9d991f66812fbadfd1baa0546eb68e12.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia An Insurance Perspective Forum for Asian Insolvency Reform (FAIR) 11 November 2003 Seoul, Korea Matthew Ellerton Euler Hermes Credit Underwriters (HK) Ltd. Hong Kong (+852) 2867 0097 ~ matthew. ellerton@eulerhermes. com
Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia An Insurance Perspective Forum for Asian Insolvency Reform (FAIR) 11 November 2003 Seoul, Korea Matthew Ellerton Euler Hermes Credit Underwriters (HK) Ltd. Hong Kong (+852) 2867 0097 ~ matthew. ellerton@eulerhermes. com
 Agenda < Trade credit insurance < Trade and trade risk in Asia < The Asian credit insurance market < Buyer risk assessment < Links with financing Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 2
Agenda < Trade credit insurance < Trade and trade risk in Asia < The Asian credit insurance market < Buyer risk assessment < Links with financing Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 2
 About Euler Hermes < Specialist credit insurance and receivables management arm of Allianz Group. < Listed on Paris stock exchange; rated A+ by S&P. < Largest credit insurer worldwide; 37% global market share. < Presence in 39 countries. < Principal activities : Credit insurance, management and financing of trade receivables (including factoring and securitisation), bonding and guarantees. < Administer the Federal state export credit scheme on behalf of the German government. < Currently protect USD 600 billion of global business transactions. < 6. 5 million current credit limits. < 40 million companies monitored in Euler Hermes database. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 3
About Euler Hermes < Specialist credit insurance and receivables management arm of Allianz Group. < Listed on Paris stock exchange; rated A+ by S&P. < Largest credit insurer worldwide; 37% global market share. < Presence in 39 countries. < Principal activities : Credit insurance, management and financing of trade receivables (including factoring and securitisation), bonding and guarantees. < Administer the Federal state export credit scheme on behalf of the German government. < Currently protect USD 600 billion of global business transactions. < 6. 5 million current credit limits. < 40 million companies monitored in Euler Hermes database. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 3
 Trade credit insurance < Commercial trade debts typically 10 -30% of the balance sheet. < Protects the supplier (the insured) against non-payment of trade debts by its customers. < Provides three key roles : prevention, collection, insurance more than merely risk transfer. < Not a typical insurance product: + no blanket coverage; + highly interactive; + closer to banking products than to standard insurance. < The manufacturer / supplier (creditor) is the policyholder. < The customer (debtor) is the risk. < Coverage falls into two broad categories: commercial risk and political risk. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 4
Trade credit insurance < Commercial trade debts typically 10 -30% of the balance sheet. < Protects the supplier (the insured) against non-payment of trade debts by its customers. < Provides three key roles : prevention, collection, insurance more than merely risk transfer. < Not a typical insurance product: + no blanket coverage; + highly interactive; + closer to banking products than to standard insurance. < The manufacturer / supplier (creditor) is the policyholder. < The customer (debtor) is the risk. < Coverage falls into two broad categories: commercial risk and political risk. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 4
 Insured risks < Commercial Risks: + insolvency (or equivalent in local jurisdiction); + default of a Promissory Note; + “Protracted Default” (non-payment at 180 days past due). < Political Risks: + currency inconvertibility; + war, civil war, insurrection; + contract cancellation; + exchange transfer delay; + cancellation or restriction of export/import license; + public buyer cover. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 5
Insured risks < Commercial Risks: + insolvency (or equivalent in local jurisdiction); + default of a Promissory Note; + “Protracted Default” (non-payment at 180 days past due). < Political Risks: + currency inconvertibility; + war, civil war, insurrection; + contract cancellation; + exchange transfer delay; + cancellation or restriction of export/import license; + public buyer cover. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 5
