a31f1590c55610a9ff92db98adf6e9fa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

‘Managing Risk, Space Invaders and your friendly, neighbourhood Burglar an introduction to an assumptions-based approach to project Risk Management presentation to Kingston and Croydon branch of the BCS 14 -Jan-2003 David Galley X Point International Ltd © 2002

Introduction § Basic approach to project risk management § Proactive + Devolved + Simple to understand § Presentation Content § Risk Management (vs Project Management) § Assumptions-based approach § Identifying Assumptions § Registers § Risk Evaluation & Prioritisation § Risk Plans § Roles & Responsibilities § Execution § Questions X Point International Ltd © 2002
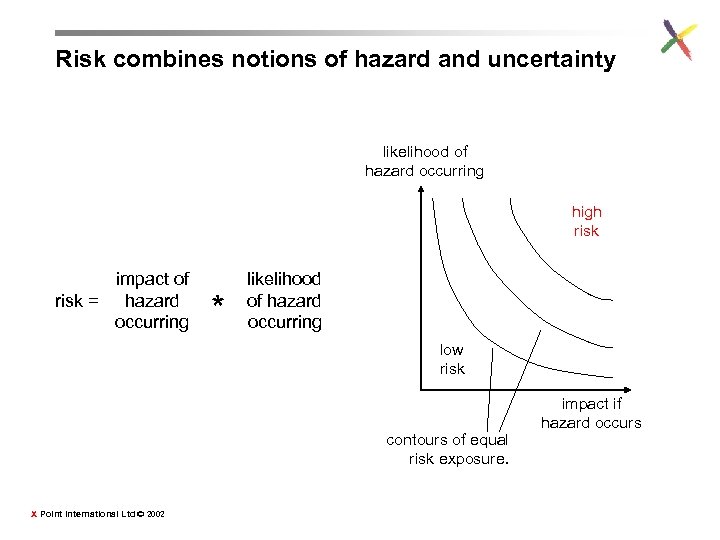
Risk combines notions of hazard and uncertainty likelihood of hazard occurring high risk impact of risk = hazard occurring * likelihood of hazard occurring low risk contours of equal risk exposure. X Point International Ltd © 2002 impact if hazard occurs
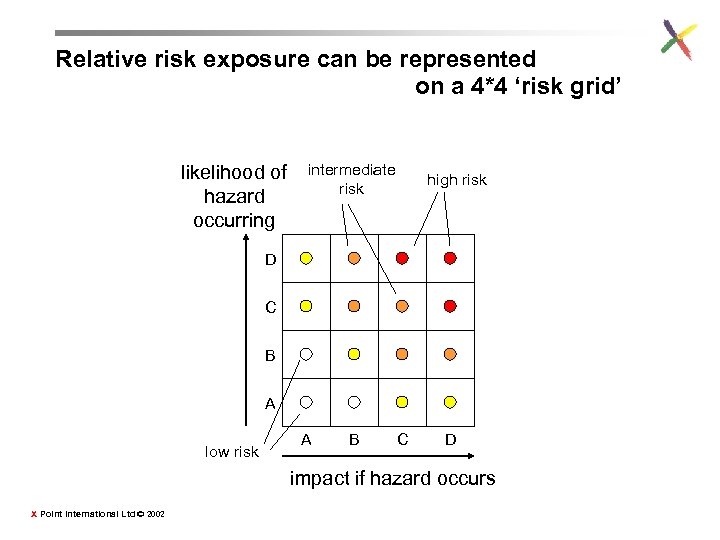
Relative risk exposure can be represented on a 4*4 ‘risk grid’ likelihood of hazard occurring intermediate risk high risk D C B A low risk A B C D impact if hazard occurs X Point International Ltd © 2002
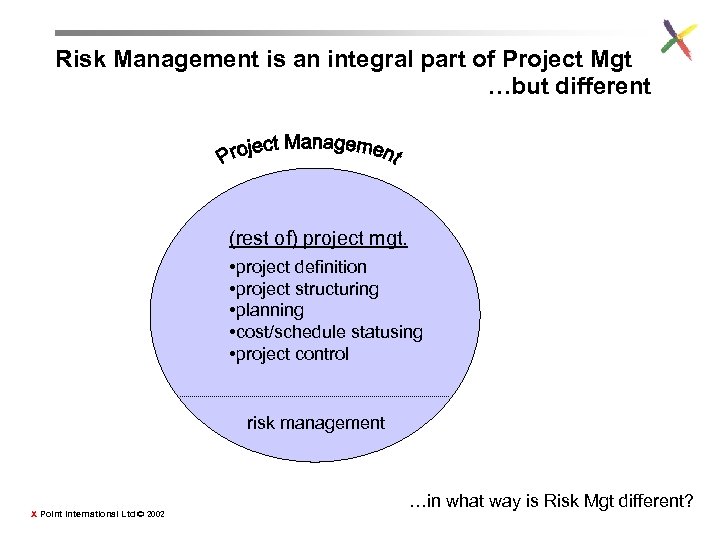
Risk Management is an integral part of Project Mgt …but different (rest of) project mgt. • project definition • project structuring • planning • cost/schedule statusing • project control risk management X Point International Ltd © 2002 …in what way is Risk Mgt different?
