e034dcbf62f7e225d6a031ca87dd4b5f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Major challenges in the food system impacting ACP countries Hans R Herren President Millennium Institute www. millennium-institute. org Co-Chair IAASTD Geopolitics of Food: implications for ACP countries Wednesday 2 nd February 2011 Wednesday, February 2, 2011 Brussels Policy Briefing n° 21
Major challenges in the food system impacting ACP countries Hans R Herren President Millennium Institute www. millennium-institute. org Co-Chair IAASTD Geopolitics of Food: implications for ACP countries Wednesday 2 nd February 2011 Wednesday, February 2, 2011 Brussels Policy Briefing n° 21
 The IAASTD Development and Sustainability Goals (=MDG) The 4 main areas where agriculture needs to transition: • Eradicating of Hunger and Poverty • Improving Rural Livelihoods • Improving Nutrition and Human Health • Facilitating Environmentally, Socially, Equitable and Economically Sustainable Development …under the Challenges of: • Climate Change • Population and Demand Growth • Shrinking Natural Resources / Energy …. to which agriculture itself is contributing negatively IAASTD…. more info @ www. agassessment. org
The IAASTD Development and Sustainability Goals (=MDG) The 4 main areas where agriculture needs to transition: • Eradicating of Hunger and Poverty • Improving Rural Livelihoods • Improving Nutrition and Human Health • Facilitating Environmentally, Socially, Equitable and Economically Sustainable Development …under the Challenges of: • Climate Change • Population and Demand Growth • Shrinking Natural Resources / Energy …. to which agriculture itself is contributing negatively IAASTD…. more info @ www. agassessment. org
 Why a new paradigm? (social/economic) Human condition need for quality and quantity of nutrition not met and increasing • One billion hungry & one billion obese • 1. 5 billion jobless people • Humanity will grow to nearly 9 billion by 2050 • Rising affluence brings diet demands for more meat, dairy & fish • Greatest population growth in the tropics where CC impact is expected to be worst, environment difficult or at limit • Today’s total food production sufficient for 9 billion people, but: – – Wrong place Access issues (poverty – hunger nexus) Post harvest losses >30% Significant retail and home losses
