3367252d108dc4f2065417b1b9876c93.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Maintaining Consistency Between System. C and RTL System Designs Presenter: Christopher Lennard, Ph. D. Authors: ARM - Alistair Bruce, Andrew Nightingale, Nizar Romdhane, Christopher Lennard Spiratech – MM Kamal Hashmi, Steve Beavis
Introduction l Testbench re-use is key to bringing system level design into standard So. C engineering practice l ESL has many benefits: ¤ ¤ ¤ Speed Flexibility Ease of design exploration l BUT quick and verifiable transfer to RTL is vital l A unified testbench for all levels guarantees consistency l The verification re-use strategy has 3 main pillars: ¤ ¤ ¤ Re-usable system testbench architecture (XVC Methodology) Interfacing multiple abstraction levels (Generated Transactors) Testbench configuration consistency (IP-XACT from The SPIRIT Consortium) l Early results support the viability of this strategy
Testbench Architecture XVC Methodology
A Modular Testbench Architecture l Common testbench architecture. . . ¤ Based on XVC Methodology l. . . across all levels of abstraction ¤ Using generated transactors l Structuring verification IP (VIP) for re-use l Delivering a VIP environment
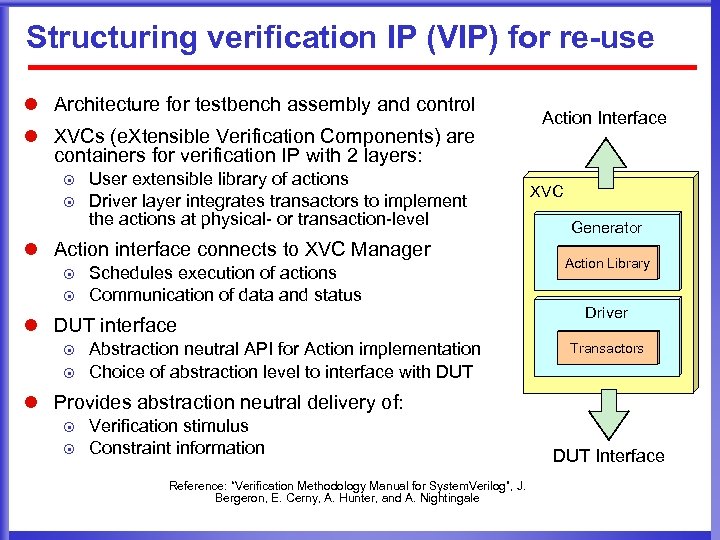
Structuring verification IP (VIP) for re-use l Architecture for testbench assembly and control l XVCs (e. Xtensible Verification Components) are containers for verification IP with 2 layers: ¤ ¤ User extensible library of actions Driver layer integrates transactors to implement the actions at physical- or transaction-level l Action interface connects to XVC Manager ¤ ¤ Schedules execution of actions Communication of data and status l DUT interface ¤ ¤ Abstraction neutral API for Action implementation Choice of abstraction level to interface with DUT Action Interface XVC Generator Action Library Driver Transactors l Provides abstraction neutral delivery of: ¤ ¤ Verification stimulus Constraint information Reference: “Verification Methodology Manual for System. Verilog”, J. Bergeron, E. Cerny, A. Hunter, and A. Nightingale DUT Interface
