7b7360cb7480d414a2c333d1b46b4402.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 123
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Clearing the fog… Then what is a Network Camera?
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Clearing the fog… Then what is a Network Camera?
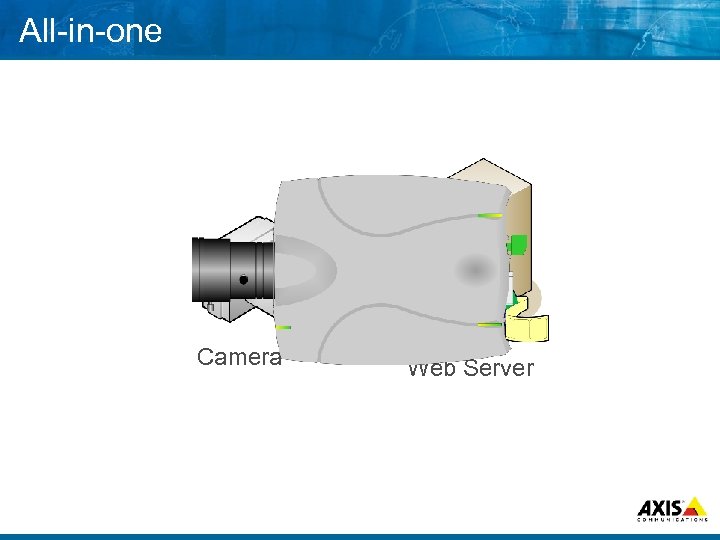 All in one Camera Web Server
All in one Camera Web Server
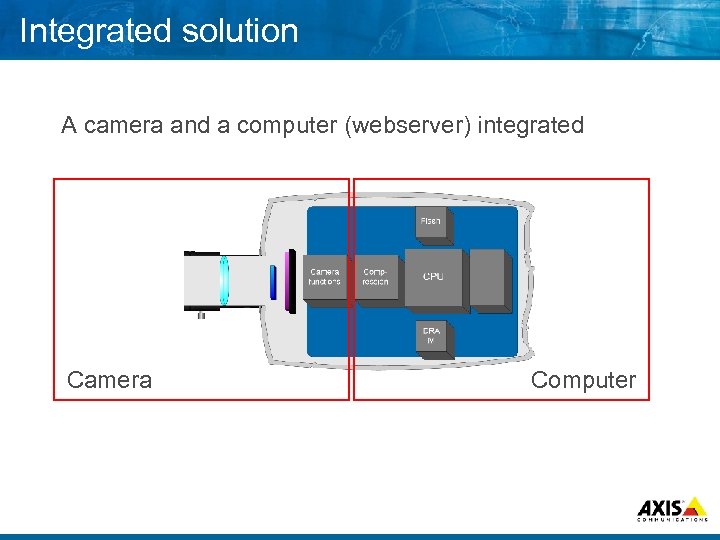 Integrated solution A camera and a computer (webserver) integrated Camera Computer
Integrated solution A camera and a computer (webserver) integrated Camera Computer
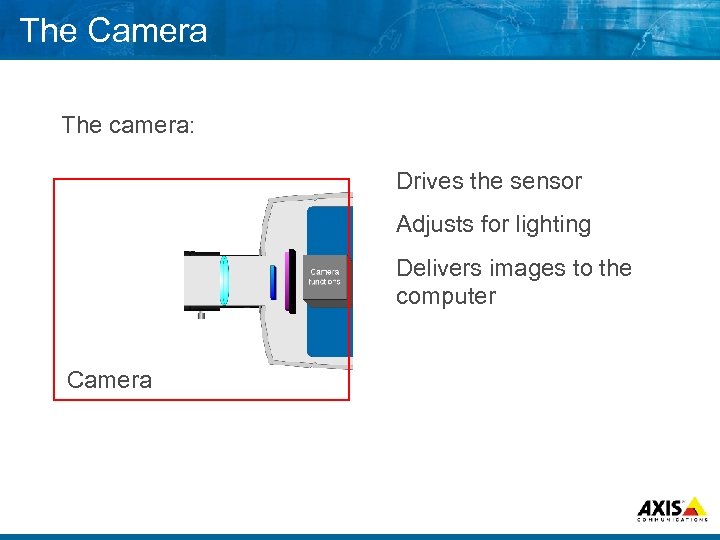 The Camera The camera: Drives the sensor Adjusts for lighting Delivers images to the computer Camera
The Camera The camera: Drives the sensor Adjusts for lighting Delivers images to the computer Camera
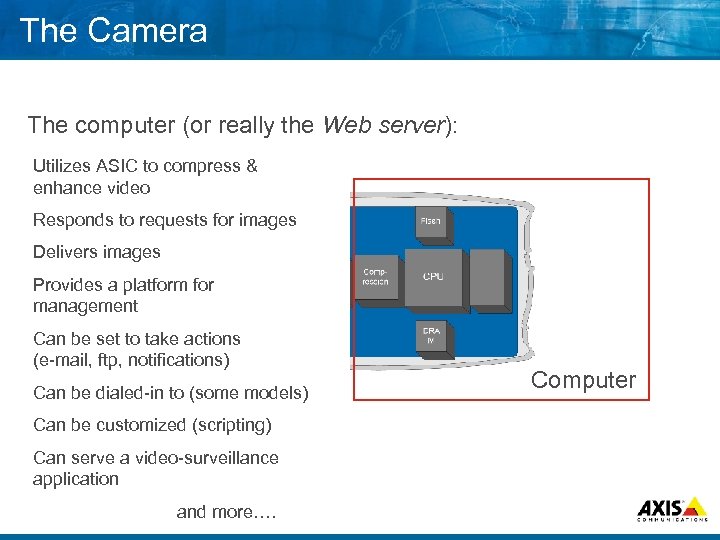 The Camera The computer (or really the Web server): Utilizes ASIC to compress & enhance video Responds to requests for images Delivers images Provides a platform for management Can be set to take actions (e mail, ftp, notifications) Can be dialed in to (some models) Can be customized (scripting) Can serve a video surveillance application and more…. Computer
The Camera The computer (or really the Web server): Utilizes ASIC to compress & enhance video Responds to requests for images Delivers images Provides a platform for management Can be set to take actions (e mail, ftp, notifications) Can be dialed in to (some models) Can be customized (scripting) Can serve a video surveillance application and more…. Computer
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Axis definition of a network solution
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Axis definition of a network solution
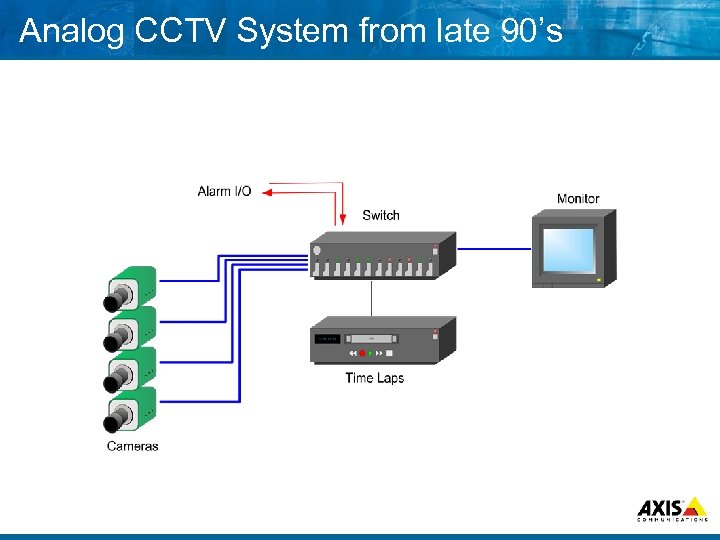 Analog CCTV System from late 90’s
Analog CCTV System from late 90’s
 Technology shifts “The approach of the digital age is unstoppable and soon all media will be in digital form”
Technology shifts “The approach of the digital age is unstoppable and soon all media will be in digital form”
 Is a DVR based solution digital?
Is a DVR based solution digital?
 No DVR’s are just a step…. IP Surveillance and DVR solutions share some benefits
No DVR’s are just a step…. IP Surveillance and DVR solutions share some benefits
 …. . to the complete digital solution “Pure” IP Surveillance offers significant advantages over DVRs
…. . to the complete digital solution “Pure” IP Surveillance offers significant advantages over DVRs
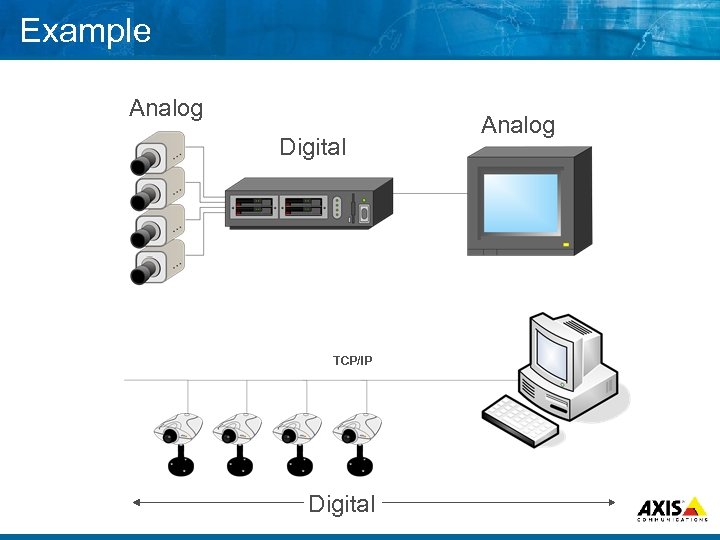 Example Analog Digital TCP/IP Digital Analog
Example Analog Digital TCP/IP Digital Analog
 “Pure Digital” Advantages 8 Unlimited flexibility 8 Unlimited scalability 8 Open standards 8 Easy replacement or expansion 8 Remote access to video from any location 8 Advanced digital image management
“Pure Digital” Advantages 8 Unlimited flexibility 8 Unlimited scalability 8 Open standards 8 Easy replacement or expansion 8 Remote access to video from any location 8 Advanced digital image management
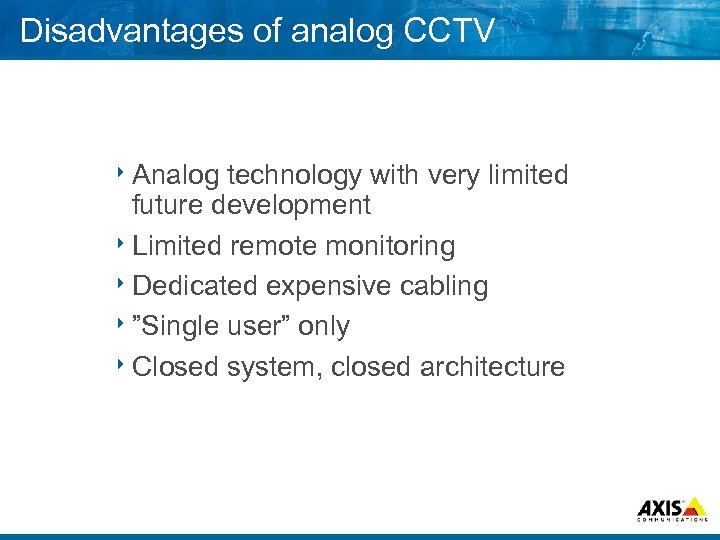 Disadvantages of analog CCTV 8 Analog technology with very limited future development 8 Limited remote monitoring 8 Dedicated expensive cabling 8”Single user” only 8 Closed system, closed architecture
Disadvantages of analog CCTV 8 Analog technology with very limited future development 8 Limited remote monitoring 8 Dedicated expensive cabling 8”Single user” only 8 Closed system, closed architecture
 So how do we make it happen? 8 Transfer 8 New legacy installations in steps. . . installations fully digital. . .
