4203863f961e3b61731ee3fa6c372dfb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 55
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 13 Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm ENHANCING MANAGEMENT DECISION-MAKING FOR THE DIGITAL FIRM 11. 1 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 13 Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm ENHANCING MANAGEMENT DECISION-MAKING FOR THE DIGITAL FIRM 11. 1 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm LEARNING OBJECTIVES • DIFFERENTIATE DECISIONSUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) FROM GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) • DESCRIBE COMPONENTS OF DSS & GDSS * 11. 2 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm LEARNING OBJECTIVES • DIFFERENTIATE DECISIONSUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) FROM GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) • DESCRIBE COMPONENTS OF DSS & GDSS * 11. 2 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm LEARNING OBJECTIVES • DEMONSTRATE HOW DSS & GDSS ENHANCE DECISION-MAKING • DESCRIBE CAPABILITIES OF EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) • ASSESS BENEFITS OF ESS * 11. 3 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm LEARNING OBJECTIVES • DEMONSTRATE HOW DSS & GDSS ENHANCE DECISION-MAKING • DESCRIBE CAPABILITIES OF EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) • ASSESS BENEFITS OF ESS * 11. 3 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm THE GAP USES DSS FOR MORE EFFICIENT DECISION MAKING • During the 1990 s, corporate America was obsessed with the California dress style. The Gap led the charge to outfit everyone in khaki pants and corporate casual attire. Sales rose, and the company launched Gap and Banana Republic stores overseas, opened Old Navy stores, and started selling on the Web. 11. 4 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm THE GAP USES DSS FOR MORE EFFICIENT DECISION MAKING • During the 1990 s, corporate America was obsessed with the California dress style. The Gap led the charge to outfit everyone in khaki pants and corporate casual attire. Sales rose, and the company launched Gap and Banana Republic stores overseas, opened Old Navy stores, and started selling on the Web. 11. 4 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm THE GAP USES DSS FOR MORE EFFICIENT DECISION MAKING • While Gap sales grew in 2001, net income started to fall because the inventories and merchandising at its 4, 100 stores became difficult to manage. • They could not predict how many boot-cut jeans to buy or when they should arrive at stores. They were forced to gather current and past sales information from separate planning and inventory allocation systems and analyze this information on their own. Deciding what to buy, how much and when to stock clothes was a slow and tedious process. 11. 5 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm THE GAP USES DSS FOR MORE EFFICIENT DECISION MAKING • While Gap sales grew in 2001, net income started to fall because the inventories and merchandising at its 4, 100 stores became difficult to manage. • They could not predict how many boot-cut jeans to buy or when they should arrive at stores. They were forced to gather current and past sales information from separate planning and inventory allocation systems and analyze this information on their own. Deciding what to buy, how much and when to stock clothes was a slow and tedious process. 11. 5 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm THE GAP USES DSS FOR MORE EFFICIENT DECISION MAKING • "Every item in a store is an investment. " Given the number of Gap stores, these items amounted to huge investments, so if they remain on store shelves too long, the company's return on its inventory investment is much lower. In March 2001, the Gap decided to address this problem by implementing. Retek's planning and forecasting software. • The Retek software provides a common set of tools for all activities across all divisions. 11. 6 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm THE GAP USES DSS FOR MORE EFFICIENT DECISION MAKING • "Every item in a store is an investment. " Given the number of Gap stores, these items amounted to huge investments, so if they remain on store shelves too long, the company's return on its inventory investment is much lower. In March 2001, the Gap decided to address this problem by implementing. Retek's planning and forecasting software. • The Retek software provides a common set of tools for all activities across all divisions. 11. 6 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm THE GAP USES DSS FOR MORE EFFICIENT DECISION MAKING • Using software on their desktops, merchants and planners will be able to: • See the current status of each other • Plans and forecasts so that they can collaborate and make better decisions about what to allocate, when to mark down, and how much to mark down. T • The software has clearly promoted more efficient decision making. 11. 7 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm THE GAP USES DSS FOR MORE EFFICIENT DECISION MAKING • Using software on their desktops, merchants and planners will be able to: • See the current status of each other • Plans and forecasts so that they can collaborate and make better decisions about what to allocate, when to mark down, and how much to mark down. T • The software has clearly promoted more efficient decision making. 11. 7 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm 11. 