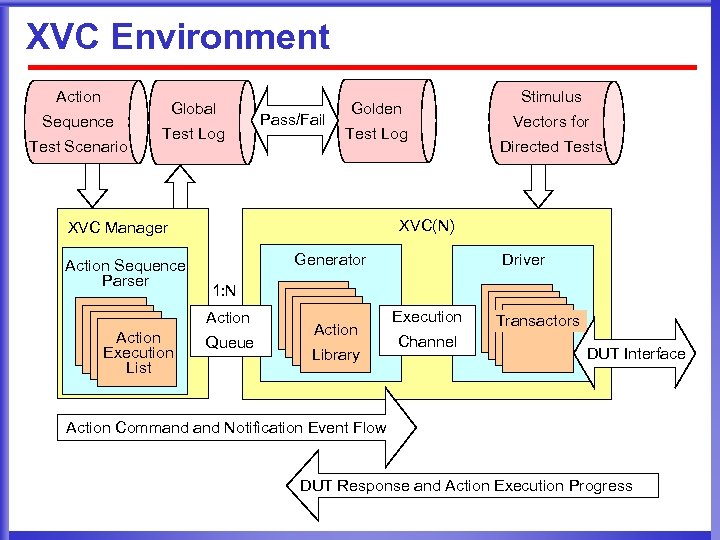
XVC Environment Action Sequence Test Scenario Global Test Log Pass/Fail Golden Test Log Generator Directed Tests Driver 1: N Action Execution List Vectors for XVC(N) XVC Manager Action Sequence Parser Stimulus Queue Action Library Execution Channel Transactors DUT Interface Action Command Notification Event Flow DUT Response and Action Execution Progress
Delivering a VIP environment l XVC Manager ¤ ¤ ¤ Coordinates test scenarios from external plain text files Abstracts away details of VIP environment Test scenarios can encapsulate common sequences of actions l XVCs (e. Xtensible Verification Components) ¤ ¤ A foundation for VIP – modular and scalable Re-usable across verification environments Can drive interconnect or external interfaces of DUT Can support other XVCs by monitoring state and providing notification l Golden test logs
Multi-Level Testbench Multi-Level XVC Methodology Transactors
Multi-Abstraction Testbench l Goal: The system testbench can be applied to all levels of abstraction without alteration l Implies: Stimulus must be applied to DUT through a driver that can handle multiple abstraction levels l Implementation: Deploy multi-level drivers called Transactors to interface DUT and the system testbench
Driving a DUT through Transactors l Given: ¤ ¤ ¤ Interface protocol Abstraction levels Mapping between levels l Can write transactors to bridge between levels l Traditionally, manually written as 2 unidirectional components: ¤ ¤ Driver Monitor l Need bi-directional transactors for XVCs as they must both drive and monitor