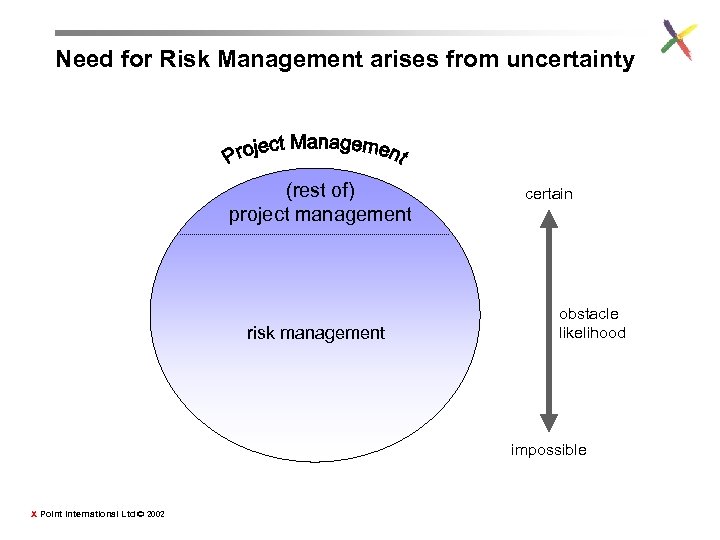
Need for Risk Management arises from uncertainty (rest of) project management risk management certain obstacle likelihood impossible X Point International Ltd © 2002
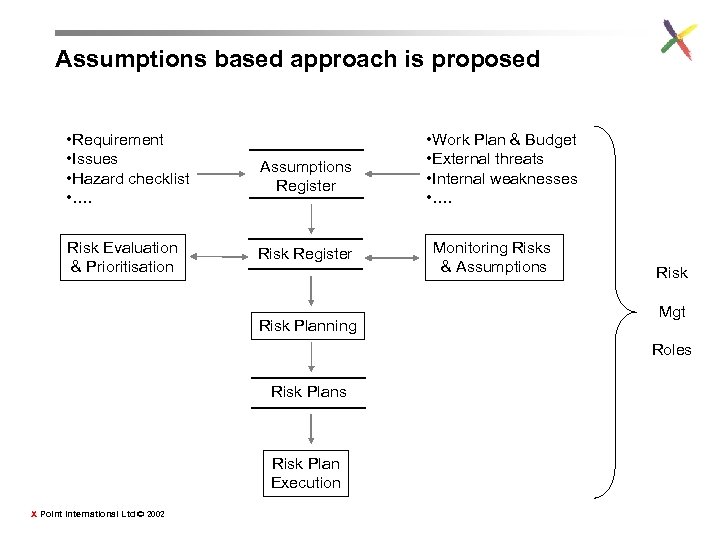
Assumptions based approach is proposed • Requirement • Issues • Hazard checklist • …. Assumptions Register Risk Evaluation & Prioritisation Risk Register Risk Planning • Work Plan & Budget • External threats • Internal weaknesses • …. Monitoring Risks & Assumptions Risk Mgt Roles Risk Plan Execution X Point International Ltd © 2002

Projects are exposed to the risk of assumption failure § Decisions are made based on limited information § Working assumptions § Conscious/Explicit § Unconscious/Implicit (become evident later, or remain hidden) § Working assumptions proven to be: § True – will not disturb the project § False – will disturb the project § For every assumption the project makes there is an inherent risk that the assumption will not be true X Point International Ltd © 2002
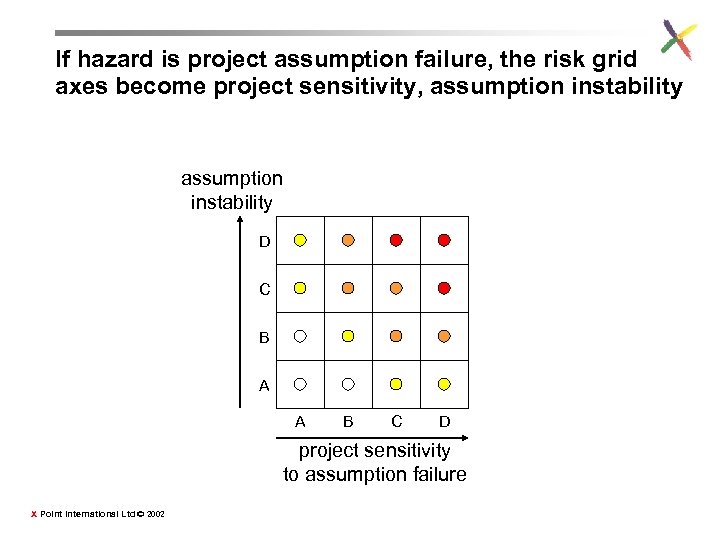
If hazard is project assumption failure, the risk grid axes become project sensitivity, assumption instability D C B A A B C D project sensitivity to assumption failure X Point International Ltd © 2002
