076326de69b8abe6ed1da5a7af597723.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Managing Operational Risk Within Your Treasury Environment
Managing Operational Risk Within Your Treasury Environment
 AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
 Why is Operational Risk a hot topic? It is still the risk responsible for the most spectacular bank failures • Barings – Index futures • Natwest – Incorrect volatilities used to value cap portfolio • AIB – Forex trading What do they have in common? • Treasury activities • Failure is mostly due to operational risk
Why is Operational Risk a hot topic? It is still the risk responsible for the most spectacular bank failures • Barings – Index futures • Natwest – Incorrect volatilities used to value cap portfolio • AIB – Forex trading What do they have in common? • Treasury activities • Failure is mostly due to operational risk
 Operational Risk – What is it? Basel Definition “Operational risk is the risk of direct or indirect loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events”
Operational Risk – What is it? Basel Definition “Operational risk is the risk of direct or indirect loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events”
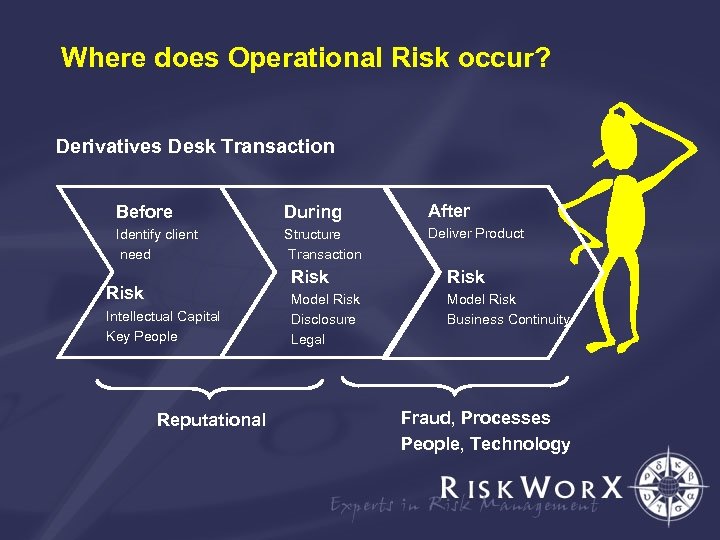 Where does Operational Risk occur? Derivatives Desk Transaction Before During After Identify client need Structure Transaction Deliver Product Risk Intellectual Capital Key People Reputational Risk Model Risk Disclosure Legal Model Risk Business Continuity Fraud, Processes People, Technology
Where does Operational Risk occur? Derivatives Desk Transaction Before During After Identify client need Structure Transaction Deliver Product Risk Intellectual Capital Key People Reputational Risk Model Risk Disclosure Legal Model Risk Business Continuity Fraud, Processes People, Technology
 AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
 The Trend • Moving from prevention to active management. • Tools and technology exist to transfer unwanted risks to other counterparties – Interest rate derivatives – Credit derivatives – Innovative insurance products using derivatives
The Trend • Moving from prevention to active management. • Tools and technology exist to transfer unwanted risks to other counterparties – Interest rate derivatives – Credit derivatives – Innovative insurance products using derivatives
 Implications Risks are intertwined. If the primary objective is to take and manage market risk • Incur credit risk (counterparty risk) • Incur operational risk (model risk, fraud etc. )
Implications Risks are intertwined. If the primary objective is to take and manage market risk • Incur credit risk (counterparty risk) • Incur operational risk (model risk, fraud etc. )