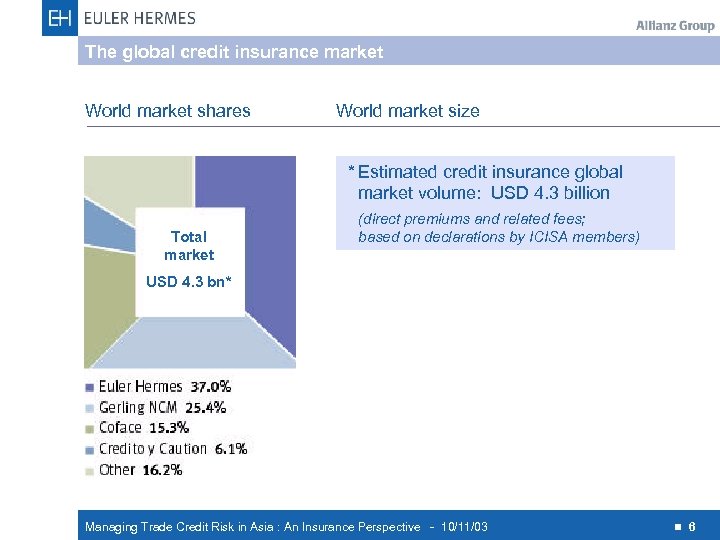 The global credit insurance market World market shares World market size * Estimated credit insurance global market volume: USD 4. 3 billion Total market (direct premiums and related fees; based on declarations by ICISA members) USD 4. 3 bn* Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 6
The global credit insurance market World market shares World market size * Estimated credit insurance global market volume: USD 4. 3 billion Total market (direct premiums and related fees; based on declarations by ICISA members) USD 4. 3 bn* Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 6
 Questions and issues facing Asian trade < General decline in credit quality. < Divergence of accounting rules and standards. < Pressure on banking systems squeezing availability of finance. < Increasing obligation to act on a global scale must be reflected in risk management programmes. < Scale and speed of change of risk exposure. < Bankruptcies inevitable and have happened to ‘big name’ companies. < Failures come from increasingly unpredictable sources. < Should the rating agencies have predicted high-profile failures? Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 7
Questions and issues facing Asian trade < General decline in credit quality. < Divergence of accounting rules and standards. < Pressure on banking systems squeezing availability of finance. < Increasing obligation to act on a global scale must be reflected in risk management programmes. < Scale and speed of change of risk exposure. < Bankruptcies inevitable and have happened to ‘big name’ companies. < Failures come from increasingly unpredictable sources. < Should the rating agencies have predicted high-profile failures? Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 7
 Characteristics of Asian trade credit < Use of promissory notes widespread in some markets, e. g. Korea, Japan. < Use of L/Cs declining in face of competitive pressures. < Regulatory and insolvency frameworks vary widely. < Corporate insolvencies rising, but comparisons by country difficult. < Increasing focus on trade risks, in particular credit risk. < Means of managing and hedging credit risk becoming more prevalent (factoring, invoice discounting, credit insurance, …). < Credit insurance previously the remit of state ECAs. < Protection often available only for export trade. < Export and domestic coverage now more widely available. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 8
Characteristics of Asian trade credit < Use of promissory notes widespread in some markets, e. g. Korea, Japan. < Use of L/Cs declining in face of competitive pressures. < Regulatory and insolvency frameworks vary widely. < Corporate insolvencies rising, but comparisons by country difficult. < Increasing focus on trade risks, in particular credit risk. < Means of managing and hedging credit risk becoming more prevalent (factoring, invoice discounting, credit insurance, …). < Credit insurance previously the remit of state ECAs. < Protection often available only for export trade. < Export and domestic coverage now more widely available. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 8
 The credit insurance market in Asia < Hong Kong, Singapore: fully open markets. < Taiwan, Thailand, Philippines : offshore insurance permitted but detrimental tax position. < China : export coverage solely via Sinosure; domestic entrants now emerging. Massive potential demand. < Korea : export and domestic both state-controlled; emergence of various state-private partnerships. High demand, but outlets limited. < Malaysia : both domestic and export cover from state, MECIB; domestic cover may be reinsured offshore. < India : partially open market; various private market players in addition to state ECGC. < Indonesia : effectively a closed market; licenses prohibitively expensive. Limited demand. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 9
