b973590c22ab4eb15765081ba3d5037e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Making Foreign and Defense Policy § Understanding Foreign and Defense Policy § The Foreign Policy and Defense Agenda § The Foreign Policy and Defense Bureaucracy § Foreign Policy and Defense Options
Making Foreign and Defense Policy § Understanding Foreign and Defense Policy § The Foreign Policy and Defense Agenda § The Foreign Policy and Defense Bureaucracy § Foreign Policy and Defense Options
 Making Foreign and Defense Policy Understanding Foreign Policy and Defense • Approaches to U. S. foreign policy and defense. The Foreign Policy and Defense Agenda • Status of each of the issues that currently dominate the foreign policy and defense agenda The Foreign Policy and Defense Bureaucracy • Structure of the foreign policy and defense bureaucracy. Foreign Policy and Defense Options • Options for achieving foreign policy and defense goals.
Making Foreign and Defense Policy Understanding Foreign Policy and Defense • Approaches to U. S. foreign policy and defense. The Foreign Policy and Defense Agenda • Status of each of the issues that currently dominate the foreign policy and defense agenda The Foreign Policy and Defense Bureaucracy • Structure of the foreign policy and defense bureaucracy. Foreign Policy and Defense Options • Options for achieving foreign policy and defense goals.
 Understanding Foreign Policy • Realism vs. Idealism o the belief that other nations are interested first and foremost in their own advancement and in strengthening their own power o the belief that nations can work together to solve common problems such as global hunger and poverty with peace, not war, as the ultimate aim • Isolationism vs. Internationalism o the belief that the U. S. should stay out of international affairs unless other nations constitute a direct threat to its existence o the belief that the U. S. must be engaged in international affairs to protect its own interests
Understanding Foreign Policy • Realism vs. Idealism o the belief that other nations are interested first and foremost in their own advancement and in strengthening their own power o the belief that nations can work together to solve common problems such as global hunger and poverty with peace, not war, as the ultimate aim • Isolationism vs. Internationalism o the belief that the U. S. should stay out of international affairs unless other nations constitute a direct threat to its existence o the belief that the U. S. must be engaged in international affairs to protect its own interests
 Understanding Foreign Policy • Unilateralism vs. Multilateralism o belief that the U. S. has the right to act alone in response to threats even without other nations’ help o belief that the U. S. should act only with the active support of other nations • Preemption vs. Provocation o Argument that the U. S. can attack first when it believes another nation constitutes a serious threat o Argument that the U. S. needs to wait to be provoked • Hard Power vs. Soft Power o Military and economic strength o Negotiation and diplomacy
Understanding Foreign Policy • Unilateralism vs. Multilateralism o belief that the U. S. has the right to act alone in response to threats even without other nations’ help o belief that the U. S. should act only with the active support of other nations • Preemption vs. Provocation o Argument that the U. S. can attack first when it believes another nation constitutes a serious threat o Argument that the U. S. needs to wait to be provoked • Hard Power vs. Soft Power o Military and economic strength o Negotiation and diplomacy
 The Foreign Policy & Defense Bureaucracy Seven Major Issues of Foreign Policy • Controlling Weapons of Mass Destruction • Ending the Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan • Fighting Terrorism • Negotiating Peace in the Middle East • Promoting Free Trade Abroad • Reducing Global Warming • Strengthening Democracy
The Foreign Policy & Defense Bureaucracy Seven Major Issues of Foreign Policy • Controlling Weapons of Mass Destruction • Ending the Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan • Fighting Terrorism • Negotiating Peace in the Middle East • Promoting Free Trade Abroad • Reducing Global Warming • Strengthening Democracy
 The Foreign Policy and Defense Agenda Foreign Policy and Defense Bureaucracy • Department of State o Staffing the Diplomatic System • National Security Council • Intelligence Community o 15 agencies o Central Intelligence Agency • Department of Defense o Joint Chiefs of Staff The Pentagon - headquarters of the U. S. DOD and employs about 23, 000 military and civilian personnel.