 Why does the use of derivatives or structured products increase the operational risk of my business? . • Characteristics of these OTC products are described legal documents/contracts • Pay-off may be linked to external events – Share prices, Bond Prices – Default of a third party • Complex mathematical models are needed to value these instruments • Skilled people for Administration and Risk management • Appropriate IT solutions end-to-end is scarce
Why does the use of derivatives or structured products increase the operational risk of my business? . • Characteristics of these OTC products are described legal documents/contracts • Pay-off may be linked to external events – Share prices, Bond Prices – Default of a third party • Complex mathematical models are needed to value these instruments • Skilled people for Administration and Risk management • Appropriate IT solutions end-to-end is scarce
 AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer techniques • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer techniques • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
 Proven techniques for control and assess Operational Risk – Within the Company • Internal audit – Ensures the quality of risk processes – Ensures compliance with internal policies & procedures. • Compliance – Ensures compliance of risk processes with external stakeholders such as regulators • Straight -Through – Processing • Adequately skilled staff
Proven techniques for control and assess Operational Risk – Within the Company • Internal audit – Ensures the quality of risk processes – Ensures compliance with internal policies & procedures. • Compliance – Ensures compliance of risk processes with external stakeholders such as regulators • Straight -Through – Processing • Adequately skilled staff
 Proven techniques for control and assess Operational Risk - External • Securities Exchanges. – Custody systems – Electronic trading systems • Settlement Systems
Proven techniques for control and assess Operational Risk - External • Securities Exchanges. – Custody systems – Electronic trading systems • Settlement Systems
 AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer techniques • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer techniques • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
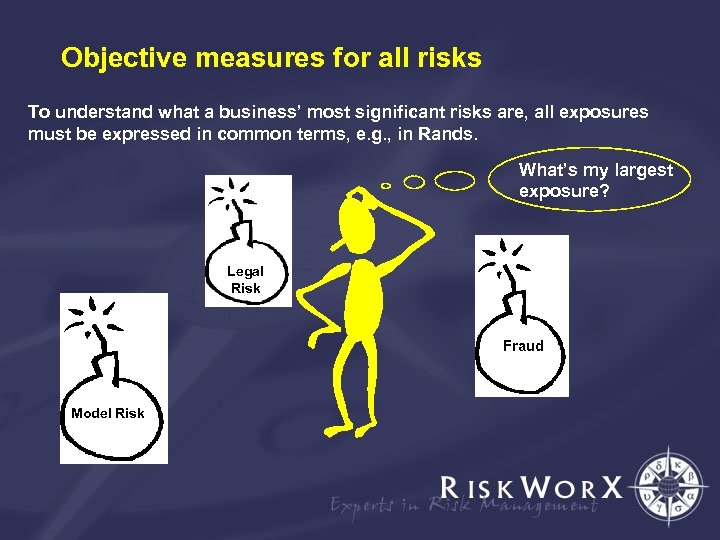 Objective measures for all risks To understand what a business’ most significant risks are, all exposures must be expressed in common terms, e. g. , in Rands. What’s my largest exposure? Legal Risk Fraud Model Risk
Objective measures for all risks To understand what a business’ most significant risks are, all exposures must be expressed in common terms, e. g. , in Rands. What’s my largest exposure? Legal Risk Fraud Model Risk
 Concept of Value-at-Risk An estimate of the level of loss on a portfolio, which is expected to be equalled or exceeded with a given, small probability. . – Measured in monetary terms – Specific Time horizon – Given level of confidence (99%)
