a025095b40fcdc1433ce6b0bfecb1751.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 MAGIC 5 meeting - Genova 2011/5/4 -6 A CAD system for cerebral glioma and therapy follow-up in DTI and FLAIR: status report Giorgio De Nunzio 1, Marina Donativi 1, Gabriella Pastore 2, Matteo Rucco 3 , Antonella Castellano 4, Andrea Falini 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Dept of Materials Science, Univ. of Salento, and INFN (National Institute of Nuclear Physics) (Lecce, Italy) PO 'Vito Fazzi' - UOC Fisica Sanitaria, and Dept of Materials Science, University of Salento (Lecce, Italy) School of Science and Technologies, University of Camerino (Italy) Neuroradiology Unit and CERMAC, San Raffaele Scientific Institute (Milano, Italy)
MAGIC 5 meeting - Genova 2011/5/4 -6 A CAD system for cerebral glioma and therapy follow-up in DTI and FLAIR: status report Giorgio De Nunzio 1, Marina Donativi 1, Gabriella Pastore 2, Matteo Rucco 3 , Antonella Castellano 4, Andrea Falini 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Dept of Materials Science, Univ. of Salento, and INFN (National Institute of Nuclear Physics) (Lecce, Italy) PO 'Vito Fazzi' - UOC Fisica Sanitaria, and Dept of Materials Science, University of Salento (Lecce, Italy) School of Science and Technologies, University of Camerino (Italy) Neuroradiology Unit and CERMAC, San Raffaele Scientific Institute (Milano, Italy)
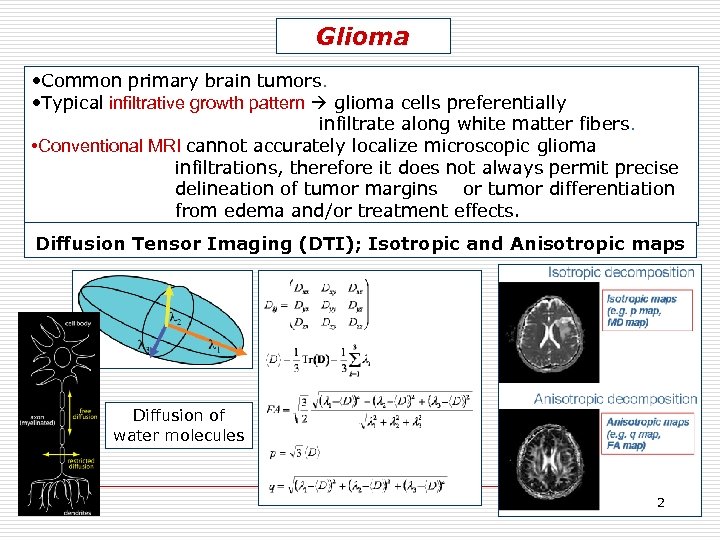 Glioma • Common primary brain tumors. • Typical infiltrative growth pattern glioma cells preferentially infiltrate along white matter fibers. • Conventional MRI cannot accurately localize microscopic glioma infiltrations, therefore it does not always permit precise delineation of tumor margins or tumor differentiation from edema and/or treatment effects. Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI); Isotropic and Anisotropic maps Diffusion of water molecules 2
Glioma • Common primary brain tumors. • Typical infiltrative growth pattern glioma cells preferentially infiltrate along white matter fibers. • Conventional MRI cannot accurately localize microscopic glioma infiltrations, therefore it does not always permit precise delineation of tumor margins or tumor differentiation from edema and/or treatment effects. Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI); Isotropic and Anisotropic maps Diffusion of water molecules 2
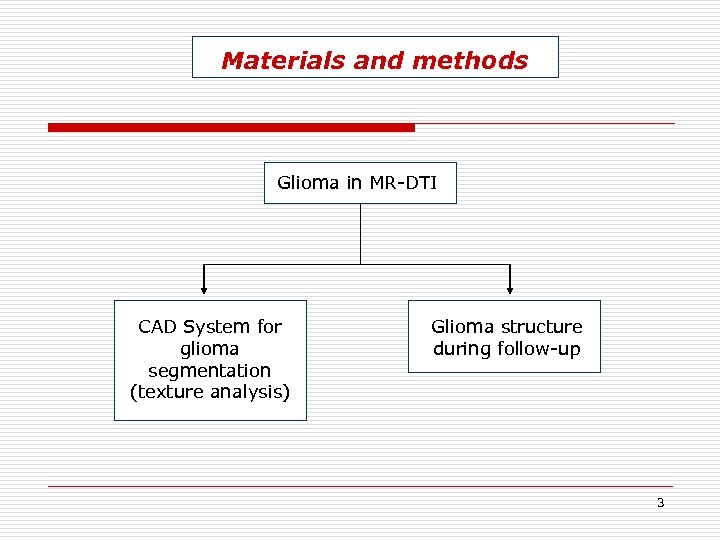 Materials and methods Glioma in MR-DTI CAD System for glioma segmentation (texture analysis) Glioma structure during follow-up 3
Materials and methods Glioma in MR-DTI CAD System for glioma segmentation (texture analysis) Glioma structure during follow-up 3
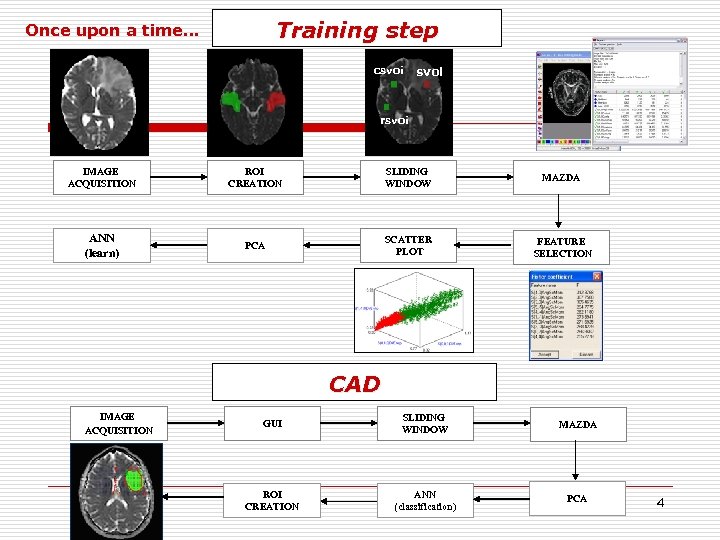 Training step Once upon a time… csvoi rsvoi IMAGE ACQUISITION ROI CREATION SLIDING WINDOW MAZDA ANN (learn) PCA SCATTER PLOT FEATURE SELECTION CAD IMAGE ACQUISITION GUI SLIDING WINDOW MAZDA ROI CREATION ANN (classification) PCA 4
Training step Once upon a time… csvoi rsvoi IMAGE ACQUISITION ROI CREATION SLIDING WINDOW MAZDA ANN (learn) PCA SCATTER PLOT FEATURE SELECTION CAD IMAGE ACQUISITION GUI SLIDING WINDOW MAZDA ROI CREATION ANN (classification) PCA 4
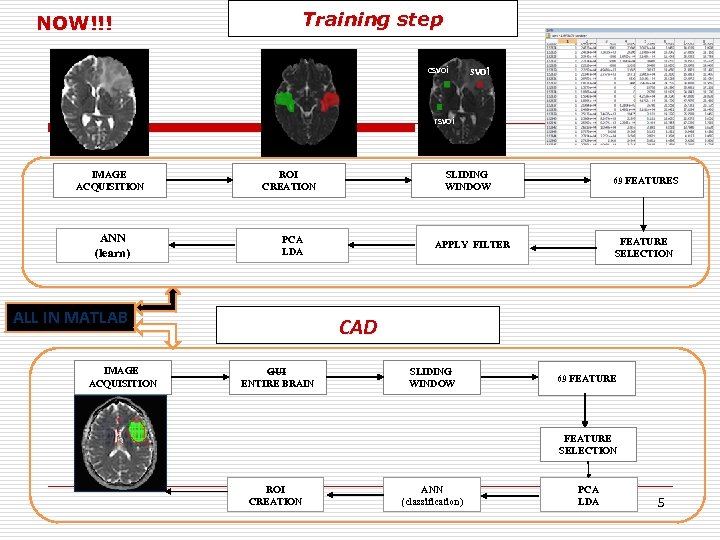 NOW!!! Training step csvoi rsvoi IMAGE ACQUISITION ANN (learn) PCA LDA ALL IN MATLAB IMAGE ACQUISITION SLIDING WINDOW ROI CREATION 69 FEATURES FEATURE SELECTION APPLY FILTER CAD GUI ENTIRE BRAIN SLIDING WINDOW 69 FEATURE SELECTION ROI CREATION ANN (classification) PCA LDA 5
NOW!!! Training step csvoi rsvoi IMAGE ACQUISITION ANN (learn) PCA LDA ALL IN MATLAB IMAGE ACQUISITION SLIDING WINDOW ROI CREATION 69 FEATURES FEATURE SELECTION APPLY FILTER CAD GUI ENTIRE BRAIN SLIDING WINDOW 69 FEATURE SELECTION ROI CREATION ANN (classification) PCA LDA 5
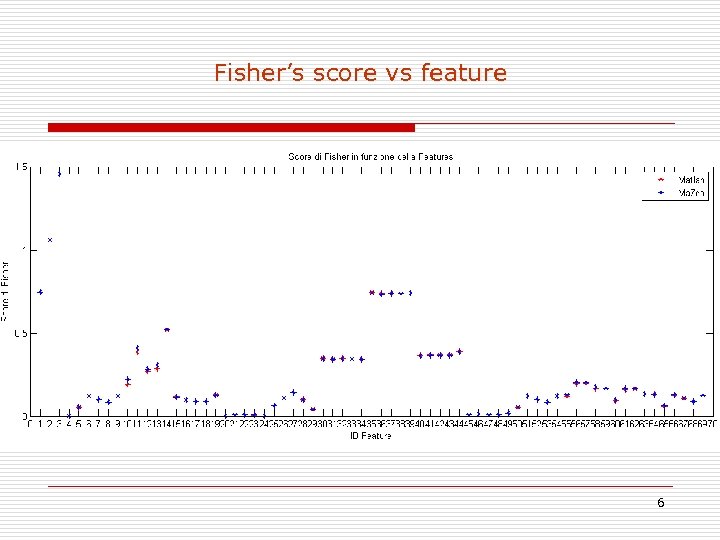 Fisher’s score vs feature 6
Fisher’s score vs feature 6
 Work in progress… PCA or LDA? 7
Work in progress… PCA or LDA? 7
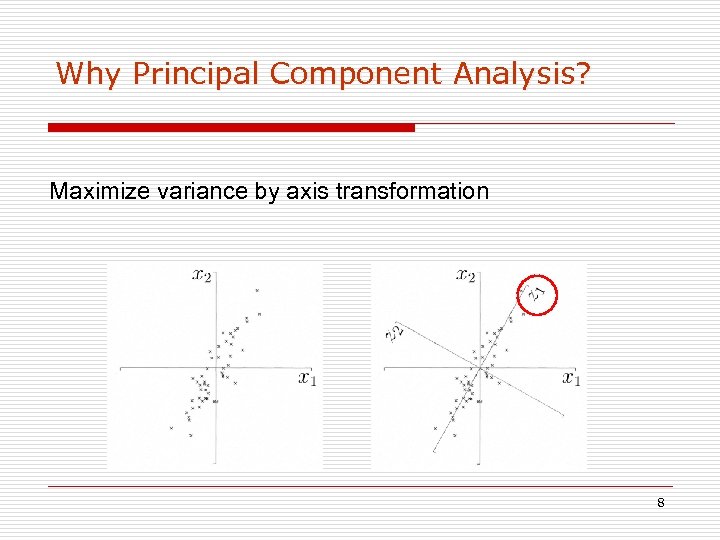 Why Principal Component Analysis? Maximize variance by axis transformation 8