The Foreign Policy and Defense Agenda Foreign Policy and Defense Bureaucracy • Department of State o Staffing the Diplomatic System • National Security Council • Intelligence Community o 15 agencies o Central Intelligence Agency • Department of Defense o Joint Chiefs of Staff The Pentagon - headquarters of the U. S. DOD and employs about 23, 000 military and civilian personnel.
 The State Department Responsible for the diplomatic realm of foreign and defense policy n. Negotiates treaties n. Protects U. S. citizens abroad n. Promotes U. S. commercial interests n. Grants visas The National Security Council n. Created by Congress in 1947 n. Traditionally consists of the president, vice president, secretary of state, and secretary of defense
The State Department Responsible for the diplomatic realm of foreign and defense policy n. Negotiates treaties n. Protects U. S. citizens abroad n. Promotes U. S. commercial interests n. Grants visas The National Security Council n. Created by Congress in 1947 n. Traditionally consists of the president, vice president, secretary of state, and secretary of defense
 The Central Intelligence Agency and the Intelligence Community Created in 1947 to coordinate the gathering and analysis of information that flows into various parts of the U. S. government from all around the world n. Reporting n. Research n. Dissemination The Department of Defense n Pre-1947 n War Department and Department of the Navy n National Security Act of 1947 n Established the offices of the Secretary of Defense and chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and created a National Military Establishment (Department of Defense)
The Central Intelligence Agency and the Intelligence Community Created in 1947 to coordinate the gathering and analysis of information that flows into various parts of the U. S. government from all around the world n. Reporting n. Research n. Dissemination The Department of Defense n Pre-1947 n War Department and Department of the Navy n National Security Act of 1947 n Established the offices of the Secretary of Defense and chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and created a National Military Establishment (Department of Defense)
