6201673840d39bd2809bb4fe502b75f7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 113
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Axis Communications Partner Training
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Axis Communications Partner Training
 Agenda 8 Overview – (8: 30 am – 12: 00 pm) Network camera housings CCTV and surveillance demystified Optics
Agenda 8 Overview – (8: 30 am – 12: 00 pm) Network camera housings CCTV and surveillance demystified Optics
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Camera Enclosures
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Camera Enclosures
 Overview 8 Rating systems 8 General considerations 8 Installation tips 8 Recommended enclosures AXIS 290 B Network Camera Housing AXIS Fusion Dome
Overview 8 Rating systems 8 General considerations 8 Installation tips 8 Recommended enclosures AXIS 290 B Network Camera Housing AXIS Fusion Dome
 Rating Systems 8 Many different systems NEMA, IEC, UL, CSA… 8 Industry action groups/companies 8 Product design, performance and application 8 Common reference & interchangeability
Rating Systems 8 Many different systems NEMA, IEC, UL, CSA… 8 Industry action groups/companies 8 Product design, performance and application 8 Common reference & interchangeability
 Rating Systems 8 International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Consists of two letter prefix IP followed by two digits Solid object ingress (first digit) Liquid ingress (second digit) 8 Examples: IP 65 dust tight, heavy water spray IP 66 dust tight, heavy jet spray IP 54 dust resistant, splashing water
Rating Systems 8 International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Consists of two letter prefix IP followed by two digits Solid object ingress (first digit) Liquid ingress (second digit) 8 Examples: IP 65 dust tight, heavy water spray IP 66 dust tight, heavy jet spray IP 54 dust resistant, splashing water
 Rating Systems: IEC 8 IP (First number) 0: No special protection 1: Solid objects > 50 mm diameter 2: Solid objects > 12 mm diameter 3: Solid objects > 2. 5 mm diameter 4: Solid objects > 1 mm diameter 5: Dust protected 6: Dust tight
Rating Systems: IEC 8 IP (First number) 0: No special protection 1: Solid objects > 50 mm diameter 2: Solid objects > 12 mm diameter 3: Solid objects > 2. 5 mm diameter 4: Solid objects > 1 mm diameter 5: Dust protected 6: Dust tight
 Rating Systems: IEC 8 IP (Second number) 0: No special protection 1: Dripping water 2: Dripping water when tilted 15 degrees 3: Spraying water 4: Splashing water 5: Water jet spray 6: Heavy jet spray 7: Immersion 8: Submersion
Rating Systems: IEC 8 IP (Second number) 0: No special protection 1: Dripping water 2: Dripping water when tilted 15 degrees 3: Spraying water 4: Splashing water 5: Water jet spray 6: Heavy jet spray 7: Immersion 8: Submersion
 Rating Systems 8 National Electrical Manufacturers Association Water ingress Solid object ingress Mechanical impact of enclosure on walls Oil resistance Corrosion resistance Door and cover latching requirements (NEMA)
Rating Systems 8 National Electrical Manufacturers Association Water ingress Solid object ingress Mechanical impact of enclosure on walls Oil resistance Corrosion resistance Door and cover latching requirements (NEMA)
 Rating Systems: NEMA 8 1: General purpose (indoor) 8 2: Water drip proof (indoor) 8 3 R: Dust tight, rain tight, ice resistant (outdoor) 8 4: Water tight and dust tight (indoor/outdoor) 8 4 X: Water tight, dust tight, corrosion resistant (indoor/outdoor)
Rating Systems: NEMA 8 1: General purpose (indoor) 8 2: Water drip proof (indoor) 8 3 R: Dust tight, rain tight, ice resistant (outdoor) 8 4: Water tight and dust tight (indoor/outdoor) 8 4 X: Water tight, dust tight, corrosion resistant (indoor/outdoor)
 Rating Systems: NEMA 8 9: Indoor hazardous locations 8 12: Industrial use – drip tight and dust tight (indoor) 8 13: Oil Tight and Dust Tight (indoor)
Rating Systems: NEMA 8 9: Indoor hazardous locations 8 12: Industrial use – drip tight and dust tight (indoor) 8 13: Oil Tight and Dust Tight (indoor)
 General Considerations 8 Local codes 8 NEMA rating of 3, 3 R, 4, 4 X, 6, or 6 P for outdoor 8 IP Rating 66, 65 8 Resistance measurement 8 4 x rule
General Considerations 8 Local codes 8 NEMA rating of 3, 3 R, 4, 4 X, 6, or 6 P for outdoor 8 IP Rating 66, 65 8 Resistance measurement 8 4 x rule
 Installation Tips Consult wiring distance chart Add up total VAC needed 8 Camera placement is important 8 Environmental conditions Heater/blower combinations Sun shrouds Cabling considerations 8 Accessories POL AXIS 2191 Audio Module 8
Installation Tips Consult wiring distance chart Add up total VAC needed 8 Camera placement is important 8 Environmental conditions Heater/blower combinations Sun shrouds Cabling considerations 8 Accessories POL AXIS 2191 Audio Module 8
 AXIS 2130 R Enclosures 8 AXIS Outdoor Fusion Dome Outdoor dome housing Tinted lower dome Heater and blower for outdoor use 8 AXIS Indoor Fusion Dome Indoor dome housing Tinted lower dome
AXIS 2130 R Enclosures 8 AXIS Outdoor Fusion Dome Outdoor dome housing Tinted lower dome Heater and blower for outdoor use 8 AXIS Indoor Fusion Dome Indoor dome housing Tinted lower dome
 AXIS 2130 R Enclosures 8 AXIS Indoor Recessed Enclosure Low profile indoor ceiling housing Can be installed in either sheetrock or drop ceilings Tinted lower dome 8 AXIS Outdoor Vandal Fusion Dome Offers vandal resistant protection in a compact size Heater and blower for outdoor use Made from durable cast aluminum
AXIS 2130 R Enclosures 8 AXIS Indoor Recessed Enclosure Low profile indoor ceiling housing Can be installed in either sheetrock or drop ceilings Tinted lower dome 8 AXIS Outdoor Vandal Fusion Dome Offers vandal resistant protection in a compact size Heater and blower for outdoor use Made from durable cast aluminum
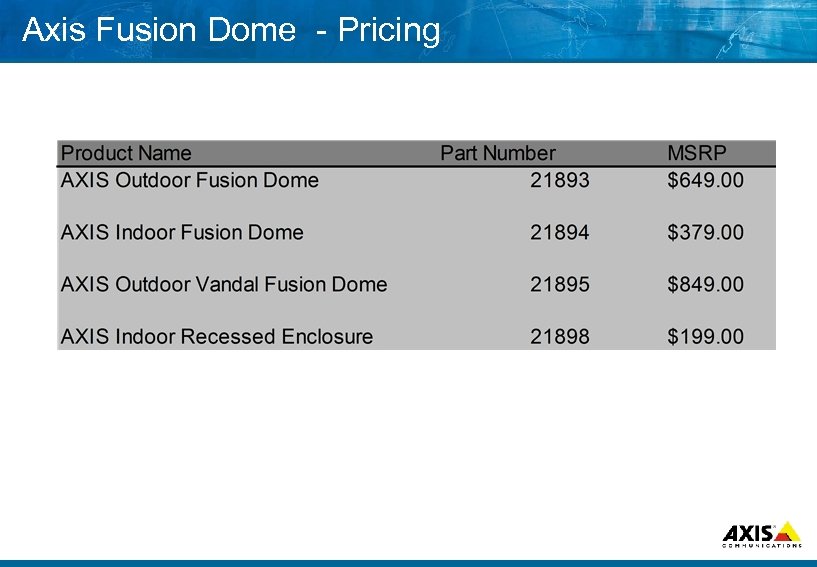 Axis Fusion Dome Pricing
Axis Fusion Dome Pricing
 AXIS 290 B Network Camera Housing 8 IP 65 classified – Protected against dust and heavy rain 8 Axis network cameras supported AXIS 2120 Network Camera AXIS 2420 Network Camera AXIS 2110 Network Camera 8 Temperature range 4° F to +108° F 8 Integral tamper proof wall mounting bracket. 8 Integrated sunshield 8 1 year limited warranty
AXIS 290 B Network Camera Housing 8 IP 65 classified – Protected against dust and heavy rain 8 Axis network cameras supported AXIS 2120 Network Camera AXIS 2420 Network Camera AXIS 2110 Network Camera 8 Temperature range 4° F to +108° F 8 Integral tamper proof wall mounting bracket. 8 Integrated sunshield 8 1 year limited warranty
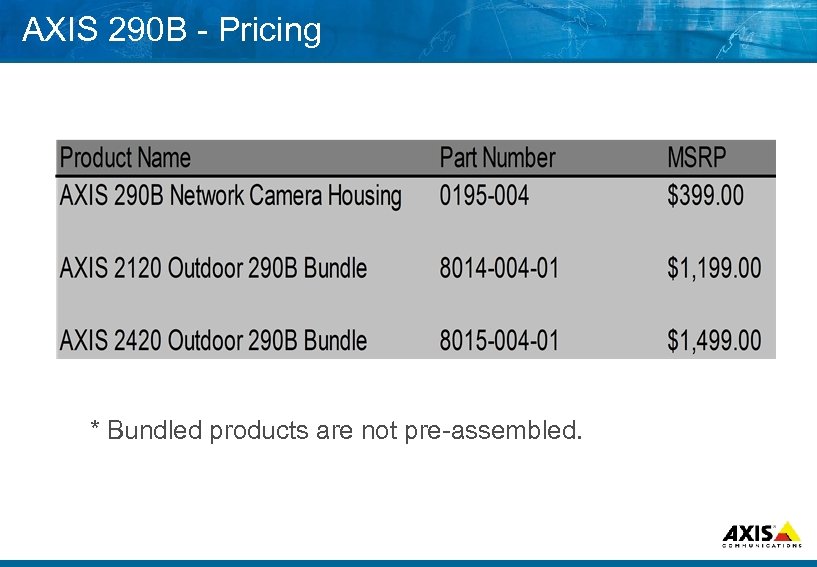 AXIS 290 B Pricing * Bundled products are not pre assembled.