Why a new paradigm? (social/economic) Human condition need for quality and quantity of nutrition not met and increasing • One billion hungry & one billion obese • 1. 5 billion jobless people • Humanity will grow to nearly 9 billion by 2050 • Rising affluence brings diet demands for more meat, dairy & fish • Greatest population growth in the tropics where CC impact is expected to be worst, environment difficult or at limit • Today’s total food production sufficient for 9 billion people, but: – – Wrong place Access issues (poverty – hunger nexus) Post harvest losses >30% Significant retail and home losses
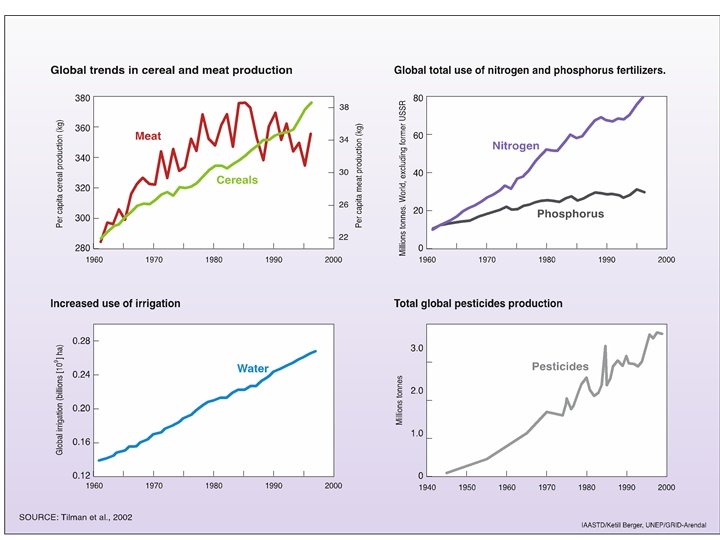 Why a new paradigm? (environment) Agriculture’s environmental impacts are substantial and are getting worse –Not sustainable • High external input conventional farming has high GHG emissions (14%) • Low input, traditional farming lower yields driving deforestation (18%) • Both farming systems lack adequate CC stress resilience & • both are inefficient in their natural resource use • Water pollution by fertilizer/pesticide runoff and soil erosion
Why a new paradigm? (environment) Agriculture’s environmental impacts are substantial and are getting worse –Not sustainable • High external input conventional farming has high GHG emissions (14%) • Low input, traditional farming lower yields driving deforestation (18%) • Both farming systems lack adequate CC stress resilience & • both are inefficient in their natural resource use • Water pollution by fertilizer/pesticide runoff and soil erosion
 Why a new paradigm? Move from NR exploitation to management Business as usual is not an option
Why a new paradigm? Move from NR exploitation to management Business as usual is not an option
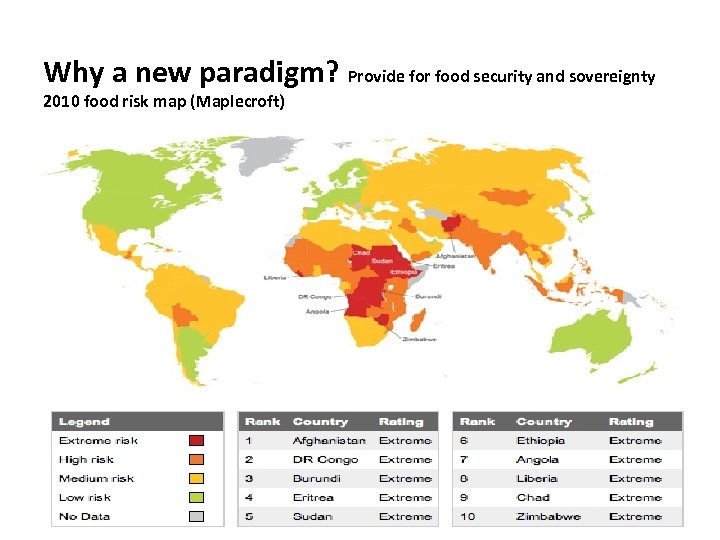 Why a new paradigm? Provide for food security and sovereignty 2010 food risk map (Maplecroft) Business as usual is not an option
Why a new paradigm? Provide for food security and sovereignty 2010 food risk map (Maplecroft) Business as usual is not an option
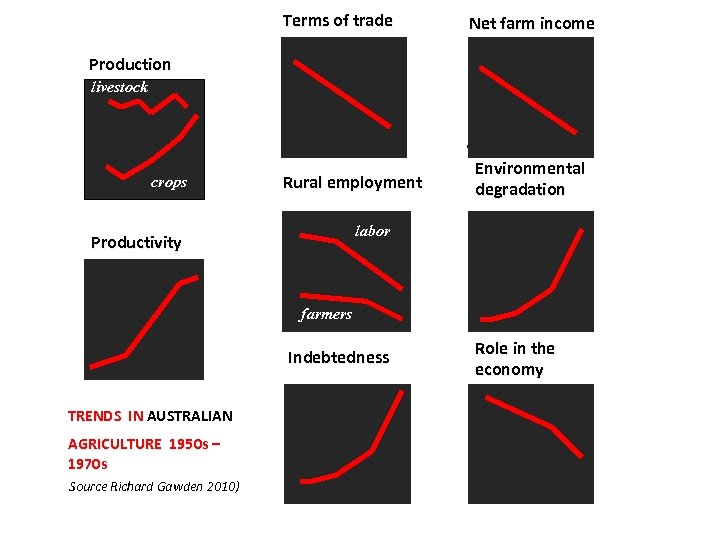 Terms of trade Net farm income Production livestock crops Rural employment Environmental degradation labor Productivity farmers Indebtedness TRENDS IN AUSTRALIAN AGRICULTURE 1950 s – 1970 s Source Richard Gawden 2010) Role in the economy
Terms of trade Net farm income Production livestock crops Rural employment Environmental degradation labor Productivity farmers Indebtedness TRENDS IN AUSTRALIAN AGRICULTURE 1950 s – 1970 s Source Richard Gawden 2010) Role in the economy
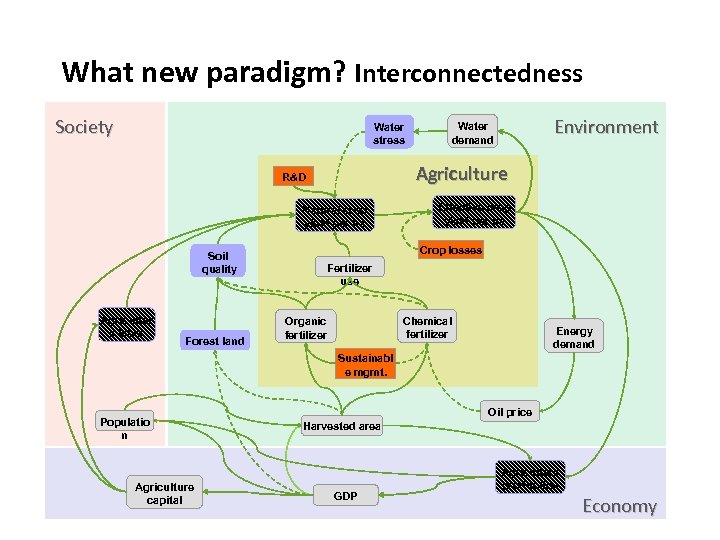 What new paradigm? Interconnectedness Society Agriculture R&D Natural crop yield per ha Soil quality Agricultur e labor Forest land Environment Water demand Water stress Effective crop yield per ha Crop losses Fertilizer use Chemical fertilizer Organic fertilizer Energy demand Sustainabl e mgmt. Populatio n Agriculture capital Oil price Harvested area GDP Agriculture production Economy