8 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm 11. 8 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) MIS • MIS primarily provide information on the firm's performance to help managers in monitoring and controlling the business. Assists in general control of the organization • They typically producefixed, regularly scheduled reportsbased on data extracted and summarized from the organization's underlying transaction processing systems (TPS). 11. 9 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) MIS • MIS primarily provide information on the firm's performance to help managers in monitoring and controlling the business. Assists in general control of the organization • They typically producefixed, regularly scheduled reportsbased on data extracted and summarized from the organization's underlying transaction processing systems (TPS). 11. 9 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm MIS • A typical MIS report might show summary of a monthly salesfor each of the major salesterritories of a company. • Sometimes MIS reports areexception reports , highlighting only exceptional conditionssuch as , when the sales quotas for a specific territory fall below an anticipated level oremployees who have exceeded their spending limit in a dental care plan. • Traditional MIS produced primarily hard copy report ( Now on the Intranet ) 11. 10 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm MIS • A typical MIS report might show summary of a monthly salesfor each of the major salesterritories of a company. • Sometimes MIS reports areexception reports , highlighting only exceptional conditionssuch as , when the sales quotas for a specific territory fall below an anticipated level oremployees who have exceeded their spending limit in a dental care plan. • Traditional MIS produced primarily hard copy report ( Now on the Intranet ) 11. 10 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm MIS Example California Pizza Kitchen • Inventory Express applicationremembers”each “ restaurant’s ordering patterns, and compares the amount of ingredientsused per menu item to predefined portion measurements established by management. • The system identifies restaurants with -of-line out portions andnotifies their management so that corrective action can be taken. 11 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm MIS Example California Pizza Kitchen • Inventory Express applicationremembers”each “ restaurant’s ordering patterns, and compares the amount of ingredientsused per menu item to predefined portion measurements established by management. • The system identifies restaurants with -of-line out portions andnotifies their management so that corrective action can be taken. 11 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS MANAGEMENT LEVEL COMPUTER SYSTEM COMBINES DATA, MODELS, USER - FRIENDLY SOFTWARE FOR SEMISTRUCTURED & UNSTRUCTURED DECISION MAKING * 11. 12 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS MANAGEMENT LEVEL COMPUTER SYSTEM COMBINES DATA, MODELS, USER - FRIENDLY SOFTWARE FOR SEMISTRUCTURED & UNSTRUCTURED DECISION MAKING * 11. 12 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS • DSS provide new sets of capabilities for nonroutinedecisions and user control. DSS emphasize change, flexibility, and rapid response. • With a DSS there is less of an effort to link users to structured information flows and a correspondinglygreater emphasison models, assumptions ad hoc queries, and , display graphics. 11. 13 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS • DSS provide new sets of capabilities for nonroutinedecisions and user control. DSS emphasize change, flexibility, and rapid response. • With a DSS there is less of an effort to link users to structured information flows and a correspondinglygreater emphasison models, assumptions ad hoc queries, and , display graphics. 11. 13 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS • Simon's description of decision making consists of four stages: • Intelligence • Design • Choice • Implementation. • DSS are intended to help design and evaluate alternatives and monitor the adoption orimplementationprocess. 11. 14 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS • Simon's description of decision making consists of four stages: • Intelligence • Design • Choice • Implementation. • DSS are intended to help design and evaluate alternatives and monitor the adoption orimplementationprocess. 11. 14 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Types of Decision-Support Systems Model-driven DSS • Primarily stand-aloneisolated from major organizational information systems • Uses model to perform “what-if” and other kinds of analysis 11. 15 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Types of Decision-Support Systems Model-driven DSS • Primarily stand-aloneisolated from major organizational information systems • Uses model to perform “what-if” and other kinds of analysis 11. 15 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Continental Airlines system for cargo revenue optimization • Continental's cargo division developed a software applicationcalled Cargo. Prof to maximize revenue from its aircraft freightcompartments. • The software ensures that Continentalsells all available freight spaceon its carriers at the most profitable price. • The system forecasts cargo capacity and sets an optimal value each night on what they need. 11. 16 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Continental Airlines system for cargo revenue optimization • Continental's cargo division developed a software applicationcalled Cargo. Prof to maximize revenue from its aircraft freightcompartments. • The software ensures that Continentalsells all available freight spaceon its carriers at the most profitable price. • The system forecasts cargo capacity and sets an optimal value each night on what they need. 11. 16 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm 11. 17 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm 11. 17 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