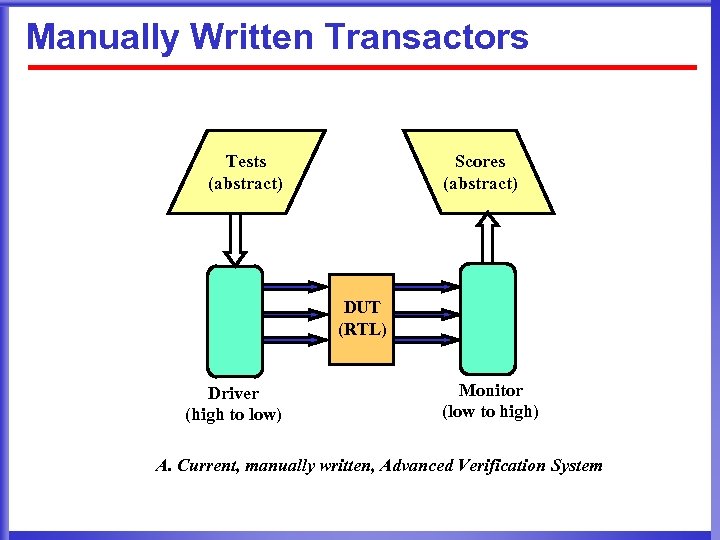
Manually Written Transactors Tests (abstract) Scores (abstract) DUT (RTL) Driver (high to low) Monitor (low to high) A. Current, manually written, Advanced Verification System
Interface Specification l Transactors are: ¤ ¤ ¤ Complex to design Time consuming to build and test Often need to connect > 2 levels of abstraction l A formal Interface Specification captures: ¤ ¤ Temporal and behavioural aspects at multiple levels Mapping between levels l Generate transactors from Interface Specification ¤ ¤ Drive and monitor Automated connectivity between levels of abstraction
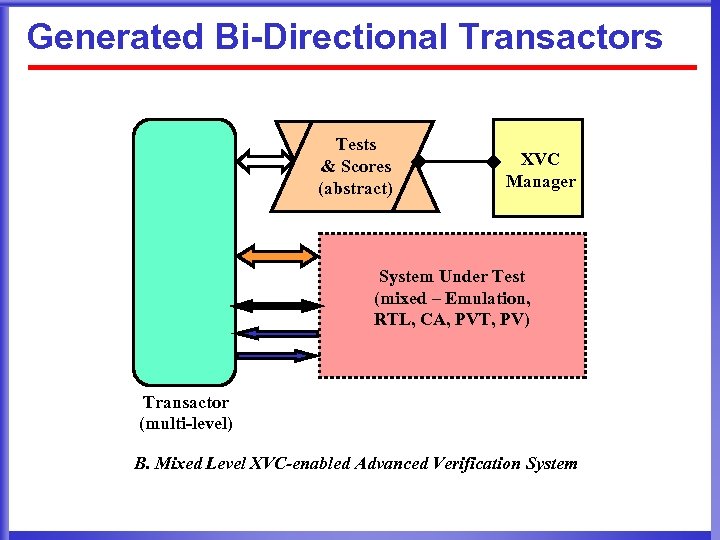
Generated Bi-Directional Transactors Tests & Scores (abstract) XVC Manager System Under Test (mixed – Emulation, RTL, CA, PVT, PV) Transactor (multi-level) B. Mixed Level XVC-enabled Advanced Verification System
Transactors for Standard TLM Interfaces l System. C method calling interface for each level of abstraction ¤ For cycle-accurate, built on the ARM Real. View® ESL APIs ¢ CASI : Cycle-Accurate Simulation Interface ¢ Cycle-based TLM transport layer supporting any bus protocol ¢ ¤ http: //www. arm. com/products/Dev. Tools/Real. View. ESLAPIs. html For progammers-view, would support PV / PVT OSCI proposal ¢ Event-based TLM transport layer for abstract models l Multi-level transactor for AXI built on top of the TLM transport layer ¤ ¤ Passes pointer to generic container Populated and manipulated during transaction lifetime Transactor can pack/unpack between container and RTL signals This bridges between System. C TLM and RTL
DUT and Testbench Configuration l Multi-abstraction design flow requires automatic alignment of testbench with design configuration ¤ e. g. , register map used by integration test may change l Alignment achieved using design meta-data ¤ ¤ Describe design configuration Automate design and verification set-up l Common meta-data needed to support multi-vendor flow l The SPIRIT Consortium is providing specifications to help standardise meta-data