So how do we make it happen? 8 Transfer 8 New legacy installations in steps. . . installations fully digital. . .
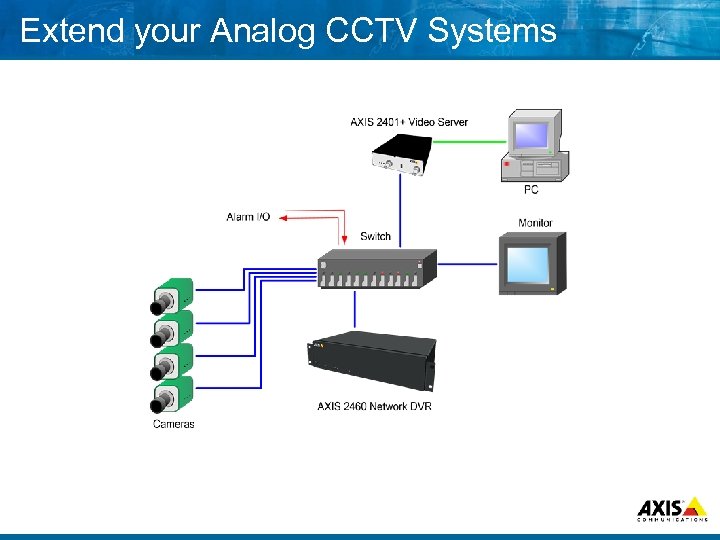 Extend your Analog CCTV Systems
Extend your Analog CCTV Systems
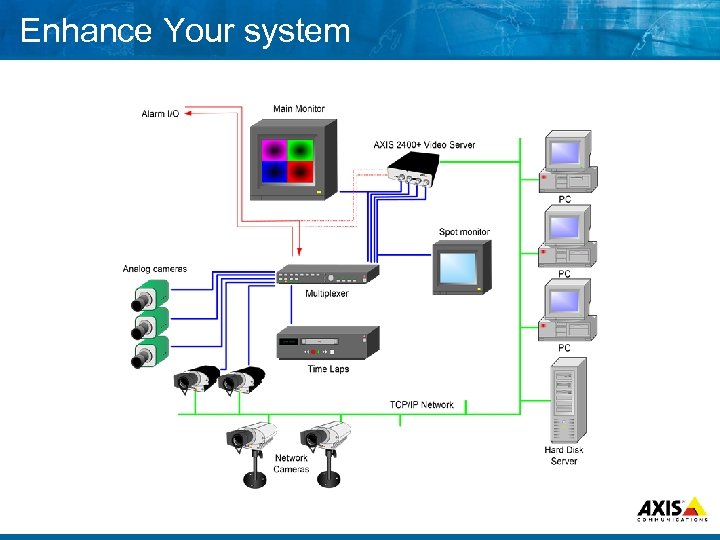 Enhance Your system
Enhance Your system
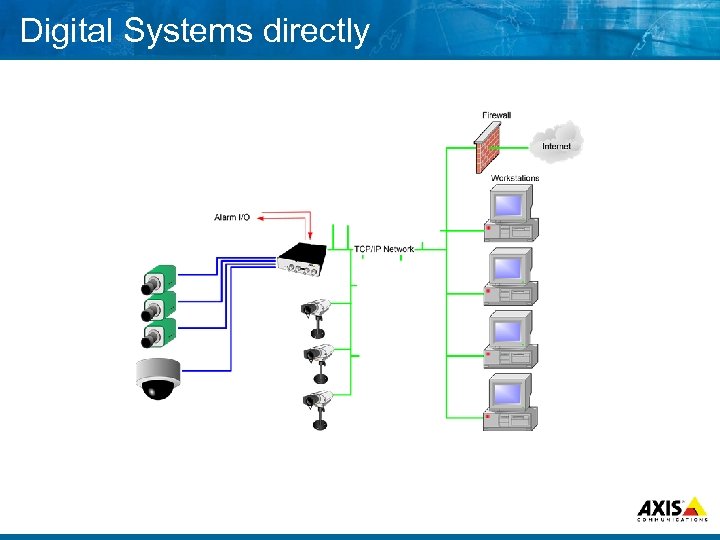 Digital Systems directly
Digital Systems directly
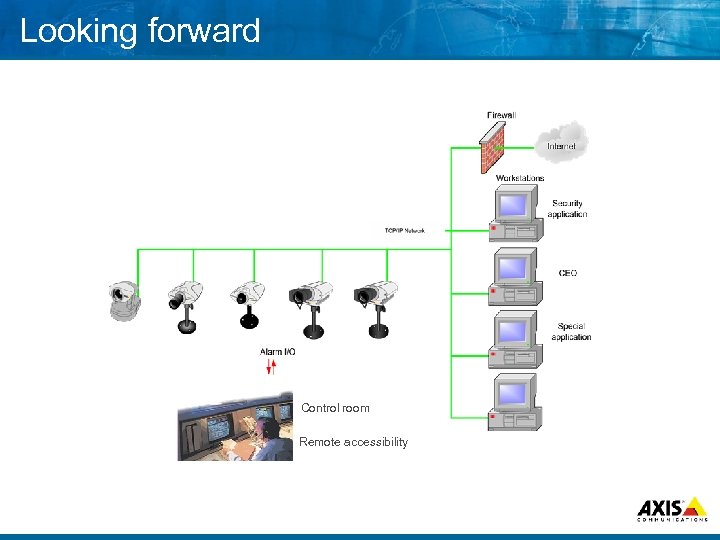 Looking forward Control room Remote accessibility
Looking forward Control room Remote accessibility
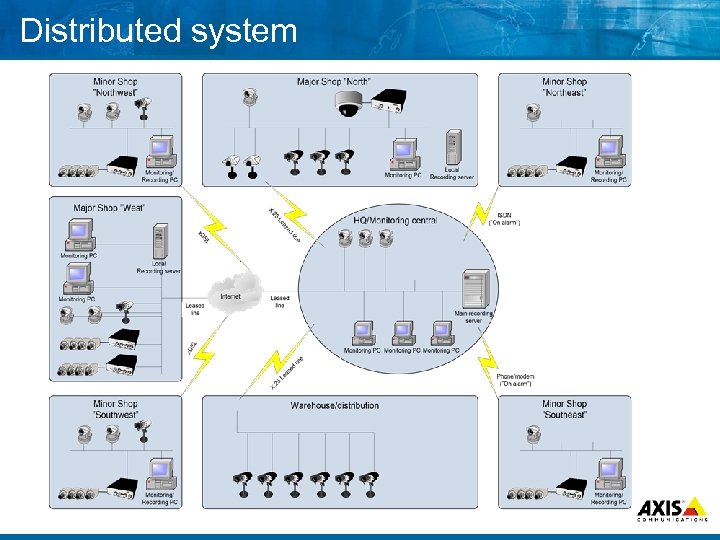 Distributed system
Distributed system
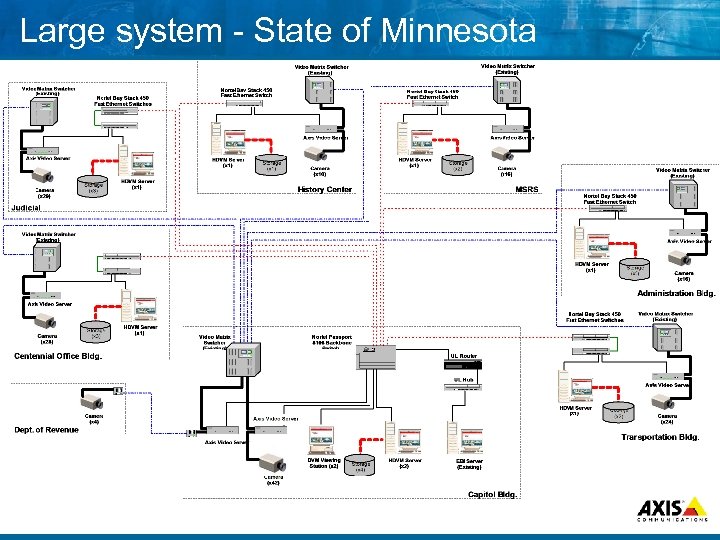 Large system State of Minnesota
Large system State of Minnesota
 Market Trends Sharing of IT networks for Security Video Ø Merger of Security and IT functions in companies Ø Security system integrator video sales up 44 % in 2002 Ø JP Freeman 2003 Report
Market Trends Sharing of IT networks for Security Video Ø Merger of Security and IT functions in companies Ø Security system integrator video sales up 44 % in 2002 Ø JP Freeman 2003 Report
 Markets in transition IT market Security Market IT Market
Markets in transition IT market Security Market IT Market
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Connection examples
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Connection examples
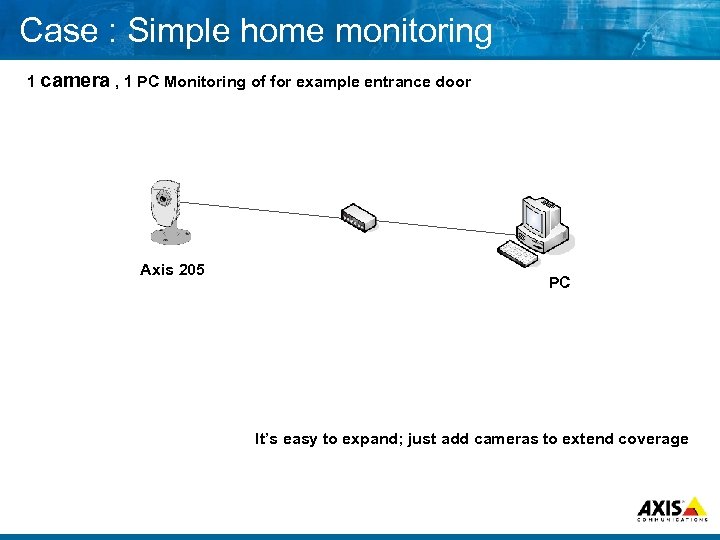 Case : Simple home monitoring 1 camera , 1 PC Monitoring of for example entrance door Axis 205 PC It’s easy to expand; just add cameras to extend coverage
Case : Simple home monitoring 1 camera , 1 PC Monitoring of for example entrance door Axis 205 PC It’s easy to expand; just add cameras to extend coverage
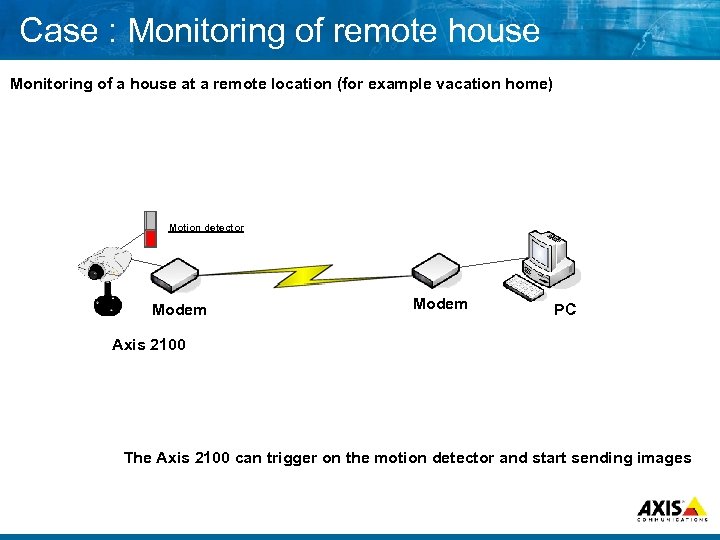 Case : Monitoring of remote house Monitoring of a house at a remote location (for example vacation home) Motion detector Modem PC Axis 2100 The Axis 2100 can trigger on the motion detector and start sending images
Case : Monitoring of remote house Monitoring of a house at a remote location (for example vacation home) Motion detector Modem PC Axis 2100 The Axis 2100 can trigger on the motion detector and start sending images
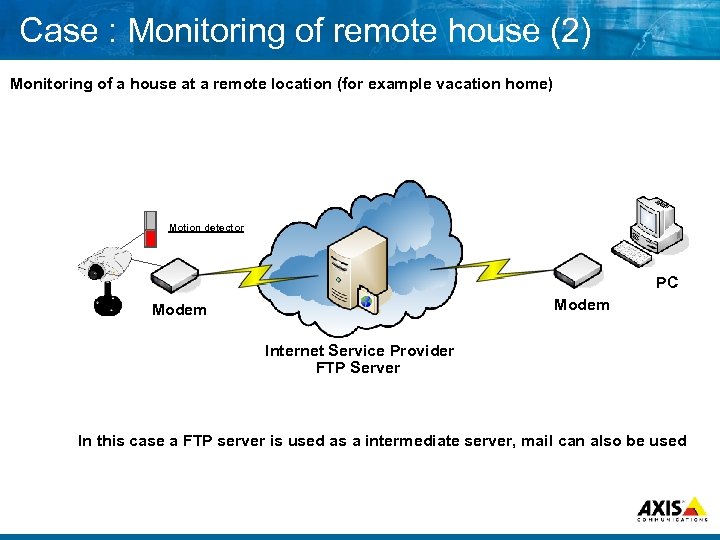 Case : Monitoring of remote house (2) Monitoring of a house at a remote location (for example vacation home) Motion detector PC Modem Internet Service Provider FTP Server In this case a FTP server is used as a intermediate server, mail can also be used
Case : Monitoring of remote house (2) Monitoring of a house at a remote location (for example vacation home) Motion detector PC Modem Internet Service Provider FTP Server In this case a FTP server is used as a intermediate server, mail can also be used
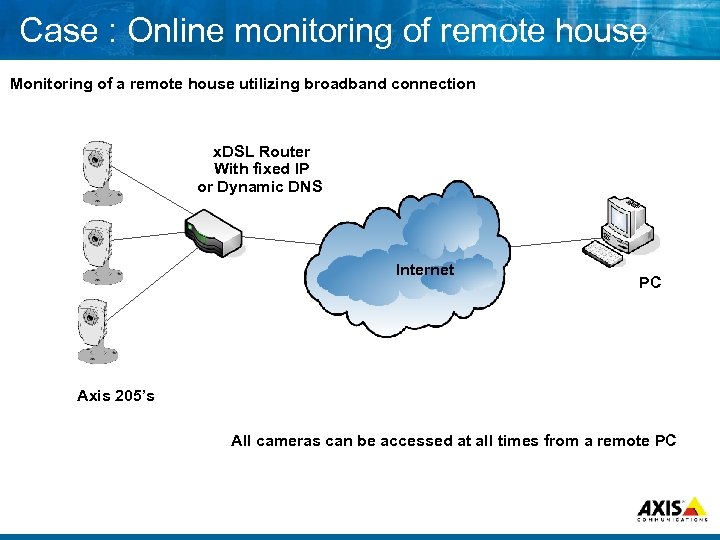 Case : Online monitoring of remote house Monitoring of a remote house utilizing broadband connection x. DSL Router With fixed IP or Dynamic DNS Internet PC Axis 205’s All cameras can be accessed at all times from a remote PC
Case : Online monitoring of remote house Monitoring of a remote house utilizing broadband connection x. DSL Router With fixed IP or Dynamic DNS Internet PC Axis 205’s All cameras can be accessed at all times from a remote PC
