77790079c76c1653ab90d36921a02d38.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 Major NCD Partners Cary Adams CEO UICC Ann Keeling CEO IDF Helen Alderson CEO WHF
Major NCD Partners Cary Adams CEO UICC Ann Keeling CEO IDF Helen Alderson CEO WHF
 Structure of presentation Cary Adams Overview of UICC Ann Keeling Overview of IDF Helen Alderson Overview of WHF Working together as partners Ann Keeling The NCD Advocacy Agenda
Structure of presentation Cary Adams Overview of UICC Ann Keeling Overview of IDF Helen Alderson Overview of WHF Working together as partners Ann Keeling The NCD Advocacy Agenda
 UICC Cary Adams, Chief Executive Officer international union against cancer January 2010
UICC Cary Adams, Chief Executive Officer international union against cancer January 2010
 Who we are – an overview The International Union Against Cancer (UICC) is the leading international nongovernmental organization dedicated to the global prevention and control of cancer. Founded in 1933, UICC unites over 360 member organizations, specialized and engaged in cancer control, in more than 100 countries across the world. UICC is non-profit, non-political, and non-sectarian. It’s headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland.
Who we are – an overview The International Union Against Cancer (UICC) is the leading international nongovernmental organization dedicated to the global prevention and control of cancer. Founded in 1933, UICC unites over 360 member organizations, specialized and engaged in cancer control, in more than 100 countries across the world. UICC is non-profit, non-political, and non-sectarian. It’s headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland.
 World Cancer Declaration ‘A global call to action to help substantially reduce the global cancer burden by 2020 and increase cancer's visibility on the international political agenda. ’ UICC encourages priority actions at local and national levels. Outlines 11 targets and a priority action plan to stop and reverse current trends. Aimed towards making significant improvements in the measurement of the global cancer burden and improvements in cancer survival rates in all countries around the world. Please help us move cancer up on the global agenda by signing online at: www. uicc. org/wcd 12 Low-income countries 10 8 6 2. 2 2. 1 8. 9 4 2 High-income countries 2. 5 5. 5 6. 7 0 2005 2015 2030
World Cancer Declaration ‘A global call to action to help substantially reduce the global cancer burden by 2020 and increase cancer's visibility on the international political agenda. ’ UICC encourages priority actions at local and national levels. Outlines 11 targets and a priority action plan to stop and reverse current trends. Aimed towards making significant improvements in the measurement of the global cancer burden and improvements in cancer survival rates in all countries around the world. Please help us move cancer up on the global agenda by signing online at: www. uicc. org/wcd 12 Low-income countries 10 8 6 2. 2 2. 1 8. 9 4 2 High-income countries 2. 5 5. 5 6. 7 0 2005 2015 2030
