719457c6c7d415e5b276f2c8de944f14.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 MANAGEMENT 1 st E D I T I O N Gulati | Mayo | Nohria Chapter 11 ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE ORGANIZATIONAL PERSPECTIVE ©South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning Power. Point Presentation by Charlie Cook
MANAGEMENT 1 st E D I T I O N Gulati | Mayo | Nohria Chapter 11 ORGANIZATIONAL CHANGE ORGANIZATIONAL PERSPECTIVE ©South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning Power. Point Presentation by Charlie Cook
 Learning Objectives • Describe the processes and activities that organizations go through to adapt or transform themselves • Outline the key drivers of change including those stemming from the external and internal environments of an organization • Differentiate between the different approaches to organizational change including proactive versus reactive, planned versus organic, and incremental versus transformative © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 2
Learning Objectives • Describe the processes and activities that organizations go through to adapt or transform themselves • Outline the key drivers of change including those stemming from the external and internal environments of an organization • Differentiate between the different approaches to organizational change including proactive versus reactive, planned versus organic, and incremental versus transformative © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 2
 Learning Objectives • Describe the change process and the key elements that comprise it • Explain how organizations and change leaders combat resistance to change © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 3
Learning Objectives • Describe the change process and the key elements that comprise it • Explain how organizations and change leaders combat resistance to change © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 3
 Organizational Change Consists of the processes and activities that organizations go through to adapt or transform themselves according to internal or external phenomena or according to future potential opportunities © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 4
Organizational Change Consists of the processes and activities that organizations go through to adapt or transform themselves according to internal or external phenomena or according to future potential opportunities © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 4
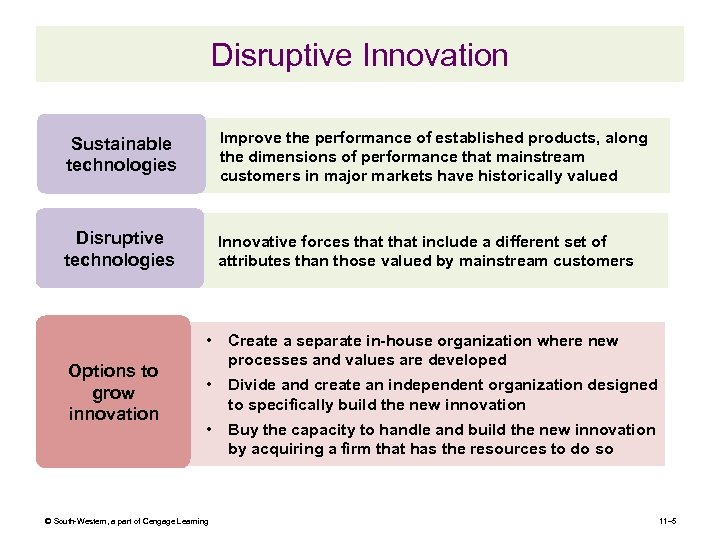 Disruptive Innovation Sustainable technologies Improve the performance of established products, along the dimensions of performance that mainstream customers in major markets have historically valued Disruptive technologies Innovative forces that include a different set of attributes than those valued by mainstream customers • Options to grow innovation Create a separate in-house organization where new processes and values are developed • Divide and create an independent organization designed to specifically build the new innovation • Buy the capacity to handle and build the new innovation by acquiring a firm that has the resources to do so © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 5
