3eabf02d4239da69b174c94d8b0abe32.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Major Asian Belief Systems Confucianism, Taoism and Buddhism

Question of the Day… What principles should guide human conduct and ensure order in society?

Confucianism

Confucianism: Origins • Confucius was born in 551 B. C. E. during the Zhou Dynasty • Teachings became popular during the Han Dynasty • Developed a philosophy to promote peace and harmony through proper behavior • Teachings collected in the Analects

Confucianism: Teachings • Five relationships govern society – Ruler and ruled – Father and son – Older brother and younger brother – Husband wife – Friend and friend* • One person has authority over the other, and has a responsibility to set a good example and take care of the other

Confucianism: Teachings cont. • Loyalty, courtesy, hard work and service are key values • Family and society are more important than the individual • Stressed filial piety • Education is the gateway to improvement of the individual and society; contributes to the practice of ethical behavior “To enrich your family, there is no need to buy good land: Books hold a thousand measures of grain. ” Confucius

Confucianism: Influence • Under the Han Dynasty (around 200 B. C. E. ) Confucian philosophy gained strong influence • Government run by the most learned men Above: Painting depicting students studying for the exam Below: Recreated cell, where students would have taken the exam – Students attended university – Had to pass a Civil Service Examination on Confucian teachings, as well as Chinese law, history and traditions – System lasted until the 1900’s • WASL?

Taoism/Daoism

Daoism: Origins • The origins of Daoism are unclear • Attributed to Lao Zi, during 500 - 400 B. C. E. • Developed a philosophy based on non-action (going with the flow!) • Teachings recorded in the Tao De Jing (The Way of Virtue)

Daoism: Teachings • Simplicity is a key value • The best way to live is the natural way • A society with rules is an artificial creation that disturbs the natural order Yin-Yang: Complimentary opposites. “You can conquer others with power, but it takes true strength to conquer yourself”. - Tao De Jing

Daoism: Influence • Led to dominance of nature in Chinese painting and poetry • Daoists made advances in science and technology – Magnetic compass – Gun powder

Question… What would Daoists say about Confucianism?

Buddhism

Buddhism: Origins • Founded around 530 B. C. E. by Siddhartha Gautama who lived in Northeast India • Rejected the Hindu caste system and materialism in favor of individual spirituality • The teachings of the Buddha were recorded in hundreds of documents Buddhapada: Footprints of the Buddha. • Arrived in Southeast and East Asia around 100 C. E.

Buddhism: Schools • Theravada – Practiced in Sri Lanka, Burma and Thailand – Considered the original school of Buddhism • Mahayana • Vajrayana – Practiced in Tibet, Nepal, Bhutan and Mongolia – The lama (or guru) is central to this practice • Zen – Practiced in China, – Practiced in Japan Korea, Japan, Vietnam and Tibet – Emphasis on meditation – Branched off from Theravada, some • These are just a few differences in scriptures examples! and practices

Buddhism: Teachings • The Four Noble Truths – 1. Life is suffering – 2. Suffering is caused by wanting and aversion – 3. Suffering can be overcome and happiness attained (Nirvana) – 4. The Eightfold Path leads to the end of suffering Dharma Wheel: Roof decoration on Tibetan temple; the wheel represents reincarnation and the Eightfold Path

Buddhism: Teachings cont. • The Eightfold Path Mudra (or symbolic hand gesture) symbolizing the Eightfold Path – 1. Right view or understanding: of nature and the path of transformation – 2. Right thought or attitude: acting from love and compassion – 3. Right speech: clear, truthful, uplifting and non-harmful speech

Buddhism: Teachings cont. • The Eightfold Path – 4. Right action: following the Five Precepts – 5. Right livelihood: based on the principal of non-exploitation – 6. Right effort: conscious evolution – 7. Right mindfulness: awareness of all things – 8. Samadhi: onepointed-ness of mind, enlightenment “Buddha with Attendants” Korea, 16 -17 th Century

Buddhism: Teachings cont. • The Five Precepts – Do not take the life of anything living – Do not take anything not freely given – Abstain from sexual misconduct and sensual overindulgence – Refrain from untrue speech – Avoid intoxication, that is, losing mindfulness

Vocab. words • Atman: The innermost essence of the individual (soul) • Nirvana: The state of perfect insight, eternal rest, and ultimate truth • Samara: The opposite of Nirvana- the indefinitely repeated cycle of birth, misery, and death. • Brahmins: The highest Hindu caste. Brahmins inherit their caste position and their occupation as priests. Siddhartha was born and raised a Brahmin. • Om: “The word of words” A verbal spell or ritual incantation used in meditative contemplation.

