79a2803a997e684f5978eade6491c519.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 MACROECONOMICS I UPF LECTURE SLIDES SET 4 Professor Antonio Ciccone UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 1
MACROECONOMICS I UPF LECTURE SLIDES SET 4 Professor Antonio Ciccone UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 1
 3. Applications of the Ramsey. Cass-Koopmans (RCK) model 3. 1 Government spending, consumption, and interest rates 3. 2 Bond versus tax financed government spending UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 2
3. Applications of the Ramsey. Cass-Koopmans (RCK) model 3. 1 Government spending, consumption, and interest rates 3. 2 Bond versus tax financed government spending UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 2
 3. 1 Government spending, consumption, and interest rates - Comparative “dynamics” in the RCK model - Permanent, surprise drop in output - Temporary, surprise drop in output - Wars, government expenditures and interest rates - The role of expectations - Permanent, anticipated drop in output - Temporary, anticipated drop in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 3
3. 1 Government spending, consumption, and interest rates - Comparative “dynamics” in the RCK model - Permanent, surprise drop in output - Temporary, surprise drop in output - Wars, government expenditures and interest rates - The role of expectations - Permanent, anticipated drop in output - Temporary, anticipated drop in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 3
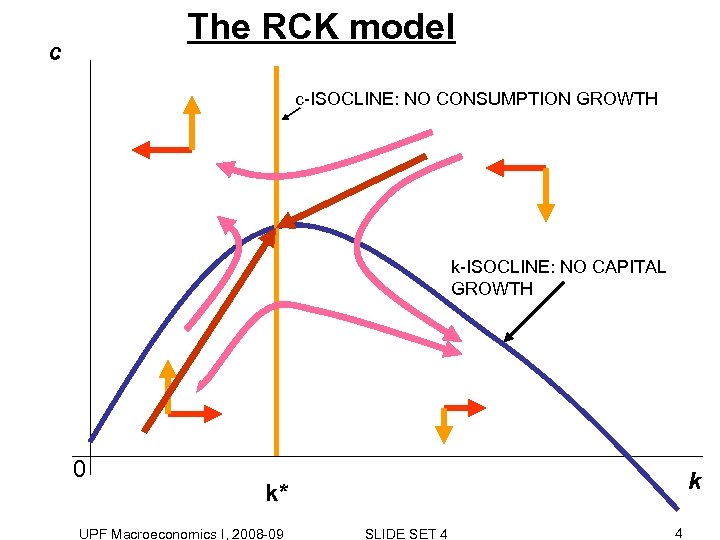 The RCK model c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 4
The RCK model c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 4
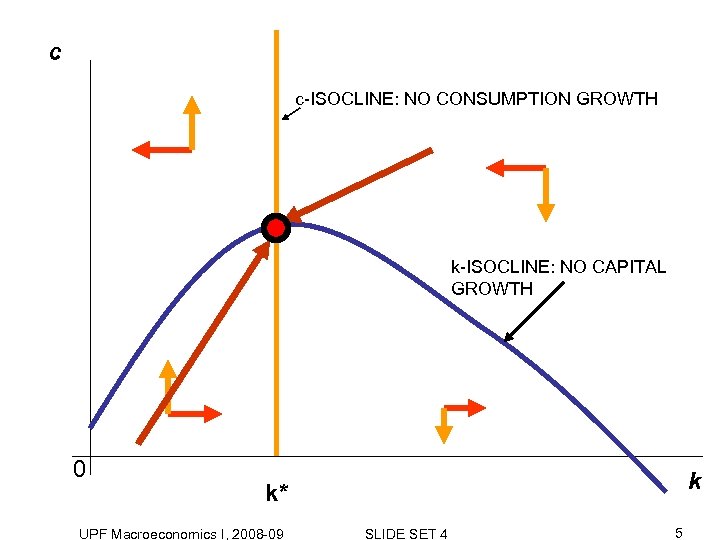 c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 5
c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 5
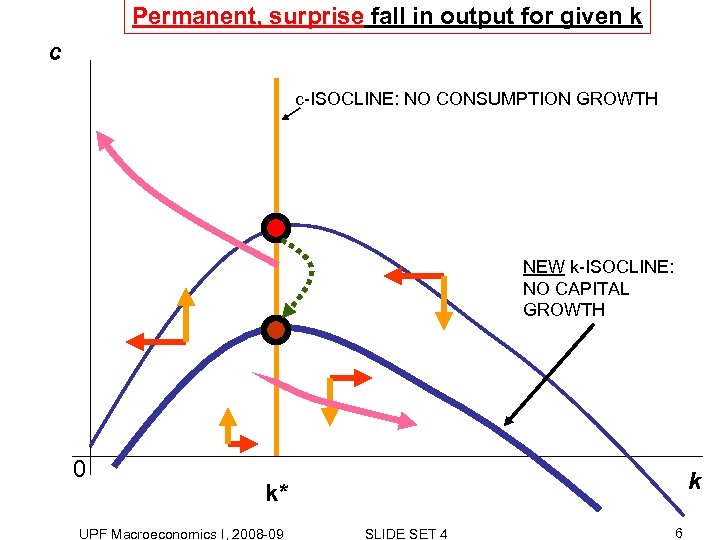 Permanent, surprise fall in output for given k c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 6
Permanent, surprise fall in output for given k c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 6
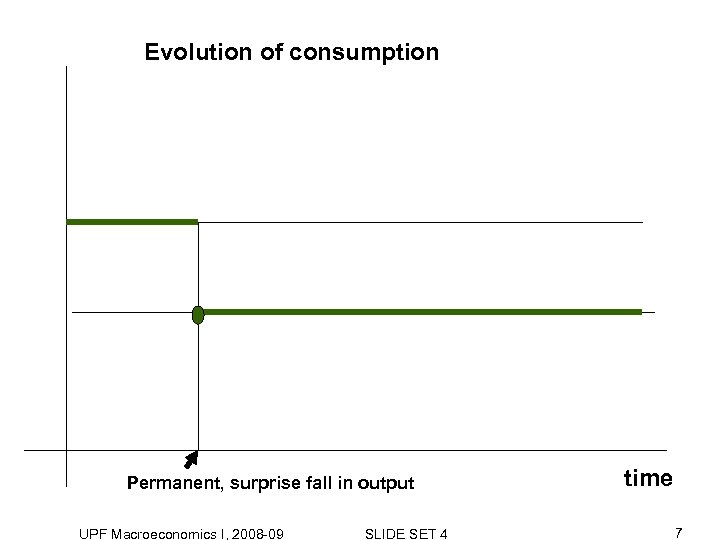 Evolution of consumption Permanent, surprise fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 time 7
Evolution of consumption Permanent, surprise fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 time 7
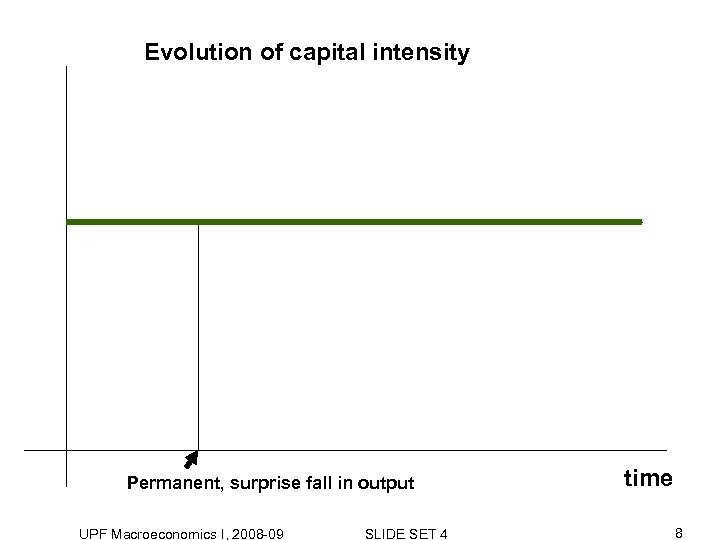 Evolution of capital intensity Permanent, surprise fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 time 8
Evolution of capital intensity Permanent, surprise fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 time 8
 -- consumption can JUMP at the time new information arrives -- but consumption must be smooth (follow the first-order condition) from than onward: There CANNOT BE an ANTICIPATED jump in consumption UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 9