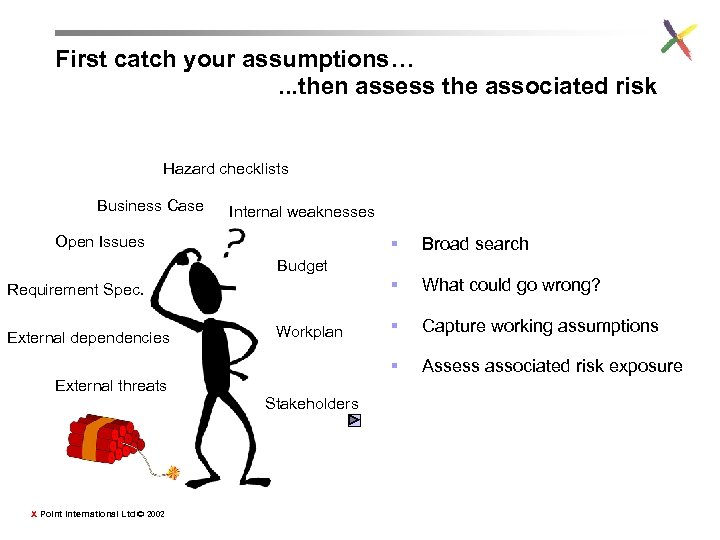
First catch your assumptions…. . . then assess the associated risk Hazard checklists Business Case Internal weaknesses Open Issues § Requirement Spec. External dependencies Workplan External threats Stakeholders X Point International Ltd © 2002 § What could go wrong? § Capture working assumptions § Budget Broad search Assess associated risk exposure
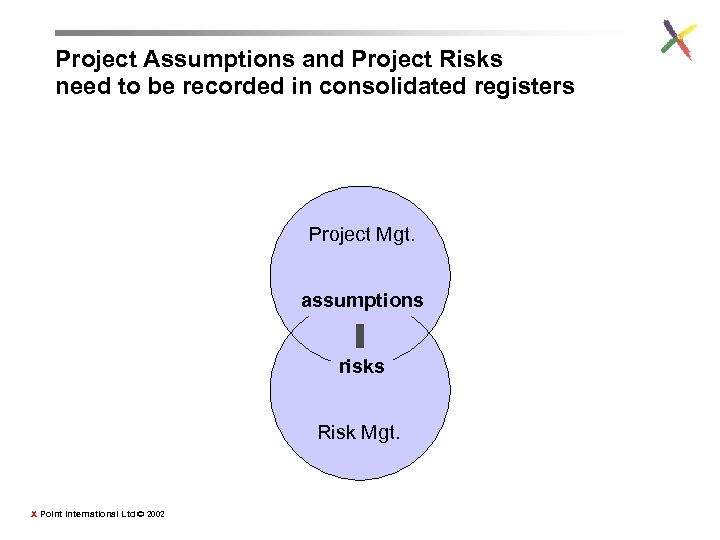
Project Assumptions and Project Risks need to be recorded in consolidated registers Project Mgt. assumptions risks Risk Mgt. X Point International Ltd © 2002
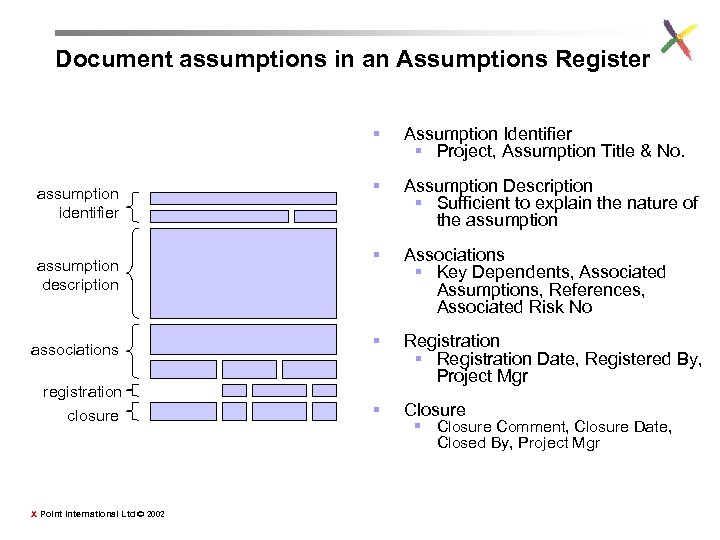
Document assumptions in an Assumptions Register § Assumption Identifier § Project, Assumption Title & No. § Assumption Description § Sufficient to explain the nature of the assumption § Associations § Key Dependents, Associated Assumptions, References, Associated Risk No associations § registration closure Registration § Registration Date, Registered By, Project Mgr § Closure assumption identifier assumption description X Point International Ltd © 2002 § Closure Comment, Closure Date, Closed By, Project Mgr