Concept of Value-at-Risk An estimate of the level of loss on a portfolio, which is expected to be equalled or exceeded with a given, small probability. . – Measured in monetary terms – Specific Time horizon – Given level of confidence (99%)
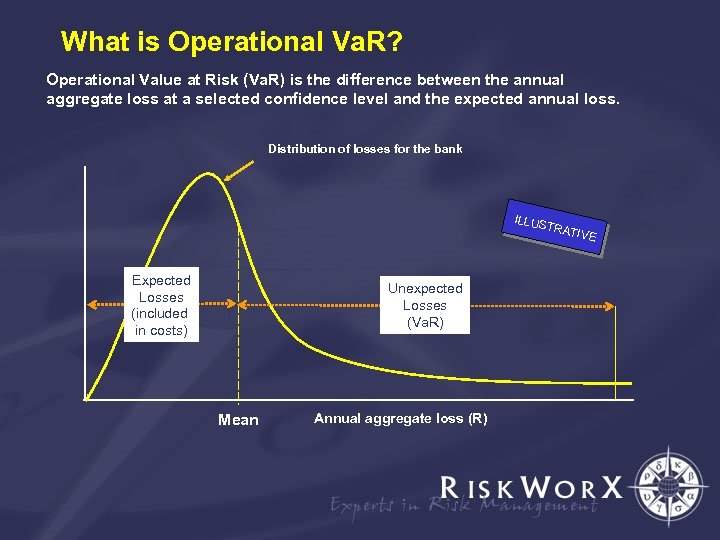 What is Operational Va. R? Operational Value at Risk (Va. R) is the difference between the annual aggregate loss at a selected confidence level and the expected annual loss. Distribution of losses for the bank ILLUS TRAT Expected Losses (included in costs) Unexpected Losses (Va. R) Mean Annual aggregate loss (R) IVE
What is Operational Va. R? Operational Value at Risk (Va. R) is the difference between the annual aggregate loss at a selected confidence level and the expected annual loss. Distribution of losses for the bank ILLUS TRAT Expected Losses (included in costs) Unexpected Losses (Va. R) Mean Annual aggregate loss (R) IVE
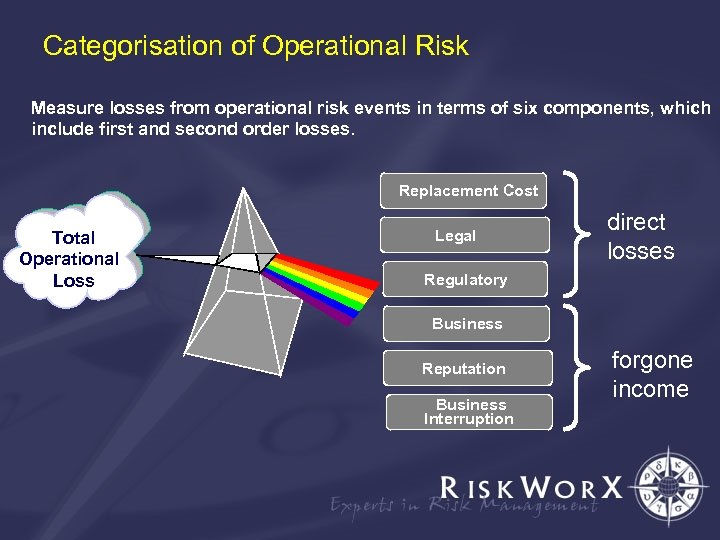 Categorisation of Operational Risk Measure losses from operational risk events in terms of six components, which include first and second order losses. Replacement Cost Total Operational Loss Legal direct losses Regulatory Business Reputation Business Interruption forgone income
Categorisation of Operational Risk Measure losses from operational risk events in terms of six components, which include first and second order losses. Replacement Cost Total Operational Loss Legal direct losses Regulatory Business Reputation Business Interruption forgone income
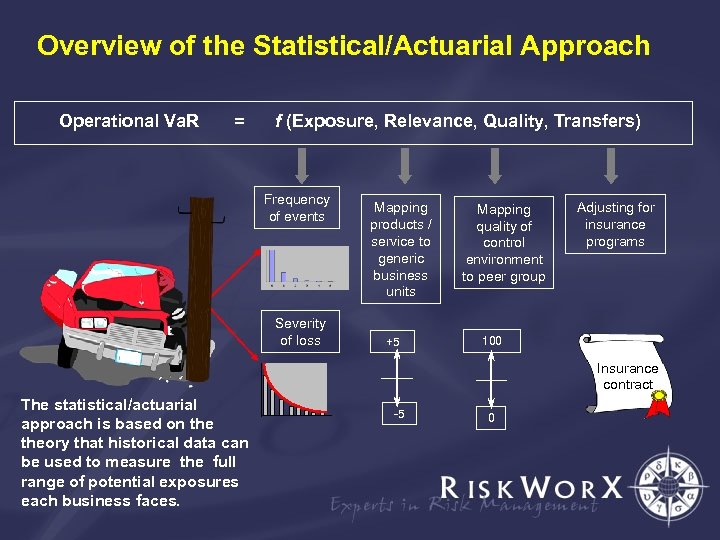 Overview of the Statistical/Actuarial Approach Operational Va. R = f (Exposure, Relevance, Quality, Transfers) Frequency of events Severity of loss Mapping products / service to generic business units +5 Mapping quality of control environment to peer group Adjusting for insurance programs 100 Insurance contract The statistical/actuarial approach is based on theory that historical data can be used to measure the full range of potential exposures each business faces. -5 0
Overview of the Statistical/Actuarial Approach Operational Va. R = f (Exposure, Relevance, Quality, Transfers) Frequency of events Severity of loss Mapping products / service to generic business units +5 Mapping quality of control environment to peer group Adjusting for insurance programs 100 Insurance contract The statistical/actuarial approach is based on theory that historical data can be used to measure the full range of potential exposures each business faces. -5 0
 Internal Loss Data • Significant commercial benefits • Quantification of operational risk • Development of management processes. • How do I transform the raw data to make it useable? • Convert to the bank’s currency, • Adjust for inflation
Internal Loss Data • Significant commercial benefits • Quantification of operational risk • Development of management processes. • How do I transform the raw data to make it useable? • Convert to the bank’s currency, • Adjust for inflation