What new paradigm? Interconnectedness Society Agriculture R&D Natural crop yield per ha Soil quality Agricultur e labor Forest land Environment Water demand Water stress Effective crop yield per ha Crop losses Fertilizer use Chemical fertilizer Organic fertilizer Energy demand Sustainabl e mgmt. Populatio n Agriculture capital Oil price Harvested area GDP Agriculture production Economy
 What new paradigm? Multifunctionality
What new paradigm? Multifunctionality
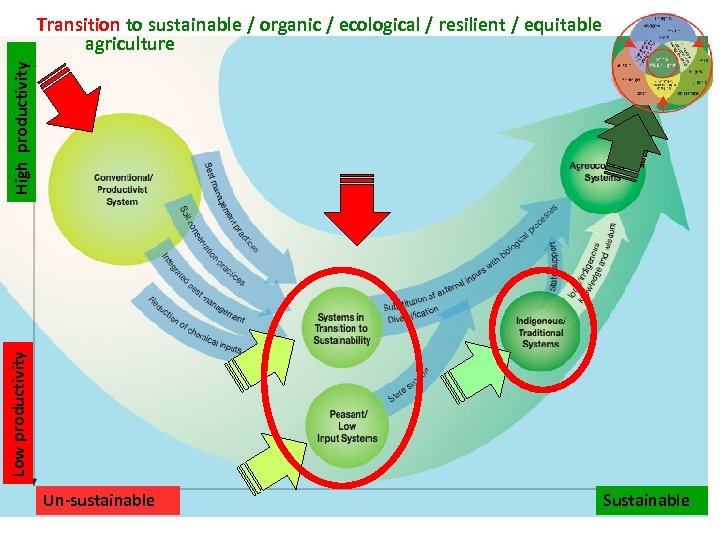 Low productivity High productivity Transition to sustainable / organic / ecological / resilient / equitable agriculture Un-sustainable Sustainable
Low productivity High productivity Transition to sustainable / organic / ecological / resilient / equitable agriculture Un-sustainable Sustainable
 How to transform / transition agriculture? Invest in agricultural R&D in ACP countries (IPG) that benefit small farmers / women especially (participatory) • • • Soil sciences Plant physiology and ecology Plant health (Insect, diseases, etc / pre and post harvest) Plant / animal breeding Plant / animal diversity, orphan species Agroforestry Water management Biotechnology (tissue culture, marker assisted breeding) Farm mechanization Aquaculture
How to transform / transition agriculture? Invest in agricultural R&D in ACP countries (IPG) that benefit small farmers / women especially (participatory) • • • Soil sciences Plant physiology and ecology Plant health (Insect, diseases, etc / pre and post harvest) Plant / animal breeding Plant / animal diversity, orphan species Agroforestry Water management Biotechnology (tissue culture, marker assisted breeding) Farm mechanization Aquaculture
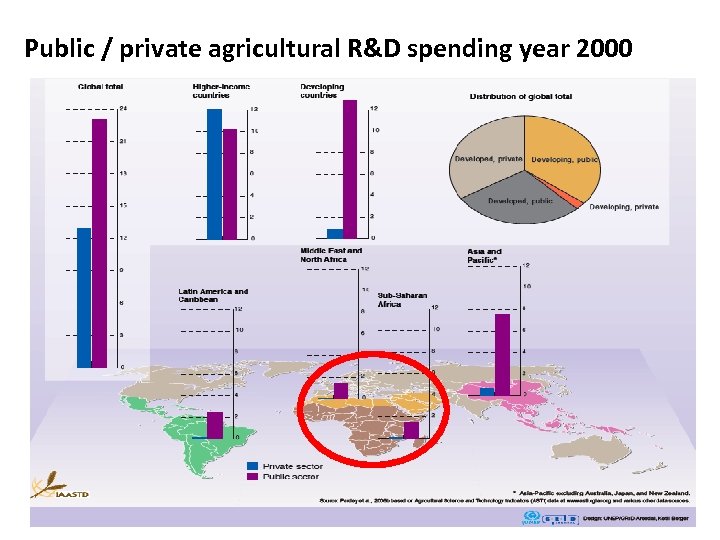 Public / private agricultural R&D spending year 2000
Public / private agricultural R&D spending year 2000
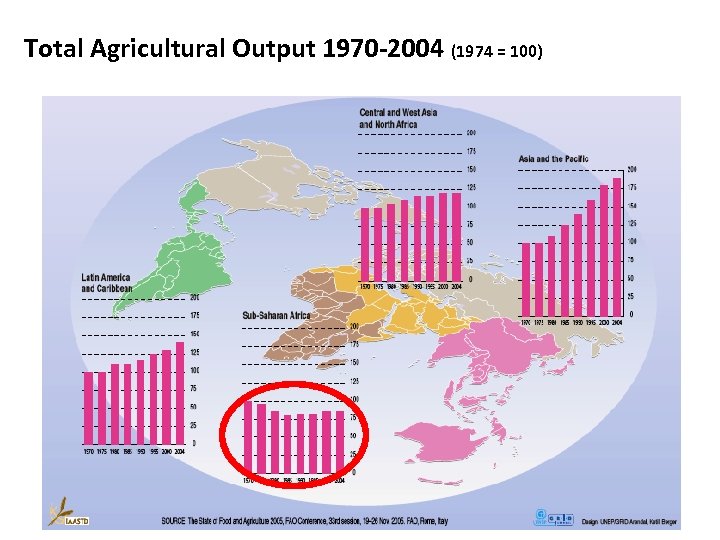 Total Agricultural Output 1970 -2004 (1974 = 100)
Total Agricultural Output 1970 -2004 (1974 = 100)
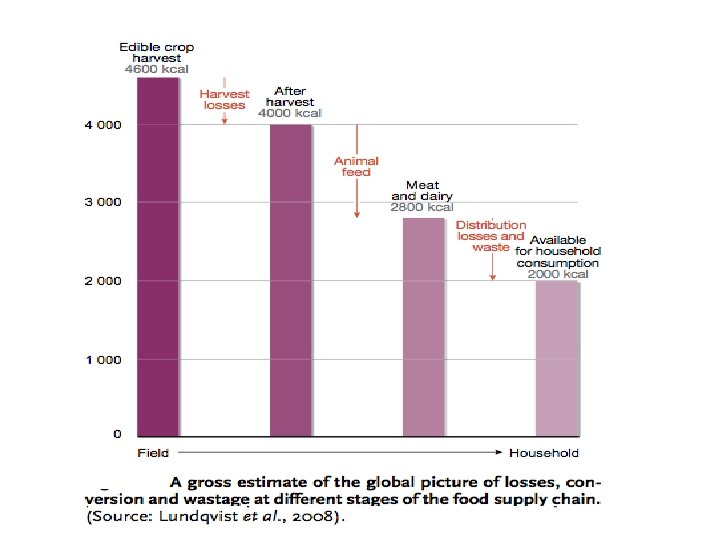
 How to transform / transition agriculture: Reducing Post Harvest Losses are as Important as Increasing Yields • 30% of harvested crops are lost to spoilage and pest damage and never reach consumers • Improving post harvest storage & handling capabilities for immediate benefits • Supporting appropriate value added food processing in rural areas also reduces losses and creates jobs • Parallel investment needed to improve market access infrastructures
