75c51a0761a75b6c66a89b839a79d68c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15

Managing Carbon in Agriculture: The Big Picture Challenges and Opportunities in Managing Agricultural Operations for a Low-Carbon Economy Jan Lewandrowski USDA Global Change Program Office July 18, 2007 West Des Moines, Iowa

Presentation at-a-glance • • Why agriculture should care about climate change GHG mitigation: Appreciating the options in agriculture Frameworks for managing carbon Key concepts

Why agriculture should care about climate change • Climate change and climate variability impact agricultural production and land use. • Crops and forests exist in an atmosphere that is increasing in concentration of CO 2. • Agriculture and forests are important sources of GHG emissions and carbon sinks. • Agricultural and forest systems have significant potential to address climate change with low-cost options for reducing GHG emissions and increasing carbon sequestration.

Mitigation Options in Agriculture Low-cost GHG mitigation opportunities include: • Reduce GHG emissions – Change manure managements – Change livestock feeds – Reduce nitrogen fertilizer use • Increase carbon sequestration in: – Agricultural Soils (conservation tillage) – Afforestation/reforestation – Forest management • Renewable energy / energy efficiency – Biofuels (liquid fuels, power generation from biomass) – Wind – Anaerobic waste digesters
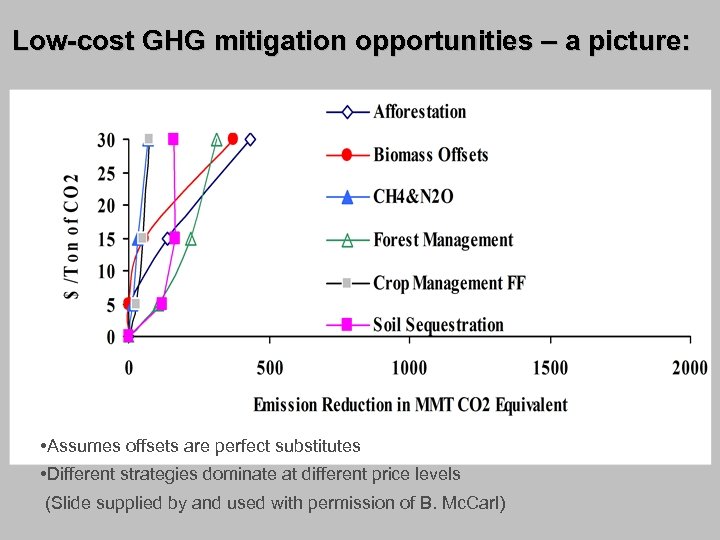
Low-cost GHG mitigation opportunities – a picture: • Assumes offsets are perfect substitutes • Different strategies dominate at different price levels (Slide supplied by and used with permission of B. Mc. Carl)

Mitigation Options: Appreciating the potential 1. Reducing N 20 emissions: Organic and synthetic commercial fertilizer Eq CO 2 = 9. 23 - 9. 35 mt per mt nitrogen applied 2. Reducing CH 4 emissions: Enteric fermentation High emissions feed mix: Low emissions feed mix: Corn silage (50% grain) Rye grain Vetch Hay Emissions per year: Per head: 0. 838 mt CO 2 Corn silage (25% grain) Barley grain light Bahiagrass Emissions per year: Per head: 0. 720 mt CO 2 Reduced emissions per year: Per head: 0. 118 mt CO 2 Per 1, 000 head: 118 mt CO 2

Mitigation Options: Appreciating the potential 3. Reducing CH 4 emissions: Manure management (Installing an anaerobic waste digester Ex: Wisconsin Dairy with 1, 000 dairy cows, 500 heifers, and 500 calves Emissions before digester installation: System Anaerobic Lagoon Liquid/Slurry/Deep pit Paddock/Range/Drylot Methane 6, 684 mt CO 2 2, 211 mt CO 2 79 mt CO 2 Emissions after digester installation: 0 mt CO 2 Nitrous Oxide 71 mt CO 2 977 mt CO 2 0 mt CO 2