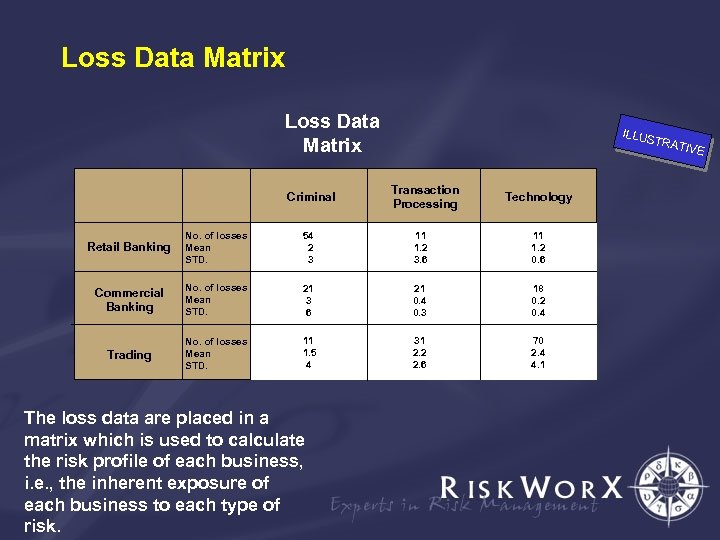 Loss Data Matrix Criminal ILLUS TRAT Transaction Processing Technology Retail Banking No. of losses Mean STD. 54 2 3 11 1. 2 3. 6 11 1. 2 0. 6 Commercial Banking No. of losses Mean STD. 21 3 6 21 0. 4 0. 3 18 0. 2 0. 4 Trading No. of losses Mean STD. 11 1. 5 4 31 2. 2 2. 6 70 2. 4 4. 1 The loss data are placed in a matrix which is used to calculate the risk profile of each business, i. e. , the inherent exposure of each business to each type of risk. IVE
Loss Data Matrix Criminal ILLUS TRAT Transaction Processing Technology Retail Banking No. of losses Mean STD. 54 2 3 11 1. 2 3. 6 11 1. 2 0. 6 Commercial Banking No. of losses Mean STD. 21 3 6 21 0. 4 0. 3 18 0. 2 0. 4 Trading No. of losses Mean STD. 11 1. 5 4 31 2. 2 2. 6 70 2. 4 4. 1 The loss data are placed in a matrix which is used to calculate the risk profile of each business, i. e. , the inherent exposure of each business to each type of risk. IVE
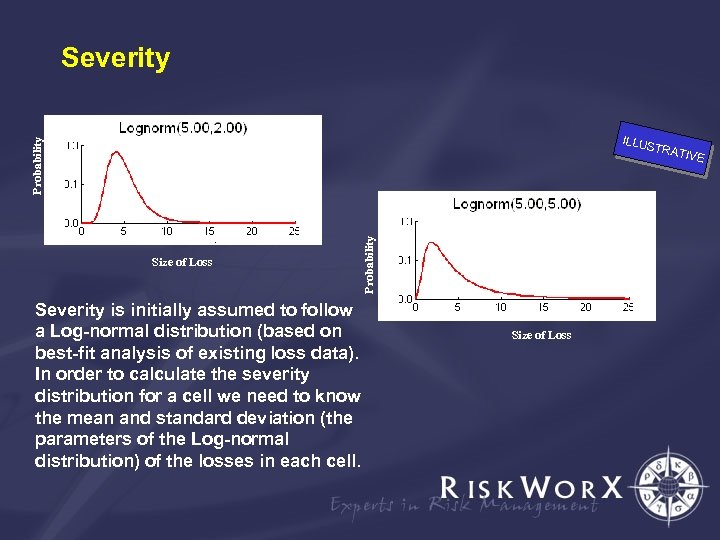 Severity Probability ILLUS Size of Loss Severity is initially assumed to follow a Log-normal distribution (based on best-fit analysis of existing loss data). In order to calculate the severity distribution for a cell we need to know the mean and standard deviation (the parameters of the Log-normal distribution) of the losses in each cell. Probability TRAT Size of Loss IVE
Severity Probability ILLUS Size of Loss Severity is initially assumed to follow a Log-normal distribution (based on best-fit analysis of existing loss data). In order to calculate the severity distribution for a cell we need to know the mean and standard deviation (the parameters of the Log-normal distribution) of the losses in each cell. Probability TRAT Size of Loss IVE
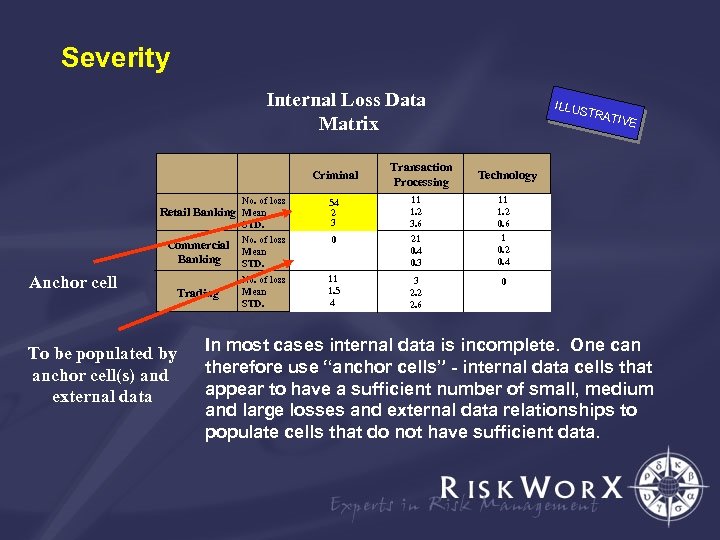 Severity Internal Loss Data Matrix Criminal Retail Banking No. of loss Mean STD. 54 2 3 Commercial Banking No. of loss Mean STD. 0 Trading No. of loss Mean STD. 11 1. 5 4 Anchor cell To be populated by anchor cell(s) and external data Transaction Processing ILLUS TRAT IVE Technology 11 1. 2 3. 6 21 0. 4 0. 3 11 1. 2 0. 6 1 0. 2 0. 4 3 2. 2 2. 6 0 In most cases internal data is incomplete. One can therefore use “anchor cells” - internal data cells that appear to have a sufficient number of small, medium and large losses and external data relationships to populate cells that do not have sufficient data.
Severity Internal Loss Data Matrix Criminal Retail Banking No. of loss Mean STD. 54 2 3 Commercial Banking No. of loss Mean STD. 0 Trading No. of loss Mean STD. 11 1. 5 4 Anchor cell To be populated by anchor cell(s) and external data Transaction Processing ILLUS TRAT IVE Technology 11 1. 2 3. 6 21 0. 4 0. 3 11 1. 2 0. 6 1 0. 2 0. 4 3 2. 2 2. 6 0 In most cases internal data is incomplete. One can therefore use “anchor cells” - internal data cells that appear to have a sufficient number of small, medium and large losses and external data relationships to populate cells that do not have sufficient data.