Why Principal Component Analysis? Maximize variance by axis transformation 8
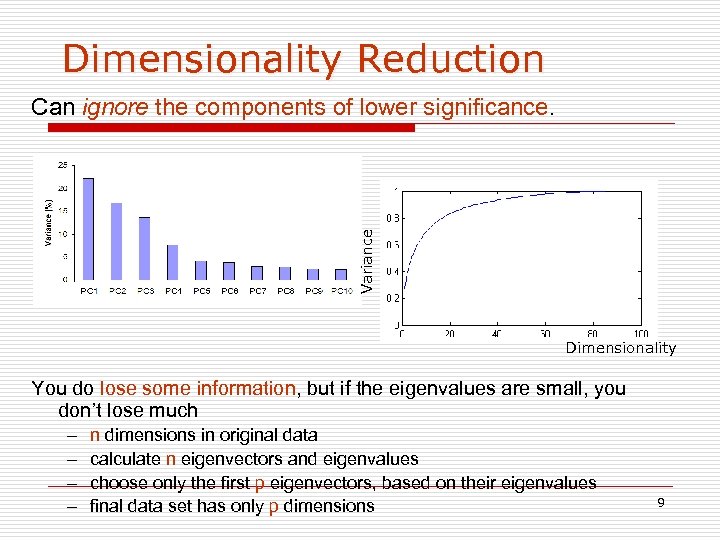 Dimensionality Reduction Variance Can ignore the components of lower significance. Dimensionality You do lose some information, but if the eigenvalues are small, you don’t lose much – – n dimensions in original data calculate n eigenvectors and eigenvalues choose only the first p eigenvectors, based on their eigenvalues final data set has only p dimensions 9
Dimensionality Reduction Variance Can ignore the components of lower significance. Dimensionality You do lose some information, but if the eigenvalues are small, you don’t lose much – – n dimensions in original data calculate n eigenvectors and eigenvalues choose only the first p eigenvectors, based on their eigenvalues final data set has only p dimensions 9
 Limitations of PCA Are the maximum-variance variables the relevant features for discrimination preservation? 10
Limitations of PCA Are the maximum-variance variables the relevant features for discrimination preservation? 10
 Linear Discriminant Analysis • What is the goal of LDA? − Perform dimensionality reduction “while preserving as much of the class discriminatory information as possible”. − Seeks to find directions along which the classes are best separated. − Takes into consideration the within-class scatter but also the between-class scatter. 11
Linear Discriminant Analysis • What is the goal of LDA? − Perform dimensionality reduction “while preserving as much of the class discriminatory information as possible”. − Seeks to find directions along which the classes are best separated. − Takes into consideration the within-class scatter but also the between-class scatter. 11
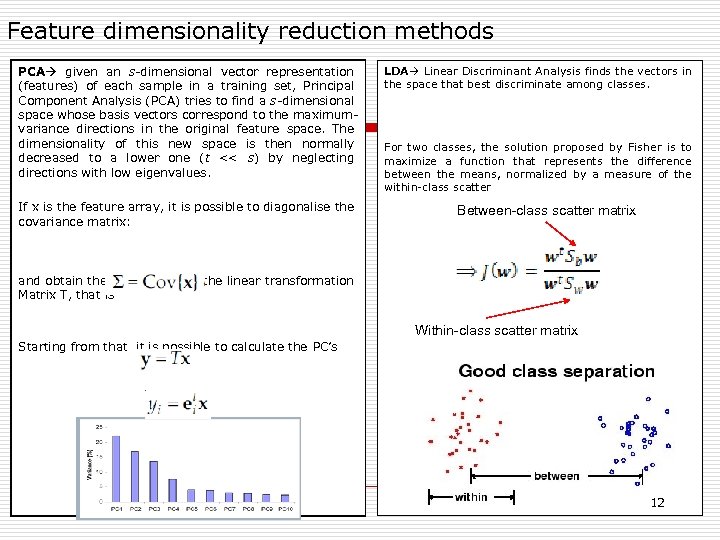 Feature dimensionality reduction methods PCA given an s-dimensional vector representation (features) of each sample in a training set, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) tries to find a s-dimensional space whose basis vectors correspond to the maximumvariance directions in the original feature space. The dimensionality of this new space is then normally decreased to a lower one (t << s) by neglecting directions with low eigenvalues. If x is the feature array, it is possible to diagonalise the covariance matrix: LDA Linear Discriminant Analysis finds the vectors in the space that best discriminate among classes. For two classes, the solution proposed by Fisher is to maximize a function that represents the difference between the means, normalized by a measure of the within-class scatter Between-class scatter matrix and obtain the eigenvalues of the linear transformation Matrix T, that is Within-class scatter matrix Starting from that, it is possible to calculate the PC’s 12
Feature dimensionality reduction methods PCA given an s-dimensional vector representation (features) of each sample in a training set, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) tries to find a s-dimensional space whose basis vectors correspond to the maximumvariance directions in the original feature space. The dimensionality of this new space is then normally decreased to a lower one (t << s) by neglecting directions with low eigenvalues. If x is the feature array, it is possible to diagonalise the covariance matrix: LDA Linear Discriminant Analysis finds the vectors in the space that best discriminate among classes. For two classes, the solution proposed by Fisher is to maximize a function that represents the difference between the means, normalized by a measure of the within-class scatter Between-class scatter matrix and obtain the eigenvalues of the linear transformation Matrix T, that is Within-class scatter matrix Starting from that, it is possible to calculate the PC’s 12
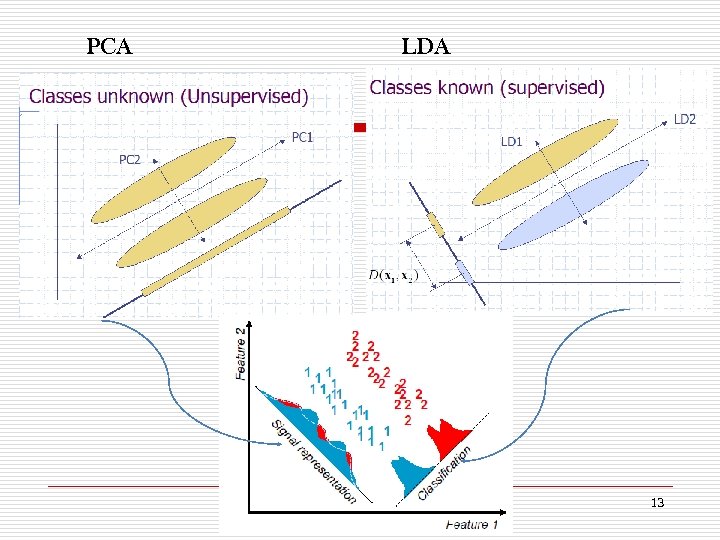 PCA LDA 13
PCA LDA 13
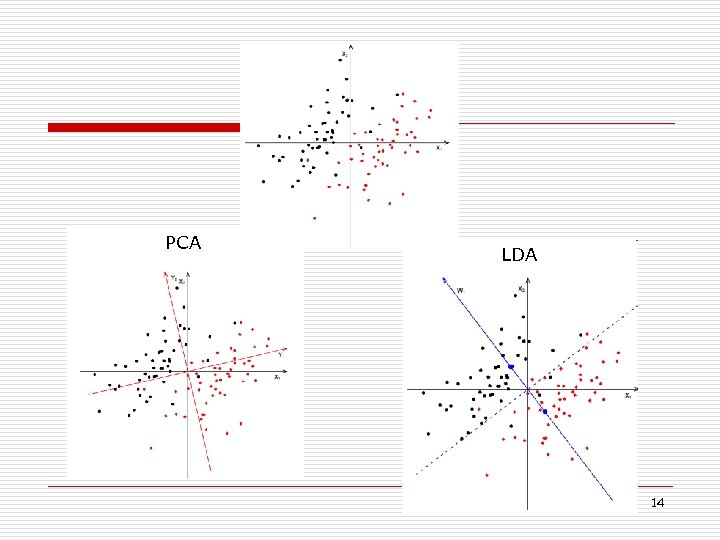 PCA LDA 14
PCA LDA 14