AXIS 290 B Pricing * Bundled products are not pre assembled.
 Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER CCTV Demystified
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER CCTV Demystified
 CCTV Closed Circuit Tele Vision
CCTV Closed Circuit Tele Vision
 Video 8 Video is Latin and means “I can see” 8 A human eye will consider 16 frames per second to be ”real time” video 8 A CCTV system provides up to 30 frames per second
Video 8 Video is Latin and means “I can see” 8 A human eye will consider 16 frames per second to be ”real time” video 8 A CCTV system provides up to 30 frames per second
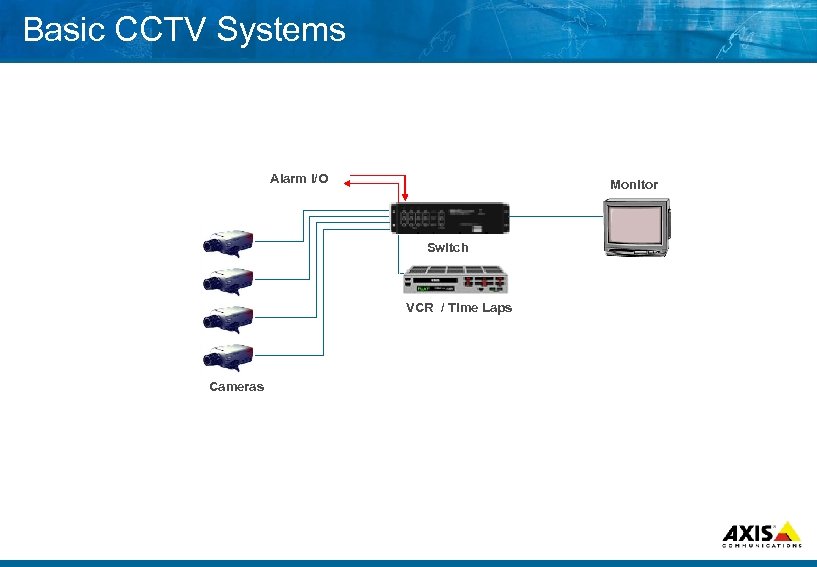 Basic CCTV Systems Alarm I/O Monitor Switch VCR / Time Laps Cameras
Basic CCTV Systems Alarm I/O Monitor Switch VCR / Time Laps Cameras
 Transmission Medium 8 Wired Coax – 75 ohm RG 59 – 300 meter RG 11 – 500 meter Twisted pair 2 wire twisted – 1000 meter Fiber optics Single mode or Multi mode fiber Long distance – >10, 000 meter 8 Wireless Laser link Microwave Radio link
Transmission Medium 8 Wired Coax – 75 ohm RG 59 – 300 meter RG 11 – 500 meter Twisted pair 2 wire twisted – 1000 meter Fiber optics Single mode or Multi mode fiber Long distance – >10, 000 meter 8 Wireless Laser link Microwave Radio link
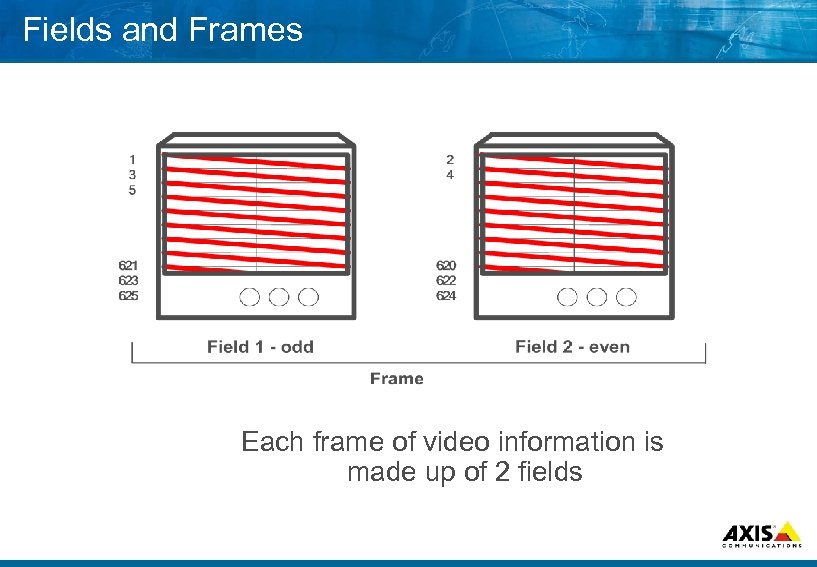 Fields and Frames Each frame of video information is made up of 2 fields
Fields and Frames Each frame of video information is made up of 2 fields
 TV Standards 8 NTSC – National Television System Committee First standard 1953 525 horizontal lines 60 fields/sec = 30 frames/sec
TV Standards 8 NTSC – National Television System Committee First standard 1953 525 horizontal lines 60 fields/sec = 30 frames/sec
 TV Standards in Countries 8 http: //www. alkenmrs. com/video/wwstandards 1. html 8 http: //www. ee. surrey. ac. uk/Contrib/World. TV/
TV Standards in Countries 8 http: //www. alkenmrs. com/video/wwstandards 1. html 8 http: //www. ee. surrey. ac. uk/Contrib/World. TV/
 The Video Signal Theory 8 Composite video The complete video includes all signals 8 Y/C video Y is the luminance signal C is the chroma signal Gives a better image quality
The Video Signal Theory 8 Composite video The complete video includes all signals 8 Y/C video Y is the luminance signal C is the chroma signal Gives a better image quality
 Resolution 8 Vertical resolution 8 Horizontal resolution Analog cameras 330 400 lines is normal – Low res >460 lines is good quality – High res
Resolution 8 Vertical resolution 8 Horizontal resolution Analog cameras 330 400 lines is normal – Low res >460 lines is good quality – High res
 Resolution 8 Resolution measurement Digital cameras 640 x 480 pixel 1280 x 1024 pixel in the future
Resolution 8 Resolution measurement Digital cameras 640 x 480 pixel 1280 x 1024 pixel in the future
 Lights 8 What is light? 8 Eye vs CCD 8 Natural light sources 8 Artificial light sources
Lights 8 What is light? 8 Eye vs CCD 8 Natural light sources 8 Artificial light sources
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Main Items in a CCTV System
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Main Items in a CCTV System
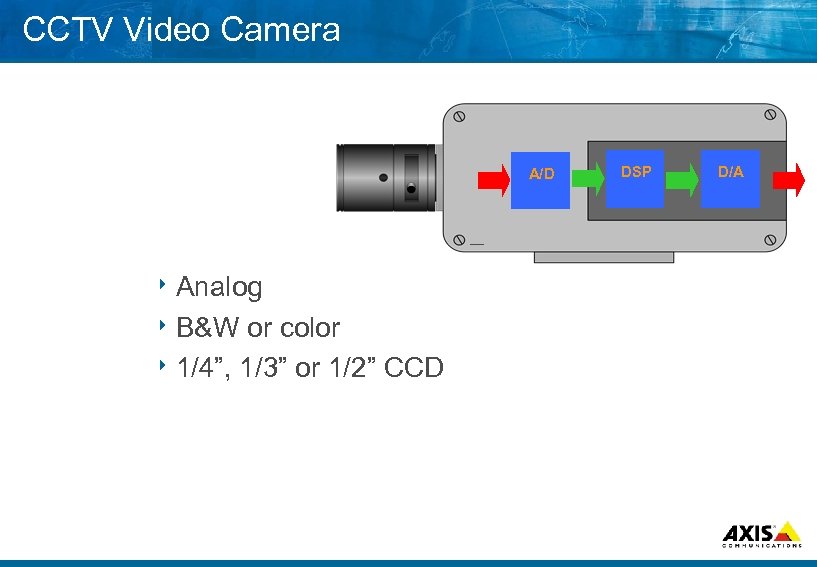 CCTV Video Camera A/D 8 Analog 8 B&W or color 8 1/4”, 1/3” or 1/2” CCD DSP D/A
CCTV Video Camera A/D 8 Analog 8 B&W or color 8 1/4”, 1/3” or 1/2” CCD DSP D/A