-- consumption can JUMP at the time new information arrives -- but consumption must be smooth (follow the first-order condition) from than onward: There CANNOT BE an ANTICIPATED jump in consumption UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 9
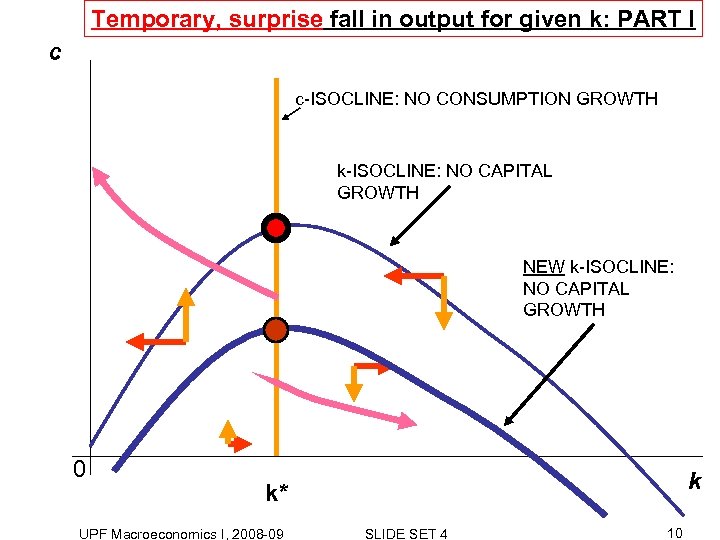 Temporary, surprise fall in output for given k: PART I c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 10
Temporary, surprise fall in output for given k: PART I c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 10
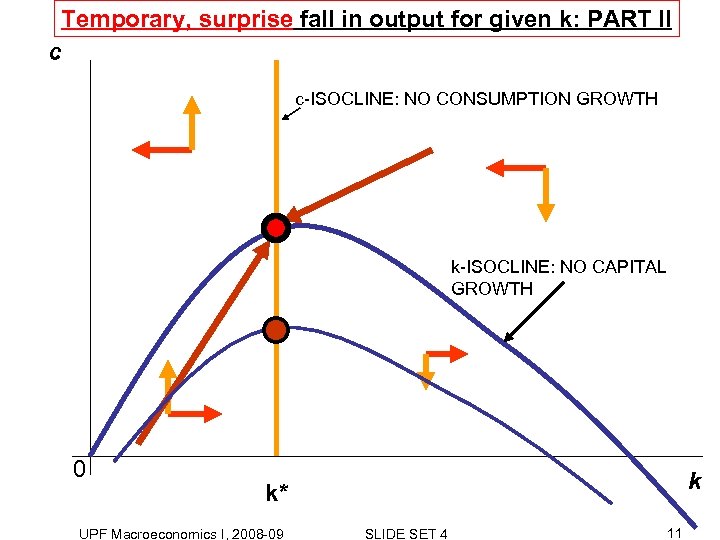 Temporary, surprise fall in output for given k: PART II c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 11
Temporary, surprise fall in output for given k: PART II c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 11
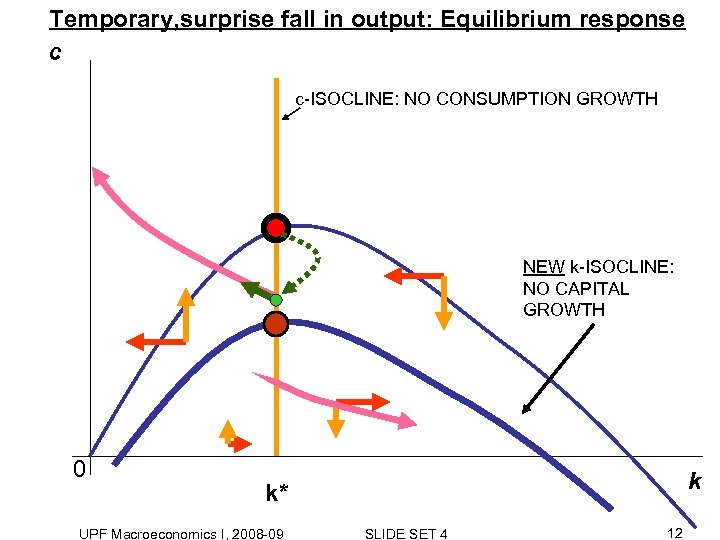 Temporary, surprise fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 12
Temporary, surprise fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 12
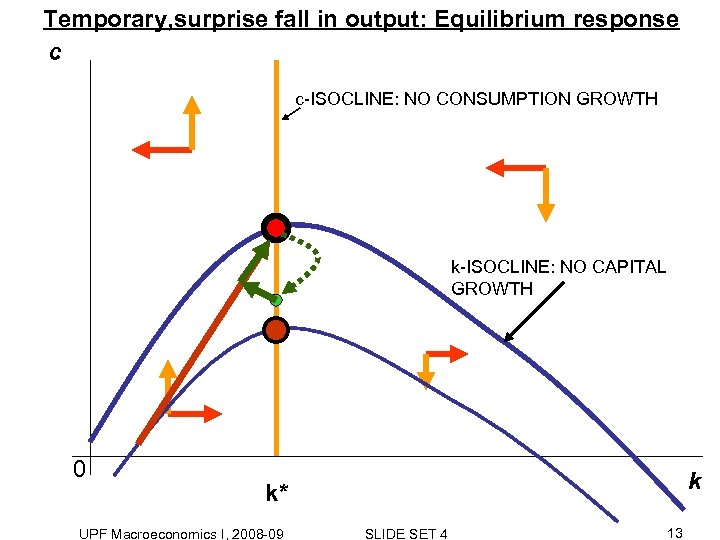 Temporary, surprise fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 13
Temporary, surprise fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 13
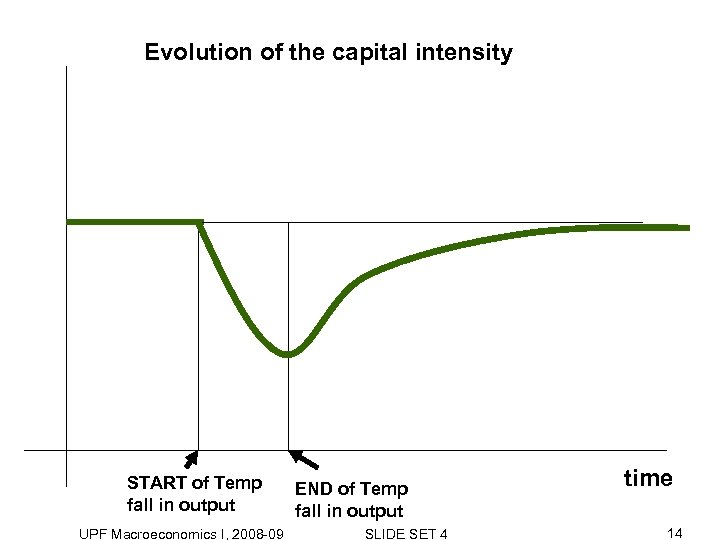 Evolution of the capital intensity START of Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 END of Temp fall in output SLIDE SET 4 time 14
Evolution of the capital intensity START of Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 END of Temp fall in output SLIDE SET 4 time 14
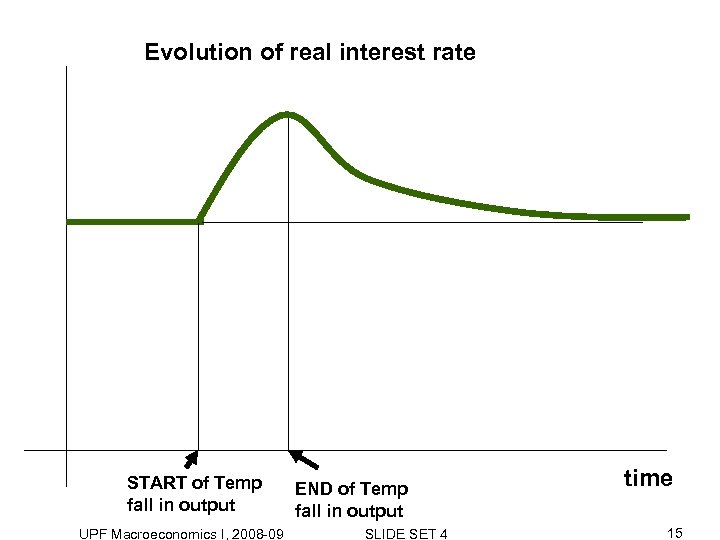 Evolution of real interest rate START of Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 END of Temp fall in output SLIDE SET 4 time 15
Evolution of real interest rate START of Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 END of Temp fall in output SLIDE SET 4 time 15
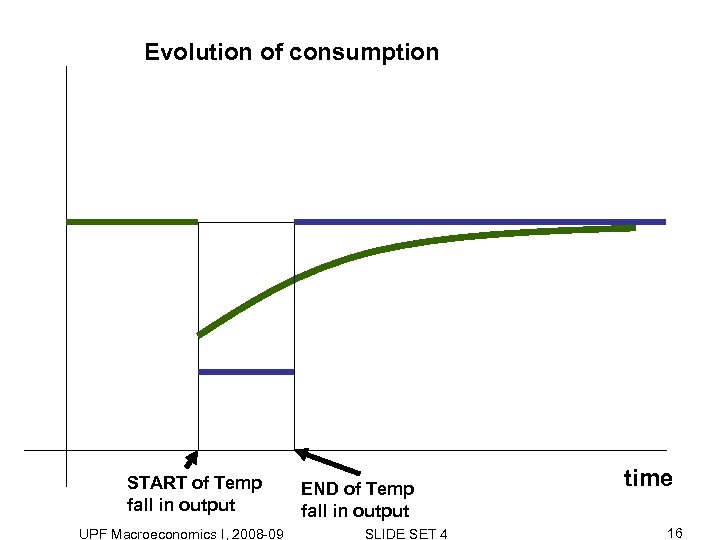 Evolution of consumption START of Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 END of Temp fall in output SLIDE SET 4 time 16
Evolution of consumption START of Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 END of Temp fall in output SLIDE SET 4 time 16
 Wars and real interest rates -- Suppose government expenditures associated with wars are surprise, temporary events -- Study the dynamic response of: capital, interest rates, and consumption to wars -- Government expenditures associated with wars decrease output available for consumption and investment INCREASE G Same effect as temporary fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 17
