23b759350bd0bd47bfd15ec270193836.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Manipulating Acquired Immunity through Gene Silencing Wei-Ping Min, MD. , Ph. D University of Western Ontario Canada
Manipulating Acquired Immunity through Gene Silencing Wei-Ping Min, MD. , Ph. D University of Western Ontario Canada
 Immune System The Immune system is a group of cells and organs that work together to fight infections in our bodies. The Immune System protects our body from pathogens and disease-causing agents, such as bacteria.
Immune System The Immune system is a group of cells and organs that work together to fight infections in our bodies. The Immune System protects our body from pathogens and disease-causing agents, such as bacteria.
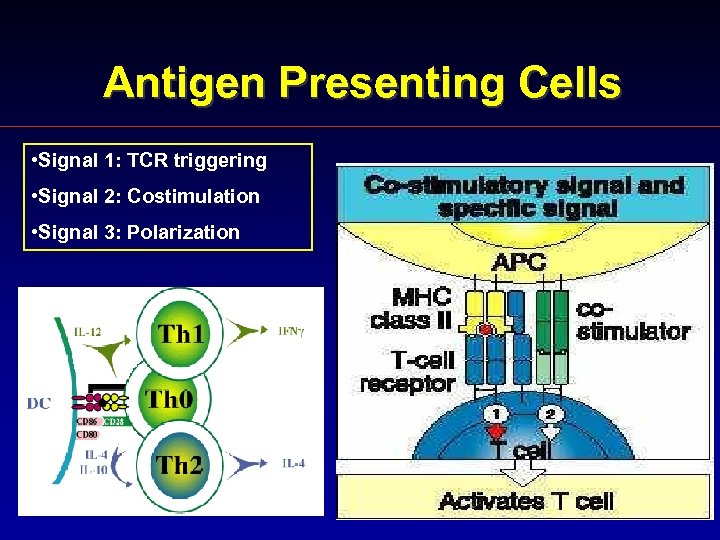 Antigen Presenting Cells • Signal 1: TCR triggering • Signal 2: Costimulation • Signal 3: Polarization
Antigen Presenting Cells • Signal 1: TCR triggering • Signal 2: Costimulation • Signal 3: Polarization
 Dendritic Cells Factors Contributing to Immunity • Antigen processing: • Active endocytosis • Phagocytosis • Receptor-mediated uptake • High MHC I and II expression • High costimulatory molecule expression • High production of IL-12 • Formation of large clusters with T cells
Dendritic Cells Factors Contributing to Immunity • Antigen processing: • Active endocytosis • Phagocytosis • Receptor-mediated uptake • High MHC I and II expression • High costimulatory molecule expression • High production of IL-12 • Formation of large clusters with T cells
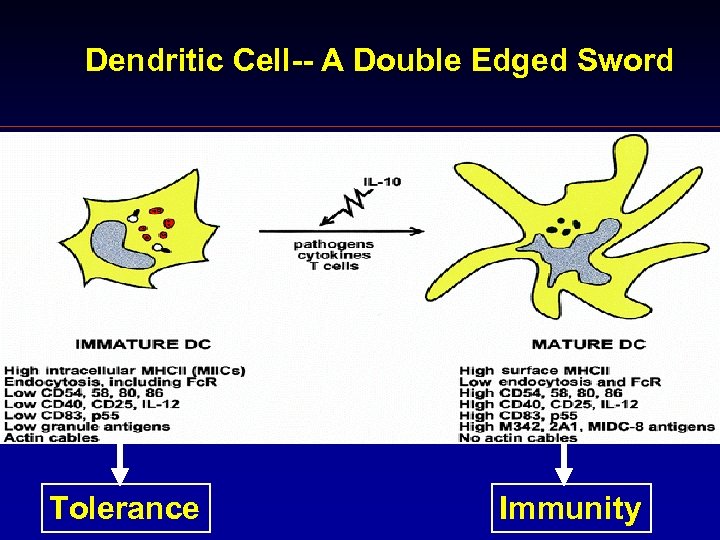 Dendritic Cell-- A Double Edged Sword Tolerance Immunity
Dendritic Cell-- A Double Edged Sword Tolerance Immunity
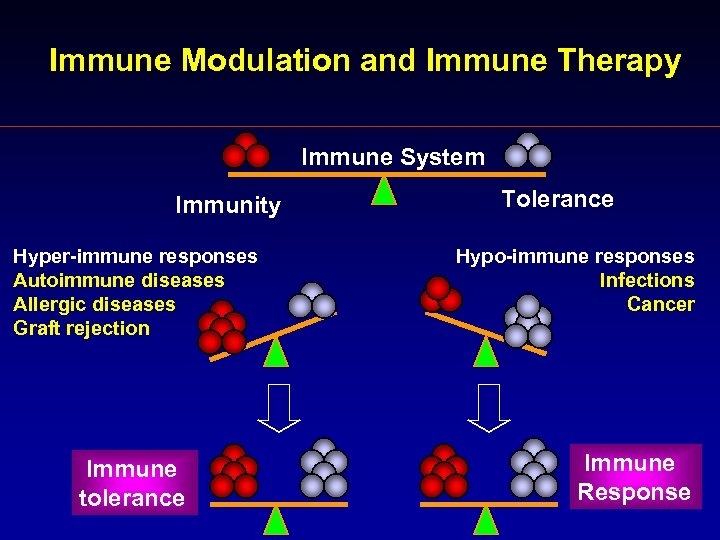 Immune Modulation and Immune Therapy Immune System Immunity Hyper-immune responses Autoimmune diseases Allergic diseases Graft rejection Immune tolerance Tolerance Hypo-immune responses Infections Cancer Immune Response