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Slightly more detailed examples…
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Slightly more detailed examples…
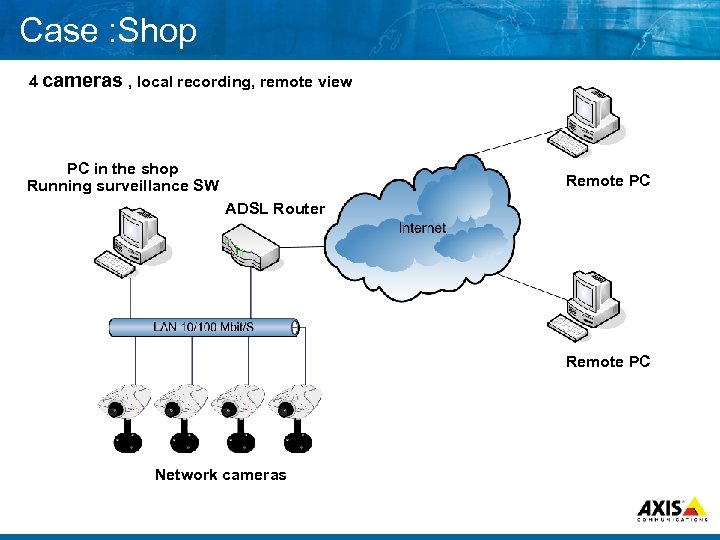 Case : Shop 4 cameras , local recording, remote view PC in the shop Running surveillance SW Remote PC ADSL Router Remote PC Network cameras
Case : Shop 4 cameras , local recording, remote view PC in the shop Running surveillance SW Remote PC ADSL Router Remote PC Network cameras
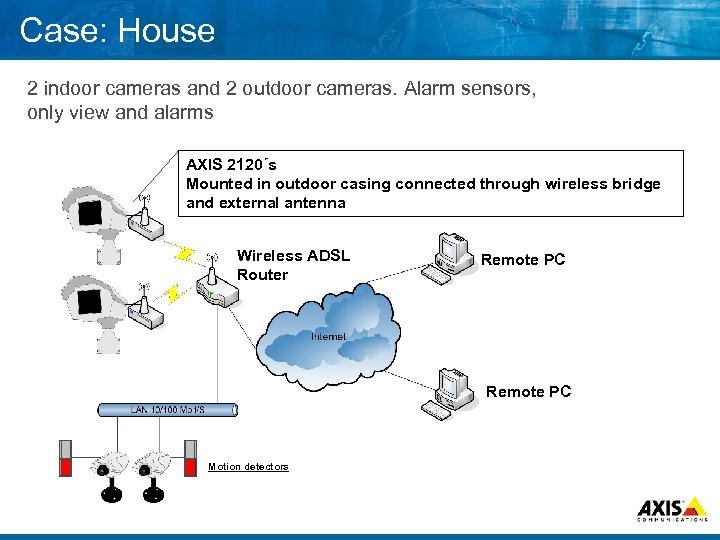 Case: House 2 indoor cameras and 2 outdoor cameras. Alarm sensors, only view and alarms AXIS 2120´s Mounted in outdoor casing connected through wireless bridge and external antenna Wireless ADSL Router Remote PC Motion detectors
Case: House 2 indoor cameras and 2 outdoor cameras. Alarm sensors, only view and alarms AXIS 2120´s Mounted in outdoor casing connected through wireless bridge and external antenna Wireless ADSL Router Remote PC Motion detectors
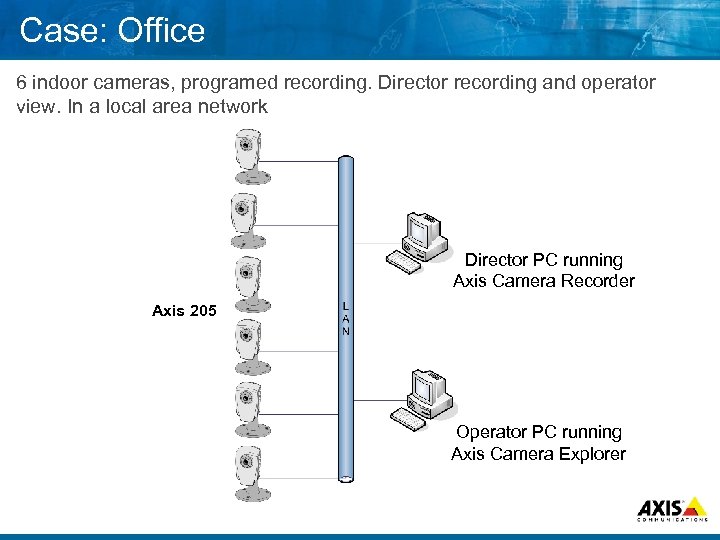 Case: Office 6 indoor cameras, programed recording. Director recording and operator view. In a local area network Director PC running Axis Camera Recorder Axis 205 Operator PC running Axis Camera Explorer
Case: Office 6 indoor cameras, programed recording. Director recording and operator view. In a local area network Director PC running Axis Camera Recorder Axis 205 Operator PC running Axis Camera Explorer
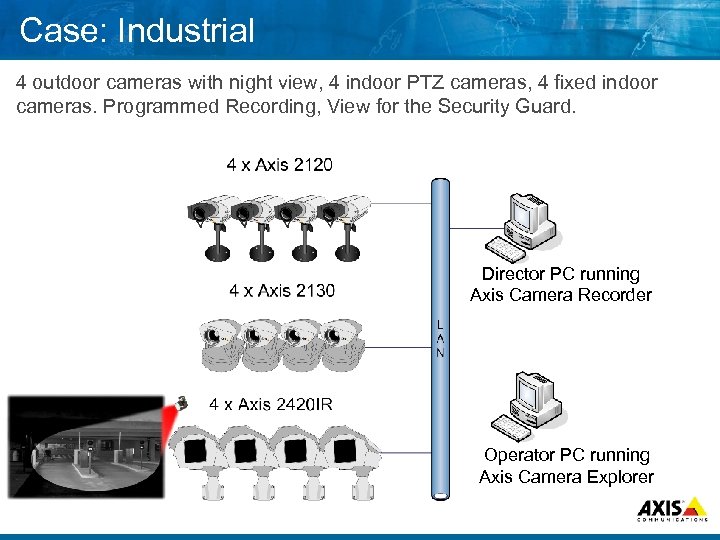 Case: Industrial 4 outdoor cameras with night view, 4 indoor PTZ cameras, 4 fixed indoor cameras. Programmed Recording, View for the Security Guard. Director PC running Axis Camera Recorder Operator PC running Axis Camera Explorer
Case: Industrial 4 outdoor cameras with night view, 4 indoor PTZ cameras, 4 fixed indoor cameras. Programmed Recording, View for the Security Guard. Director PC running Axis Camera Recorder Operator PC running Axis Camera Explorer
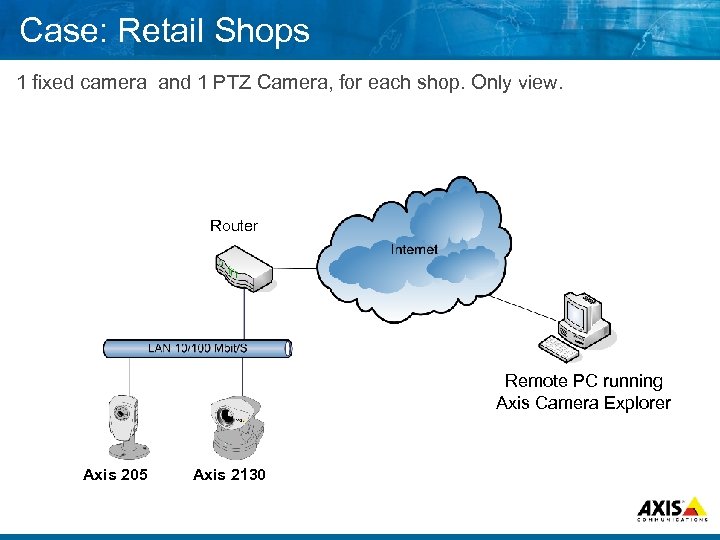 Case: Retail Shops 1 fixed camera and 1 PTZ Camera, for each shop. Only view. Router Remote PC running Axis Camera Explorer Axis 205 Axis 2130
Case: Retail Shops 1 fixed camera and 1 PTZ Camera, for each shop. Only view. Router Remote PC running Axis Camera Explorer Axis 205 Axis 2130
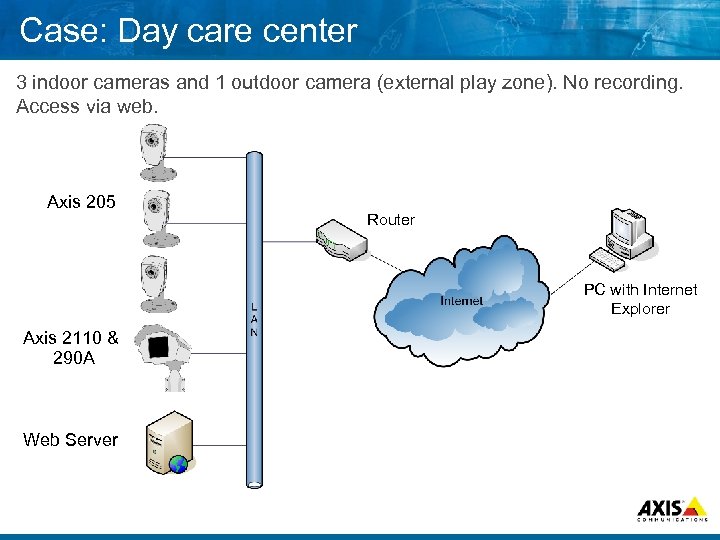 Case: Day care center 3 indoor cameras and 1 outdoor camera (external play zone). No recording. Access via web. Axis 205 Router PC with Internet Explorer Axis 2110 & 290 A Web Server
Case: Day care center 3 indoor cameras and 1 outdoor camera (external play zone). No recording. Access via web. Axis 205 Router PC with Internet Explorer Axis 2110 & 290 A Web Server
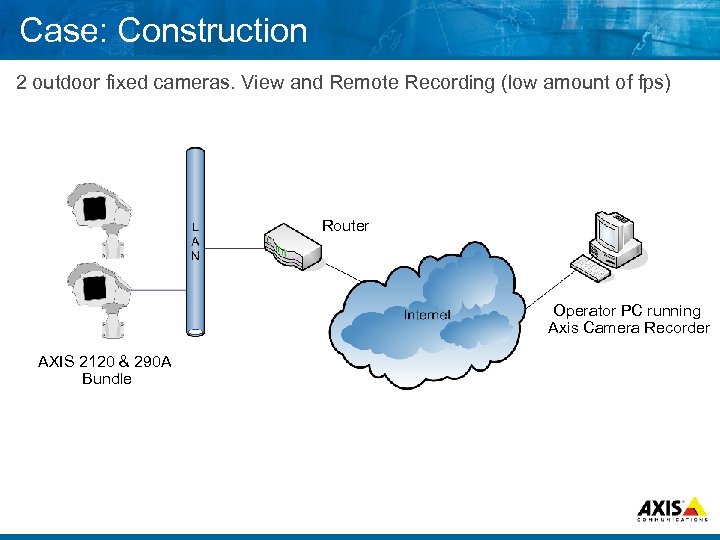 Case: Construction 2 outdoor fixed cameras. View and Remote Recording (low amount of fps) Router Operator PC running Axis Camera Recorder AXIS 2120 & 290 A Bundle
Case: Construction 2 outdoor fixed cameras. View and Remote Recording (low amount of fps) Router Operator PC running Axis Camera Recorder AXIS 2120 & 290 A Bundle
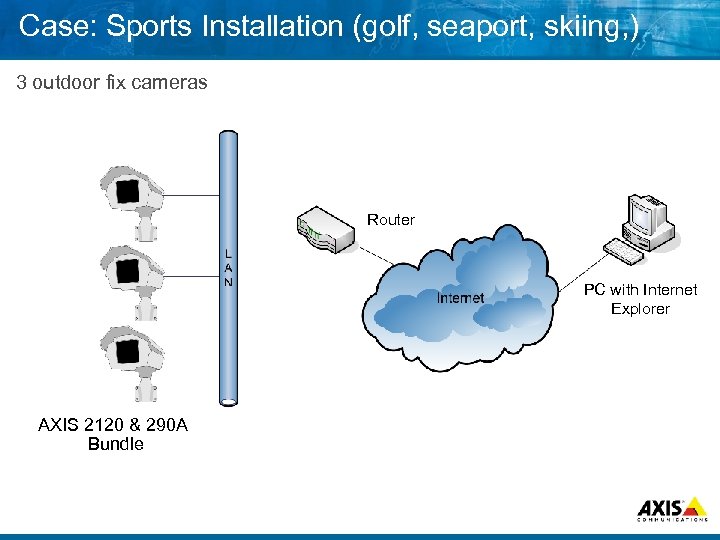 Case: Sports Installation (golf, seaport, skiing, ) 3 outdoor fix cameras Router PC with Internet Explorer AXIS 2120 & 290 A Bundle