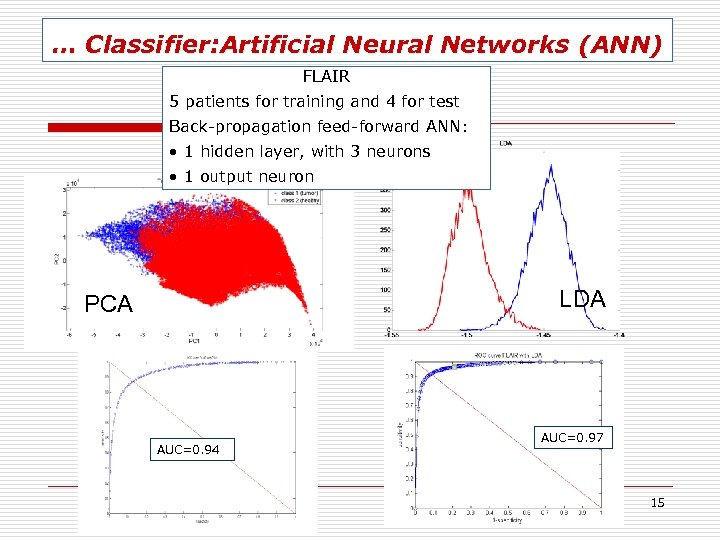 … Classifier: Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) FLAIR 5 patients for training and 4 for test Back-propagation feed-forward ANN: • 1 hidden layer, with 3 neurons • 1 output neuron LDA PCA AUC=0. 94 AUC=0. 97 15
… Classifier: Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) FLAIR 5 patients for training and 4 for test Back-propagation feed-forward ANN: • 1 hidden layer, with 3 neurons • 1 output neuron LDA PCA AUC=0. 94 AUC=0. 97 15
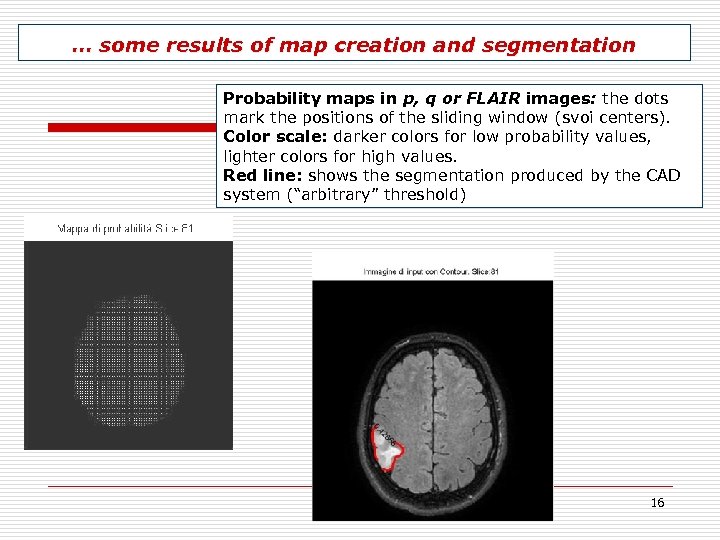 … some results of map creation and segmentation Probability maps in p, q or FLAIR images: the dots mark the positions of the sliding window (svoi centers). Color scale: darker colors for low probability values, lighter colors for high values. Red line: shows the segmentation produced by the CAD system (“arbitrary” threshold) 16
… some results of map creation and segmentation Probability maps in p, q or FLAIR images: the dots mark the positions of the sliding window (svoi centers). Color scale: darker colors for low probability values, lighter colors for high values. Red line: shows the segmentation produced by the CAD system (“arbitrary” threshold) 16
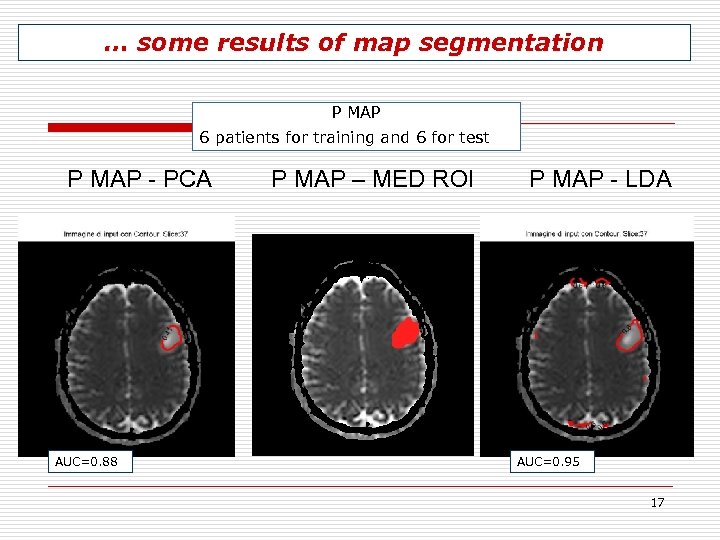 … some results of map segmentation P MAP 6 patients for training and 6 for test P MAP - PCA AUC=0. 88 P MAP – MED ROI P MAP - LDA AUC=0. 95 17
… some results of map segmentation P MAP 6 patients for training and 6 for test P MAP - PCA AUC=0. 88 P MAP – MED ROI P MAP - LDA AUC=0. 95 17
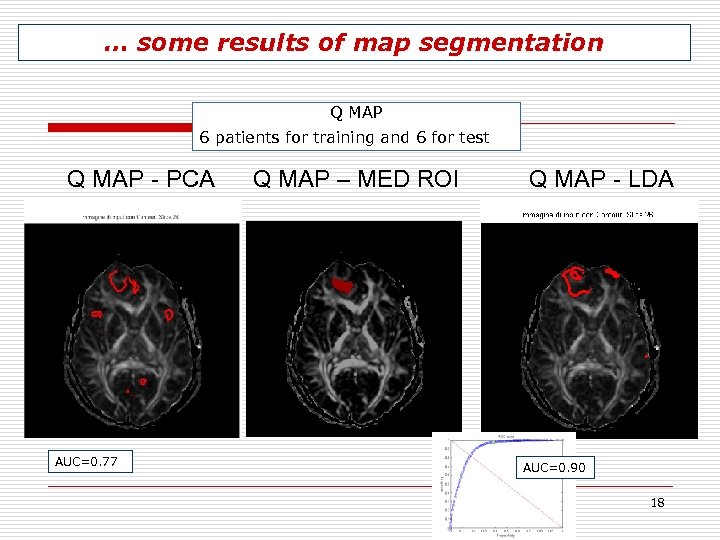 … some results of map segmentation Q MAP 6 patients for training and 6 for test Q MAP - PCA AUC=0. 77 Q MAP – MED ROI Q MAP - LDA AUC=0. 90 18
… some results of map segmentation Q MAP 6 patients for training and 6 for test Q MAP - PCA AUC=0. 77 Q MAP – MED ROI Q MAP - LDA AUC=0. 90 18
 … some results of map segmentation FLAIR 5 patients for training and 4 for test FLAIR - PCA AUC=0. 94 Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery FLAIR – MED ROI FLAIR - LDA AUC=0. 97 19
… some results of map segmentation FLAIR 5 patients for training and 4 for test FLAIR - PCA AUC=0. 94 Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery FLAIR – MED ROI FLAIR - LDA AUC=0. 97 19
 Prospects • Feature reduction or selection? PCA Fisher score LDA ICA • • Both selection and reduction? ? Fisher score (with a threshold according to the AUC plateau [as a function of the FS]) Jaccard Coefficient to set the ‘best’ ANN threshold for segmentation FLAIR segmentation is promising! 20
Prospects • Feature reduction or selection? PCA Fisher score LDA ICA • • Both selection and reduction? ? Fisher score (with a threshold according to the AUC plateau [as a function of the FS]) Jaccard Coefficient to set the ‘best’ ANN threshold for segmentation FLAIR segmentation is promising! 20
 Changes in glioma water diffusion values after chemotherapy: work in progress!! LGG (low-grade glioma) cells grow and diffuse typically along the white matter tracts Diffusion Tensor Imaging in glial tumors allows to depict white matter alterations not visible by conventional MRI Price et al. , Clin Radiol 2003; Wang et al. , AJNR 2009 Starting from Diffusion Tensor it is possible to obtain two maps: isotropic (p) and anisotropic (q) Pena et al. , BJR 2006; Price et al. , Eur Radiol 2004 Isotropic (p) and Anisotropic (q) Maps allow a better characterization of the diffusion features of tumoral and peritumoral areas Price et al. , AJNR 2006; Price et al. , Eur Radiol 2007; Wang et al. , AJNR 2009 21
Changes in glioma water diffusion values after chemotherapy: work in progress!! LGG (low-grade glioma) cells grow and diffuse typically along the white matter tracts Diffusion Tensor Imaging in glial tumors allows to depict white matter alterations not visible by conventional MRI Price et al. , Clin Radiol 2003; Wang et al. , AJNR 2009 Starting from Diffusion Tensor it is possible to obtain two maps: isotropic (p) and anisotropic (q) Pena et al. , BJR 2006; Price et al. , Eur Radiol 2004 Isotropic (p) and Anisotropic (q) Maps allow a better characterization of the diffusion features of tumoral and peritumoral areas Price et al. , AJNR 2006; Price et al. , Eur Radiol 2007; Wang et al. , AJNR 2009 21
