502907d3b3bd815fc614d9be34c27f9f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 MANAGING INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY FIFTH EDITION CHAPTER 1 MANAGING IT IN AN E-WORLD E. Wainright Martin Carol V. Brown Daniel W. De. Hayes Jeffrey A. Hoffer William C. Perkins
MANAGING INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY FIFTH EDITION CHAPTER 1 MANAGING IT IN AN E-WORLD E. Wainright Martin Carol V. Brown Daniel W. De. Hayes Jeffrey A. Hoffer William C. Perkins
 CHAPTER 1 MANAGING IT IN AN E-WORLD Information technology (IT) – computer technology (hardware and software) for processing and storing information, as well as communications technology for transmitting information © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 2 2 Page 1
CHAPTER 1 MANAGING IT IN AN E-WORLD Information technology (IT) – computer technology (hardware and software) for processing and storing information, as well as communications technology for transmitting information © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 2 2 Page 1
 CHAPTER 1 MANAGING IT IN AN E-WORLD n Managing IT in business today is very different from managing in a prebrowser world n Business managers now expect: Information on firm’s internal operations Data about external market conditions Automated personal organizers Networks always available Applications that are easy to use © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 3 3 Page 2
CHAPTER 1 MANAGING IT IN AN E-WORLD n Managing IT in business today is very different from managing in a prebrowser world n Business managers now expect: Information on firm’s internal operations Data about external market conditions Automated personal organizers Networks always available Applications that are easy to use © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 3 3 Page 2
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS n Hard to predict trends due to rate of change in IT industry n Consider several mis-predictions … © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 4 4 Page 2
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS n Hard to predict trends due to rate of change in IT industry n Consider several mis-predictions … © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 4 4 Page 2
 MISPREDICTIONS BY IT INDUSTRY LEADERS This “telephone” has too many shortcomings to be seriously considered as a means of communication. The device is inherently of no value to us. -Western Union internal memo, 1876 I think there is a world market for maybe five computers. -Thomas Watson, chairman of IBM, 1943 But what [is a microchip] good for? -Engineer at the Advanced Computing Systems Division of IBM, 1968 There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home. -Ken Olson, president, chairman, and founder of Digital Equipment Corp. , 1977 640 K ought to be enough for anybody. -Attributed to Bill Gates, chairman of Microsoft, 1981 Dell has a great business model, but that dog won’t scale. -John Shoemaker, head of Sun’s server division, 2000 © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 5 5 Page 2
MISPREDICTIONS BY IT INDUSTRY LEADERS This “telephone” has too many shortcomings to be seriously considered as a means of communication. The device is inherently of no value to us. -Western Union internal memo, 1876 I think there is a world market for maybe five computers. -Thomas Watson, chairman of IBM, 1943 But what [is a microchip] good for? -Engineer at the Advanced Computing Systems Division of IBM, 1968 There is no reason anyone would want a computer in their home. -Ken Olson, president, chairman, and founder of Digital Equipment Corp. , 1977 640 K ought to be enough for anybody. -Attributed to Bill Gates, chairman of Microsoft, 1981 Dell has a great business model, but that dog won’t scale. -John Shoemaker, head of Sun’s server division, 2000 © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 5 5 Page 2
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Computer Hardware: Faster, Smaller, Cheaper n 1981: first IBM PC n 1990 s: PCs commonplace n Now. . . Easy-to-use operating system with graphical interface Web browser ready Point-and-click technology Plays music and videos Notebook versions common for business travel © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 6 6 Page 2
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Computer Hardware: Faster, Smaller, Cheaper n 1981: first IBM PC n 1990 s: PCs commonplace n Now. . . Easy-to-use operating system with graphical interface Web browser ready Point-and-click technology Plays music and videos Notebook versions common for business travel © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 6 6 Page 2
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Computer Software: Standardized and Integrated n Majority of microcomputers: Microsoft Windows – operating system software Microsoft Office Suite – productivity software ü Word processing ü Spreadsheet ü Database ü Presentation ü E-mail ü Web browser © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 7 7 Page 3
