63e7d0c574a1fb40dbda38efcb4b67bb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

MANAGING BY DESIGN Diagrams from Section B This set of slides contains the diagrams contained in Section B of the book ‘Managing by Design’. Please do not attempt to use these slides as part of a presentation until you have read and fully understood the relevant sections of ‘Managing by Design’, and you are clear on the points you wish to make with them. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 1
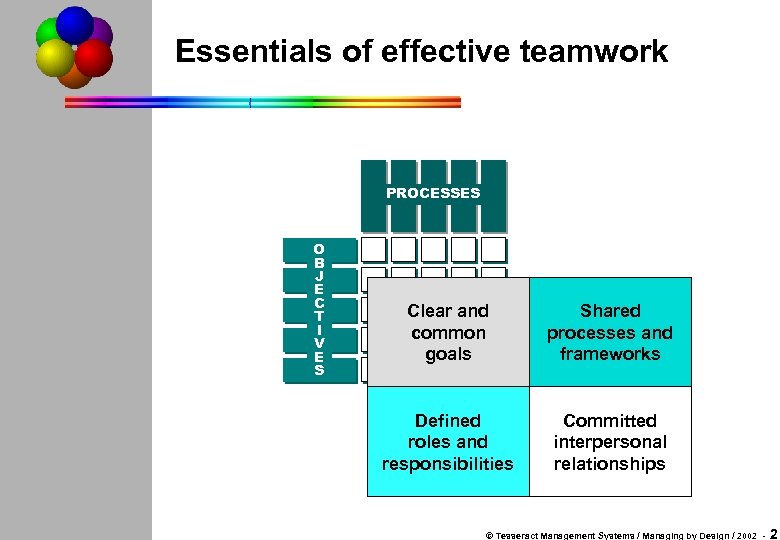
Essentials of effective teamwork PROCESSES O B J E C T I V E S Clear and common goals Shared processes and frameworks Defined roles and responsibilities Committed interpersonal relationships © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 2
Measurement and Perspective © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 3
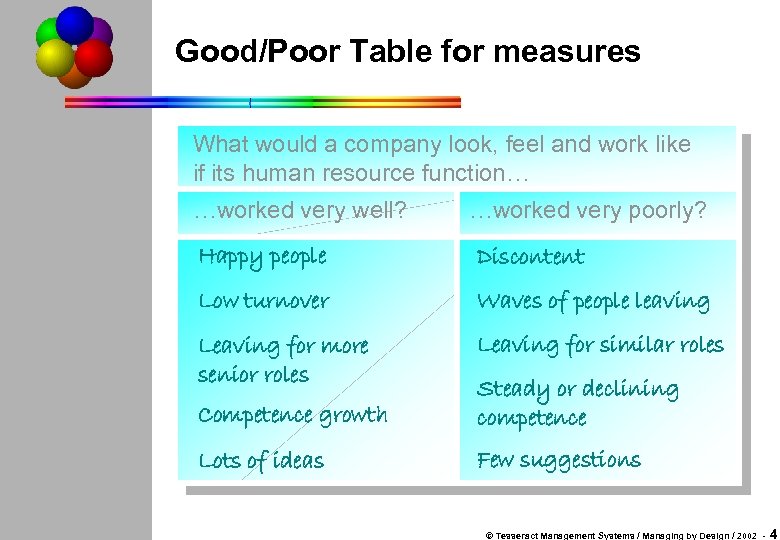
Good/Poor Table for measures What would a company look, feel and work like if its human resource function… …worked very well? …worked very poorly? Happy people Discontent Low turnover Waves of people leaving Leaving for more senior roles Leaving for similar roles Competence growth Steady or declining competence Lots of ideas Few suggestions © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 4

Performance Targets Target setting process: n Everybody considers what target they would set and writes it clearly on a card provided n We identify the highest and the lowest and peg them on the clothes line, others peg their cards at appropriate points in between n Everyone stands where they currently believe the target should be n We hear the arguments for and against the extremes, and people move as they are swayed n After five minutes, or after all the arguments are heard, we take the point at which most people are standing © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 5
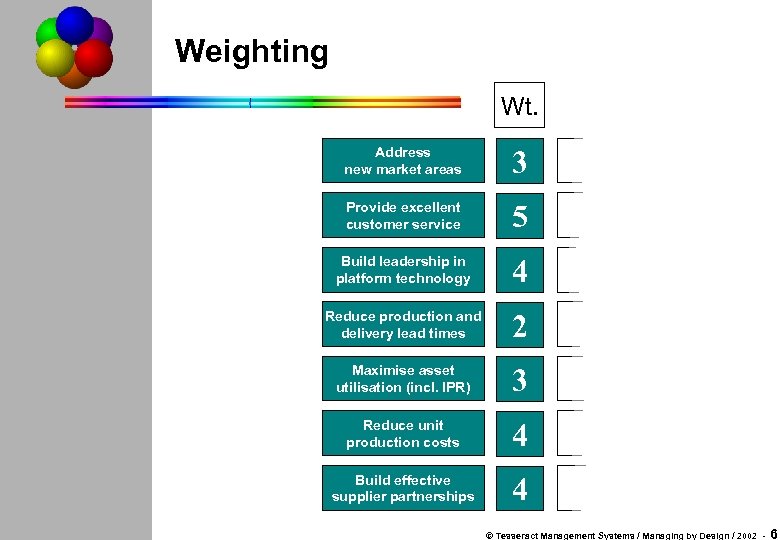
Weighting Wt. Address new market areas 3 Provide excellent customer service 5 Build leadership in platform technology 4 Reduce production and delivery lead times 2 Maximise asset utilisation (incl. IPR) 3 Reduce unit production costs 4 Build effective supplier partnerships 4 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 6
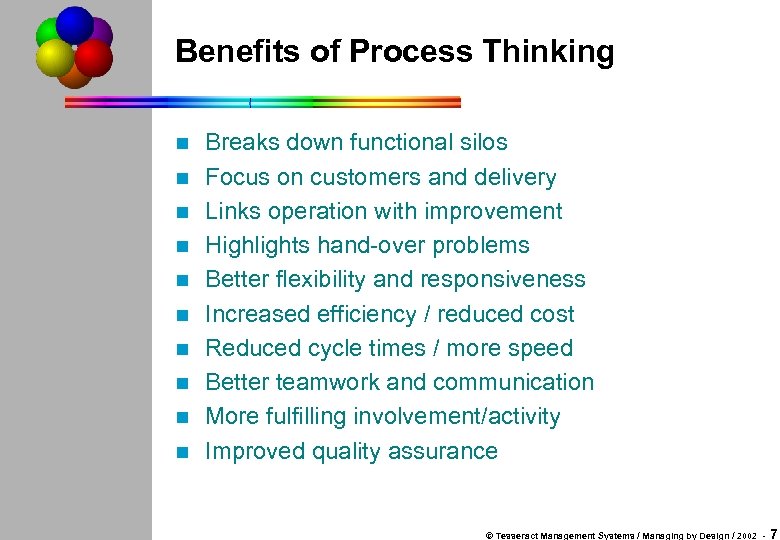