 Camera Lens 8 Basic lens types Manual iris Automatic iris 8 Lens function Fixed focal length Varifocal length Zoom lens 8 Lens / chip 1/3” 1/2” size 8 Mounting standards CS mount C mount
Camera Lens 8 Basic lens types Manual iris Automatic iris 8 Lens function Fixed focal length Varifocal length Zoom lens 8 Lens / chip 1/3” 1/2” size 8 Mounting standards CS mount C mount
 Domes 8 A Dome camera combines the design elegance of a dome enclosure, color camera, a fast pan and tilt mechanism and an environmental enclosure 8 The result is an “all in one” product trend has been very clear the last years: Fewer pan and tilt devices and more Domes
Domes 8 A Dome camera combines the design elegance of a dome enclosure, color camera, a fast pan and tilt mechanism and an environmental enclosure 8 The result is an “all in one” product trend has been very clear the last years: Fewer pan and tilt devices and more Domes
 Video Monitors 8 A monitor is very similar to a standard television set, however, it lacks the electronics to pick up regular television, the tuner Monochrome – up to 1000 lines Color – up to 800 lines 8 Market different between plastic cased monitors and metal cased monitors
Video Monitors 8 A monitor is very similar to a standard television set, however, it lacks the electronics to pick up regular television, the tuner Monochrome – up to 1000 lines Color – up to 800 lines 8 Market different between plastic cased monitors and metal cased monitors
 Video Recorders 8 Time lapse VCR A special slow recording VCR Max 540, 000 images (VHS standard) Up to 960 hours on a single VHS tape Controllable via RS 232 8 VCR with DAT 8 Digital Video Recorder (DVR)
Video Recorders 8 Time lapse VCR A special slow recording VCR Max 540, 000 images (VHS standard) Up to 960 hours on a single VHS tape Controllable via RS 232 8 VCR with DAT 8 Digital Video Recorder (DVR)
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Control Devices in CCTV
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Control Devices in CCTV
 Video Switchers 8 Units that provide automated as well as manual switching of full screen images 8 Larger units will normally also provide an ability to control dome cameras and PTZ’s 8 When one camera is on selected for recording, the other cameras are NOT being recorded at all
Video Switchers 8 Units that provide automated as well as manual switching of full screen images 8 Larger units will normally also provide an ability to control dome cameras and PTZ’s 8 When one camera is on selected for recording, the other cameras are NOT being recorded at all
 Video Multiplexers 8 Multiplexer units are high speed switchers that provide full screen images from up to 16 cameras 8 Available in two models Simplex Duplex 8 Normally also provide the ability for viewing multiple cameras in 2 x 2, 4 x 4 etc
Video Multiplexers 8 Multiplexer units are high speed switchers that provide full screen images from up to 16 cameras 8 Available in two models Simplex Duplex 8 Normally also provide the ability for viewing multiple cameras in 2 x 2, 4 x 4 etc
 Quads 8 A quad sends up to four cameras to the monitor and to the recorder at the same time, each camera gets a quarter of the monitor 8 All of the information from each camera gets recorded but ONLY in small quarter screen clarity