 World Cancer Declaration The Declaration sets 11 targets to stop and reverse current cancer trends and aims to increase cancer’s visibility on the global agenda. Targets 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Sustainable delivery systems Improved measurement of the global cancer burden Decreased global tobacco consumption, obesity, and alcohol intake HBV and HPV vaccination programs and screenings Shift in public attitude towards cancer Earlier and accurate diagnosis Appropriate cancer treatments and supportive care Effective pain control measures accessible to all patients Improved professional training opportunities Decrease in emigration of health workers with specialist training in cancer control There will be major improvements in cancer survival rates in all countries
World Cancer Declaration The Declaration sets 11 targets to stop and reverse current cancer trends and aims to increase cancer’s visibility on the global agenda. Targets 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Sustainable delivery systems Improved measurement of the global cancer burden Decreased global tobacco consumption, obesity, and alcohol intake HBV and HPV vaccination programs and screenings Shift in public attitude towards cancer Earlier and accurate diagnosis Appropriate cancer treatments and supportive care Effective pain control measures accessible to all patients Improved professional training opportunities Decrease in emigration of health workers with specialist training in cancer control There will be major improvements in cancer survival rates in all countries
 Promoting diabetes care, prevention and a cure worldwide President Jean Claude Mbanya Cameroon
Promoting diabetes care, prevention and a cure worldwide President Jean Claude Mbanya Cameroon
 International Diabetes Federation 220+ member associations in 160+ countries with 2 million+ members US$ 700 million combined income 7 regional offices UN Resolution on Diabetes December 2007
International Diabetes Federation 220+ member associations in 160+ countries with 2 million+ members US$ 700 million combined income 7 regional offices UN Resolution on Diabetes December 2007
 IDF’s role • Global advocacy and campaigning • Gathering the evidence: IDF Diabetes Atlas, health economics • Research • Best practice projects eg diabetes education • Global guidelines and advice • Humanitarian programmes eg Life for a Child • Convening the global diabetes community – World Diabetes Congress