Conceptual frameworks: • Encourage voluntary actions and markets – This has been the approach favored to date • Cap-and-trade systems – Set over-all limit on emissions (could apply to sectors, regions, country) – Issue permits equal to that emissions level and require all emitters to have a permit for all covered emissions – Distribute emissions permits via an allocation rule or auction – Allow entities to trade permits - those needing additional permits buy/ those with excess permits sell • Government incentive payments – Government sets an emissions reduction target and offers entities carbon payments to meet it – higher targets require higher payments – Conceptually similar to USDA’s conservation programs • Regulatory approaches – Require entities to meet emissions reductions targets – Example: mandating fuel efficiency standards – Generally the most difficult to accomplish politically

USDA’s conservation and energy programs • Conservation Reserve Program – Enrollment criteria (EBI) rewards bids with carbon benefits – Continuous sign-up provision includes program to afforest 500, 000 acres of bottomland hardwood • Environment Quality Incentives Program – Field staff directed to consider carbon benefits in enrollment – Anaerobic digesters added to approved conservation practices – Farmers can get paid for adopting nutrient management systems • 9006 Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Program – Awards competitive grants, loans, and loan guarantees to farmers, ranchers and small business owners to install renewable energy systems and improve energy efficiency – 2004 awards included: • $21 million in grants for 37 digesters, 37 wind power projects, and 20 other renewable energy systems • $1. 8 million in energy efficiency grants to 48 individuals/small businesses.

Legislation proposed in the 110 th Congress • Senate – – – S. 1766 (Bingaman / Specter) S. 280 (Lieberman / Mc. Cain) S. 309 (Sanders / Boxer) S. 317 (Feinstein / Carper) S. 485 (Kerry / Snowe) • House – HR. 620 (Oliver / Gilchrest) – HR. 1590 (Waxman) • Depending on the Bill - provisions include setting emissions limits, implementing cap-and-trade systems, allowing for offsets from agriculture and forestry, and increasing biomass energy.

Private, State, and regional activities. • Private markets: Chicago Climate Exchange – Presently the only formal carbon market in the U. S. – Voluntary to join but legally binding for members • State: California Global Warming Solutions Act of 2006 – Set statewide GHG emissions cap for 2020, based on 1990 emissions by January 1, 2008. – Adopt mandatory reporting rules for significant GHG sources by January 1, 2009. – Adopt a plan by January 1, 2009 indicating how emission reductions will be achieved via regulations, market mechanisms and other actions. – Adopt regulations by January 1, 2011 to achieve the maximum technologically feasible and cost-effective GHG reductions, including provisions for using both market and alternative compliance mechanisms. – Prior to implementation, requires evaluation of impacts on California's economy, the environment and public health; equity

Private, State, and regional activities. • Region: Regional GHG Initiative (10 Northest and Mid. Atlantic states) – Starting in January 2009, limits emissions from coal-fired, oil-fired, and gas-fired power plants at 121 million tons annually – Limit will be implemented via a cap-and-trade system – System explicitly allows for emissions offsets from reforestation and methane capture for farming facilities.

Key concepts: • Offsets – Associated with, but are outside of, cap-and trade systems – Allows covered entities to meet some of their system obligations with emissions reductions and/or carbon sequestration obtained from entities outside the system – Allows entities outside of system to participate – Lowers the cost to those inside • Measurement – – You cannot trade what you cannot quantify Approaches: direct, models, engineering approaches Approaches typically trade-off accuracy and cost Related issues include verification, uncertainty, and bias

Key concepts: • Permanence: To mitigate GHG emissions, carbon sequestered in terrestrial systems must remain out of the atmosphere. – Carbon in terrestrial systems can be released through natural and human driven processes. – Allowing carbon sequestration in a GHG mitigation program requires accounting for the possibility/inevitability that the carbon will be emitted at some point in the future – Solutions include banking credits, discounting relative to emissions reductions, annual rental payments, insurance policies against future releases. • Additionality: Are responses to a policy the result of that policy or would they have happened without it? – – Want to motivate new actions that contribute toward GHG mitigation. Do not want to penalize early actions. Want to avoid moral hazard. Can be difficult to assess what would have happened in a situation that did not happen.

Thank you Jan Lewandrowski USDA Global Change Program Office
75c51a0761a75b6c66a89b839a79d68c.ppt