Disruptive Innovation Sustainable technologies Improve the performance of established products, along the dimensions of performance that mainstream customers in major markets have historically valued Disruptive technologies Innovative forces that include a different set of attributes than those valued by mainstream customers • Options to grow innovation Create a separate in-house organization where new processes and values are developed • Divide and create an independent organization designed to specifically build the new innovation • Buy the capacity to handle and build the new innovation by acquiring a firm that has the resources to do so © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 5
 Change Driven by the Internal Environment Inertia: The inability of organizations to change as rapidly as the environment © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 6
Change Driven by the Internal Environment Inertia: The inability of organizations to change as rapidly as the environment © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 6
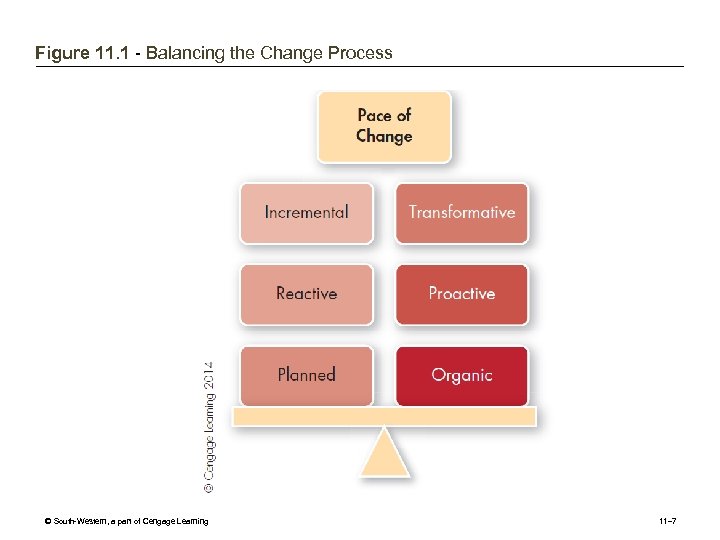 Figure 11. 1 - Balancing the Change Process © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 7
Figure 11. 1 - Balancing the Change Process © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 7
 Types of Organizational Change A process where change efforts are planned and driven from corporate strategy departments or topdown directives Planned change Organic change A process by which change emerges from individuals or teams as they innovate, solve problems, seek more effective ways to accomplish their work, react to large environmental shifts, or interact with others in crossfunctional positions © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 8
Types of Organizational Change A process where change efforts are planned and driven from corporate strategy departments or topdown directives Planned change Organic change A process by which change emerges from individuals or teams as they innovate, solve problems, seek more effective ways to accomplish their work, react to large environmental shifts, or interact with others in crossfunctional positions © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 8
 Types of Organizational Change Reactive change A process in which change is initiated in response to some known external threat or opportunity Proactive change A process in which change is initiated based on some anticipatory event or opportunity on the horizon Incremental change A process in which small improvements or changes are made to processes and approaches on an ongoing basis Transformative change A process in which change is radical or disruptive, typically in response to a major competitive threat and/or significant change in the external or internal environments © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 9