Benefits of Process Thinking n n n n n Breaks down functional silos Focus on customers and delivery Links operation with improvement Highlights hand-over problems Better flexibility and responsiveness Increased efficiency / reduced cost Reduced cycle times / more speed Better teamwork and communication More fulfilling involvement/activity Improved quality assurance © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 7
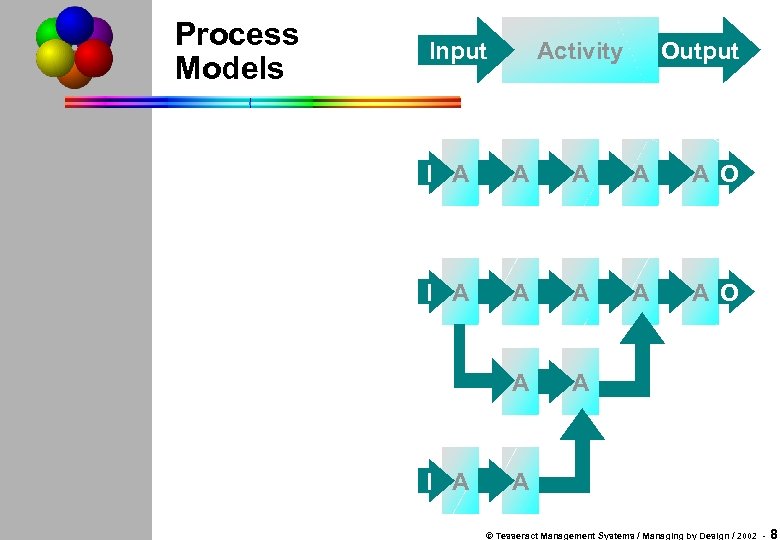
Process Models Output Activity Input I A A A A A O A A I A A © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 8
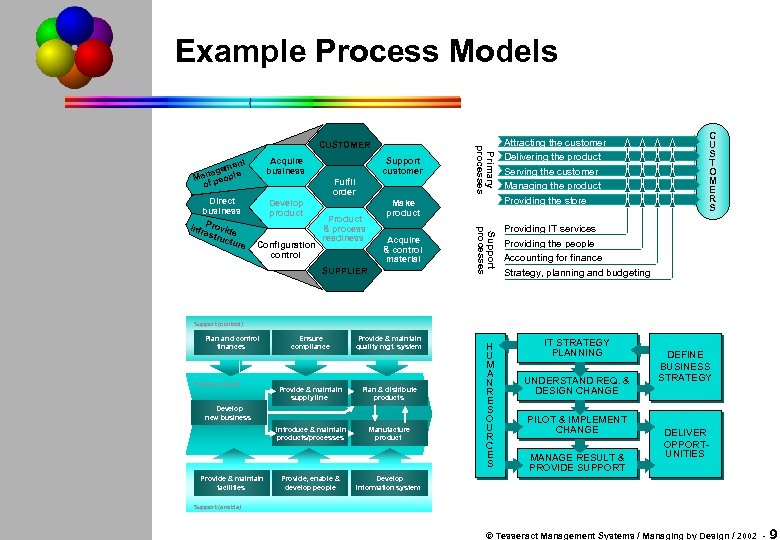
Example Process Models Acquire Business business Direct Business business P i Infr rovid astr e uct ure Develop product Product Support customer Customer Fulfil order Order Configuration Control control Product & Process process readiness Readiness Attracting the customer Delivering the product Serving the customer Managing the product Providing the store Support processes ent gem ana eople M p of Primary processes CUSTOMER Providing IT services Providing the people Accounting for finance Strategy, planning and budgeting Make product Product Acquire & Control control material Materiel SUPPLIER C U S T O M E R S Support (control) Plan and control finances Provide & maintain quality mgt. system Provide & maintain supply line Plan & distribute products Introduce & maintain products/processes Primary process Ensure compliance Manufacture product Develop new business Provide & maintain facilities Provide, enable & develop people H U M A N R E S O U R C E S IT STRATEGY PLANNING UNDERSTAND REQ. & DESIGN CHANGE PILOT & IMPLEMENT CHANGE MANAGE RESULT & PROVIDE SUPPORT DEFINE BUSINESS STRATEGY DELIVER OPPORTUNITIES Develop information system Support (enable) © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 9
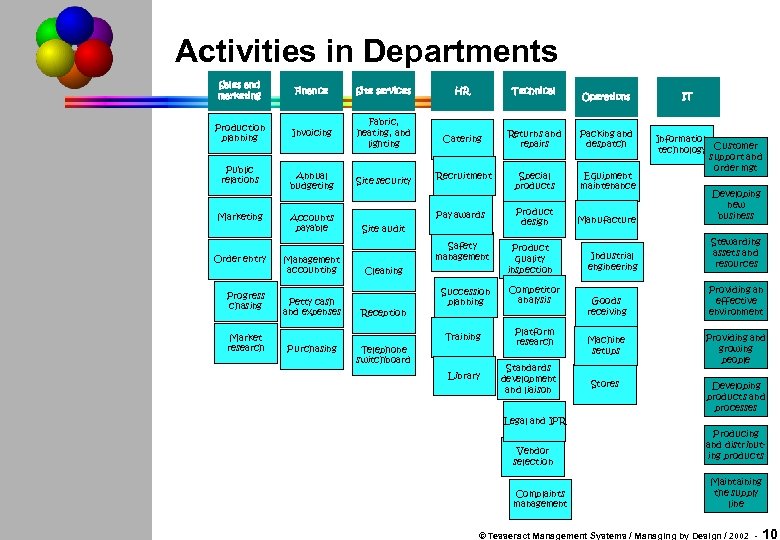
Activities in Departments Sales and marketing Finance Site services Production planning Invoicing Fabric, heating, and lighting Annual budgeting Site security Public relations Marketing Order entry Progress chasing Market research Accounts payable Management accounting Petty cash and expenses Purchasing HR Technical Catering Returns and repairs Packing and despatch Special products Equipment maintenance Product design Manufacture Developing new business Product quality inspection Industrial engineering Stewarding assets and resources Goods receiving Providing an effective environment Recruitment Pay awards Site audit Safety management Cleaning Reception Succession planning Competitor analysis Training Platform research Library Standards development and liaison Telephone switchboard Operations IT Information technology Customer support and order mgt Machine setups Providing and growing people Stores Developing products and processes Legal and IPR Vendor selection Complaints management Producing and distributing products Maintaining the supply line © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 10