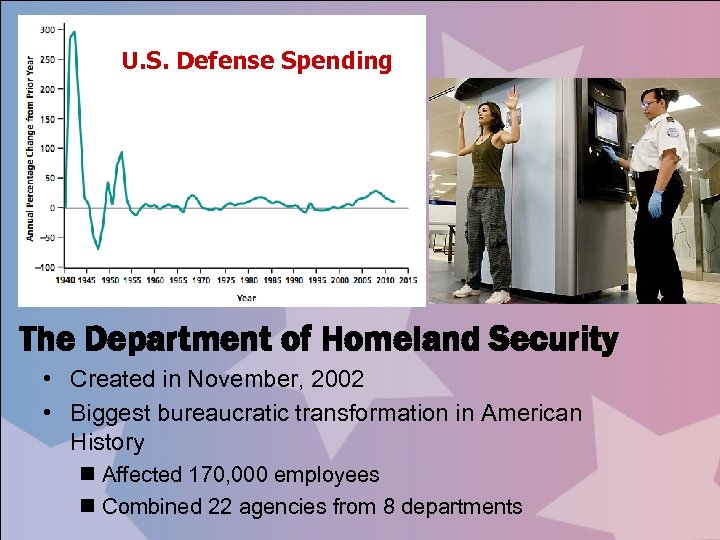 U. S. Defense Spending The Department of Homeland Security • Created in November, 2002 • Biggest bureaucratic transformation in American History n Affected 170, 000 employees n Combined 22 agencies from 8 departments
U. S. Defense Spending The Department of Homeland Security • Created in November, 2002 • Biggest bureaucratic transformation in American History n Affected 170, 000 employees n Combined 22 agencies from 8 departments
 Foreign Policy and Defense Options Soft Power • Conventional Diplomacy o United Nations • Public Diplomacy o Propaganda techniques blended with modern information warfare • Foreign Aid Hard Power • Economic Sanctions - Denial of export, import, or financial relations with a target country in an effort to change that nation’s policies • Military Intervention
Foreign Policy and Defense Options Soft Power • Conventional Diplomacy o United Nations • Public Diplomacy o Propaganda techniques blended with modern information warfare • Foreign Aid Hard Power • Economic Sanctions - Denial of export, import, or financial relations with a target country in an effort to change that nation’s policies • Military Intervention
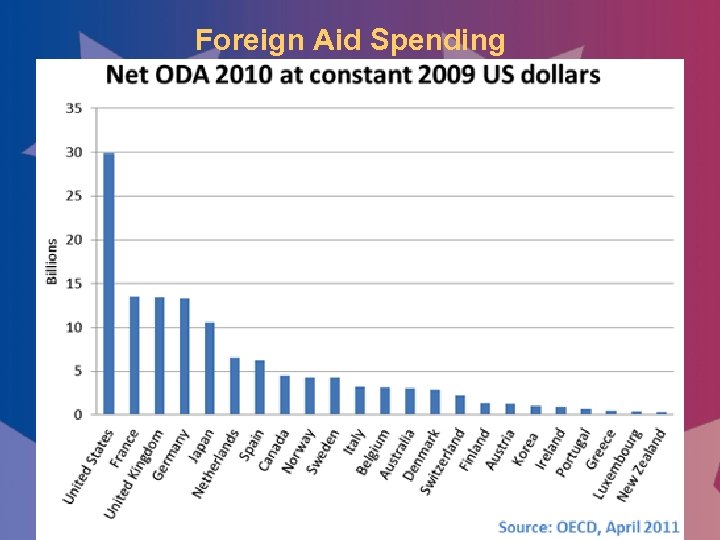 Foreign Aid Spending
Foreign Aid Spending
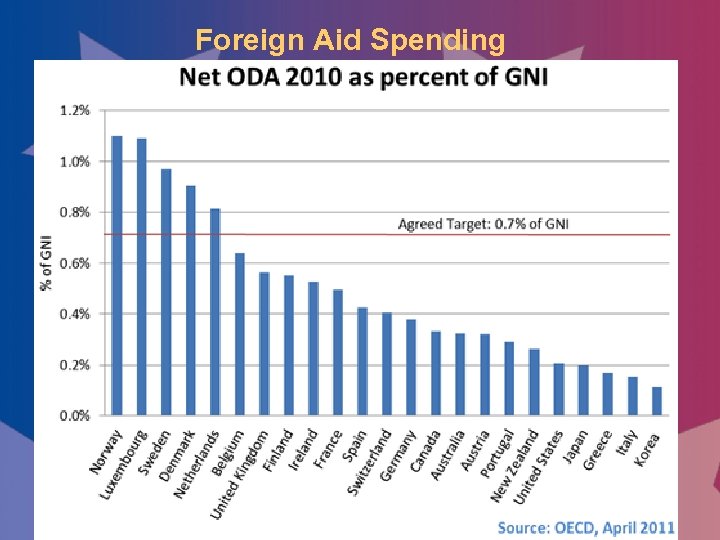 Foreign Aid Spending
Foreign Aid Spending
 Making Foreign and Defense Policy n Public Opinion - As the cost of foreign policy increases, requiring that domestic programs be cancelled, support foreign policy decreases n Interest Groups - Business groups can play a role in foreign and defense policy decisions n Foreign Nations - the United Nations n Political Parties - Bi-partisanship in foreign affairs 1. Collaboration between the executive and congressional leaders of both parties 2. Support of presidential foreign policies by both parties in Congress 3. Downplaying major foreign policy differences in national elections and presidential debates n Congress - Presidential-congressional relations in foreign policy depend on level of congressional activity and level of assertiveness congressional