IDF’s role • Global advocacy and campaigning • Gathering the evidence: IDF Diabetes Atlas, health economics • Research • Best practice projects eg diabetes education • Global guidelines and advice • Humanitarian programmes eg Life for a Child • Convening the global diabetes community – World Diabetes Congress
 World Heart Federation Helen Alderson, Chief Executive Officer
World Heart Federation Helen Alderson, Chief Executive Officer
 The World Heart Federation Mission The World Heart Federation helps people achieve a longer and better life through prevention and control of heart disease and stroke, with a focus on low- and middle-income countries.
The World Heart Federation Mission The World Heart Federation helps people achieve a longer and better life through prevention and control of heart disease and stroke, with a focus on low- and middle-income countries.
 The World Heart Federation § Leads a united community of over 200 member organizations in the global fight against heart disease and stroke. § Brings together the societies of cardiology as well as heart health charities. § Advocates for greater attention to CVD at the policy level, generates and exchanges ideas, shares best practice and advances scientific knowledge to tackle the world’s number one killer. § As the only global body that unifies a community dedicated to CVD prevention and control, we lead the creation and sharing of ideas among members, partners and policy-makers ensuring people all over the world have longer and better lives
The World Heart Federation § Leads a united community of over 200 member organizations in the global fight against heart disease and stroke. § Brings together the societies of cardiology as well as heart health charities. § Advocates for greater attention to CVD at the policy level, generates and exchanges ideas, shares best practice and advances scientific knowledge to tackle the world’s number one killer. § As the only global body that unifies a community dedicated to CVD prevention and control, we lead the creation and sharing of ideas among members, partners and policy-makers ensuring people all over the world have longer and better lives
 Working in partnership
Working in partnership
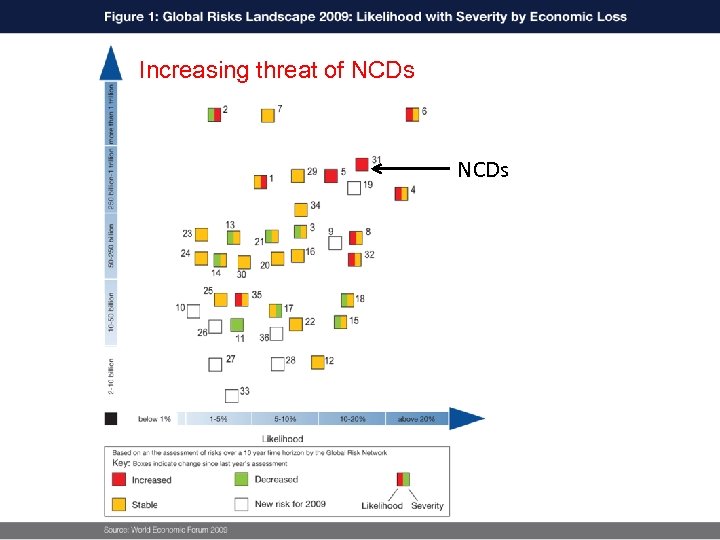 Increasing threat of NCDs
Increasing threat of NCDs
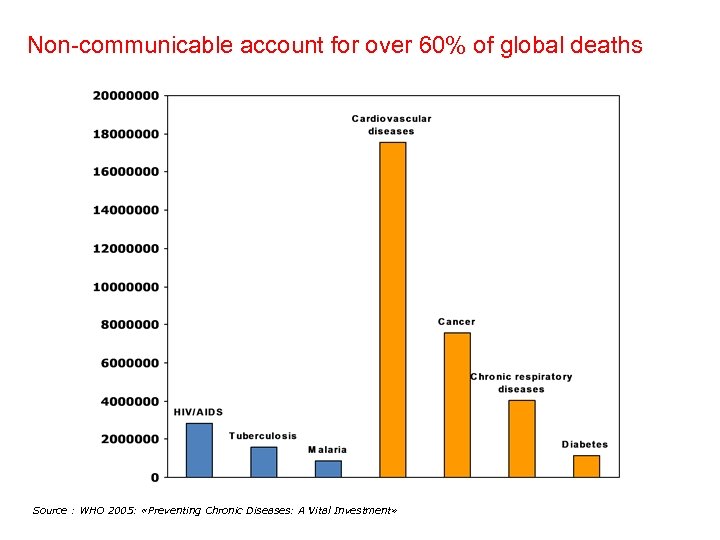 Non-communicable account for over 60% of global deaths Source : WHO 2005: «Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Vital Investment»
Non-communicable account for over 60% of global deaths Source : WHO 2005: «Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Vital Investment»
