7948cc8ca9aafb2b12733732e9648230.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE 461 Lecture 1 a – Introduction September 9, 2008
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE 461 Lecture 1 a – Introduction September 9, 2008
 2 Contact Information Chris Neuman Phone 442 -6426 Email 1: cneuman@ualberta. ca Office: Shadowy and Vague Office hours: By appointment (after 4: 30) Intros…
2 Contact Information Chris Neuman Phone 442 -6426 Email 1: cneuman@ualberta. ca Office: Shadowy and Vague Office hours: By appointment (after 4: 30) Intros…
 3 Website https: //ulearn. ualberta. ca All class material will be posted (spreadsheets, lecture slides, etc) Grade info, digital dropbox, course conferencing
3 Website https: //ulearn. ualberta. ca All class material will be posted (spreadsheets, lecture slides, etc) Grade info, digital dropbox, course conferencing
 4 Syllabus Information Textbook Classroom Grading Homeworks 35% Quizzes 25% Project 40%
4 Syllabus Information Textbook Classroom Grading Homeworks 35% Quizzes 25% Project 40%
 5 Homework Policies Code of Student Behaviour Peer help is the best way to learn Discussion of HW problems is healthy and encouraged Just don’t copy each other’s work.
5 Homework Policies Code of Student Behaviour Peer help is the best way to learn Discussion of HW problems is healthy and encouraged Just don’t copy each other’s work.
 6 Operations Research The Science of Better Quantitative tools used to make better decisions Broad range of applications, broad range of tools We are specifically addressing …
6 Operations Research The Science of Better Quantitative tools used to make better decisions Broad range of applications, broad range of tools We are specifically addressing …
 7 Distribution Management The process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, effective flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from point of origin to point of consumption for the purpose of conforming to customer requirements. - Council of Logistics Management
7 Distribution Management The process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, effective flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from point of origin to point of consumption for the purpose of conforming to customer requirements. - Council of Logistics Management
 8 DM Cost Drivers Inventory Transportation Carrier selection, shipment size, distance and travel time Facilities (production and storage) Raw materials, WIP, finished goods What? When? Where? Why? Information Availability, price, forecasting demand, shipping options
8 DM Cost Drivers Inventory Transportation Carrier selection, shipment size, distance and travel time Facilities (production and storage) Raw materials, WIP, finished goods What? When? Where? Why? Information Availability, price, forecasting demand, shipping options
 9 Planning Levels Strategic: long-term, long-range, potentially reshaping the way business is done Tactical: medium-range, designed to raise competitiveness and customer service levels Operational: day-to-day; Efficiency at low cost
9 Planning Levels Strategic: long-term, long-range, potentially reshaping the way business is done Tactical: medium-range, designed to raise competitiveness and customer service levels Operational: day-to-day; Efficiency at low cost
 10 Examples Distribution network configuration Strategic - a new flow of goods throughout the network Inventory control Tactical - determine inventory policy to minimize ordering and holding costs Crossdocking Tactical - warehouses serve as coordinators and as transshipment points but do not keep stock themselves
10 Examples Distribution network configuration Strategic - a new flow of goods throughout the network Inventory control Tactical - determine inventory policy to minimize ordering and holding costs Crossdocking Tactical - warehouses serve as coordinators and as transshipment points but do not keep stock themselves
 11 Examples Integration of inventory and transportation Tactical - determine balance between inventory and transportation costs Vehicle fleet management Operational - assign loads to vehicles and determine vehicle routes
11 Examples Integration of inventory and transportation Tactical - determine balance between inventory and transportation costs Vehicle fleet management Operational - assign loads to vehicles and determine vehicle routes
 12 Examples Truck routing Operational - determine the minimal length route (time or distance) to follow Packing problems Operational - pack items such that the number of bins used is minimized
12 Examples Truck routing Operational - determine the minimal length route (time or distance) to follow Packing problems Operational - pack items such that the number of bins used is minimized
 13 Trends Reality: DM problems are computationally intensive, complex, and multi-faceted Intuition plays a major role in how we approach DM problems Tools models – what’s happening now? Prescriptive models – what should we do? Descriptive
13 Trends Reality: DM problems are computationally intensive, complex, and multi-faceted Intuition plays a major role in how we approach DM problems Tools models – what’s happening now? Prescriptive models – what should we do? Descriptive
 14 Course focus The focus in this class is on mathematically welldefined problems that can be solved using algorithmic and heuristic techniques IS, outsourcing, 3 PL and 4 PL, strategic partnerships, B 2 B and many other buzzwords are difficult to quantify and will be addressed lightly (MGTSC 488)
14 Course focus The focus in this class is on mathematically welldefined problems that can be solved using algorithmic and heuristic techniques IS, outsourcing, 3 PL and 4 PL, strategic partnerships, B 2 B and many other buzzwords are difficult to quantify and will be addressed lightly (MGTSC 488)
 Dayjet
Dayjet
 17 Why Models? Reality bites Data overload, but not information overload Reliance on computers: Data is masked Allocation of responsibility (must justify decisions) Decisions and numbers Many decisions are numbers How many distribution centers do we need? Capacity of new plant? How many workers assigned to line? Most decisions depend on numbers Should we introduce a new product? Make or buy?
