164e7d4ebaaab85b9fb6f1a9c39d2130.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 MAJOR DRUG CONVENTIONS
MAJOR DRUG CONVENTIONS
 What is Convention • A set of agreed , stipulated or generally accepted social norms , standards or criteria. • An accord between states or nations, which resemble a treaty: ordinarily applied to agreement prior to an execution of an official treaty or which serve as its foundation. • An agreement between states , sides , or military forces , especially an international agreement dealing on a specific subject.
What is Convention • A set of agreed , stipulated or generally accepted social norms , standards or criteria. • An accord between states or nations, which resemble a treaty: ordinarily applied to agreement prior to an execution of an official treaty or which serve as its foundation. • An agreement between states , sides , or military forces , especially an international agreement dealing on a specific subject.
 International Drug Control • International drug control is one of the oldest forms of multilateralism. • The international Opium Commission was convened in Shanghai , China in 1909 • The first instrument of international law to deal with psychoactive substances- the Hague Opium Convention of 1912.
International Drug Control • International drug control is one of the oldest forms of multilateralism. • The international Opium Commission was convened in Shanghai , China in 1909 • The first instrument of international law to deal with psychoactive substances- the Hague Opium Convention of 1912.
 International Drug Control • 1931 Convention International control over compounds derived from natural raw materials , for example , natural alkaloids, such as morphine or cocaine, and semi-synthetic derivatives of opium alkaloids , such as heroin. • The 1948 Protocol Brought synthetic narcotic drugs under international control • The 1953 Protocol Specially prohibited the non medical use of opium , and it required each producing country to establish a monopoly to control the cultivation of the opium poppy and the production of opium.
International Drug Control • 1931 Convention International control over compounds derived from natural raw materials , for example , natural alkaloids, such as morphine or cocaine, and semi-synthetic derivatives of opium alkaloids , such as heroin. • The 1948 Protocol Brought synthetic narcotic drugs under international control • The 1953 Protocol Specially prohibited the non medical use of opium , and it required each producing country to establish a monopoly to control the cultivation of the opium poppy and the production of opium.
 UN DRUG CONVENTIONS • THREE MAJOR UNITED NATIONS DRUG CONVENTIONS Ø United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 as amended by the 1972 protocol. Ø United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances , 1971. Ø The Convention Against Illicit Traffic of Narcotic Drug and Psychotropic Substances , 1988 (Vienna Convention)
UN DRUG CONVENTIONS • THREE MAJOR UNITED NATIONS DRUG CONVENTIONS Ø United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 as amended by the 1972 protocol. Ø United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances , 1971. Ø The Convention Against Illicit Traffic of Narcotic Drug and Psychotropic Substances , 1988 (Vienna Convention)
 United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 • International treaty against illicit drug manufacture and trafficking that forms the bedrock of the global drug control regime. • Previous treaties had only controlled opium , coca , and derivatives such as morphine and heroin. • The single Convention adopted in 1961 , consolidated those treaties , broadening their scope to include cannabis and allow control of any drugs with similar effects. • The Single Convention entered into force on December 13 , 1964.
United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 • International treaty against illicit drug manufacture and trafficking that forms the bedrock of the global drug control regime. • Previous treaties had only controlled opium , coca , and derivatives such as morphine and heroin. • The single Convention adopted in 1961 , consolidated those treaties , broadening their scope to include cannabis and allow control of any drugs with similar effects. • The Single Convention entered into force on December 13 , 1964.
 United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 • This Convention aims to combat drug abuse by coordinating international action. • There are two forms of intervention and control that work together: - First , it seeks to limit the possession , use , trade in , distribution , import , export , manufacture and production of drugs exclusively to medical and scientific purposes. - Second, it combats drug trafficking through international cooperation to deter and discourage drug traffickers.
United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 • This Convention aims to combat drug abuse by coordinating international action. • There are two forms of intervention and control that work together: - First , it seeks to limit the possession , use , trade in , distribution , import , export , manufacture and production of drugs exclusively to medical and scientific purposes. - Second, it combats drug trafficking through international cooperation to deter and discourage drug traffickers.
 United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 • This Convention affirms the importance of medical use of controlled substances. • It unambiguously condemns drug addiction. • It takes a prohibitionist approach to the problem of drug abuse , attempting to stop all non-medical , non-scientific use of narcotic drugs. • It mandates International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) to administer provisions of this convention.
United Nations Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 • This Convention affirms the importance of medical use of controlled substances. • It unambiguously condemns drug addiction. • It takes a prohibitionist approach to the problem of drug abuse , attempting to stop all non-medical , non-scientific use of narcotic drugs. • It mandates International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) to administer provisions of this convention.