Making Foreign and Defense Policy n Public Opinion - As the cost of foreign policy increases, requiring that domestic programs be cancelled, support foreign policy decreases n Interest Groups - Business groups can play a role in foreign and defense policy decisions n Foreign Nations - the United Nations n Political Parties - Bi-partisanship in foreign affairs 1. Collaboration between the executive and congressional leaders of both parties 2. Support of presidential foreign policies by both parties in Congress 3. Downplaying major foreign policy differences in national elections and presidential debates n Congress - Presidential-congressional relations in foreign policy depend on level of congressional activity and level of assertiveness congressional
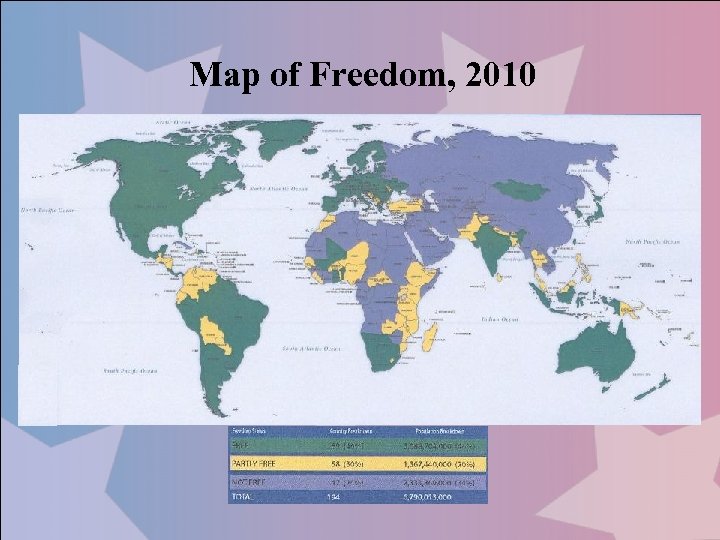 Map of Freedom, 2010
Map of Freedom, 2010
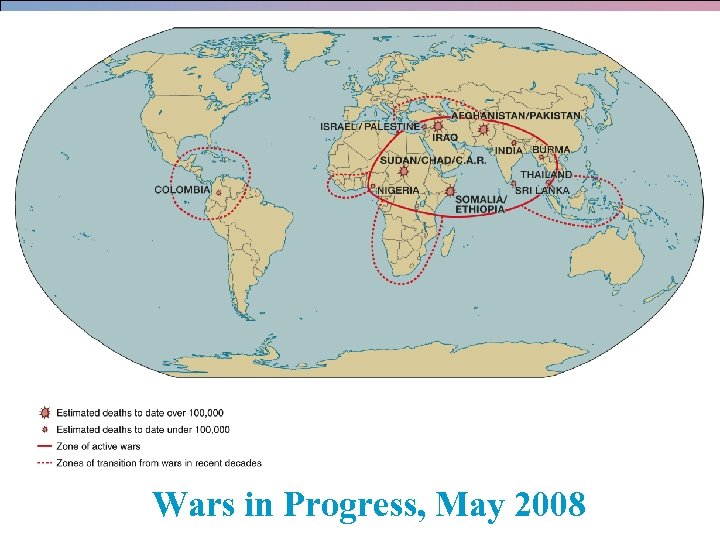 Wars in Progress, May 2008
Wars in Progress, May 2008
 Defining Vital U. S. Interests Whether Americans like it or not, events far from home affect their life, liberty, and pursuit of happiness The War On Terrorism Weapons of Mass Destruction Other Foreign Policy Goals • Middle East Peace • International Trade • Economic Development & International Understanding
Defining Vital U. S. Interests Whether Americans like it or not, events far from home affect their life, liberty, and pursuit of happiness The War On Terrorism Weapons of Mass Destruction Other Foreign Policy Goals • Middle East Peace • International Trade • Economic Development & International Understanding
 Weapons of Mass Destruction The U. S. gained nuclear weapons in 1945 The Soviet Union in 1949 Britain in 1952 China in 1964 France in 1960 These powers remained the only ones with open nuclear weapons programs until 1998, when Pakistan and India tested nuclear weapons. Now Israel, North Korea and Iran may have joined this elite group of nations. The New Power: China • American policy has been to engage the Chinese in diplomatic and economic relationships in the hope of turning the nation in a more pro-Western direction. • Chinese-American Trade Ties • Chinese-American Tensions