How to transform / transition agriculture: Reducing Post Harvest Losses are as Important as Increasing Yields • 30% of harvested crops are lost to spoilage and pest damage and never reach consumers • Improving post harvest storage & handling capabilities for immediate benefits • Supporting appropriate value added food processing in rural areas also reduces losses and creates jobs • Parallel investment needed to improve market access infrastructures
 How to transform / transition agriculture: Ecological Agriculture provides the best prospects for sustainability –more of what works • Uses organic nutrient and N-fixing crop rotations to restore soil fertility (Microorganism mediated nutrient mobilization) • Organic matter & crop residue build soil carbon EA reduces use of fossil fuels & agrochemicals and GHG emissions • EA sequesters carbon (neutral / positive impact on CC) • EA improves yields by 70% vs traditional farming
How to transform / transition agriculture: Ecological Agriculture provides the best prospects for sustainability –more of what works • Uses organic nutrient and N-fixing crop rotations to restore soil fertility (Microorganism mediated nutrient mobilization) • Organic matter & crop residue build soil carbon EA reduces use of fossil fuels & agrochemicals and GHG emissions • EA sequesters carbon (neutral / positive impact on CC) • EA improves yields by 70% vs traditional farming
 What new paradigm? Organic agriculture Organic bananas in the Dominican Republic Organic Conventional In 1995 –drought year
What new paradigm? Organic agriculture Organic bananas in the Dominican Republic Organic Conventional In 1995 –drought year
 What new paradigm? Push-Pull Organic maize in Kenya
What new paradigm? Push-Pull Organic maize in Kenya
 How to transform agriculture: Appropriate scaled mechanization for small farmers and cooperatives • Financing for farmers to buy mechanized ag equipment to improve labor productivity • R&D for No Till equipment; and incentives for domestic marketing/tech support supply chain • Local production of biofuels & power to enable use of mechanized systems
How to transform agriculture: Appropriate scaled mechanization for small farmers and cooperatives • Financing for farmers to buy mechanized ag equipment to improve labor productivity • R&D for No Till equipment; and incentives for domestic marketing/tech support supply chain • Local production of biofuels & power to enable use of mechanized systems