Quads 8 A quad sends up to four cameras to the monitor and to the recorder at the same time, each camera gets a quarter of the monitor 8 All of the information from each camera gets recorded but ONLY in small quarter screen clarity
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Accessories
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Accessories
 Housings 8 Outdoor 8 Indoor 8 Aluminium and plastic common 8 Blower, heater optional 8 Housings for special applications Process industry Explosion proof
Housings 8 Outdoor 8 Indoor 8 Aluminium and plastic common 8 Blower, heater optional 8 Housings for special applications Process industry Explosion proof
 Pan and Tilt Head 8 A normal camera can be placed on pan and tilt devices which will allow the camera to be moved up, down, left and right from a remote location 8 A zoom lens will allow a closer view 8 In and outdoor version
Pan and Tilt Head 8 A normal camera can be placed on pan and tilt devices which will allow the camera to be moved up, down, left and right from a remote location 8 A zoom lens will allow a closer view 8 In and outdoor version
 Infrared (IR) Illuminator 8 IR light can not be seen by human eye 8 IR sensitive B&W cameras can see in darkness with IR light 8 Illuminators exist in two versions Lamp based LED versions 8 Distance to the object 20 W 10 15 m 300 W 80 120 m
Infrared (IR) Illuminator 8 IR light can not be seen by human eye 8 IR sensitive B&W cameras can see in darkness with IR light 8 Illuminators exist in two versions Lamp based LED versions 8 Distance to the object 20 W 10 15 m 300 W 80 120 m
 Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Lenses & Filters
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Lenses & Filters
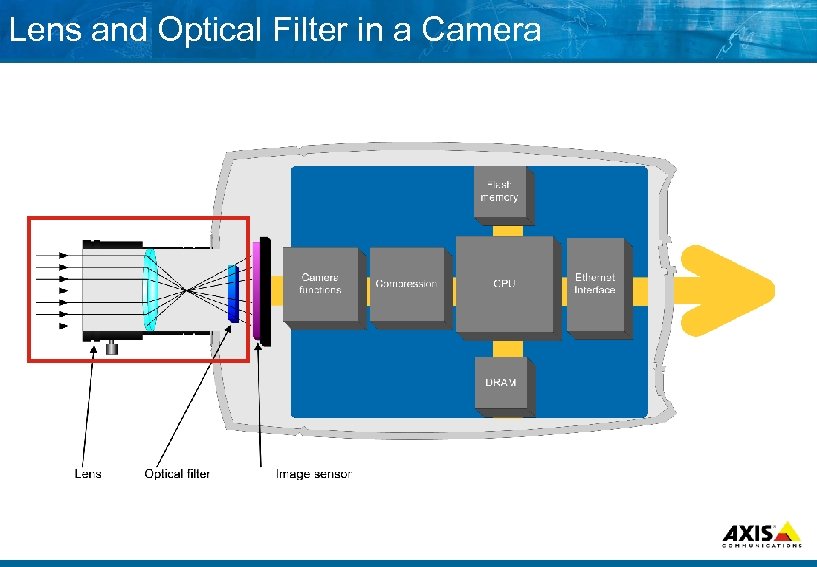 Lens and Optical Filter in a Camera
Lens and Optical Filter in a Camera
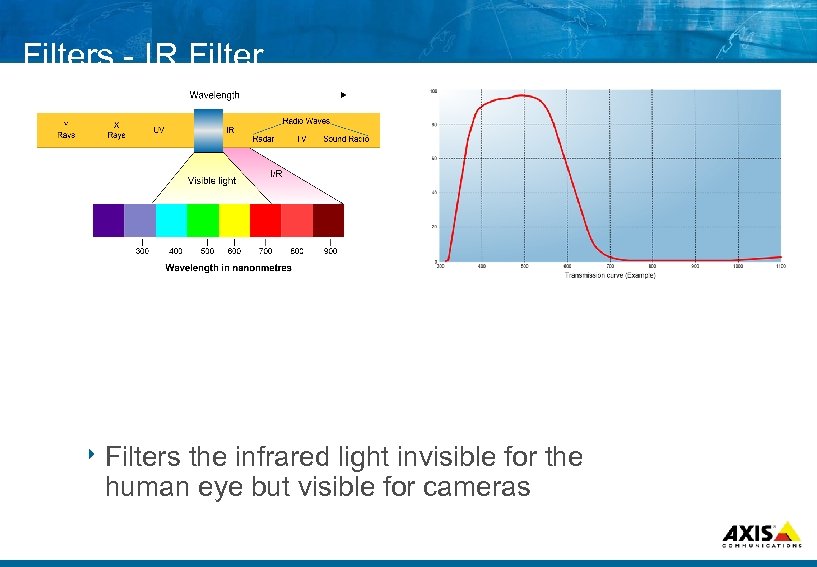 Filters IR Filter 8 Filters the infrared light invisible for the human eye but visible for cameras
Filters IR Filter 8 Filters the infrared light invisible for the human eye but visible for cameras
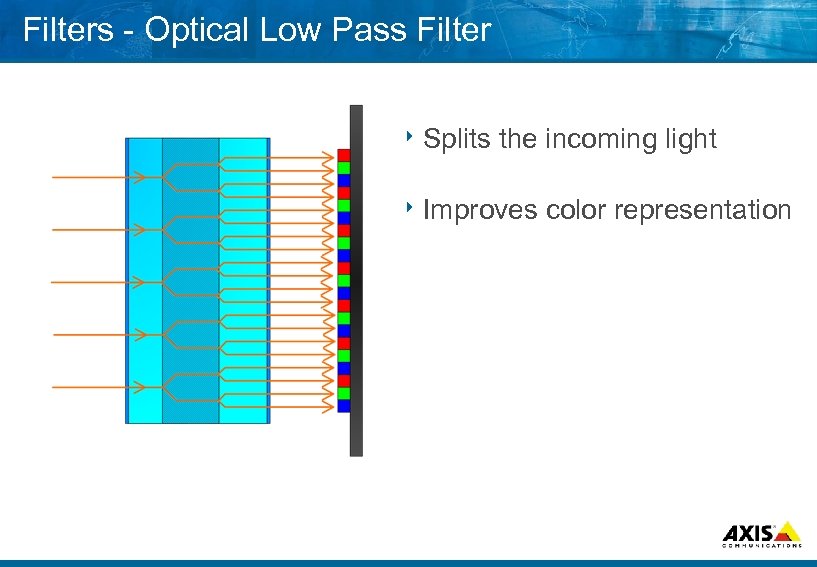 Filters Optical Low Pass Filter 8 Splits the incoming light 8 Improves color representation
Filters Optical Low Pass Filter 8 Splits the incoming light 8 Improves color representation
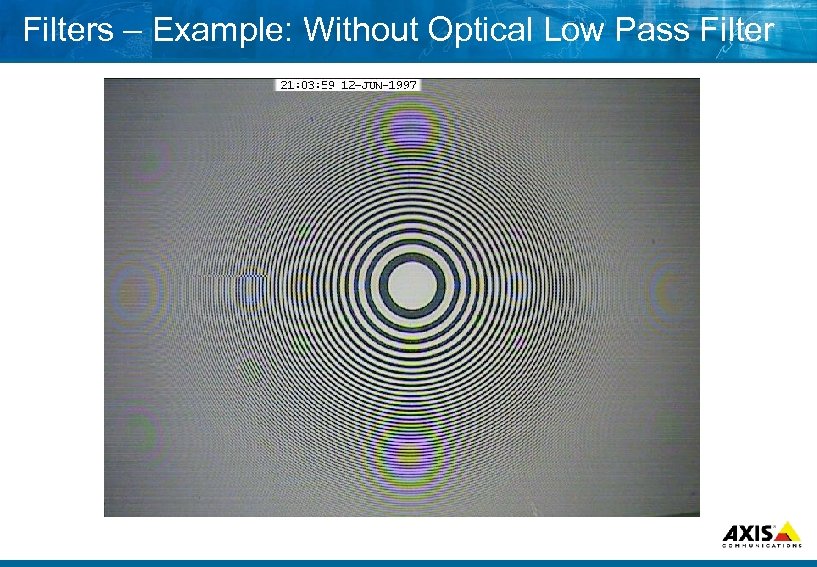 Filters – Example: Without Optical Low Pass Filter
Filters – Example: Without Optical Low Pass Filter
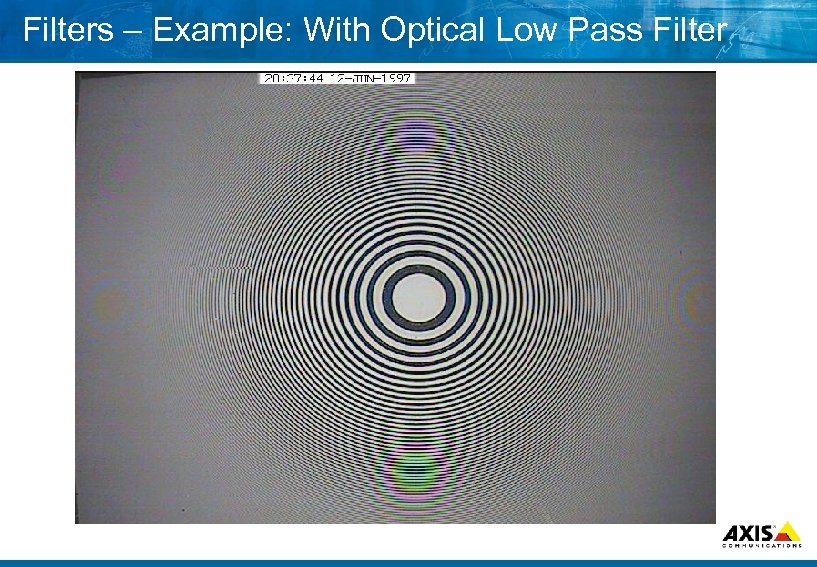 Filters – Example: With Optical Low Pass Filter
Filters – Example: With Optical Low Pass Filter
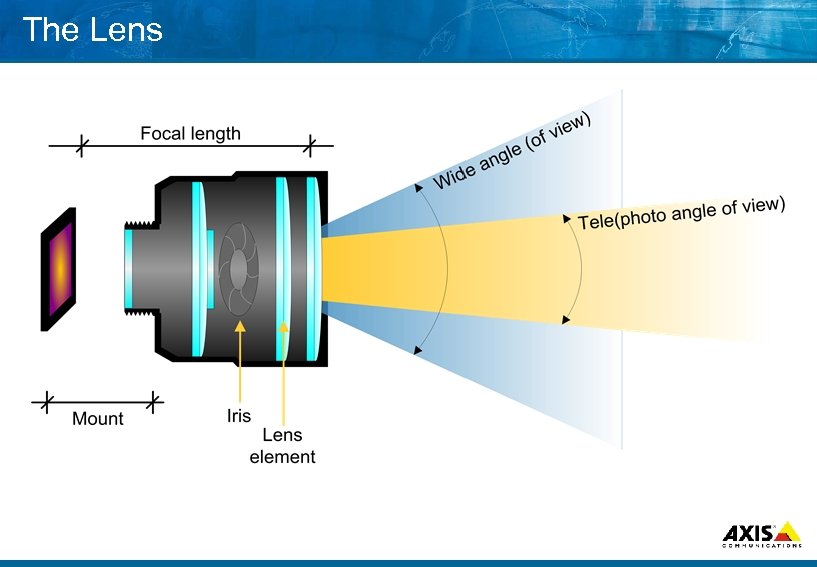 The Lens
The Lens
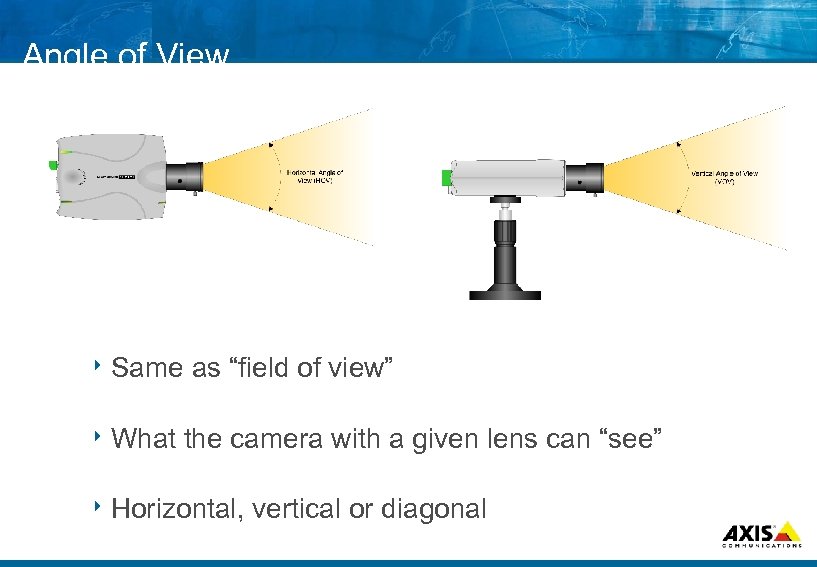 Angle of View 8 Same 8 What as “field of view” the camera with a given lens can “see” 8 Horizontal, vertical or diagonal
Angle of View 8 Same 8 What as “field of view” the camera with a given lens can “see” 8 Horizontal, vertical or diagonal
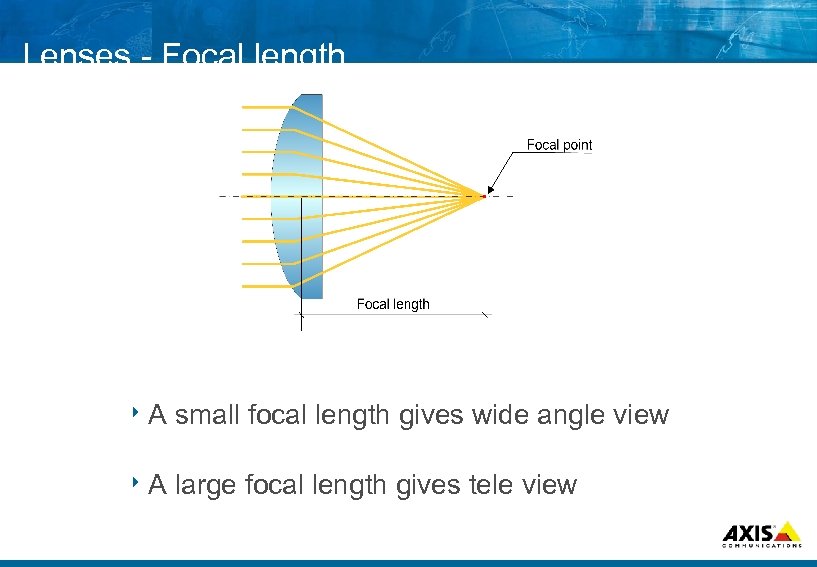 Lenses Focal length 8 A small focal length gives wide angle view 8 A large focal length gives tele view
Lenses Focal length 8 A small focal length gives wide angle view 8 A large focal length gives tele view
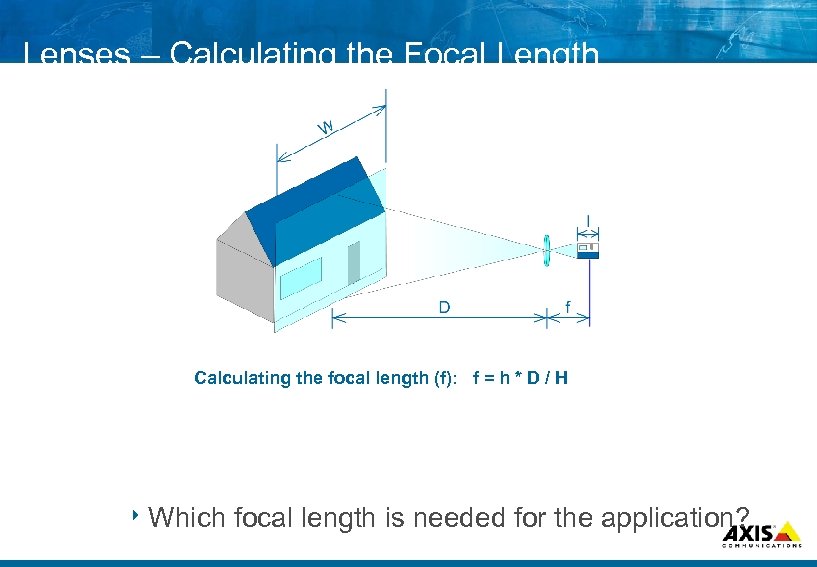 Lenses – Calculating the Focal Length Calculating the focal length (f): f = h * D / H 8 Which focal length is needed for the application?
