102c6b1965ab30196588fbe65dbca32a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Managing State Assets in Brazil: The Case of the National Development Bank Armando Castelar Pinheiro BNDES - UFRJ Budapeste, September 19, 2000

The Creation of SOEs in Brazil ë Industrialization drive ë National security ë Nationalization of foreign assets (utilities) ë Verticalization and diversification of SOEs ë Bankrupt private companies

Controlling SOEs in Brazil 4 1960 s: Creation of holding companies (steel, telecom, electricity, etc. ) 4 1967 -78: Administrative reform reduced controls over SOEs while keeping privileges 4 1979 -89: Creating centralized expenditure controls and legal restrictions on SOE creation (census) + sale of small formely private SOEs + performance contracts 4 1990 -98: Privatization of large traditional SOEs 4 1999 -: Change in corporate governance



Remaining State Assets in Brazil ë Power generation (being privatized) ë Real estate (being privatized) ë Roads (to be partly privatized) ë Water and sanitation (to be partly privatized) ë Banks (to be partly privatized) ë Oil company (not to be privatized, but end of monopoly and sale of shares)

Banks: ongoing discussion on what to do ë Federal Q Q Q ë 2 commercial banks (agriculture and housing) largest commercial banks in Brazil 2 regional development banks (also commercial) 1 investment bank (BNDES) Local states Q Q Several commercial banks being privatized Investment banks turned into development agencies

BNDES The Brazilian Development Bank 4 Founded in 1952 4 100% owned by the Federal Government 4 The main source of medium and long-term financing in the Brazilian economy 3 Main Brazilian partner of multilateral credit organizations 3 1, 600 employees