Testbench Consistency Multi-Level XVC Methodology Transactors SPIRIT IP-XACT
The SPIRIT Consortium Specifications l IP-XACT is an XML schema and semantics providing: ¤ ¤ Unified authoring, exchange and processing of design meta-data Complete API for meta-data exchange and database querying l An IP-XACT enabled design environment has: ¤ ¤ Libraries of component descriptions Definitions of component interfaces l Design meta-data describes: ¤ ¤ Component instances Connectivity l Generator plug-ins support automated design configuration ¤ ¤ LGI (Loose Generator Interface) meta-data dumping mechanism TGI (Tight Generator Interface) API based on SOAP

Applying IP-XACT to the System Testbench l Current version of The SPIRIT Consortium Spec, v 1. 2 ¤ ¤ Complete for RTL design and verification component descriptions Released as IP-XACT into IEEE 1685 process l It enables the automated composition, integration and configuration of an RTL verification environment l Testbench specified as ¤ ¤ Component instances (design and verification) Connections between components l Supports verification components (at RTL) ¤ ¤ Monitor interfaces White-box interfaces l IP-XACT enabled meta-data provides language (and vendor) independent description of the testbench configuration and connection to DUT
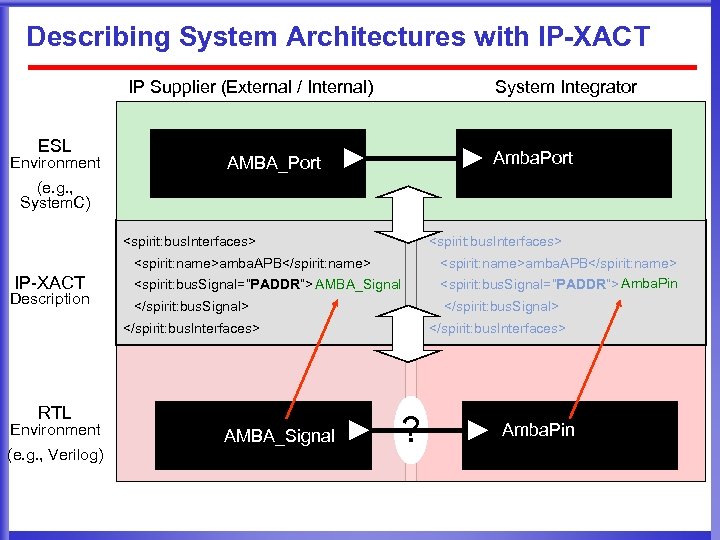
Describing System Architectures with IP-XACT IP Supplier (External / Internal) ESL Environment System Integrator e. g. , Published AMBA SPIRIT bus. Definitions Amba. Port AMBA_Port (e. g. , System. C) <spirit: bus. Interfaces> <spirit: name>amba. APB</spirit: name> IP-XACT Description <spirit: bus. Signal=“PADDR”> AMBA_Signal <spirit: name>amba. APB</spirit: name> <spirit: bus. Signal=“PADDR”> Amba. Pin </spirit: bus. Signal> </spirit: bus. Interfaces> RTL Environment (e. g. , Verilog) AMBA_Signal </spirit: bus. Interfaces> ? Amba. Pin
