d6a0b05454ef39e8c32ced90eff52913.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Managing Across Cultures
Managing Across Cultures
 Course Roadmap Personality Relationships Group Context I I I
Course Roadmap Personality Relationships Group Context I I I
 2 Ways to Think About Culture Within organizations – Beliefs, values, norms – Assessing culture – Leaders: create culture Across countries – Global markets – Skills – Even the “best” stumble
2 Ways to Think About Culture Within organizations – Beliefs, values, norms – Assessing culture – Leaders: create culture Across countries – Global markets – Skills – Even the “best” stumble
 Top 10 Rejected New Names for Euro. Disney Letterman, D. (1995) 1. Ooh-La-Lame 2. Have-you-forgotten-we-saved-your-ass-in-World-War-Two-Land 3. Boutros-Goofy 4. Johnny Depp’s Hotel of Destruction 5. Beaucoup de Crap Americain 6. Gumpworld 7. La Veal de Guys in Big Smelly Costumes 8. Never-Profit Land 9. El Biggo Mistako 10. Euro Disaster
Top 10 Rejected New Names for Euro. Disney Letterman, D. (1995) 1. Ooh-La-Lame 2. Have-you-forgotten-we-saved-your-ass-in-World-War-Two-Land 3. Boutros-Goofy 4. Johnny Depp’s Hotel of Destruction 5. Beaucoup de Crap Americain 6. Gumpworld 7. La Veal de Guys in Big Smelly Costumes 8. Never-Profit Land 9. El Biggo Mistako 10. Euro Disaster
 Disney’s trip to Paris Strong internal culture – “Americana” (Main Street USA) – “Cast” members Conformity Homogeniety U. S. - European culture clash – Explicit culture – Implicit culture Individualistic American ideals
Disney’s trip to Paris Strong internal culture – “Americana” (Main Street USA) – “Cast” members Conformity Homogeniety U. S. - European culture clash – Explicit culture – Implicit culture Individualistic American ideals
 How should a company determine compensation of its employees? a) A company should take into account the size of the employee’s family. The company should be responsible for paying additional compensation for each additional family member. b) An employee should be paid on the basis of the work s/he is doing for the company. Therefore, the company does not have to take into account the employee’s family.
How should a company determine compensation of its employees? a) A company should take into account the size of the employee’s family. The company should be responsible for paying additional compensation for each additional family member. b) An employee should be paid on the basis of the work s/he is doing for the company. Therefore, the company does not have to take into account the employee’s family.
 A boss asks his subordinate to help paint his house. The subordinate, who doesn’t feel like doing it, discusses the issue with two colleagues. Which argument do you agree with most? a) Colleague A argues: You don’t have to paint his house if you don’t feel like it. He’s your boss in the company, but outside work he has little authority. b) Colleague B argues: Despite the fact that you don’t feel like it you should paint the house anyway. He is your boss, and you can’t ignore that outside of work either.
A boss asks his subordinate to help paint his house. The subordinate, who doesn’t feel like doing it, discusses the issue with two colleagues. Which argument do you agree with most? a) Colleague A argues: You don’t have to paint his house if you don’t feel like it. He’s your boss in the company, but outside work he has little authority. b) Colleague B argues: Despite the fact that you don’t feel like it you should paint the house anyway. He is your boss, and you can’t ignore that outside of work either.
 Determining compensation Percentage of people who agree with “b”: Family size of the employee is not relevant in determining compensation. n ly pa Ja Ita A an gl US En d
Determining compensation Percentage of people who agree with “b”: Family size of the employee is not relevant in determining compensation. n ly pa Ja Ita A an gl US En d
 Painting your Boss’ House Percentage of People who agree with “a”: You don’t have to help if you don’t want to a in Ch ico ex M s nd rla e th Ne A US
Painting your Boss’ House Percentage of People who agree with “a”: You don’t have to help if you don’t want to a in Ch ico ex M s nd rla e th Ne A US
 Culture as Normal Distributions A B
Culture as Normal Distributions A B
 Cultural Styles Task-Focused Relationships Social-Emotional Relationships Work Business Partners Merchants Family Friends Significant-Others “Task Cultures” Cultures
Cultural Styles Task-Focused Relationships Social-Emotional Relationships Work Business Partners Merchants Family Friends Significant-Others “Task Cultures” Cultures
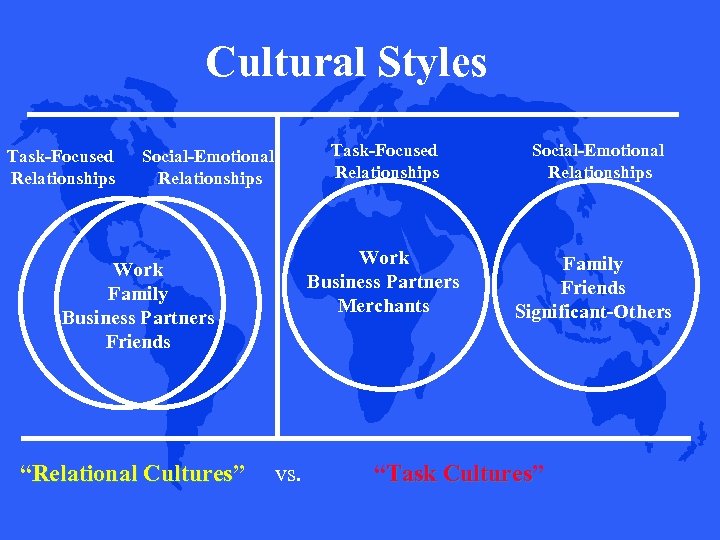 Cultural Styles Task-Focused Relationships Work Family Business Partners Friends “Relational Cultures” Cultures vs. Social-Emotional Relationships Work Business Partners Merchants Social-Emotional Relationships Family Friends Significant-Others “Task Cultures” Cultures
Cultural Styles Task-Focused Relationships Work Family Business Partners Friends “Relational Cultures” Cultures vs. Social-Emotional Relationships Work Business Partners Merchants Social-Emotional Relationships Family Friends Significant-Others “Task Cultures” Cultures
 The degree of overlap influences: 1. Goals and expectations at work: Maintain relationships vs. Task performance
The degree of overlap influences: 1. Goals and expectations at work: Maintain relationships vs. Task performance
 The degree of overlap influences: 2. How people relate to others: Trust, collaborate and work hard for people inside your “circle” vs. Formal, contractual agreements
The degree of overlap influences: 2. How people relate to others: Trust, collaborate and work hard for people inside your “circle” vs. Formal, contractual agreements
 The degree of overlap influences: 3. Beliefs about solve problems at work: Reaffirm ties vs. Re-focus on task; keep “personal issues” out
The degree of overlap influences: 3. Beliefs about solve problems at work: Reaffirm ties vs. Re-focus on task; keep “personal issues” out
 Course Evaluations
Course Evaluations
 Exam 2 Short answer questions on course web page 12/9 Thursday 9 am-10 am – Sections 3, 5, 8, 9 EH 1324 – Sections 2, 7 Angell Aud C – Sections 4, 6 Angell Aud D Review sessions – Free form Q&A – 12/8 Wed 1 -2: 30 EH 3048 – 12/8 Wed 5 -6: 30 EH 3048
Exam 2 Short answer questions on course web page 12/9 Thursday 9 am-10 am – Sections 3, 5, 8, 9 EH 1324 – Sections 2, 7 Angell Aud C – Sections 4, 6 Angell Aud D Review sessions – Free form Q&A – 12/8 Wed 1 -2: 30 EH 3048 – 12/8 Wed 5 -6: 30 EH 3048