Immune Modulation and Immune Therapy Immune System Immunity Hyper-immune responses Autoimmune diseases Allergic diseases Graft rejection Immune tolerance Tolerance Hypo-immune responses Infections Cancer Immune Response
 Concept of RNA Interference • Double-stranded RNA (ds. RNA) is frequently produced when foreign genes (eg. , viral infection or transgenes) enter animals or plants. • RNA interference (RNAi) is the process by which cells destroy ds. RNA and endogenous transcripts with homology to the ds. RNA. • Small interfering RNA (si. RNA) is cleaved from ds. RNA by Dicer RNAse III, and is the mediator of RNAi.
Concept of RNA Interference • Double-stranded RNA (ds. RNA) is frequently produced when foreign genes (eg. , viral infection or transgenes) enter animals or plants. • RNA interference (RNAi) is the process by which cells destroy ds. RNA and endogenous transcripts with homology to the ds. RNA. • Small interfering RNA (si. RNA) is cleaved from ds. RNA by Dicer RNAse III, and is the mediator of RNAi.
 Milestones of RNAi • 1998 -First RNA interference using ds. RNA in C. elegans (Fire et al, Nature 391: 806) • 2001 -First RNA interference using si. RNA in mammalian cells (Tuschl, Nature 411: 494) • 2002 -Inhibition of HIV entry and replication using si. RNA to silence CD 4 and gag genes (Sharp, Nature Medicine 8: 681) • 2002 -Silencing DC genes for immune modulation (Min, Arthritis & Rheumatism 46: s 563)
Milestones of RNAi • 1998 -First RNA interference using ds. RNA in C. elegans (Fire et al, Nature 391: 806) • 2001 -First RNA interference using si. RNA in mammalian cells (Tuschl, Nature 411: 494) • 2002 -Inhibition of HIV entry and replication using si. RNA to silence CD 4 and gag genes (Sharp, Nature Medicine 8: 681) • 2002 -Silencing DC genes for immune modulation (Min, Arthritis & Rheumatism 46: s 563)