Wars and real interest rates -- Suppose government expenditures associated with wars are surprise, temporary events -- Study the dynamic response of: capital, interest rates, and consumption to wars -- Government expenditures associated with wars decrease output available for consumption and investment INCREASE G Same effect as temporary fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 17
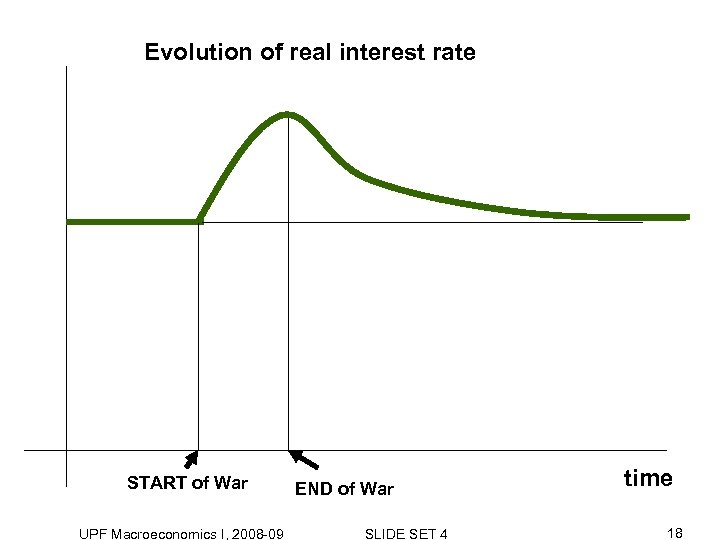 Evolution of real interest rate START of War UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 END of War SLIDE SET 4 time 18
Evolution of real interest rate START of War UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 END of War SLIDE SET 4 time 18
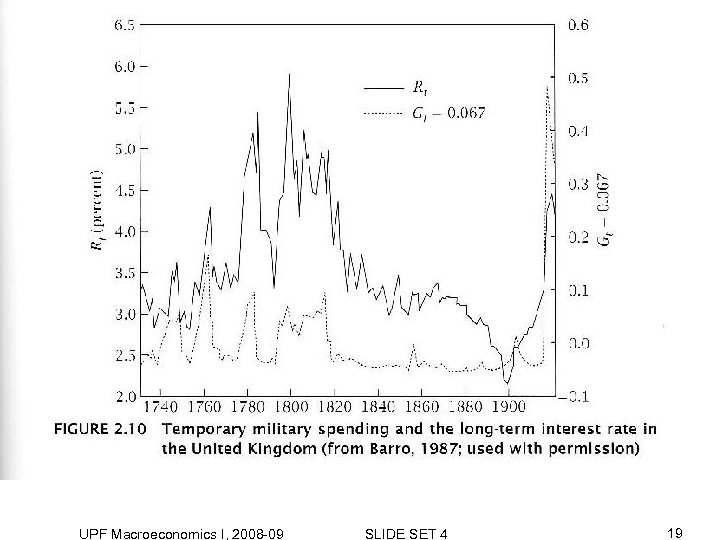 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 19
UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 19
 - The role of expectations - Permanent, anticipated drop in output - Temporary, anticipated drop in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 20
- The role of expectations - Permanent, anticipated drop in output - Temporary, anticipated drop in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 20
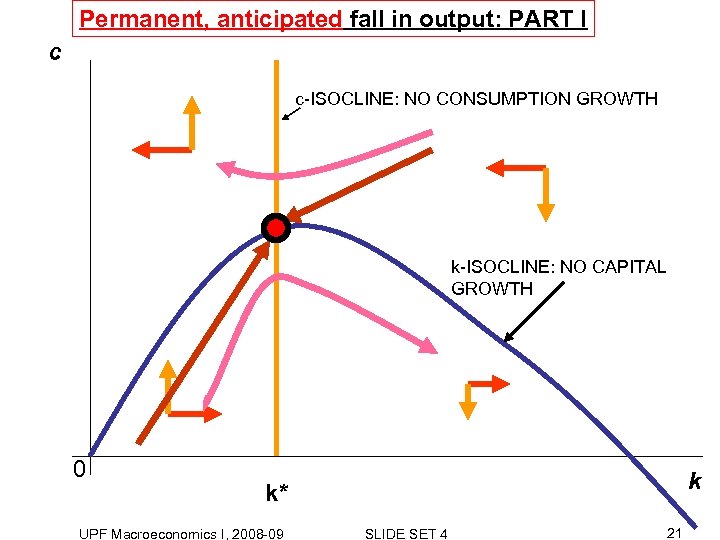 Permanent, anticipated fall in output: PART I c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 21
Permanent, anticipated fall in output: PART I c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 21
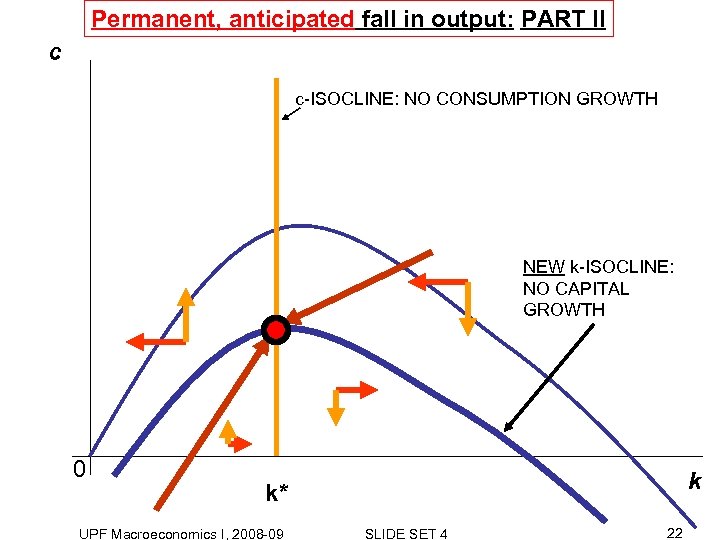 Permanent, anticipated fall in output: PART II c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 22
Permanent, anticipated fall in output: PART II c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 22
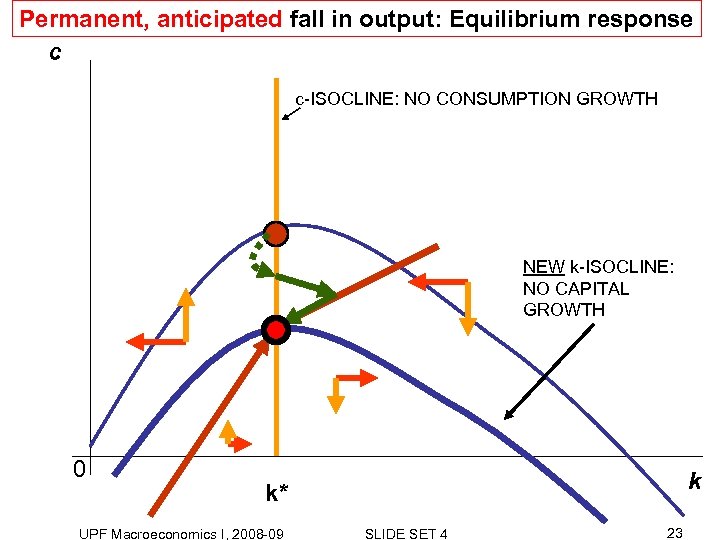 Permanent, anticipated fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 23
Permanent, anticipated fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 23
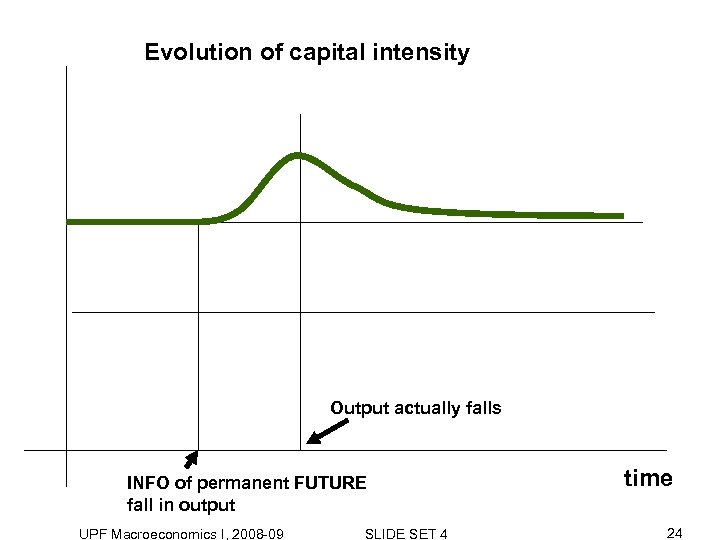 Evolution of capital intensity Output actually falls INFO of permanent FUTURE fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 time 24
Evolution of capital intensity Output actually falls INFO of permanent FUTURE fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 time 24
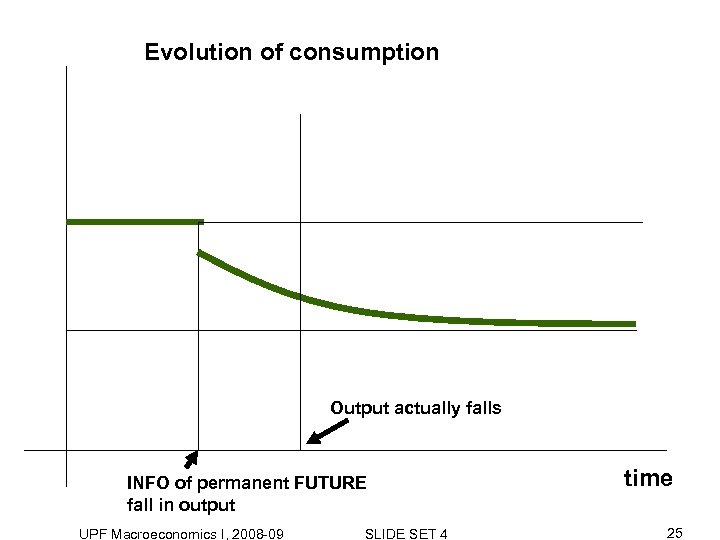 Evolution of consumption Output actually falls INFO of permanent FUTURE fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 time 25
Evolution of consumption Output actually falls INFO of permanent FUTURE fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 time 25
 - The role of expectations - Permanent, anticipated drop in output - Temporary, UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 anticipated drop in output SLIDE SET 4 26
- The role of expectations - Permanent, anticipated drop in output - Temporary, UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 anticipated drop in output SLIDE SET 4 26
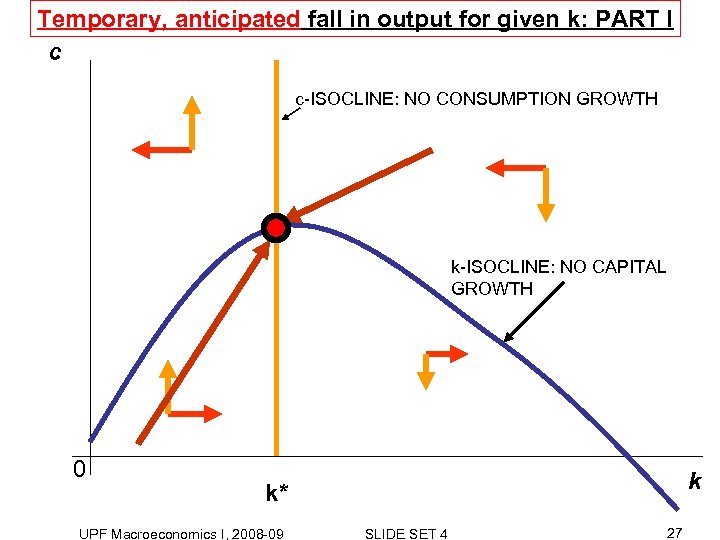 Temporary, anticipated fall in output for given k: PART I c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 27