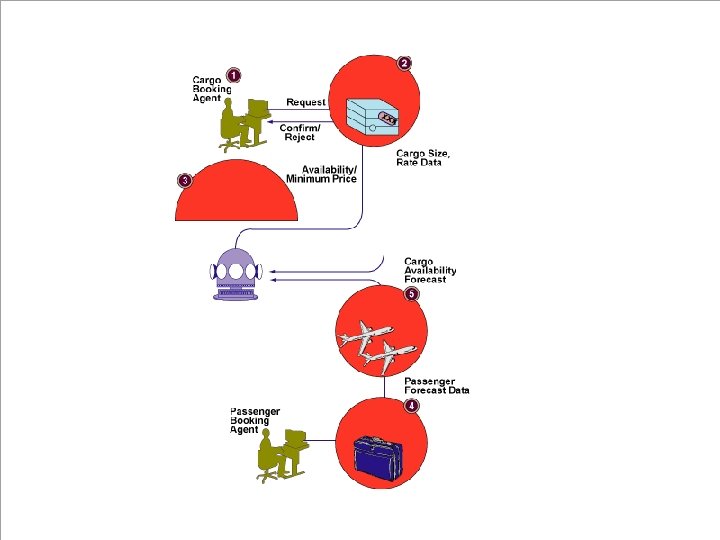
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Continental Airlines system for cargo revenue optimization • Cargo Revenue Optimization at Continental Airlines. When a booking agent (1) requests a cargo reservation the cargo , reservation system (2)passes the shipment details and customer contract rate to Cargo. Prof (3). Meanwhile, the passenger reservation system feeds a passenger forecast (4) to the flightschedule server's cargocapacity forecaster (5), which calculates expected cargo capacity each night for every flight It passes this capacity data to. Cargo. Prof, which. calculates for each flight with available cargo space the minimum prices that a booking must meet or exceed in order to be profitable. The cargo reservation system then accepts or rejects the request. Agents with rejected requests can then either try a different day or route to sell the customer into a higher rate class. 11. 18 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Continental Airlines system for cargo revenue optimization • Cargo Revenue Optimization at Continental Airlines. When a booking agent (1) requests a cargo reservation the cargo , reservation system (2)passes the shipment details and customer contract rate to Cargo. Prof (3). Meanwhile, the passenger reservation system feeds a passenger forecast (4) to the flightschedule server's cargocapacity forecaster (5), which calculates expected cargo capacity each night for every flight It passes this capacity data to. Cargo. Prof, which. calculates for each flight with available cargo space the minimum prices that a booking must meet or exceed in order to be profitable. The cargo reservation system then accepts or rejects the request. Agents with rejected requests can then either try a different day or route to sell the customer into a higher rate class. 11. 18 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DATA-DRIVEN DSS. • The second type of DSS is a data-driven DSS. These systems analyze large pools of data found in major organizational systems. • They support decision making by allowing users to extract useful information that was previously buried in large quantities of data. Often data from transaction processing systems. TPS ) are ( collected indata warehouses for this purpose. • Online analytical processing (OLAP) and datamining can then be used to analyze the data. Companies are starting to build data-driven DSS to mine customer data gathered from their Web sites as well as data from enterprise systems. 11. 19 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DATA-DRIVEN DSS. • The second type of DSS is a data-driven DSS. These systems analyze large pools of data found in major organizational systems. • They support decision making by allowing users to extract useful information that was previously buried in large quantities of data. Often data from transaction processing systems. TPS ) are ( collected indata warehouses for this purpose. • Online analytical processing (OLAP) and datamining can then be used to analyze the data. Companies are starting to build data-driven DSS to mine customer data gathered from their Web sites as well as data from enterprise systems. 11. 19 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Multidimensional analysis • Traditional database queries answer such questions as, "How many units of product 403 were shipped in November 2000? " OLAP, or multidimensionalanalysis, supports much more complex requests for information, such as, "Compare sales of product 403 relative to plan by quarter and sales region for the past two years 11. 20 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Multidimensional analysis • Traditional database queries answer such questions as, "How many units of product 403 were shipped in November 2000? " OLAP, or multidimensionalanalysis, supports much more complex requests for information, such as, "Compare sales of product 403 relative to plan by quarter and sales region for the past two years 11. 20 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) Types of Decision-Support Systems Datamining • Finds hidden patterns and relationships in large databases to infer rules • Knowledge discovery • The types of information that can be yielded from datamining include associations , sequences, classifications, clusters and , forecasts. 11. 21 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) Types of Decision-Support Systems Datamining • Finds hidden patterns and relationships in large databases to infer rules • Knowledge discovery • The types of information that can be yielded from datamining include associations , sequences, classifications, clusters and , forecasts. 11. 21 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Associations • Associationsare occurrences linked to a single event. For instance, a study of supermarket purchasing patterns might reveal that when corn chipsare purchased, a cola drink is purchased 65 percent of the time, but when there is apromotion cola is , purchased 85 percent of the time. With this information, managers can make better decisions because they have learned the profitability of a promotion. 