Case: Sports Installation (golf, seaport, skiing, ) 3 outdoor fix cameras Router PC with Internet Explorer AXIS 2120 & 290 A Bundle
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Setting a IP Address
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Setting a IP Address
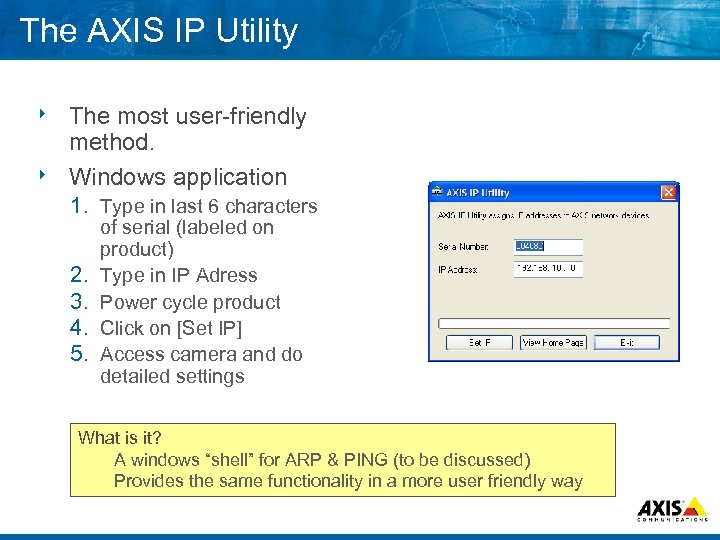 The AXIS IP Utility The most user friendly method. 8 Windows application 8 1. Type in last 6 characters 2. 3. 4. 5. of serial (labeled on product) Type in IP Adress Power cycle product Click on [Set IP] Access camera and do detailed settings What is it? A windows “shell” for ARP & PING (to be discussed) Provides the same functionality in a more user friendly way
The AXIS IP Utility The most user friendly method. 8 Windows application 8 1. Type in last 6 characters 2. 3. 4. 5. of serial (labeled on product) Type in IP Adress Power cycle product Click on [Set IP] Access camera and do detailed settings What is it? A windows “shell” for ARP & PING (to be discussed) Provides the same functionality in a more user friendly way
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER ARP and Ping The manual method
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER ARP and Ping The manual method
 Topics 8 ARP protocol 8 Ping utility 8 Setting ping an IP address using ARP and
Topics 8 ARP protocol 8 Ping utility 8 Setting ping an IP address using ARP and
 ARP 8 Address Resolution Protocol 8 Associates with IP MAC (hardware) address
ARP 8 Address Resolution Protocol 8 Associates with IP MAC (hardware) address
 Ping 8 Will test basic TCP/IP connectivity 8 Sends a packet & waits for responce
Ping 8 Will test basic TCP/IP connectivity 8 Sends a packet & waits for responce
 More Info 8 ARP/Ping must be done on the same network segment 8 Axis product must be rebooted during the ping 8 The IP you try to assign must be compatible with yours (i. e. in the same range) Note: This also applies to the Axis IP Utility as the utility is a graphical interface to Arp & ping
More Info 8 ARP/Ping must be done on the same network segment 8 Axis product must be rebooted during the ping 8 The IP you try to assign must be compatible with yours (i. e. in the same range) Note: This also applies to the Axis IP Utility as the utility is a graphical interface to Arp & ping
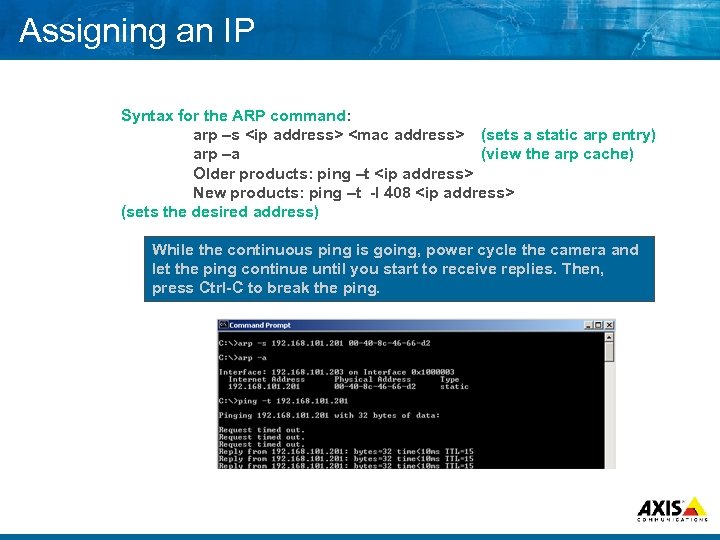 Assigning an IP Syntax for the ARP command: arp –s
Assigning an IP Syntax for the ARP command: arp –s
 In pictures C: >arp –s 192. 168. 0. 10 00 -40 -8 C-AA-BB-CC C: > The computers arp table is updated with the entry and “ties” the hardware (MAC) address to the IP address
In pictures C: >arp –s 192. 168. 0. 10 00 -40 -8 C-AA-BB-CC C: > The computers arp table is updated with the entry and “ties” the hardware (MAC) address to the IP address
 In pictures C: >arp –s 192. 168. 0. 10 00 -40 -8 C-AA-BB-CC C: > ping –t 192. 168. 0. 10 Pinging 192. 168. 0. 10 Request timed out. Computer sends “ping” packets to the camera using arp table as address source
In pictures C: >arp –s 192. 168. 0. 10 00 -40 -8 C-AA-BB-CC C: > ping –t 192. 168. 0. 10 Pinging 192. 168. 0. 10 Request timed out. Computer sends “ping” packets to the camera using arp table as address source
