96bd25f088ecd70a4a4bc3d24a0027fb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS UNIT-V - MARKET STRUCTURE Equilibrium of the Market 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 1

Market • Market is defined as the institutional relationship between buyers and sellers; • It refers to the interaction between sellers and buyers of a good or service at a mutually agreed upon price. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 2

Market Equilibrium • Market equilibrium is a market state where the supply in the market is equal to the demand in the market. • The equilibrium price is the price of a good or service when the supply of it is equal to the demand for it in the market. • If a market is at equilibrium, the price will not change unless an external factor changes the supply or demand, which results in a disruption of the equilibrium. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 3

• If the market price is above the equilibrium value, there is an excess supply in the market (a surplus), which means there is more supply than demand. • In this situation, sellers will tend to reduce the price of their good or service to clear their inventories. • They probably will also slow down their production or stop ordering new inventory. • The lower price entices more people to buy, which will reduce the supply further. • This process will result in demand increasing and supply decreasing until the market price equals the equilibrium price. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 4

• If the market price is below the equilibrium value, then there is excess in demand (supply shortage). • In this case, buyers will bid up the price of the good or service in order to obtain the good or service in short supply. • As the price goes up, some buyers will quit trying because they don't want to, or can't, pay the higher price. • Additionally, sellers, more than happy to see the demand, will start to supply more of it. • Eventually, the upward pressure on price and supply will stabilize at market equilibrium. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 5