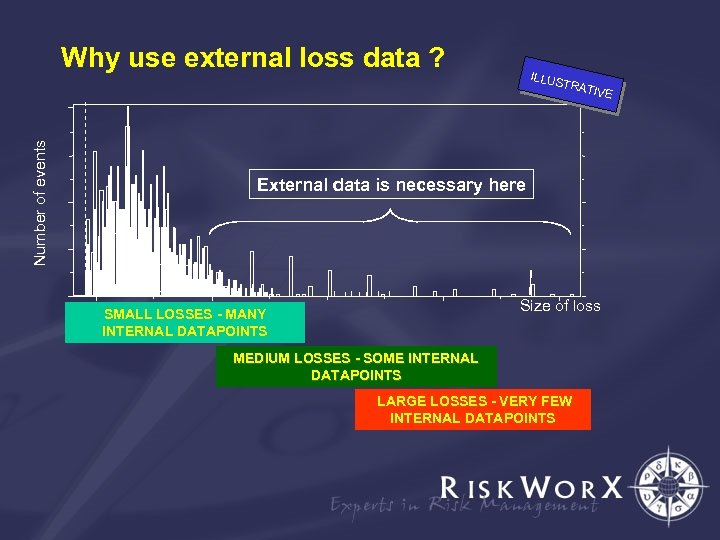 Why use external loss data ? ILLUS TRAT Number of events IVE External data is necessary here Size of loss SMALL LOSSES - MANY INTERNAL DATAPOINTS MEDIUM LOSSES - SOME INTERNAL DATAPOINTS LARGE LOSSES - VERY FEW INTERNAL DATAPOINTS
Why use external loss data ? ILLUS TRAT Number of events IVE External data is necessary here Size of loss SMALL LOSSES - MANY INTERNAL DATAPOINTS MEDIUM LOSSES - SOME INTERNAL DATAPOINTS LARGE LOSSES - VERY FEW INTERNAL DATAPOINTS
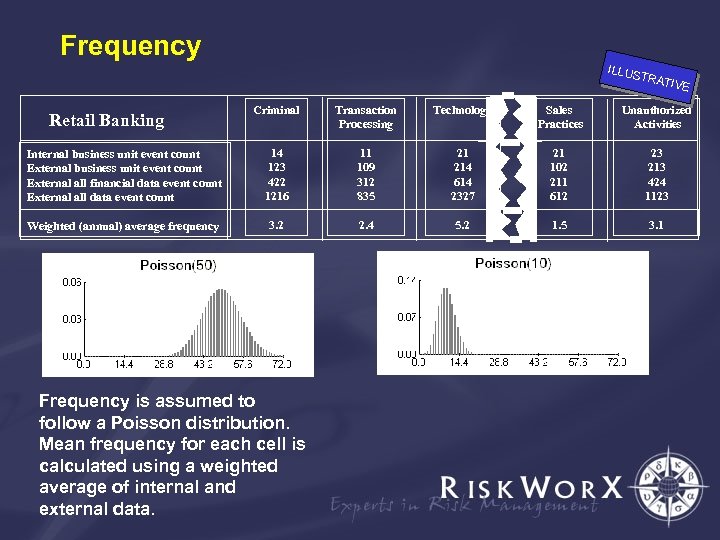 Frequency ILLUS TRAT IVE Criminal Transaction Processing Technology Sales Practices Unauthorized Activities Internal business unit event count External all financial data event count External all data event count 14 123 422 1216 11 109 312 835 21 214 614 2327 21 102 211 612 23 213 424 1123 Weighted (annual) average frequency 3. 2 2. 4 5. 2 1. 5 3. 1 Retail Banking Frequency is assumed to follow a Poisson distribution. Mean frequency for each cell is calculated using a weighted average of internal and external data.
Frequency ILLUS TRAT IVE Criminal Transaction Processing Technology Sales Practices Unauthorized Activities Internal business unit event count External all financial data event count External all data event count 14 123 422 1216 11 109 312 835 21 214 614 2327 21 102 211 612 23 213 424 1123 Weighted (annual) average frequency 3. 2 2. 4 5. 2 1. 5 3. 1 Retail Banking Frequency is assumed to follow a Poisson distribution. Mean frequency for each cell is calculated using a weighted average of internal and external data.
