079a09ed0fb5f0bc68171c4f16f5041d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE 6. 1 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE 6. 1 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software OBJECTIVES • What computer hardware does our organization need? • What networking arrangement is best for our organization? • What software do we need to run our business, and how do we select it? • How should we acquire and manage the firm’s hardware and software assets? 6. 2 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software OBJECTIVES • What computer hardware does our organization need? • What networking arrangement is best for our organization? • What software do we need to run our business, and how do we select it? • How should we acquire and manage the firm’s hardware and software assets? 6. 2 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software Networking • • – – – • Small desktop or portable computer Server Mid size computer, ‘front-end’ Provides services to other computers over a network Mainframe – – • Large computer, ‘back-end’ processing Provides management of corporate data base Centralized Processing – • Processing done by mainframe Client-Server Computing – 6. 3 Personal Computer (PC) Splits processing between “clients” and “servers” on network Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software Networking • • – – – • Small desktop or portable computer Server Mid size computer, ‘front-end’ Provides services to other computers over a network Mainframe – – • Large computer, ‘back-end’ processing Provides management of corporate data base Centralized Processing – • Processing done by mainframe Client-Server Computing – 6. 3 Personal Computer (PC) Splits processing between “clients” and “servers” on network Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
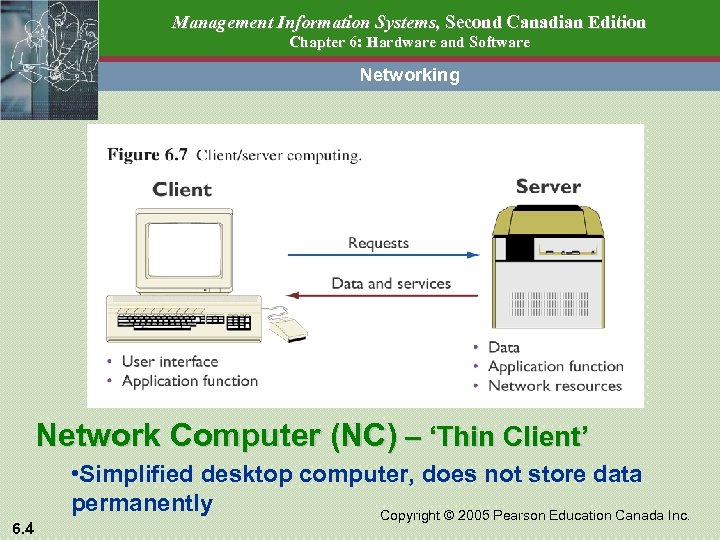 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software Networking Network Computer (NC) – ‘Thin Client’ 6. 4 • Simplified desktop computer, does not store data permanently Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software Networking Network Computer (NC) – ‘Thin Client’ 6. 4 • Simplified desktop computer, does not store data permanently Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software OBJECTIVES • What computer hardware does our organization need? • What networking arrangement is best for our organization? • What software do we need to run our business, and how do we select it? • How should we acquire and manage the firm’s hardware and software assets? 6. 5 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software OBJECTIVES • What computer hardware does our organization need? • What networking arrangement is best for our organization? • What software do we need to run our business, and how do we select it? • How should we acquire and manage the firm’s hardware and software assets? 6. 5 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE Program: • instructions to the computer System Software: • manages computer’s resources so that application software can run efficiently • eg multiprogramming, multiprocessing Application Software: • Programs to serve end users • eg MS Access 6. 6 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE Program: • instructions to the computer System Software: • manages computer’s resources so that application software can run efficiently • eg multiprogramming, multiprocessing Application Software: • Programs to serve end users • eg MS Access 6. 6 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE 6. 7 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE 6. 7 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE Operating Systems – How do they differ? • Interface – GUI - uses icons and a mouse to control OS – command-line interface – uses typed commands • Open-Source vs Proprietary Software – Proprietary – only vendor can modify – Open-source – users can modify code to improve or fix errors – if sold, vendor must give purchaser same rights • Popularity – Windows – most common PC OS – UNIX/Linux – most common web server OS – MAC OS – most popular for graphics intensive work 6. 8 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE Operating Systems – How do they differ? • Interface – GUI - uses icons and a mouse to control OS – command-line interface – uses typed commands • Open-Source vs Proprietary Software – Proprietary – only vendor can modify – Open-source – users can modify code to improve or fix errors – if sold, vendor must give purchaser same rights • Popularity – Windows – most common PC OS – UNIX/Linux – most common web server OS – MAC OS – most popular for graphics intensive work 6. 