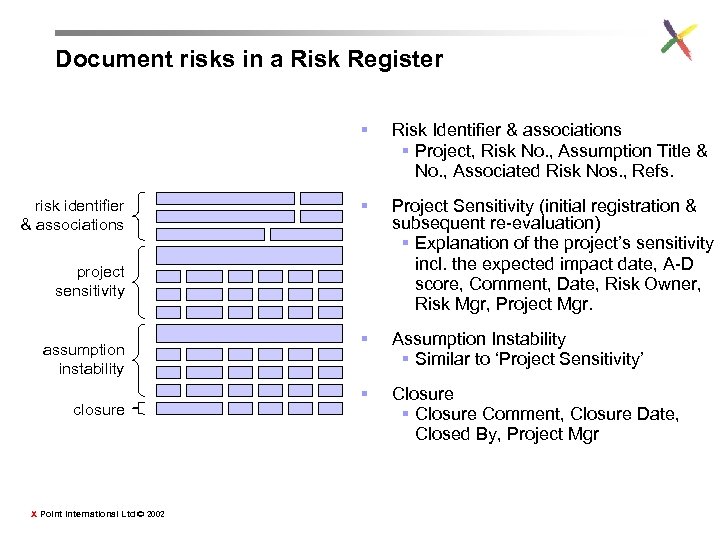
Document risks in a Risk Register § risk identifier & associations Risk Identifier & associations § Project, Risk No. , Assumption Title & No. , Associated Risk Nos. , Refs. § Project Sensitivity (initial registration & subsequent re-evaluation) § Explanation of the project’s sensitivity incl. the expected impact date, A-D score, Comment, Date, Risk Owner, Risk Mgr, Project Mgr. § Assumption Instability § Similar to ‘Project Sensitivity’ § Closure Comment, Closure Date, Closed By, Project Mgr project sensitivity assumption instability closure X Point International Ltd © 2002

Having identified your risks, you need to manage them too many risks. . . which one first? . . . what do I do? risk plan. . . what’s that? § § Risk Plans § Roles & Responsibilities § X Point International Ltd © 2002 Risk Prioritisation Execution & Monitoring
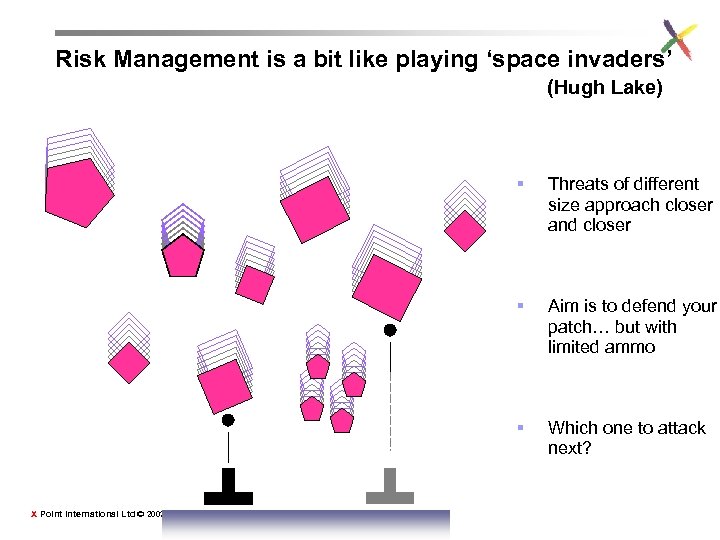
Risk Management is a bit like playing ‘space invaders’ (Hugh Lake) § § Aim is to defend your patch… but with limited ammo § X Point International Ltd © 2002 Threats of different size approach closer and closer Which one to attack next?