17 Why Models? Reality bites Data overload, but not information overload Reliance on computers: Data is masked Allocation of responsibility (must justify decisions) Decisions and numbers Many decisions are numbers How many distribution centers do we need? Capacity of new plant? How many workers assigned to line? Most decisions depend on numbers Should we introduce a new product? Make or buy?
 18 Why Models? Data + Model = Information Managers who do not understand models either: Don’t put faith in analysis, lose valuable information, or Put too much faith in analysis, are swayed by stacks of computer output
18 Why Models? Data + Model = Information Managers who do not understand models either: Don’t put faith in analysis, lose valuable information, or Put too much faith in analysis, are swayed by stacks of computer output
 19 Why Models? Tradeoff analysis Provides a structure for DM Powerful engineering tool, but a key management skill too (re-engineering) Value of model is its usefulness Modeling is an iterative process
19 Why Models? Tradeoff analysis Provides a structure for DM Powerful engineering tool, but a key management skill too (re-engineering) Value of model is its usefulness Modeling is an iterative process
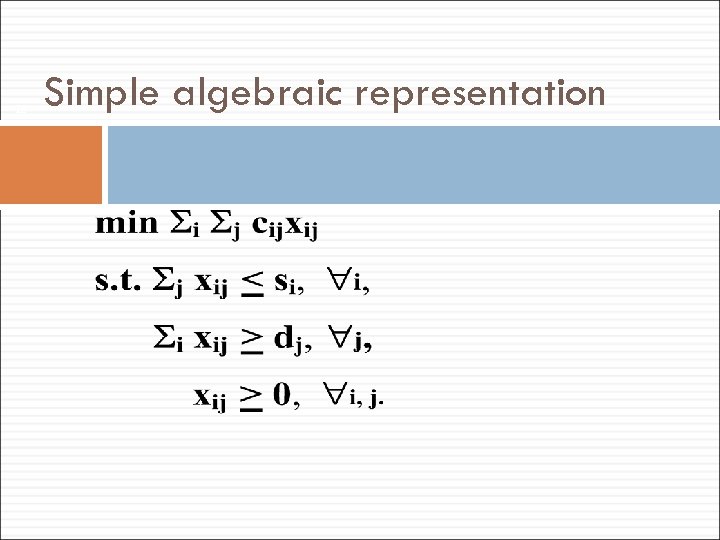 20 Simple algebraic representation