Types of Organizational Change Reactive change A process in which change is initiated in response to some known external threat or opportunity Proactive change A process in which change is initiated based on some anticipatory event or opportunity on the horizon Incremental change A process in which small improvements or changes are made to processes and approaches on an ongoing basis Transformative change A process in which change is radical or disruptive, typically in response to a major competitive threat and/or significant change in the external or internal environments © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 9
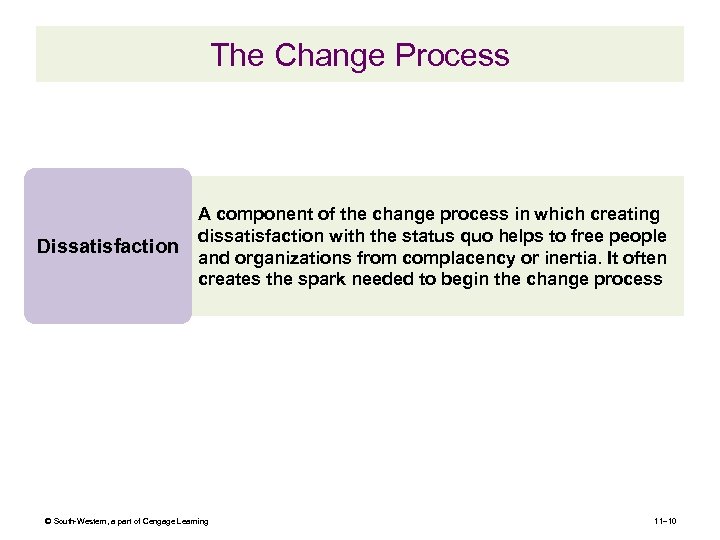 The Change Process Dissatisfaction A component of the change process in which creating dissatisfaction with the status quo helps to free people and organizations from complacency or inertia. It often creates the spark needed to begin the change process © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 10
The Change Process Dissatisfaction A component of the change process in which creating dissatisfaction with the status quo helps to free people and organizations from complacency or inertia. It often creates the spark needed to begin the change process © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 10
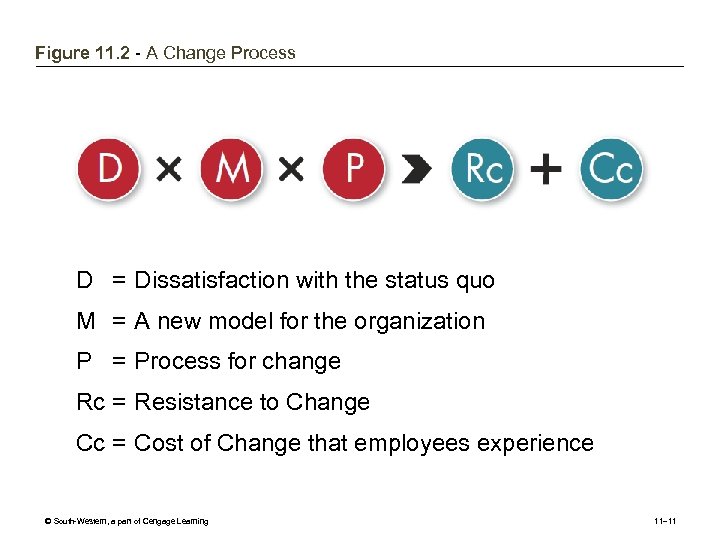 Figure 11. 2 - A Change Process D = Dissatisfaction with the status quo M = A new model for the organization P = Process for change Rc = Resistance to Change Cc = Cost of Change that employees experience © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 11
Figure 11. 2 - A Change Process D = Dissatisfaction with the status quo M = A new model for the organization P = Process for change Rc = Resistance to Change Cc = Cost of Change that employees experience © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 11
 Developing a New Model for the Future • Model: A vision for change • Change model – Tells clearly what is being changed and why – Offers employees hope and a higher sense of meaning – Fits with the firm’s expected contextual landscape • Communicating the model requires: – An appeal to both logic and emotions – Making a compelling case for change based on benchmarking © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 12
Developing a New Model for the Future • Model: A vision for change • Change model – Tells clearly what is being changed and why – Offers employees hope and a higher sense of meaning – Fits with the firm’s expected contextual landscape • Communicating the model requires: – An appeal to both logic and emotions – Making a compelling case for change based on benchmarking © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 12
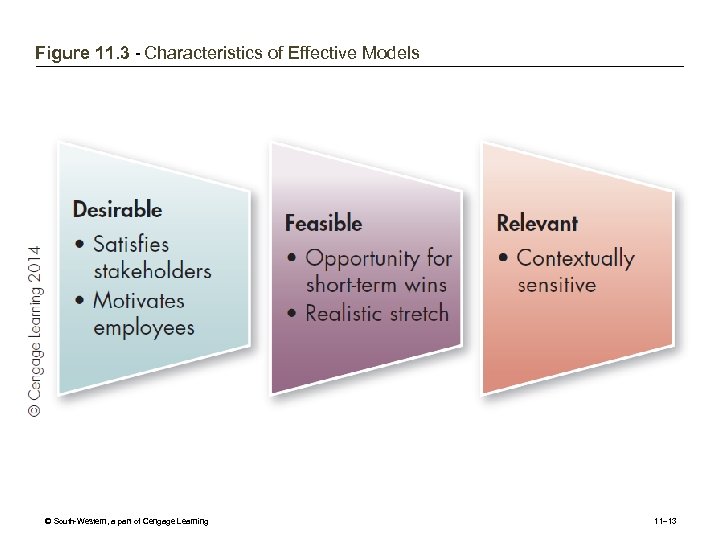 Figure 11. 3 - Characteristics of Effective Models © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 13