Deciding which risks to ‘attack’ is a complex decision § So many risks… which should I attack? § consider size, ie. risk exposure § consider timing… when will it ‘hit’? § How effective would an attack be? § how will I deal with each risk? § what chance that it’ll work? § how much residual risk exposure? § What about the cost? § Will attacking a risk be worth the cost? § Can I afford to attack a particular risk? § Can I afford not to attack that risk? § How do we ‘attack’ risks? X Point International Ltd © 2002
Risk Handling Techniques – four main categories proactive Risk Plans X Point International Ltd © 2002 reactive Risk Plans
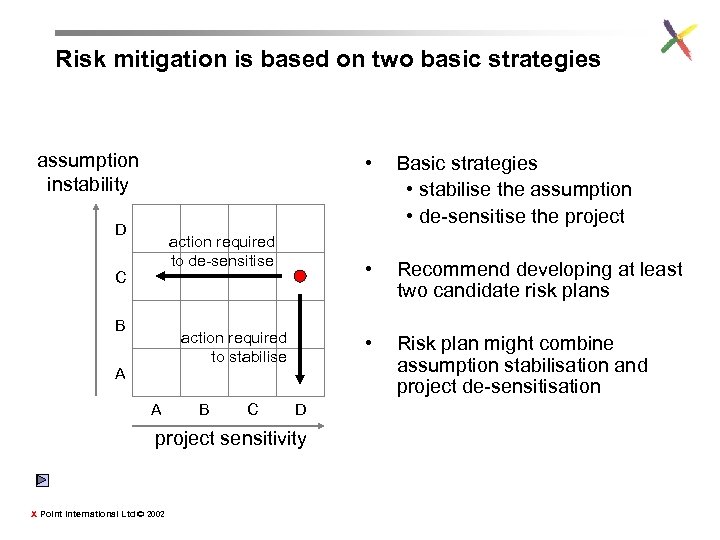
Risk mitigation is based on two basic strategies assumption instability • D • C B action required to stabilise A A B C D project sensitivity X Point International Ltd © 2002 Recommend developing at least two candidate risk plans • action required to de-sensitise Basic strategies • stabilise the assumption • de-sensitise the project Risk plan might combine assumption stabilisation and project de-sensitisation

Exercise: Risk Management applied to House Burglary § Background § You’ve just moved to a new town and you’ve a 1001 things to sort out § You learn that a number of burglaries have taken place in your new neighbourhood. § § X Point International Ltd © 2002 Do you lock your self in, and refuse leave your house? – No. You’ve got a life to lead! What is your working assumption?

Exercise: Risk Management applied to House Burglary § Background § You’ve just moved to a new town and you’ve a 1001 things to sort out § You learn that a number of burglaries have taken place in your new neighbourhood. § Do you lock your self in, and refuse leave your house? – No. You’ve got a life to lead! § The principal working assumption is an implicit assertion ‘We will not get burgled today’. § The assumption wasn’t ‘I might get burgled’ That isn’t an assumption, it’s an infallible truism. § But your working assumption might be wrong! § Failure of that working assumption constitutes the hazard. You’ve identified a risk. § How are you going to manage it? X Point International Ltd © 2002