Temporary, anticipated fall in output for given k: PART I c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 27
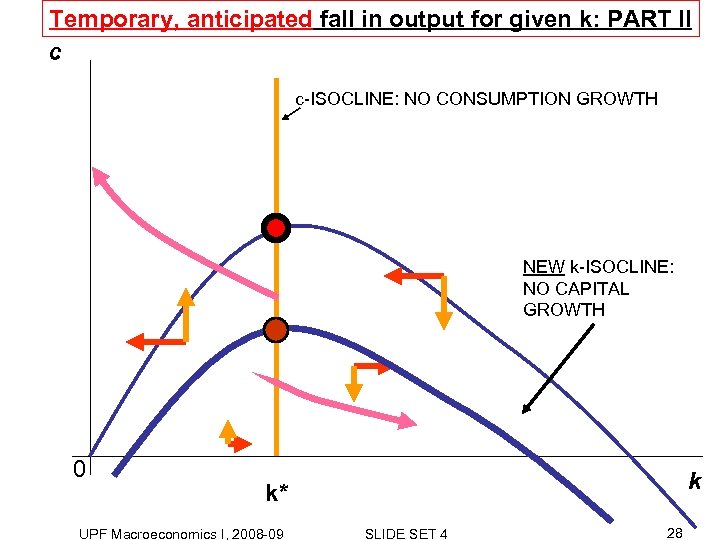 Temporary, anticipated fall in output for given k: PART II c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 28
Temporary, anticipated fall in output for given k: PART II c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH NEW k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 28
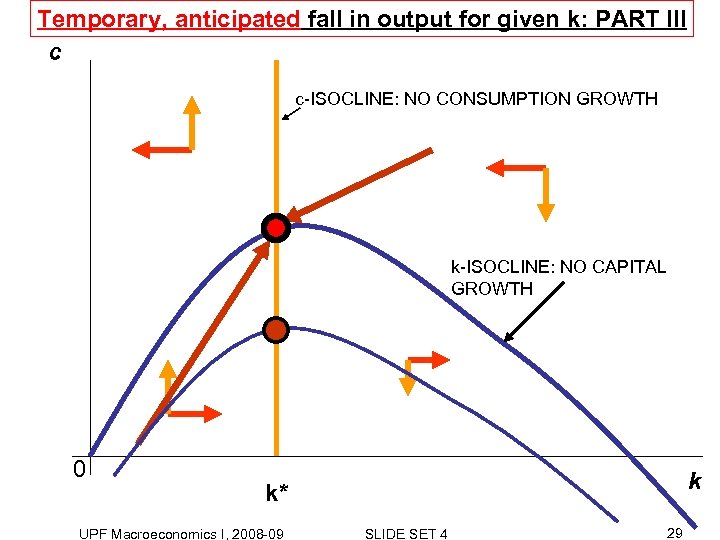 Temporary, anticipated fall in output for given k: PART III c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 29
Temporary, anticipated fall in output for given k: PART III c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 29
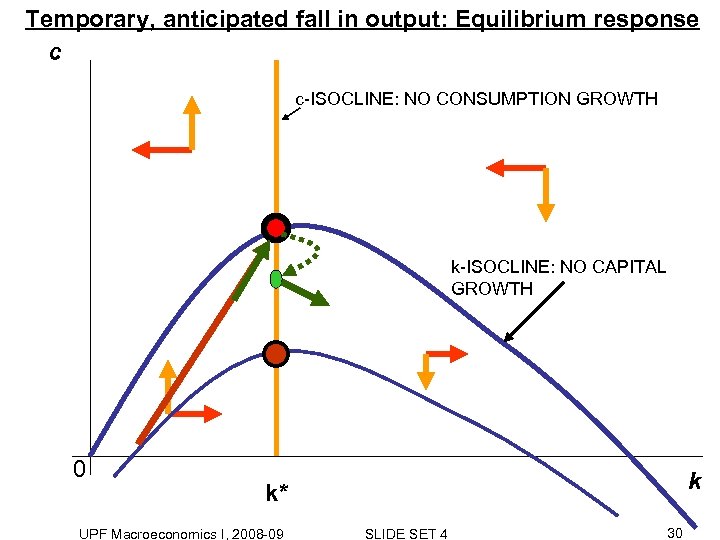 Temporary, anticipated fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 30
Temporary, anticipated fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 30
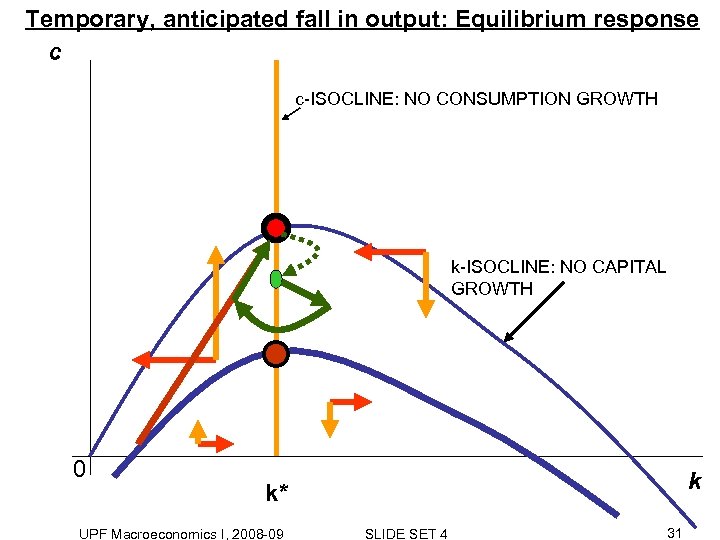 Temporary, anticipated fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 31
Temporary, anticipated fall in output: Equilibrium response c c-ISOCLINE: NO CONSUMPTION GROWTH k-ISOCLINE: NO CAPITAL GROWTH 0 k k* UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 31
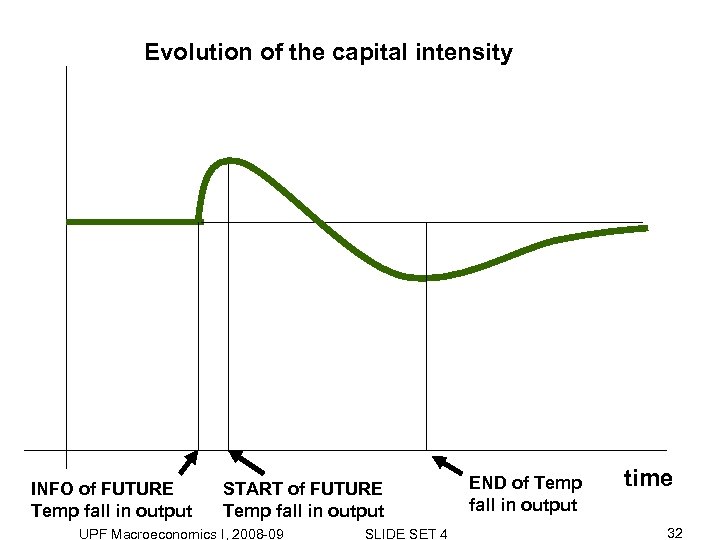 Evolution of the capital intensity INFO of FUTURE Temp fall in output START of FUTURE Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 END of Temp fall in output time 32
Evolution of the capital intensity INFO of FUTURE Temp fall in output START of FUTURE Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 END of Temp fall in output time 32
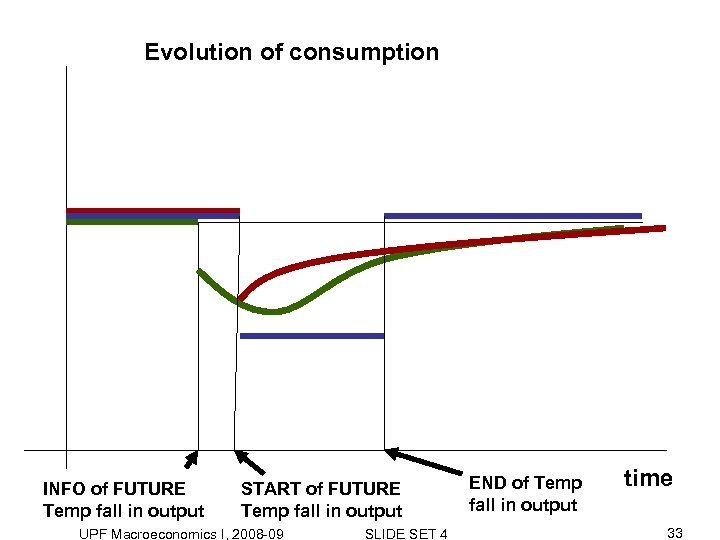 Evolution of consumption INFO of FUTURE Temp fall in output START of FUTURE Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 END of Temp fall in output time 33
Evolution of consumption INFO of FUTURE Temp fall in output START of FUTURE Temp fall in output UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 END of Temp fall in output time 33
 3. Application of the Ramsey. Cass-Koopmans (RCK) model 3. 1 Government spending, consumption, and interest rates 3. 2 Bond versus tax financed government spending UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 34
3. Application of the Ramsey. Cass-Koopmans (RCK) model 3. 1 Government spending, consumption, and interest rates 3. 2 Bond versus tax financed government spending UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 34
 Government expenditures and taxes Government intertemporal budget constraint UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 35
Government expenditures and taxes Government intertemporal budget constraint UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 35
