the content of the file remains unchanged !
Rename a file (cont. ) • Illustrated: Notice that after the file is renamed, the content of the file remains unchanged !
 Move a file from one directory (folder) to another directory (folder) • The command (application) used to mv a file with name file-Path into the directory dir-Path is: mv file-Path dir. Path
Move a file from one directory (folder) to another directory (folder) • The command (application) used to mv a file with name file-Path into the directory dir-Path is: mv file-Path dir. Path
 Move a file from one directory (folder) to another directory (folder) (cont. ) • Important: • This is in fact the same command for renaming a file • The difference is: dir-Path must be the path of an existing directory. (If dir-Path, the command will perform a rename operation !!!)
Move a file from one directory (folder) to another directory (folder) (cont. ) • Important: • This is in fact the same command for renaming a file • The difference is: dir-Path must be the path of an existing directory. (If dir-Path, the command will perform a rename operation !!!)
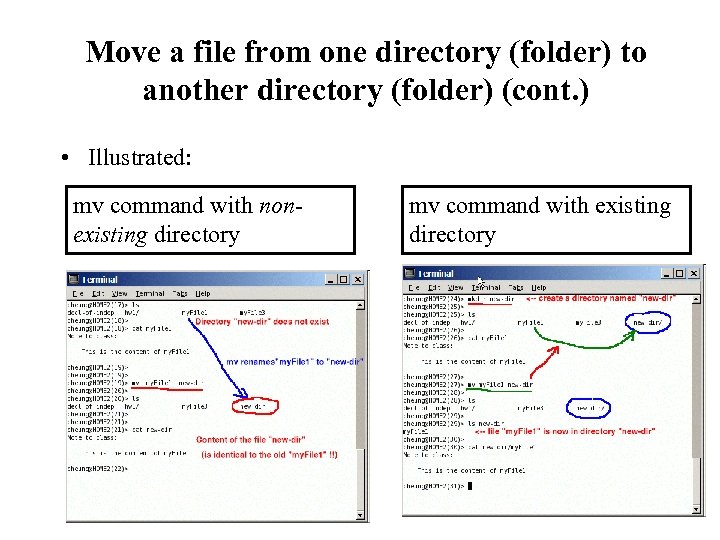 Move a file from one directory (folder) to another directory (folder) (cont. ) • Illustrated: mv command with nonexisting directory mv command with existing directory
Move a file from one directory (folder) to another directory (folder) (cont. ) • Illustrated: mv command with nonexisting directory mv command with existing directory