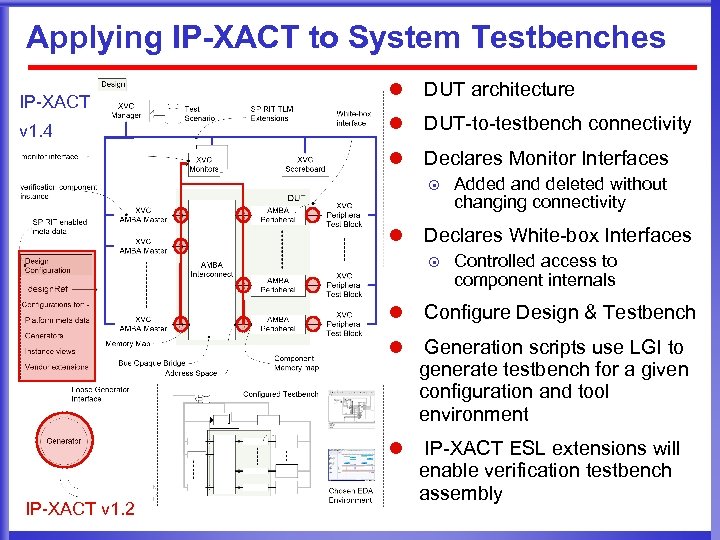
Applying IP-XACT to System Testbenches v 1. 4 l DUT architecture l DUT-to-testbench connectivity l IP-XACT Declares Monitor Interfaces ¤ l Added and deleted without changing connectivity Declares White-box Interfaces ¤ Controlled access to component internals l l Generation scripts use LGI to generate testbench for a given configuration and tool environment l IP-XACT v 1. 2 Configure Design & Testbench IP-XACT ESL extensions will enable verification testbench assembly
Maintaining Consistency Between System. C and RTL System Designs XVC Methodology Multi-Level Transactors SPIRIT IP-XACT
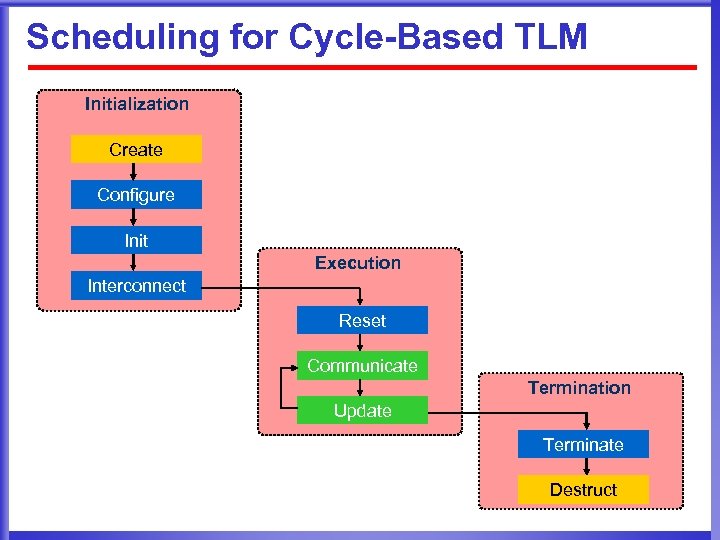
Scheduling for Cycle-Based TLM Initialization Create Configure Init Execution Interconnect Reset Communicate Termination Update Terminate Destruct
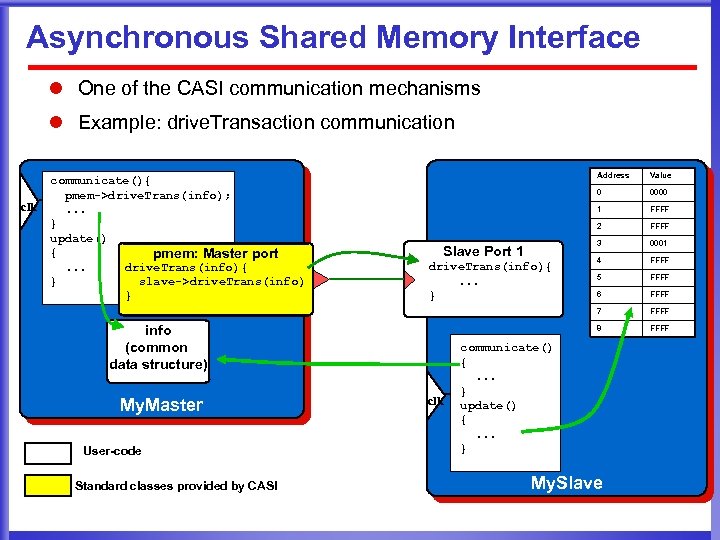
Asynchronous Shared Memory Interface l One of the CASI communication mechanisms l Example: drive. Transaction communication clk Address 0 My. Master User-code Standard classes provided by CASI clk FFFF 3 0001 4 FFFF 5 FFFF 6 FFFF 8 info (common data structure) FFFF 2 drive. Trans(info){. . . } 0000 1 Slave Port 1 Value 7 communicate(){ pmem->drive. Trans(info); . . . } update() { pmem: Master port drive. Trans(info){. . . slave->drive. Trans(info) } } FFFF communicate() {. . . } update() {. . . } My. Slave
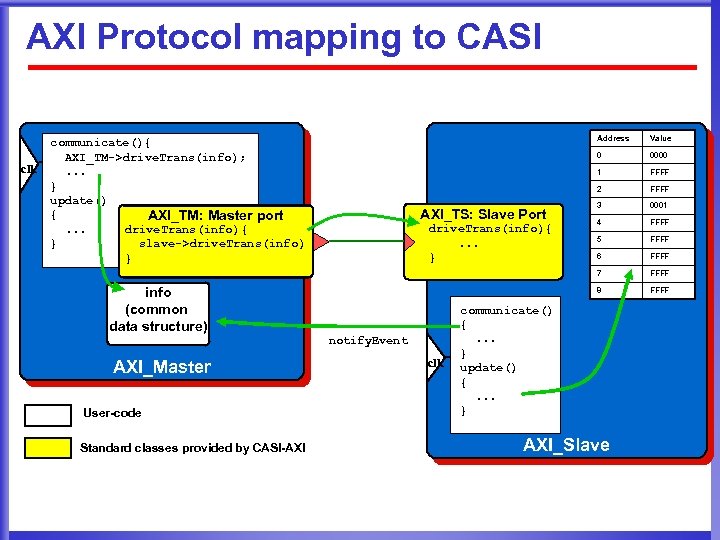
