5e5ef15a6f969308c4ac46885137bd0d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Managing Resources A resource is a natural product used by man. Present by Yen-Hsiao Lu.
Managing Resources A resource is a natural product used by man. Present by Yen-Hsiao Lu.
 Wiki
Wiki
 Key Terms
Key Terms
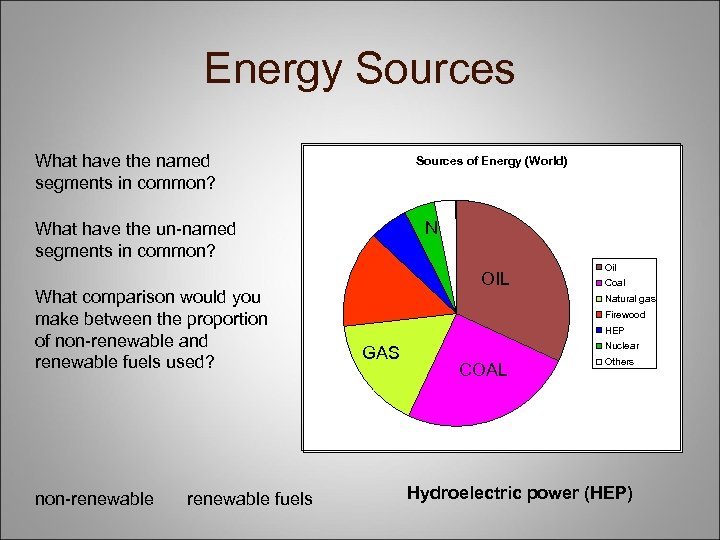 Energy Sources What have the named segments in common? Sources of Energy (World) N What have the un-named segments in common? What comparison would you make between the proportion of non-renewable and renewable fuels used? non-renewable fuels OIL Oil Coal Natural gas Firewood HEP GAS Nuclear COAL Others Hydroelectric power (HEP)
Energy Sources What have the named segments in common? Sources of Energy (World) N What have the un-named segments in common? What comparison would you make between the proportion of non-renewable and renewable fuels used? non-renewable fuels OIL Oil Coal Natural gas Firewood HEP GAS Nuclear COAL Others Hydroelectric power (HEP)
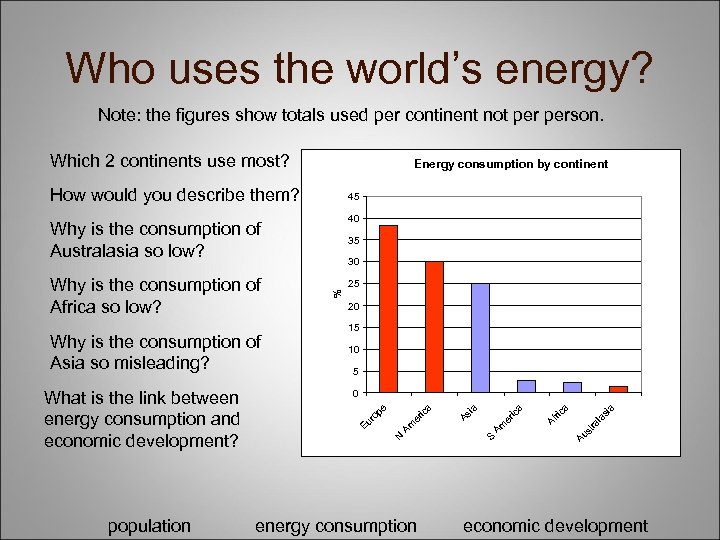 Who uses the world’s energy? Note: the figures show totals used per continent not person. Which 2 continents use most? Energy consumption by continent How would you describe them? 45 40 Why is the consumption of Australasia so low? Why is the consumption of Asia so misleading? population 25 20 15 10 5 energy consumption a a Au st ra la si ric er Am S Af a ic ia As a ic N A m er ro pe 0 Eu What is the link between energy consumption and economic development? 30 % Why is the consumption of Africa so low? 35 economic development
Who uses the world’s energy? Note: the figures show totals used per continent not person. Which 2 continents use most? Energy consumption by continent How would you describe them? 45 40 Why is the consumption of Australasia so low? Why is the consumption of Asia so misleading? population 25 20 15 10 5 energy consumption a a Au st ra la si ric er Am S Af a ic ia As a ic N A m er ro pe 0 Eu What is the link between energy consumption and economic development? 30 % Why is the consumption of Africa so low? 35 economic development
 Comparing LEDC & MEDC Global energy use is set to rise by 50% in next 20 years. 75% of world population but only use 20% of world’s energy. 25% of world population but use 80% of world’s energy. Population growing quickly. Population growing slowly. Rarely have good reserves of energy, often rely on biomass. Have access to or can afford to buy energy often from LEDC. What impact on demand will the growing population have? Use 35 times as much energy person as a person in India. LEDC Lower Economically Developed Country MEDC More Economically Developed Country