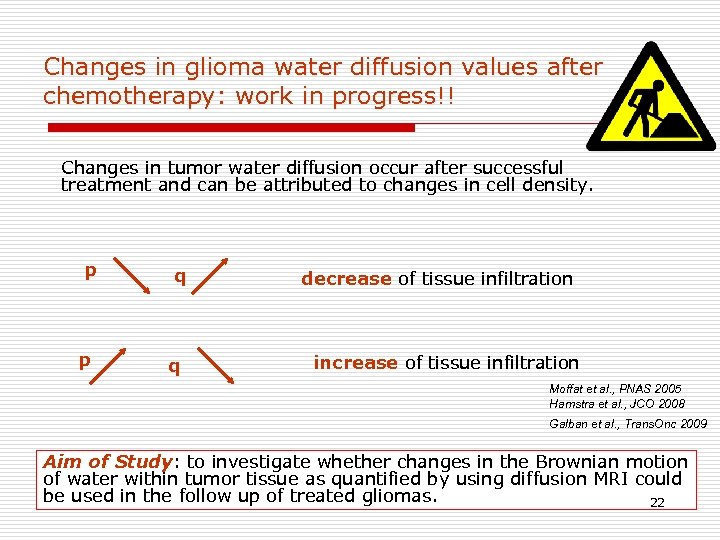 Changes in glioma water diffusion values after chemotherapy: work in progress!! Changes in tumor water diffusion occur after successful treatment and can be attributed to changes in cell density. p p q q decrease of tissue infiltration increase of tissue infiltration Moffat et al. , PNAS 2005 Hamstra et al. , JCO 2008 Galban et al. , Trans. Onc 2009 Aim of Study: to investigate whether changes in the Brownian motion of water within tumor tissue as quantified by using diffusion MRI could be used in the follow up of treated gliomas. 22
Changes in glioma water diffusion values after chemotherapy: work in progress!! Changes in tumor water diffusion occur after successful treatment and can be attributed to changes in cell density. p p q q decrease of tissue infiltration increase of tissue infiltration Moffat et al. , PNAS 2005 Hamstra et al. , JCO 2008 Galban et al. , Trans. Onc 2009 Aim of Study: to investigate whether changes in the Brownian motion of water within tumor tissue as quantified by using diffusion MRI could be used in the follow up of treated gliomas. 22
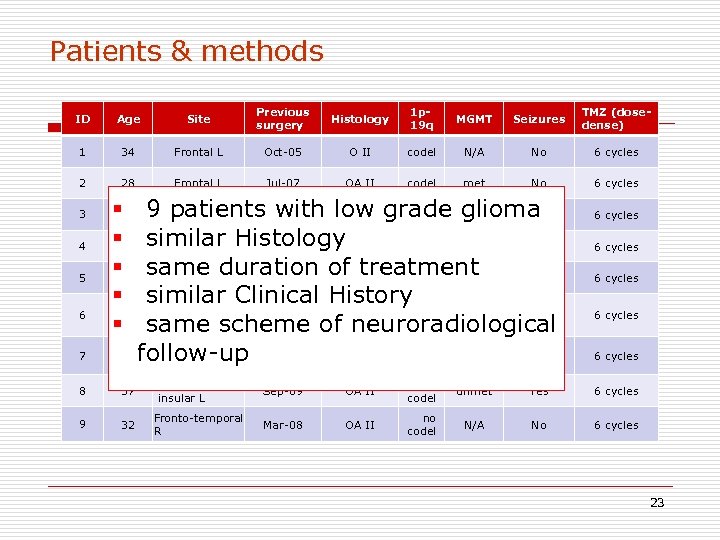 Patients & methods ID Age Site Previous surgery Histology 1 p 19 q MGMT Seizures TMZ (dosedense) 1 34 Frontal L Oct-05 O II codel N/A No 6 cycles 2 28 Frontal L Jul-07 OA II codel met No 6 cycles 3 4 5 6 7 Fronto-tempo. N/A § 33 9 patients with low grade glioma Jul-04 O II No insular R Fronto-tempono § 25 similar Histology O II codel N/A Sep-07 Yes insular L § 36 same duration of treatment no Frontal L Apr-07 A II met Yes codel § similar Clinical History. N/A Fronto-tempo 56 Jul-04 A II Yes insular L § same scheme of neuroradiological N/A 45 follow-up Nov-04 Frontal L O II Yes 6 cycles 6 cycles 8 37 Fronto-tempoinsular L Sep-09 OA II no codel unmet Yes 6 cycles 9 32 Fronto-temporal R Mar-08 OA II no codel N/A No 6 cycles 23
Patients & methods ID Age Site Previous surgery Histology 1 p 19 q MGMT Seizures TMZ (dosedense) 1 34 Frontal L Oct-05 O II codel N/A No 6 cycles 2 28 Frontal L Jul-07 OA II codel met No 6 cycles 3 4 5 6 7 Fronto-tempo. N/A § 33 9 patients with low grade glioma Jul-04 O II No insular R Fronto-tempono § 25 similar Histology O II codel N/A Sep-07 Yes insular L § 36 same duration of treatment no Frontal L Apr-07 A II met Yes codel § similar Clinical History. N/A Fronto-tempo 56 Jul-04 A II Yes insular L § same scheme of neuroradiological N/A 45 follow-up Nov-04 Frontal L O II Yes 6 cycles 6 cycles 8 37 Fronto-tempoinsular L Sep-09 OA II no codel unmet Yes 6 cycles 9 32 Fronto-temporal R Mar-08 OA II no codel N/A No 6 cycles 23
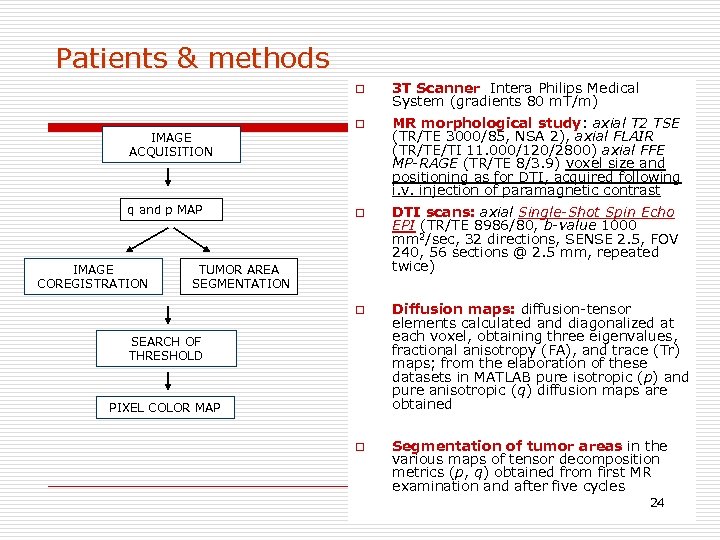 Patients & methods o q and p MAP IMAGE COREGISTRATION o MR morphological study: axial T 2 TSE (TR/TE 3000/85, NSA 2), axial FLAIR (TR/TE/TI 11. 000/120/2800) axial FFE MP-RAGE (TR/TE 8/3. 9) voxel size and positioning as for DTI, acquired following i. v. injection of paramagnetic contrast o DTI scans: axial Single-Shot Spin Echo EPI (TR/TE 8986/80, b-value 1000 mm 2/sec, 32 directions, SENSE 2. 5, FOV 240, 56 sections @ 2. 5 mm, repeated twice) o IMAGE ACQUISITION 3 T Scanner Intera Philips Medical System (gradients 80 m. T/m) Diffusion maps: diffusion-tensor elements calculated and diagonalized at each voxel, obtaining three eigenvalues, fractional anisotropy (FA), and trace (Tr) maps; from the elaboration of these datasets in MATLAB pure isotropic (p) and pure anisotropic (q) diffusion maps are obtained o Segmentation of tumor areas in the various maps of tensor decomposition metrics (p, q) obtained from first MR examination and after five cycles TUMOR AREA SEGMENTATION SEARCH OF THRESHOLD PIXEL COLOR MAP 24