Weapons of Mass Destruction The U. S. gained nuclear weapons in 1945 The Soviet Union in 1949 Britain in 1952 China in 1964 France in 1960 These powers remained the only ones with open nuclear weapons programs until 1998, when Pakistan and India tested nuclear weapons. Now Israel, North Korea and Iran may have joined this elite group of nations. The New Power: China • American policy has been to engage the Chinese in diplomatic and economic relationships in the hope of turning the nation in a more pro-Western direction. • Chinese-American Trade Ties • Chinese-American Tensions
 Regional Conflicts • Cubans in Miami celebrate the news that Cuban leader Fidel Castro was ill and had ceded power to his brother. • Cuban Americans bitterness toward Castro has influenced U. S. policy toward Cuba. • Israel and the Palestinians • Health issues in Sub Saharan Africa • African Civil Wars • Protests in Tunisia, Egypt, Algeria, Yemen, Jordan, Syria
Regional Conflicts • Cubans in Miami celebrate the news that Cuban leader Fidel Castro was ill and had ceded power to his brother. • Cuban Americans bitterness toward Castro has influenced U. S. policy toward Cuba. • Israel and the Palestinians • Health issues in Sub Saharan Africa • African Civil Wars • Protests in Tunisia, Egypt, Algeria, Yemen, Jordan, Syria
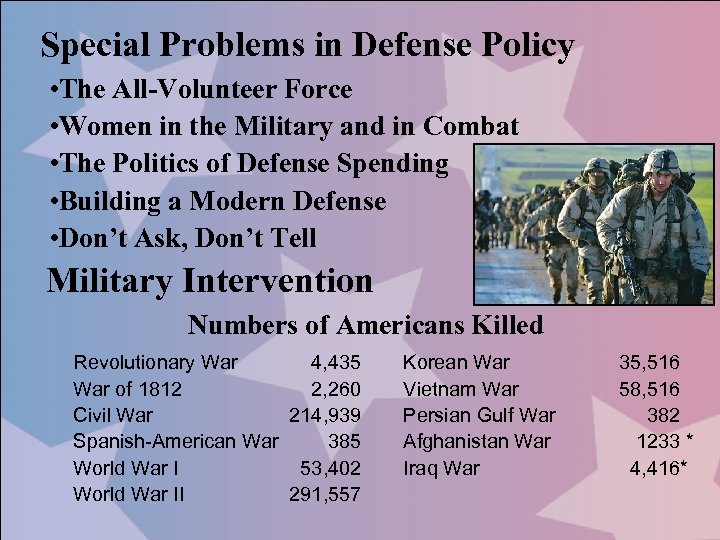 Special Problems in Defense Policy • The All-Volunteer Force • Women in the Military and in Combat • The Politics of Defense Spending • Building a Modern Defense • Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell Military Intervention Numbers of Americans Killed Revolutionary War 4, 435 War of 1812 2, 260 Civil War 214, 939 Spanish-American War 385 World War I 53, 402 World War II 291, 557 Korean War Vietnam War Persian Gulf War Afghanistan War Iraq War 35, 516 58, 516 382 1233 * 4, 416*