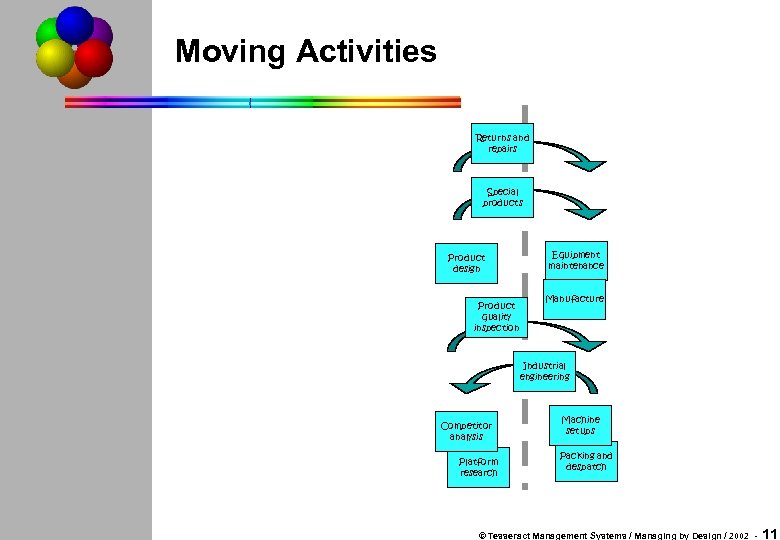
Moving Activities Returns and repairs Special products Product design Product quality inspection Equipment maintenance Manufacture Industrial engineering Competitor analysis Platform research Machine setups Packing and despatch © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 11
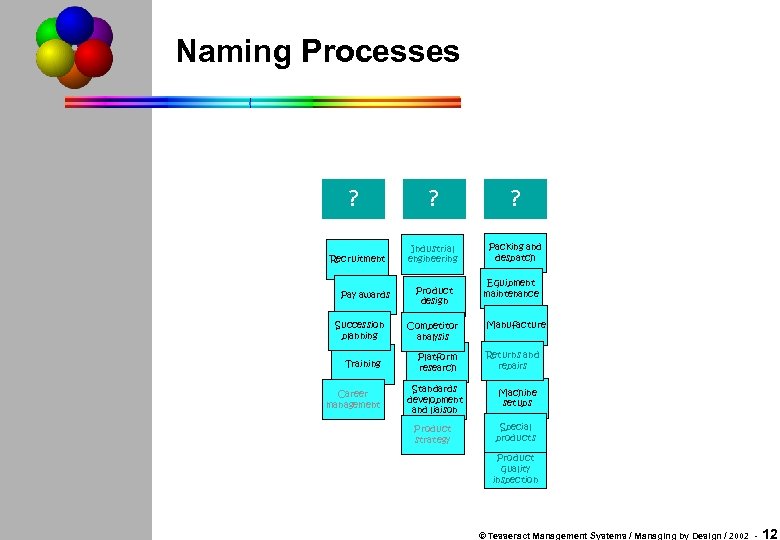
Naming Processes ? Recruitment Pay awards Succession planning Training Career management ? ? Industrial engineering Packing and despatch Product design Competitor analysis Platform research Equipment maintenance Manufacture Returns and repairs Standards development and liaison Machine setups Product strategy Special products Product quality inspection © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 12

Examples of Direct/Indirect Processes for a Manufacturing Business Direct Processes n Sales Order Management n Product Manufacturing n Purchasing n Order Despatch n Product Distribution Indirect Processes n Quality Assurance n People Development n Facilities Management n Financial Management © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 13
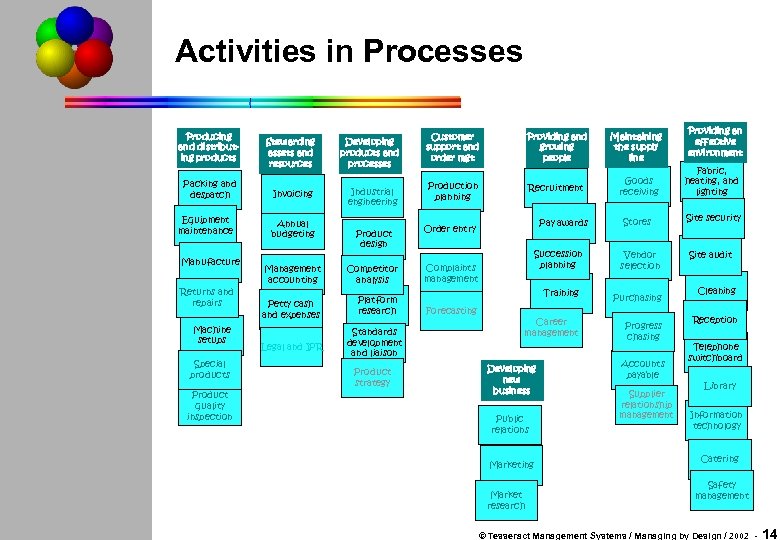
Activities in Processes Producing and distributing products Packing and despatch Equipment maintenance Manufacture Returns and repairs Machine setups Special products Product quality inspection Stewarding assets and resources Invoicing Annual budgeting Developing products and processes Industrial engineering Product design Management accounting Competitor analysis Petty cash and expenses Platform research Legal and IPR Standards development and liaison Product strategy Customer support and order mgt Maintaining the supply line Recruitment Production planning Goods receiving Fabric, heating, and lighting Stores Site security Pay awards Order entry Succession planning Complaints management Training Forecasting Providing an effective environment Providing and growing people Career management Developing new business Public relations Marketing Market research Vendor selection Purchasing Progress chasing Accounts payable Supplier relationship management Site audit Cleaning Reception Telephone switchboard Library Information technology Catering Safety management © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 14