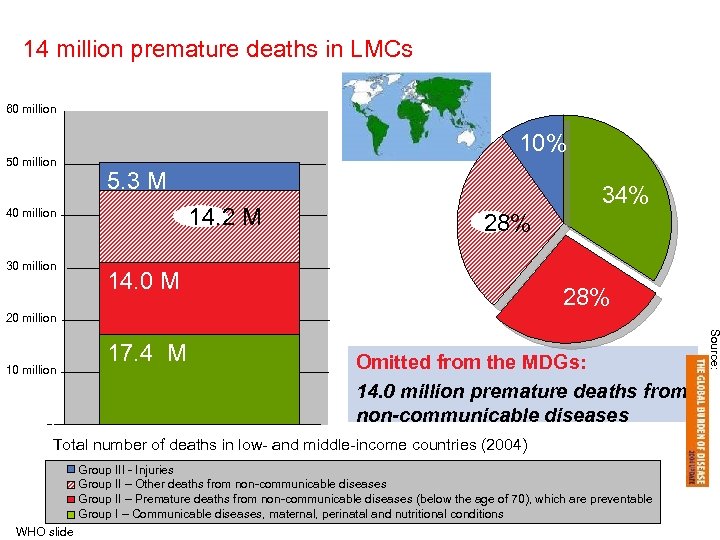 14 million premature deaths in LMCs 60 million 50 million 10% 5. 3 M 14. 2 M 40 million 34% 28% 14. 0 M 28% 20 million 17. 4 M Omitted from the MDGs: 14. 0 million premature deaths from non-communicable diseases Total number of deaths in low- and middle-income countries (2004) Group III - Injuries Low-income countries Group II – Other deaths from non-communicable diseases Group II – Premature deaths from non-communicable diseases (below the age of 70), which are preventable Group I – Communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions WHO slide Source: 10 million
14 million premature deaths in LMCs 60 million 50 million 10% 5. 3 M 14. 2 M 40 million 34% 28% 14. 0 M 28% 20 million 17. 4 M Omitted from the MDGs: 14. 0 million premature deaths from non-communicable diseases Total number of deaths in low- and middle-income countries (2004) Group III - Injuries Low-income countries Group II – Other deaths from non-communicable diseases Group II – Premature deaths from non-communicable diseases (below the age of 70), which are preventable Group I – Communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions WHO slide Source: 10 million
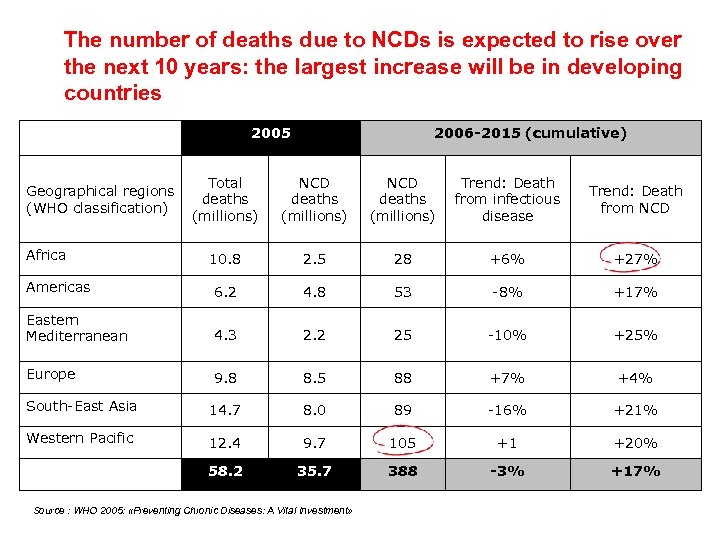 The number of deaths due to NCDs is expected to rise over the next 10 years: the largest increase will be in developing countries 2005 2006 -2015 (cumulative) Total deaths (millions) NCD deaths (millions) Trend: Death from infectious disease Trend: Death from NCD 10. 8 2. 5 28 +6% +27% Americas 6. 2 4. 8 53 -8% +17% Eastern Mediterranean 4. 3 2. 2 25 -10% +25% Europe 9. 8 8. 5 88 +7% +4% South-East Asia 14. 7 8. 0 89 -16% +21% Western Pacific 12. 4 9. 7 105 +1 +20% Total 58. 2 35. 7 388 -3% +17% Geographical regions (WHO classification) Africa Source : WHO 2005: «Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Vital Investment»
The number of deaths due to NCDs is expected to rise over the next 10 years: the largest increase will be in developing countries 2005 2006 -2015 (cumulative) Total deaths (millions) NCD deaths (millions) Trend: Death from infectious disease Trend: Death from NCD 10. 8 2. 5 28 +6% +27% Americas 6. 2 4. 8 53 -8% +17% Eastern Mediterranean 4. 3 2. 2 25 -10% +25% Europe 9. 8 8. 5 88 +7% +4% South-East Asia 14. 7 8. 0 89 -16% +21% Western Pacific 12. 4 9. 7 105 +1 +20% Total 58. 2 35. 7 388 -3% +17% Geographical regions (WHO classification) Africa Source : WHO 2005: «Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Vital Investment»
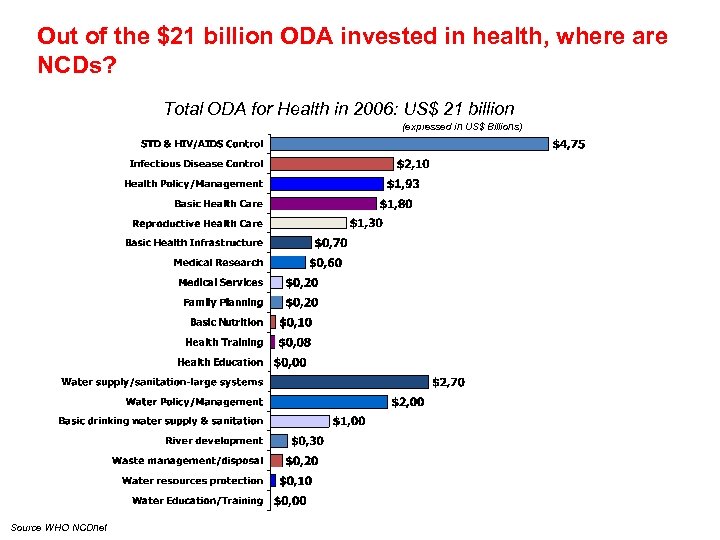 Out of the $21 billion ODA invested in health, where are NCDs? Total ODA for Health in 2006: US$ 21 billion (expressed in US$ Billions) Source WHO NCDnet
Out of the $21 billion ODA invested in health, where are NCDs? Total ODA for Health in 2006: US$ 21 billion (expressed in US$ Billions) Source WHO NCDnet
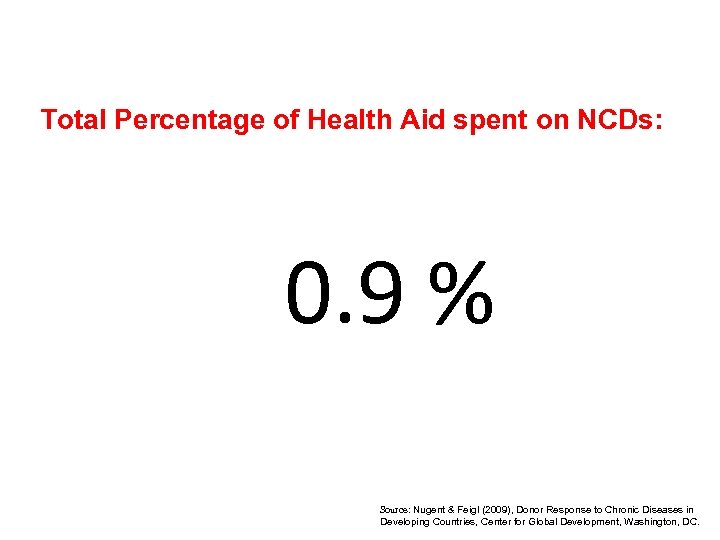 Total Percentage of Health Aid spent on NCDs: 0. 9 % Source: Nugent & Feigl (2009), Donor Response to Chronic Diseases in Developing Countries, Center for Global Development, Washington, DC.