Comparing LEDC & MEDC Global energy use is set to rise by 50% in next 20 years. 75% of world population but only use 20% of world’s energy. 25% of world population but use 80% of world’s energy. Population growing quickly. Population growing slowly. Rarely have good reserves of energy, often rely on biomass. Have access to or can afford to buy energy often from LEDC. What impact on demand will the growing population have? Use 35 times as much energy person as a person in India. LEDC Lower Economically Developed Country MEDC More Economically Developed Country
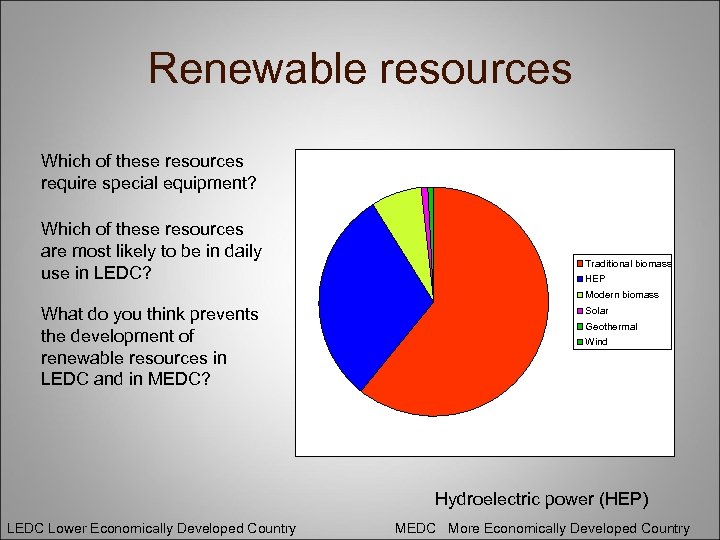 Renewable resources Which of these resources require special equipment? Which of these resources are most likely to be in daily use in LEDC? Traditional biomass HEP Modern biomass What do you think prevents the development of renewable resources in LEDC and in MEDC? Solar Geothermal Wind Hydroelectric power (HEP) LEDC Lower Economically Developed Country MEDC More Economically Developed Country
Renewable resources Which of these resources require special equipment? Which of these resources are most likely to be in daily use in LEDC? Traditional biomass HEP Modern biomass What do you think prevents the development of renewable resources in LEDC and in MEDC? Solar Geothermal Wind Hydroelectric power (HEP) LEDC Lower Economically Developed Country MEDC More Economically Developed Country
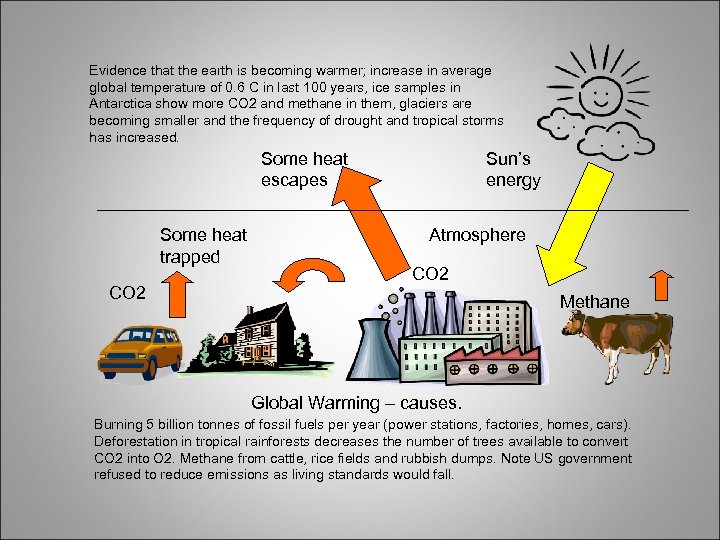 Evidence that the earth is becoming warmer; increase in average global temperature of 0. 6 C in last 100 years, ice samples in Antarctica show more CO 2 and methane in them, glaciers are becoming smaller and the frequency of drought and tropical storms has increased. Some heat escapes Some heat trapped CO 2 Sun’s energy Atmosphere CO 2 Methane Global Warming – causes. Burning 5 billion tonnes of fossil fuels per year (power stations, factories, homes, cars). Deforestation in tropical rainforests decreases the number of trees available to convert CO 2 into O 2. Methane from cattle, rice fields and rubbish dumps. Note US government refused to reduce emissions as living standards would fall.