11. 22 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Associations • Associationsare occurrences linked to a single event. For instance, a study of supermarket purchasing patterns might reveal that when corn chipsare purchased, a cola drink is purchased 65 percent of the time, but when there is apromotion cola is , purchased 85 percent of the time. With this information, managers can make better decisions because they have learned the profitability of a promotion. 11. 22 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Sequences • In sequences, events are linked over time. One might find, for example, that if a house is purchased then a new , refrigeratorwill be purchased within two weeks 65 percent of the time, and an oven will be bought within one month of the home purchase 45 percent of the time. 11. 23 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Sequences • In sequences, events are linked over time. One might find, for example, that if a house is purchased then a new , refrigeratorwill be purchased within two weeks 65 percent of the time, and an oven will be bought within one month of the home purchase 45 percent of the time. 11. 23 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Classification • Classificationrecognizes patterns that describe the groupto which an item belongs by examining existing items that have been classified and by inferring a set of rules. For example, businesses such as credit card or telephone companies worry about the loss of steady customers. Classification can help discover thecharacteristics of customers who are likely to leave and can provide a model to help managers predict who they are so that they can devise special campaigns to retain such customers. 11. 24 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Classification • Classificationrecognizes patterns that describe the groupto which an item belongs by examining existing items that have been classified and by inferring a set of rules. For example, businesses such as credit card or telephone companies worry about the loss of steady customers. Classification can help discover thecharacteristics of customers who are likely to leave and can provide a model to help managers predict who they are so that they can devise special campaigns to retain such customers. 11. 24 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Clustering • Clustering works in a manner similar to classification when no groups have yet been defined. A datamining tool will discover differentgroupings within data, such as finding affinity groups for bank cards or partitioning a database into groups of customers based on demographics and types of personal investments 11. 25 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Clustering • Clustering works in a manner similar to classification when no groups have yet been defined. A datamining tool will discover differentgroupings within data, such as finding affinity groups for bank cards or partitioning a database into groups of customers based on demographics and types of personal investments 11. 25 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
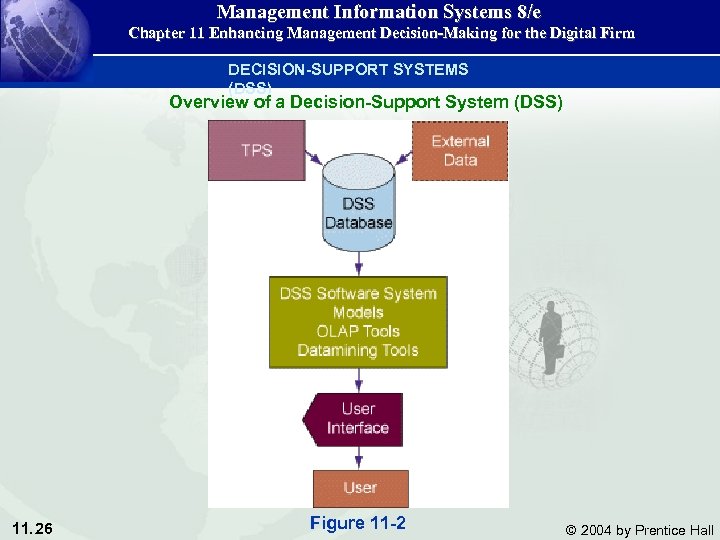 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) Overview of a Decision-Support System (DSS) 11. 26 Figure 11 -2 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) Overview of a Decision-Support System (DSS) 11. 26 Figure 11 -2 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems DSS database: The DSS database is a collection of current or historicaldata from a number of applications or groups. DSS database may be a massive data warehousethat is continuously updated by major organizational TPS (including enterprise systems and data generated by Web site transactions. ) • The data in DSS databases are generally extracts or copies of productiondatabases so that using the DSS does not interfere with critical operational systems. 11. 27 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems DSS database: The DSS database is a collection of current or historicaldata from a number of applications or groups. DSS database may be a massive data warehousethat is continuously updated by major organizational TPS (including enterprise systems and data generated by Web site transactions. ) • The data in DSS databases are generally extracts or copies of productiondatabases so that using the DSS does not interfere with critical operational systems. 11. 27 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems DSS software system • The DSS software systemcontains the software tools that are used for data analysis. • It may contain various. OLAP tools, datamining tools, or a collection of mathematical and analytical models that easily can be made accessible to the DSS user. 11. 28 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems DSS software system • The DSS software systemcontains the software tools that are used for data analysis. • It may contain various. OLAP tools, datamining tools, or a collection of mathematical and analytical models that easily can be made accessible to the DSS user. 11. 28 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