Here’s a heap of ‘risk plans’… assign each to a category of risk handling technique Risk avoidance §… §… Risk mitigation (stabilise the assumption) § keep stock of glass, timber to repair windows §… § store valuable items in a safe, or at bank §… § adopt non-materialistic philosophy § arrange house contents insurance Risk mitigation (de § install extra high-security locks -sensitise impact) §… § take any burglary ‘on the chin’ §… § move away to safer district § install a burglar alarm Risk transfer § buy a big, noisy dog §… § buy a quiet crocodile §… …what else? X Point International Ltd © 2002 Risk retention §… §…
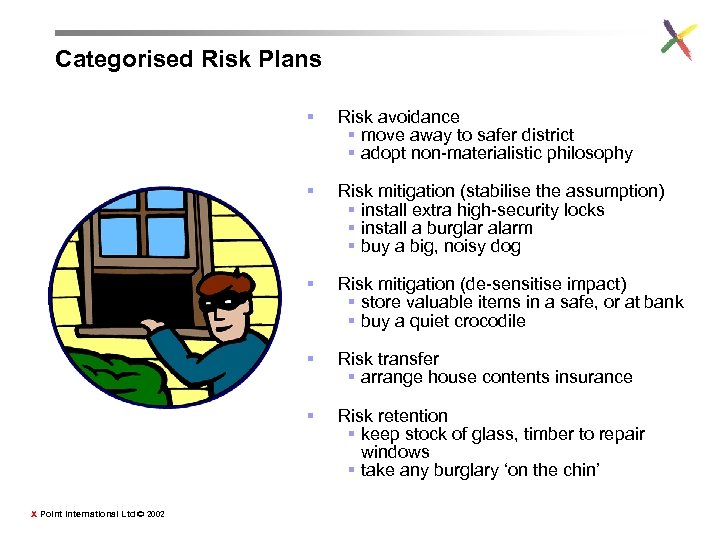
Categorised Risk Plans § § Risk mitigation (stabilise the assumption) § install extra high-security locks § install a burglar alarm § buy a big, noisy dog § Risk mitigation (de-sensitise impact) § store valuable items in a safe, or at bank § buy a quiet crocodile § Risk transfer § arrange house contents insurance § X Point International Ltd © 2002 Risk avoidance § move away to safer district § adopt non-materialistic philosophy Risk retention § keep stock of glass, timber to repair windows § take any burglary ‘on the chin’
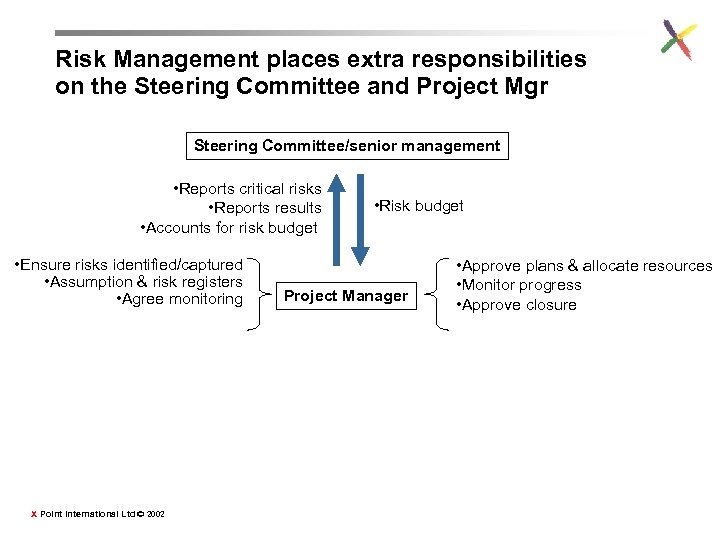
Risk Management places extra responsibilities on the Steering Committee and Project Mgr Steering Committee/senior management • Reports critical risks • Reports results • Accounts for risk budget • Ensure risks identified/captured • Assumption & risk registers • Agree monitoring X Point International Ltd © 2002 • Risk budget Project Manager • Approve plans & allocate resources • Monitor progress • Approve closure
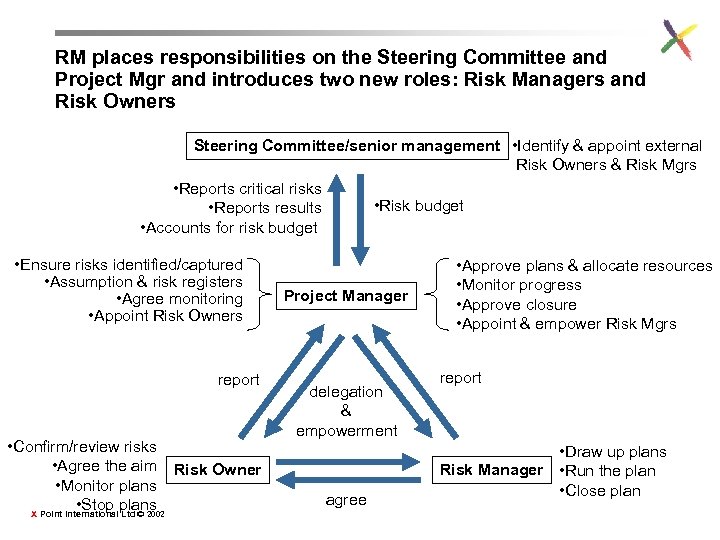