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Computer Software: Standardized and Integrated n Majority of microcomputers: Microsoft Windows – operating system software Microsoft Office Suite – productivity software ü Word processing ü Spreadsheet ü Database ü Presentation ü E-mail ü Web browser © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 7 7 Page 3
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Computer Software: Standardized and Integrated Enterprise system packages – software packages with integrated modules that pass common business transactions across groups, divisions, and national boundaries in “real time” Widely adopted by manufacturing and service firms of all sizes Often tailored to specific industries Integrate data across traditional and Web-based channels for internal use, customers, and suppliers © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 8 8 Page 3
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Computer Software: Standardized and Integrated Enterprise system packages – software packages with integrated modules that pass common business transactions across groups, divisions, and national boundaries in “real time” Widely adopted by manufacturing and service firms of all sizes Often tailored to specific industries Integrate data across traditional and Web-based channels for internal use, customers, and suppliers © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 8 8 Page 3
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Computer Networks: High Bandwidth, Global, and Wireless n 1990 s: Standards for browser applications and Internet communications (TCP/IP) Fiber-optic lines used by more telecommunications providers High-speed access (high-bandwidth lines) available both to businesses and home owners n 2000: Commonplace for company networks linked to the Internet n 2003: Home owners using modems to connect to cable lines or digital subscriber lines (DSL) via telephone lines n Today: More companies investing in wireless technology © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 9 9 Page 3
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Computer Networks: High Bandwidth, Global, and Wireless n 1990 s: Standards for browser applications and Internet communications (TCP/IP) Fiber-optic lines used by more telecommunications providers High-speed access (high-bandwidth lines) available both to businesses and home owners n 2000: Commonplace for company networks linked to the Internet n 2003: Home owners using modems to connect to cable lines or digital subscriber lines (DSL) via telephone lines n Today: More companies investing in wireless technology © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 9 9 Page 3
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Consider: n By 2000, more than half of U. S. business capital expenditures were for IT n Today, IT can not only enable, but can also help shape business strategies © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 10 10 Page 4
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Consider: n By 2000, more than half of U. S. business capital expenditures were for IT n Today, IT can not only enable, but can also help shape business strategies © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 10 10 Page 4
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Traditional Ways to Compete n Three ways to compete (Porter, 1980): Cost – by being a low-cost producer of a good or service Differentiation – by offering products or services customers prefer due to superiority with innovativeness, image, quality, or customer service Focus – competing on cost or differentiation within a specific market niche © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 11 11 Page 3
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Traditional Ways to Compete n Three ways to compete (Porter, 1980): Cost – by being a low-cost producer of a good or service Differentiation – by offering products or services customers prefer due to superiority with innovativeness, image, quality, or customer service Focus – competing on cost or differentiation within a specific market niche © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 11 11 Page 3
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Traditional Ways to Compete n IT can help with cost Examples: ü Automating transaction time ü Shortening order cycle time ü Providing operational information for decision making n IT can help with differentiation Examples: ü Giving sales personnel information to better serve customers ü Providing just-in-time supplies for customers ü Creating new information-based products © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 12 12 Page 4