 In pictures C: >arp –s 192. 168. 0. 10 00 -40 -8 C-AA-BB-CC C: > ping –t 192. 168. 0. 10 Pinging 192. 168. 0. 10 Request timed out. Reply from 192. 168. 0. 10 Camera receives packets sets it’s IP address and sends responses to the computer
In pictures C: >arp –s 192. 168. 0. 10 00 -40 -8 C-AA-BB-CC C: > ping –t 192. 168. 0. 10 Pinging 192. 168. 0. 10 Request timed out. Reply from 192. 168. 0. 10 Camera receives packets sets it’s IP address and sends responses to the computer
 Q&A
Q&A
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Image/Video Compression
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Image/Video Compression
 Image Compression 8 Why compression in the first place A video sequence in accordance to CCIR 601 (720 x 485 pixels) require 165 Mbit/sec ! One channel !
Image Compression 8 Why compression in the first place A video sequence in accordance to CCIR 601 (720 x 485 pixels) require 165 Mbit/sec ! One channel !
 Image Compression 8 Image or Video ?
Image Compression 8 Image or Video ?
 Image Compression 8 The result of the Compression depends on Picture size, pixels Content
Image Compression 8 The result of the Compression depends on Picture size, pixels Content
 Image Compression 8 The different image compressions fundamentals Differential method Non differential method Loss vs. No Loss of information
Image Compression 8 The different image compressions fundamentals Differential method Non differential method Loss vs. No Loss of information
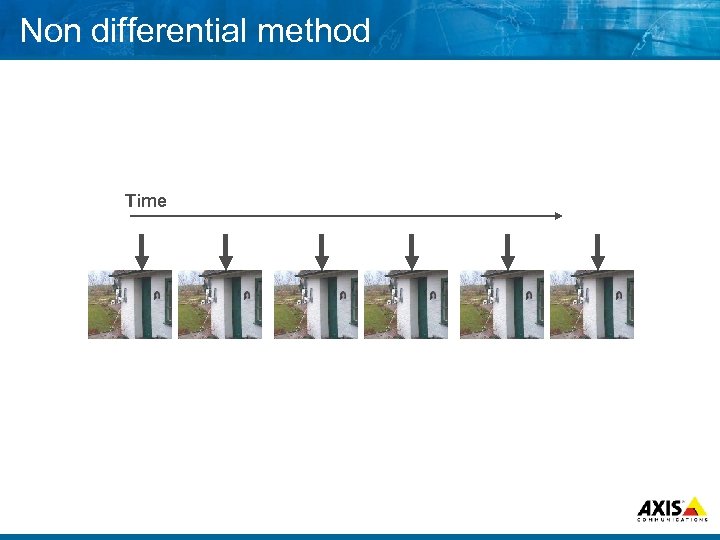 Non differential method Time
Non differential method Time
 Non differential method 8 Single pictures No information discarded or All information transferred Varying degree of lost information Quality less depending on transfer rate
Non differential method 8 Single pictures No information discarded or All information transferred Varying degree of lost information Quality less depending on transfer rate
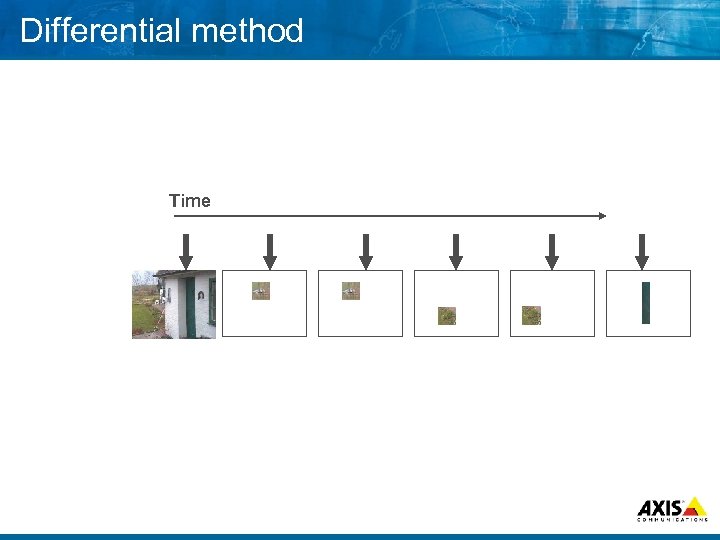 Differential method Time
Differential method Time
 Differential method 8 Group of pictures (GOP) and updates Less noticeable information discarded or Only noticeable information transferred Quality more depending on transfer rate
Differential method 8 Group of pictures (GOP) and updates Less noticeable information discarded or Only noticeable information transferred Quality more depending on transfer rate
 Compression 8 To organize and remove information without loss of “visible” content Moving pictures, H. 261, H. 263 MPEG Still pictures, JPEG
Compression 8 To organize and remove information without loss of “visible” content Moving pictures, H. 261, H. 263 MPEG Still pictures, JPEG
 JPEG and MJPEG 8 International standard 8 Joint Photographic Experts Group 8 Different level of compression within the standard 8 Compression rate determines amount of bytes per picture 8 Variable pictures per second
JPEG and MJPEG 8 International standard 8 Joint Photographic Experts Group 8 Different level of compression within the standard 8 Compression rate determines amount of bytes per picture 8 Variable pictures per second
 JPEG compression, Axis ARTPEC Low compression 100% ≈ 108 Kb
JPEG compression, Axis ARTPEC Low compression 100% ≈ 108 Kb
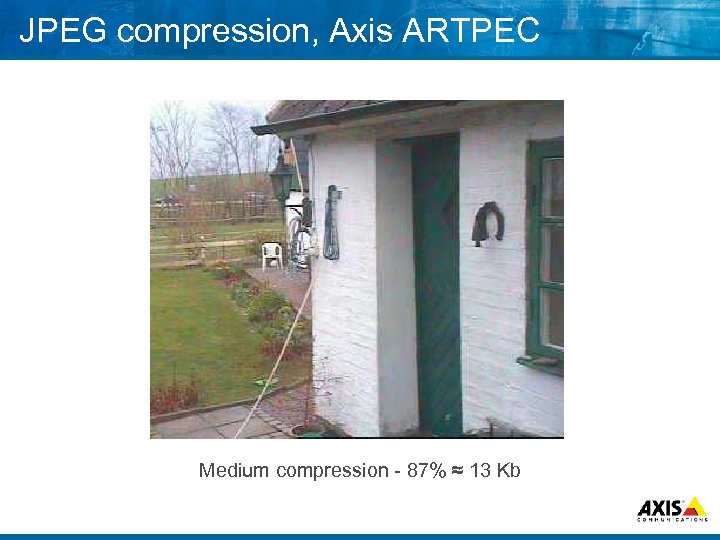 JPEG compression, Axis ARTPEC Medium compression 87% ≈ 13 Kb