Lenses – Calculating the Focal Length Calculating the focal length (f): f = h * D / H 8 Which focal length is needed for the application?
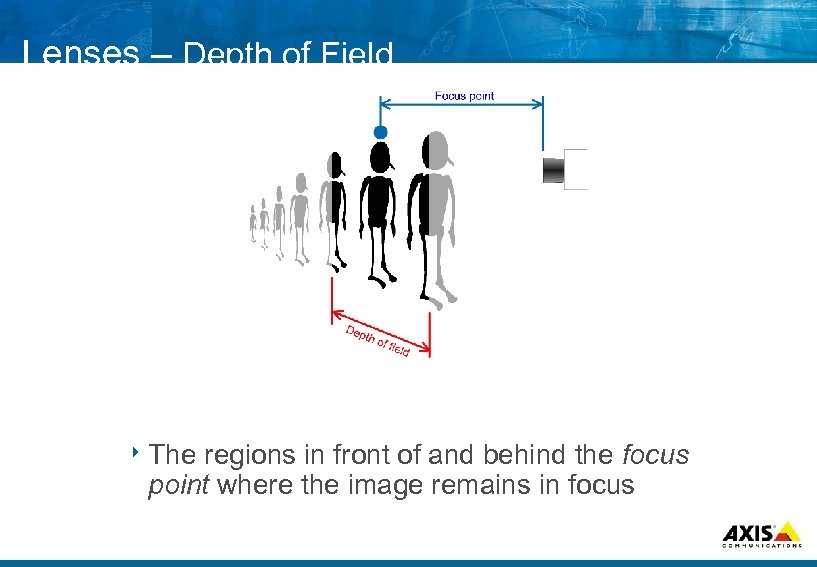 Lenses – Depth of Field 8 The regions in front of and behind the focus point where the image remains in focus
Lenses – Depth of Field 8 The regions in front of and behind the focus point where the image remains in focus
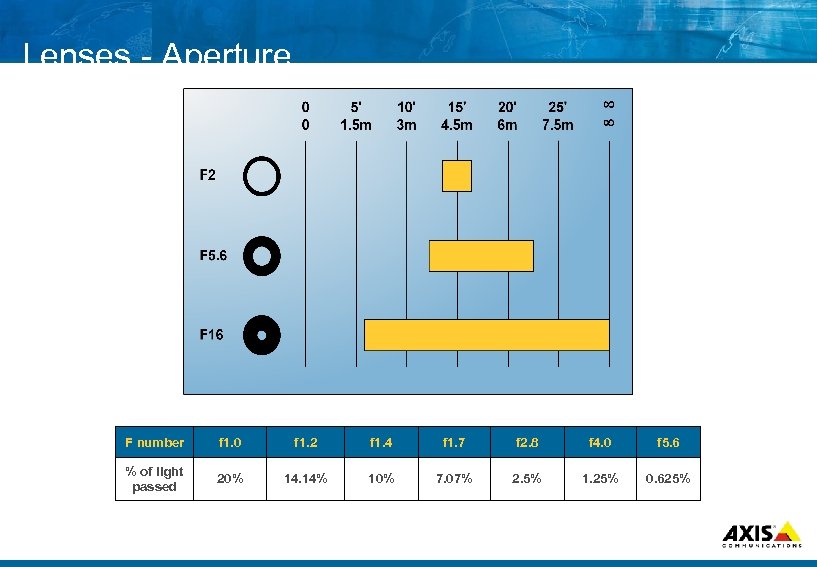 Lenses Aperture F number f 1. 0 f 1. 2 f 1. 4 f 1. 7 f 2. 8 f 4. 0 f 5. 6 % of light passed 20% 14. 14% 10% 7. 07% 2. 5% 1. 25% 0. 625%
Lenses Aperture F number f 1. 0 f 1. 2 f 1. 4 f 1. 7 f 2. 8 f 4. 0 f 5. 6 % of light passed 20% 14. 14% 10% 7. 07% 2. 5% 1. 25% 0. 625%
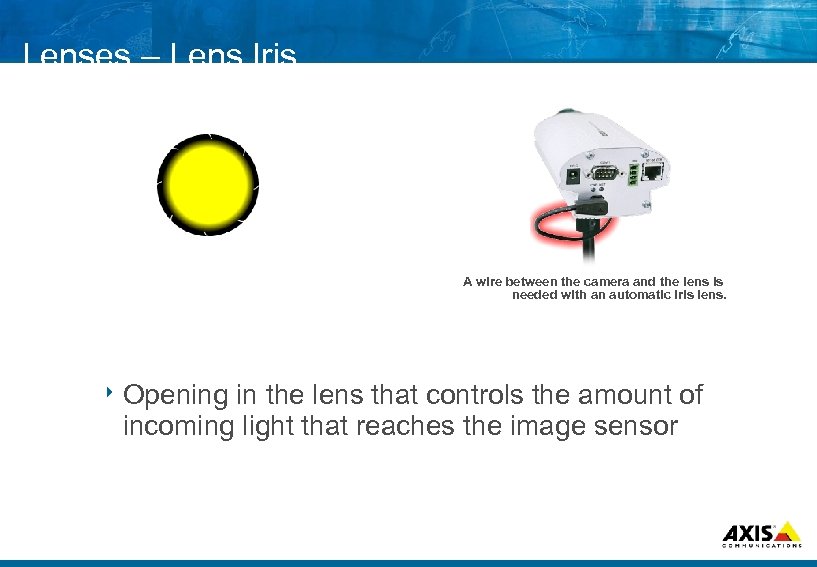 Lenses – Lens Iris A wire between the camera and the lens is needed with an automatic iris lens. 8 Opening in the lens that controls the amount of incoming light that reaches the image sensor
Lenses – Lens Iris A wire between the camera and the lens is needed with an automatic iris lens. 8 Opening in the lens that controls the amount of incoming light that reaches the image sensor
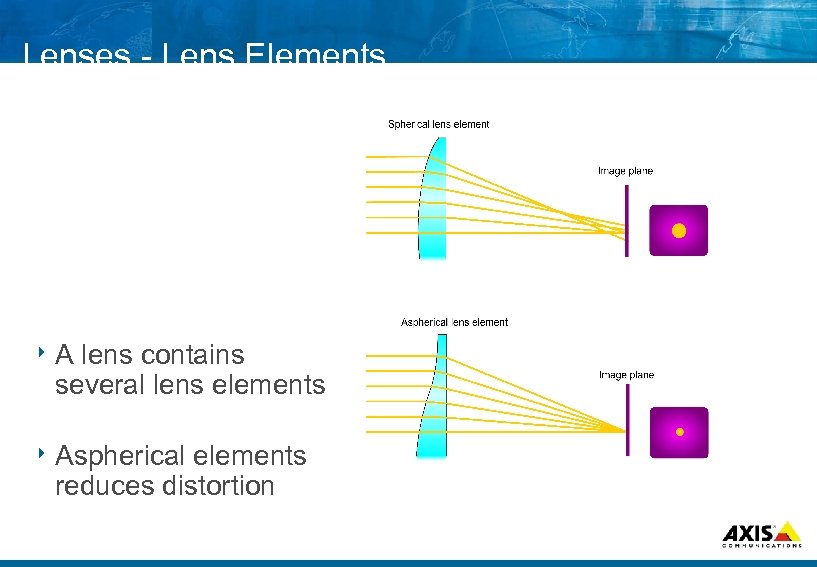 Lenses Lens Elements 8 A lens contains several lens elements 8 Aspherical elements reduces distortion
Lenses Lens Elements 8 A lens contains several lens elements 8 Aspherical elements reduces distortion
 Lenses Mount Standards 8 CS mount 12. 5 mm from camera edge to sensor 8 C mount 17. 5 mm from camera edge to sensor Conversion C to CS is possible
Lenses Mount Standards 8 CS mount 12. 5 mm from camera edge to sensor 8 C mount 17. 5 mm from camera edge to sensor Conversion C to CS is possible
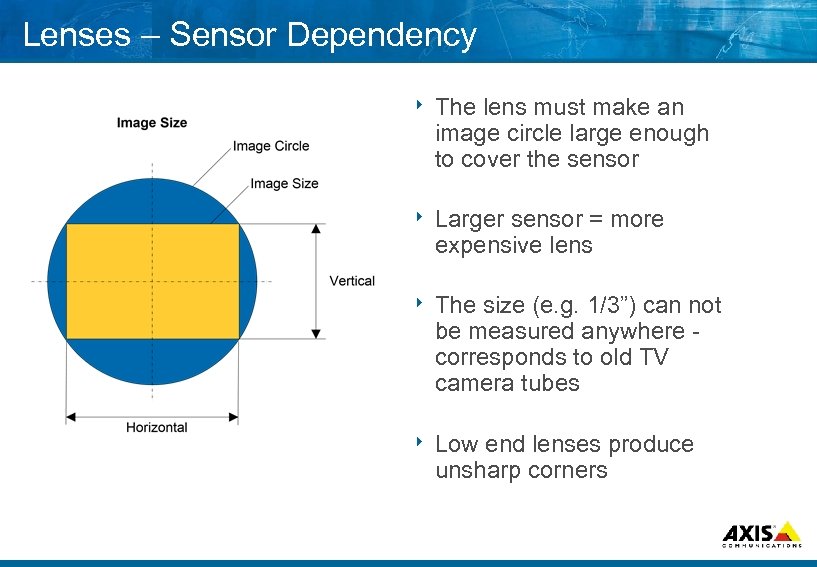 Lenses – Sensor Dependency 8 The lens must make an image circle large enough to cover the sensor 8 Larger sensor = more expensive lens 8 The size (e. g. 1/3”) can not be measured anywhere corresponds to old TV camera tubes 8 Low end lenses produce unsharp corners
Lenses – Sensor Dependency 8 The lens must make an image circle large enough to cover the sensor 8 Larger sensor = more expensive lens 8 The size (e. g. 1/3”) can not be measured anywhere corresponds to old TV camera tubes 8 Low end lenses produce unsharp corners
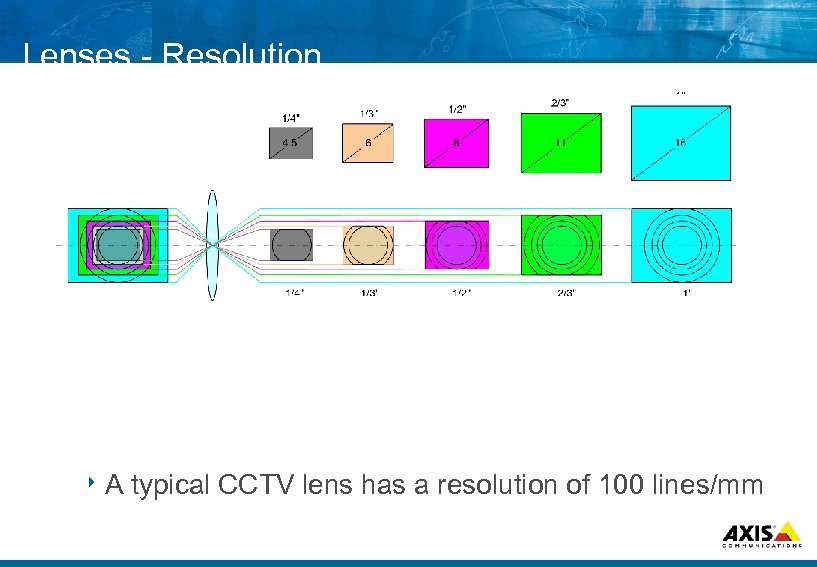 Lenses Resolution 8 A typical CCTV lens has a resolution of 100 lines/mm
Lenses Resolution 8 A typical CCTV lens has a resolution of 100 lines/mm
 Lab Exercise 1. Field of view calculation
Lab Exercise 1. Field of view calculation
 Lenses – Types: Wide Angle C Large angle of view C Good in low light C Good depth of field D “Barrel” distortion D Not for long distances
Lenses – Types: Wide Angle C Large angle of view C Good in low light C Good depth of field D “Barrel” distortion D Not for long distances
 Lenses – Types: Wide Angle Image Example 8 Example of barrel distortion & missing optical low pass filter
Lenses – Types: Wide Angle Image Example 8 Example of barrel distortion & missing optical low pass filter
 Lenses – Types: Telephoto C Good on long distance C No barrel distortion D Shallow (small) depth of field D Bad in low light
Lenses – Types: Telephoto C Good on long distance C No barrel distortion D Shallow (small) depth of field D Bad in low light
 Lenses – Types: Vari focal 8 The focal length can be adjusted 8 Needs refocusing after focal length adjustment 8 Less precision needed in focal length calculation
Lenses – Types: Vari focal 8 The focal length can be adjusted 8 Needs refocusing after focal length adjustment 8 Less precision needed in focal length calculation
 Lenses – Types: Zoom 8 Zoom – the focal length can be adjusted with maintained focus 8 Often motorized
Lenses – Types: Zoom 8 Zoom – the focal length can be adjusted with maintained focus 8 Often motorized
 Special Lenses – Fish Eye 8 Extremely wide angle (~180 deg) lenses are called “fish eye lenses”