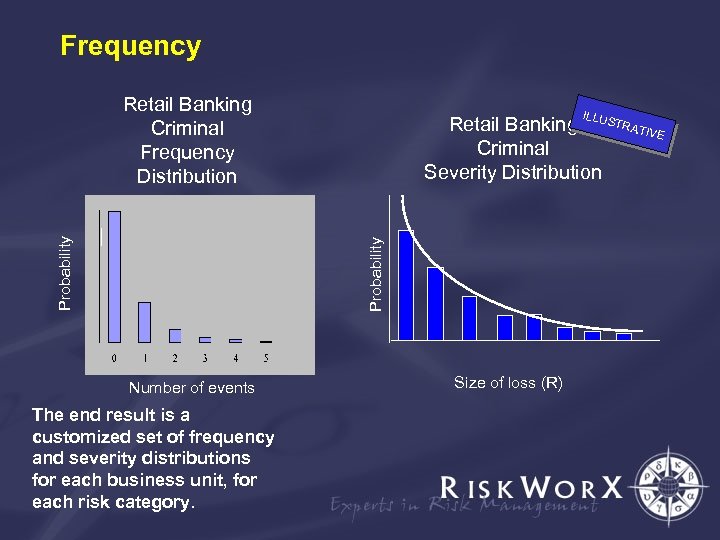 Frequency IL Retail Banking LUSTRATIVE Criminal Severity Distribution Probability Retail Banking Criminal Frequency Distribution Number of events The end result is a customized set of frequency and severity distributions for each business unit, for each risk category. Size of loss (R)
Frequency IL Retail Banking LUSTRATIVE Criminal Severity Distribution Probability Retail Banking Criminal Frequency Distribution Number of events The end result is a customized set of frequency and severity distributions for each business unit, for each risk category. Size of loss (R)
 AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer techniques • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
AGENDA • General points • Impact of modern risk transfer techniques • Proven techniques to control and assess operational risk • Objective approach to managing operational risk • Exploiting operational Va. R
 Operational Va. R – Value Proposition • Create objective measure – Expected Losses (Cost of operational failure) – Unexpected losses (Largest exposures) • Provide framework for cost-benefit analysis • Link controls to performance measurement – Quantifying Operational Risk Capital – Link to shareholder value • Rationalise Insurance Programs
Operational Va. R – Value Proposition • Create objective measure – Expected Losses (Cost of operational failure) – Unexpected losses (Largest exposures) • Provide framework for cost-benefit analysis • Link controls to performance measurement – Quantifying Operational Risk Capital – Link to shareholder value • Rationalise Insurance Programs
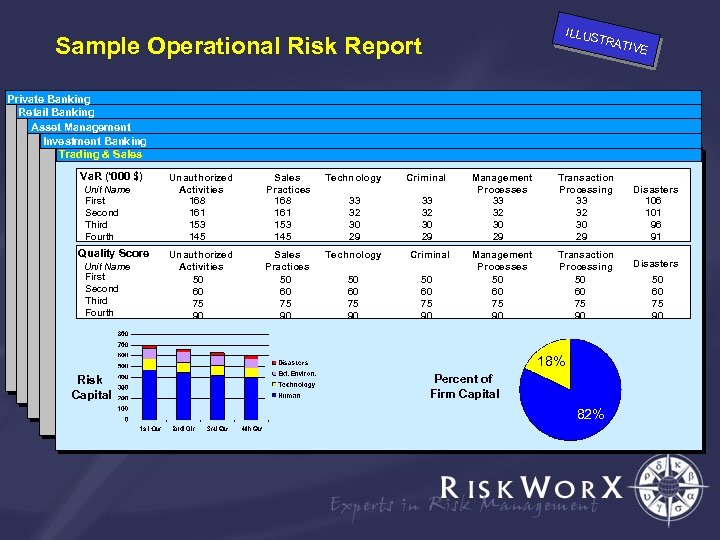 ILLUS TRAT Sample Operational Risk Report IVE Private Banking Retail Banking Asset Management Investment Banking Trading & Sales Va. R (‘ 000 $) Unit Name First Second Third Fourth Quality Score Unit Name First Second Third Fourth Unauthorized Activities 168 161 153 145 Sales Practices 168 161 153 145 Technology Criminal 33 32 30 29 Unauthorized Activities 50 60 75 90 Sales Practices 50 60 75 90 Technology Criminal 50 60 75 90 Management Processes 33 32 30 29 Transaction Processing 33 32 30 29 Management Processes 50 60 75 90 Transaction Processing 50 60 75 90 18% Risk Capital Percent of Firm Capital 82% Disasters 106 101 96 91 Disasters 50 60 75 90