Patients & methods o q and p MAP IMAGE COREGISTRATION o MR morphological study: axial T 2 TSE (TR/TE 3000/85, NSA 2), axial FLAIR (TR/TE/TI 11. 000/120/2800) axial FFE MP-RAGE (TR/TE 8/3. 9) voxel size and positioning as for DTI, acquired following i. v. injection of paramagnetic contrast o DTI scans: axial Single-Shot Spin Echo EPI (TR/TE 8986/80, b-value 1000 mm 2/sec, 32 directions, SENSE 2. 5, FOV 240, 56 sections @ 2. 5 mm, repeated twice) o IMAGE ACQUISITION 3 T Scanner Intera Philips Medical System (gradients 80 m. T/m) Diffusion maps: diffusion-tensor elements calculated and diagonalized at each voxel, obtaining three eigenvalues, fractional anisotropy (FA), and trace (Tr) maps; from the elaboration of these datasets in MATLAB pure isotropic (p) and pure anisotropic (q) diffusion maps are obtained o Segmentation of tumor areas in the various maps of tensor decomposition metrics (p, q) obtained from first MR examination and after five cycles TUMOR AREA SEGMENTATION SEARCH OF THRESHOLD PIXEL COLOR MAP 24
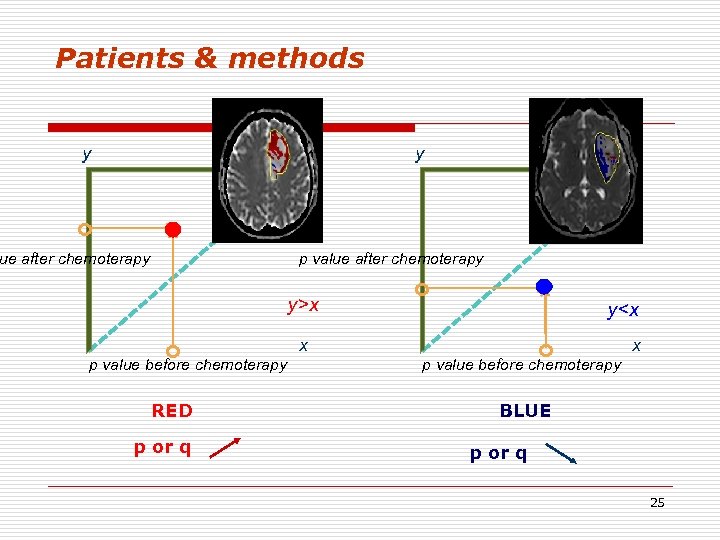 Patients & methods y y ue after chemoterapy p value after chemoterapy y>x p value before chemoterapy RED p or q y
Patients & methods y y ue after chemoterapy p value after chemoterapy y>x p value before chemoterapy RED p or q y
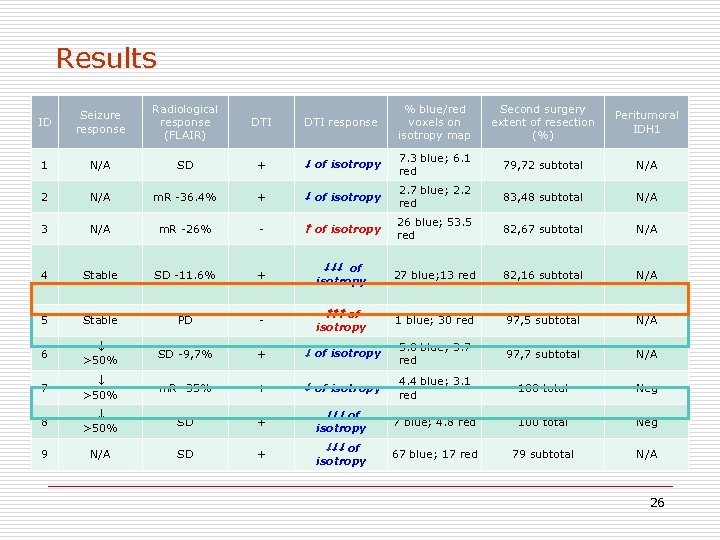 Results ID Seizure response Radiological response (FLAIR) DTI response % blue/red voxels on isotropy map Second surgery extent of resection (%) Peritumoral IDH 1 1 N/A SD + of isotropy 7. 3 blue; 6. 1 red 79, 72 subtotal N/A 2 N/A m. R -36. 4% + of isotropy 2. 7 blue; 2. 2 red 83, 48 subtotal N/A 3 N/A m. R -26% - of isotropy 26 blue; 53. 5 red 82, 67 subtotal N/A 4 Stable SD -11. 6% + 27 blue; 13 red 82, 16 subtotal N/A 5 Stable PD - of isotropy 1 blue; 30 red 97, 5 subtotal N/A 6 >50% SD -9, 7% + of isotropy 5. 8 blue; 3. 7 red 97, 7 subtotal N/A 7 >50% m. R -35% + of isotropy 4. 4 blue; 3. 1 red 100 total Neg 8 >50% SD + 7 blue; 4. 8 red 100 total Neg 9 N/A SD + 67 blue; 17 red 79 subtotal N/A of isotropy 26
Results ID Seizure response Radiological response (FLAIR) DTI response % blue/red voxels on isotropy map Second surgery extent of resection (%) Peritumoral IDH 1 1 N/A SD + of isotropy 7. 3 blue; 6. 1 red 79, 72 subtotal N/A 2 N/A m. R -36. 4% + of isotropy 2. 7 blue; 2. 2 red 83, 48 subtotal N/A 3 N/A m. R -26% - of isotropy 26 blue; 53. 5 red 82, 67 subtotal N/A 4 Stable SD -11. 6% + 27 blue; 13 red 82, 16 subtotal N/A 5 Stable PD - of isotropy 1 blue; 30 red 97, 5 subtotal N/A 6 >50% SD -9, 7% + of isotropy 5. 8 blue; 3. 7 red 97, 7 subtotal N/A 7 >50% m. R -35% + of isotropy 4. 4 blue; 3. 1 red 100 total Neg 8 >50% SD + 7 blue; 4. 8 red 100 total Neg 9 N/A SD + 67 blue; 17 red 79 subtotal N/A of isotropy 26
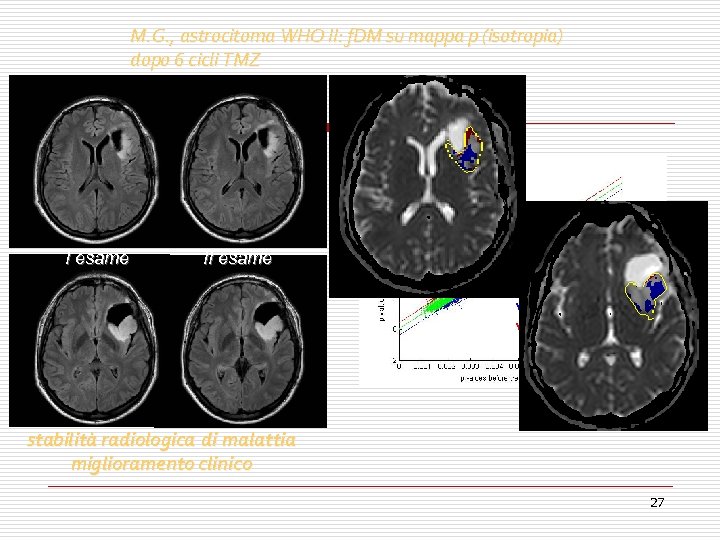 M. G. , astrocitoma WHO II: f. DM su mappa p (isotropia) dopo 6 cicli TMZ I esame II esame voxel blu: 7% voxel rossi: 4. 8% 4. 8 stabilità radiologica di malattia miglioramento clinico 27
M. G. , astrocitoma WHO II: f. DM su mappa p (isotropia) dopo 6 cicli TMZ I esame II esame voxel blu: 7% voxel rossi: 4. 8% 4. 8 stabilità radiologica di malattia miglioramento clinico 27
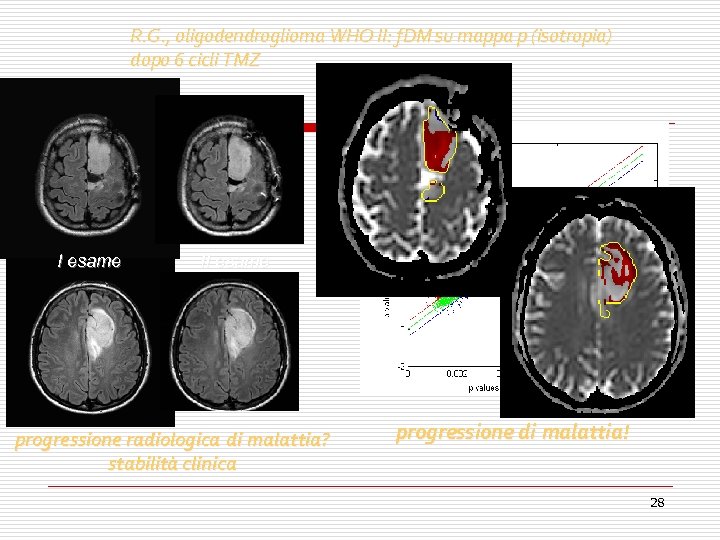 R. G. , oligodendroglioma WHO II: f. DM su mappa p (isotropia) dopo 6 cicli TMZ I esame II esame voxel blu: 1% voxel rossi: 30% 30 progressione radiologica di malattia? stabilità clinica progressione di malattia! 28
R. G. , oligodendroglioma WHO II: f. DM su mappa p (isotropia) dopo 6 cicli TMZ I esame II esame voxel blu: 1% voxel rossi: 30% 30 progressione radiologica di malattia? stabilità clinica progressione di malattia! 28
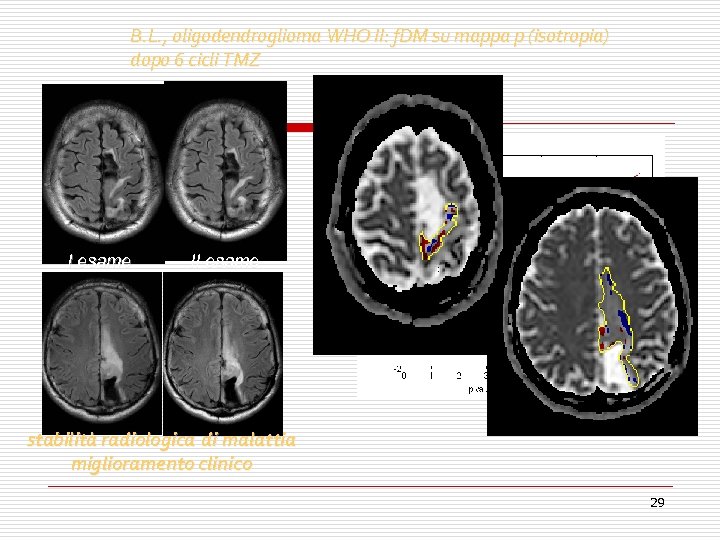 B. L. , oligodendroglioma WHO II: f. DM su mappa p (isotropia) dopo 6 cicli TMZ I esame II esame voxel blu: 7. 3% voxel rossi: 6. 1% 6. 1 stabilità radiologica di malattia miglioramento clinico 29
B. L. , oligodendroglioma WHO II: f. DM su mappa p (isotropia) dopo 6 cicli TMZ I esame II esame voxel blu: 7. 3% voxel rossi: 6. 1% 6. 1 stabilità radiologica di malattia miglioramento clinico 29