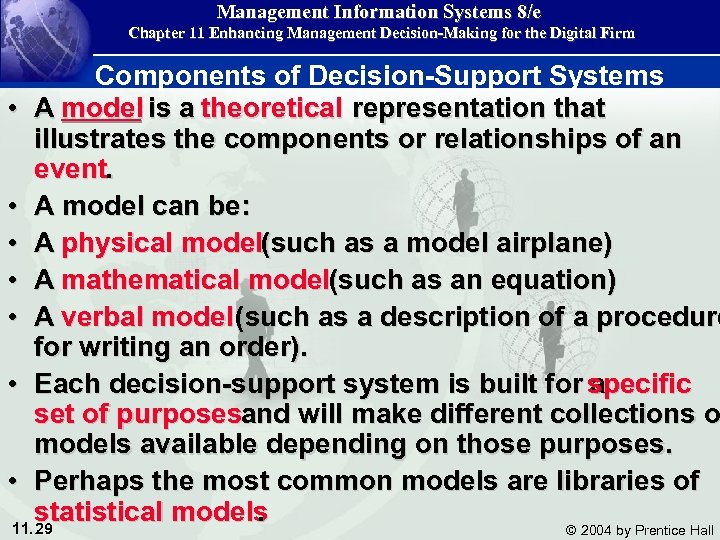 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems • A model is a theoretical representation that illustrates the components or relationships of an event. • A model can be: • A physical model(such as a model airplane) • A mathematical model(such as an equation) • A verbal model (such as a description of a procedure for writing an order). • Each decision-support system is built for specific a set of purposesand will make different collections o models available depending on those purposes. • Perhaps the most common models are libraries of statistical models. 11. 29 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems • A model is a theoretical representation that illustrates the components or relationships of an event. • A model can be: • A physical model(such as a model airplane) • A mathematical model(such as an equation) • A verbal model (such as a description of a procedure for writing an order). • Each decision-support system is built for specific a set of purposesand will make different collections o models available depending on those purposes. • Perhaps the most common models are libraries of statistical models. 11. 29 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems Sensitivity analysis • Among the most widely used models are sensitivity analysis models that ask " what-if" questions repeatedly to determine the impact of changes in one or more factors on outcomes. • Backward sensitivity analysis software is used for goal seeking If I want to sell one : million product units next year, how much must I reduce the price of the product? 11. 30 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems Sensitivity analysis • Among the most widely used models are sensitivity analysis models that ask " what-if" questions repeatedly to determine the impact of changes in one or more factors on outcomes. • Backward sensitivity analysis software is used for goal seeking If I want to sell one : million product units next year, how much must I reduce the price of the product? 11. 30 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
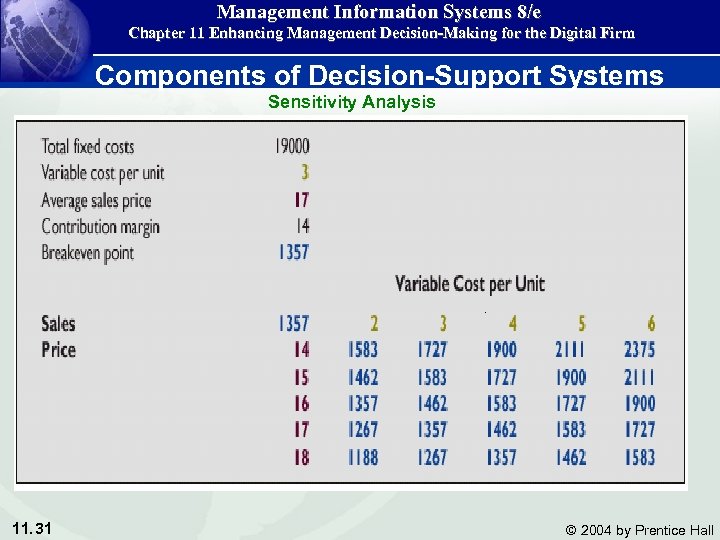 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems Sensitivity Analysis 11. 31 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems Sensitivity Analysis 11. 31 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems User Interface • The DSS user interface permits easy interactionbetween users of the system and the. DSS software tools A. graphic, easy-to-use, flexible user interface supports the dialogue between the user and the DSS. 11. 32 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Components of Decision-Support Systems User Interface • The DSS user interface permits easy interactionbetween users of the system and the. DSS software tools A. graphic, easy-to-use, flexible user interface supports the dialogue between the user and the DSS. 11. 32 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS Applications and the Digital Firm 1. DSS for Supply Chain Management 2. DSS for Customer Relationship Management 3. Data Visualization and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) 11. 33 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS Applications and the Digital Firm 1. DSS for Supply Chain Management 2. DSS for Customer Relationship Management 3. Data Visualization and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) 11. 33 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS Applications and the Digital Firm • General Accident Insurance: Customer buying patterns and fraud detection • Bank of America: Customer profiles • United Airlines: Flight scheduling, passenger demand forecasting 11. 34 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS Applications and the Digital Firm • General Accident Insurance: Customer buying patterns and fraud detection • Bank of America: Customer profiles • United Airlines: Flight scheduling, passenger demand forecasting 11. 34 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS for Supply Chain Management • Supply chain decisions involve determining "who, what, when, and where" frompurchasingand transportingmaterials and parts through manufacturingproducts anddistributingand delivering those products to customers. • Supply chain management systems contain data about • Inventory • Supplier performance • Logistics of materials • Finished goods. 11. 35 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS for Supply Chain Management • Supply chain decisions involve determining "who, what, when, and where" frompurchasingand transportingmaterials and parts through manufacturingproducts anddistributingand delivering those products to customers. • Supply chain management systems contain data about • Inventory • Supplier performance • Logistics of materials • Finished goods. 11. 35 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS for Supply Chain Management • DSS can draw on previous data to help managers examine this complex chain comprehensively and search among a huge number of alternatives for the combinations that are most efficientand cost-effective. • The prime management goal might be to reduce overall costswhile increasing the speed and accuracyof filling customer orders. 11. 36 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS for Supply Chain Management • DSS can draw on previous data to help managers examine this complex chain comprehensively and search among a huge number of alternatives for the combinations that are most efficientand cost-effective. • The prime management goal might be to reduce overall costswhile increasing the speed and accuracyof filling customer orders. 11. 