 Limitations of 1961 Single Convention • The single Convention allows only drugs with morphine , cocaine, and cannabis like effects to be added to the Schedules. • The strength of the drug is not relevant; only the similarity of its effects to the substances already controlled. • The Single Convention of Narcotics Drugs of 1961 could not regulate the many newly discovered substances , since its scope was limited to drugs with cannabis, coca, and opium like effects. • The abuse of barbiturates, tranquilizers , LSD and amphetamines etc , increased greatly around the world in 1960 s, especially in Western nations , while they were kept outside the scope of the Single Convention.
Limitations of 1961 Single Convention • The single Convention allows only drugs with morphine , cocaine, and cannabis like effects to be added to the Schedules. • The strength of the drug is not relevant; only the similarity of its effects to the substances already controlled. • The Single Convention of Narcotics Drugs of 1961 could not regulate the many newly discovered substances , since its scope was limited to drugs with cannabis, coca, and opium like effects. • The abuse of barbiturates, tranquilizers , LSD and amphetamines etc , increased greatly around the world in 1960 s, especially in Western nations , while they were kept outside the scope of the Single Convention.
 Convention on Psychotropic Substances 1971 • The Convention established an international control system for psychotropic substances such as amphetamines , barbiturates , and LSD. • It responded to the diversification and expansion of the spectrum of drugs of abuse and introduced controls over a number of synthetic drugs • The convention contains import and export restrictions and other rules aimed at limiting use of psychotropic substance to scientific and medical purposes.
Convention on Psychotropic Substances 1971 • The Convention established an international control system for psychotropic substances such as amphetamines , barbiturates , and LSD. • It responded to the diversification and expansion of the spectrum of drugs of abuse and introduced controls over a number of synthetic drugs • The convention contains import and export restrictions and other rules aimed at limiting use of psychotropic substance to scientific and medical purposes.
 Limitations of United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances 1971 • The 1971 Convention was designed to control legitimate pharmaceutical markets, rather than illicit markets , a limitation that hampered efforts to stem clandestine production and trade of ATS like amphetamines methamphetamine , MDMA (ecstasy) and other stimulants. • 1971 convention failed to be applied to “precursors” i. e. substances “ readily convertible “ into a substance under control.
Limitations of United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances 1971 • The 1971 Convention was designed to control legitimate pharmaceutical markets, rather than illicit markets , a limitation that hampered efforts to stem clandestine production and trade of ATS like amphetamines methamphetamine , MDMA (ecstasy) and other stimulants. • 1971 convention failed to be applied to “precursors” i. e. substances “ readily convertible “ into a substance under control.
 Convention against the Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances , 1988 • This Convention provides comprehensive measures against drug trafficking , including provisions against money laundering and diversion of precursor chemicals. • It provides for international cooperation through , for example, extradition of drug traffickers , controlled deliveries and transfer of proceedings.
Convention against the Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances , 1988 • This Convention provides comprehensive measures against drug trafficking , including provisions against money laundering and diversion of precursor chemicals. • It provides for international cooperation through , for example, extradition of drug traffickers , controlled deliveries and transfer of proceedings.
 The Convention against the Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances , 1988 The Precincts behind the Convention : • There is link between illicit traffic in drugs and other related organized criminal activities which undermine the legitimate economies and effect the stability , security and sovereignty of States. • Illicit traffic is an international criminal activity the suppression of which demands urgent attention and highest priority. • Illicit traffic generates large financial profits and wealth enabling transitional criminal organizations to penetrate, contaminate and corrupt the structures of Government , legitimate commercial and financial business and society at all its levels. • Eradication of illicit traffic is the collective responsibility of all the states and the coordinated action within the framework of International cooperation is necessary for the purpose. • There was a need to reinforce and supplement the measures provided in the Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 and the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances , in order to counter the magnitude and extent of illicit traffic and its grave consequences.
The Convention against the Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances , 1988 The Precincts behind the Convention : • There is link between illicit traffic in drugs and other related organized criminal activities which undermine the legitimate economies and effect the stability , security and sovereignty of States. • Illicit traffic is an international criminal activity the suppression of which demands urgent attention and highest priority. • Illicit traffic generates large financial profits and wealth enabling transitional criminal organizations to penetrate, contaminate and corrupt the structures of Government , legitimate commercial and financial business and society at all its levels. • Eradication of illicit traffic is the collective responsibility of all the states and the coordinated action within the framework of International cooperation is necessary for the purpose. • There was a need to reinforce and supplement the measures provided in the Single Convention on Narcotics Drugs , 1961 and the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances , in order to counter the magnitude and extent of illicit traffic and its grave consequences.