 How to transform agriculture (Institution building) EA is knowledge intensive: need for human and social capital development • Improve and expand extension services and farmer field schools to train and demonstrate EA practices and values • Introduce capacity building for cooperatives to enable locally owned and operated input and output firms • Increase higher education for implementation of EA • Agriculture is very localized = regional and local solutions
How to transform agriculture (Institution building) EA is knowledge intensive: need for human and social capital development • Improve and expand extension services and farmer field schools to train and demonstrate EA practices and values • Introduce capacity building for cooperatives to enable locally owned and operated input and output firms • Increase higher education for implementation of EA • Agriculture is very localized = regional and local solutions
 How to transform agriculture: (Trade and markets) Improving small farmer access to local, urban and foreign markets • Improving food safety • quality control (compliance with organic, fare trade, Global Gap and other certification standards) Essential policy Actions to stimulate transition to EA • Remove perverse subsidies (fossil fuels, commodity crops, power, etc…) • Account for externalities (reward positive externalities) • Introduce support for transition to EA • Allow countries to implement trade policies that protect local farmers
How to transform agriculture: (Trade and markets) Improving small farmer access to local, urban and foreign markets • Improving food safety • quality control (compliance with organic, fare trade, Global Gap and other certification standards) Essential policy Actions to stimulate transition to EA • Remove perverse subsidies (fossil fuels, commodity crops, power, etc…) • Account for externalities (reward positive externalities) • Introduce support for transition to EA • Allow countries to implement trade policies that protect local farmers
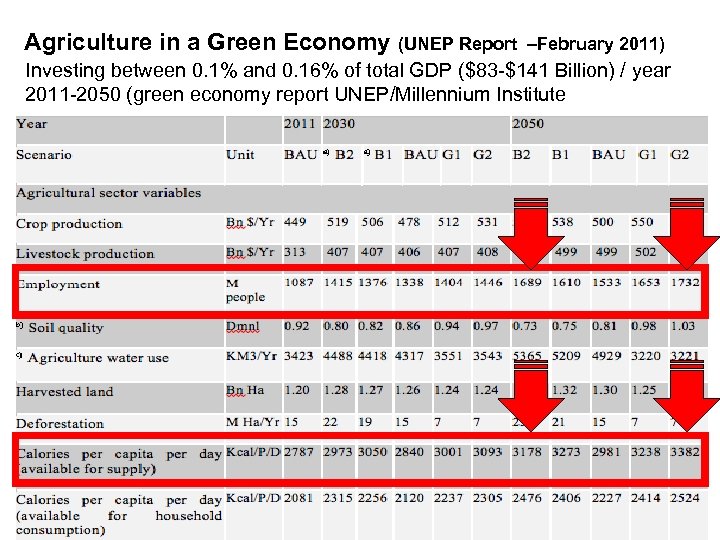 Agriculture in a Green Economy (UNEP Report –February 2011) Investing between 0. 1% and 0. 16% of total GDP ($83 -$141 Billion) / year 2011 -2050 (green economy report UNEP/Millennium Institute
Agriculture in a Green Economy (UNEP Report –February 2011) Investing between 0. 1% and 0. 16% of total GDP ($83 -$141 Billion) / year 2011 -2050 (green economy report UNEP/Millennium Institute
 You cannot solve a problem with the same thinking that created it. A Einstein Thank you for your attention
You cannot solve a problem with the same thinking that created it. A Einstein Thank you for your attention