36 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS for Supply Chain Management 1. Comprehensive examination of supply management chain 2. Searches for most efficient and costeffective combination 3. Reduces overall costs 4. Increases speed and accuracy of filling customer orders 11. 37 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS for Supply Chain Management 1. Comprehensive examination of supply management chain 2. Searches for most efficient and costeffective combination 3. Reduces overall costs 4. Increases speed and accuracy of filling customer orders 11. 37 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Example of DSS for SCM • The IBM Personal Systems Group (PSG) used AMT to reduce supply chain costs to cope with the large volumes dropping prices and slim profit , , margins in the personal computer market PSG. was able to reduce overall inventory by over 50 percent in 1997 and 1998. • The system helped PSG reduce payments made to distributorsand resellers to compensate for product price reductions by more than $750 million in 1998. • PSG's cycle time from component procurement to product salewas reduced byfour to sixweeks, bringing reductions of to 7 percent in overall 5 product cost. 11. 38 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Example of DSS for SCM • The IBM Personal Systems Group (PSG) used AMT to reduce supply chain costs to cope with the large volumes dropping prices and slim profit , , margins in the personal computer market PSG. was able to reduce overall inventory by over 50 percent in 1997 and 1998. • The system helped PSG reduce payments made to distributorsand resellers to compensate for product price reductions by more than $750 million in 1998. • PSG's cycle time from component procurement to product salewas reduced byfour to sixweeks, bringing reductions of to 7 percent in overall 5 product cost. 11. 38 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS for Customer Relationship Management • Uses data mining to guide decisions • Consolidates customer information into massive data warehouses • Uses various analytical tools to slice information into small segments 11. 39 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DSS for Customer Relationship Management • Uses data mining to guide decisions • Consolidates customer information into massive data warehouses • Uses various analytical tools to slice information into small segments 11. 39 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
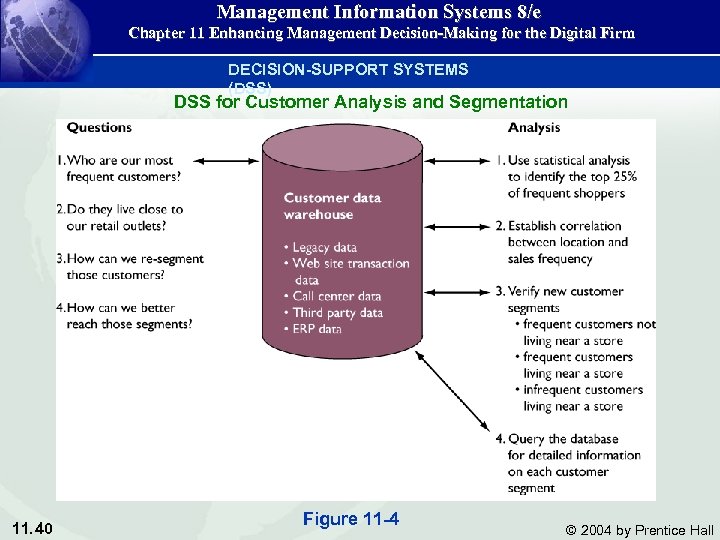 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) DSS for Customer Analysis and Segmentation 11. 40 Figure 11 -4 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) DSS for Customer Analysis and Segmentation 11. 40 Figure 11 -4 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm • • • 11. 41 Example DSS for CRM Royal Bank of Canada has developed a DSS for customer segmentation that can tailor messagesto very small groups of people and offer them products, services, and prices that are more likely to appeal to them. This DSS consolidates data from various systems in the organization into a data warehouse. The Royal Bank's main customer database is its marketing information file (MIF) which also contains data from every document a customer fills out as well as data fromchecking accounts credit , cards, and the Royal Bank'senterprise and billing systems. © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm • • • 11. 41 Example DSS for CRM Royal Bank of Canada has developed a DSS for customer segmentation that can tailor messagesto very small groups of people and offer them products, services, and prices that are more likely to appeal to them. This DSS consolidates data from various systems in the organization into a data warehouse. The Royal Bank's main customer database is its marketing information file (MIF) which also contains data from every document a customer fills out as well as data fromchecking accounts credit , cards, and the Royal Bank'senterprise and billing systems. © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Data Visualization and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) • Data from information systems can be made easier for users to digest and act upon by using charts, tables, graphs, maps, digital images three, dimensional presentationsanimations , . • By presenting data in graphical form, data visualizationtools help users see patterns and relationships in large amounts of data that would be difficult to discern if the data were presented as traditionallists of text. • Some data visualization tools are interactive , allowing users tomanipulate data and see the graphical displays changein response to the changes they make. 11. 42 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Data Visualization and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) • Data from information systems can be made easier for users to digest and act upon by using charts, tables, graphs, maps, digital images three, dimensional presentationsanimations , . • By presenting data in graphical form, data visualizationtools help users see patterns and relationships in large amounts of data that would be difficult to discern if the data were presented as traditionallists of text. • Some data visualization tools are interactive , allowing users tomanipulate data and see the graphical displays changein response to the changes they make. 11. 