Evidence that the earth is becoming warmer; increase in average global temperature of 0. 6 C in last 100 years, ice samples in Antarctica show more CO 2 and methane in them, glaciers are becoming smaller and the frequency of drought and tropical storms has increased. Some heat escapes Some heat trapped CO 2 Sun’s energy Atmosphere CO 2 Methane Global Warming – causes. Burning 5 billion tonnes of fossil fuels per year (power stations, factories, homes, cars). Deforestation in tropical rainforests decreases the number of trees available to convert CO 2 into O 2. Methane from cattle, rice fields and rubbish dumps. Note US government refused to reduce emissions as living standards would fall.
 The Energy Debate • • • What are the issues? Non-renewable resources are limited. Many renewable resources are not yet fully developed. Energy demand is set to rise by 50% by 2020. Renewable energy sources are more expensive to develop than present fossil fuels. MEDC use much more energy than LEDC person. LEDC will demand more energy as they develop. Burning fossil fuels releases chemicals into the atmosphere leading to global warming, climate change and acid rain. Emissions! Strategies for Reducing Emissions Population control Changes to lifestyle More efficient technology New technology Fewer journeys Burn fewer fossil fuels Develop more renewable resources
The Energy Debate • • • What are the issues? Non-renewable resources are limited. Many renewable resources are not yet fully developed. Energy demand is set to rise by 50% by 2020. Renewable energy sources are more expensive to develop than present fossil fuels. MEDC use much more energy than LEDC person. LEDC will demand more energy as they develop. Burning fossil fuels releases chemicals into the atmosphere leading to global warming, climate change and acid rain. Emissions! Strategies for Reducing Emissions Population control Changes to lifestyle More efficient technology New technology Fewer journeys Burn fewer fossil fuels Develop more renewable resources
 Geothermal Power - Iceland Blue Lagoon, Iceland Power Station, Iceland Hothouse flowers Iceland is situated over the mid-Atlantic ridge, volcanoes and lava flows are common. Geothermal energy is available over most of the country. It provides about 50% of the country’s total primary energy supply. 86% of all houses heated with geothermal water +100 public swimming pools. 183, 000 m 2 of greenhouses and 105, 000 m 2 of soil heating. 50 fish farms + seaweed processing plant + snow melting.
Geothermal Power - Iceland Blue Lagoon, Iceland Power Station, Iceland Hothouse flowers Iceland is situated over the mid-Atlantic ridge, volcanoes and lava flows are common. Geothermal energy is available over most of the country. It provides about 50% of the country’s total primary energy supply. 86% of all houses heated with geothermal water +100 public swimming pools. 183, 000 m 2 of greenhouses and 105, 000 m 2 of soil heating. 50 fish farms + seaweed processing plant + snow melting.
