6330daee96bf3dd9ce032662e55bc859.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy Chapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and Monopolistically Competitive Markets
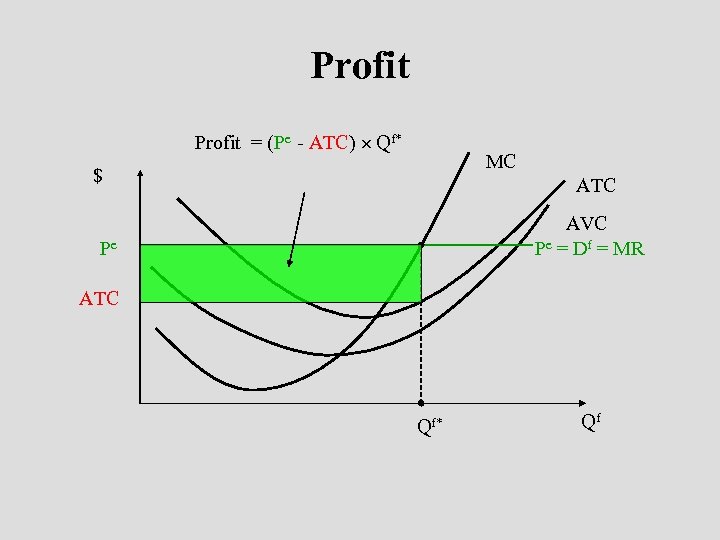
Profit = (Pe - ATC) Qf* MC $ ATC AVC Pe = Df = MR Pe ATC Qf* Qf

A Numerical Example • Given n n P=$10 C(Q) = 5 + Q 2 • Optimal Price? n P=$10 • Optimal Output? n n n MR = P = $10 and MC = 2 Q 10 = 2 Q Q = 5 units • Maximum Profits? n PQ - C(Q) = (10)(5) - (5 + 25) = $20
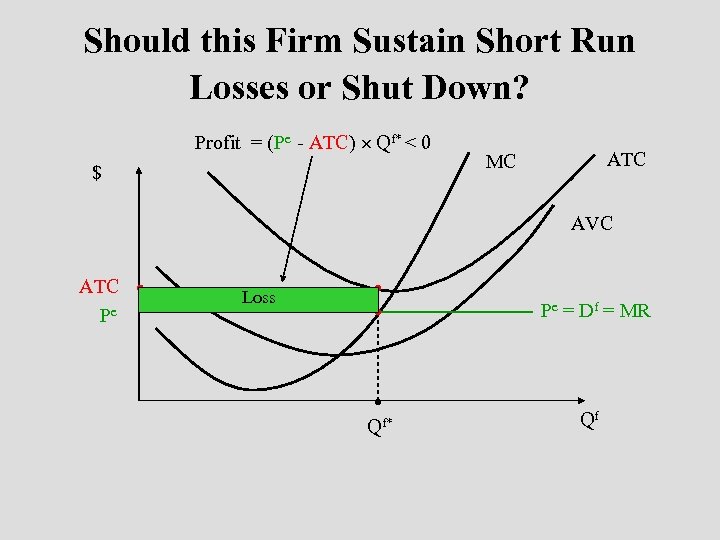
Should this Firm Sustain Short Run Losses or Shut Down? Profit = (Pe - ATC) Qf* < 0 $ ATC MC AVC ATC Pe Loss Pe = Df = MR Qf* Qf

Shutdown Decision Rule • A profit-maximizing firm should continue to operate (sustain short-run losses) if its operating loss is less than its fixed costs. n Operating results in a smaller loss than ceasing operations. • Decision rule: n n A firm should shutdown when P < min AVC. Continue operating as long as P ≥ min AVC.
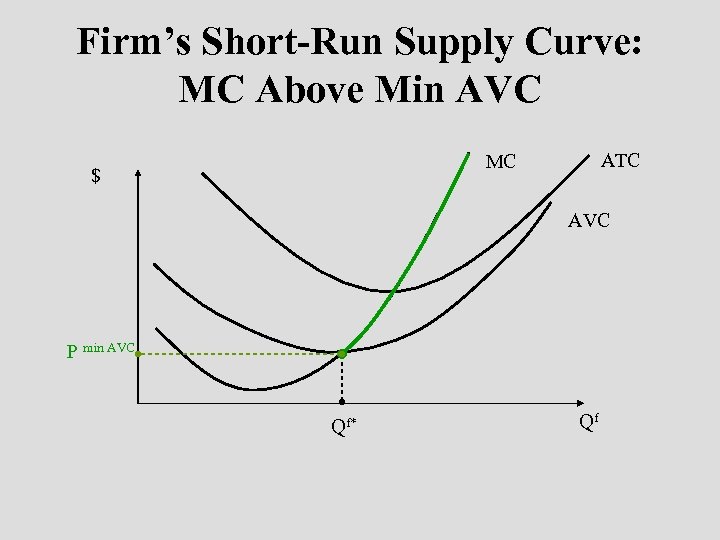
Firm’s Short-Run Supply Curve: MC Above Min AVC ATC MC $ AVC P min AVC Qf* Qf