Buddhism: Influence • Where Confucianism and Daoism focused on life on earth, Buddhism offered an afterlife • Buddhist monasteries and temples became centers of village life Young monks-intraining in Cambodia. Buddhist temple in Kyoto, Japan.

Appeal: Confucianism and Daoism dealt with life on Earth. Buddhism was a religion that offered an escape from the suffering of an earthly life. The Chinese could accept diverse ideas, As a result, many Chinese followed Buddhist, Daoist, and Confucian beliefs at the same time.

Review Buddhism Confucianism Daoism

Question. . Do you think it is possible to follow Confucianism, Daoism, and Buddhism simultaneously?
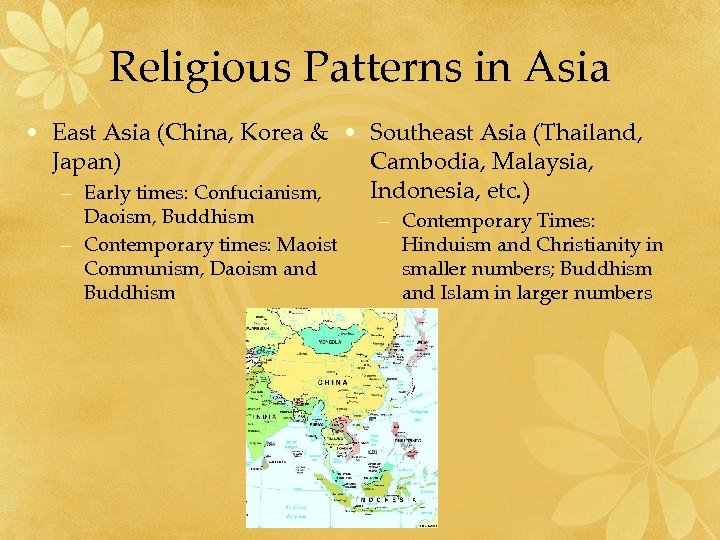
Religious Patterns in Asia • East Asia (China, Korea & • Southeast Asia (Thailand, Japan) Cambodia, Malaysia, Indonesia, etc. ) – Early times: Confucianism, Daoism, Buddhism – Contemporary times: Maoist Communism, Daoism and Buddhism – Contemporary Times: Hinduism and Christianity in smaller numbers; Buddhism and Islam in larger numbers
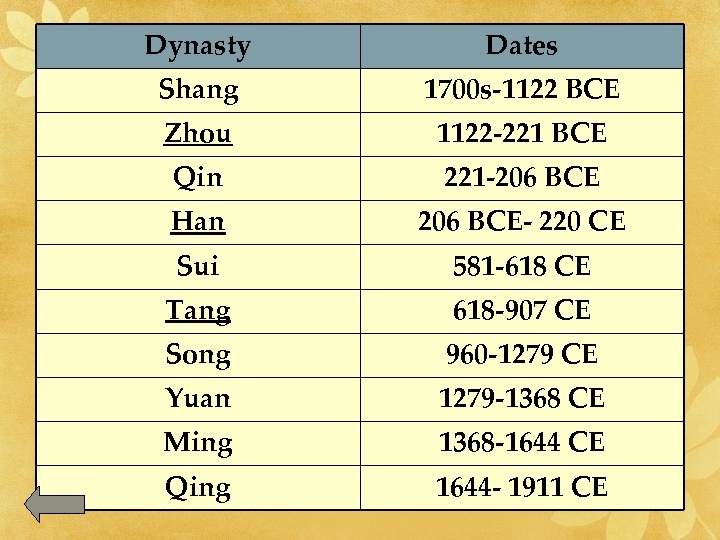
Dynasty Dates Shang 1700 s-1122 BCE Zhou 1122 -221 BCE Qin 221 -206 BCE Han 206 BCE- 220 CE Sui 581 -618 CE Tang 618 -907 CE Song 960 -1279 CE Yuan 1279 -1368 CE Ming 1368 -1644 CE Qing 1644 - 1911 CE
3eabf02d4239da69b174c94d8b0abe32.ppt