RM places responsibilities on the Steering Committee and Project Mgr and introduces two new roles: Risk Managers and Risk Owners Steering Committee/senior management • Identify & appoint external Risk Owners & Risk Mgrs • Reports critical risks • Risk budget • Reports results • Accounts for risk budget • Ensure risks identified/captured • Assumption & risk registers • Agree monitoring • Appoint Risk Owners report • Confirm/review risks • Agree the aim Risk Owner • Monitor plans • Stop plans X Point International Ltd © 2002 Project Manager delegation & empowerment agree • Approve plans & allocate resources • Monitor progress • Approve closure • Appoint & empower Risk Mgrs report • Draw up plans Risk Manager • Run the plan • Close plan
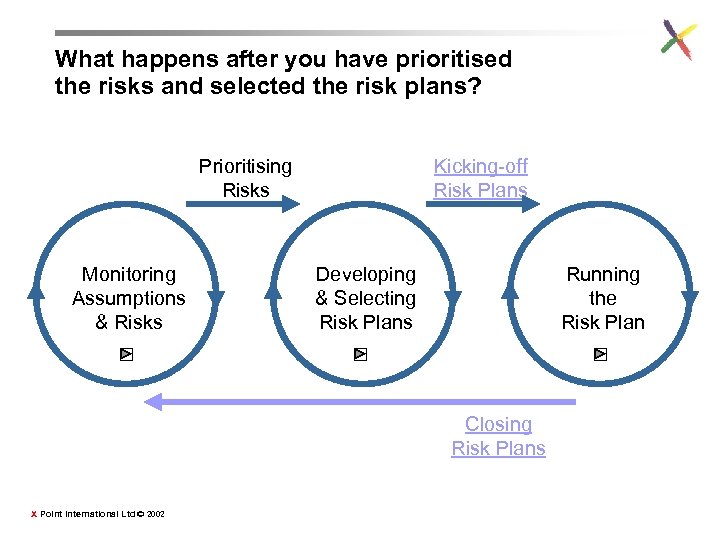
What happens after you have prioritised the risks and selected the risk plans? Prioritising Risks Monitoring Assumptions & Risks Kicking-off Risk Plans Developing & Selecting Risk Plans Running the Risk Plan Closing Risk Plans X Point International Ltd © 2002

Summary § Risk as a product of hazard likelihood and hazard impact § Risk Management relative to Project Management § Proactive, Assumptions-based approach § Assumption-failure as the source of project risk § Integrated assumption & risk registers § Complexity of deciding what risks to attack § Risk handling: avoidance, mitigation, transfer, retention § Devolved Risk Management organisation - responsibility and ownership devolved throughout, and outside, the project team § Questions X Point International Ltd © 2002

Annexe X Point International Ltd © 2002
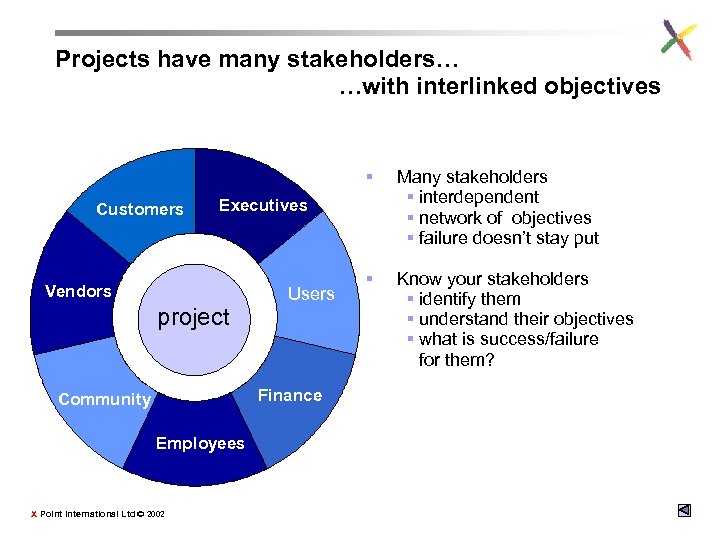
Projects have many stakeholders… …with interlinked objectives § Customers § Know your stakeholders § identify them § understand their objectives § what is success/failure for them? Executives Vendors project Users Finance Community Employees X Point International Ltd © 2002 Many stakeholders § interdependent § network of objectives § failure doesn’t stay put
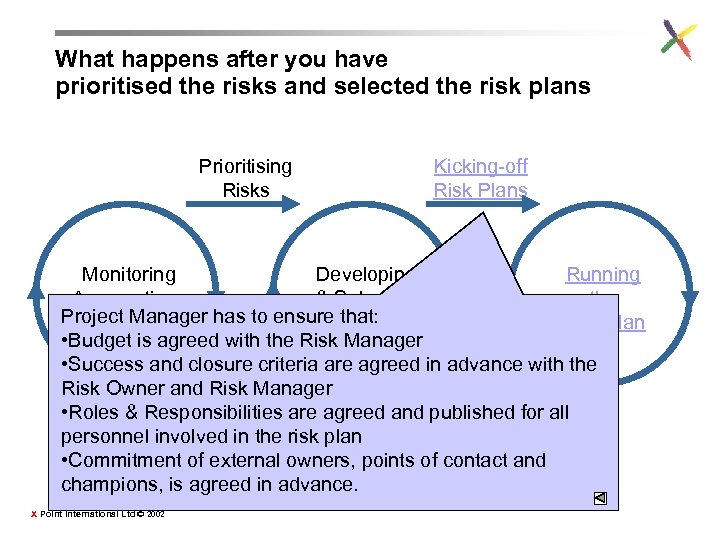