 -- Suppose that households believe in government budget constraint -- The government cut taxes at time t -- But there is no indication that the government cuts expenditures -- WHAT HAPPENS TO DISCOUNTED FLOW OF TAXES? UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 36
-- Suppose that households believe in government budget constraint -- The government cut taxes at time t -- But there is no indication that the government cuts expenditures -- WHAT HAPPENS TO DISCOUNTED FLOW OF TAXES? UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 36
 Nothing, because: and the right-hand side of this equation has not changed. Government will have to compensate current tax cut by tax increase sometime in the future. UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 37
Nothing, because: and the right-hand side of this equation has not changed. Government will have to compensate current tax cut by tax increase sometime in the future. UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 37
 Now let’s look at household intertemporal budget constraint: -- current tax cut does NOT affect this constraint at all as only the DISCOUNTERD PRESENT VALUE OF TAXES MATTERS -- and present value of taxes remains constant if expenditures do not change UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 38
Now let’s look at household intertemporal budget constraint: -- current tax cut does NOT affect this constraint at all as only the DISCOUNTERD PRESENT VALUE OF TAXES MATTERS -- and present value of taxes remains constant if expenditures do not change UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 38
 -- TAX CUT DOES NOT CHANGE HH CONSUMPTION -- AS A RESULT IT DOES NOT CHANGE THE NATIONAL SAVINGS RATE: -- DOES NOT AFFECT: - INVESTMENT(!) - AND INTEREST RATES (!) -- HH SAVINGS INCREASES, BUT IS OFFSET BY AN INCREASE IN GOVERNMENT DEFICIT: UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 39
-- TAX CUT DOES NOT CHANGE HH CONSUMPTION -- AS A RESULT IT DOES NOT CHANGE THE NATIONAL SAVINGS RATE: -- DOES NOT AFFECT: - INVESTMENT(!) - AND INTEREST RATES (!) -- HH SAVINGS INCREASES, BUT IS OFFSET BY AN INCREASE IN GOVERNMENT DEFICIT: UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 39
 Hence, government cuts taxes Has to issue debt (government bonds) Government ensures that real interest rate on bond mimics market interest rate (before issue of new bonds) Households buy these new bonds with their tax savings Hence, Household use to buy government bonds what they “save” in current taxes UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 40
Hence, government cuts taxes Has to issue debt (government bonds) Government ensures that real interest rate on bond mimics market interest rate (before issue of new bonds) Households buy these new bonds with their tax savings Hence, Household use to buy government bonds what they “save” in current taxes UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 40