Special Problems in Defense Policy • The All-Volunteer Force • Women in the Military and in Combat • The Politics of Defense Spending • Building a Modern Defense • Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell Military Intervention Numbers of Americans Killed Revolutionary War 4, 435 War of 1812 2, 260 Civil War 214, 939 Spanish-American War 385 World War I 53, 402 World War II 291, 557 Korean War Vietnam War Persian Gulf War Afghanistan War Iraq War 35, 516 58, 516 382 1233 * 4, 416*
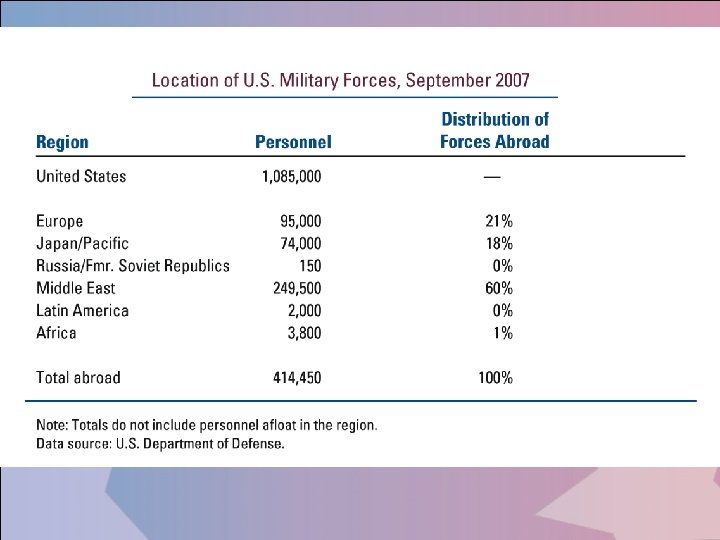
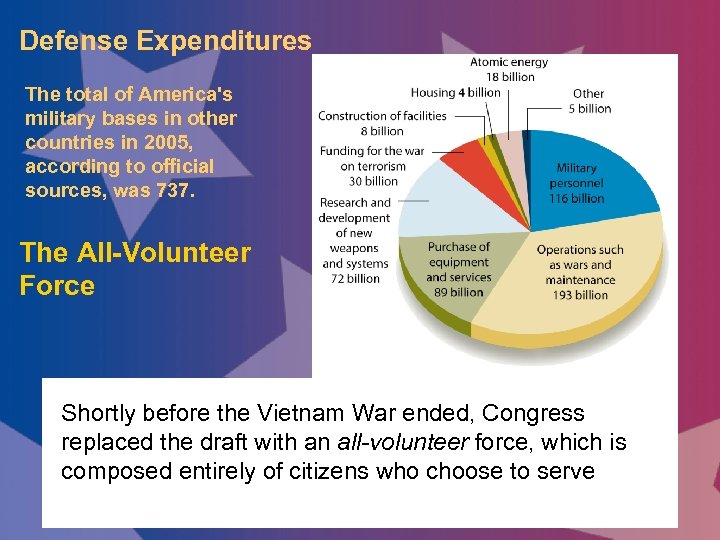 Defense Expenditures The total of America's military bases in other countries in 2005, according to official sources, was 737. The All-Volunteer Force Shortly before the Vietnam War ended, Congress replaced the draft with an all-volunteer force, which is composed entirely of citizens who choose to serve
Defense Expenditures The total of America's military bases in other countries in 2005, according to official sources, was 737. The All-Volunteer Force Shortly before the Vietnam War ended, Congress replaced the draft with an all-volunteer force, which is composed entirely of citizens who choose to serve
 Which two were part of the Bush Doctrine? A. Realism and isolationism B. Idealism and interventionism C. Unilateralism and preemption D. Unilateralism and hard power
Which two were part of the Bush Doctrine? A. Realism and isolationism B. Idealism and interventionism C. Unilateralism and preemption D. Unilateralism and hard power
 Which agenda item is most closely connected to 9/11? A. Weapons of mass destruction B. War on terrorism C. Promoting democracy D. Free trade
Which agenda item is most closely connected to 9/11? A. Weapons of mass destruction B. War on terrorism C. Promoting democracy D. Free trade
 Which agency is closest to the president? A. Department of State B. National Security Council C. Department of Defense D. Central Intelligence Agency
Which agency is closest to the president? A. Department of State B. National Security Council C. Department of Defense D. Central Intelligence Agency
 Soft power includes all of the following EXCEPT _____. A. Conventional diplomacy B. Public diplomacy C. Foreign aid D. Economic sanctions
Soft power includes all of the following EXCEPT _____. A. Conventional diplomacy B. Public diplomacy C. Foreign aid D. Economic sanctions