What happens after you have prioritised the risks and selected the risk plans Prioritising Risks Kicking-off Risk Plans Monitoring Developing Running Assumptions & Selecting the Project Manager has to ensure that: & Risks Risk Plan • Budget is agreed with the Risk Manager • Success and closure criteria are agreed in advance with the Risk Owner and Risk Manager • Roles & Responsibilities are agreed and published for all Closing personnel involved in the risk plan Risk Plans • Commitment of external owners, points of contact and champions, is agreed in advance. X Point International Ltd © 2002
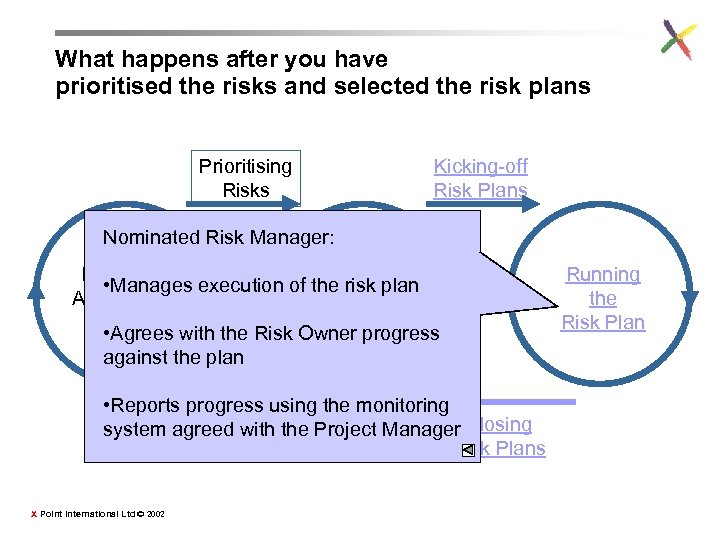
What happens after you have prioritised the risks and selected the risk plans Prioritising Risks Kicking-off Risk Plans Nominated Risk Manager: Monitoring Developing • Manages execution of the risk plan Assumptions & Selecting & Risks Risk Plans • Agrees with the Risk Owner progress against the plan • Reports progress using the monitoring system agreed with the Project Manager Closing Risk Plans X Point International Ltd © 2002 Running the Risk Plan
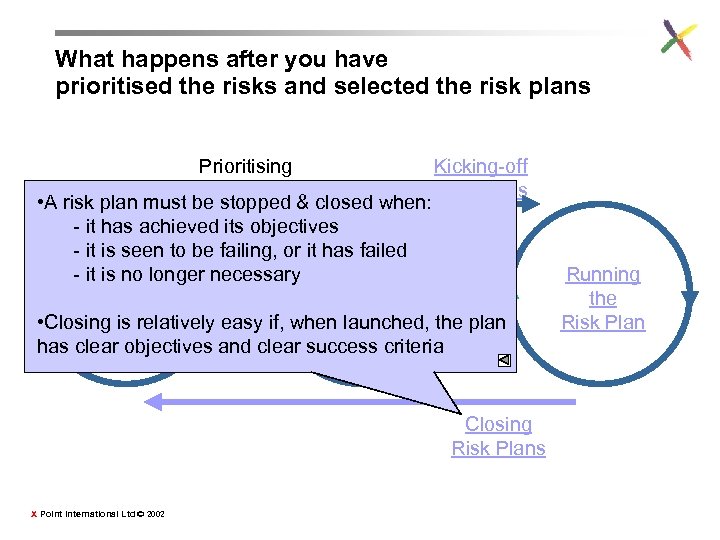
What happens after you have prioritised the risks and selected the risk plans Prioritising Kicking-off Risks Risk Plans • A risk plan must be stopped & closed when: - it has achieved its objectives - it is seen to be failing, or it has failed - Monitoring it is no longer necessary Developing Assumptions & Selecting • Closing Risks & is relatively easy if, when launched, the plan Risk Plans has clear objectives and clear success criteria Closing Risk Plans X Point International Ltd © 2002 Running the Risk Plan
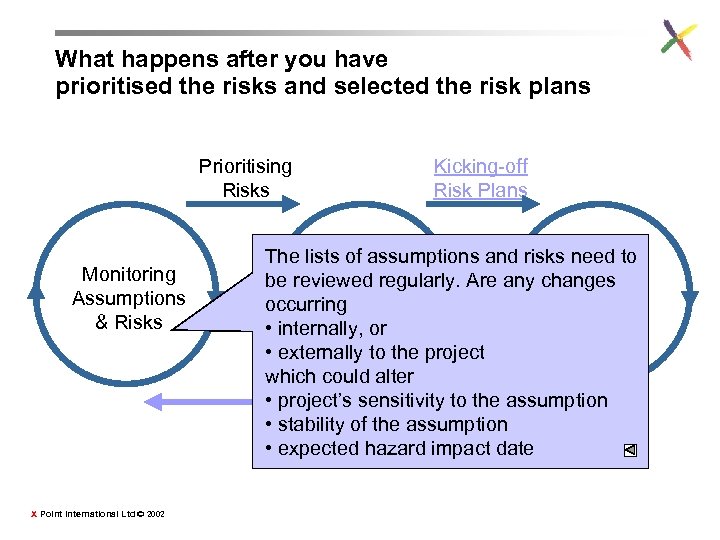
What happens after you have prioritised the risks and selected the risk plans Prioritising Risks Monitoring Assumptions & Risks X Point International Ltd © 2002 Kicking-off Risk Plans The lists of assumptions and risks need to Developing Running be reviewed regularly. Are any changes & Selecting the occurring Risk or Risk Plan • internally, Plans • externally to the project which could alter • project’s sensitivity to the assumption Closing • stability of the assumption Risk Plans • expected hazard impact date
a31f1590c55610a9ff92db98adf6e9fa.ppt