JPEG compression, Axis ARTPEC Medium compression 87% ≈ 13 Kb
 JPEG compression, Axis ARTPEC High compression 95% ≈ 5 Kb
JPEG compression, Axis ARTPEC High compression 95% ≈ 5 Kb
 MJPEG – Key properties 8 Same quality on each and every frame 8 Variable bandwidth / storage requirement 8 MJPEG focuses on Quality
MJPEG – Key properties 8 Same quality on each and every frame 8 Variable bandwidth / storage requirement 8 MJPEG focuses on Quality
 MPEG – Key properties 8 Maintained bandwidth 8 Maintained framerate 8 MPEG focuses on consistent bandwidth/maintained framerate
MPEG – Key properties 8 Maintained bandwidth 8 Maintained framerate 8 MPEG focuses on consistent bandwidth/maintained framerate
 MPEG, 1, 2 & 4 8 International standard Motion Pictures Experts Group Always 30 pictures per second Picture size determines required transfer rate
MPEG, 1, 2 & 4 8 International standard Motion Pictures Experts Group Always 30 pictures per second Picture size determines required transfer rate
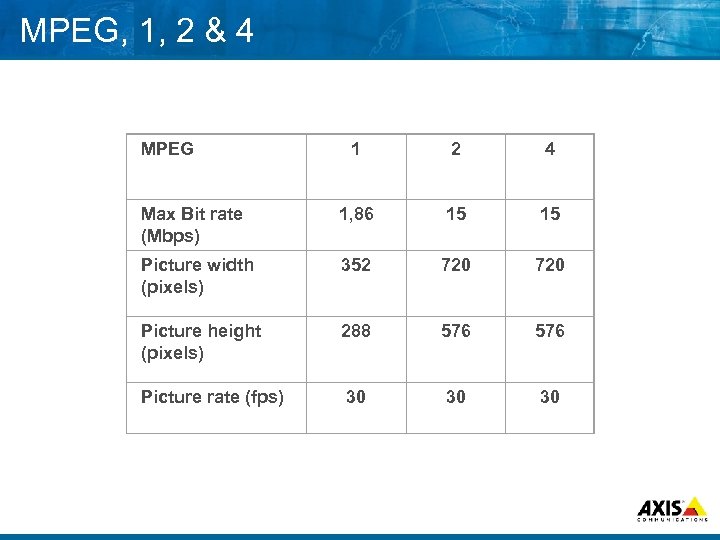 MPEG, 1, 2 & 4 MPEG 1 2 4 Max Bit rate (Mbps) 1, 86 15 15 Picture width (pixels) 352 720 Picture height (pixels) 288 576 Picture rate (fps) 30 30 30
MPEG, 1, 2 & 4 MPEG 1 2 4 Max Bit rate (Mbps) 1, 86 15 15 Picture width (pixels) 352 720 Picture height (pixels) 288 576 Picture rate (fps) 30 30 30
 Applications JPEG 8 Typically where single images are of interest Gate entry Cashier Visual verification of status
Applications JPEG 8 Typically where single images are of interest Gate entry Cashier Visual verification of status
 Applications MPEG 8 Typically when a continuous process is of interest Traffic Assembly Process flow High end Security Continuous movement
Applications MPEG 8 Typically when a continuous process is of interest Traffic Assembly Process flow High end Security Continuous movement
 Q&A
Q&A
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Lenses & Filters
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Lenses & Filters
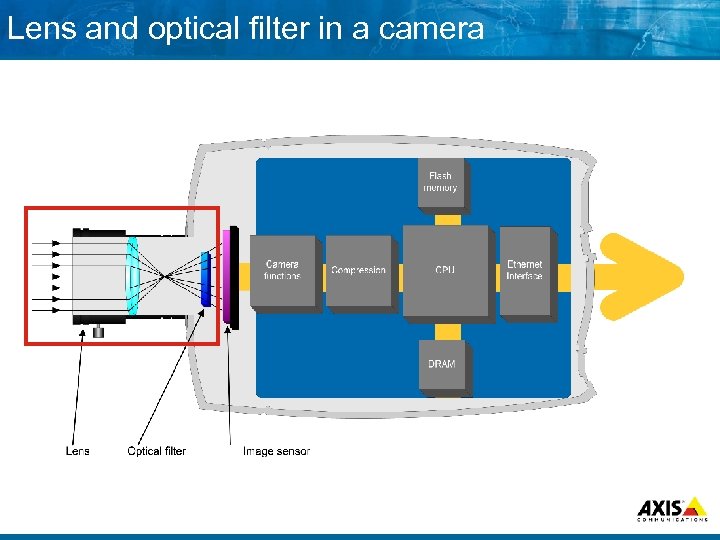 Lens and optical filter in a camera
Lens and optical filter in a camera
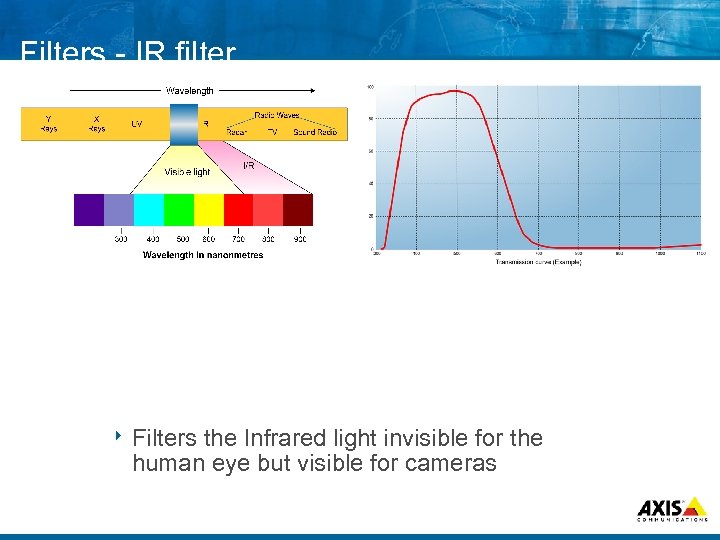 Filters IR filter 8 Filters the Infrared light invisible for the human eye but visible for cameras
Filters IR filter 8 Filters the Infrared light invisible for the human eye but visible for cameras
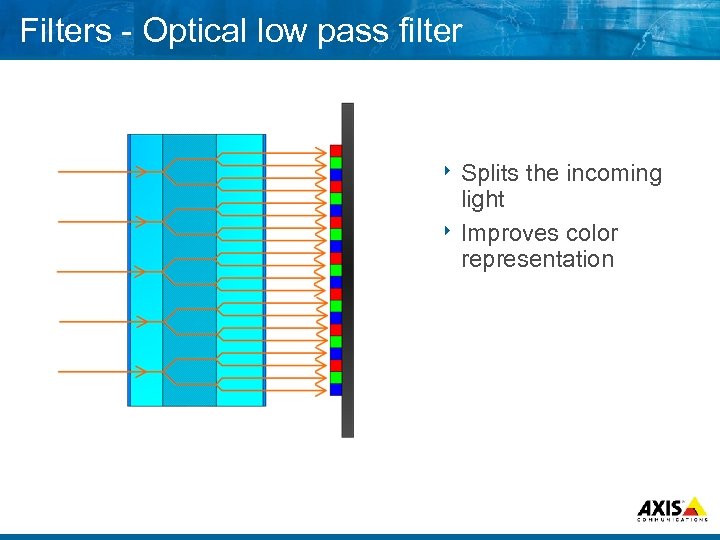 Filters Optical low pass filter 8 Splits the incoming light 8 Improves color representation
Filters Optical low pass filter 8 Splits the incoming light 8 Improves color representation
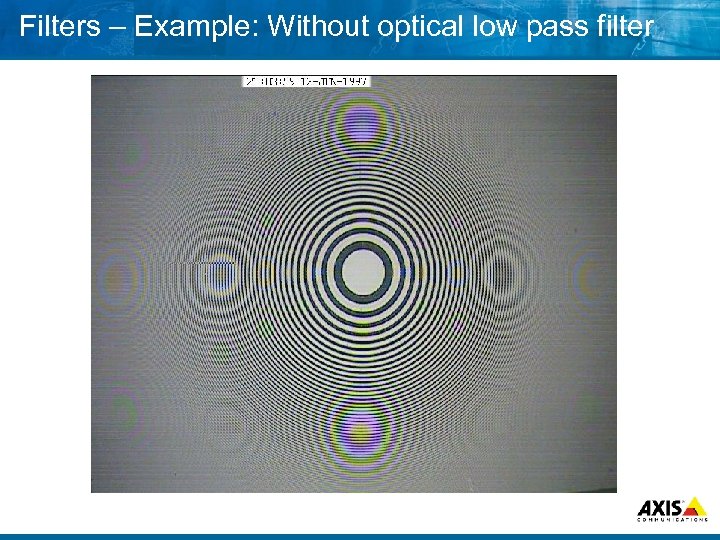 Filters – Example: Without optical low pass filter
Filters – Example: Without optical low pass filter
 Filters – Example: With optical low pass filter
Filters – Example: With optical low pass filter
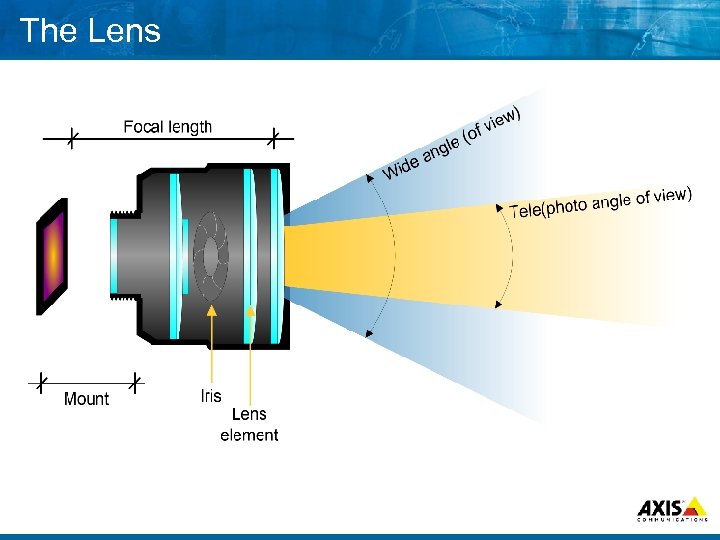 The Lens
The Lens
 Angle of view 8 Same as “Field of view” 8 What the camera with a given lens can “see” 8 Horizontal, vertical or diagonal
Angle of view 8 Same as “Field of view” 8 What the camera with a given lens can “see” 8 Horizontal, vertical or diagonal
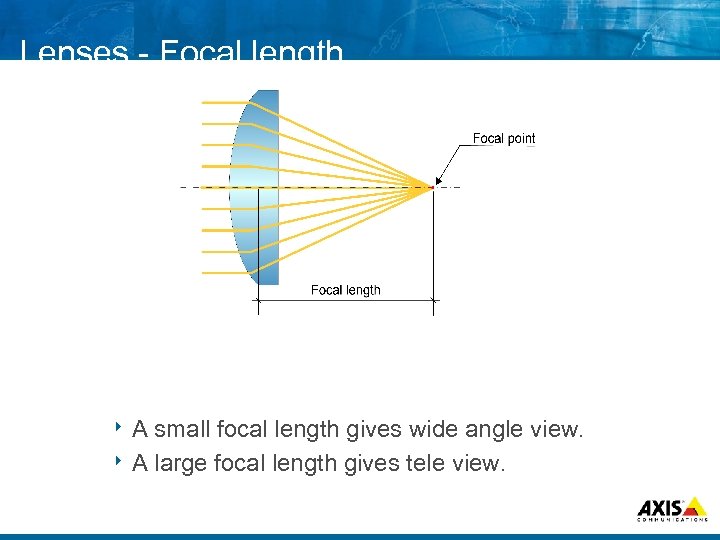 Lenses Focal length 8 A small focal length gives wide angle view. 8 A large focal length gives tele view.