 3. The Diamond model 1. 2. 3. 3. 4. 1. 2. Overlapping generations models Setup of the Diamond model Technology Household behavior Dynamic equilibrium system Equilibrium growth and optimality Applications of the Diamond model Government spending, consumption, and interest rates Bond versus tax financed government spending UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 41
3. The Diamond model 1. 2. 3. 3. 4. 1. 2. Overlapping generations models Setup of the Diamond model Technology Household behavior Dynamic equilibrium system Equilibrium growth and optimality Applications of the Diamond model Government spending, consumption, and interest rates Bond versus tax financed government spending UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 41
 1. Overlapping Generations models -- Discrete time model -- Households live for two periods, and only work in the first UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 42
1. Overlapping Generations models -- Discrete time model -- Households live for two periods, and only work in the first UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 42
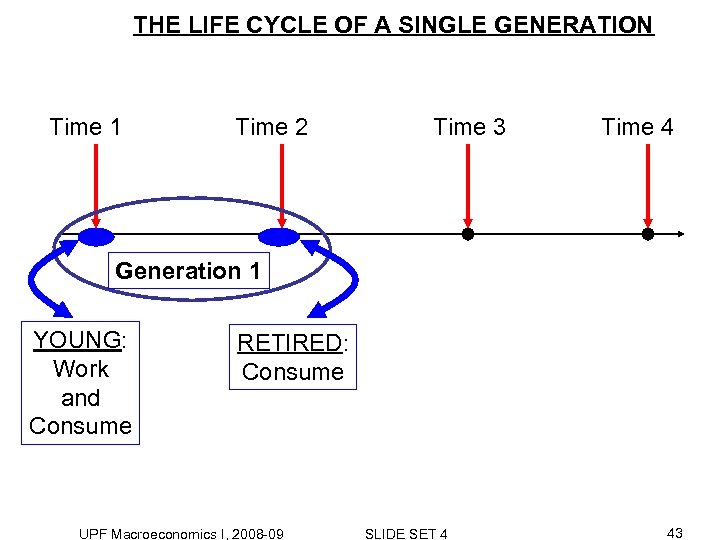 THE LIFE CYCLE OF A SINGLE GENERATION Time 1 Time 2 Time 3 Time 4 Generation 1 YOUNG: Work and Consume RETIRED: Consume UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 43
THE LIFE CYCLE OF A SINGLE GENERATION Time 1 Time 2 Time 3 Time 4 Generation 1 YOUNG: Work and Consume RETIRED: Consume UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 43
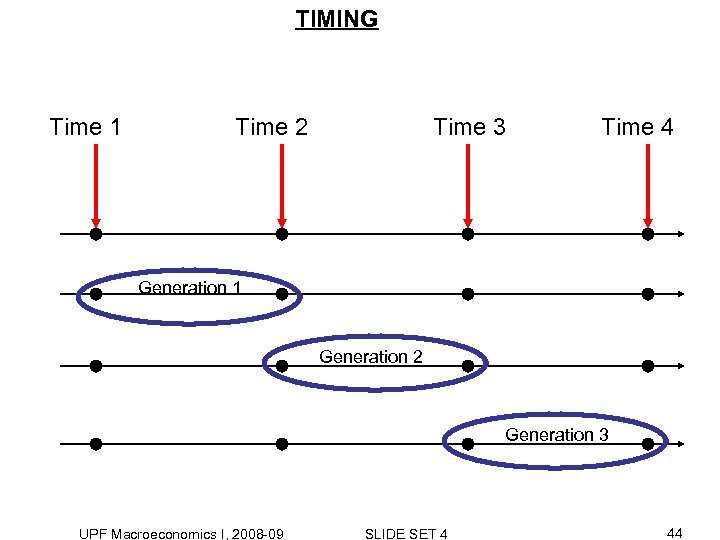 TIMING Time 1 Time 2 Time 3 Time 4 Generation 1 Generation 2 Generation 3 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 44
TIMING Time 1 Time 2 Time 3 Time 4 Generation 1 Generation 2 Generation 3 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 44
 2. Setup of the Diamond model 1. 2. 3. Technology Household behavior Dynamic equilibrium system UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 45
2. Setup of the Diamond model 1. 2. 3. Technology Household behavior Dynamic equilibrium system UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 45
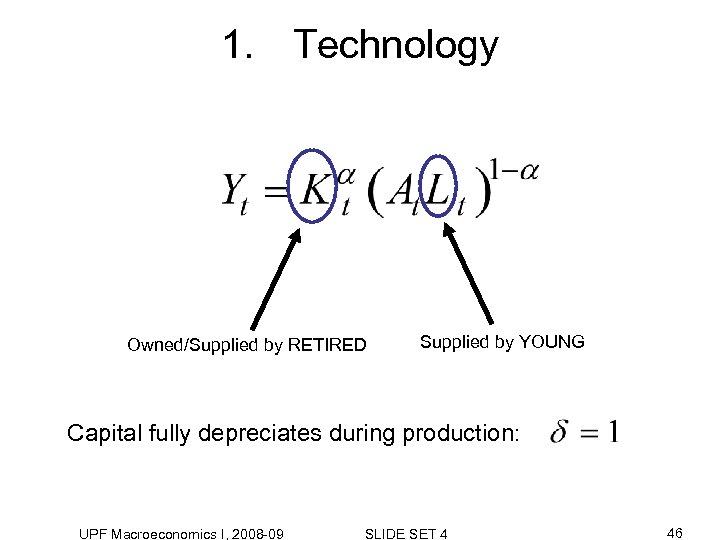 1. Technology Owned/Supplied by RETIRED Supplied by YOUNG Capital fully depreciates during production: UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 46
1. Technology Owned/Supplied by RETIRED Supplied by YOUNG Capital fully depreciates during production: UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 46