Total Percentage of Health Aid spent on NCDs: 0. 9 % Source: Nugent & Feigl (2009), Donor Response to Chronic Diseases in Developing Countries, Center for Global Development, Washington, DC.
 Millennium Development Goals drive the global development agenda 1. Eradicate poverty and hunger 2. Achieve primary universal education 3. Promote gender equality and empower women 4. Reduce child mortality Where are NCDs? 5. Improve maternal health 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases 7. Ensure environmental sustainability 8. Develop a global partnership for development
Millennium Development Goals drive the global development agenda 1. Eradicate poverty and hunger 2. Achieve primary universal education 3. Promote gender equality and empower women 4. Reduce child mortality Where are NCDs? 5. Improve maternal health 6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases 7. Ensure environmental sustainability 8. Develop a global partnership for development
 The Framework WHO Action Plan: Defines NCDs as 4 diseases: cancers, diabetes, cardiovascular, chronic respiratory Agreed by governments NCDs are a development issue
The Framework WHO Action Plan: Defines NCDs as 4 diseases: cancers, diabetes, cardiovascular, chronic respiratory Agreed by governments NCDs are a development issue
 January 2009: The three NCD federation’s formed an alliance: 780 national associations in 170+ countries
January 2009: The three NCD federation’s formed an alliance: 780 national associations in 170+ countries
 Call for action at a global level
Call for action at a global level
 Why are the poorest people What will NCDnet be doing? in low- and middle-income countries affected the most? Objective 5 – Promoting partnerships NCDnet: New network to combat noncommunicable diseases Mission: Help implement the Action Plan by catalyzing a multi-sectoral, multi-level response, with a particular focus on developing countries Goals: ● ● ● WHO slide Increase focus on prevention and control of non-communicable diseases through collective advocacy Increase resource availability (both financial and human capital) Catalyze effective multi-stakeholder action with a focus on country-level implementation
Why are the poorest people What will NCDnet be doing? in low- and middle-income countries affected the most? Objective 5 – Promoting partnerships NCDnet: New network to combat noncommunicable diseases Mission: Help implement the Action Plan by catalyzing a multi-sectoral, multi-level response, with a particular focus on developing countries Goals: ● ● ● WHO slide Increase focus on prevention and control of non-communicable diseases through collective advocacy Increase resource availability (both financial and human capital) Catalyze effective multi-stakeholder action with a focus on country-level implementation