The credit insurance market in Asia < Hong Kong, Singapore: fully open markets. < Taiwan, Thailand, Philippines : offshore insurance permitted but detrimental tax position. < China : export coverage solely via Sinosure; domestic entrants now emerging. Massive potential demand. < Korea : export and domestic both state-controlled; emergence of various state-private partnerships. High demand, but outlets limited. < Malaysia : both domestic and export cover from state, MECIB; domestic cover may be reinsured offshore. < India : partially open market; various private market players in addition to state ECGC. < Indonesia : effectively a closed market; licenses prohibitively expensive. Limited demand. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 9
 Buyer risk assessment < Core principle of credit insurance. < Involves the assessment and continuous monitoring of buyers’ financial risks in terms of their : + financial performance; + business / sectoral sensitivity; + shareholders; + industry trends; + competitive outlook; + adverse information; + growth prospects; + . . . < Requires proximity to the risk. < Mix of manual and automatic underwriting, based on internal models of risk gradings. < Manual underwriting for large, high-risk or more complex decisions. < Mix of public and proprietary information. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 10
Buyer risk assessment < Core principle of credit insurance. < Involves the assessment and continuous monitoring of buyers’ financial risks in terms of their : + financial performance; + business / sectoral sensitivity; + shareholders; + industry trends; + competitive outlook; + adverse information; + growth prospects; + . . . < Requires proximity to the risk. < Mix of manual and automatic underwriting, based on internal models of risk gradings. < Manual underwriting for large, high-risk or more complex decisions. < Mix of public and proprietary information. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 10
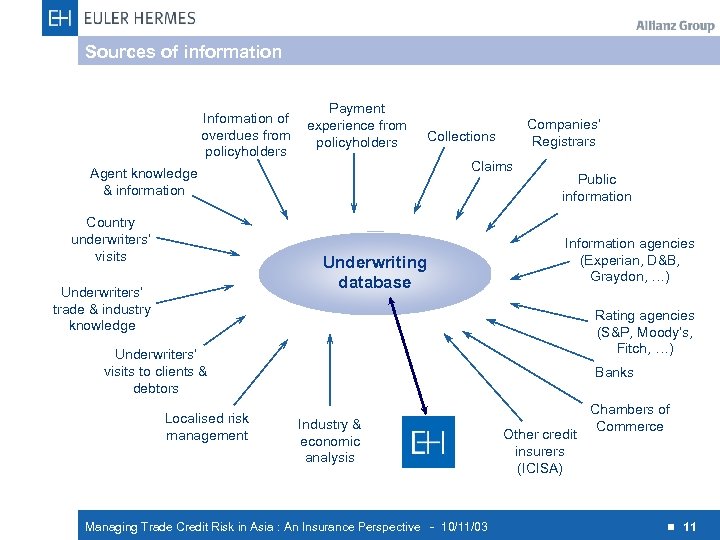 Sources of information Information of overdues from policyholders Payment experience from policyholders Claims Agent knowledge & information Country underwriters’ visits Underwriting database Underwriters’ trade & industry knowledge Companies’ Registrars Collections Public information Information agencies (Experian, D&B, Graydon, …) Rating agencies (S&P, Moody’s, Fitch, …) Underwriters’ visits to clients & debtors Localised risk management Banks Industry & economic analysis Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 Other credit insurers (ICISA) Chambers of Commerce n 11
Sources of information Information of overdues from policyholders Payment experience from policyholders Claims Agent knowledge & information Country underwriters’ visits Underwriting database Underwriters’ trade & industry knowledge Companies’ Registrars Collections Public information Information agencies (Experian, D&B, Graydon, …) Rating agencies (S&P, Moody’s, Fitch, …) Underwriters’ visits to clients & debtors Localised risk management Banks Industry & economic analysis Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 Other credit insurers (ICISA) Chambers of Commerce n 11
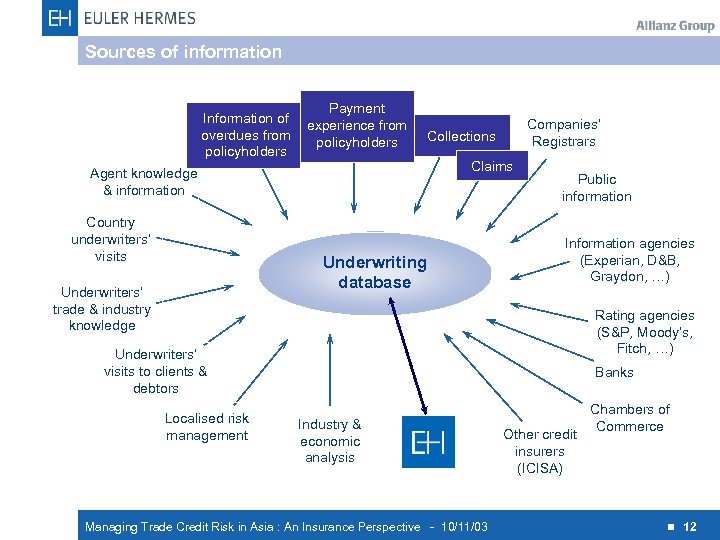 Sources of information Information of overdues from policyholders Payment experience from policyholders Claims Agent knowledge & information Country underwriters’ visits Underwriting database Underwriters’ trade & industry knowledge Companies’ Registrars Collections Public information Information agencies (Experian, D&B, Graydon, …) Rating agencies (S&P, Moody’s, Fitch, …) Underwriters’ visits to clients & debtors Localised risk management Banks Industry & economic analysis Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 Other credit insurers (ICISA) Chambers of Commerce n 12
Sources of information Information of overdues from policyholders Payment experience from policyholders Claims Agent knowledge & information Country underwriters’ visits Underwriting database Underwriters’ trade & industry knowledge Companies’ Registrars Collections Public information Information agencies (Experian, D&B, Graydon, …) Rating agencies (S&P, Moody’s, Fitch, …) Underwriters’ visits to clients & debtors Localised risk management Banks Industry & economic analysis Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 Other credit insurers (ICISA) Chambers of Commerce n 12