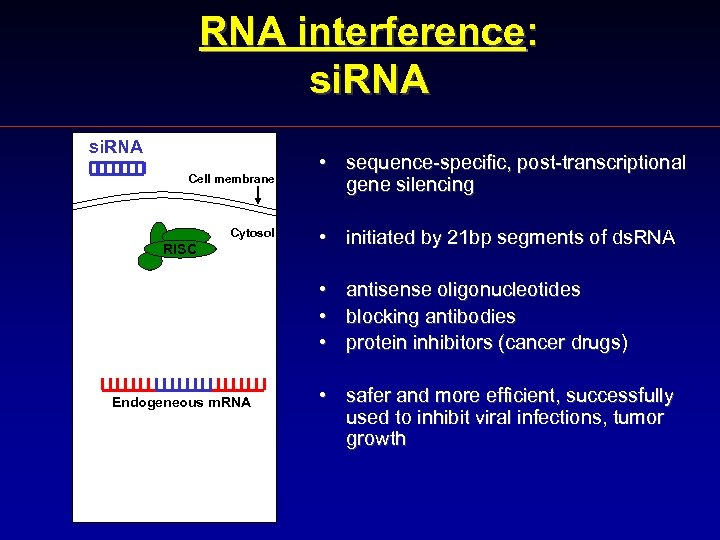 RNA interference: si. RNA Cell membrane Cytosol RISC • sequence-specific, post-transcriptional gene silencing • initiated by 21 bp segments of ds. RNA • antisense oligonucleotides • blocking antibodies • protein inhibitors (cancer drugs) Endogeneous m. RNA • safer and more efficient, successfully used to inhibit viral infections, tumor growth
RNA interference: si. RNA Cell membrane Cytosol RISC • sequence-specific, post-transcriptional gene silencing • initiated by 21 bp segments of ds. RNA • antisense oligonucleotides • blocking antibodies • protein inhibitors (cancer drugs) Endogeneous m. RNA • safer and more efficient, successfully used to inhibit viral infections, tumor growth
 Gene Silencing: si. RNA compared to other methods • si. RNA vs Antisense Oligos: • si. RNA more stable and efficient in gene silencing 1, 2 • Gene silencing occurs at much lower concentrations 1 • si. RNA vs Blocking antibodies: • Blocking Abs can be toxic and induce an immune response • Abs are not long lasting • si. RNA vs Protein inhibitors (cancer): • si. RNA is much more specific • si. RNA is longer lasting 1. 2. Bertrand et al. , Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2002), 296: 1000 Thompson JD, Drug Discovery Today (2002) 7: 912
Gene Silencing: si. RNA compared to other methods • si. RNA vs Antisense Oligos: • si. RNA more stable and efficient in gene silencing 1, 2 • Gene silencing occurs at much lower concentrations 1 • si. RNA vs Blocking antibodies: • Blocking Abs can be toxic and induce an immune response • Abs are not long lasting • si. RNA vs Protein inhibitors (cancer): • si. RNA is much more specific • si. RNA is longer lasting 1. 2. Bertrand et al. , Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2002), 296: 1000 Thompson JD, Drug Discovery Today (2002) 7: 912