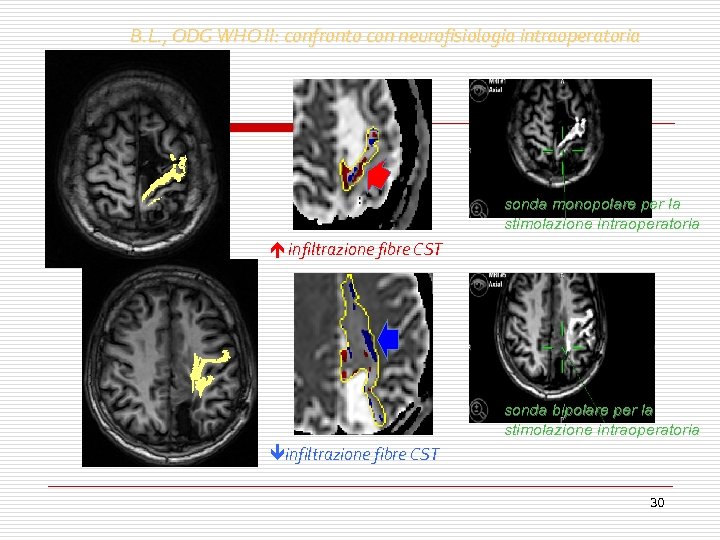 B. L. , ODG WHO II: confronto con neurofisiologia intraoperatoria sonda monopolare per la stimolazione intraoperatoria infiltrazione fibre CST sonda bipolare per la stimolazione intraoperatoria infiltrazione fibre CST 30
B. L. , ODG WHO II: confronto con neurofisiologia intraoperatoria sonda monopolare per la stimolazione intraoperatoria infiltrazione fibre CST sonda bipolare per la stimolazione intraoperatoria infiltrazione fibre CST 30
 Some conclusions: • Tissue analysis with DTI could help the physicians in evaluating the chemotherapy responses. • The p or q value variation could suggest a tumor progression or regression also for cases in which the tumor volume does not change. • These preliminary results are in accordance with neurophysiological results and with intraoperative bioptic samples. 31
Some conclusions: • Tissue analysis with DTI could help the physicians in evaluating the chemotherapy responses. • The p or q value variation could suggest a tumor progression or regression also for cases in which the tumor volume does not change. • These preliminary results are in accordance with neurophysiological results and with intraoperative bioptic samples. 31
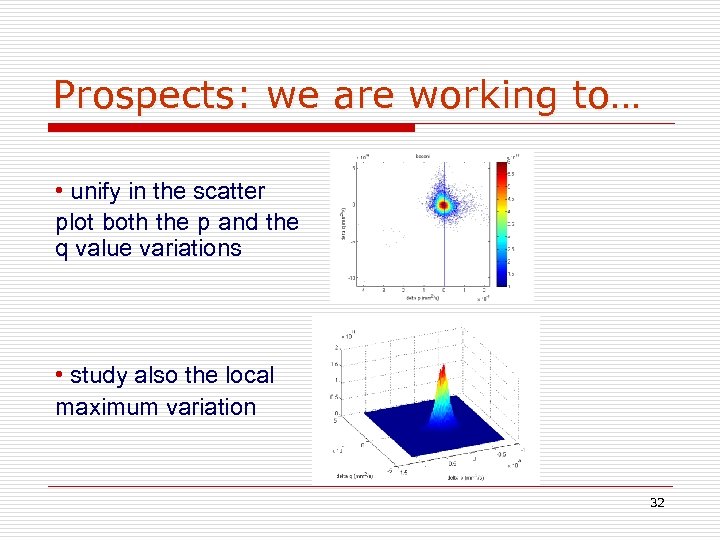 Prospects: we are working to… • unify in the scatter plot both the p and the q value variations • study also the local maximum variation 32
Prospects: we are working to… • unify in the scatter plot both the p and the q value variations • study also the local maximum variation 32
 Conferences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. A. CASTELLANO, M. DONATIVI, L. BELLO, G. DE NUNZIO, M. RIVA, G. PASTORE, G. CASACELI, R. RUDÀ, R. SOFFIETTI, AND A. FALINI(2011). Evaluation of changes in gliomas structural features after chemotherapy using DTI-based Functional Diffusion Maps (f. DMs): a preliminary study with intraoperative correlation. In: 2011 Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB. Montréal, May 7 -13, 2011 G. DE NUNZIO, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, A. CASTELLANO, A. FALINI, L. BELLO, R. SOFFIETTI, (2010). A CAD system for cerebral glioma and therapy follow-up in Diffusion-Tensor Images. In II Workshop Plasmi Sorgenti Biofisica e Applicazioni, Lecce (Italy) 26 Ottobre 2010 A. CASTELLANO, L. BELLO, E. FAVA, G. CASACELI, M. RIVA, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, G. DE NUNZIO, R. RUDA', L. BERTERO, R. SOFFIETTI, A. FALINI (2010) DTI-MR 3 D Texture Analysis per la valutazione delle modificazioni delle caratteristiche strutturali dei gliomi cerebrali dopo trattamento con Temodal: studio preliminare. In XV Congresso Nazionale della Associazione Italiana di Neuro-Oncologia (AINO), Fiuggi (FR, Italy) 3 -6 Ottobre 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, G. PASTORE, M. DONATIVI, A. FALINI, A. CASTELLANO, L. BELLO, R. SOFFIETTI (2010). DT-MR images: A CAD System for Cerebral Glioma and Therapy Follow-up. In IVth European Conference of Medical Physics - Advances in High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Udine (Italy) September 22 -25 (2010) G. DE NUNZIO, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, A. CASTELLANO, G. SCOTTI, L. BELLO, A. FALINI (2010). Automatic Segmentation and Therapy Follow-up of Cerebral Glioma in Diffusion-Tensor Images. In 2010 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and Applications (CIMSA 2010). Taranto (Italy) September 6 -8, 2010 CASTELLANO, L. BELLO, E. FAVA, M. RIVA, G. CASACELI, G. DE NUNZIO, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, R. RUDA', R. SOFFIETTI, A. FALINI (2010) Changes in gliomas structural features after Temodal treatment evaluated by DTI-MR texture analysis: a preliminary study. In 9 th International Meeting UPDATES IN NEURO-ONCOLOGY, Brain Tumor Symposium, Cortona (AR, Italy), July 2 -4, 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, G. PASTORE, M. DONATIVI, A. CASTELLANO, A. FALINI (2010). A CAD system for cerebral glioma based on texture features in DT-MR images. In International Conference on Imaging