Lenses Focal length 8 A small focal length gives wide angle view. 8 A large focal length gives tele view.
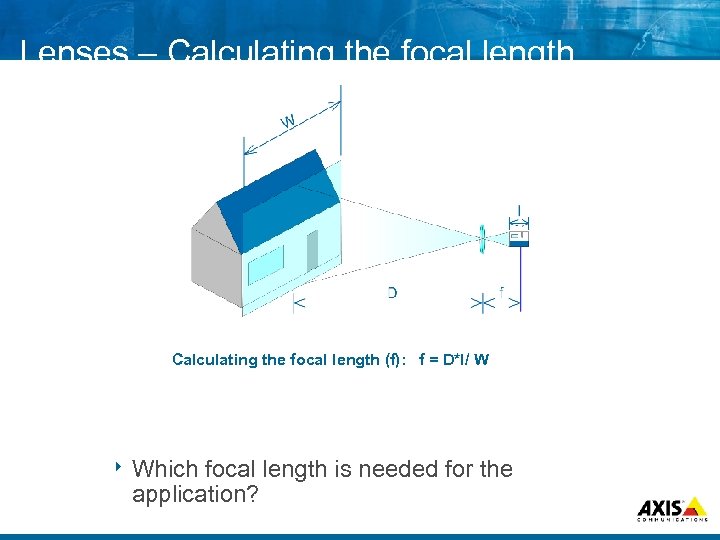 Lenses – Calculating the focal length (f): f = D*I/ W 8 Which focal length is needed for the application?
Lenses – Calculating the focal length (f): f = D*I/ W 8 Which focal length is needed for the application?
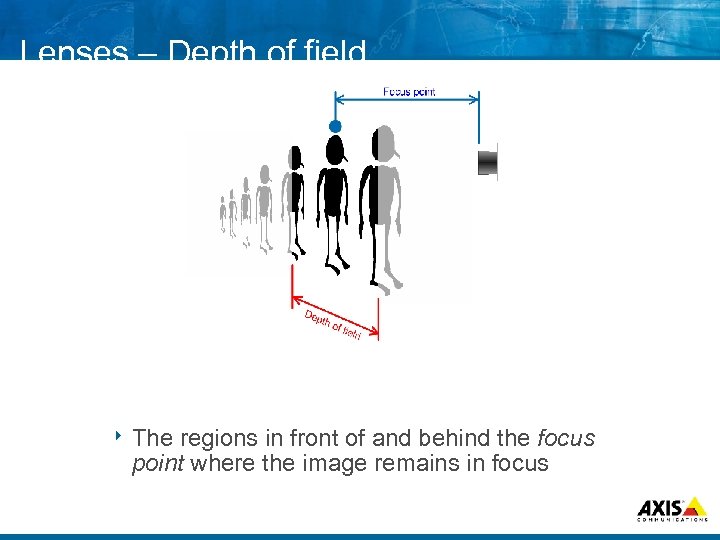 Lenses – Depth of field 8 The regions in front of and behind the focus point where the image remains in focus
Lenses – Depth of field 8 The regions in front of and behind the focus point where the image remains in focus
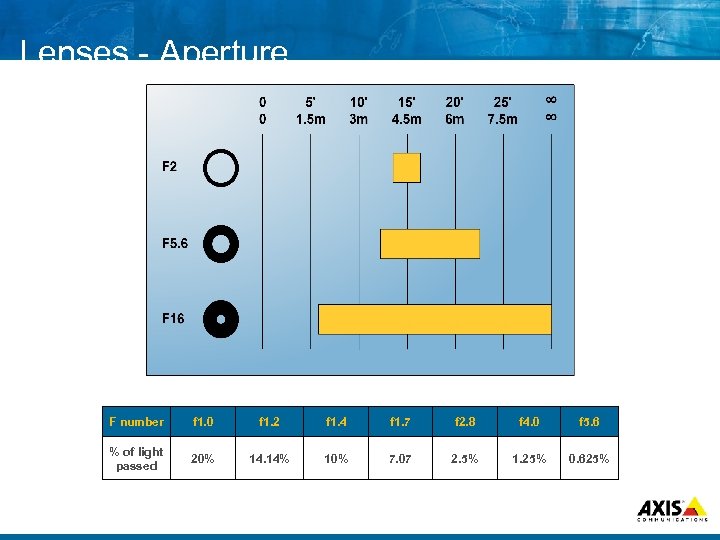 Lenses Aperture F number f 1. 0 f 1. 2 f 1. 4 f 1. 7 f 2. 8 f 4. 0 f 5. 6 % of light passed 20% 14. 14% 10% 7. 07 2. 5% 1. 25% 0. 625%
Lenses Aperture F number f 1. 0 f 1. 2 f 1. 4 f 1. 7 f 2. 8 f 4. 0 f 5. 6 % of light passed 20% 14. 14% 10% 7. 07 2. 5% 1. 25% 0. 625%
 Lenses – Lens Iris A wire between the camera and the lens is needed with an automatic iris lens. 8 Opening in the lens that controls the amount of incoming light that reaches the image sensor
Lenses – Lens Iris A wire between the camera and the lens is needed with an automatic iris lens. 8 Opening in the lens that controls the amount of incoming light that reaches the image sensor
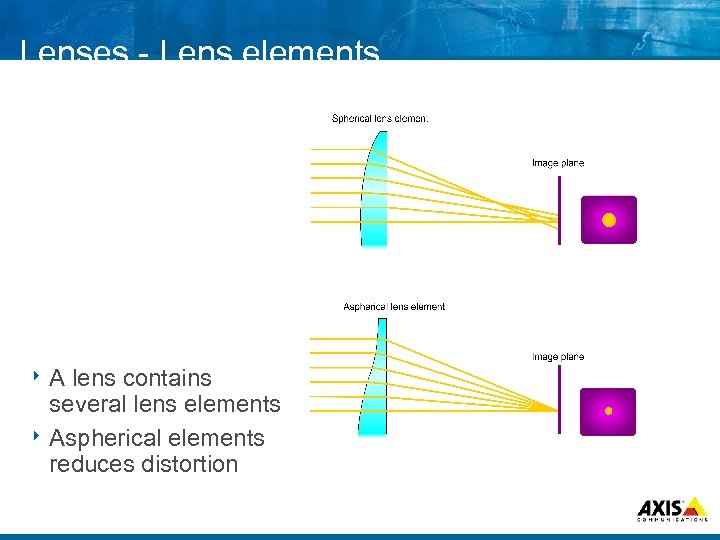 Lenses Lens elements 8 A lens contains several lens elements 8 Aspherical elements reduces distortion
Lenses Lens elements 8 A lens contains several lens elements 8 Aspherical elements reduces distortion
 Lenses Mount standards 8 CS mount 12. 5 mm from camera edge to sensor 8 C mount 17. 5 mm from camera edge to sensor Conversion C to CS is possible
Lenses Mount standards 8 CS mount 12. 5 mm from camera edge to sensor 8 C mount 17. 5 mm from camera edge to sensor Conversion C to CS is possible
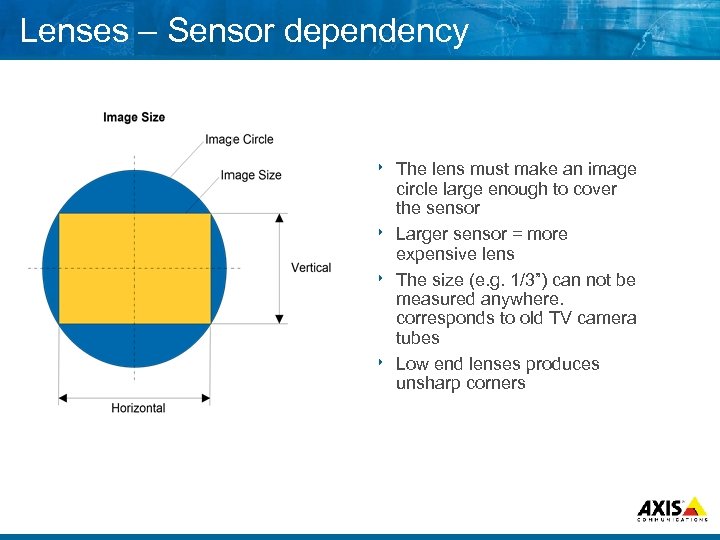 Lenses – Sensor dependency The lens must make an image circle large enough to cover the sensor 8 Larger sensor = more expensive lens 8 The size (e. g. 1/3”) can not be measured anywhere. corresponds to old TV camera tubes 8 Low end lenses produces unsharp corners 8
Lenses – Sensor dependency The lens must make an image circle large enough to cover the sensor 8 Larger sensor = more expensive lens 8 The size (e. g. 1/3”) can not be measured anywhere. corresponds to old TV camera tubes 8 Low end lenses produces unsharp corners 8
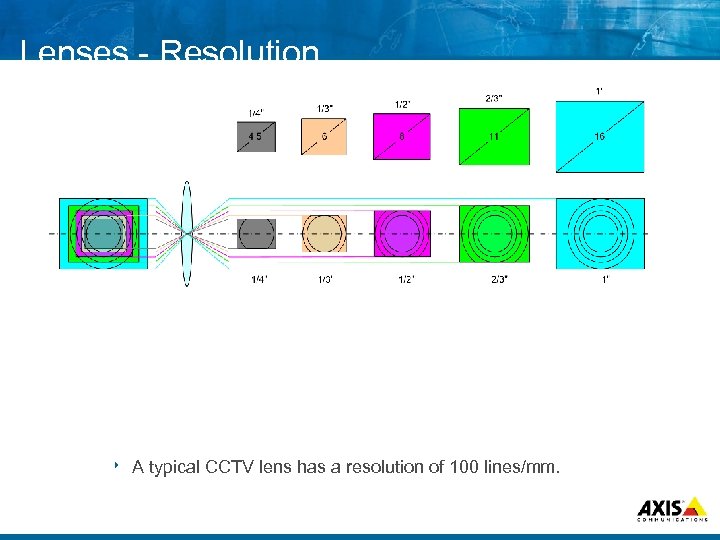 Lenses Resolution 8 A typical CCTV lens has a resolution of 100 lines/mm.
Lenses Resolution 8 A typical CCTV lens has a resolution of 100 lines/mm.