ILLUS TRAT Sample Operational Risk Report IVE Private Banking Retail Banking Asset Management Investment Banking Trading & Sales Va. R (‘ 000 $) Unit Name First Second Third Fourth Quality Score Unit Name First Second Third Fourth Unauthorized Activities 168 161 153 145 Sales Practices 168 161 153 145 Technology Criminal 33 32 30 29 Unauthorized Activities 50 60 75 90 Sales Practices 50 60 75 90 Technology Criminal 50 60 75 90 Management Processes 33 32 30 29 Transaction Processing 33 32 30 29 Management Processes 50 60 75 90 Transaction Processing 50 60 75 90 18% Risk Capital Percent of Firm Capital 82% Disasters 106 101 96 91 Disasters 50 60 75 90
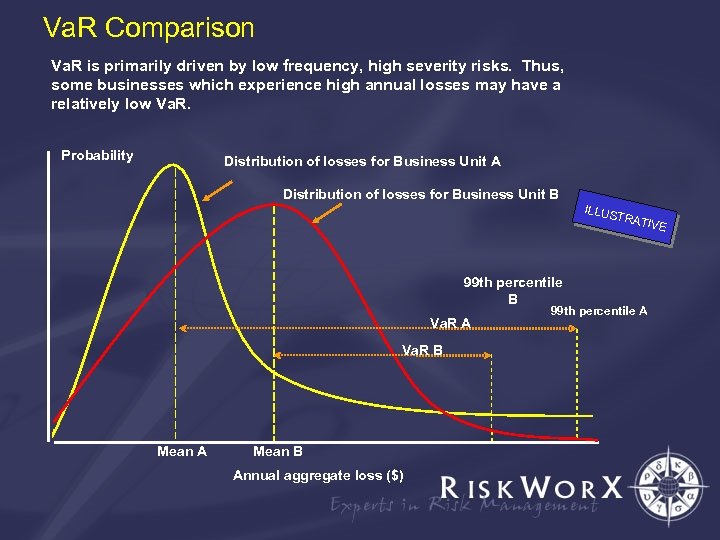 Va. R Comparison Va. R is primarily driven by low frequency, high severity risks. Thus, some businesses which experience high annual losses may have a relatively low Va. R. Probability Distribution of losses for Business Unit A Distribution of losses for Business Unit B ILLUS TRAT 99 th percentile B Va. R A Va. R B Mean A Mean B Annual aggregate loss ($) IVE 99 th percentile A
Va. R Comparison Va. R is primarily driven by low frequency, high severity risks. Thus, some businesses which experience high annual losses may have a relatively low Va. R. Probability Distribution of losses for Business Unit A Distribution of losses for Business Unit B ILLUS TRAT 99 th percentile B Va. R A Va. R B Mean A Mean B Annual aggregate loss ($) IVE 99 th percentile A
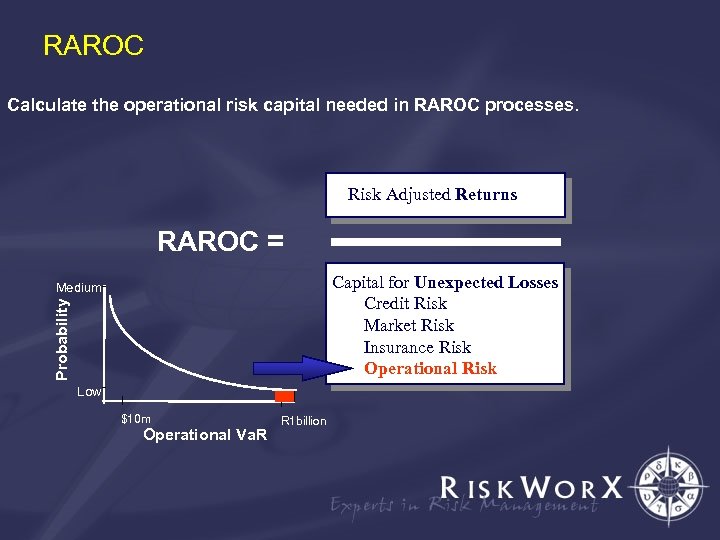 RAROC Calculate the operational risk capital needed in RAROC processes. Risk Adjusted Returns RAROC = Capital for Unexpected Losses Credit Risk Market Risk Insurance Risk Operational Risk Probability Medium Low $10 m Operational Va. R R 1 billion
RAROC Calculate the operational risk capital needed in RAROC processes. Risk Adjusted Returns RAROC = Capital for Unexpected Losses Credit Risk Market Risk Insurance Risk Operational Risk Probability Medium Low $10 m Operational Va. R R 1 billion
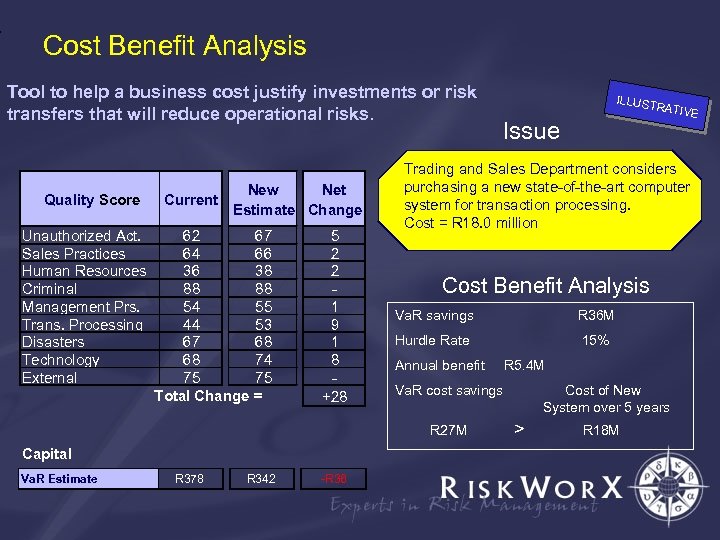 Cost Benefit Analysis Tool to help a business cost justify investments or risk transfers that will reduce operational risks. Quality Score Unauthorized Act. Sales Practices Human Resources Criminal Management Prs. Trans. Processing Disasters Technology External Current New Net Estimate Change 62 67 64 66 36 38 88 88 54 55 44 53 67 68 68 74 75 75 Total Change = 5 2 2 1 9 1 8 +28 Va. R Estimate R 378 R 342 -R 36 RATIV Issue Trading and Sales Department considers purchasing a new state-of-the-art computer system for transaction processing. Cost = R 18. 0 million Cost Benefit Analysis Va. R savings R 36 M Hurdle Rate 15% Annual benefit R 5. 4 M Va. R cost savings R 27 M Capital ILLUST Cost of New System over 5 years > R 18 M E