Techniques in Subatomic Physics, Astrophysics, Medicine and Biology (Imaging 2010), Stockholm (Sweden) 8 -11 June 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, A. CASTELLANO, G. PASTORE, M. DONATIVI, G. SCOTTI, L. BELLO, A. FALINI (2010). Semi-automated evaluation of structural characteristics and extension of cerebral gliomas using DTI-MR 3 D Texture Analysis. In: 2010 Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB. Stockholm, May 1 -7, 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, A. CASTELLANO, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, A. FALINI. (2010). A semi-automated DTI-based approach to evaluate structural characteristics and extension of cerebral gliomas (poster No C-2926). In: European Congress of Radiology (ECR 2010). Vienna, March 4 -8, 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, G. PASTORE, A. CASTELLANO, M. DONATIVI, A. FALINI (2010). Automatic Segmentation of Cerebral Glioma in DT-MR Images by 3 D Texture Analysis. In: Risonanza magnetica in medicina: dalla ricerca tecnologica avanzata alla pratica clinica (Italian Chapter of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine). Milano, 4 -5 febbraio 2010 33
Conferences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. A. CASTELLANO, M. DONATIVI, L. BELLO, G. DE NUNZIO, M. RIVA, G. PASTORE, G. CASACELI, R. RUDÀ, R. SOFFIETTI, AND A. FALINI(2011). Evaluation of changes in gliomas structural features after chemotherapy using DTI-based Functional Diffusion Maps (f. DMs): a preliminary study with intraoperative correlation. In: 2011 Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB. Montréal, May 7 -13, 2011 G. DE NUNZIO, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, A. CASTELLANO, A. FALINI, L. BELLO, R. SOFFIETTI, (2010). A CAD system for cerebral glioma and therapy follow-up in Diffusion-Tensor Images. In II Workshop Plasmi Sorgenti Biofisica e Applicazioni, Lecce (Italy) 26 Ottobre 2010 A. CASTELLANO, L. BELLO, E. FAVA, G. CASACELI, M. RIVA, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, G. DE NUNZIO, R. RUDA', L. BERTERO, R. SOFFIETTI, A. FALINI (2010) DTI-MR 3 D Texture Analysis per la valutazione delle modificazioni delle caratteristiche strutturali dei gliomi cerebrali dopo trattamento con Temodal: studio preliminare. In XV Congresso Nazionale della Associazione Italiana di Neuro-Oncologia (AINO), Fiuggi (FR, Italy) 3 -6 Ottobre 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, G. PASTORE, M. DONATIVI, A. FALINI, A. CASTELLANO, L. BELLO, R. SOFFIETTI (2010). DT-MR images: A CAD System for Cerebral Glioma and Therapy Follow-up. In IVth European Conference of Medical Physics - Advances in High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Udine (Italy) September 22 -25 (2010) G. DE NUNZIO, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, A. CASTELLANO, G. SCOTTI, L. BELLO, A. FALINI (2010). Automatic Segmentation and Therapy Follow-up of Cerebral Glioma in Diffusion-Tensor Images. In 2010 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and Applications (CIMSA 2010). Taranto (Italy) September 6 -8, 2010 CASTELLANO, L. BELLO, E. FAVA, M. RIVA, G. CASACELI, G. DE NUNZIO, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, R. RUDA', R. SOFFIETTI, A. FALINI (2010) Changes in gliomas structural features after Temodal treatment evaluated by DTI-MR texture analysis: a preliminary study. In 9 th International Meeting UPDATES IN NEURO-ONCOLOGY, Brain Tumor Symposium, Cortona (AR, Italy), July 2 -4, 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, G. PASTORE, M. DONATIVI, A. CASTELLANO, A. FALINI (2010). A CAD system for cerebral glioma based on texture features in DT-MR images. In International Conference on Imaging Techniques in Subatomic Physics, Astrophysics, Medicine and Biology (Imaging 2010), Stockholm (Sweden) 8 -11 June 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, A. CASTELLANO, G. PASTORE, M. DONATIVI, G. SCOTTI, L. BELLO, A. FALINI (2010). Semi-automated evaluation of