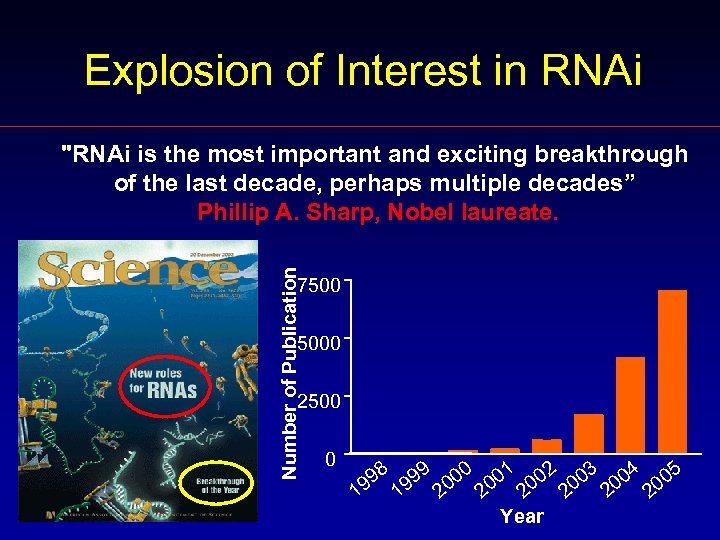 Explosion of Interest in RNAi Number of Publication "RNAi is the most important and exciting breakthrough of the last decade, perhaps multiple decades” Phillip A. Sharp, Nobel laureate. 7500 5000 2500 0 4 0 2 3 1 8 5 9 99 199 200 200 200 1 Year
Explosion of Interest in RNAi Number of Publication "RNAi is the most important and exciting breakthrough of the last decade, perhaps multiple decades” Phillip A. Sharp, Nobel laureate. 7500 5000 2500 0 4 0 2 3 1 8 5 9 99 199 200 200 200 1 Year
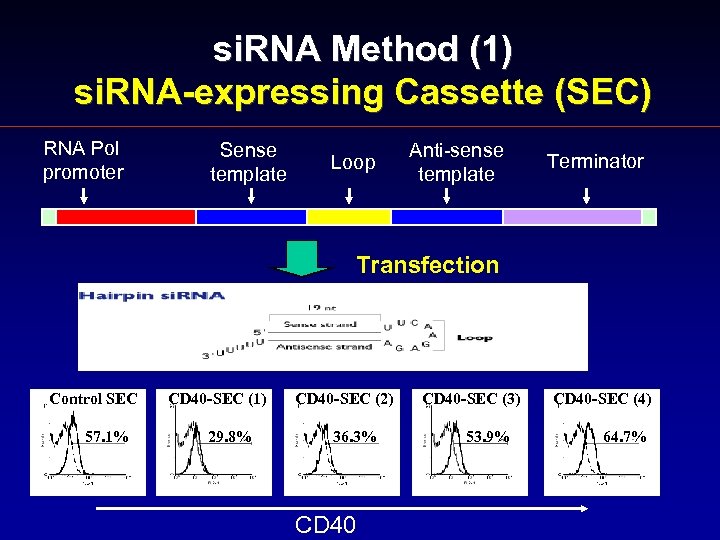 si. RNA Method (1) si. RNA-expressing Cassette (SEC) RNA Pol promoter Sense template 57. 1% Anti-sense template Terminator Transfection Control SEC Loop CD 40 -SEC (1) 29. 8% CD 40 -SEC (2) 36. 3% CD 40 -SEC (3) 53. 9% CD 40 -SEC (4) 64. 7%
si. RNA Method (1) si. RNA-expressing Cassette (SEC) RNA Pol promoter Sense template 57. 1% Anti-sense template Terminator Transfection Control SEC Loop CD 40 -SEC (1) 29. 8% CD 40 -SEC (2) 36. 3% CD 40 -SEC (3) 53. 9% CD 40 -SEC (4) 64. 7%
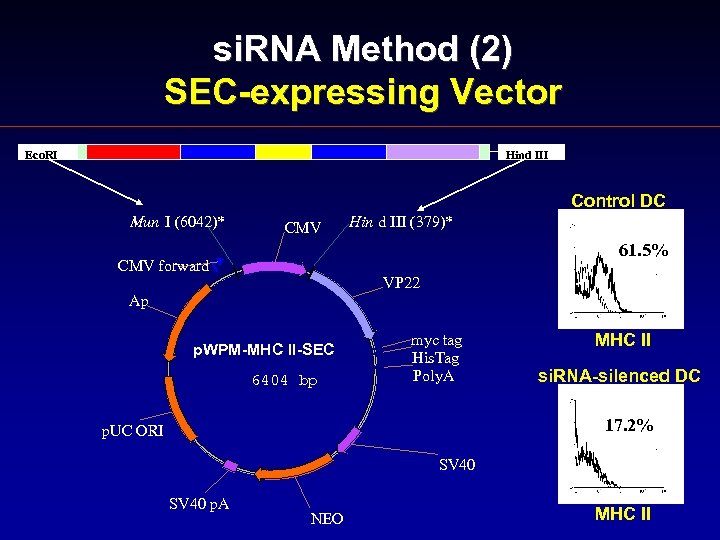 si. RNA Method (2) SEC-expressing Vector Eco. RI Hind III Control DC Mun I (6042)* CMV Hin d III (379)* 61. 5% CMV forward VP 22 Ap p. WPM-MHC II-SEC 6404 bp myc tag His. Tag Poly. A MHC II si. RNA-silenced DC 17. 2% p. UC ORI SV 40 p. A NEO MHC II
si. RNA Method (2) SEC-expressing Vector Eco. RI Hind III Control DC Mun I (6042)* CMV Hin d III (379)* 61. 5% CMV forward VP 22 Ap p. WPM-MHC II-SEC 6404 bp myc tag His. Tag Poly. A MHC II si. RNA-silenced DC 17. 2% p. UC ORI SV 40 p. A NEO MHC II
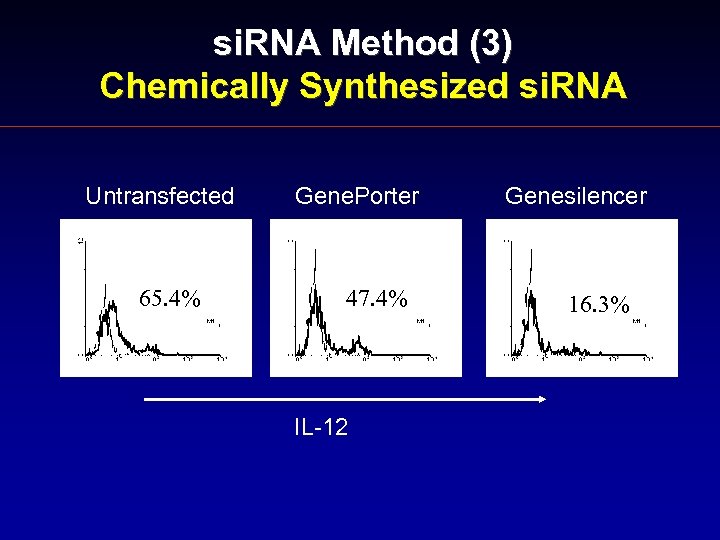 si. RNA Method (3) Chemically Synthesized si. RNA Untransfected 65. 4% Gene. Porter 47. 4% IL-12 Genesilencer 16. 3%
si. RNA Method (3) Chemically Synthesized si. RNA Untransfected 65. 4% Gene. Porter 47. 4% IL-12 Genesilencer 16. 3%