Long run supply curve • In long run, the supply of the firms in the industry can be fully adjusted to meet the changes in demand. • Consequently the shift in demand will be met by greater adjustment in output and smaller adjustments in price. • However, the new price in the long period may not go in the same direction as demand. • The new price may be more than, equal to or less than the initial price, depending upon whether the industry operates under increasing, constant or decreasing cost conditions. • The long run supply curve of the industry shows the relation between equilibrium price and the output that firms will be willing to supply after all derived entry or exit has occurred. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 6
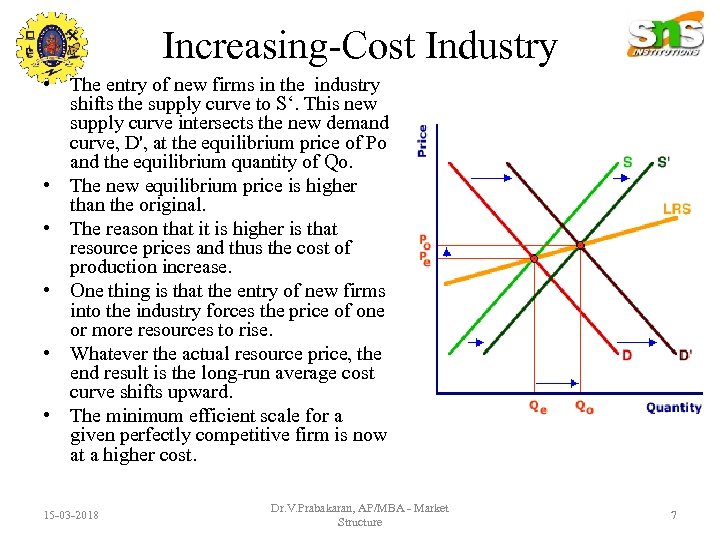
Increasing-Cost Industry • The entry of new firms in the industry shifts the supply curve to S‘. This new supply curve intersects the new demand curve, D', at the equilibrium price of Po and the equilibrium quantity of Qo. • The new equilibrium price is higher than the original. • The reason that it is higher is that resource prices and thus the cost of production increase. • One thing is that the entry of new firms into the industry forces the price of one or more resources to rise. • Whatever the actual resource price, the end result is the long-run average cost curve shifts upward. • The minimum efficient scale for a given perfectly competitive firm is now at a higher cost. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 7
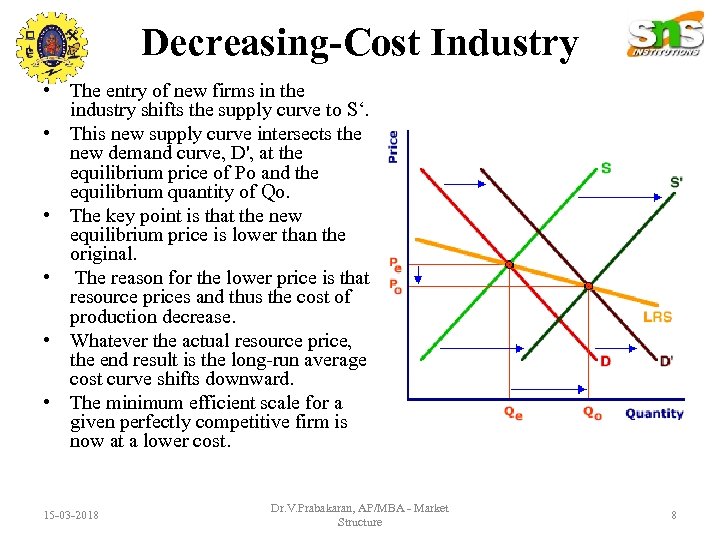
Decreasing-Cost Industry • The entry of new firms in the industry shifts the supply curve to S‘. • This new supply curve intersects the new demand curve, D', at the equilibrium price of Po and the equilibrium quantity of Qo. • The key point is that the new equilibrium price is lower than the original. • The reason for the lower price is that resource prices and thus the cost of production decrease. • Whatever the actual resource price, the end result is the long-run average cost curve shifts downward. • The minimum efficient scale for a given perfectly competitive firm is now at a lower cost. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 8
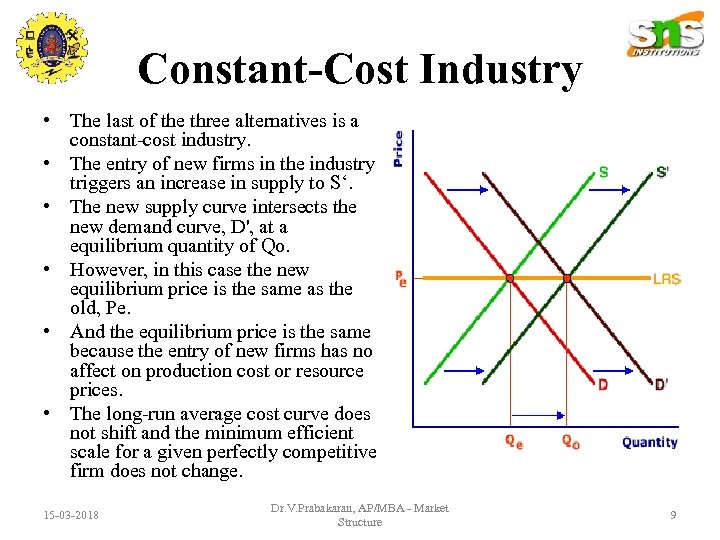
Constant-Cost Industry • The last of the three alternatives is a constant-cost industry. • The entry of new firms in the industry triggers an increase in supply to S‘. • The new supply curve intersects the new demand curve, D', at a equilibrium quantity of Qo. • However, in this case the new equilibrium price is the same as the old, Pe. • And the equilibrium price is the same because the entry of new firms has no affect on production cost or resource prices. • The long-run average cost curve does not shift and the minimum efficient scale for a given perfectly competitive firm does not change. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 9

• The path taken by an industry depends on underlying changes in resource prices and production cost. • If the expansion of an industry causes higher resource prices and production cost, then the result is an increasing-cost industry. • If expansion causes lower resource prices and production cost, then the result is a decreasingcost industry. • If expansion has no affect on resource prices and production cost, then the result is a constant-cost industry. 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 10

Thanks… 15 -03 -2018 Dr. V. Prabakaran, AP/MBA - Market Structure 11
96bd25f088ecd70a4a4bc3d24a0027fb.ppt