Cost Benefit Analysis Tool to help a business cost justify investments or risk transfers that will reduce operational risks. Quality Score Unauthorized Act. Sales Practices Human Resources Criminal Management Prs. Trans. Processing Disasters Technology External Current New Net Estimate Change 62 67 64 66 36 38 88 88 54 55 44 53 67 68 68 74 75 75 Total Change = 5 2 2 1 9 1 8 +28 Va. R Estimate R 378 R 342 -R 36 RATIV Issue Trading and Sales Department considers purchasing a new state-of-the-art computer system for transaction processing. Cost = R 18. 0 million Cost Benefit Analysis Va. R savings R 36 M Hurdle Rate 15% Annual benefit R 5. 4 M Va. R cost savings R 27 M Capital ILLUST Cost of New System over 5 years > R 18 M E
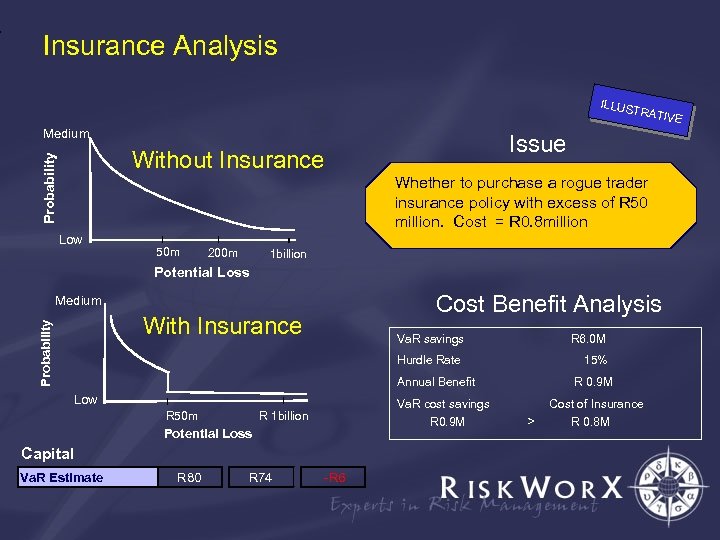 Insurance Analysis ILLUS TRATI VE Medium Issue Probability Without Insurance Whether to purchase a rogue trader insurance policy with excess of R 50 million. Cost = R 0. 8 million Low 50 m 200 m 1 billion Potential Loss Cost Benefit Analysis Medium Probability With Insurance Va. R savings R 6. 0 M Hurdle Rate 15% Annual Benefit Low Va. R cost savings R 0. 9 M R 1 billion R 50 m Potential Loss Capital Va. R Estimate R 80 R 74 -R 6 R 0. 9 M > Cost of Insurance R 0. 8 M
Insurance Analysis ILLUS TRATI VE Medium Issue Probability Without Insurance Whether to purchase a rogue trader insurance policy with excess of R 50 million. Cost = R 0. 8 million Low 50 m 200 m 1 billion Potential Loss Cost Benefit Analysis Medium Probability With Insurance Va. R savings R 6. 0 M Hurdle Rate 15% Annual Benefit Low Va. R cost savings R 0. 9 M R 1 billion R 50 m Potential Loss Capital Va. R Estimate R 80 R 74 -R 6 R 0. 9 M > Cost of Insurance R 0. 8 M
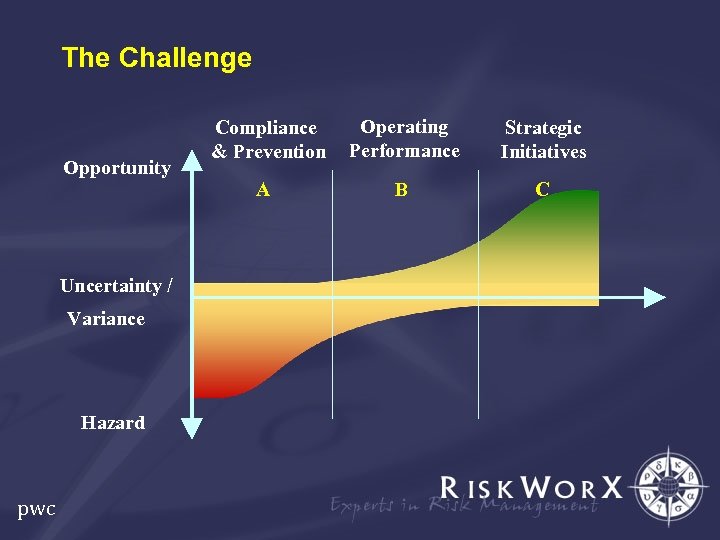 The Challenge Uncertainty / Variance Hazard pwc Operating Performance Strategic Initiatives A Opportunity Compliance & Prevention B C
The Challenge Uncertainty / Variance Hazard pwc Operating Performance Strategic Initiatives A Opportunity Compliance & Prevention B C
 Managing Operational Risk Within Your Treasury Environment
Managing Operational Risk Within Your Treasury Environment