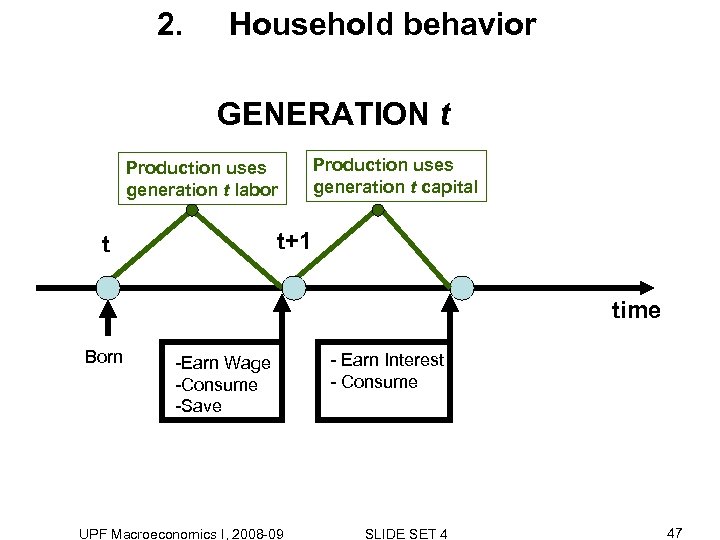 2. Household behavior GENERATION t Production uses generation t labor Production uses generation t capital t+1 t time Born -Earn Wage -Consume -Save UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 - Earn Interest - Consume SLIDE SET 4 47
2. Household behavior GENERATION t Production uses generation t labor Production uses generation t capital t+1 t time Born -Earn Wage -Consume -Save UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 - Earn Interest - Consume SLIDE SET 4 47
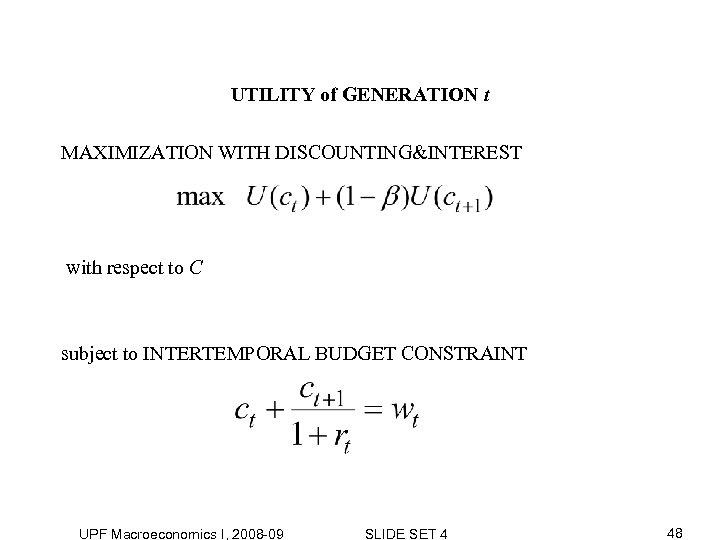 UTILITY of GENERATION t MAXIMIZATION WITH DISCOUNTING&INTEREST with respect to C subject to INTERTEMPORAL BUDGET CONSTRAINT UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 48
UTILITY of GENERATION t MAXIMIZATION WITH DISCOUNTING&INTEREST with respect to C subject to INTERTEMPORAL BUDGET CONSTRAINT UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 48
 FIRST-ORDER CONDITIONS FOR GENERATION t “EFFECTIVE TIME DISCOUNTING” UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 49
FIRST-ORDER CONDITIONS FOR GENERATION t “EFFECTIVE TIME DISCOUNTING” UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 49
 Take the following CES utility function: with CONSUMPTION PROFILE BECOMES UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 50
Take the following CES utility function: with CONSUMPTION PROFILE BECOMES UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 50
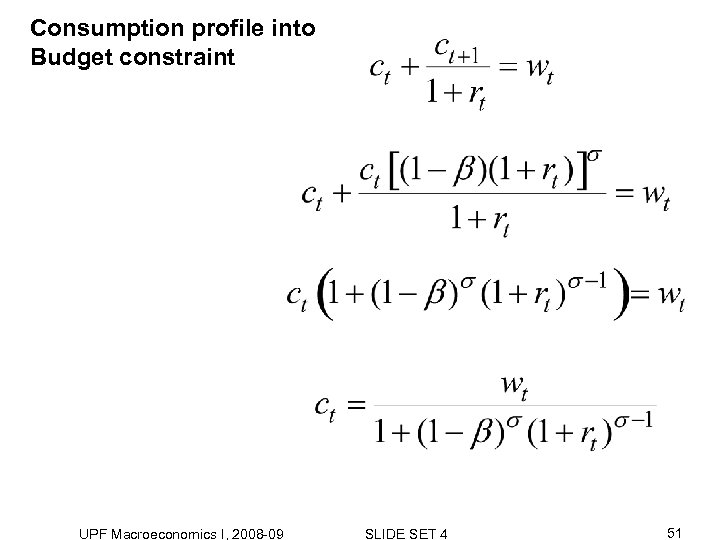 Consumption profile into Budget constraint UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 51
Consumption profile into Budget constraint UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 51
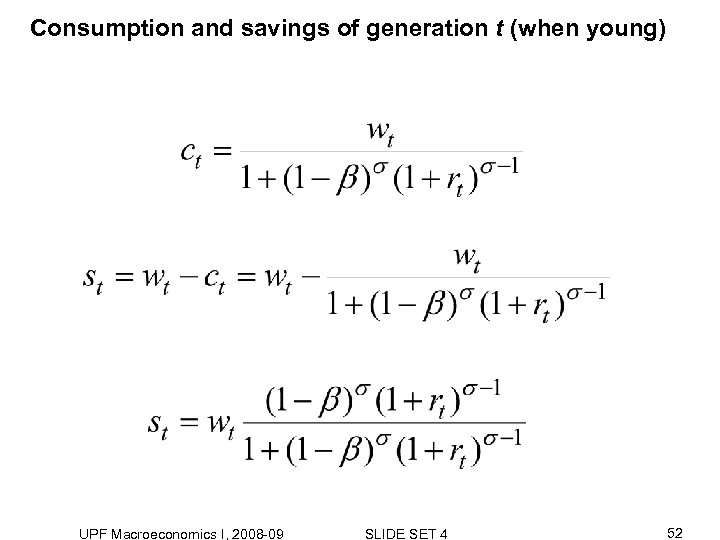 Consumption and savings of generation t (when young) UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 52
Consumption and savings of generation t (when young) UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 52
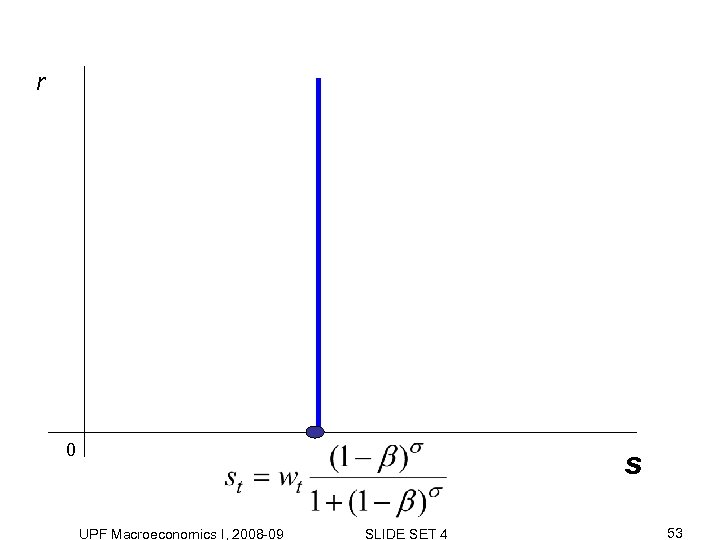 r 0 s UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 53
r 0 s UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 53
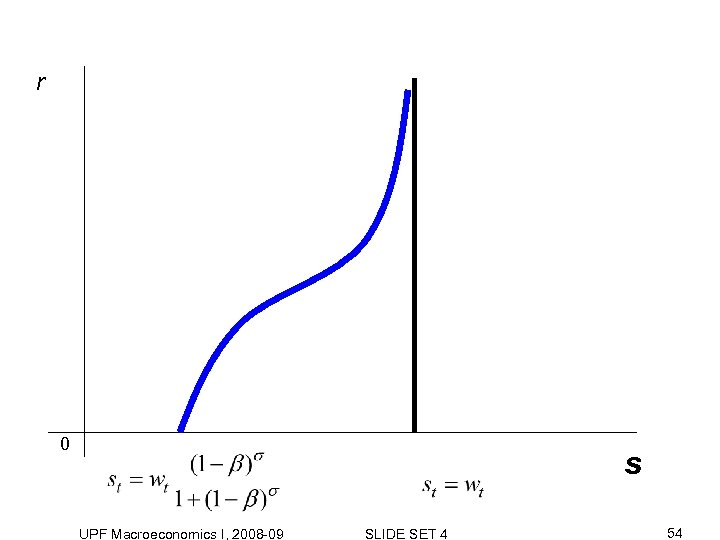 r 0 s UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 54
r 0 s UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 54
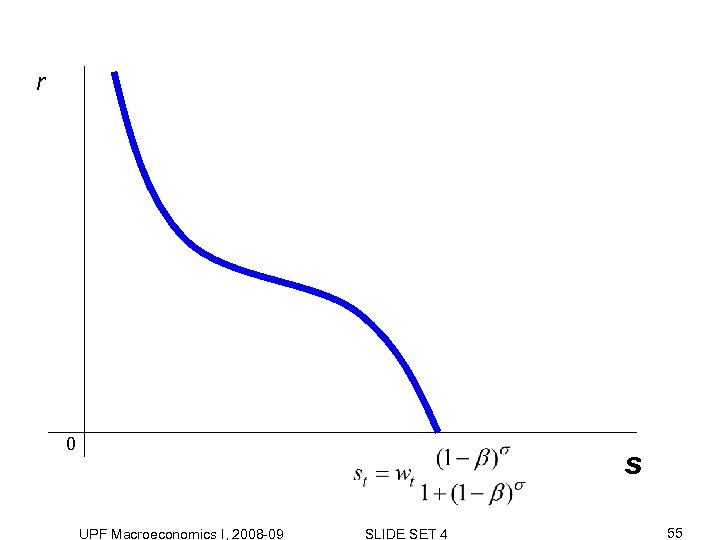 r 0 s UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 55
r 0 s UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 55
 3. Dynamic equilibrium system Savings per young person UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 56
3. Dynamic equilibrium system Savings per young person UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 56
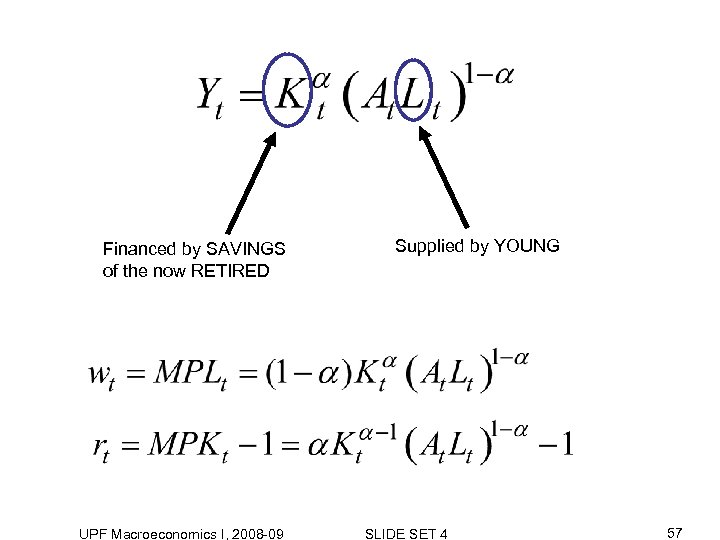 Financed by SAVINGS of the now RETIRED UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 Supplied by YOUNG SLIDE SET 4 57
Financed by SAVINGS of the now RETIRED UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 Supplied by YOUNG SLIDE SET 4 57