20 Simple algebraic representation
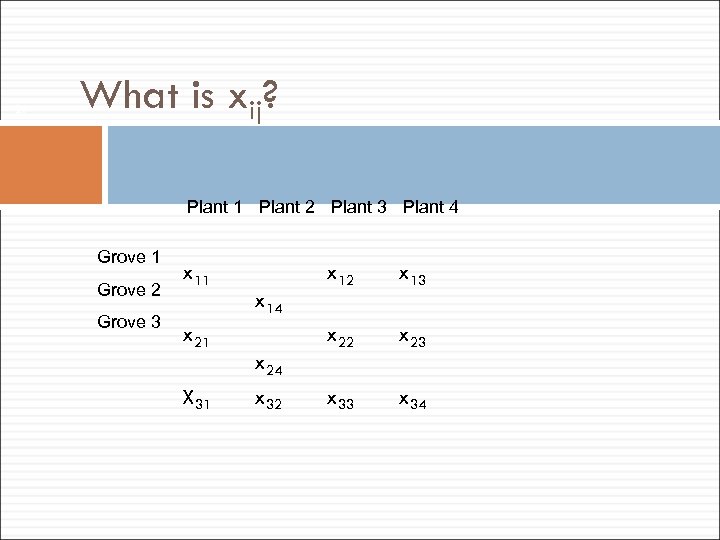 21 What is xij? Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 Grove 1 Grove 2 Grove 3 x 11 x 21 X 31 x 14 x 24 x 32 x 13 x 22 x 23 x 34
21 What is xij? Plant 1 Plant 2 Plant 3 Plant 4 Grove 1 Grove 2 Grove 3 x 11 x 21 X 31 x 14 x 24 x 32 x 13 x 22 x 23 x 34
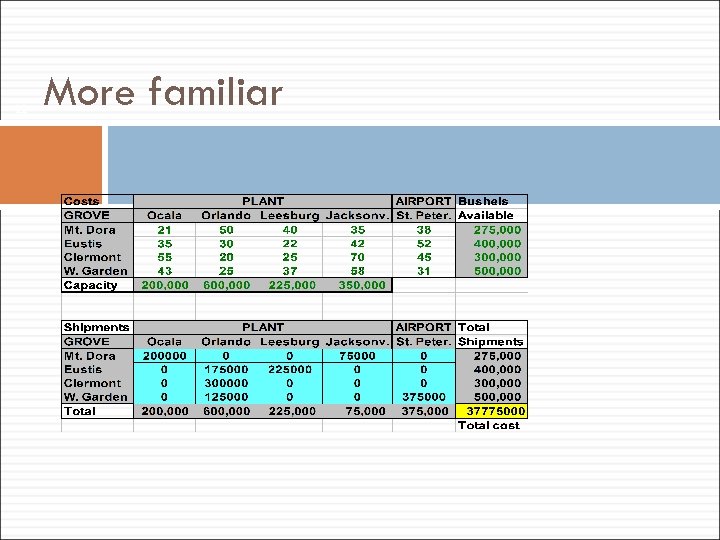 22 More familiar
22 More familiar
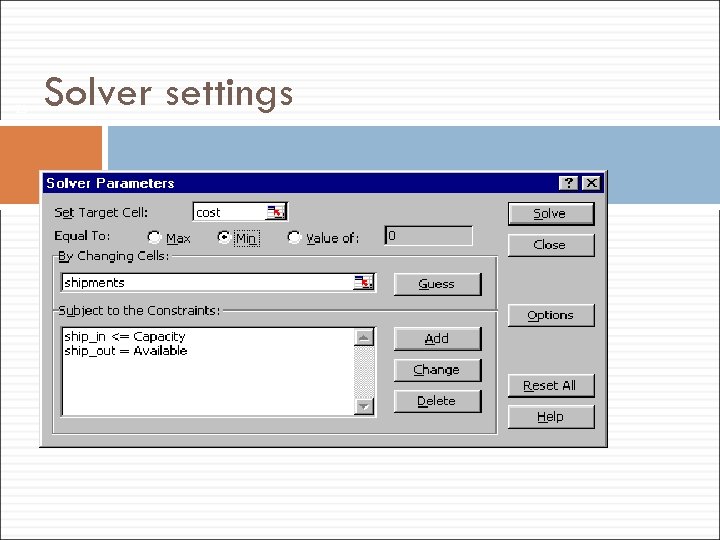 23 Solver settings
23 Solver settings
 24 A Note on Spreadsheets The good things Lift the algebraic curtain Powerful what-if tools Can analyze, optimize, simulate, build DSS, etc. 40 million users One in every office
24 A Note on Spreadsheets The good things Lift the algebraic curtain Powerful what-if tools Can analyze, optimize, simulate, build DSS, etc. 40 million users One in every office
 25 A Note on Spreadsheets The bad things What is a formula, what is data? What feeds into what? Scalability: add a product Dimensionality: add products? Time? Excel is a powerful tool…but not the answer to every problem
25 A Note on Spreadsheets The bad things What is a formula, what is data? What feeds into what? Scalability: add a product Dimensionality: add products? Time? Excel is a powerful tool…but not the answer to every problem