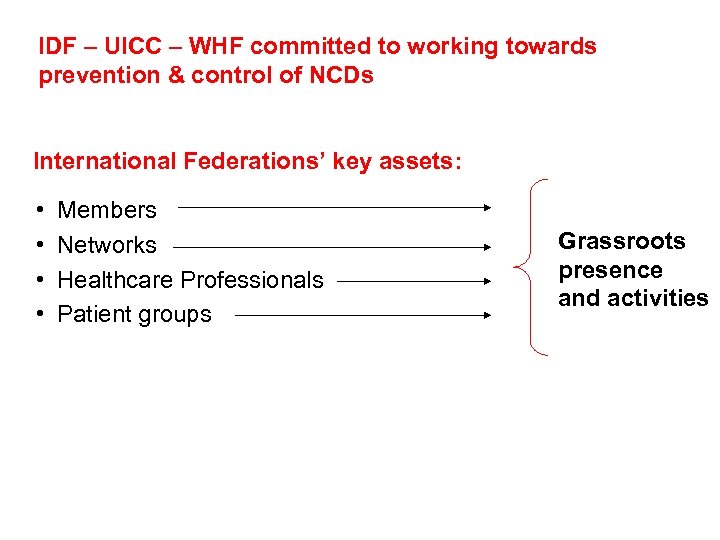 IDF – UICC – WHF committed to working towards prevention & control of NCDs International Federations’ key assets: • • Members Networks Healthcare Professionals Patient groups Grassroots presence and activities
IDF – UICC – WHF committed to working towards prevention & control of NCDs International Federations’ key assets: • • Members Networks Healthcare Professionals Patient groups Grassroots presence and activities
 NCDs: the global advocacy agenda
NCDs: the global advocacy agenda
 What are we asking for? • United Nations special session on NCDs (UNGASS) in 2010/2011 • MDGs: adding a new NCD indicator(s) at MDG Review meeting Sept 2010 • NCDs in the successor goals to the MDGs • International funding for essential NCD medicines/care • Integration of NCDs, especially into primary healthcare
What are we asking for? • United Nations special session on NCDs (UNGASS) in 2010/2011 • MDGs: adding a new NCD indicator(s) at MDG Review meeting Sept 2010 • NCDs in the successor goals to the MDGs • International funding for essential NCD medicines/care • Integration of NCDs, especially into primary healthcare
 UN General Assembly Special Session on NCDs • An UNGASS on NCDs will raise political profile/commitment (the UNGASS on HIV/AIDS resulted in the Global Fund) • Earliest 2010/2011 UN session starting Sept 2010 • 56 Commonwealth and Caribbean Countries already committed to an UNGASS
UN General Assembly Special Session on NCDs • An UNGASS on NCDs will raise political profile/commitment (the UNGASS on HIV/AIDS resulted in the Global Fund) • Earliest 2010/2011 UN session starting Sept 2010 • 56 Commonwealth and Caribbean Countries already committed to an UNGASS
 NCDs and the MDGs • 8 MDG goals determine agenda for international funding to LMCs till end date 2015 • MDGs specify particular diseases eg HIV/AIDS, TB – not meant to be taken literally – don’t include NCDs • Adding an indicator would catalyse funding/technical assistance for NCDs • Discussion of an NCD indicator would set scene for inclusion of NCDs in successor goals to MDGs • Sept 2010 MDG review meeting at UN last opportunity before 2015
NCDs and the MDGs • 8 MDG goals determine agenda for international funding to LMCs till end date 2015 • MDGs specify particular diseases eg HIV/AIDS, TB – not meant to be taken literally – don’t include NCDs • Adding an indicator would catalyse funding/technical assistance for NCDs • Discussion of an NCD indicator would set scene for inclusion of NCDs in successor goals to MDGs • Sept 2010 MDG review meeting at UN last opportunity before 2015