 Lenses – Types: Wide angle C Large angle of view C Good in low light C Good depth of field D “Barrel” distortion D Not for long distances
Lenses – Types: Wide angle C Large angle of view C Good in low light C Good depth of field D “Barrel” distortion D Not for long distances
 Lenses – Types: Wide angle image example 8 Example of barrel distortion & missing optical low pass filter
Lenses – Types: Wide angle image example 8 Example of barrel distortion & missing optical low pass filter
 Lenses – Types: Telephoto C Good on long distance C No barrel distortion D Shallow (small ) depth of field D Bad in low light
Lenses – Types: Telephoto C Good on long distance C No barrel distortion D Shallow (small ) depth of field D Bad in low light
 Lenses – Types: Vari focal 8 The focal length can be adjusted 8 Needs refocusing after focal length adjustment 8 Less precision needed in focal length calculation
Lenses – Types: Vari focal 8 The focal length can be adjusted 8 Needs refocusing after focal length adjustment 8 Less precision needed in focal length calculation
 Lenses – Types: Zoom 8 Zoom – the focal length can be adjusted with maintained focus 8 Often motorised.
Lenses – Types: Zoom 8 Zoom – the focal length can be adjusted with maintained focus 8 Often motorised.
 Special Lenses – Fish eye 8 Extremely wide angle (~180 deg) lenses are called “Fish eye lenses”
Special Lenses – Fish eye 8 Extremely wide angle (~180 deg) lenses are called “Fish eye lenses”
 Lenses – Example: Fisheye image 8 A fish eye lens on a high resolution camera can work as a pan/tilt/zoom camera
Lenses – Example: Fisheye image 8 A fish eye lens on a high resolution camera can work as a pan/tilt/zoom camera
 Special Lenses – Pin hole Exit pupil is 1 3 mm. 8 Can be either low end $1 lenses or high end >$500 lenses. 8
Special Lenses – Pin hole Exit pupil is 1 3 mm. 8 Can be either low end $1 lenses or high end >$500 lenses. 8
 Questions & Answers
Questions & Answers
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Applications & Solutions
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Applications & Solutions
 What is a solution? 8 Network video solutions Several network video products and an application Specialized applications Integration with other systems
What is a solution? 8 Network video solutions Several network video products and an application Specialized applications Integration with other systems
 The value of applications Applications are the key complement for network video solutions 8 Applications adds critical functionality 8 For example: Advanced storage Databases Advanced event handling Video management Scalability Integration Languages Customization
The value of applications Applications are the key complement for network video solutions 8 Applications adds critical functionality 8 For example: Advanced storage Databases Advanced event handling Video management Scalability Integration Languages Customization
 AXIS strategy 8 Partner program Axis Application Development Partner 8 Own software (Of a more generic type) Axis Camera Explorer Axis Camera Recorder Axis Camera Station
AXIS strategy 8 Partner program Axis Application Development Partner 8 Own software (Of a more generic type) Axis Camera Explorer Axis Camera Recorder Axis Camera Station
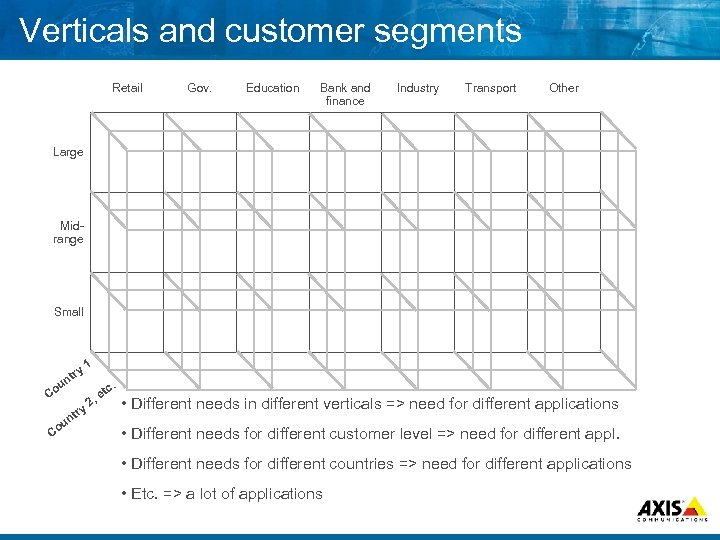 Verticals and customer segments Retail Gov. Education Bank and finance Industry Transport Other Large Mid range Small ry nt 1 u Co ry Co t un . c et 2, • Different needs in different verticals => need for different applications • Different needs for different customer level => need for different appl. • Different needs for different countries => need for different applications • Etc. => a lot of applications
Verticals and customer segments Retail Gov. Education Bank and finance Industry Transport Other Large Mid range Small ry nt 1 u Co ry Co t un . c et 2, • Different needs in different verticals => need for different applications • Different needs for different customer level => need for different appl. • Different needs for different countries => need for different applications • Etc. => a lot of applications
 ADP Program – Summary Win –W 8 For distributors and Axis: Increased market size and sales 8 For partners: Marketing and technical assistance Large installed base of network video products business opportunities 8 For end users: Access to a wide range of complete application solutions in – Win
ADP Program – Summary Win –W 8 For distributors and Axis: Increased market size and sales 8 For partners: Marketing and technical assistance Large installed base of network video products business opportunities 8 For end users: Access to a wide range of complete application solutions in – Win
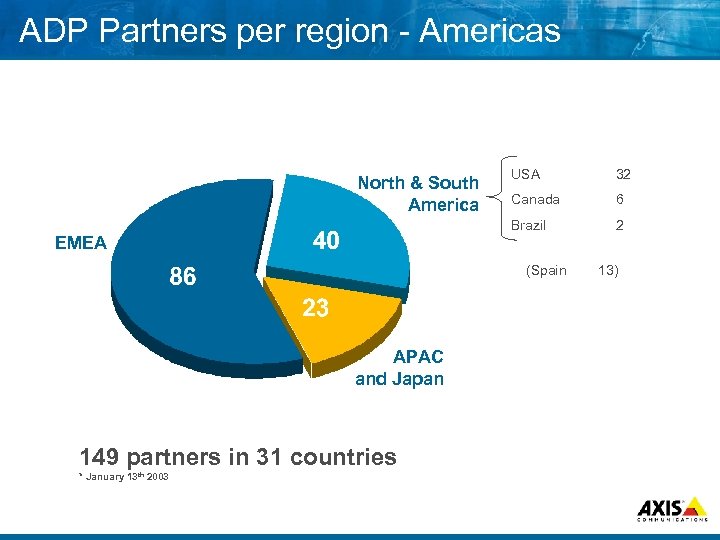 ADP Partners per region Americas USA 32 Canada 6 Brazil North & South America 2 EMEA (Spain APAC and Japan 149 partners in 31 countries * January 13 th 2003 13)
ADP Partners per region Americas USA 32 Canada 6 Brazil North & South America 2 EMEA (Spain APAC and Japan 149 partners in 31 countries * January 13 th 2003 13)
 Q&A
Q&A
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Designing IP Surveillance Solutions
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Designing IP Surveillance Solutions
 The basics 8 In some ways similar to analog: What do we need to monitor? When do we need to monitor it? How many cameras is needed to cover? How much video do we need to transfer How much video do we need to save? Do we need to identify or detect?
The basics 8 In some ways similar to analog: What do we need to monitor? When do we need to monitor it? How many cameras is needed to cover? How much video do we need to transfer How much video do we need to save? Do we need to identify or detect?
 What do we need to monitor 8 Define the scene(s) Lighting conditions Distances Angle of view needed High traffic or low traffic
What do we need to monitor 8 Define the scene(s) Lighting conditions Distances Angle of view needed High traffic or low traffic
 When do we need monitor it? 8 Same need to monitor day/night/weekend? 8 Schedule the needs for every “scene”
When do we need monitor it? 8 Same need to monitor day/night/weekend? 8 Schedule the needs for every “scene”
 How many cameras is needed to cover? 8 Which types of cameras Light sensitivity? Video quality? Which type of lens? Speed? PTZ? I/O Needs? are needed?
How many cameras is needed to cover? 8 Which types of cameras Light sensitivity? Video quality? Which type of lens? Speed? PTZ? I/O Needs? are needed?
 How much video do we need to transfer 30 fps transferred around the clock?
How much video do we need to transfer 30 fps transferred around the clock?
 How much video do we need to save 30 fps saved around the clock?
How much video do we need to save 30 fps saved around the clock?
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER The network
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER The network
 LAN/WAN inventory 8 Congestion level of current LAN 8 Congestion level of current WAN links 8 Schedule of congestion levels 8 Redundancy of WAN links
LAN/WAN inventory 8 Congestion level of current LAN 8 Congestion level of current WAN links 8 Schedule of congestion levels 8 Redundancy of WAN links
 Network (LAN) New network or existing infrastructure? The answer might be in the needs discussed earlier
Network (LAN) New network or existing infrastructure? The answer might be in the needs discussed earlier
 New network (LAN) 8 Speed? 8 100 Mbit/s switches 8 1 Gbit/s Backbone
New network (LAN) 8 Speed? 8 100 Mbit/s switches 8 1 Gbit/s Backbone
 New network (LAN) 8 Guidelines: Calculate 30% extra capacity Avoid cross use with public (parallel) network as long as possible
New network (LAN) 8 Guidelines: Calculate 30% extra capacity Avoid cross use with public (parallel) network as long as possible
 New network (WAN) 8 Share WAN links with the public network? 8 Extra links needed for redundancy? 8 Distributed storage needed?
New network (WAN) 8 Share WAN links with the public network? 8 Extra links needed for redundancy? 8 Distributed storage needed?
 Existing network (LAN) Possible at all?
Existing network (LAN) Possible at all?
 Existing network (LAN) 8“Mixed mode” Separate network for backbone/main installation, public network where needed 8 VLAN A “logical” way to separate the surveillance network from the public 8 Qo. S Ensure the available bandwidth for surveillance equipment on the public network
Existing network (LAN) 8“Mixed mode” Separate network for backbone/main installation, public network where needed 8 VLAN A “logical” way to separate the surveillance network from the public 8 Qo. S Ensure the available bandwidth for surveillance equipment on the public network
 Existing network (WAN) 8 Use VPN’s? (compare with VLAN’s) 8 Distributed storage? 8 Nightly transfers of recorded material?
Existing network (WAN) 8 Use VPN’s? (compare with VLAN’s) 8 Distributed storage? 8 Nightly transfers of recorded material?
 Conclusions 8 The basic’s still apply Do a thorough inventory of the needs 8 High performance Infrastructure equipment are dropping in price/usage complexity 8 Avoid “free” sharing with public networks 8 VLANS, Qo. S & VPN’s are excellent tools for a surveillance network
Conclusions 8 The basic’s still apply Do a thorough inventory of the needs 8 High performance Infrastructure equipment are dropping in price/usage complexity 8 Avoid “free” sharing with public networks 8 VLANS, Qo. S & VPN’s are excellent tools for a surveillance network
 Cases 8 Case examples: Education Large scale Distributed systems Services
Cases 8 Case examples: Education Large scale Distributed systems Services
 Questions & Answers
Questions & Answers


