ea098871573671189f438dc469ca676a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Managing Trust and Security in Online Auctions Samira Sadaoui Computer Science Department University of Regina March 6, 2012
Managing Trust and Security in Online Auctions Samira Sadaoui Computer Science Department University of Regina March 6, 2012
 Current Research Interests Software Engineering: - Development of Software Systems - Object-Oriented Methodology - Formal Methods - Multi-Agent Technology Artificial Intelligence: - Trust Management - Multi-Attribute and Reverse Auctions - Web Service Selection
Current Research Interests Software Engineering: - Development of Software Systems - Object-Oriented Methodology - Formal Methods - Multi-Agent Technology Artificial Intelligence: - Trust Management - Multi-Attribute and Reverse Auctions - Web Service Selection
 Software Systems Development Ø Problem Requirements Specification: - Functional requirements - Quality requirements (correctness, robustness, usability, portability, performance, maintainability). Ø Software Design/Architecture: a high-quality solution. Ø Complex systems: distributed, dynamic, concurrent software systems.
Software Systems Development Ø Problem Requirements Specification: - Functional requirements - Quality requirements (correctness, robustness, usability, portability, performance, maintainability). Ø Software Design/Architecture: a high-quality solution. Ø Complex systems: distributed, dynamic, concurrent software systems.
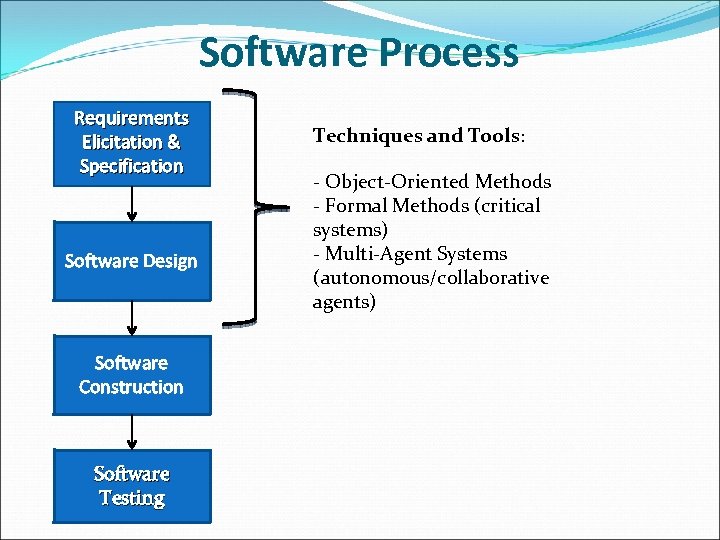 Software Process Requirements Elicitation & Specification Software Design Software Construction Software Testing Techniques and Tools: - Object-Oriented Methods - Formal Methods (critical systems) - Multi-Agent Systems (autonomous/collaborative agents)
Software Process Requirements Elicitation & Specification Software Design Software Construction Software Testing Techniques and Tools: - Object-Oriented Methods - Formal Methods (critical systems) - Multi-Agent Systems (autonomous/collaborative agents)
 Online Auctions Ø Most popular trading mechanisms in e-commerce. Ø Popular auction houses: e. Bay, u. Bid, Bidz, Overstock, Online. Auction, Webidz Ø Different features: - Ø Single vs. Multiple Attributes Forward vs. Reverse Single vs. Multiple rounds Bidding protocol: Open: English, Dutch Sealed: Vickery, First-Price Sealed-Bid Complex and trust-critical systems.
Online Auctions Ø Most popular trading mechanisms in e-commerce. Ø Popular auction houses: e. Bay, u. Bid, Bidz, Overstock, Online. Auction, Webidz Ø Different features: - Ø Single vs. Multiple Attributes Forward vs. Reverse Single vs. Multiple rounds Bidding protocol: Open: English, Dutch Sealed: Vickery, First-Price Sealed-Bid Complex and trust-critical systems.
 Problems in Online Auctions Lack of research for reverse (competing sellers) and multiattribute auctions. Ø Buyer’s constraints/preferences elicitation and specification. Ø Winner determination based on buyer’s preferences and sellers’ bids. Ø Human cheating behaviors detection. Ø Design of a high quality auction house.
Problems in Online Auctions Lack of research for reverse (competing sellers) and multiattribute auctions. Ø Buyer’s constraints/preferences elicitation and specification. Ø Winner determination based on buyer’s preferences and sellers’ bids. Ø Human cheating behaviors detection. Ø Design of a high quality auction house.