 Main Features of 1988 Convention üPrecursor Control üConfiscation of Proceeds of Drugs üControlled Delivery üEradication of Illicit Cultivation üExtradition üMutual Legal Assistance üTransfer of Proceedings
Main Features of 1988 Convention üPrecursor Control üConfiscation of Proceeds of Drugs üControlled Delivery üEradication of Illicit Cultivation üExtradition üMutual Legal Assistance üTransfer of Proceedings
 Precursor Control • This Convention Lists the substance frequently used in the illicit manufacture of narcotics drugs and psychotropic substances , commonly referred to as precursors , in two Tables called Tables I and II. • Any party exporting the notified substance in Table I is required to issue pre-export notification to the importing country. • Parties to take measures to prevent diversion of these substances from the licit channels to the illicit manufacture of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
Precursor Control • This Convention Lists the substance frequently used in the illicit manufacture of narcotics drugs and psychotropic substances , commonly referred to as precursors , in two Tables called Tables I and II. • Any party exporting the notified substance in Table I is required to issue pre-export notification to the importing country. • Parties to take measures to prevent diversion of these substances from the licit channels to the illicit manufacture of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
 Major International Drug Control Organizations • The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) • The Commission on Narcotics Drugs (CND) • The International Narcotics Control Board ( INCB) • Other agencies like INTERPOL, EUROPOL, World Customs Organization, etc.
Major International Drug Control Organizations • The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) • The Commission on Narcotics Drugs (CND) • The International Narcotics Control Board ( INCB) • Other agencies like INTERPOL, EUROPOL, World Customs Organization, etc.
 United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime( UNODC) • UNODC is the lead agency on international drug control • The United Nations International Drug Control Programme (UNDCP) was established in 1991. • In October 2002 , UNDCP was renamed as the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) , which also administers the Fund of UNDCP. • UNODC is mandated to assist Member States in their struggle against illicit drugs , crime and terrorism. • UNODC relies on voluntary contributors, mainly from governments , for 90 percent of its budget.
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime( UNODC) • UNODC is the lead agency on international drug control • The United Nations International Drug Control Programme (UNDCP) was established in 1991. • In October 2002 , UNDCP was renamed as the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) , which also administers the Fund of UNDCP. • UNODC is mandated to assist Member States in their struggle against illicit drugs , crime and terrorism. • UNODC relies on voluntary contributors, mainly from governments , for 90 percent of its budget.
 United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime( UNODC) • UNODC works to Educate the world about the dangers of drug abuse ; and q to strengthen q international action against drug production , trafficking and drugrelated crime through q Alternative development Projects. q Illicit crop monitoring and q Anti-money laundering programmes.
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime( UNODC) • UNODC works to Educate the world about the dangers of drug abuse ; and q to strengthen q international action against drug production , trafficking and drugrelated crime through q Alternative development Projects. q Illicit crop monitoring and q Anti-money laundering programmes.
 Functions of UNODC Research and analytical work - To increase knowledge and understanding of drugs and crime issues and expand the evidence-base for policy and operational decisions; Assist States - In the ratification and implementation of the international treaties. - The development of domestic legislation on drugs, crime , and terrorism, and Field-based technical cooperation projects - To enhance the capacity of Member States to counteract illicit drugs, crime and terrorism. ExamplesØ Container Control Pilot Project Ø Tajikistan Drug Control Agency (DCA) Ø Central Asian Regional Information and Coordination Centre (CARICC)
Functions of UNODC Research and analytical work - To increase knowledge and understanding of drugs and crime issues and expand the evidence-base for policy and operational decisions; Assist States - In the ratification and implementation of the international treaties. - The development of domestic legislation on drugs, crime , and terrorism, and Field-based technical cooperation projects - To enhance the capacity of Member States to counteract illicit drugs, crime and terrorism. ExamplesØ Container Control Pilot Project Ø Tajikistan Drug Control Agency (DCA) Ø Central Asian Regional Information and Coordination Centre (CARICC)
 Structure of UNODC Structure UNODC provides secretariat services to two important bodies: v The International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) v The Commission on Narcotics Drugs (CND) UNODC is in fact the executive arm of the CND.
Structure of UNODC Structure UNODC provides secretariat services to two important bodies: v The International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) v The Commission on Narcotics Drugs (CND) UNODC is in fact the executive arm of the CND.