 In vivo si. RNA Delivery methods (1) Viral Methods • Adenoviral /retroviral/ lentiviral vectors • Have tissue-specificity, high in vivo transduction, stable expression • Pre-existing immunity, may cause inflammation, cannot control site of integration Pictures adapted from http: //www. rkm. com. au/biograph. html
In vivo si. RNA Delivery methods (1) Viral Methods • Adenoviral /retroviral/ lentiviral vectors • Have tissue-specificity, high in vivo transduction, stable expression • Pre-existing immunity, may cause inflammation, cannot control site of integration Pictures adapted from http: //www. rkm. com. au/biograph. html
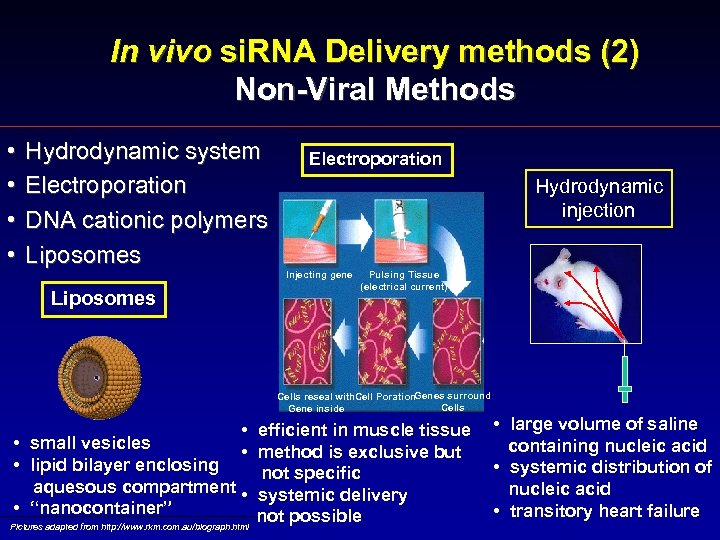 In vivo si. RNA Delivery methods (2) Non-Viral Methods • • Hydrodynamic system Electroporation DNA cationic polymers Liposomes Electroporation Hydrodynamic injection Injecting gene Pulsing Tissue (electrical current) Cells reseal with. Cell Poration. Genes surround Cells Gene inside • efficient in muscle tissue • small vesicles • method is exclusive but • lipid bilayer enclosing not specific aquesous compartment • systemic delivery • “nanocontainer” not possible Pictures adapted from http: //www. rkm. com. au/biograph. html • large volume of saline containing nucleic acid • systemic distribution of nucleic acid • transitory heart failure
In vivo si. RNA Delivery methods (2) Non-Viral Methods • • Hydrodynamic system Electroporation DNA cationic polymers Liposomes Electroporation Hydrodynamic injection Injecting gene Pulsing Tissue (electrical current) Cells reseal with. Cell Poration. Genes surround Cells Gene inside • efficient in muscle tissue • small vesicles • method is exclusive but • lipid bilayer enclosing not specific aquesous compartment • systemic delivery • “nanocontainer” not possible Pictures adapted from http: //www. rkm. com. au/biograph. html • large volume of saline containing nucleic acid • systemic distribution of nucleic acid • transitory heart failure