42 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Data Visualization and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) • They are a special categoryof DSS that use data visualizationtechnology to analyze and display data for planning and decision making in the form ofdigitized maps. • The software can assemble, store, manipulate, and displaygeographically referenced information tying data to points, , lines, and areas on a map. 11. 43 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Data Visualization and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) • They are a special categoryof DSS that use data visualizationtechnology to analyze and display data for planning and decision making in the form ofdigitized maps. • The software can assemble, store, manipulate, and displaygeographically referenced information tying data to points, , lines, and areas on a map. 11. 43 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Geographic Information Systems (GIS) • Sonny's Bar-B-Q, the Gainesville, Florida-based restaurant chain used GIS with federal and local , survey data on median age, household income, total population, and population distributionto help management decide where to open new restaurants. • The company's growth planspecifies that it will only expand into regions where barbecue foodis very popular but where the number of barbecue restaurants is very small. • Sonny's restaurants must also be at least seven miles away from each other. 11. 44 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Geographic Information Systems (GIS) • Sonny's Bar-B-Q, the Gainesville, Florida-based restaurant chain used GIS with federal and local , survey data on median age, household income, total population, and population distributionto help management decide where to open new restaurants. • The company's growth planspecifies that it will only expand into regions where barbecue foodis very popular but where the number of barbecue restaurants is very small. • Sonny's restaurants must also be at least seven miles away from each other. 11. 44 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) Web-Based Customer Decision-Support Systems (CDSS) • DSS based on the Web and the Internet can support decision making, by providing online accessto various databases and informationpools along with software for data analysis. • Some of these DSS are targeted toward management, but many have been developed to attract customersby providing information and tools to assist their decision making as they select products and services. 11. 45 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (DSS) Web-Based Customer Decision-Support Systems (CDSS) • DSS based on the Web and the Internet can support decision making, by providing online accessto various databases and informationpools along with software for data analysis. • Some of these DSS are targeted toward management, but many have been developed to attract customersby providing information and tools to assist their decision making as they select products and services. 11. 45 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Web-Based Customer Decision-Support Systems • People are now using more information from multiple sources to make purchasing decisions (such as purchasing a car or computer) before they interact with the product or sales staff. • People interested in purchasing a product or service can use Internetsearch engines , online catalogs Web directories newsgroup , , discussions e-mail, and other tools to help , them locate the information they need to help with their decision. 11. 46 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Web-Based Customer Decision-Support Systems • People are now using more information from multiple sources to make purchasing decisions (such as purchasing a car or computer) before they interact with the product or sales staff. • People interested in purchasing a product or service can use Internetsearch engines , online catalogs Web directories newsgroup , , discussions e-mail, and other tools to help , them locate the information they need to help with their decision. 11. 46 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Example Web-Based Customer Decision-Support Systems Homes. com • Provides a nationwide listing of homes for sale, apartments for rent, and mortgages available. Visitors can find out what mortgages they qualify for and calculate the maximum mortgage they can afford and alternative monthly mortgage payments. They can also use tools to help them determine whether they should rent or buy. 11. 47 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm Example Web-Based Customer Decision-Support Systems Homes. com • Provides a nationwide listing of homes for sale, apartments for rent, and mortgages available. Visitors can find out what mortgages they qualify for and calculate the maximum mortgage they can afford and alternative monthly mortgage payments. They can also use tools to help them determine whether they should rent or buy. 11. 47 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) What Is a GDSS • Interactive computer-based system • Facilitates solution to unstructured problems • Set of decision makers working together as a group 11. 48 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) What Is a GDSS • Interactive computer-based system • Facilitates solution to unstructured problems • Set of decision makers working together as a group 11. 