Long Run Adjustments? • If firms are price takers but there are barriers to entry, profits will persist. • If the industry is perfectly competitive, firms are not only price takers but there is free entry. n Other “greedy capitalists” enter the market.
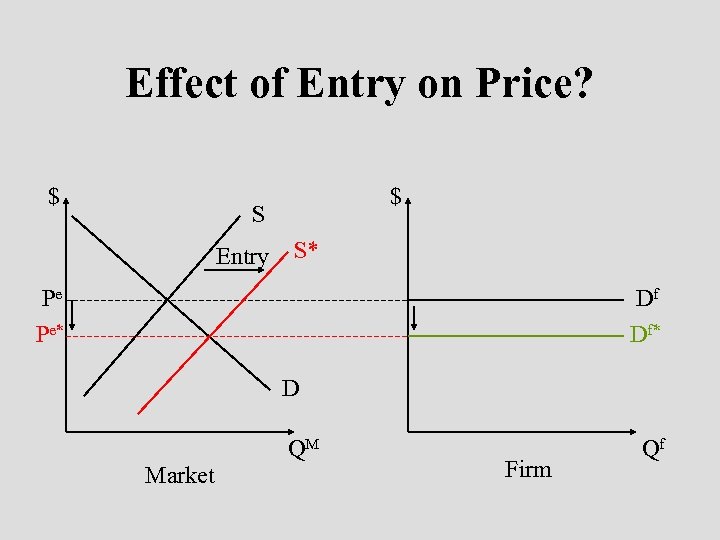
Effect of Entry on Price? $ $ S Entry S* Df Pe Pe* Df* D QM Market Firm Qf
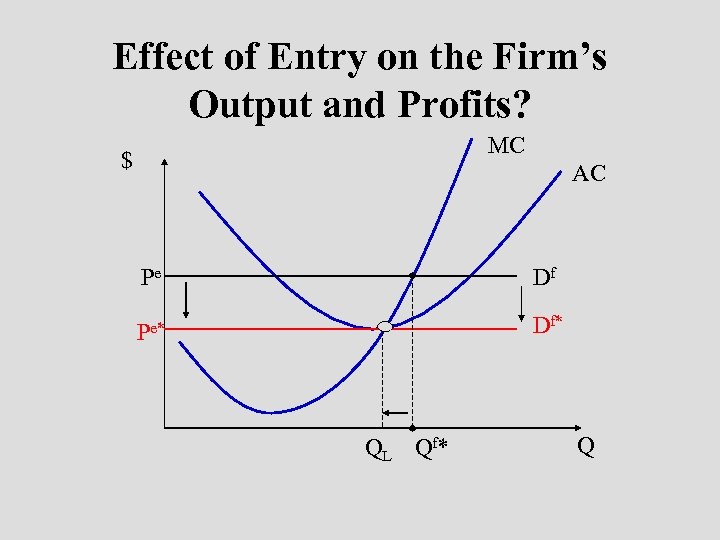
Effect of Entry on the Firm’s Output and Profits? MC $ AC Pe Df Pe* Df* Q L Q f* Q

Summary of Logic • Short run profits leads to entry. • Entry increases market supply, drives down the market price, increases the market quantity. • Demand for individual firm’s product shifts down. • Firm reduces output to maximize profit. • Long run profits are zero.

Features of Long Run Competitive Equilibrium • P = MC n Socially efficient output. • P = minimum AC n n Efficient plant size. Zero profits • Firms are earning just enough to offset their opportunity cost.

Can we do it? ? • Number 2 n A firm sells its product in a perfectly competitive market where other firms charge a price of $80 per unit. The firm’s TC are C(Q) = 40+8 Q+2 Q 2 • How much output should the firm produce in the short run? – – MR = MC 80 = 8+4 Q 72 = 4 Q Q= 18 • What price should the firm charge in the short run? – Same price as others = $80 • What are the firm’s short run profits? – 80*18 – (40+8(18)+2(182)=608 • What adjustments should be anticipated in the long run? – More firms will enter and prices will fall, output will have to be reduced, and profits will end at the breakeven point
6330daee96bf3dd9ce032662e55bc859.ppt