Special Lenses – Fish Eye 8 Extremely wide angle (~180 deg) lenses are called “fish eye lenses”
 Lenses – Example: Fisheye Image 8 A fish eye lens on a high resolution camera can work as a pan/tilt/zoom camera
Lenses – Example: Fisheye Image 8 A fish eye lens on a high resolution camera can work as a pan/tilt/zoom camera
 Special Lenses – Pin Hole Exit pupil is 1 3 mm 8 Can be either low end $1 lenses or high end >$500 lenses 8
Special Lenses – Pin Hole Exit pupil is 1 3 mm 8 Can be either low end $1 lenses or high end >$500 lenses 8
 Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
 Agenda 8 Overview – (1: 00 pm – 4: 00 pm) Designing IP Surveillance solutions AXIS Camera Station Axis product roadmap
Agenda 8 Overview – (1: 00 pm – 4: 00 pm) Designing IP Surveillance solutions AXIS Camera Station Axis product roadmap
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Designing IP Surveillance Solutions
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Designing IP Surveillance Solutions
 The Basics 8 In some ways similar to analog: What do we need to monitor? When do we need to monitor it? How many cameras are needed to cover? How much video do we need to transfer? How much video do we need to save? Do we need to identify or detect?
The Basics 8 In some ways similar to analog: What do we need to monitor? When do we need to monitor it? How many cameras are needed to cover? How much video do we need to transfer? How much video do we need to save? Do we need to identify or detect?
 What do we need to monitor? 8 Define the scene(s) Lighting conditions Distances Angle of view needed High traffic or low traffic
What do we need to monitor? 8 Define the scene(s) Lighting conditions Distances Angle of view needed High traffic or low traffic
 When do we need to monitor it? 8 Same need to monitor day/night/weekend? 8 Schedule the needs for every “scene”
When do we need to monitor it? 8 Same need to monitor day/night/weekend? 8 Schedule the needs for every “scene”
 How many cameras are needed to cover? 8 Which types of cameras Light sensitivity? Video quality? Which type of lens? Speed? PTZ? IO needs? are needed?
How many cameras are needed to cover? 8 Which types of cameras Light sensitivity? Video quality? Which type of lens? Speed? PTZ? IO needs? are needed?
 How much video do we need to transfer? 30 fps transferred around the clock?
How much video do we need to transfer? 30 fps transferred around the clock?
 How much video do we need to save? 30 fps saved around the clock?
How much video do we need to save? 30 fps saved around the clock?
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER The Network
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER The Network
 LAN/WAN Inventory 8 Congestion level of current LAN 8 Congestion level of current WAN links 8 Schedule of congestion levels 8 Redundancy of WAN links
LAN/WAN Inventory 8 Congestion level of current LAN 8 Congestion level of current WAN links 8 Schedule of congestion levels 8 Redundancy of WAN links
 Network (LAN) New network or existing infrastructure? The answer might be in the needs discussed earlier
Network (LAN) New network or existing infrastructure? The answer might be in the needs discussed earlier
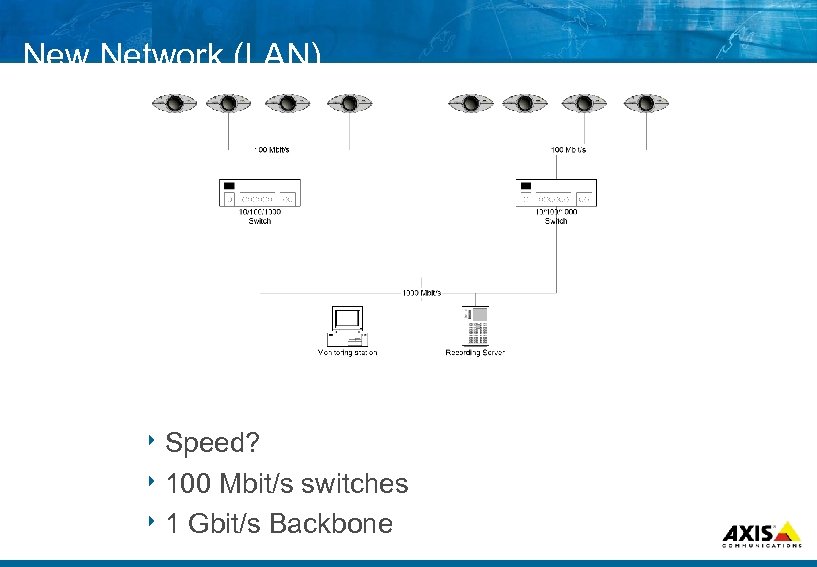 New Network (LAN) 8 Speed? 8 100 Mbit/s switches 8 1 Gbit/s Backbone
New Network (LAN) 8 Speed? 8 100 Mbit/s switches 8 1 Gbit/s Backbone
 New Network (LAN) 8 Guidelines: Calculate 30% extra capacity Avoid cross use with public (parallel) network as long as possible
New Network (LAN) 8 Guidelines: Calculate 30% extra capacity Avoid cross use with public (parallel) network as long as possible
 New Network (WAN) 8 Share 8 Extra WAN links with the public network? links needed for redundancy? 8 Distributed storage needed?