Defining Processes Syndicate n n n In syndicate groups, take the yellow sticky notes and, using the affinity approach group the activities into sensible process groups. Once the silent grouping has settled down, discuss the process model which you have arrived at, and determine suitable ‘summary statements’ for each of the groups - ideally using verbs and nouns. Having done this, or maybe during this, you may make further movements of sticky notes to refine your process model By discussion you may choose to split or regroup ‘processes’ to develop new ways of looking at your organisation Be prepared to present back your model, and its underlying logic, to the group © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 15

Process Owner Responsibilities n n n n To adopt as their first responsibility, as part of the top team, the overall performance of the organisation as a whole To understand clearly the needs and expectations of their process (their part of the collective responsibility) by the business, their customers, and their colleagues To translate these needs and expectations (aspirations) into clear and specific performance improvement targets agreed by the business, their colleagues, and their customers To convene a team of people who have a strong interest in the process, and to have built a commitment in that team to improving its performance to meet the agreed targets To develop and document (e. g. in a process map) an accurate understanding of how the process works in practice, and how its operation is controlled and influenced To routinely measure process performance against target, graphically trend it, and undertake rigorous analysis of any adverse trends or performance deficiencies To develop plans for addressing root causes of any issues, ensure commitment for their implementation, and forecast the impact of this on future performance to meet target To seek best practice related to their process, review it for applicability and implement it where appropriate © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 16
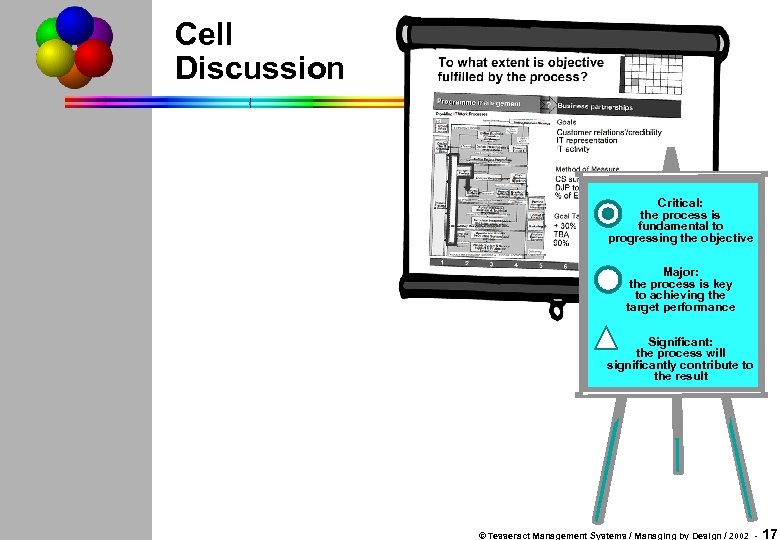
Cell Discussion Critical: the process is fundamental to progressing the objective Major: the process is key to achieving the target performance Significant: the process will significantly contribute to the result © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 17