 Links with financing < Credit insurers have worked closely with financial institutions for decades. < Private market insurers developing new ways of working with banks. < Credit insurance enhances the quality of trade receivables. < Main driver for credit insurance purchase in Asia is to access finance. < Assignment of claim payments to bank provides bank with increased security, allowing client greater capacity to access funds. < Participation in more complex finance structures: + Structuring of trade debt financing solutions, such as credit insured non-recourse factoring / invoice discounting. + Participation in wholesale trade debt financing structures. + Securitisation of receivables. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 13
Links with financing < Credit insurers have worked closely with financial institutions for decades. < Private market insurers developing new ways of working with banks. < Credit insurance enhances the quality of trade receivables. < Main driver for credit insurance purchase in Asia is to access finance. < Assignment of claim payments to bank provides bank with increased security, allowing client greater capacity to access funds. < Participation in more complex finance structures: + Structuring of trade debt financing solutions, such as credit insured non-recourse factoring / invoice discounting. + Participation in wholesale trade debt financing structures. + Securitisation of receivables. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 13
 Securitisation < Asset-backed securitisation (ABS) using trade receivables as the underlying asset. < Developed in US and Europe, but beginning to see signs in Asia. < Allows company to raise capital based on securitised assets. < Purely finance-driven; risk transfer with no risk mitigation. < Insurance provides credit enhancement. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 14
Securitisation < Asset-backed securitisation (ABS) using trade receivables as the underlying asset. < Developed in US and Europe, but beginning to see signs in Asia. < Allows company to raise capital based on securitised assets. < Purely finance-driven; risk transfer with no risk mitigation. < Insurance provides credit enhancement. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 14
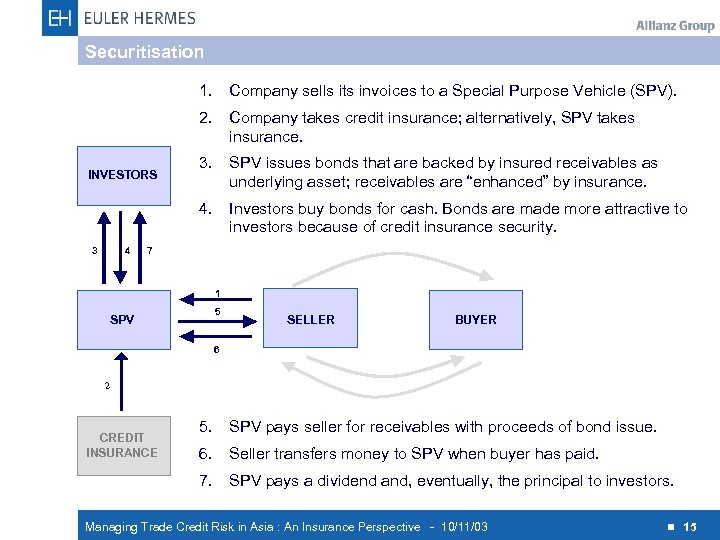 Securitisation 1. 2. 3 4 Company takes credit insurance; alternatively, SPV takes insurance. 3. SPV issues bonds that are backed by insured receivables as underlying asset; receivables are “enhanced” by insurance. 4. INVESTORS Company sells its invoices to a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). Investors buy bonds for cash. Bonds are made more attractive to investors because of credit insurance security. 7 1 5 SPV SELLER BUYER 6 2 5. SPV pays seller for receivables with proceeds of bond issue. 6. Seller transfers money to SPV when buyer has paid. 7. CREDIT INSURANCE SPV pays a dividend and, eventually, the principal to investors. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 15
Securitisation 1. 2. 3 4 Company takes credit insurance; alternatively, SPV takes insurance. 3. SPV issues bonds that are backed by insured receivables as underlying asset; receivables are “enhanced” by insurance. 4. INVESTORS Company sells its invoices to a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). Investors buy bonds for cash. Bonds are made more attractive to investors because of credit insurance security. 7 1 5 SPV SELLER BUYER 6 2 5. SPV pays seller for receivables with proceeds of bond issue. 6. Seller transfers money to SPV when buyer has paid. 7. CREDIT INSURANCE SPV pays a dividend and, eventually, the principal to investors. Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 15
 Questions 9/F, One International Finance Centre 1 Harbour View Street, Central, Hong Kong Tel. (+852) 2867 0061 Fax (+852) 2869 8655 www. eulerhermes. com Matthew Ellerton Business Development Manager - North Asia Direct (+852) 2867 0097 matthew. ellerton@eulerhermes. com Euler Hermes, a company of the Allianz Group Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 16
Questions 9/F, One International Finance Centre 1 Harbour View Street, Central, Hong Kong Tel. (+852) 2867 0061 Fax (+852) 2869 8655 www. eulerhermes. com Matthew Ellerton Business Development Manager - North Asia Direct (+852) 2867 0097 matthew. ellerton@eulerhermes. com Euler Hermes, a company of the Allianz Group Managing Trade Credit Risk in Asia : An Insurance Perspective - 10/11/03 n 16