New Network (WAN) 8 Share 8 Extra WAN links with the public network? links needed for redundancy? 8 Distributed storage needed?
 Existing Network (LAN) Possible at all?
Existing Network (LAN) Possible at all?
 Existing Network (LAN) 8 “Mixed mode” Separate network for backbone/main installation, public network where needed 8 VLAN A “logical” way to separate the surveillance network from the public 8 Qo. S Ensure the available bandwidth for surveillance equipment on the public network
Existing Network (LAN) 8 “Mixed mode” Separate network for backbone/main installation, public network where needed 8 VLAN A “logical” way to separate the surveillance network from the public 8 Qo. S Ensure the available bandwidth for surveillance equipment on the public network
 Existing Network (WAN) 8 Use VPN’s? (compare with VLAN’s) 8 Distributed 8 Nightly storage? transfers of recorded material?
Existing Network (WAN) 8 Use VPN’s? (compare with VLAN’s) 8 Distributed 8 Nightly storage? transfers of recorded material?
 Conclusions 8 The basics still apply Do a thorough inventory of the needs 8 High performance infrastructure equipment is dropping in price/usage complexity 8 Avoid “free” sharing with public networks 8 VLANS, Qo. S, VPN’s are excellent tools for a surveillance network
Conclusions 8 The basics still apply Do a thorough inventory of the needs 8 High performance infrastructure equipment is dropping in price/usage complexity 8 Avoid “free” sharing with public networks 8 VLANS, Qo. S, VPN’s are excellent tools for a surveillance network
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK Cases SMARTER
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK Cases SMARTER
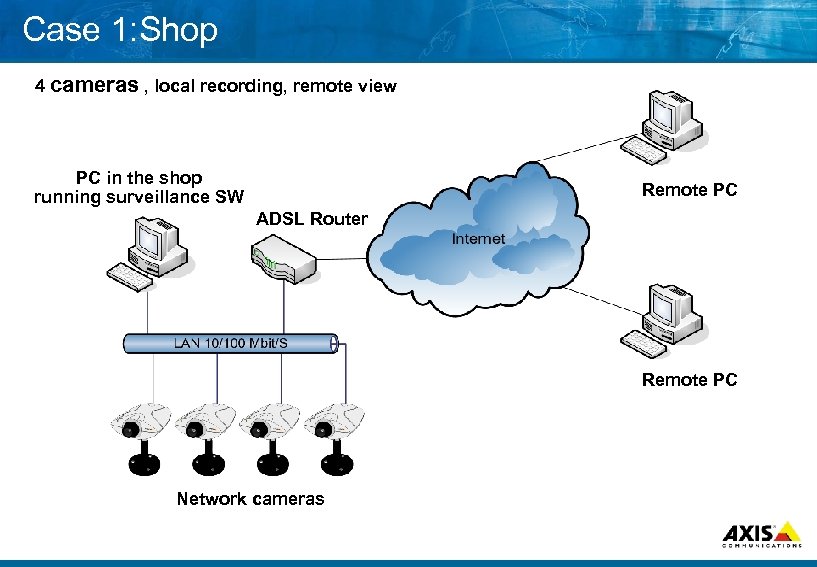 Case 1: Shop 4 cameras , local recording, remote view PC in the shop running surveillance SW Remote PC ADSL Router Remote PC Network cameras
Case 1: Shop 4 cameras , local recording, remote view PC in the shop running surveillance SW Remote PC ADSL Router Remote PC Network cameras
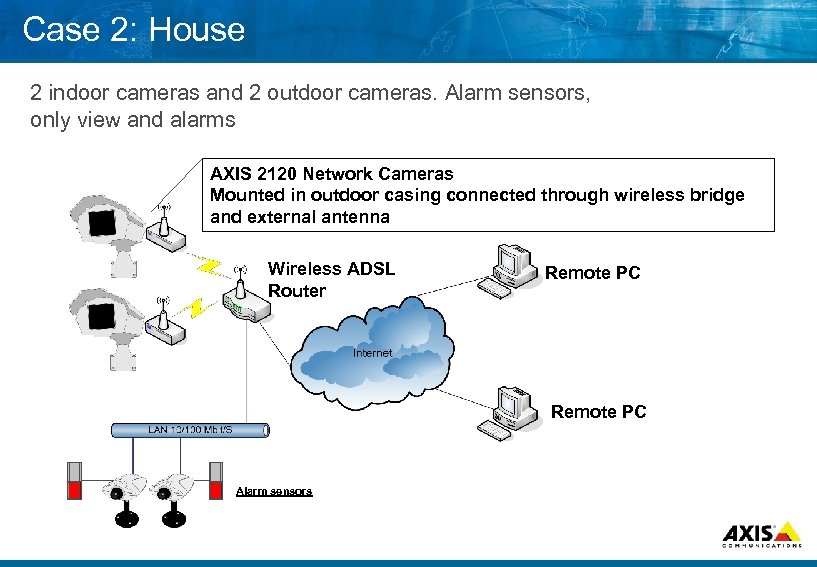 Case 2: House 2 indoor cameras and 2 outdoor cameras. Alarm sensors, only view and alarms AXIS 2120 Network Cameras Mounted in outdoor casing connected through wireless bridge and external antenna Wireless ADSL Router Remote PC Alarm sensors
Case 2: House 2 indoor cameras and 2 outdoor cameras. Alarm sensors, only view and alarms AXIS 2120 Network Cameras Mounted in outdoor casing connected through wireless bridge and external antenna Wireless ADSL Router Remote PC Alarm sensors
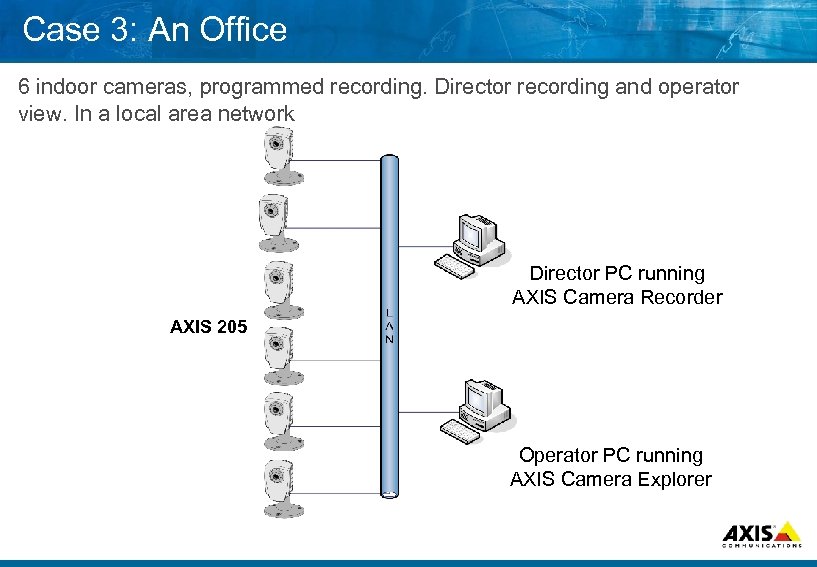 Case 3: An Office 6 indoor cameras, programmed recording. Director recording and operator view. In a local area network Director PC running AXIS Camera Recorder AXIS 205 Operator PC running AXIS Camera Explorer
Case 3: An Office 6 indoor cameras, programmed recording. Director recording and operator view. In a local area network Director PC running AXIS Camera Recorder AXIS 205 Operator PC running AXIS Camera Explorer
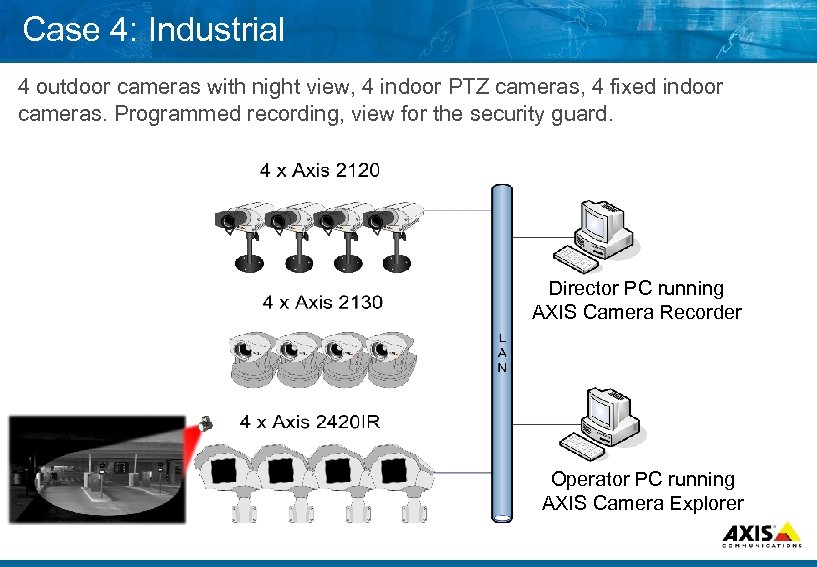 Case 4: Industrial 4 outdoor cameras with night view, 4 indoor PTZ cameras, 4 fixed indoor cameras. Programmed recording, view for the security guard. Director PC running AXIS Camera Recorder Operator PC running AXIS Camera Explorer
Case 4: Industrial 4 outdoor cameras with night view, 4 indoor PTZ cameras, 4 fixed indoor cameras. Programmed recording, view for the security guard. Director PC running AXIS Camera Recorder Operator PC running AXIS Camera Explorer
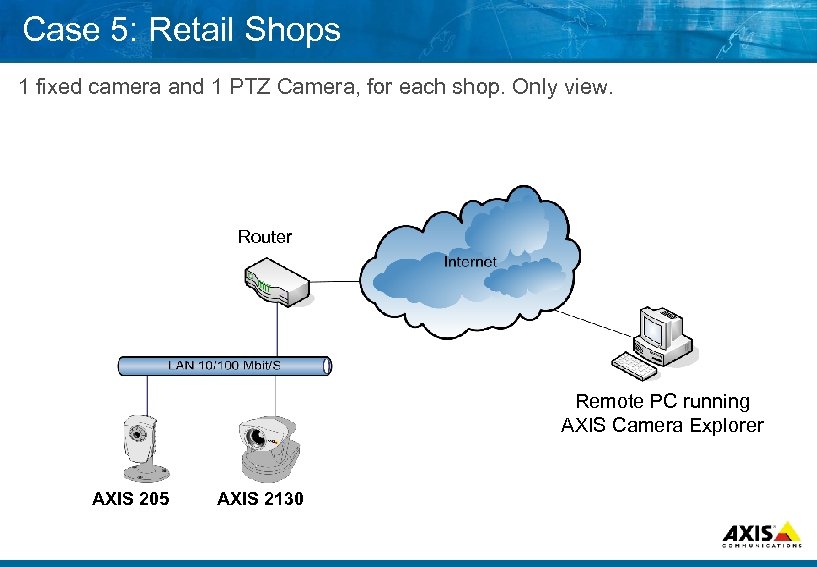 Case 5: Retail Shops 1 fixed camera and 1 PTZ Camera, for each shop. Only view. Router Remote PC running AXIS Camera Explorer AXIS 205 AXIS 2130
Case 5: Retail Shops 1 fixed camera and 1 PTZ Camera, for each shop. Only view. Router Remote PC running AXIS Camera Explorer AXIS 205 AXIS 2130
 Case 6: Nursery 3 indoor cameras and 1 outdoor camera (external play zone). No recording. Access via web. AXIS 205 Router PC with Internet Explorer AXIS 2110 & AXIS 290 B Web Server