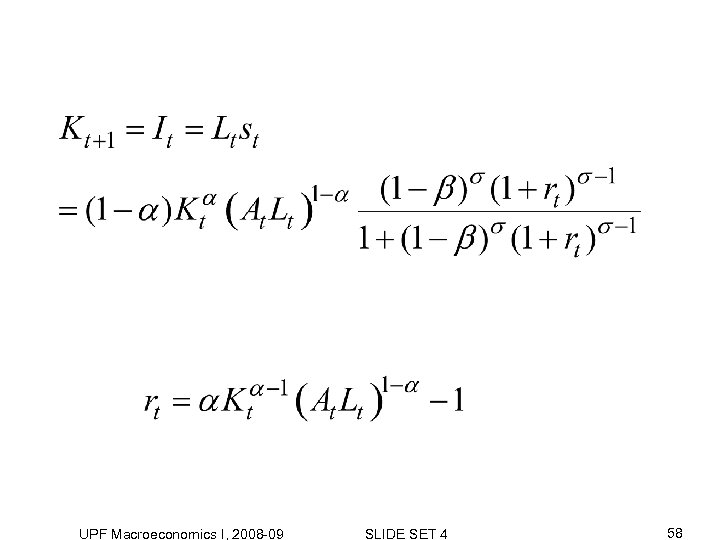 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 58
UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 58
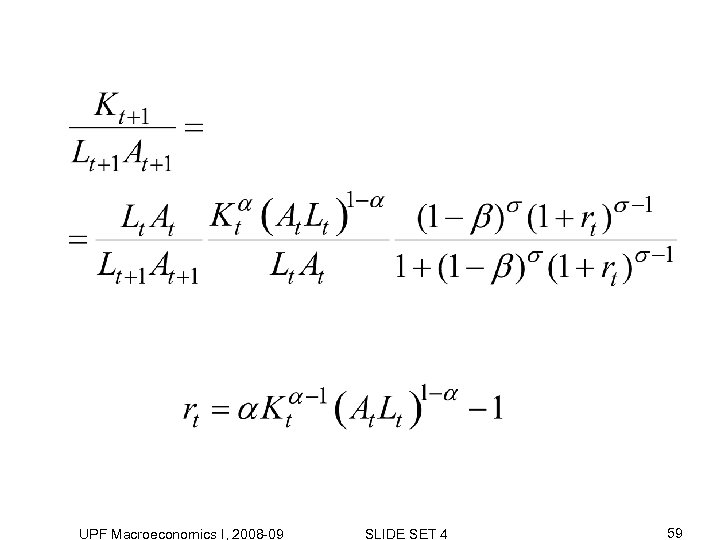 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 59
UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 59
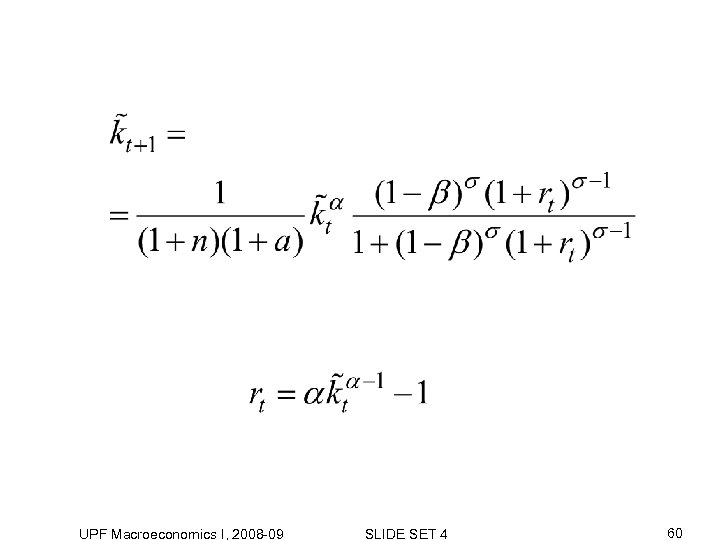 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 60
UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 60
 3. Equilibrium growth and optimality UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 61
3. Equilibrium growth and optimality UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 61
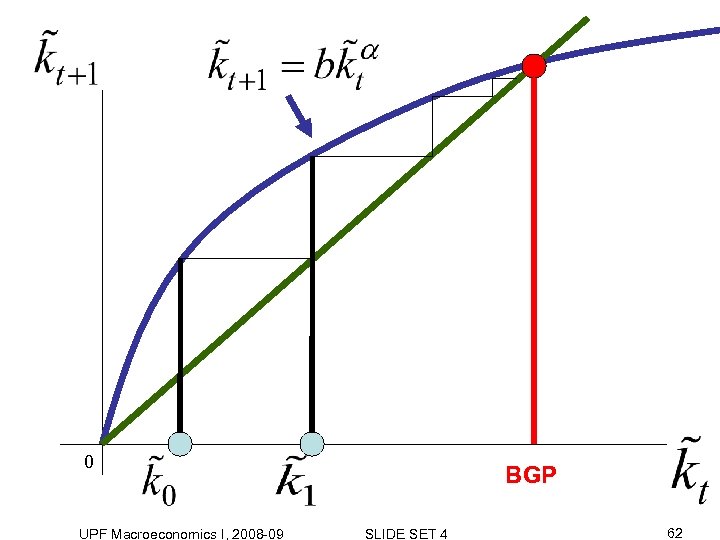 0 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 BGP SLIDE SET 4 62
0 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 BGP SLIDE SET 4 62
 Optimality • How to weight different generations unclear. • Is the allocation at least Pareto efficient? UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 63
Optimality • How to weight different generations unclear. • Is the allocation at least Pareto efficient? UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 63
 Dynamic Inefficiency • A situation where the allocation is not even Pareto efficient • I. e. we can increase consumption of at least one generation without decreasing consumption of all others UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 64
Dynamic Inefficiency • A situation where the allocation is not even Pareto efficient • I. e. we can increase consumption of at least one generation without decreasing consumption of all others UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 64
 Consider case without technological progress a=0. How much do we need to invest person at time t to keep capital intensity constant? UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 65
Consider case without technological progress a=0. How much do we need to invest person at time t to keep capital intensity constant? UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 65
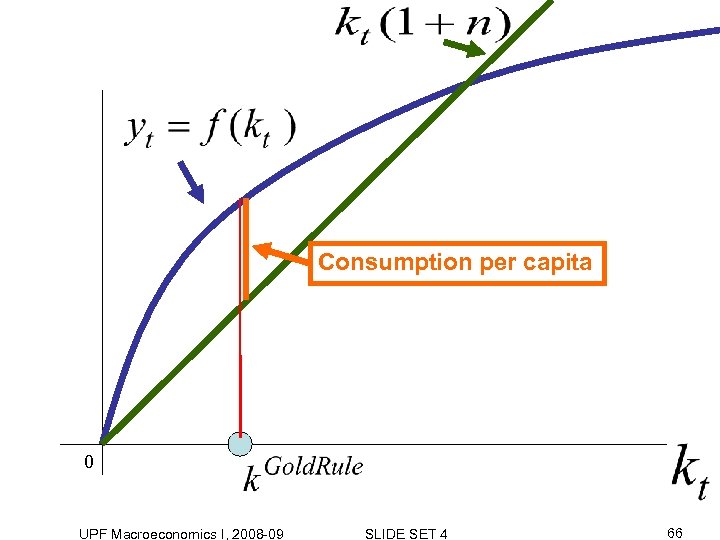 Consumption per capita 0 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 66
Consumption per capita 0 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 66
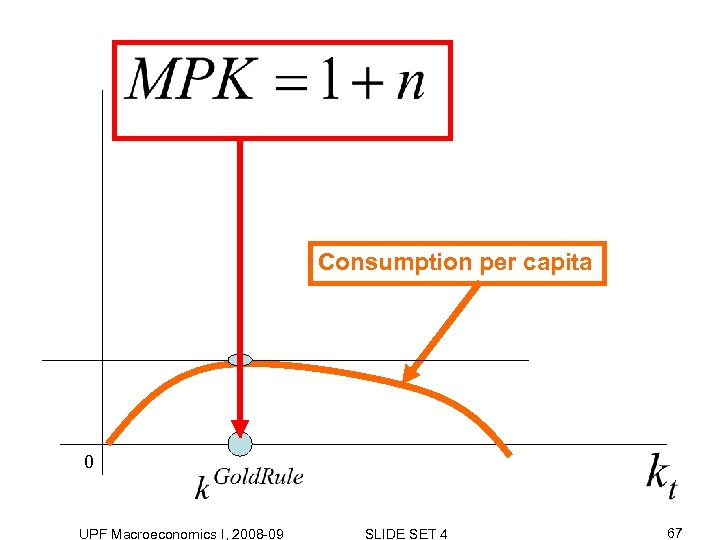 Consumption per capita 0 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 67
Consumption per capita 0 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 67
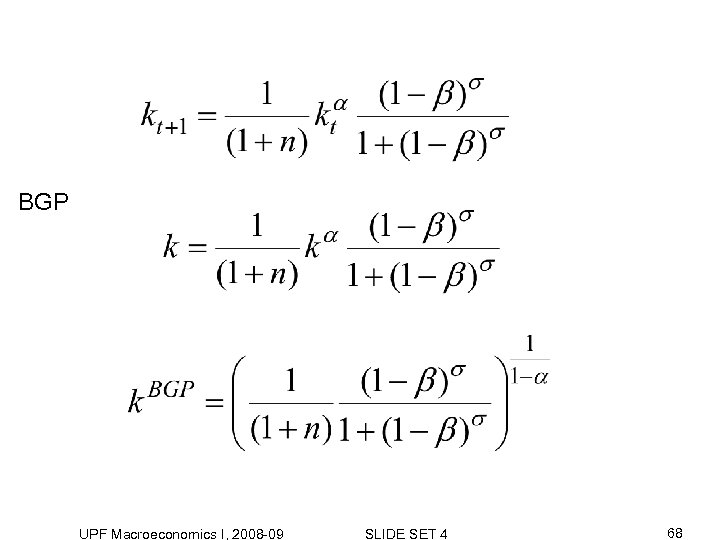 BGP UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 68
BGP UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 68
 UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 69
UPF Macroeconomics I, 2008 -09 SLIDE SET 4 69