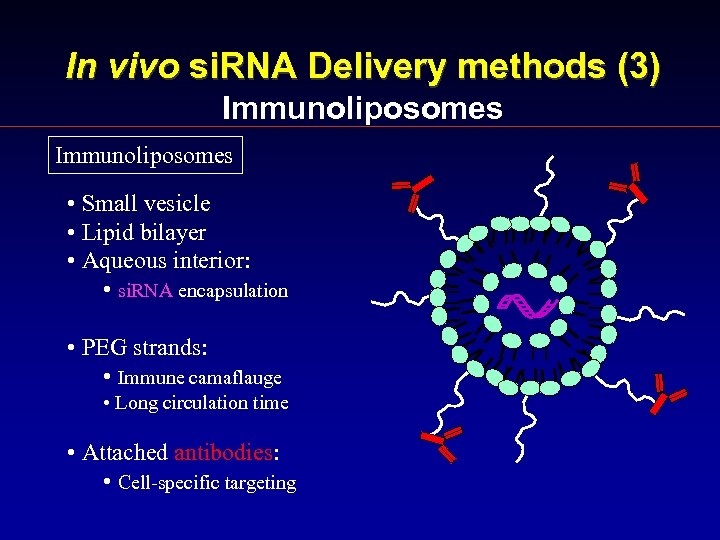 In vivo si. RNA Delivery methods (3) Immunoliposomes • Small vesicle • Lipid bilayer • Aqueous interior: • si. RNA encapsulation • PEG strands: • Immune camaflauge • Long circulation time • Attached antibodies: • Cell-specific targeting
In vivo si. RNA Delivery methods (3) Immunoliposomes • Small vesicle • Lipid bilayer • Aqueous interior: • si. RNA encapsulation • PEG strands: • Immune camaflauge • Long circulation time • Attached antibodies: • Cell-specific targeting
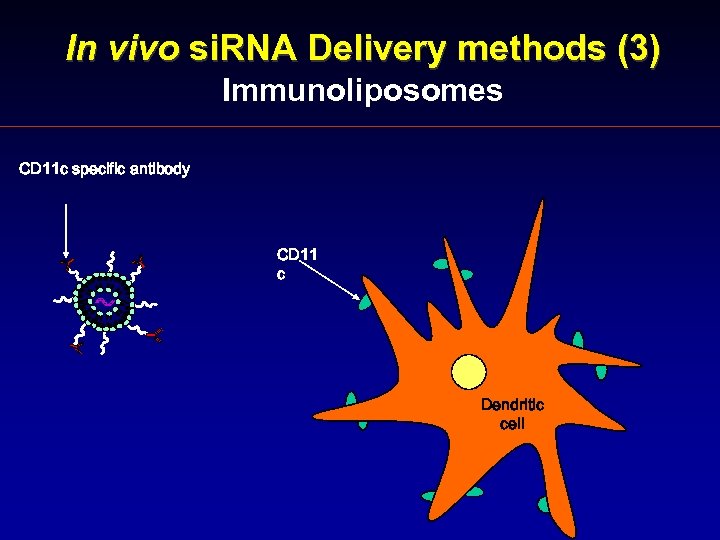 In vivo si. RNA Delivery methods (3) Immunoliposomes CD 11 c specific antibody CD 11 c Dendritic cell
In vivo si. RNA Delivery methods (3) Immunoliposomes CD 11 c specific antibody CD 11 c Dendritic cell
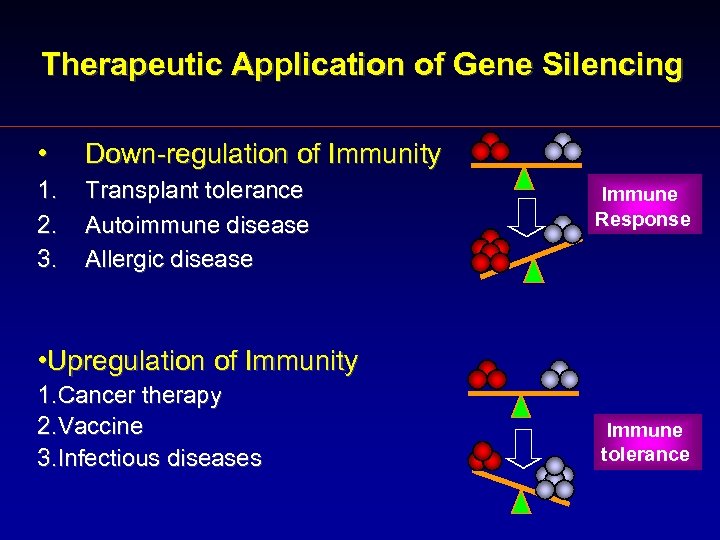 Therapeutic Application of Gene Silencing • Down-regulation of Immunity 1. 2. 3. Transplant tolerance Autoimmune disease Allergic disease Immune Response • Upregulation of Immunity 1. Cancer therapy 2. Vaccine 3. Infectious diseases Immune tolerance
Therapeutic Application of Gene Silencing • Down-regulation of Immunity 1. 2. 3. Transplant tolerance Autoimmune disease Allergic disease Immune Response • Upregulation of Immunity 1. Cancer therapy 2. Vaccine 3. Infectious diseases Immune tolerance
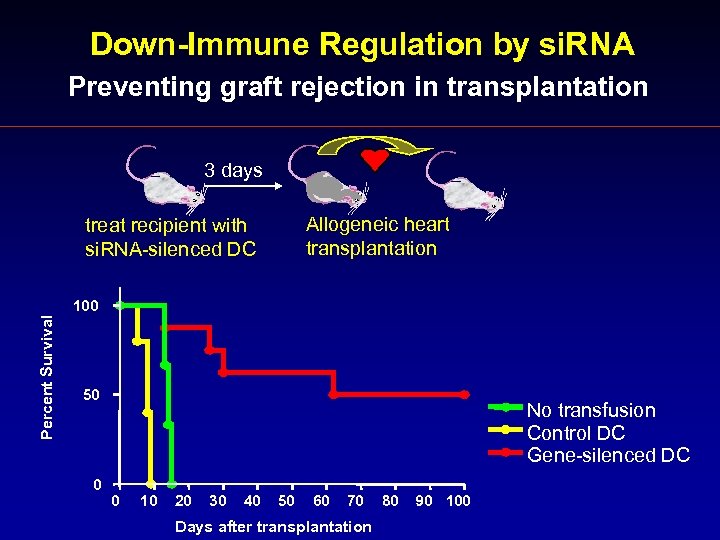 Down-Immune Regulation by si. RNA Preventing graft rejection in transplantation 3 days Allogeneic heart transplantation treat recipient with si. RNA-silenced DC Percent Survival 100 50 No transfusion Control DC Gene-silenced DC 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Days after transplantation 80 90 100