48 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) • Groupware and Web-based tools for videoconferencing and electronic meetings can support some group decision processes, but their focus is primarily on communication. • GDSS, however, provide tools and technologies geared explicitly toward group decision making and were developed in response to a growing concern over the quality and effectiveness of meetings. 11. 49 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) • Groupware and Web-based tools for videoconferencing and electronic meetings can support some group decision processes, but their focus is primarily on communication. • GDSS, however, provide tools and technologies geared explicitly toward group decision making and were developed in response to a growing concern over the quality and effectiveness of meetings. 11. 49 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) • Problems in group decision making: 1. Decision-maker meetings • The growing length of those meetings • The increased number ofattendees. Estimates on the amount of a manager's time spent in meetings range from 35 percent to 70 percent. 11. 50 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) • Problems in group decision making: 1. Decision-maker meetings • The growing length of those meetings • The increased number ofattendees. Estimates on the amount of a manager's time spent in meetings range from 35 percent to 70 percent. 11. 50 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) Characteristics of GDSS • Hardware: Conference facility, electronic hardware • Software tools: Tools for organizing ideas, gathering information, and ranking and seeking priorities • People: Participants, trained facilitator, staff supporting hardware and software 11. 51 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) Characteristics of GDSS • Hardware: Conference facility, electronic hardware • Software tools: Tools for organizing ideas, gathering information, and ranking and seeking priorities • People: Participants, trained facilitator, staff supporting hardware and software 11. 51 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) GDSS Software Tools • Electronic questionnaires: the organizers in preaid meeting planning by identifying issues of concern and by helping to ensure that key planning informationis not overlooked. • Electronic brainstorming tools: allow individuals , simultaneouslyand anonymously to contribute , ideas on the topics of the meeting. • Idea organizers: facilitate the organized integration and mixing of ideas generated during brainstorming • 11. 52 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) GDSS Software Tools • Electronic questionnaires: the organizers in preaid meeting planning by identifying issues of concern and by helping to ensure that key planning informationis not overlooked. • Electronic brainstorming tools: allow individuals , simultaneouslyand anonymously to contribute , ideas on the topics of the meeting. • Idea organizers: facilitate the organized integration and mixing of ideas generated during brainstorming • 11. 52 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm • Questionnaire tools: support thefacilitatorsand group leaders as they gather information before and during the process of setting priorities. • Tools for voting: or setting priorities make available a range of methods from simple voting, to ranking in order, to a range of weighted techniques for setting priorities or voting. • Stakeholder identification: evaluate the impact of an emerging proposal on the organization and to identify stakeholders and evaluate the potential impact of those stakeholders on the proposed project. • Group dictionaries: document group agreement on definitions of words and terms central to the project. • People: refers not only to the participants but also to a trained facilitator and often to a staff that supports the hardware and software. 11. 53 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm • Questionnaire tools: support thefacilitatorsand group leaders as they gather information before and during the process of setting priorities. • Tools for voting: or setting priorities make available a range of methods from simple voting, to ranking in order, to a range of weighted techniques for setting priorities or voting. • Stakeholder identification: evaluate the impact of an emerging proposal on the organization and to identify stakeholders and evaluate the potential impact of those stakeholders on the proposed project. • Group dictionaries: document group agreement on definitions of words and terms central to the project. • People: refers not only to the participants but also to a trained facilitator and often to a staff that supports the hardware and software. 11. 53 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) How GDSS can Enhance Group Decision-Making • Improved preplanning • Increased participation • Open, collaborative meeting atmosphere • Criticism-free idea generation • Evaluation objectivity 11. 54 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm GROUP DECISION-SUPPORT SYSTEMS (GDSS) How GDSS can Enhance Group Decision-Making • Improved preplanning • Increased participation • Open, collaborative meeting atmosphere • Criticism-free idea generation • Evaluation objectivity 11. 54 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
 Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm ENHANCING MANAGEMENT DECISION-MAKING FOR THE DIGITAL FIRM 11. 55 © 2004 by Prentice Hall
Management Information Systems 8/e Chapter 11 Enhancing Management Decision-Making for the Digital Firm ENHANCING MANAGEMENT DECISION-MAKING FOR THE DIGITAL FIRM 11. 55 © 2004 by Prentice Hall