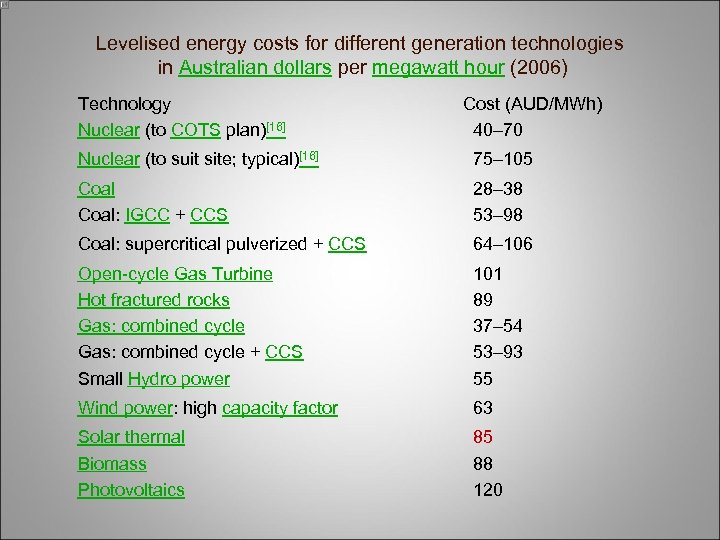 Levelised energy costs for different generation technologies in Australian dollars per megawatt hour (2006) Technology Nuclear (to COTS plan)[16] Cost (AUD/MWh) 40– 70 Nuclear (to suit site; typical)[16] 75– 105 Coal: IGCC + CCS 28– 38 53– 98 Coal: supercritical pulverized + CCS 64– 106 Open-cycle Gas Turbine Hot fractured rocks Gas: combined cycle + CCS Small Hydro power 101 89 37– 54 53– 93 55 Wind power: high capacity factor 63 Solar thermal Biomass Photovoltaics 85 88 120
Levelised energy costs for different generation technologies in Australian dollars per megawatt hour (2006) Technology Nuclear (to COTS plan)[16] Cost (AUD/MWh) 40– 70 Nuclear (to suit site; typical)[16] 75– 105 Coal: IGCC + CCS 28– 38 53– 98 Coal: supercritical pulverized + CCS 64– 106 Open-cycle Gas Turbine Hot fractured rocks Gas: combined cycle + CCS Small Hydro power 101 89 37– 54 53– 93 55 Wind power: high capacity factor 63 Solar thermal Biomass Photovoltaics 85 88 120
 How Does Solar Power Work? • When sunlight hits the solar panels on your roof a DC electric current is produced. An inverter, connected between the solar panels and your switchboard, converts the DC current into AC current, which powers your home or is fed into the electricity grid. The solar power system is simple and connects directly into the electricity grid, with no batteries required.
How Does Solar Power Work? • When sunlight hits the solar panels on your roof a DC electric current is produced. An inverter, connected between the solar panels and your switchboard, converts the DC current into AC current, which powers your home or is fed into the electricity grid. The solar power system is simple and connects directly into the electricity grid, with no batteries required.
 Carbon tax Debate in Australia On February 24, 2011, Australian Federal government announced a framework to implement a Carbon Tax from July 1 2012. It is set to be implemented over 3 -5 year period upon which it will switch to a cap and trade system. The price has not been set but various proposals have been discussed in the recent past, such as $23/t and $26/t.
Carbon tax Debate in Australia On February 24, 2011, Australian Federal government announced a framework to implement a Carbon Tax from July 1 2012. It is set to be implemented over 3 -5 year period upon which it will switch to a cap and trade system. The price has not been set but various proposals have been discussed in the recent past, such as $23/t and $26/t.
 http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Cost_of_electricity_by_source http: //www. aph. gov. au/library/pubs/Climate. Change/responses/economic/carb ontax. htm
http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/Cost_of_electricity_by_source http: //www. aph. gov. au/library/pubs/Climate. Change/responses/economic/carb ontax. htm
 Key words • • • Renewable Non-renewable Finite Fossil fuels Geothermal Solar Biomass Global warming Greenhouse effect Sustainable Recycling Management has a definite lifespan heat from beneath the surface can be used and replaced energy from the sun once used cannot be replaced natural fuel such as wood or dung can be supported in an area looking after resources formed from dead organisms re-using resources rise of earth’s average temperature linked to increased emissions
Key words • • • Renewable Non-renewable Finite Fossil fuels Geothermal Solar Biomass Global warming Greenhouse effect Sustainable Recycling Management has a definite lifespan heat from beneath the surface can be used and replaced energy from the sun once used cannot be replaced natural fuel such as wood or dung can be supported in an area looking after resources formed from dead organisms re-using resources rise of earth’s average temperature linked to increased emissions