Down-Immune Regulation by si. RNA Preventing graft rejection in transplantation 3 days Allogeneic heart transplantation treat recipient with si. RNA-silenced DC Percent Survival 100 50 No transfusion Control DC Gene-silenced DC 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Days after transplantation 80 90 100
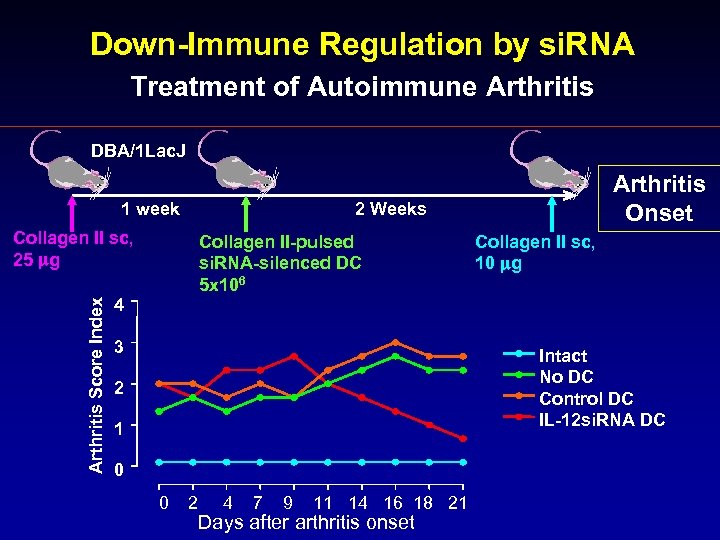 Down-Immune Regulation by si. RNA Treatment of Autoimmune Arthritis DBA/1 Lac. J 1 week Arthritis Score Index Collagen II sc, 25 mg Arthritis Onset 2 Weeks Collagen II-pulsed si. RNA-silenced DC 5 x 106 Collagen II sc, 10 mg 4 3 Intact No DC Control DC IL-12 si. RNA DC 2 1 0 0 2 4 7 9 11 14 16 18 21 Days after arthritis onset
Down-Immune Regulation by si. RNA Treatment of Autoimmune Arthritis DBA/1 Lac. J 1 week Arthritis Score Index Collagen II sc, 25 mg Arthritis Onset 2 Weeks Collagen II-pulsed si. RNA-silenced DC 5 x 106 Collagen II sc, 10 mg 4 3 Intact No DC Control DC IL-12 si. RNA DC 2 1 0 0 2 4 7 9 11 14 16 18 21 Days after arthritis onset
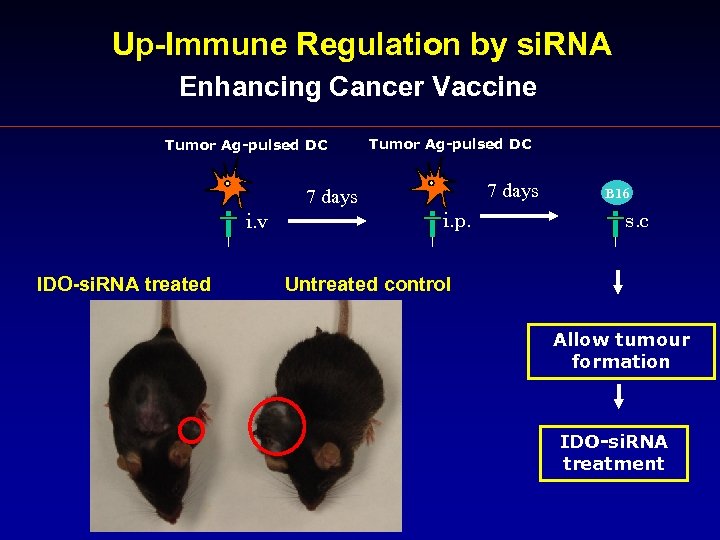 Up-Immune Regulation by si. RNA Enhancing Cancer Vaccine Tumor Ag-pulsed DC 7 days i. v IDO-si. RNA treated i. p. B 16 s. c Untreated control Allow tumour formation IDO-si. RNA treatment
Up-Immune Regulation by si. RNA Enhancing Cancer Vaccine Tumor Ag-pulsed DC 7 days i. v IDO-si. RNA treated i. p. B 16 s. c Untreated control Allow tumour formation IDO-si. RNA treatment
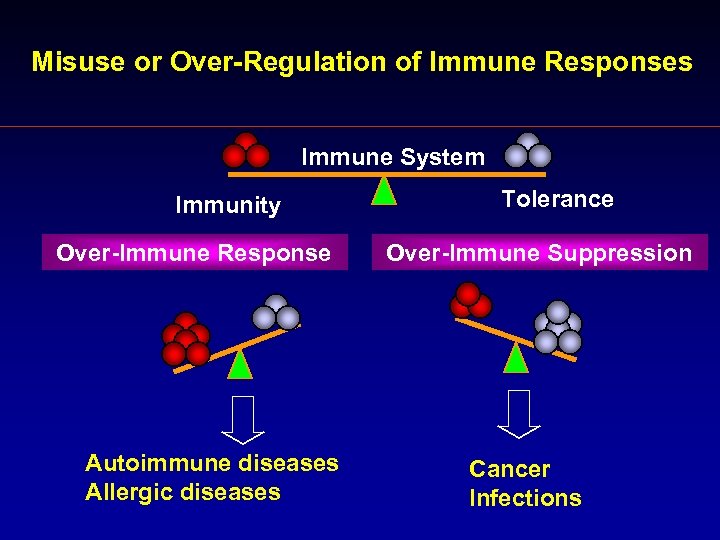 Misuse or Over-Regulation of Immune Responses Immune System Immunity Over-Immune Response Autoimmune diseases Allergic diseases Tolerance Over-Immune Suppression Cancer Infections
Misuse or Over-Regulation of Immune Responses Immune System Immunity Over-Immune Response Autoimmune diseases Allergic diseases Tolerance Over-Immune Suppression Cancer Infections