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS Traditional Ways to Compete n IT can help with cost Examples: ü Automating transaction time ü Shortening order cycle time ü Providing operational information for decision making n IT can help with differentiation Examples: ü Giving sales personnel information to better serve customers ü Providing just-in-time supplies for customers ü Creating new information-based products © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 12 12 Page 4
 RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS New Ways to Compete n Using the Internet Examples: üEntire travel industry restructured because of competition via the Internet üWal-Mart, Dell, and Lands’ End leverage Internet to compete Results: achieve additional cost savings, mass customize products, and reach even more customers © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 13 13 Page 4
RECENT INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY TRENDS New Ways to Compete n Using the Internet Examples: üEntire travel industry restructured because of competition via the Internet üWal-Mart, Dell, and Lands’ End leverage Internet to compete Results: achieve additional cost savings, mass customize products, and reach even more customers © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 13 13 Page 4
 WORKING IN AN E-WORLD n Business invests more in IT support for today’s knowledge workers n IT infrastructure now must support workers anytime and anywhere n Sales force personnel are now telecommuters Telecommuters – One who works from a location outside the firm’s regular offices and “commutes” via telecommunications lines in order to do his or her work © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 14 14 Page 5
WORKING IN AN E-WORLD n Business invests more in IT support for today’s knowledge workers n IT infrastructure now must support workers anytime and anywhere n Sales force personnel are now telecommuters Telecommuters – One who works from a location outside the firm’s regular offices and “commutes” via telecommunications lines in order to do his or her work © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 14 14 Page 5
 WORKING IN AN E-WORLD More Productive Teams n E-mail n Document sharing n Software to support collaborative teamwork n Videoconferencing © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 15 15 Page 5
WORKING IN AN E-WORLD More Productive Teams n E-mail n Document sharing n Software to support collaborative teamwork n Videoconferencing © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 15 15 Page 5
 WORKING IN AN E-WORLD Virtual Organizations and Free Agents n Virtual Organizations Temporary alliances between organizations and individuals Contracts often gain scarce expertise or cheaper labor costs Some might have no real office; employees can be located anywhere © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 16 16 Page 6
WORKING IN AN E-WORLD Virtual Organizations and Free Agents n Virtual Organizations Temporary alliances between organizations and individuals Contracts often gain scarce expertise or cheaper labor costs Some might have no real office; employees can be located anywhere © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 16 16 Page 6
 WORKING IN AN E-WORLD Virtual Organizations and Free Agents n Free Agents Are telecommuters who do knowledge work without being at a specific location Have specialized skills and IT linkages to work as independent contractors Often post resumes and sell skills globally © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 17 17 Page 6
WORKING IN AN E-WORLD Virtual Organizations and Free Agents n Free Agents Are telecommuters who do knowledge work without being at a specific location Have specialized skills and IT linkages to work as independent contractors Often post resumes and sell skills globally © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 17 17 Page 6
 LIVING IN AN E-WORLD n Advantages Fast, convenient communication with cell phones Vast amounts of “free” information via the Internet n Disadvantages Loss of individual privacy Vulnerability to computer crimes Social inequalities due to lack of access to computers © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 18 18 Page 6
LIVING IN AN E-WORLD n Advantages Fast, convenient communication with cell phones Vast amounts of “free” information via the Internet n Disadvantages Loss of individual privacy Vulnerability to computer crimes Social inequalities due to lack of access to computers © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 18 18 Page 6
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Information systems (IS) organization – department or unit that has primary responsibility for managing IT – hardware, software, networks, and IS professionals © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 19 19 Page 6
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Information systems (IS) organization – department or unit that has primary responsibility for managing IT – hardware, software, networks, and IS professionals © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 19 19 Page 6