Figure 11. 3 - Characteristics of Effective Models © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 13
 The Implementation Process: Steps to Success • Process: A series of plans and approaches to implement a change effort • Establish a sense of urgency and form a powerful guiding coalition • Develop a vision and communicate it • Empower others to act on the vision • Plan for and create short-term wins • Consolidate improvements and produce more changes • Institutionalize changes in the culture © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 14
The Implementation Process: Steps to Success • Process: A series of plans and approaches to implement a change effort • Establish a sense of urgency and form a powerful guiding coalition • Develop a vision and communicate it • Empower others to act on the vision • Plan for and create short-term wins • Consolidate improvements and produce more changes • Institutionalize changes in the culture © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 14
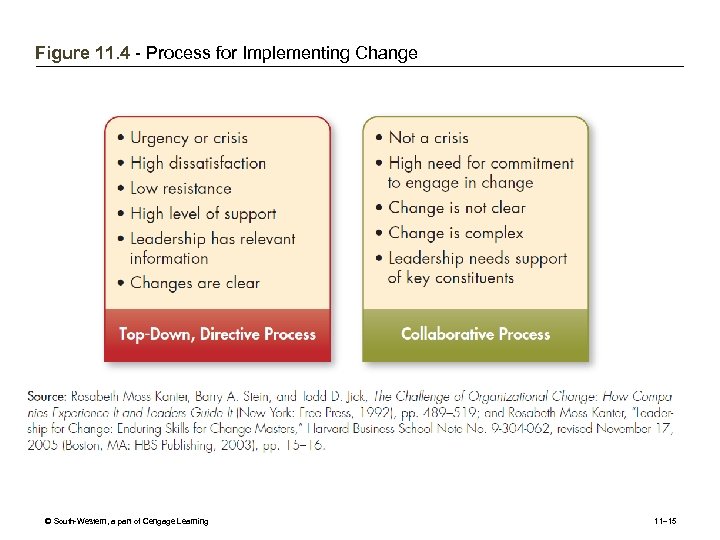 Figure 11. 4 - Process for Implementing Change © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 15
Figure 11. 4 - Process for Implementing Change © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 15
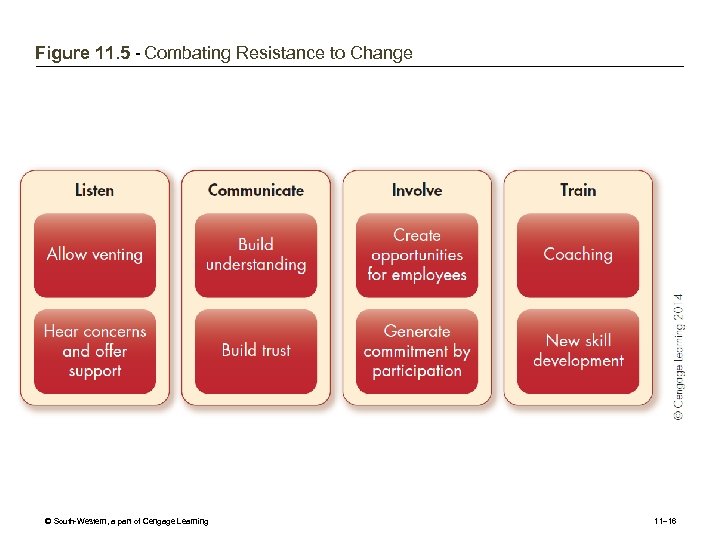 Figure 11. 5 - Combating Resistance to Change © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 16
Figure 11. 5 - Combating Resistance to Change © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 16
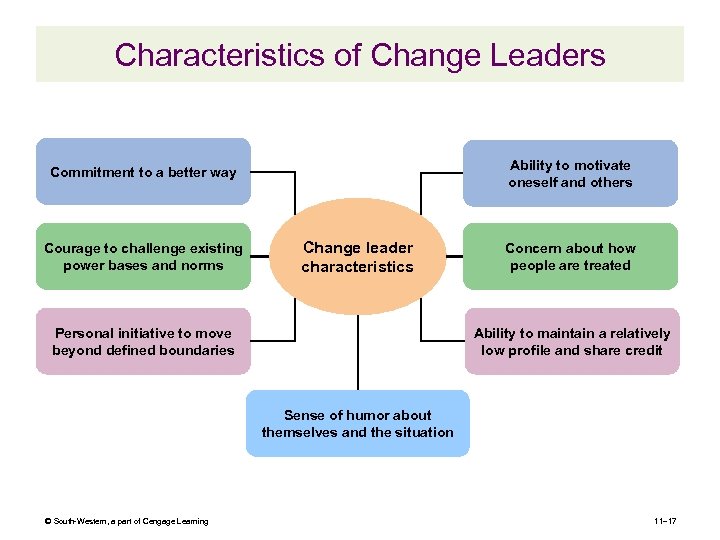 Characteristics of Change Leaders Ability to motivate oneself and others Commitment to a better way Courage to challenge existing power bases and norms Change leader characteristics Personal initiative to move beyond defined boundaries Concern about how people are treated Ability to maintain a relatively low profile and share credit Sense of humor about themselves and the situation © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 17
Characteristics of Change Leaders Ability to motivate oneself and others Commitment to a better way Courage to challenge existing power bases and norms Change leader characteristics Personal initiative to move beyond defined boundaries Concern about how people are treated Ability to maintain a relatively low profile and share credit Sense of humor about themselves and the situation © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning 11– 17
 KEY TERMS Disruptive technologies Dissatisfaction Incremental change Inertia Model Organic change © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning Organizational change Planned change Proactive change Process Reactive change Transformative change 11– 18
KEY TERMS Disruptive technologies Dissatisfaction Incremental change Inertia Model Organic change © South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning Organizational change Planned change Proactive change Process Reactive change Transformative change 11– 18