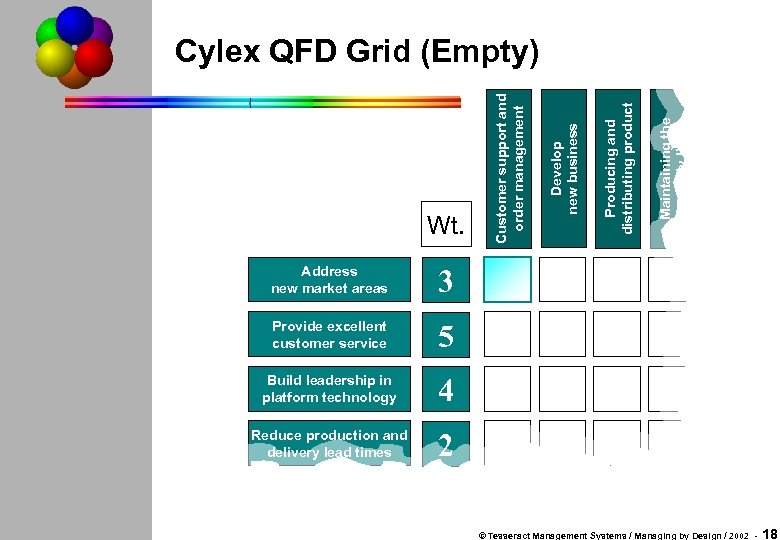
Address new market areas 4 Reduce production and delivery lead times Maintaining the supply line 5 Build leadership in platform technology Producing and distributing product 3 Provide excellent customer service Develop new business Wt. Customer support and order management Cylex QFD Grid (Empty) 2 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 18
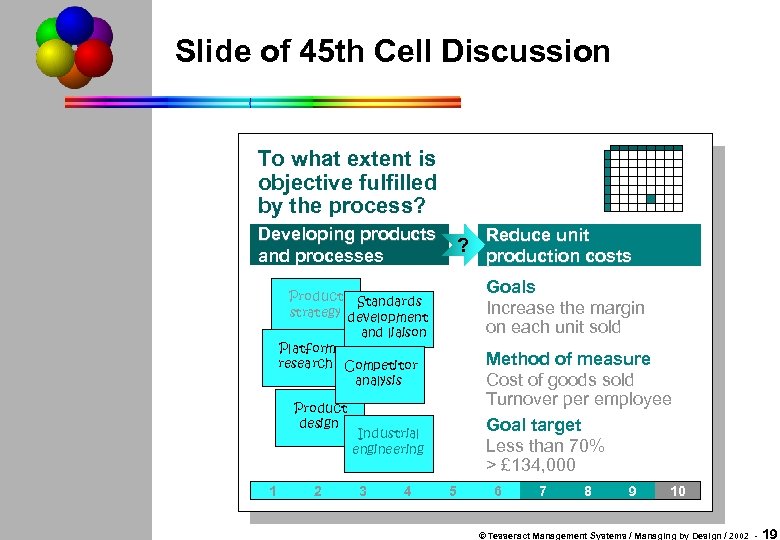
Slide of 45 th Cell Discussion To what extent is objective fulfilled by the process? Developing products and processes ? Goals Increase the margin on each unit sold Product Standards product standards strategy development and liaison Platform platform research competitor Competitor analysis Product product design 1 2 Method of measure Cost of goods sold Turnover per employee Goal target Less than 70% > £ 134, 000 Industrial industrial engineering 3 4 Reduce unit production costs 5 6 7 8 9 10 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 19
Voting Cards © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 20
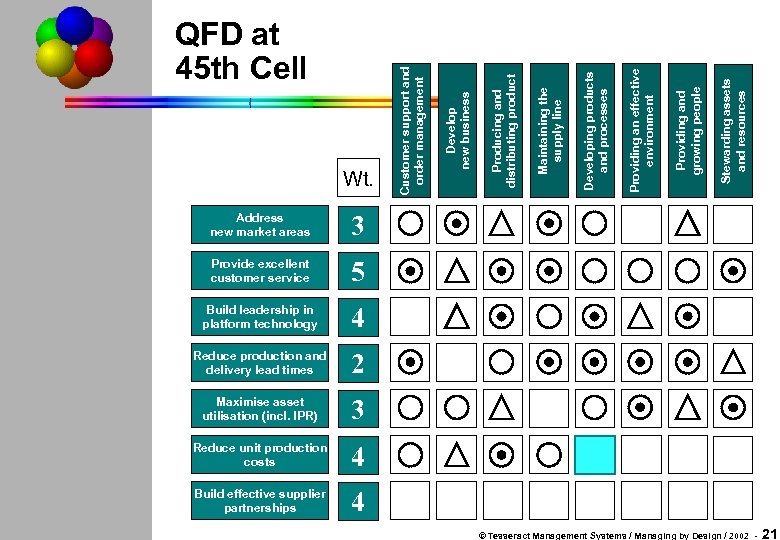
Address new market areas Stewarding assets and resources 4 Build effective supplier partnerships Providing and growing people 3 Reduce unit production costs Providing an effective environment 2 Maximise asset utilisation (incl. IPR) Developing products and processes 4 Reduce production and delivery lead times Maintaining the supply line 5 Build leadership in platform technology Producing and distributing product 3 Provide excellent customer service Develop new business Wt. Customer support and order management QFD at 45 th Cell 4 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 21

GROUNDRULES n n n n Be candid and honest Endeavour to keep to agreed times Everybody has an opportunity to speak on each issue Focus on the current task Only one person to speak at a time - no side conversations Everybody to remain involved with the discussion in hand Seek to understand rather than explain Have fun © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 22

Session Plan Time Item/ Objective description Inputs Process Output © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 23
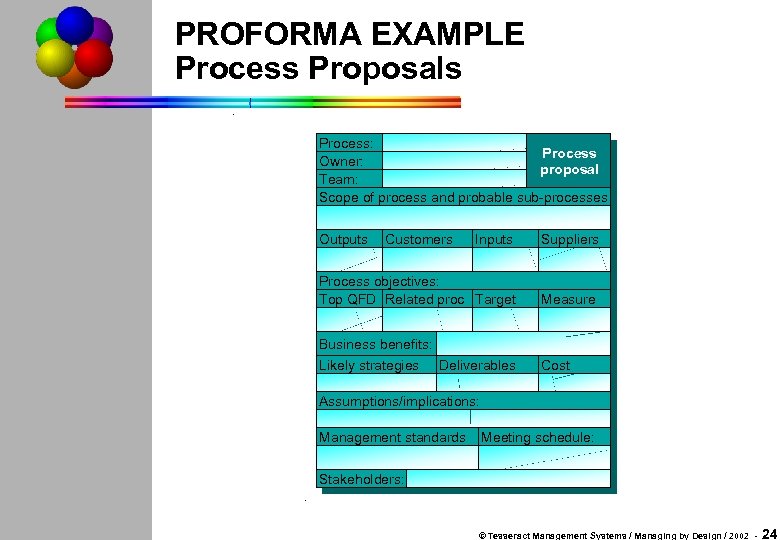
PROFORMA EXAMPLE Process Proposals Process: Process Owner: proposal Team: Scope of process and probable sub-processes Outputs Customers Inputs Suppliers Process objectives: Top QFD Related proc Target Measure Business benefits: Likely strategies Deliverables Cost Assumptions/implications: Management standards Meeting schedule: Stakeholders: © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 24