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Accounting Era Back-office computer automation began with accounting IS professionals were primary decision makers but reported into an accounting function 1950 s to mid-1960 s © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 20 Transaction processing automated with use of computers for single functions (transactions were aggregated and then processed in a single run or “batch” – magnetic tape storage) Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 20 Page 7
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Accounting Era Back-office computer automation began with accounting IS professionals were primary decision makers but reported into an accounting function 1950 s to mid-1960 s © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 20 Transaction processing automated with use of computers for single functions (transactions were aggregated and then processed in a single run or “batch” – magnetic tape storage) Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 20 Page 7
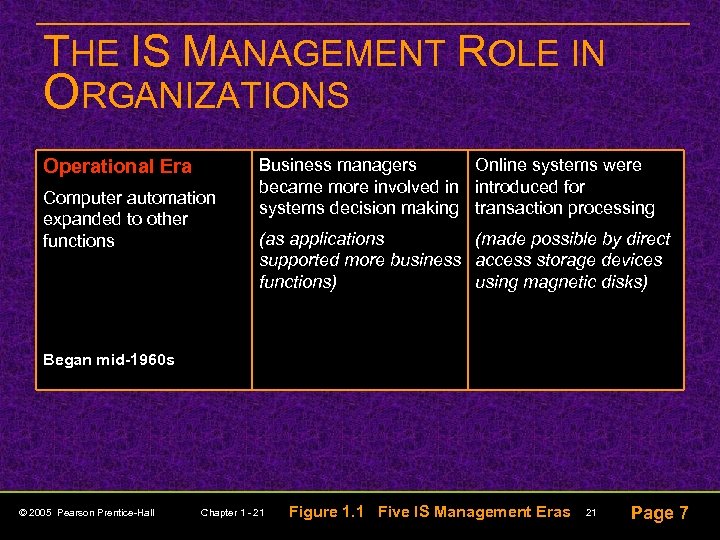 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Operational Era Computer automation expanded to other functions Business managers Online systems were became more involved in introduced for systems decision making transaction processing (as applications (made possible by direct supported more business access storage devices functions) using magnetic disks) Began mid-1960 s © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 21 Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 21 Page 7
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Operational Era Computer automation expanded to other functions Business managers Online systems were became more involved in introduced for systems decision making transaction processing (as applications (made possible by direct supported more business access storage devices functions) using magnetic disks) Began mid-1960 s © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 21 Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 21 Page 7
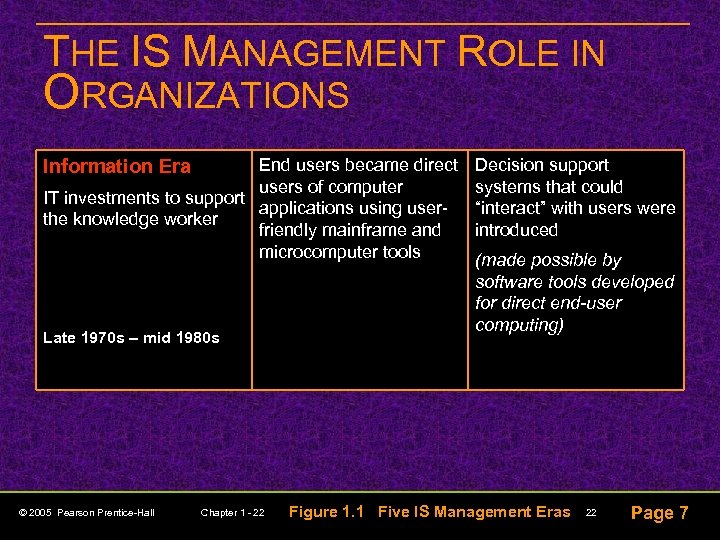 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS End users became direct users of computer IT investments to support applications using userthe knowledge worker friendly mainframe and microcomputer tools Information Era Late 1970 s – mid 1980 s © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 22 Decision support systems that could “interact” with users were introduced (made possible by software tools developed for direct end-user computing) Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 22 Page 7
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS End users became direct users of computer IT investments to support applications using userthe knowledge worker friendly mainframe and microcomputer tools Information Era Late 1970 s – mid 1980 s © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 22 Decision support systems that could “interact” with users were introduced (made possible by software tools developed for direct end-user computing) Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 22 Page 7
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Network Era IT investments in interenterprise systems Business managers began to take more of an “ownership” role in IT investments Computer networking enabled applications with business partners (custom-developed interorganizational applications) Began mid-1980 s © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 23 Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 23 Page 7
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Network Era IT investments in interenterprise systems Business managers began to take more of an “ownership” role in IT investments Computer networking enabled applications with business partners (custom-developed interorganizational applications) Began mid-1980 s © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 23 Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 23 Page 7
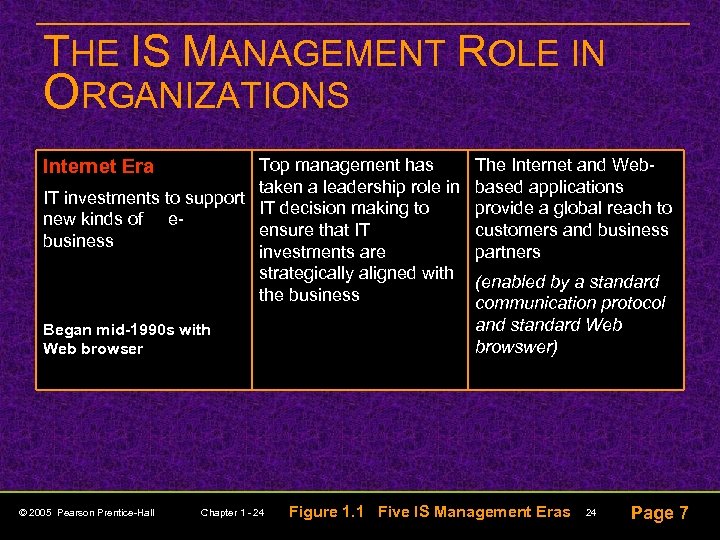 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Top management has taken a leadership role in IT investments to support IT decision making to new kinds of eensure that IT business investments are strategically aligned with the business Internet Era Began mid-1990 s with Web browser © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 24 The Internet and Webbased applications provide a global reach to customers and business partners (enabled by a standard communication protocol and standard Web browswer) Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 24 Page 7