 Commission on Narcotics Drugs (CND) The Commission on Narcotics Drugs (CND) was established in 1946 by the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations. It is the central policy-making body within the UN system for dealing with all drugrelated matters The Commission analyses the world drug abuse situation and develops proposals to strengthen international drug control
Commission on Narcotics Drugs (CND) The Commission on Narcotics Drugs (CND) was established in 1946 by the Economic and Social Council of the United Nations. It is the central policy-making body within the UN system for dealing with all drugrelated matters The Commission analyses the world drug abuse situation and develops proposals to strengthen international drug control
 International Narcotics Control Board ( INCB) The International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) is the independent and quasi-judicial control body for the implementation of the United Nations drug conventions. It was established in 1968 by the Single Convention of Narcotics drugs of 1961 INCB is independent of Governments as well as of the United Nations; its 13 members serve their personal capacity. It monitors compliance with the provisions of the international drug control treaties.
International Narcotics Control Board ( INCB) The International Narcotics Control Board (INCB) is the independent and quasi-judicial control body for the implementation of the United Nations drug conventions. It was established in 1968 by the Single Convention of Narcotics drugs of 1961 INCB is independent of Governments as well as of the United Nations; its 13 members serve their personal capacity. It monitors compliance with the provisions of the international drug control treaties.
 Functions of INCB Licit manufacture , trade and use of Drugs. v. Ensures that adequate supplies of legal drugs are available for the medical and scientific purposes. v. Also makes certain that no diversion from licit sources of drugs to illicit channels occurs. v. Monitors Government’s control over chemicals used in the illicit manufacture of drugs and assists them in preventing the diversion of those chemicals into the illicit traffic.
Functions of INCB Licit manufacture , trade and use of Drugs. v. Ensures that adequate supplies of legal drugs are available for the medical and scientific purposes. v. Also makes certain that no diversion from licit sources of drugs to illicit channels occurs. v. Monitors Government’s control over chemicals used in the illicit manufacture of drugs and assists them in preventing the diversion of those chemicals into the illicit traffic.
 Functions of INCB Illicit manufacture , trade and use of Drugs. v. Identifies weaknesses in national and international drug control systems and contributes to correcting such situation. v. Assesses chemicals used in the illicit manufacture of drugs , in order to determine which chemicals used to illicitly manufacture drugs should be under international control.
Functions of INCB Illicit manufacture , trade and use of Drugs. v. Identifies weaknesses in national and international drug control systems and contributes to correcting such situation. v. Assesses chemicals used in the illicit manufacture of drugs , in order to determine which chemicals used to illicitly manufacture drugs should be under international control.
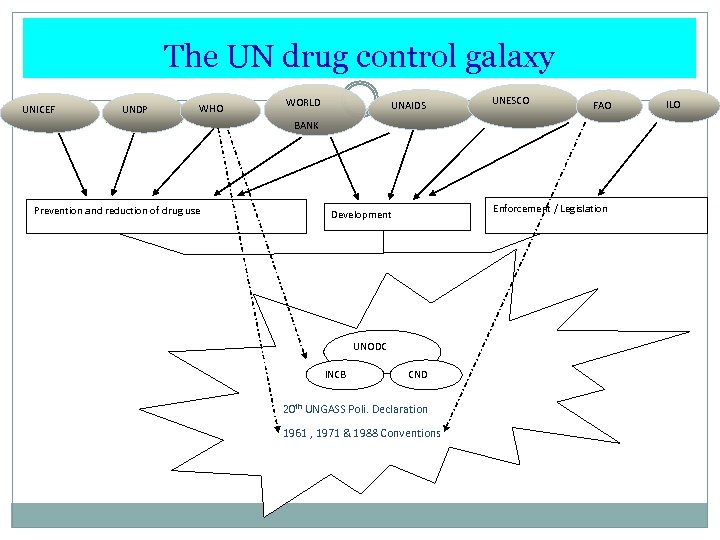 The UN drug control galaxy UNICEF UNDP WHO WORLD UNAIDS UNESCO FAO BANK Prevention and reduction of drug use Enforcement / Legislation Development UNODC INCB CND 20 th UNGASS Poli. Declaration 1961 , 1971 & 1988 Conventions ILO
The UN drug control galaxy UNICEF UNDP WHO WORLD UNAIDS UNESCO FAO BANK Prevention and reduction of drug use Enforcement / Legislation Development UNODC INCB CND 20 th UNGASS Poli. Declaration 1961 , 1971 & 1988 Conventions ILO