Consensus Process n n n YES NO Each proposal will be presented in turn. The proposer will make a brief argument as to why they feel proposal should be accepted. The group will present an initial show of the ‘Yes’, ‘No’ cards to indicate their current agreement. By invitation, the arguments for and against its acceptance will be heard in turn until the group is comfortable that all the main arguments have been heard and understood by themselves and their colleagues. The group will confirm that it will be happy to abide by the majority viewpoint at this time. A final show of the ‘Yes’, ‘No’ cards will be taken. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 25
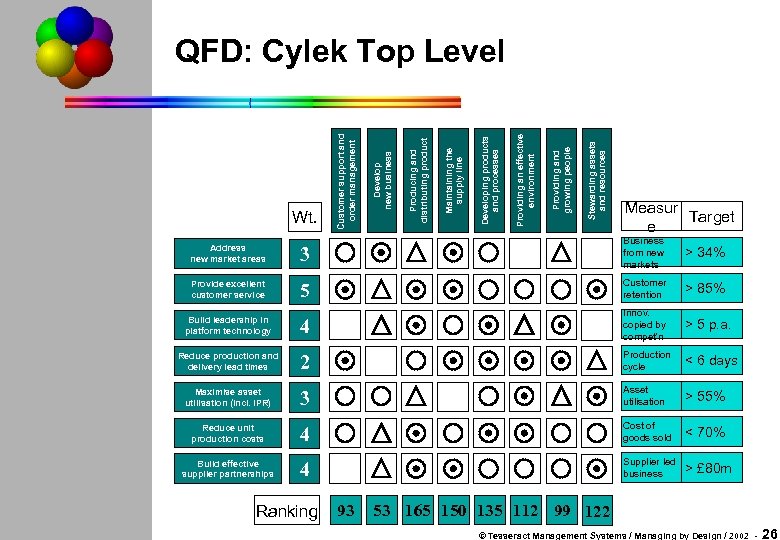
Stewarding assets and resources Providing and growing people Providing an effective environment Developing products and processes Maintaining the supply line Producing and distributing product Develop new business Wt. Customer support and order management QFD: Cylek Top Level Measur Target e 3 Business from new markets > 34% 5 Customer retention > 85% Build leadership in platform technology 4 Innov. copied by compet'n > 5 p. a. Reduce production and delivery lead times 2 Production cycle < 6 days Maximise asset utilisation (incl. IPR) 3 Asset utilisation > 55% Reduce unit production costs 4 Cost of goods sold < 70% Build effective supplier partnerships 4 Supplier led business > £ 80 m Address new market areas Provide excellent customer service Ranking 93 53 165 150 135 112 99 122 © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 26
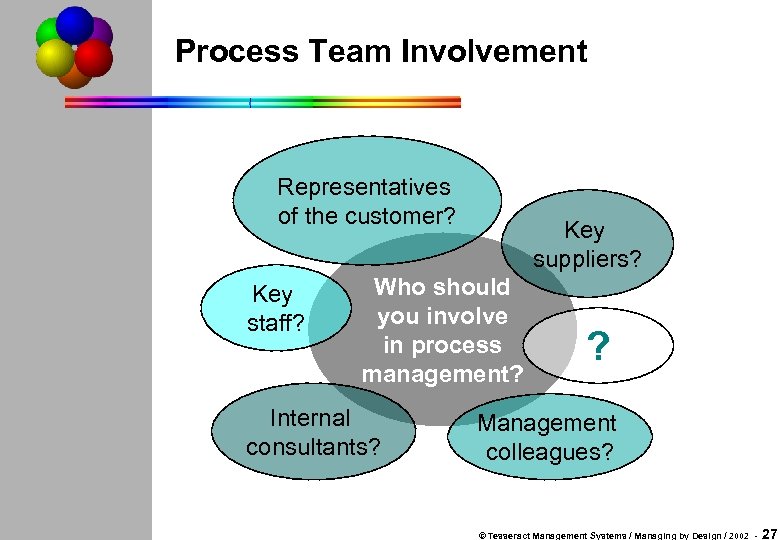
Process Team Involvement Representatives of the customer? Key staff? Key suppliers? Who should you involve in process management? Internal consultants? ? Management colleagues? © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 27
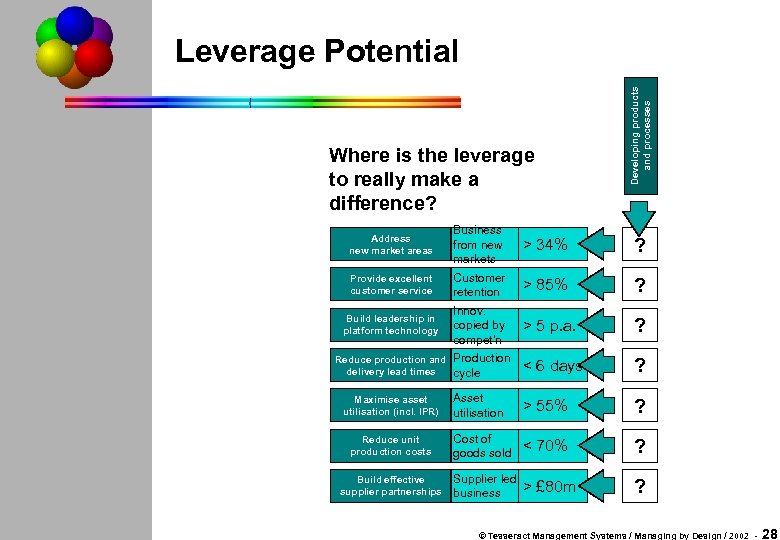
Where is the leverage to really make a difference? Developing products and processes Leverage Potential Address new market areas Business from new markets > 34% ? Provide excellent customer service Customer retention > 85% ? Build leadership in platform technology Innov. copied by compet'n > 5 p. a. ? Reduce production and delivery lead times Production cycle < 6 days ? Asset utilisation > 55% ? Reduce unit production costs Cost of goods sold < 70% ? Build effective supplier partnerships Supplier led business > £ 80 m ? Maximise asset utilisation (incl. IPR) © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 28