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Top management has taken a leadership role in IT investments to support IT decision making to new kinds of eensure that IT business investments are strategically aligned with the business Internet Era Began mid-1990 s with Web browser © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 24 The Internet and Webbased applications provide a global reach to customers and business partners (enabled by a standard communication protocol and standard Web browswer) Figure 1. 1 Five IS Management Eras 24 Page 7
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Managing the IT Assets © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 25 Figure 1. 2 Three IT Assets 25 Page 8
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS Managing the IT Assets © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 25 Figure 1. 2 Three IT Assets 25 Page 8
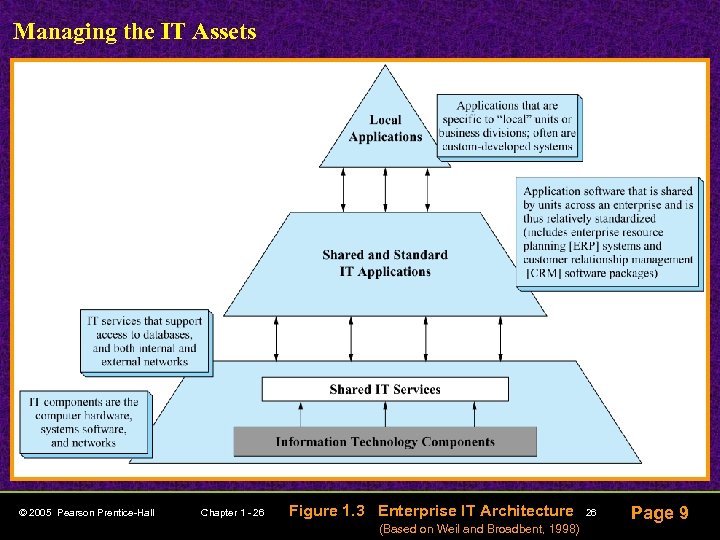 Managing the IT Assets © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 26 Figure 1. 3 Enterprise IT Architecture (Based on Weil and Broadbent, 1998) 26 Page 9
Managing the IT Assets © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 26 Figure 1. 3 Enterprise IT Architecture (Based on Weil and Broadbent, 1998) 26 Page 9
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n IS Leaders n Other IS Managers n IS Professionals n Business Managers n End Users © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 27 27 Page 10
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n IS Leaders n Other IS Managers n IS Professionals n Business Managers n End Users © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 27 27 Page 10
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n IS Leaders Chief Information Officer (CIO) – a firm’s high-level general IT asset manager with both technology and business leadership experience who, together with the executive management team, plans for integration of IT for strategic advantage © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 28 28 Page 10
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n IS Leaders Chief Information Officer (CIO) – a firm’s high-level general IT asset manager with both technology and business leadership experience who, together with the executive management team, plans for integration of IT for strategic advantage © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 28 28 Page 10
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n Other IS Managers … accountable for: Data centers Network operations New applications development © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 29 29 Page 10
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n Other IS Managers … accountable for: Data centers Network operations New applications development © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 29 29 Page 10
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n IS Professionals … include: Programmers Software engineers Systems analysts Database developers Web developers LAN administrators Technical support specialists © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 30 30 Page 10
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n IS Professionals … include: Programmers Software engineers Systems analysts Database developers Web developers LAN administrators Technical support specialists © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 30 30 Page 10
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n Business Managers … Are internal customers of the IT organization Need to be IT-savvy May jointly lead strategic IT projects Provide other IT-related roles: ü Serve on committees to prioritize and approve IT requests ü Act as sponsor or “owner” of an IT project ü Serve as process or functional expert on project team ü Participate in planning and execution of IT implementation © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 31 31 Page 11
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n Business Managers … Are internal customers of the IT organization Need to be IT-savvy May jointly lead strategic IT projects Provide other IT-related roles: ü Serve on committees to prioritize and approve IT requests ü Act as sponsor or “owner” of an IT project ü Serve as process or functional expert on project team ü Participate in planning and execution of IT implementation © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 31 31 Page 11
 THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n End Users … Provide business expertise to project teams Participate in redesign of business processes Give feedback to prototype screens and reports during system development Help gather customer input when they are directly affected by IT project © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 32 32 Page 11
THE IS MANAGEMENT ROLE IN ORGANIZATIONS People Roles n End Users … Provide business expertise to project teams Participate in redesign of business processes Give feedback to prototype screens and reports during system development Help gather customer input when they are directly affected by IT project © 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall Chapter 1 - 32 32 Page 11