 Summary 1. si. RNA is a useful tool for gene-specific inhibition for manipulating immune system. 2. Up-regulating Immune responses is achievable by silencing immune suppressive genes, which can be used for anti-cancer therapy, vaccine development. 3. Down-regulating immune responses through silencing immune responsive genes possesses therapeutic potential in treatments of autoimmune and allergic diseases as well as graft rejection in transplantation. 4. Misuse of si. RNA and over-manipulation of immune system may cause hyper- or hypo-immune responses, which may lead to various diseases.
Summary 1. si. RNA is a useful tool for gene-specific inhibition for manipulating immune system. 2. Up-regulating Immune responses is achievable by silencing immune suppressive genes, which can be used for anti-cancer therapy, vaccine development. 3. Down-regulating immune responses through silencing immune responsive genes possesses therapeutic potential in treatments of autoimmune and allergic diseases as well as graft rejection in transplantation. 4. Misuse of si. RNA and over-manipulation of immune system may cause hyper- or hypo-immune responses, which may lead to various diseases.
 Acknowledgement • Canadian Institutes of Health Research • Roche Organ Transplant Research Foundation • Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada • Kidney Foundation of Canada • The Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation • Multi-Organ Transplant Program Research Fund, LHSC
Acknowledgement • Canadian Institutes of Health Research • Roche Organ Transplant Research Foundation • Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada • Kidney Foundation of Canada • The Physicians’ Services Incorporated Foundation • Multi-Organ Transplant Program Research Fund, LHSC
 Acknowledgement Jacob Mu Ying Cecilia Xusheng Igor Costin Weiping Francis Xiufen Jessica
Acknowledgement Jacob Mu Ying Cecilia Xusheng Igor Costin Weiping Francis Xiufen Jessica