Visioning Exploration Questions to inspire thoughts about vision n To what areas of your customer’s operations could your service provide additional impact; areas where it is not currently used to its full potential? n What is your customer’s biggest blind-spot in the area of your service and offering? n Where could you transform the operations of your customer over and above what exists now? n What is the most outrageous thought you have in your head about how your service could develop? n What is impossible for you at this point, but if you could do it, it would obsolete all your current projects? n What sort of future for your organisation would you personally, find so inspiring that you would move heaven and earth to get it? © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 29
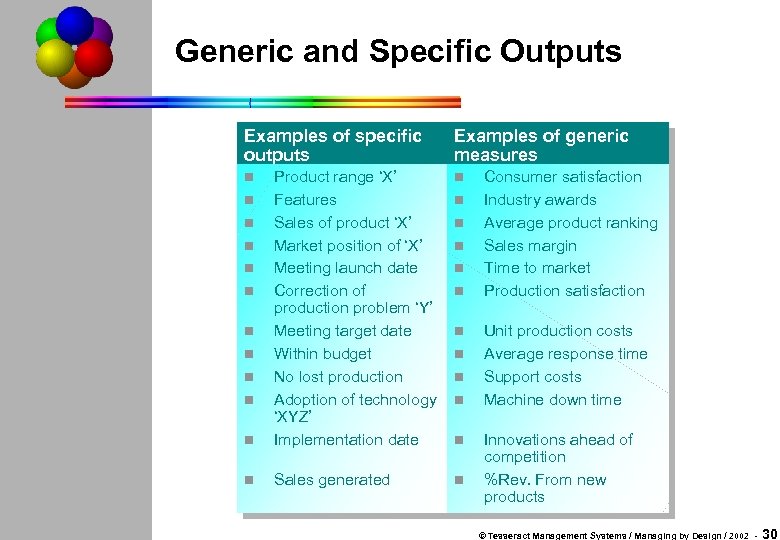
Generic and Specific Outputs Examples of specific outputs Examples of generic measures n n Product range ‘X’ Features Sales of product ‘X’ Market position of ‘X’ Meeting launch date Correction of production problem ‘Y’ Meeting target date Within budget No lost production Adoption of technology ‘XYZ’ Implementation date n Sales generated n n n n n n Consumer satisfaction Industry awards Average product ranking Sales margin Time to market Production satisfaction Unit production costs Average response time Support costs Machine down time Innovations ahead of competition %Rev. From new products © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 30

Process Proposal Process: Owner: Team: Scope of process (boundaries) and probable sub-processes Process outputs Related customers Process objectives: Top qfd objective Related process objective Process proposal Process inputs Target Related suppliers Measure Business benefits: Likely strategies Intended deliverables Effort/cost/resource Assumptions/implications: Management standards to be followed by team when relevant: Meeting schedule: Primary stakeholders: © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 31
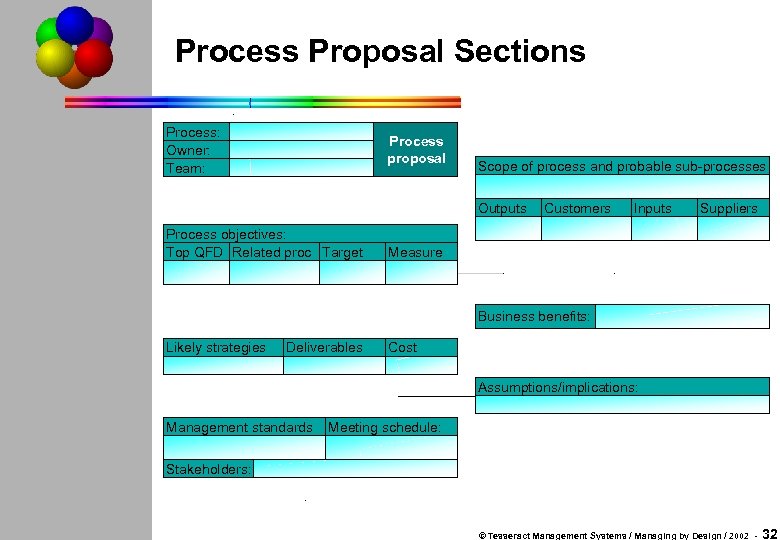
Process Proposal Sections Process: Owner: Team: Process proposal Scope of process and probable sub-processes Outputs Process objectives: Top QFD Related proc Target Customers Inputs Suppliers Measure Business benefits: Likely strategies Deliverables Cost Assumptions/implications: Management standards Meeting schedule: Stakeholders: © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 32