 Auction Frauds Ø Online auction frauds: the largest part of all Internet crimes. Ø Trust is difficult to establish because transactions occur among complete strangers. Ø Number of Internet users is increasing. Ø Many opportunities for cheating: siphoning, shielding, shilling, sniping, auctioneer-bidder collusion, lack of bid privacy, non-delivery and non-payment of goods, information misrepresentation.
Auction Frauds Ø Online auction frauds: the largest part of all Internet crimes. Ø Trust is difficult to establish because transactions occur among complete strangers. Ø Number of Internet users is increasing. Ø Many opportunities for cheating: siphoning, shielding, shilling, sniping, auctioneer-bidder collusion, lack of bid privacy, non-delivery and non-payment of goods, information misrepresentation.
![Online Crimes [Internet Fraud Complaint Center] http: //www. secureputer. com/series-do-not-fall-victim-to-internet-auction-fraud/ Online Crimes [Internet Fraud Complaint Center] http: //www. secureputer. com/series-do-not-fall-victim-to-internet-auction-fraud/](https://present5.com/presentation/ea098871573671189f438dc469ca676a/image-8.jpg) Online Crimes [Internet Fraud Complaint Center] http: //www. secureputer. com/series-do-not-fall-victim-to-internet-auction-fraud/
Online Crimes [Internet Fraud Complaint Center] http: //www. secureputer. com/series-do-not-fall-victim-to-internet-auction-fraud/
 Research goal: - prevent frauds and increase trust in online auctions. - build a trustful (multi-attribute & reverse) auction house. Proposed Solutions: ØMulti-round & semi-sealed protocol to cope with bid snaping shielding and siphoning, auctioneer cheating and lack of bid privacy. ØAn efficient trust management framework: - to maintain the reputation of bidders, - to ensure security in the auction protocol.
Research goal: - prevent frauds and increase trust in online auctions. - build a trustful (multi-attribute & reverse) auction house. Proposed Solutions: ØMulti-round & semi-sealed protocol to cope with bid snaping shielding and siphoning, auctioneer cheating and lack of bid privacy. ØAn efficient trust management framework: - to maintain the reputation of bidders, - to ensure security in the auction protocol.
 Proposed Solutions Ø Agent technology to reduce misconduct: - automate the entire auction house with software agents (all the security rules are implemented) - to achieve efficiency, robustness and maintainability of the entire auction house. Ø Formal methods to specify and verify different patterns of abnormal behaviors.
Proposed Solutions Ø Agent technology to reduce misconduct: - automate the entire auction house with software agents (all the security rules are implemented) - to achieve efficiency, robustness and maintainability of the entire auction house. Ø Formal methods to specify and verify different patterns of abnormal behaviors.
 Security Management Behavior-based: - monitor in run time the bidding activities to detect shill behaviors. Ø Ø Signature-based: - using Internet communication protocols (IP address tracking).
Security Management Behavior-based: - monitor in run time the bidding activities to detect shill behaviors. Ø Ø Signature-based: - using Internet communication protocols (IP address tracking).
 Shill Behaviors Ø The most severe fraud. Ø The hardest type of frauds to detect. Ø Shill bidder creates fake identities to provoke war among bidders and generate an interest for the item. Ø Auction failure, buyer pays more for the item, seller gets less payment. Ø Around $250 million may have been lost to shilling in 2008 [P. Cohen. Shill Bidding on e. Bay: a Case Study (Or, the facilitating and concealing of fraud by e. Bay). In Auction. Bytes Forum, Online Auction News Forum, August 2009]
Shill Behaviors Ø The most severe fraud. Ø The hardest type of frauds to detect. Ø Shill bidder creates fake identities to provoke war among bidders and generate an interest for the item. Ø Auction failure, buyer pays more for the item, seller gets less payment. Ø Around $250 million may have been lost to shilling in 2008 [P. Cohen. Shill Bidding on e. Bay: a Case Study (Or, the facilitating and concealing of fraud by e. Bay). In Auction. Bytes Forum, Online Auction News Forum, August 2009]
 Run-Time Monitoring of Shills Ø Detection of shills: - large volume of data are analyzed at the end of the auction, which is too late as the auction has already resulted in losses for bidders. - live auctions is harder than offline auctions. Ø Reaction to shills: stop the auction, send warnings, remove the shill bidder, update its reputation score, Suspend shill bidders' account temporarily/permanently, etc
Run-Time Monitoring of Shills Ø Detection of shills: - large volume of data are analyzed at the end of the auction, which is too late as the auction has already resulted in losses for bidders. - live auctions is harder than offline auctions. Ø Reaction to shills: stop the auction, send warnings, remove the shill bidder, update its reputation score, Suspend shill bidders' account temporarily/permanently, etc