Infrastructure - Steel Energy - Intermediate inputs - Consumer goods Import substitution of intermediate and capital goods Private industry and agribusiness Private infrastructure and exports Management of privatization process
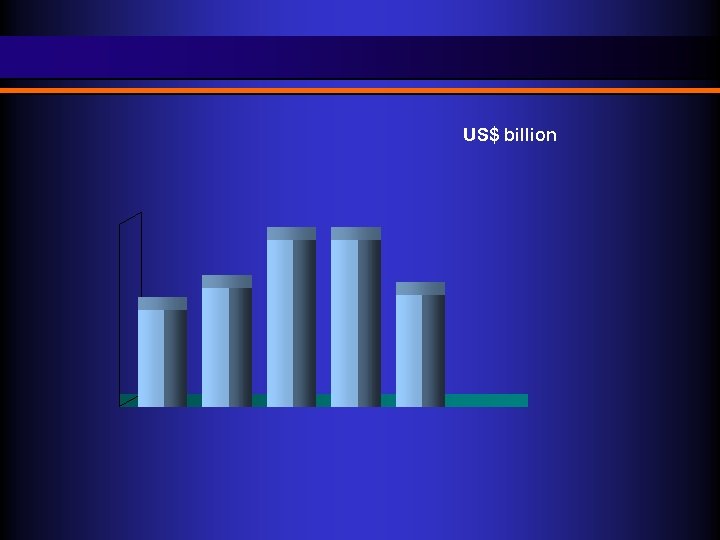
US$ billion
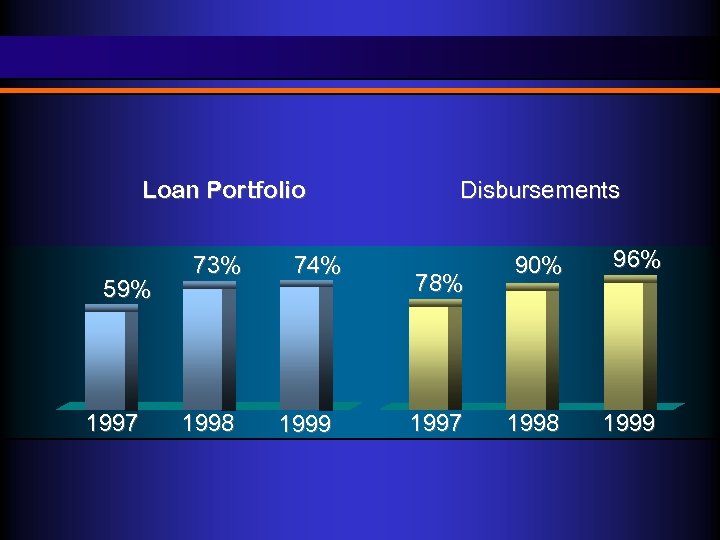
Loan Portfolio Disbursements 73% 90% 96% 1998 1999 59% 1997 1998 74% 1999 78% 1997
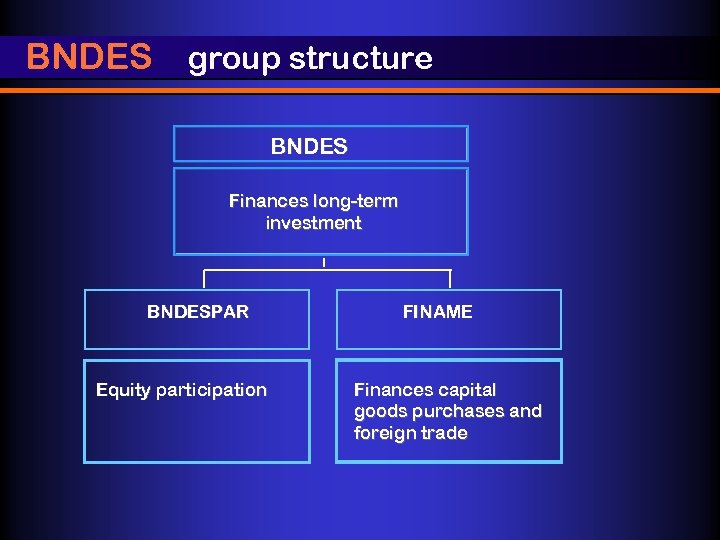
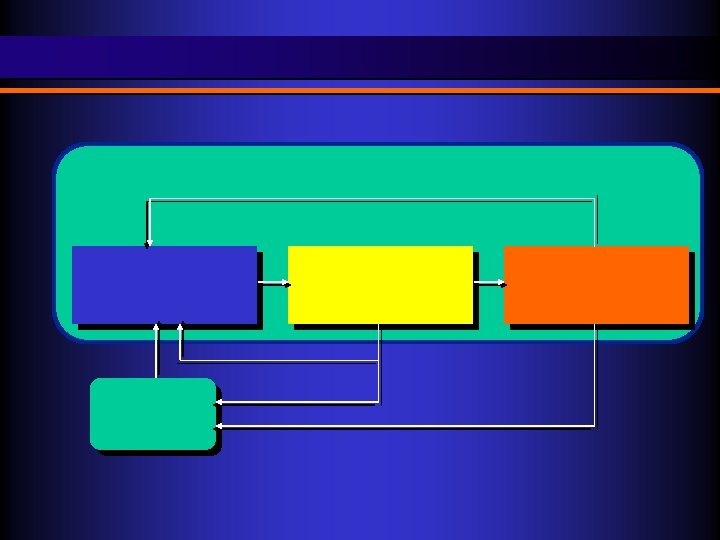
BNDES group structure BNDES Finances long-term investment BNDESPAR Equity participation FINAME Finances capital goods purchases and foreign trade





BNDES access to credit 3 Up to R$ 7 million ( around US$ 4 million ) BNDES Automatic - financing through a network of accredited financial institutions (pass-through lending ) 3 In excess of R$ 7 million FINEM - Direct financing 3 Unlimited FINAME - Machinery and equipment (pass-through lending )

credit policy & procedures Exposure limits: sectors and clients Rating policy and Credit Committee No foreign capital discrimination All loans require collateral and repayment capacity Onlending through financial intermediaries, which assume the final credit risk

Changes in SOE Corporate Governance Failure of performance contracts ë More active board members (outsiders) ë Minister as president of board ë More transparent accounting practices ë BNDES on board of directors of privatized companies with left overs in state hands

BNDES - The Brazilian Development Bank
102c6b1965ab30196588fbe65dbca32a.ppt