structural characteristics and extension of cerebral gliomas using DTI-MR 3 D Texture Analysis. In: 2010 Joint Annual Meeting ISMRM-ESMRMB. Stockholm, May 1 -7, 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, A. CASTELLANO, M. DONATIVI, G. PASTORE, A. FALINI. (2010). A semi-automated DTI-based approach to evaluate structural characteristics and extension of cerebral gliomas (poster No C-2926). In: European Congress of Radiology (ECR 2010). Vienna, March 4 -8, 2010 G. DE NUNZIO, G. PASTORE, A. CASTELLANO, M. DONATIVI, A. FALINI (2010). Automatic Segmentation of Cerebral Glioma in DT-MR Images by 3 D Texture Analysis. In: Risonanza magnetica in medicina: dalla ricerca tecnologica avanzata alla pratica clinica (Italian Chapter of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine). Milano, 4 -5 febbraio 2010 33
 34
34
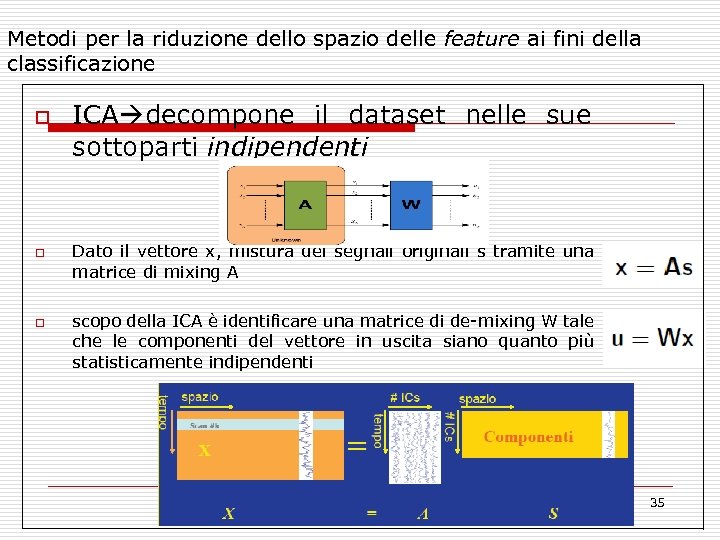 Metodi per la riduzione dello spazio delle feature ai fini della classificazione o o o ICA decompone il dataset nelle sue sottoparti indipendenti Dato il vettore x, mistura dei segnali originali s tramite una matrice di mixing A scopo della ICA è identificare una matrice di de-mixing W tale che le componenti del vettore in uscita siano quanto più statisticamente indipendenti 35
Metodi per la riduzione dello spazio delle feature ai fini della classificazione o o o ICA decompone il dataset nelle sue sottoparti indipendenti Dato il vettore x, mistura dei segnali originali s tramite una matrice di mixing A scopo della ICA è identificare una matrice di de-mixing W tale che le componenti del vettore in uscita siano quanto più statisticamente indipendenti 35
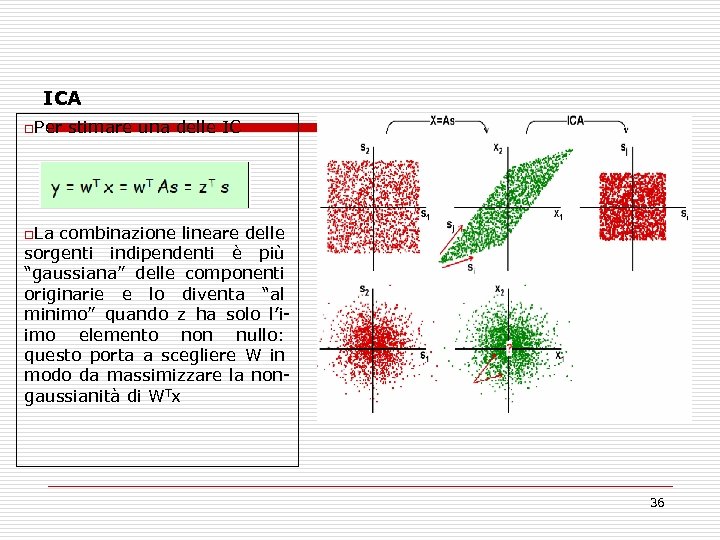 ICA o. Per stimare una delle IC o. La combinazione lineare delle sorgenti indipendenti è più “gaussiana” delle componenti originarie e lo diventa “al minimo” quando z ha solo l’iimo elemento non nullo: questo porta a scegliere W in modo da massimizzare la nongaussianità di WTx 36
ICA o. Per stimare una delle IC o. La combinazione lineare delle sorgenti indipendenti è più “gaussiana” delle componenti originarie e lo diventa “al minimo” quando z ha solo l’iimo elemento non nullo: questo porta a scegliere W in modo da massimizzare la nongaussianità di WTx 36
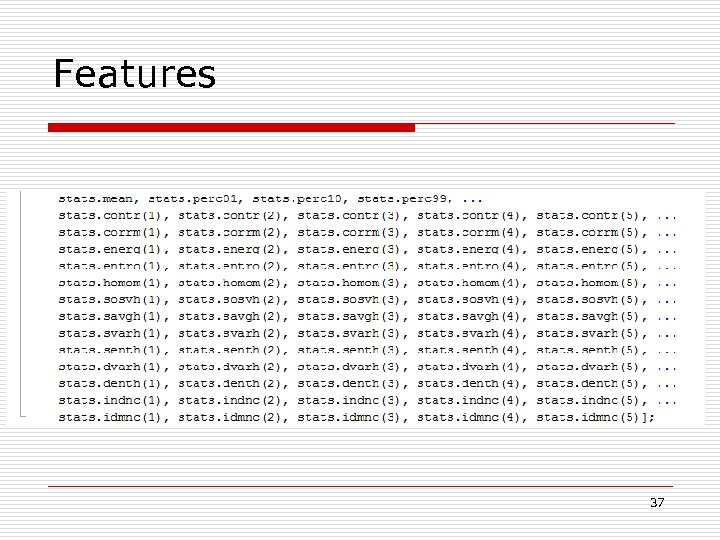 Features 37
Features 37
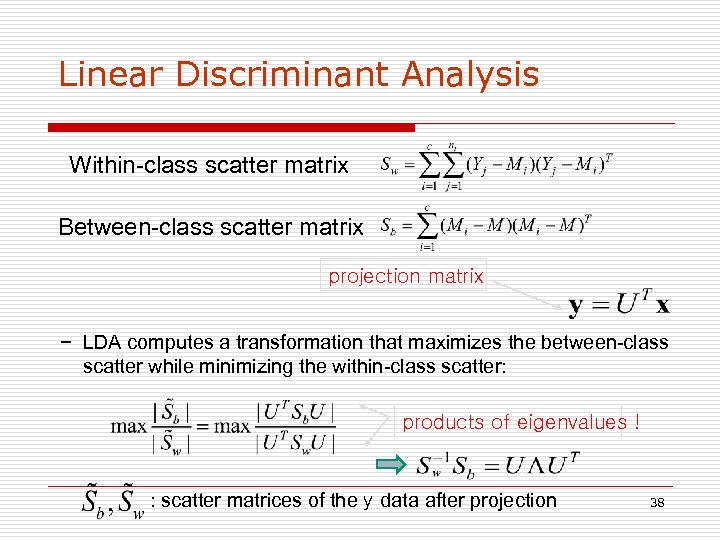 Linear Discriminant Analysis Within-class scatter matrix Between-class scatter matrix projection matrix − LDA computes a transformation that maximizes the between-class scatter while minimizing the within-class scatter: products of eigenvalues ! : scatter matrices of the y data after projection 38
Linear Discriminant Analysis Within-class scatter matrix Between-class scatter matrix projection matrix − LDA computes a transformation that maximizes the between-class scatter while minimizing the within-class scatter: products of eigenvalues ! : scatter matrices of the y data after projection 38
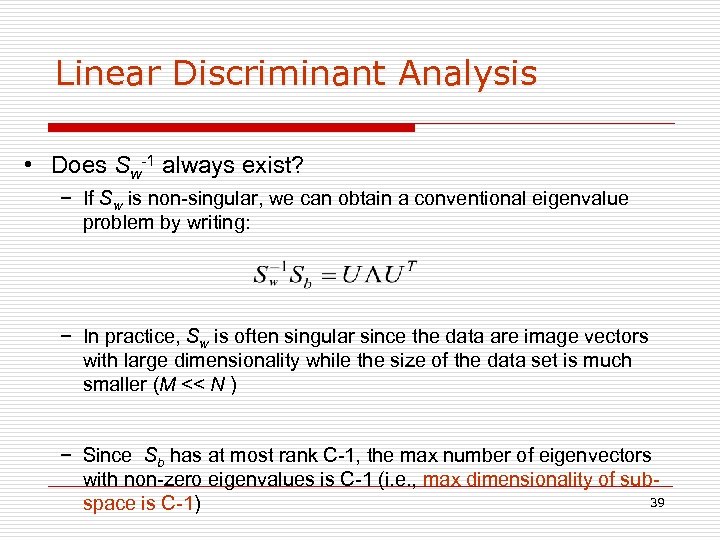 Linear Discriminant Analysis • Does Sw-1 always exist? − If Sw is non-singular, we can obtain a conventional eigenvalue problem by writing: − In practice, Sw is often singular since the data are image vectors with large dimensionality while the size of the data set is much smaller (M << N ) − Since Sb has at most rank C-1, the max number of eigenvectors with non-zero eigenvalues is C-1 (i. e. , max dimensionality of sub 39 space is C-1)
Linear Discriminant Analysis • Does Sw-1 always exist? − If Sw is non-singular, we can obtain a conventional eigenvalue problem by writing: − In practice, Sw is often singular since the data are image vectors with large dimensionality while the size of the data set is much smaller (M << N ) − Since Sb has at most rank C-1, the max number of eigenvectors with non-zero eigenvalues is C-1 (i. e. , max dimensionality of sub 39 space is C-1)
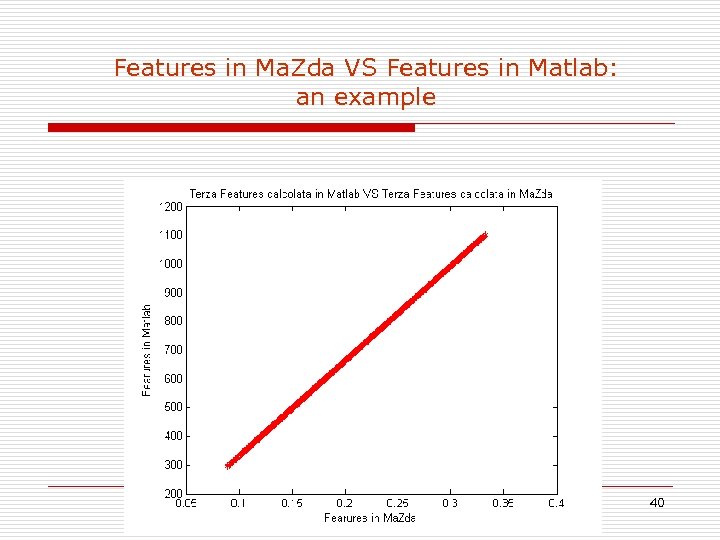 Features in Ma. Zda VS Features in Matlab: an example 40
Features in Ma. Zda VS Features in Matlab: an example 40