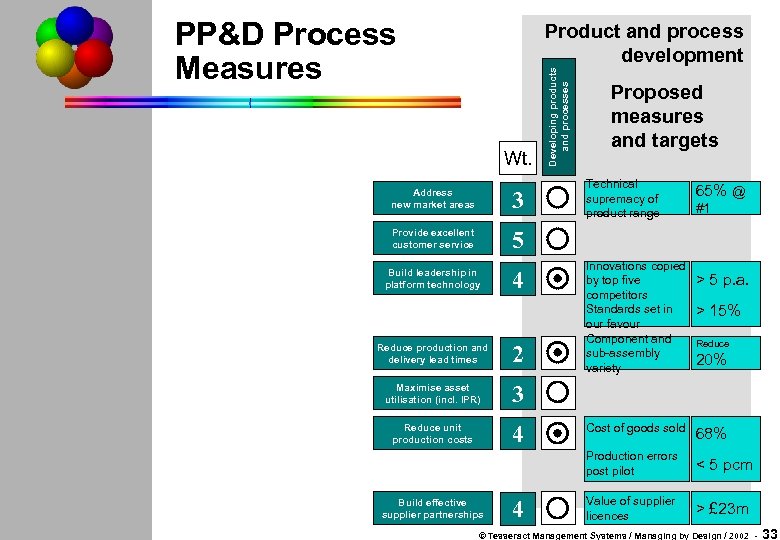
PP&D Process Measures Wt. Address new market areas 3 Provide excellent customer service Developing products and processes Product and process development Proposed measures and targets Technical supremacy of product range 65% @ 5 Build leadership in platform technology 4 Reduce production and delivery lead times 2 Maximise asset utilisation (incl. IPR) 4 Innovations copied by top five > 5 p. a. competitors Standards set in > 15% our favour Component and Reduce sub-assembly 20% variety 3 Reduce unit production costs #1 Cost of goods sold 68% Production errors post pilot Build effective supplier partnerships 4 < 5 pcm Value of supplier licences > £ 23 m © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 33
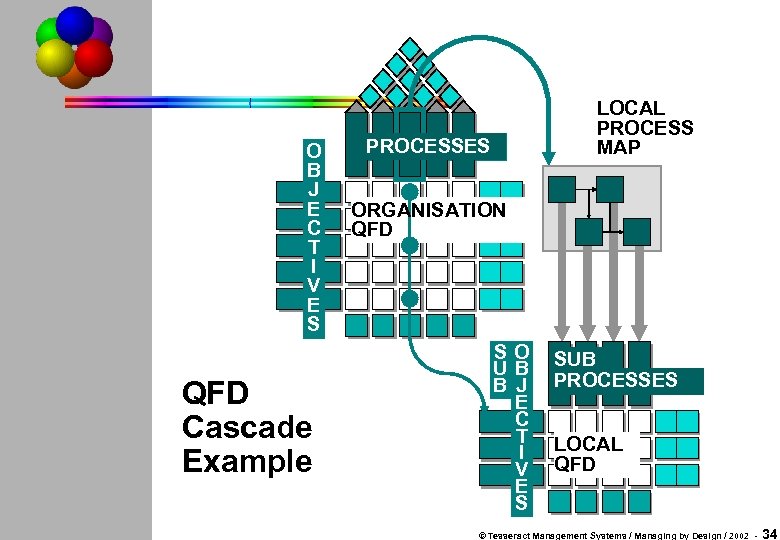
O B J E C T I V E S QFD Cascade Example LOCAL PROCESS MAP PROCESSES ORGANISATION QFD SO UB B J E C T I V E S SUB PROCESSES LOCAL QFD © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 34

Potential Problem Analysis (the fun version) n n n Imagine that you are a group of saboteurs, intent on derailing the plans of the team List out, down one side of a flipchart, all of the things that you could do to make sure that the plan fails, or has disastrous results Then come out of role, and create a second list, on the other side, of all the ways that these things could happen accidentally When you have finished work through the second list and evaluate the probability and impact of these things happening on a scale of high, medium and low. Think out what you will do to avoid, remove, or cope with the high risk items. © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 35
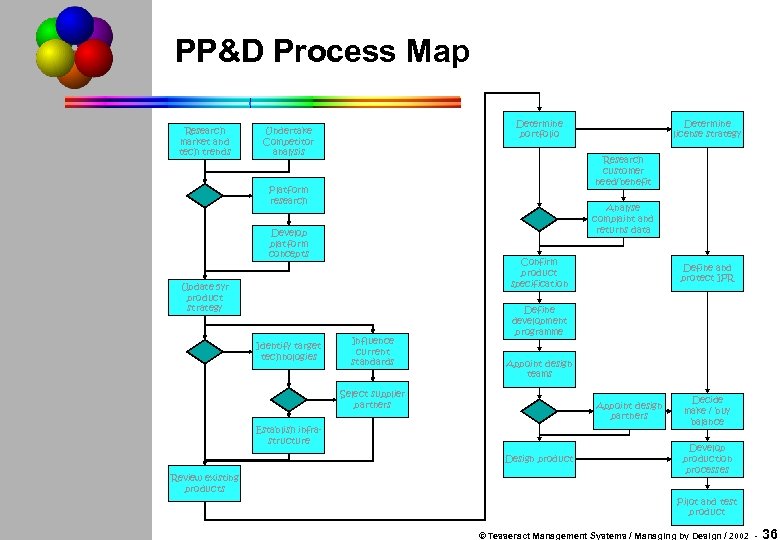
PP&D Process Map Research market and tech trends Determine portfolio Undertake Competitor analysis Research customer need/benefit Platform research Analyse complaint and returns data Develop platform concepts Confirm product specification Update 5 yr product strategy Identify target technologies Influence current standards Define and protect IPR Define development programme Appoint design teams Select supplier partners Appoint design partners Establish infrastructure Design product Review existing products Determine license strategy Decide make / buy balance Develop production processes Pilot and test product © Tesseract Management Systems / Managing by Design / 2002 - 36
63e7d0c574a1fb40dbda38efcb4b67bb.ppt