AXI Protocol mapping to CASI clk Address AXI_Master User-code Standard classes provided by CASI-AXI clk 3 0001 4 FFFF 5 FFFF 6 FFFF 8 notify. Event FFFF 7 info (common data structure) FFFF 2 drive. Trans(info){. . . } 0000 1 AXI_TS: Slave Port Value 0 clk communicate(){ AXI_TM->drive. Trans(info); . . . } update() { AXI_TM: Master port drive. Trans(info){. . . slave->drive. Trans(info) } } FFFF communicate() {. . . } update() {. . . } AXI_Slave
Unified Testbench in Practice l Techniques applied to a subsystem testbench ¤ ¤ PL 190 Vectored Interrupt Controller modelled at RTL AHB interconnect modelled at PVT, with Real. View ESL APIs interfaces l Building the System and Testbench ¤ ¤ ¤ Meta-data design file specifies required components and VIP environment Parameters of design and verification components (e. g. bus_width) Design configuration file l Creating and inserting the Transactors ¤ ¤ Select and instantiate transactors as required by abstraction level selections in meta-data Transactors generated and configured using parameters captured in meta-data
Testbench in AMBA Designer
Executing a Simulation l Example shows an integration test l Consistency of levels demonstrated by comparison of results at each level l Simulation speed in mixed level simulations dominated by RTL (~95% spent in RTL) l Tenison VTOC Generate ¤ ¤ Abstracts RTL to cycle accurate C++ Minimises impact of RTL on simulation speed l An alternative is to run the RTL on an emulation platform
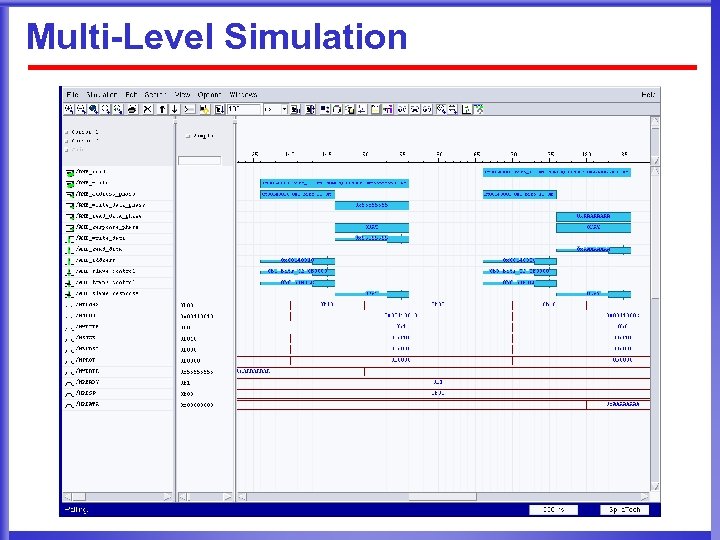
Multi-Level Simulation
Conclusions and Futures l Three key concepts enable a unified system testbench: 1. 2. 3. XVC Methodology Transactor Technology The SPIRIT Consortium IP-XACT meta-data specifications l Is in use today XVCs Transactors IP-XACT l Future industry standardisation ¤ ¤ System. C PV level interfaces IP-XACT for abstract design specification l Methodology will soon be applicable across the entire systemlevel modelling and verification flow
3367252d108dc4f2065417b1b9876c93.ppt