 International Funding for NCDs • Many LMC health budgets reliant on foreign aid (eg 40% Malawi’s health budget financed by aid) • Effective NCD medicines exist but the poor in LMCs have no access • Prevention/technical assistance urgently needed to save lives/stem epidemic April meeting with DANIDA and bilateral donors
International Funding for NCDs • Many LMC health budgets reliant on foreign aid (eg 40% Malawi’s health budget financed by aid) • Effective NCD medicines exist but the poor in LMCs have no access • Prevention/technical assistance urgently needed to save lives/stem epidemic April meeting with DANIDA and bilateral donors
 Major players in aid to LMCs • Global Fund for AIDS, TB and Malaria: 2008 disbursed US$2. 3 billion - almost none on NCDs • Gates Foundation: 2008 disbursed US$3. 6 billion (all sectors including health) – almost none on NCDs • UNITAID: 2008 expenditure US$232 million – none on NCDs BUT the global agenda is driven by bilateral aid donors eg Netherlands, DFID, SIDA, NORAD etc (who also fund Global Fund, UNITAID, WHO, World Bank etc)
Major players in aid to LMCs • Global Fund for AIDS, TB and Malaria: 2008 disbursed US$2. 3 billion - almost none on NCDs • Gates Foundation: 2008 disbursed US$3. 6 billion (all sectors including health) – almost none on NCDs • UNITAID: 2008 expenditure US$232 million – none on NCDs BUT the global agenda is driven by bilateral aid donors eg Netherlands, DFID, SIDA, NORAD etc (who also fund Global Fund, UNITAID, WHO, World Bank etc)
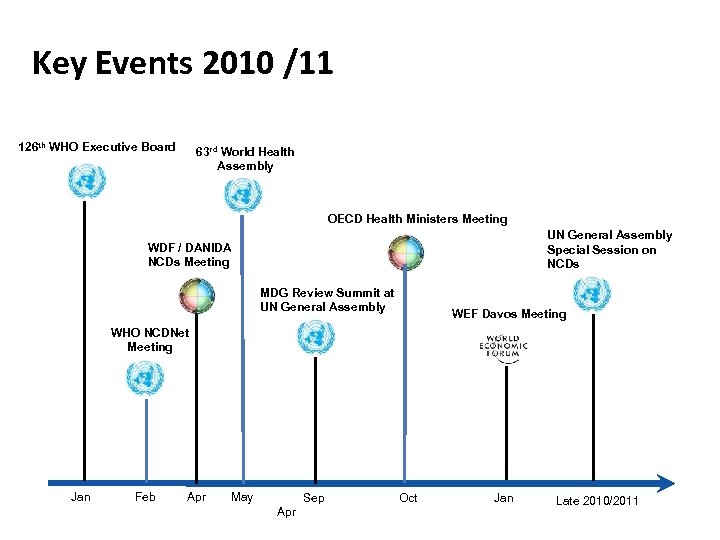 Key Events 2010 /11 126 th WHO Executive Board 63 rd World Health Assembly OECD Health Ministers Meeting UN General Assembly Special Session on NCDs WDF / DANIDA NCDs Meeting MDG Review Summit at UN General Assembly WEF Davos Meeting WHO NCDNet Meeting Jan Feb Apr May Sep Apr Oct Jan Late 2010/2011
Key Events 2010 /11 126 th WHO Executive Board 63 rd World Health Assembly OECD Health Ministers Meeting UN General Assembly Special Session on NCDs WDF / DANIDA NCDs Meeting MDG Review Summit at UN General Assembly WEF Davos Meeting WHO NCDNet Meeting Jan Feb Apr May Sep Apr Oct Jan Late 2010/2011
 What we are asking from you • To recognise NCDs and integrate into heath systems strengthening • Design and disseminate good practice models of prevention and chronic care to share • Respect the rights of people with NCDs • Lobby your government to be a global champion for NCDs – support the UNGASS!
What we are asking from you • To recognise NCDs and integrate into heath systems strengthening • Design and disseminate good practice models of prevention and chronic care to share • Respect the rights of people with NCDs • Lobby your government to be a global champion for NCDs – support the UNGASS!
 Major NCD Partners Cary Adams CEO UICC Ann Keeling CEO IDF Helen Alderson CEO WHF
Major NCD Partners Cary Adams CEO UICC Ann Keeling CEO IDF Helen Alderson CEO WHF