Case 6: Nursery 3 indoor cameras and 1 outdoor camera (external play zone). No recording. Access via web. AXIS 205 Router PC with Internet Explorer AXIS 2110 & AXIS 290 B Web Server
 Case 7: Construction 2 outdoor fixed cameras. View and remote recording (low amount of fps) Router Operator PC running AXIS Camera Recorder AXIS 2120 & AXIS 290 B Bundle
Case 7: Construction 2 outdoor fixed cameras. View and remote recording (low amount of fps) Router Operator PC running AXIS Camera Recorder AXIS 2120 & AXIS 290 B Bundle
 Case 8: Sports Installation (golf, seaport, skiing, ) 3 outdoor fixed cameras Router PC with Internet Explorer AXIS 2120 & 290 B Bundle
Case 8: Sports Installation (golf, seaport, skiing, ) 3 outdoor fixed cameras Router PC with Internet Explorer AXIS 2120 & 290 B Bundle
 Case 9: An Office 6 access controls with audio, 3 indoor cameras AXIS 205 PC running Internet Explorer PC running AXIS Camera Explorer AXIS 2100 Network Cameras & AXIS 2191 Audio Modules
Case 9: An Office 6 access controls with audio, 3 indoor cameras AXIS 205 PC running Internet Explorer PC running AXIS Camera Explorer AXIS 2100 Network Cameras & AXIS 2191 Audio Modules
 Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
 Lab Exercise 1. Designing an IP Surveillance solution
Lab Exercise 1. Designing an IP Surveillance solution
 Demonstration 8 AXIS Camera Station
Demonstration 8 AXIS Camera Station
 . . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Axis Road Map roadmap. ppt DE 031119
. . . MAKE YOUR NETWORK SMARTER Axis Road Map roadmap. ppt DE 031119
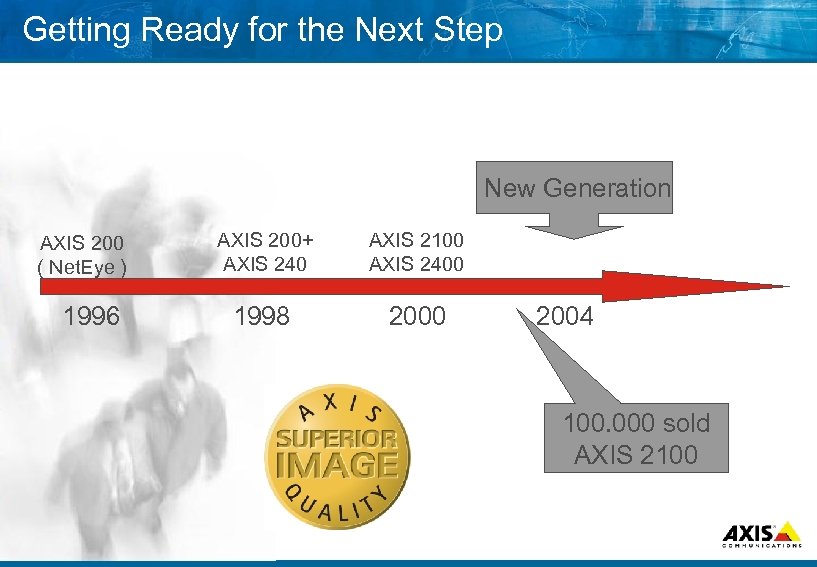 Getting Ready for the Next Step New Generation AXIS 200 ( Net. Eye ) 1996 AXIS 200+ AXIS 240 AXIS 2100 AXIS 2400 1998 2000 2004 100. 000 sold AXIS 2100
Getting Ready for the Next Step New Generation AXIS 200 ( Net. Eye ) 1996 AXIS 200+ AXIS 240 AXIS 2100 AXIS 2400 1998 2000 2004 100. 000 sold AXIS 2100
 Recent Launches 8 New Generation Products AXIS 241 Q/S Video Servers AXIS 210 Network Camera 8 Accessories AXIS 290 B Network Camera Housing AXIS IR Illuminator AXIS Fusion Dome
Recent Launches 8 New Generation Products AXIS 241 Q/S Video Servers AXIS 210 Network Camera 8 Accessories AXIS 290 B Network Camera Housing AXIS IR Illuminator AXIS Fusion Dome
 Products in Final R&D 8 Products in final R&D AXIS 241 Q/S Blade AXIS 211 Network Camera AXIS 206 W Network Camera AXIS 206 M Network Camera
Products in Final R&D 8 Products in final R&D AXIS 241 Q/S Blade AXIS 211 Network Camera AXIS 206 W Network Camera AXIS 206 M Network Camera
 AXIS 241 S/Q Blades 1 channel (S) or 4 channel (Q) 8 120 / 100 frames per second 8 Motion JPEG 8 Built in video motion detection 8 Event management 8 External I/O 8 Watch dog 8 IP adress filtering 8 Serial ports 8
AXIS 241 S/Q Blades 1 channel (S) or 4 channel (Q) 8 120 / 100 frames per second 8 Motion JPEG 8 Built in video motion detection 8 Event management 8 External I/O 8 Watch dog 8 IP adress filtering 8 Serial ports 8
 AXIS 211 Network Camera 8 1/3” Progressive Scan Sony HAD CCD 8 Backlight Compensation 8 CS Mount 8 Vari focal DC iris lens 8 30 FPS for all resolutions up to 640 x 480 8 MJPEG MPEG 4 Upgrade 8 VMD 8 June 2004
AXIS 211 Network Camera 8 1/3” Progressive Scan Sony HAD CCD 8 Backlight Compensation 8 CS Mount 8 Vari focal DC iris lens 8 30 FPS for all resolutions up to 640 x 480 8 MJPEG MPEG 4 Upgrade 8 VMD 8 June 2004
 AXIS 206 W Network Camera 8 Advanced ¼ CMOS Progressive Scan Sensor 8 802. 11 b 8 MJPEG 8 3 10, 000 lux 8 No Ethernet! 8 USB 8 June 2004
AXIS 206 W Network Camera 8 Advanced ¼ CMOS Progressive Scan Sensor 8 802. 11 b 8 MJPEG 8 3 10, 000 lux 8 No Ethernet! 8 USB 8 June 2004
 AXIS 206 M Network Camera 8 Advanced ½ CMOS Progressive Scan Sensor 8 Megapixel 1280 x 1024 at 12 FPS 8 MJPEG 8 10 10, 000 lux 8 10/100 Base. T 8 HDTV widescreen format (16: 9) 8 June 2004
AXIS 206 M Network Camera 8 Advanced ½ CMOS Progressive Scan Sensor 8 Megapixel 1280 x 1024 at 12 FPS 8 MJPEG 8 10 10, 000 lux 8 10/100 Base. T 8 HDTV widescreen format (16: 9) 8 June 2004
 Q&A 8 Questions and Answers
Q&A 8 Questions and Answers