8 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE System Software and PC Operating Systems 6. 9 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE System Software and PC Operating Systems 6. 9 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE Programming Languages: • Machine Language • Consists of the 0 s and 1 s of binary code • High Level Languages • Must be ‘complied’ (translated to machine language) • eg - COBOL, C++, Visual BASIC • Programming tools designed to support the Web • HTML, XML – page formatting tools • Java - Platform-independent programming language • . NET - Microsoft business strategy aimed at convergence of personal computing and the Web 6. 10 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE Programming Languages: • Machine Language • Consists of the 0 s and 1 s of binary code • High Level Languages • Must be ‘complied’ (translated to machine language) • eg - COBOL, C++, Visual BASIC • Programming tools designed to support the Web • HTML, XML – page formatting tools • Java - Platform-independent programming language • . NET - Microsoft business strategy aimed at convergence of personal computing and the Web 6. 10 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
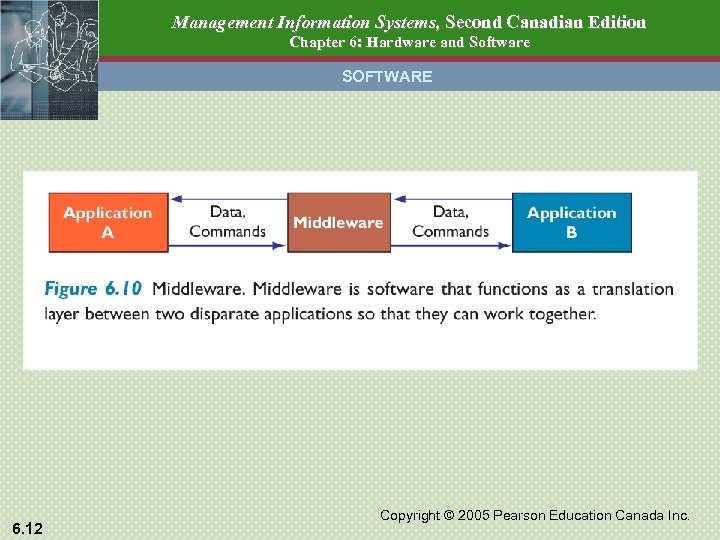
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE Types of Software Suites – Integrated Applications - eg MS Office XP – Word Processor, Spreadsheet, Database Manager Enterprise Software – Integrated modules allowing data sharing across major business functions - eg SAP Middleware • Allows two disparate applications to exchange data 6. 11 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE Types of Software Suites – Integrated Applications - eg MS Office XP – Word Processor, Spreadsheet, Database Manager Enterprise Software – Integrated modules allowing data sharing across major business functions - eg SAP Middleware • Allows two disparate applications to exchange data 6. 11 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE 6. 12 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software SOFTWARE 6. 12 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software OBJECTIVES • What computer hardware does our organization need? • What networking arrangement is best for our organization? • What software do we need to run our business, and how do we select it? • How should we acquire and manage the firm’s hardware and software assets? 6. 13 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software OBJECTIVES • What computer hardware does our organization need? • What networking arrangement is best for our organization? • What software do we need to run our business, and how do we select it? • How should we acquire and manage the firm’s hardware and software assets? 6. 13 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software MANAGING HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE ASSETS • Capacity Planning: Process of predicting the computing power needed • Scalability: Ability of a computer system to expand without breaking down • Management of TCO: total cost of owning IT resources includes: • initial cost of hardware and software • cost of maintenance, upgrades, training etc. • In-house vs Out sourcing: Use of service providers? 6. 14 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software MANAGING HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE ASSETS • Capacity Planning: Process of predicting the computing power needed • Scalability: Ability of a computer system to expand without breaking down • Management of TCO: total cost of owning IT resources includes: • initial cost of hardware and software • cost of maintenance, upgrades, training etc. • In-house vs Out sourcing: Use of service providers? 6. 14 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software MANAGING HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE ASSETS 6. 15 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software MANAGING HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE ASSETS 6. 15 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
 Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE 6. 16 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.
Management Information Systems, Second Canadian Edition Chapter 6: Hardware and Software HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE 6. 16 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc.


